Abstract
The ultra-rapid satellite clock product based on the satellite clock batch estimation is commonly used for high-precision and reliable precise point positioning (PPP) services. In order to clarify the effect of different ranging errors on the satellite clock batch estimation accuracy, the source of the satellite clock bias induced by the batch observation model is classified into the initial clock bias (ICB) and time-dependent bias (TDB). In addition to the effect of the ICB and TDB, the analytic relationship between the observation redundancy and the satellite clock batch estimation accuracy are derived and verified. The suitable number of stations is suggested to be 40 for the satellite clock batch estimation to achieve the counterbalance between the efficiency and saturable accuracy. For the PPP based on the batch-estimated satellite clock, the impacts of the ICB and TDB on PPP are clarified. The satellite clock batch estimation and PPP experiments are carried out to investigate the impacts of the ICB and TDB on the satellite clock batch estimation accuracy and the PPP performance. The ICB causes a significant bias for the batch-estimated satellite clock. The TDB is impacted by the assimilation ability of the batch-estimated satellite clock to the satellite orbit error. The convergence time and the positioning accuracy after the convergence of PPP are primarily affected by the ICB and TDB, respectively.
1. Introduction
The precise satellite clock product is indispensable to obtain high-precision and reliable precise point positioning (PPP) services [1], which can be divided into the real-time, ultra-rapid, rapid and final satellite clock products [2,3]. Compared with the other satellite clock products, the ultra-rapid satellite clock product offers better performance in terms of stability and latency [4,5]. Therefore, the ultra-rapid satellite clock product can be beneficial for the PPP with the relatively low real-time requirement [6]. However, the accuracy of the ultra-rapid satellite clock product needs to be improved to meet the centimeter-level PPP application.
The ultra-rapid satellite clock product typically includes the observation and prediction sessions [7]. The observation session is batch estimated based on the observed receiver–satellite range [8]. In the prediction session, the satellite clock is obtained by the fitting and extrapolation based on the observation session and an accurate satellite clock prediction model [9]. It is noted that the satellite clock batch estimation accuracy determines the quality of the ultra-rapid satellite clock product in the observation and prediction sessions. For the PPP application based on the ultra-rapid satellite clock product, the PPP performance is affected by the satellite clock batch estimation accuracy [3]. Therefore, clarifying the error propagation of the satellite clock batch estimation and its effect on PPP can improve the accuracy of the ultra-rapid satellite clock product and the performance for the PPP application.
The batch observation model needs to be constructed for the satellite clock batch estimation. The traditional observation models for the satellite clock estimation generally include undifferenced, epoch-differenced and mixed-differenced models [10,11]. The undifferenced and mixed-differenced observation models for the satellite clock estimation are analytically equivalent [10], whilst the epoch-differenced model suffers from the quality of the initial satellite clock, resulting in significant satellite clock biases [11]. For the generation of the ultra-rapid satellite clock product in the observation session, the undifferenced observation model is extensively applied due to the lower observation noise and smaller satellite clock biases than the others. Given the batch observation model, the batch-estimated satellite clock assimilates the ranging errors due to the model strength. Hence, the satellite clock bias is introduced so that the accuracy of the batch-estimated satellite clock is affected. The ranging errors absorbed by the batch-estimated satellite clock mainly include the code hardware delay for satellites and the fixed satellite orbit error. Considering the characteristic of the hardware delay over time, the time-invariant and time-variant hardware delays affect the satellite clock estimation accuracy [10]. For the satellite clock batch estimation within observation arcs, the time-variant hardware delay can be roughly ignored due to its stability [12]. Additionally, the impacts of the satellite orbit error on the real-time satellite clock estimation were already analyzed and verified preliminarily in previous studies [13,14]. The radial and tangential satellite orbit errors can be absorbed to various extents by the estimated satellite clock. This absorption increases as the size of the station network used for the satellite clock estimation decreases, especially for the regional distributed network [13]. In view of the ultra-rapid satellite clock product for the global PPP service, the satellite clock is batch estimated based on the global distributed network [8]. The impacts of the satellite orbit error on the satellite clock batch estimation based on the global distributed network need to be further analyzed. Therefore, the satellite clock batch estimation observation model can be constructed in the observation session by considering the time-invariant hardware delays and the satellite orbit error.
Based on the constructed batch estimation observation model, the satellite clock bias is induced by the assimilated ranging errors and the model accuracy. For the real-time satellite clock estimation based on the undifferenced observation model, the satellite clock biases induced by the model are grouped into the initial clock bias and time-dependent bias [10,15]. The initial clock bias is the satellite clock error at the initial epoch, which depends on the accuracy of the initial satellite clock and the bias introduced by the pseudorange observation [16,17]. The time-dependent bias is determined by phase observation [10]. This classification can be used as the reference for the satellite clock batch estimation. However, for the satellite clock batch estimation, the initial clock bias was predetermined with relatively high precision. The impacts of the initial satellite clock accuracy on the initial clock bias can be ignored, which will not be further analyzed in this contribution. Moreover, the accuracy of the fixed satellite orbit product is not precise enough. The satellite orbit error needs to be considered in the classification of the batch-estimated satellite clock bias. Therefore, referring to the typical classification of the satellite clock bias in [10], we clarify the source of the batch-estimated satellite clock biases to analyze the impacts of these biases on the satellite clock batch estimation accuracy.
In addition to satellite clock biases, observation redundancy is another critical factor affecting the satellite clock batch estimation accuracy. Generally, the parameter estimation accuracy depends on the observation redundancy [18,19]. Since the satellite clock estimation accuracy becomes approximately saturable when the observation redundancy has adequately increased. The benefit of increasing more observation redundancy is negligible for the accuracy improvement of the satellite clock estimation [20]. Furthermore, the excessive observation redundancy will burden the efficiency and may increase the update delay, which is not conducive for the generation of the ultra-rapid satellite clock product with low latency [4,5]. The lower latency for the batch-estimated satellite clock brings the better performance for the satellite clock prediction and the PPP based on the predicted satellite clock [21,22]. The update interval and the update rate simultaneously determine the latency of the batch-estimated satellite clock, which can be improved by the efficient sliding satellite clock batch estimation with a short window and the satellite clock prediction with a short period [23,24]. In order to achieve the counterbalance between efficiency and estimation accuracy, many studies have shown the number of stations suitable for the real-time satellite clock estimation [11,20]. Such a number of stations may not be suitable for satellite clock batch estimation because the observation redundancy has already been improved for the batch estimation model by combining observations within observation arcs. In addition, the variations in the number of stations may affect the station distribution. Since the ultra-rapid satellite clock product for the global PPP users is based on the global distributed network, the impacts of the baseline distance among stations on the satellite clock batch estimation can be ignored and will not be considered in this contribution [25]. Therefore, the number of stations suitable for the satellite clock batch estimation needs to be determined to achieve the counterbalance between the efficiency and the batch estimation accuracy.
For the PPP based on the estimated satellite clock, the impacts of the estimated satellite clock on PPP have already been studied in many studies [10,26]. The absolute accuracy, latency and sampling interval of the satellite clock product are the main factors affecting PPP performance, including the convergence time and the positioning accuracy after convergence [21,26]. Furthermore, for the PPP based on the real-time satellite clock, the impacts of the classified satellite clock biases on PPP are analyzed [10]. Two such types of satellite clock biases, i.e., the initial clock bias and the time-dependent bias, affect the pseudorange and phase observations in the typical PPP observation model, which determine the convergence time and the positioning accuracy after convergence, respectively [15,27]. However, few studies have performed the comprehensive analysis for the impacts of the batch-estimated satellite clock on PPP. Therefore, we clarify the error propagation of the batch-estimated satellite clock biases in the PPP observation model and analyze their impacts on PPP.
We begin by constructing the batch observation model for the satellite clock batch estimation and clarify the error propagation of the satellite clock batch estimation. Then, the batch-estimated satellite clock biases are classified according to their impacts on the satellite clock batch estimation accuracy. Furthermore, we derive the analytic relationship between the observation redundancy and the satellite clock batch estimation accuracy to determine the number of stations suitable for satellite clock batch estimation. Moreover, we clarify the error propagation of the batch-estimated satellite clock biases in the PPP observation model. In the experimental verification, we present the data collection and validation strategies for the satellite clock batch estimation and PPP. The effect analysis of the satellite clock batch estimation and the PPP based on the batch-estimated satellite clock are verified. Finally, we give the discussion and summarize the main conclusions of this study.
2. Methodology
We first introduce the typical observation model of the satellite clock batch estimation. The source of the satellite clock bias induced by the batch observation model is clarified and classified. Then, based on the constructed batch observation model, the observation redundancy suitable for the satellite clock batch estimation is determined by deriving the covariance–variance matrix. Finally, the impacts of the classified satellite clock biases from the batch estimation on PPP are illustrated.
2.1. Sources of Batch-Estimated Satellite Clock Biases
The undifferenced observation model based on the batch estimation is adopted due to the lower observation noise and the smaller satellite clock biases than other traditional satellite clock estimation models [10]. Limited by the model strength, the batch observation model causes satellite clock biases in the batch-estimated satellite clock [10,28]. According to the impacts of the resulting satellite clock biases on the satellite clock batch estimation accuracy, they are categorized to clarify the error propagation in the satellite clock batch estimation.
The dual-frequency ionosphere-free (IF) combination is widely used for the undifferenced observation model to eliminate the higher-order ionospheric delay. The tropospheric delay is usually corrected for its dry component with the a priori model, and the wet component is estimated with the zenith tropospheric delay and its corresponding mapping function [29]. The station coordinate and the satellite orbit are usually fixed in the IF observation model [30]. It is assumed that the station coordinate is precisely known, which is normally fixed to the PPP weekly solution, while the error exists in the fixed ultra-rapid satellite orbit product due to the different processing strategies for the satellite orbit determination such as the satellite attitude model and the solar radiation pressure model [31,32]. For the batch observation model, all the observations and parameters in the observation session are constructed, which can be expressed as
where , , , , is the designed matrix for the satellite clock batch estimation model, is the satellite, is the receiver, is an identity matrix, is an vector with all elements equal to 1, is an vector containing the tropospheric mapping function for each receiver, is the number of the observations, is the number of the observed satellites at different stations, is the Kronecker product operation [33], is the pseudorange observation, is the phase observation, is the IF combination, is the vector of the a posterior observation residual for each observation, is the unit vector from the satellite to the receiver, is the vector of the satellite orbit error for each satellite, is the vector of the receiver clock for each receiver, is the vector of the satellite clock for each satellite, is the vector of the zenith tropospheric delay for each receiver, is the vector of the ambiguity for each satellite and each receiver, is the vector of the code hardware delay for each receiver, is the vector of the code hardware delay for each satellite, is the vector of the phase hardware delay for each receiver, is the vector of the phase hardware delay for each satellite and is the vector of the a priori observation residual for each observation. In addition to the ranging errors in (1), the satellite and receiver antenna phase center offsets and variations, relativity, tidal loadings and phase windup should be modeled and precisely corrected in the a priori observation residual [30].
It can be seen from (1) that all the unknown parameters except the zenith tropospheric delay are linearly dependent. The satellite clock, receiver clock, zenith tropospheric delay and ambiguity parameters are the parameters to be estimated. Hence, other unknown parameters are absorbed by the estimated parameters or remain in the observation residual. Such absorption should satisfy the requirement of minimizing the weighted sum of the squares of residuals. According to the correlation between the parameters, and the consistency of the batch observation equation, , , , and are absorbed by , , , and , respectively.
We focus on the ranging errors absorbed by the batch-estimated satellite clock, i.e., the code hardware delay for satellites and the satellite orbit error. Since the hardware delay can be treated as the constant within the observation session, the absorbed code hardware delay for satellites causes the time-invariant bias dependent with satellites. The time-invariant bias of the batch-estimated satellite clock will not affect the standard deviation (STD). For the satellite orbit error, not all of the satellite orbit errors are absorbed by the batch-estimated satellite clock. The assimilation ability depends on the station network distribution used for the satellite clock batch estimation [13]. The pseudorange and phase observations of the global distributed network are used for generating the worldwide satellite clock product. Since the satellite can be approximately regarded always directly above the global distributed network, the projection directions of the satellite orbit radial and tangential errors for each satellite in the signal propagation direction are identical and opposite, respectively. It is well known that the angles of the satellite parallax for the global distributed stations are different, resulting in different projection amounts of the satellite orbit errors. Therefore, the common satellite orbit radial errors observed by different stations in the signal propagation direction can be absorbed by the batch-estimated satellite clock. On the contrary, the satellite orbit tangential error cannot be absorbed due to the opposite projection direction. Therefore, the common satellite orbit error can be absorbed by the batch-estimated satellite clock epoch-wise, which belongs to the time-variant bias and affects the STD of the satellite clock batch estimation. Furthermore, the satellite orbit error not absorbed by the batch-estimated satellite clock is absorbed by the observation residual. The STD of the satellite clock batch estimation is still affected.
It can be seen from (1) that the rank of the coefficient matrix presents deficiency due to the linear dependency between the satellite clock and receiver clock. The clock constraint should be introduced to avoid the rank deficient [34,35]. Therefore, the batch-estimated receiver and satellite clocks are aligned as the clock relative to the reference clock. The reference clock strategies include selecting one satellite clock as zero, one receiver clock as zero and the mean value of satellite clocks as zero, which are equivalent to each other [36]. In order to ensure the stability of the satellite clock batch estimation, we select the zero-mean condition as the reference clock [37]. Inevitably, the batch-estimated satellite clock contains the timescale difference caused by the clock bias of the selected reference clock [15]. The timescale difference belongs to the time-invariant bias independent with satellites, which does not affect the satellite clock batch estimation accuracy when the accuracy of the reference clock is better than 10−6 s [15].
In summary, the reparametrized satellite clock batch estimation model due to the parameter assimilation can be redefined as
where , , , and are the reparametrized receiver clock, satellite clock, ambiguity, a priori pseudorange observation residual and a priori phase observation residual, respectively. They can be rewritten as
where is the timescale difference, and are the satellite orbit radial and tangential errors, and are the assimilation proportion of the batch-estimated satellite clock to the satellite orbit radial and tangential errors. The absorption ability can be calculated by using the range of the satellite parallax angle during satellite regular motion [13]. Taking GPS as an example, the estimated satellite clock can absorb 97.1% of the satellite orbit error in the radial direction at least, and 24.0% in the tangential direction at most. The specific assimilation proportion depends on the station network distribution used for the satellite clock batch estimation.
The impact of the observation noise needs to be accounted for the satellite clock batch estimation. Influenced by the ambiguity in the phase observation, the variation and the absolute bias of the batch-estimated satellite clock are determined by the phase and pseudorange observation, respectively [38]. Furthermore, any biases in the ambiguity or the undetected cycle slips in the data preprocessing will cause the time-invariant bias in the batch-estimated satellite clock. Moreover, for the real-time satellite clock estimation, the time-invariant bias will also be introduced by the initial satellite clock with poor accuracy, which arises from the broadcast clock or the predicted satellite clock [10]. However, the impacts of the initial satellite clock on the satellite clock batch estimation can be ignored. This is because the initial value of the satellite clock can be predetermined with high precision in the batch estimation.
In order to categorically analyze the impacts of the satellite clock biases on the accuracy of the batch-estimated satellite clock, the time-invariant and time-variant bias induced by the batch observation model are denoted as the initial clock bias (ICB) and time-dependent bias (TDB), respectively. The ICB and TDB are both estimated satellite clock biases, which cause the satellite clock error compared with the satellite clock reference product. The only difference between them is that the ICB and TDB contribute to the constant and variable components of the batch-estimated satellite clock errors, respectively. The ICBs caused by the code hardware delay assimilation, the reference clock selection and the pseudorange observation noise will not affect the STD of the batch-estimated satellite clock, but will affect the root mean square (RMS). The TDB induced by the satellite orbit error and the phase observation noise will affect the STD and RMS.
2.2. Suitable Observation Redundancy for Satellite Clock Batch Estimation
In addition to the ICB and TDB, the observation redundancy correlated with the number of stations also affects the satellite clock batch estimation. The accuracy of the batch-estimated satellite clock becomes saturable when the observation redundancy adequately increases. The benefit of increased observation redundancy is negligible for the accuracy improvement of the satellite clock batch estimation [20]. Furthermore, excessive observation redundancy will reduce the efficiency, which needs to be considered in the satellite clock batch estimation with low latency. Therefore, based on the clarified batch observation model, we derive the analytic relationship between the observation and the parameter to be estimated, and simultaneously consider the solution efficiency to determine the saturable accuracy of the batch-estimated satellite clock.
In order to reduce the computation burden of estimating all parameters in the normal equation with large dimensions, the parameter pre-elimination and back-substitution are generally adopted in the batch estimation [39]. The parameters to be estimated are divided into the time-variant and time-invariant parameters to perform the parameter pre-elimination and back-substitution [2]. The satellite clock and receiver clock are denoted as the time-variant parameter and estimated as epoch-wise. The zenith tropospheric delay is denoted as the time-invariant parameter and estimated as piece-wise. The ambiguity is generally regarded as the constant in the absence of cycle slips, which is also denoted as the time-invariant parameter. For the processing strategy of the satellite clock batch estimation, the time-variant parameter is generally set up and pre-eliminated epoch-wise due to its potentially large number. The back-substitution is used to obtain the solution of the time-variant parameter. The observation model can be rewritten as
Combining with the pseudorange and phase observations, the observation error is accurately characterized by the corresponding weighting matrix. In order to simply represent the processing of the pre-eliminated parameter and back-substitution, the normal equation of the satellite clock batch estimation can be abbreviated in the matrix form as
where is the weighting matrix related to the observation error, and are the vectors of the time-variant and time-invariant parameters, and are their corresponding coefficient matrices, and are the vectors of the a posteriori and the a priori observation residuals. According to the principle of the least square parameter estimation based on the parameter pre-elimination and back-substitution, the batch-estimated parameters can be expressed as
where , , , , , , . The diagonal element in the covariance–variance matrix can reflect the STD of the parameter to be estimated. The satellite clock batch estimation accuracy can be obtained by extracting the diagonal elements of the covariance–variance matrix corresponding to the satellite clocks. This evaluated accuracy does not require the additional satellite clock reference product. The clock covariance–variance matrix of the satellite clock batch estimation derived by (6) can be expressed as
It can be found that the clock covariance–variance matrix consists of the coefficient matrix and the weighting matrix for the satellite clock batch estimation model. The satellite clock batch estimation accuracy depends on the number of stations and the observation error, which are closely related to the coefficient matrix dimension and the weighting matrix, respectively. Thus, the analytic relationship between the observation and the parameter to be estimated has clearly been derived. However, the number of stations suitable for the satellite clock batch estimation and the corresponding saturable estimation accuracy still cannot be determined directly from the analytic expression. This is because the coefficient matrix dimension is also affected by the number of visible satellites at different stations and different epochs, which needs to be determined experimentally.
The GPS data from the day of the year (DOY) 045 to 051 in 2021 are used for determining the number of stations suitable for the satellite clock batch estimation and the corresponding saturable estimation accuracy. We ignore the impacts of different stations with identical quantities on the satellite clock batch estimation. This is due to the identical full coverage for visible satellites in the observation session and the little difference in the observation quality between different International GNSS Service (IGS) stations used. The efficiency of the satellite clock batch estimation has limitations due to the low latency requirements, which should be controlled within one hour including the consumption of hourly data collection. We count the processing time to reflect the efficiency of satellite clock batch estimation [40]. The satellite clock batch estimation based on the final satellite orbit product provided by IGS is performed on the PowerEdge R7525 Server (AMD EPYC 7F72 24-Core Processor @3.69 GHz). The STD is extracted from (7) based on the gradually increasing number of the global distributed network stations and the elevation-dependent stochastic model, whose consistency with the STD for the external coincidence is verified. The STD for the external coincidence is conducted by calculating the batch-estimated satellite clock error based on the double difference strategy [10]. Moreover, the criteria for gradually increasing stations serve to maximize the observation, which is mainly relative to the observed satellites. The mean values of the STD for all satellites and the processing time of the satellite clock batch estimation with a gradually increasing number of stations are shown in Figure 1.
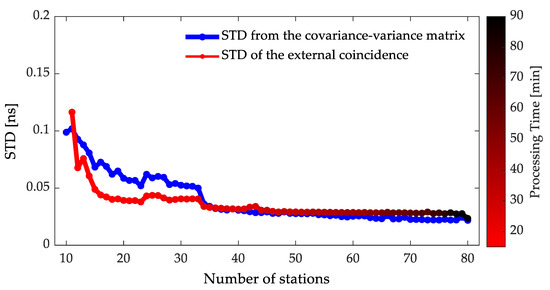
Figure 1.
STD and processing time with a gradually increasing number of stations for one week.
It can be seen from Figure 1 that the satellite clock batch estimation accuracy is gradually improved as the increasing number of stations. The satellite clock batch estimation accuracy is greatly affected by the observation redundancy for less than 40 stations and ranges from 0.03 to 0.10 ns. However, the GPS satellite clock batch estimation accuracy tends to be stable when the number of stations is more than 40. This indicates that the satellite clock batch estimation accuracy becomes saturable. Considering the counterbalance between the efficiency and estimation accuracy, we suggest that the number of stations suitable for GPS hourly updated satellite clock batch estimation is to be 40.
2.3. Impacts of Batch-Estimated Satellite Clock Biases on PPP
Based on the suitable observation redundancy for the satellite clock batch estimation, the ICB and TDB of the batch-estimated satellite clock affect the PPP performance. We will clarify the error propagation of these satellite clock biases in the PPP observation model. For the conventional dual-frequency IF combined PPP processing, the consistent satellite clock and orbit products are generally fixed [41]. Since the satellite clock batch estimation is performed based on the ultra-rapid satellite orbit product, the error exists in the fixed satellite clock product for the PPP observation model. Due to the consistency between the satellite clock and orbit product used for PPP, the fixed ultra-rapid satellite orbit product is also fixed in PPP. Thus, the satellite clock and orbit errors cannot be ignored in the PPP observation model. For a typical PPP observation model [42,43], the observations and the parameters are epoch-wise constructed, which can be expressed as
where , , , , is the designed matrix for the PPP observation model, is the number of the observations, is the number of observed satellites at different stations and is the increment for the a priori receiver position vector. The receiver position increment, the receiver clock, the zenith tropospheric delay and the ambiguity parameters are the parameters to be estimated in the PPP observation model. Given that the hardware delay is time-invariant, the redefined PPP observation model due to the correlation among the unknown parameters can be expressed as
where , , and are the reparametrized receiver clock, ambiguity, a priori pseudorange observation residual and a priori phase observation residual, respectively. They can be rewritten as
where is the ICB of the fixed batch-estimated satellite clock at the initial epoch , is the TDB of the fixed batch-estimated satellite clock at the epoch.
We focus on the impacts of the satellite clock bias for the fixed batch-estimated satellite clock on the PPP observation model. It can be found from (10) that the timescale difference can be absorbed by the receiver clock in the PPP observation model without affecting the PPP positioning accuracy. The ICB caused by the code hardware delay for satellites can be canceled by the code hardware delay for satellites in the PPP observation model if the identical combination of observation is used for PPP and satellite clock batch estimation, i.e., the dual-frequency IF combination. The TDB induced by the absorbed satellite orbit error can mostly be canceled by the fixed satellite orbit error in the PPP observation model. The reason for the cancellation is that the satellite clock and orbit product used for PPP is consistent. Furthermore, the cancellation depends on the assimilation ability of the batch-estimated satellite clock to the satellite orbit error, resulting in incomplete cancellation.
It can be found from (10) that the ICB not caused by the code hardware delay for satellites is absorbed by ambiguity in the PPP observation model. Furthermore, the TDB caused by the unabsorbed satellite orbit error or others is absorbed by the observation residual in the PPP observation model. For the ICB and TDB of the batch-estimated satellite clock caused by these reasons, we investigate their impacts on the PPP positioning performance, including the convergence time and the positioning accuracy after convergence. The convergence time and positioning accuracy after convergence depend on the speed of accurately estimating parameters and the observation noise, respectively. Since the ICB is absorbed by the ambiguity, the estimation of the ambiguity requires a long convergence process and mainly impacts the convergence time of PPP. Furthermore, the inaccurate ambiguity parameter may impact the phase observation, resulting in affecting the positioning accuracy after convergence. The TDB can be treated as impacting the observation noise when estimating the receiver coordinates. The large TDB is equivalent to increasing the observation noise, and mainly impacts the accuracy of the receiver coordinate estimation, i.e., the positioning accuracy after convergence. Meanwhile, the speed of accurately estimating the receiver coordinate, i.e., the convergence time of PPP, may also be affected.
3. Results
The satellite clock batch estimation based on the global distributed network is implemented to verify the impacts of the ICB and TDB. Since the long absence of the satellite clock reference product and the fixed satellite orbit product for G11, the satellite clock batch estimation and the evaluation does not include this satellite. The experimental setup and processing strategy is shown in Table 1. The station selection of the global distributed network is performed in the preprocessing of satellite clock batch estimation, which depends on the quality of observations at different stations. One example of the station selection is shown in Figure 2. The number of selected stations is 40, which is the suitable observation redundancy for the satellite clock batch estimation verified in the previous experiments. In order to evaluate the batch-estimated satellite clock and the fixed satellite orbit, the GPS final satellite clock and orbit product provided by IGS are introduced as the reference, respectively.

Table 1.
Experimental setup and processing strategy.
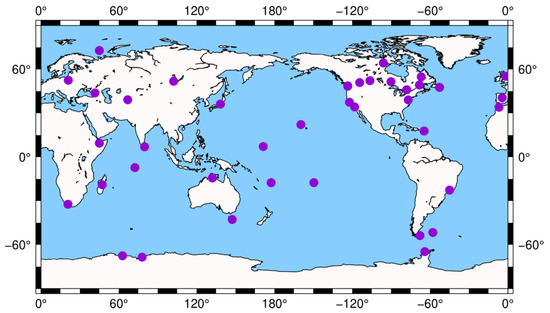
Figure 2.
One example of station selection with 40 stations for satellite clock batch estimation. The purple circles represent selected stations.
The TDB due to the satellite orbit error assimilation on satellite clock batch estimation IS clarified by the correlation analysis between the satellite clock error and the satellite orbit error. The batch-estimated satellite clock errors are evaluated to verify the impacts of the ICB and TDB on the satellite clock batch estimation. Furthermore, the convergence time and the positioning accuracy after convergence are analyzed to reveal the impacts of the ICB and TDB on PPP.
3.1. Effect Analysis of Satellite Clock Batch Estimation
The bias and dispersion of the batch-estimated satellite clock error can reveal the ICB and TDB, respectively. We use the double difference strategy to extract the batch-estimated satellite clock error. The reference satellite needs be selected in advance. The reference satellite clock strategies typically include selecting one satellite clock and the mean value of satellite clocks for all satellites. In order to preserve the satellite clock error sequences for all satellites, the mean value of all satellite clocks is selected as the reference in this contribution, which can be expressed as
where is the double difference operator, is the satellite clock reference product provided by IGS, is the total number of epochs and is the epoch. In addition, we used the metrics of the RMS and STD to reflect the bias and dispersion for the batch-estimated satellite clock error, respectively.
There are two classifications of biases contributing to the batch-estimated satellite clock, i.e., the ICB and the TDB, in which we will not conduct additional experiments to verify the impacts of the ICB on the satellite clock batch estimation. The ICB is reflected by the RMS of the batch-estimated satellite clock error. The TDB, another classification of the batch-estimated satellite clock, is impacted by the assimilation of the satellite orbit error. The assimilation ability can be indicated by the correlation coefficients between the satellite clock error and the satellite orbit error. The epoch-wise satellite orbit error can be obtained by comparing it with the satellite orbit reference product provided by IGS. The satellite orbit errors in the radial, along-track and cross-track directions can be computed as [44]
where , and are the satellite orbit errors in the radial, along-track and cross-track directions, respectively. , and are the satellite orbit errors in the Earth-centered Earth-fixed (ECEF) frame. and is the satellite position and the inertial velocity in the ECEF frame.
The satellite clock batch estimation is implemented based on the fixed ultra-rapid satellite orbit products in observation sessions provided by the three different analysis centers including Wuhan University, Geo Forschungs Zentrum (GFZ) and IGS. These three data sources are abbreviated as WHU, GFU and IGU, respectively. The 1DRMS accuracy of the three ultra-rapid satellite orbit products in the observation session for one-year data are 1.86 cm, 1.31 cm and 0.83 cm, respectively. We use the three different ultra-rapid satellite orbit products to investigate the assimilation ability of the batch-estimated satellite clock to different types of the satellite orbit error [45]. The correlation between the batch-estimated satellite clock error and the fixed satellite orbit error is shown in Figure 3.
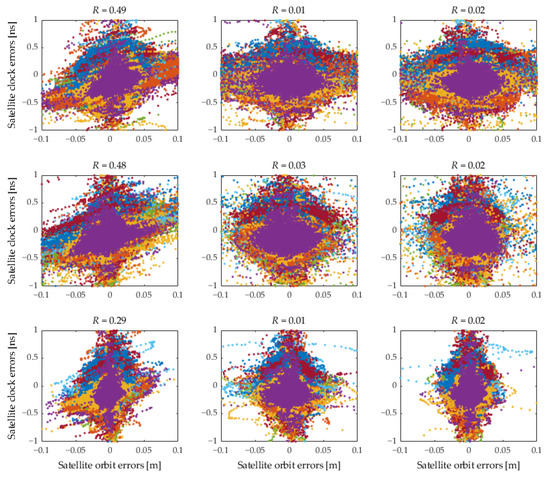
Figure 3.
Correlation between batch-estimated satellite clock errors and fixed satellite orbit errors for one year. The row panels from top to bottom show the results based on the fixed satellite orbit product provided by WHU, GFU and IGU, respectively. The column panels from left to right show the results of the satellite orbit error in the radial, along-track and cross-track directions. The dots with different colors represent different satellites.
It can be seen from Figure 3 that the batch-estimated satellite clock error and the fixed satellite orbit error in the radial direction are positively correlated, whilst the correlation in the along-track and cross-track directions can be neglected. This demonstrates that the batch-estimated satellite clock error based on the global distributed network can assimilate the satellite orbit radial error more than the other two directions. Moreover, the correlation coefficient of WHU, GFU and IGU is different, especially that of IGU, which is much lower than WHU and GFU. This is because the station selection for the global distributed network is specific, which depends on the station observation quality correlated with the fixed satellite orbit accuracy. Thus, the common satellite orbit radial error absorbed by the batch-estimated satellite clock is different, resulting in the difference in the assimilation ability and the corresponding correlation coefficient.
In addition to the absorbed satellite orbit error, the unabsorbed satellite orbit error is absorbed by the observation residual and also affects the TDB of the batch-estimated satellite clock. In order to investigate the impacts of the satellite orbit error on TDB, we extracted the batch-estimated satellite clock error based on the fixed satellite orbit products provided by WHU, GFU and IGU. The TDB is indicated by the dispersion of the batch-estimated satellite clock error. The bias of the batch-estimated satellite clock error reflects the ICB. Furthermore, the satellite clock batch estimation based on the final satellite orbit product provided by IGS is also performed as the reference for comparison. The batch-estimated satellite clock errors based on the fixed four satellite orbit products, named BEST-WHUO, BEST-GFUO, BEST-IGUO and BEST-IGSO, are shown in Figure 4.
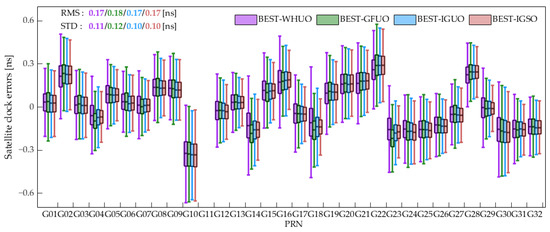
Figure 4.
Batch-estimated satellite clock errors based on fixed WHUO, GFUO, IGUO and IGSO for one year.
It can be seen from Figure 4 that the batch-estimated satellite clock errors based on these four satellite orbit products have significant biases. This is because the batch-estimated satellite clock error contains the ICB, which is induced by the assimilation of the code hardware delay for satellites. The dispersion of the batch-estimated satellite clock errors based on the three ultra-rapid satellite orbit products is significant relative to the IGS final satellite orbit product. This is because the satellite orbit error, including the absorbed and unabsorbed components, affects the TDB of the batch-estimated satellite clock. Furthermore, the STD difference among the BEST-WHUO, BEST-GFUO and BEST-IGUO indicates that the TDB of the batch-estimated satellite clock is different, in which the STD of BEST-IGUO is slightly lower than BEST-WHUO and BEST-GFUO. This is because the assimilation of the satellite orbit radial error based on the IGUO is less than that of WHUO and GFUO. Meanwhile, the unabsorbed component of IGUO has better accuracy than WHUO and GFUO.
3.2. Effect Analysis of PPP Based on Batch-Estimated Satellite Clock
In order to investigate the impacts of the ICB and TDB for the batch-estimated satellite clock on PPP, the PPP in the kinematic mode will be carried out. The observation model of PPP comes from (9). The elevation-dependent weighting model is used for constructing the stochastic model of PPP. The PPP solution is implemented based on the GAMP software [43]. The PPP positioning errors of the east, north and up directions are calculated epoch-wise by comparing with the reference coordinates provided by IGS. We excluded the positioning results from the last 15 min to avoid the impacts of the satellite orbit extrapolation error on PPP. Furthermore, the convergence time and the positioning accuracy after convergence were used as the indicators to evaluate the PPP positioning performance.
We firstly perform the simulation experiment to clarify the impacts of the ICB on PPP by injecting the artificial constant bias into the satellite clock batch estimation result. The injected bias for each satellite is the time-invariant bias in days, which is consistent with the period of PPP solutions. It is noted that the magnitude of the simulated bias is obtained from the normal distribution with the STD of 3 ns for each satellite, which is consistent with the accuracy of the broadcast clock. One example of the injected bias for each satellite in one day is shown as Figure 5.
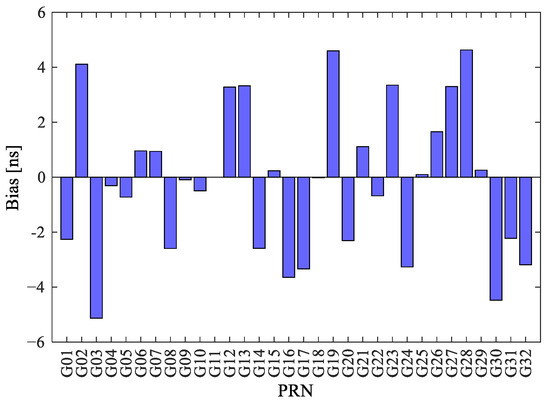
Figure 5.
One example of injected bias for each satellite in one day.
The IGS final satellite orbit product is used for the satellite clock batch estimation and PPP to avoid the impacts of the satellite orbit error on TDB and PPP. The resulting simulated batch-estimated satellite clock is named BEST + ICB. The PPP experiment based on BEST + ICB can illustrate the impacts of the ICB on PPP. Moreover, we set 20 cm as the convergence threshold to determine the convergence time of PPP. The PPP results for BEST and BEST + ICB are shown in Figure 6.

Figure 6.
PPP results for BEST and BEST + ICB at 20 arbitrary stations for one year. The two subplots on the left show the STD of the convergence time. The two subplots on the right show the 3DRMS of the positioning accuracy after convergence.
The convergence time for each station varies daily. The STD of the convergence time indicates the variation degree for the observation quality from day to day, including the observation accuracy and the satellite distribution. It can be seen from Figure 6 that the STD of the convergence time for BEST + ICB is longer than BEST. This is because the ICB is absorbed by the ambiguity in the PPP observation model and impacts the convergence time of PPP. Furthermore, we can find that the impacts of the ICB on the convergence time across different stations. It can be explained that the convergence time of PPP is affected by the magnitude of the ICB with different satellites. Moreover, the positioning accuracy after convergence for BEST + ICB is slightly worse than BEST, which is attributed to the injected ICB.
In order to explore the impacts of the TDB on PPP, we simulated the random biases epoch-wise and injected the simulated biases into the batch-estimated satellite clock. The injected bias for each satellite is time-variant, which is the main difference from the injected ICBs. It is noted that the STD of the simulated biases is obtained from the normal distribution with the STD of 0.3 ns for all satellites. The value of the simulated biases comes from three times the STD of the satellite clock error. The impacts of the TDBs on PPP can be amplified and verified. Similarly to the injected ICB, the injected random bias for each satellite is also in days. Furthermore, the batch-estimated satellite clock data for simulation is also based on the fixed final satellite orbit product provided by IGS. The resulting simulated batch-estimated satellite clock is named BEST + TDB. The PPP based on BEST + TDB can illustrate the impacts of the TDB on PPP. Moreover, we set the positioning convergence threshold as 50 cm because of the injected simulated random biases. The PPP results for BEST and BEST + TDB are shown in Figure 7.
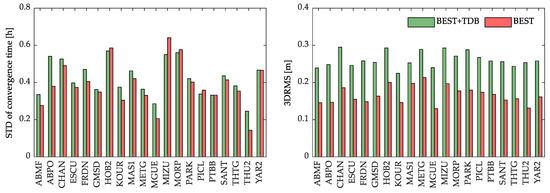
Figure 7.
PPP results for the BEST and BEST + TDB at 20 arbitrary stations for one year. The two subplots on the left show the STD of the convergence time. The two subplots on the right show the 3DRMS of the positioning accuracy after convergence.
It can be seen from Figure 7 that the STD of the convergence time is certainly shortened. This is because of the expanding convergence threshold, so that the positioning result for BEST + TDB can be regarded as the convergence. From Figure 7, we can see that the positioning accuracy after convergence for BEST + TDB is worse than BEST. This is because the simulated TDB based on the normal distribution is absorbed by the observation residual, which impacts the positioning accuracy after convergence. Furthermore, the STD of the convergence time for BEST + TDB is slightly longer than BEST, which does not exceed 30 min. This is because the absorbed observation residual impacts the PPP observation model strength.
4. Discussion
In order to obtain the PPP results at the centimeter level using ultra-rapid satellite products, the satellite clock batch estimation accuracy and its impacts on PPP are analyzed in this contribution.
The traditional observation models for satellite clock estimation generally include undifferenced, epoch-differenced and mixed-differenced models. For satellite clock batch estimation, the undifferenced observation model is typically used. The ICB and TDB are induced by the batch observation model, including the assimilated ranging errors and the model accuracy. The theoretical analysis and experimental results show that the ICB affects the RMS without affecting the STD, whilst the TDB affects the RMS and the STD of the batch-estimated satellite clock. Furthermore, we primarily analyze the impacts of the fixed satellite orbit error on the TDB. The experimental results show that the assimilation of the satellite orbit radial error to the TDB is more than the along-track and the cross-track directions. The assimilation ability depends on the station distribution used for the satellite clock batch estimation.
In addition to the satellite clock biases, the observation redundancy also affects the STD of the batch-estimated satellite clock. Many studies have shown the number of stations suitable for the real-time satellite clock estimation. Such results may not be suitable for the satellite clock batch estimation. We derive the analytic relationship between the observation redundancy and the satellite clock batch estimation accuracy. The experimental results show that the suitable number of stations is suggested to be 40 to achieve the counterbalance between the efficiency and saturable accuracy.
We perform the simulation experiment to clarify the impacts of the ICB and the TDB on PPP. The experiment results show that the convergence time and the positioning accuracy after convergence of PPP are mainly affected by the ICB and TDB of the batch-estimated satellite clock, respectively. Moreover, besides the ICB and the TDB, the impacts of the observation quality on PPP, including the observation accuracy and the satellite distribution, cannot be ignored.
5. Conclusions
As one of the typical PPP methods to achieve the centimeter-level positioning by using ultra-rapid satellite clock and orbit products, the satellite clock batch estimation accuracy and its impacts on PPP are analyzed in this contribution.
The source of the satellite clock bias induced by the batch observation model is clarified and divided into the ICB and the TDB. The ICB affects the RMS without affecting the STD, whilst the TDB affects the RMS and the STD of the batch-estimated satellite clock. Furthermore, based on the clarified batch observation model, the observation redundancy suitable for the satellite clock batch estimation is determined by deriving the covariance–variance matrix. The number of stations for GPS satellite clock batch estimation is suggested to be 40 because the accuracy of the batch-estimated satellite clock is saturable. For the application of the batch-estimated satellite clock on PPP, the ICB and TDB are absorbed by the PPP observation model, which impact the convergence time and the positioning accuracy after convergence, respectively.
Based on the experimental results of the satellite clock batch estimation, it can be found that the ICB causes a significant bias for the batch-estimated satellite clock. The TDB is impacted by the assimilation ability of the batch-estimated satellite clock to the satellite orbit error. Furthermore, the simulation experiments of PPP show that the convergence time and the positioning accuracy after convergence are affected by the ICB and TDB of the batch-estimated satellite clock.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.L., W.H. and H.L.; methodology, M.L. and H.L.; validation, M.L., R.W. and P.C.; formal analysis, M.L. and H.L.; investigation, M.L. and H.L.; resources, W.H. and H.L.; data curation, M.L. and H.L.; writing—original draft preparation, M.L.; writing—review and editing, M.L.; visualization, M.L. and R.W.; supervision, M.L. and H.L.; project administration, W.H. and H.L.; funding acquisition, W.H. and H.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was jointly funded by the National Key Research and Development Program (No. 2021YFB3901300), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61773132, 61633008, 61803115, 62003108 and 62003109), the 145 High-Tech Ship Innovation Project sponsored by the Chinese Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, the Heilongjiang Province Research Science Fund for Excellent Young Scholars (No. YQ2020F009) and the Fundamental Research Funds for Central Universities (Nos. 3072019CF0401, 3072020CFT0403).
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting this research can be found at the hyperlinks as: https://cddis.nasa.gov, accessed on 1 March 2022.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to appreciate the analysis center of WHU, GFZ and IGS for providing the data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Nie, Z.; Xu, X.; Wang, Z.; Du, J. Initial Assessment of BDS PPP-B2b Service: Precision of Orbit and Clock Corrections, and PPP Performance. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, G. Real-time estimation of BDS/GPS high-rate satellite clock offsets using sequential least squares. Adv. Space Res. 2018, 62, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogutcu, S.; Farhan, H.T. Assessment of the GNSS PPP performance using ultra-rapid and rapid products from different analysis centres. Surv. Rev. 2020, 54, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Song, S.; Zhou, W. Accuracy Analysis of GNSS Hourly Ultra-Rapid Orbit and Clock Products from SHAO AC of iGMAS. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, G.; Song, S. High-Rate One-Hourly Updated Ultra-Rapid Multi-GNSS Satellite Clock Offsets Estimation and Its Application in Real-Time Precise Point Positioning. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liao, X.; Li, B.; Yang, L. Modeling of the GPS satellite clock error and its performance evaluation in precise point positioning. Adv. Space Res. 2018, 62, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Li, N.; Li, H.; Wang, R.; Li, M. BDS Satellite Clock Prediction Considering Periodic Variations. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauschild, A.; Montenbruck, O. Kalman-filter-based GPS clock estimation for near real-time positioning. GPS Solut. 2008, 13, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, G. Real-time clock offset prediction with an improved model. GPS Solut. 2013, 18, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Zhao, L.; Song, J.; Chen, D.; Jiang, W. Analysis of estimated satellite clock biases and their effects on precise point positioning. GPS Solut. 2017, 22, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, L.; Grace, X.G.; Walter, T.; Enge, P. Statistical Characterization of GPS Signal-In-Space Errors. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Technical Meeting of the Institute of Navigation, San Diego, CA, USA, 24–26 January 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Montenbruck, O.; Hauschild, A.; Steigenberger, P. Differential Code Bias Estimation using Multi-GNSS Observations and Global Ionosphere Maps. Navigation 2014, 61, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, C.; Yao, X.; Shi, C.; Liu, J. The impact of orbital errors on the estimation of satellite clock errors and PPP. Adv. Space Res. 2014, 54, 1571–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douša, J. The impact of errors in predicted GPS orbits on zenith troposphere delay estimation. GPS Solut. 2009, 14, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; He, Y.; Yi, W.; Song, W.; Cao, C.; Chen, M. Method for evaluating real-time GNSS satellite clock offset products. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 1417–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Lou, Y.; Zheng, F.; Gu, S.; Shi, C.; Liu, J.; Jing, G. Evaluation and calibration of BeiDou receiver-related pseudorange biases. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Gu, S.; Zheng, F.; Wu, Q.; Liu, S.; Lou, Y. Improving GPS and Galileo precise data processing based on calibration of signal distortion biases. Measurement 2021, 174, 108981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, L.; Yang, F.; Li, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, R. Integrity monitoring for undifferenced and uncombined PPP under local environmental conditions. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2022, 33, 065010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, X.; Jia, C.; Cheng, C.; Li, J.; Zhao, L. Integrity monitoring of carrier phase-based ephemeris fault detection. GPS Solut. 2020, 24, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, Q.; Xue, S. Random Optimization Algorithm on GNSS Monitoring Stations Selection for Ultra-Rapid Orbit Determination and Real-Time Satellite Clock Offset Estimation. Math. Probl. Eng. 2019, 2019, 7579185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Xu, C.; Gao, Y. Analysis of GPS satellite clock prediction performance with different update intervals and application to real-time PPP. Surv. Rev. 2017, 51, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Yang, H.; Xiao, G.; Du, L.; Gao, Y. Estimation of GPS LNAV based on IGS products for real-time PPP. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Huang, M.; Wang, C.; Hu, R.; Duan, T. A New BDS-2 Satellite Clock Bias Prediction Algorithm with an Improved Exponential Smoothing Method. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, C.; Hu, D. A Novel Short-Medium Term Satellite Clock Error Prediction Algorithm Based on Modified Exponential Smoothing Method. Math. Probl. Eng. 2018, 2018, 7486925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.; Dai, X.; Song, W. Research on the influence of stations’ distance in high-accuracy GPS satellite clock offset estimation. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2011, 36, 397–400. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Guo, F. Satellite clock estimation at 1 Hz for realtime kinematic PPP applications. GPS Solut. 2010, 15, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Song, W.; Yi, W.; Shi, C.; Lou, Y.; Guo, H. Research on a method of real-time combination of precise GPS clock corrections. GPS Solut. 2016, 21, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Zhang, X.; Guo, F.; Liu, J. GPS inter-frequency clock bias estimation for both uncombined and ionospheric-free combined triple-frequency precise point positioning. J. Geod. 2018, 93, 473–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xiong, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, K.; Huang, J. Real-time estimation of multi-GNSS integer recovery clock with undifferenced ambiguity resolution. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 2515–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Yoon, S.; Stressler, B.; Hilla, S.; Schenewerk, M. GPS satellite clock estimation using global atomic clock network. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Xu, X.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, J. Precise orbit determination for quad-constellation satellites at Wuhan University: Strategy, result validation, and comparison. J. Geod. 2015, 90, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, F.; Ye, S.; Chen, D.; Tang, L.; Wang, C.; Ge, M.; Neitzel, F. Advancing the Solar Radiation Pressure Model for BeiDou-3 IGSO Satellites. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Wang, L.; Chen, R.; Han, Y.; Zhou, H.; Li, T. Combined BDS-2/BDS-3 real-time satellite clock estimation with the overlapping B1I/B3I signals. Adv. Space Res. 2021, 68, 4470–4483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, B.; Yuan, Y.; Zha, J.; Zhao, C. An efficient undifferenced method for estimating multi-GNSS high-rate clock corrections with data streams in real time. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 1435–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Huang, G.; Fu, W.; Li, P.; Cui, B. An efficient clock offset datum switching compensation method for BDS real-time satellite clock offset estimation. Adv. Space Res. 2021, 68, 1802–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Xie, W.; Wenju, F.; Li, P.; Wang, H.; Yue, F. BDS Real-time Satellite Clock Offsets Estimation with Three Different Datum Constraints. J. Glob. Position. Syst. 2021, 17, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Cheng, C.; Li, L.; Wang, R.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhao, L. BDS signal-in-space anomaly probability analysis over the last 6 years. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defraigne, P.; Bruyninx, C. On the link between GPS pseudorange noise and day-boundary discontinuities in geodetic time transfer solutions. GPS Solut. 2007, 11, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, H.; Dach, R.; Jäggi, A.; Beutler, G. High-rate GPS clock corrections from CODE: Support of 1 Hz applications. J. Geod. 2009, 83, 1083–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Gu, S.; Lou, Y.; Zheng, F.; Ge, M.; Liu, J. An efficient solution of real-time data processing for multi-GNSS network. J. Geod. 2017, 92, 797–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Gao, Y. GPS Satellite Orbit Prediction at User End for Real-Time PPP System. Sensors 2017, 17, 1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, G.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, Y.; Xiao, G. FCB estimation with three different PPP models: Equivalence analysis and experiment tests. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Dong, D.; Li, W.; Jiang, X.; Wickert, J.; Schuh, H. GAMP: An open-source software of multi-GNSS precise point positioning using undifferenced and uncombined observations. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhai, Y.; Zhan, X. Characterizing BDS signal-in-space performance from integrity perspective. Navigation 2021, 68, 157–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, K.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, G.; Xiong, Y. Precise Orbit and Clock Products of Galileo, BDS and QZSS from MGEX Since 2018: Comparison and PPP Validation. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).