A Controllable Success Fix Rate Threshold Determination Method for GNSS Ambiguity Acceptance Tests
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Estimating and with the standard least-squares or Kalman filter. The integer nature of is not considered and its real-value estimates are treated as ‘float solution’. The real-valued estimates of and , and their variance-covariance matrix are denoted as:
- Mapping the real-valued ambiguity vector to an integer vector with an integer estimator. The integer estimation procedure can be described as , with .
- Validating the fixed integer with the ambiguity acceptance tests. If is rejected by the acceptance test, it means that the fixed integer is not considered as a correct integer solution
- Updating the real-valued parameters by if is accepted by ambiguity acceptance test. If is rejected by the test, the float solution is used as the final solution.
2. The Fixed Likelihood Ratio Threshold Determination Approach
2.1. Related Threshold Determination Methods
2.2. The Likelihood Ratio Integer Aperture Estimation
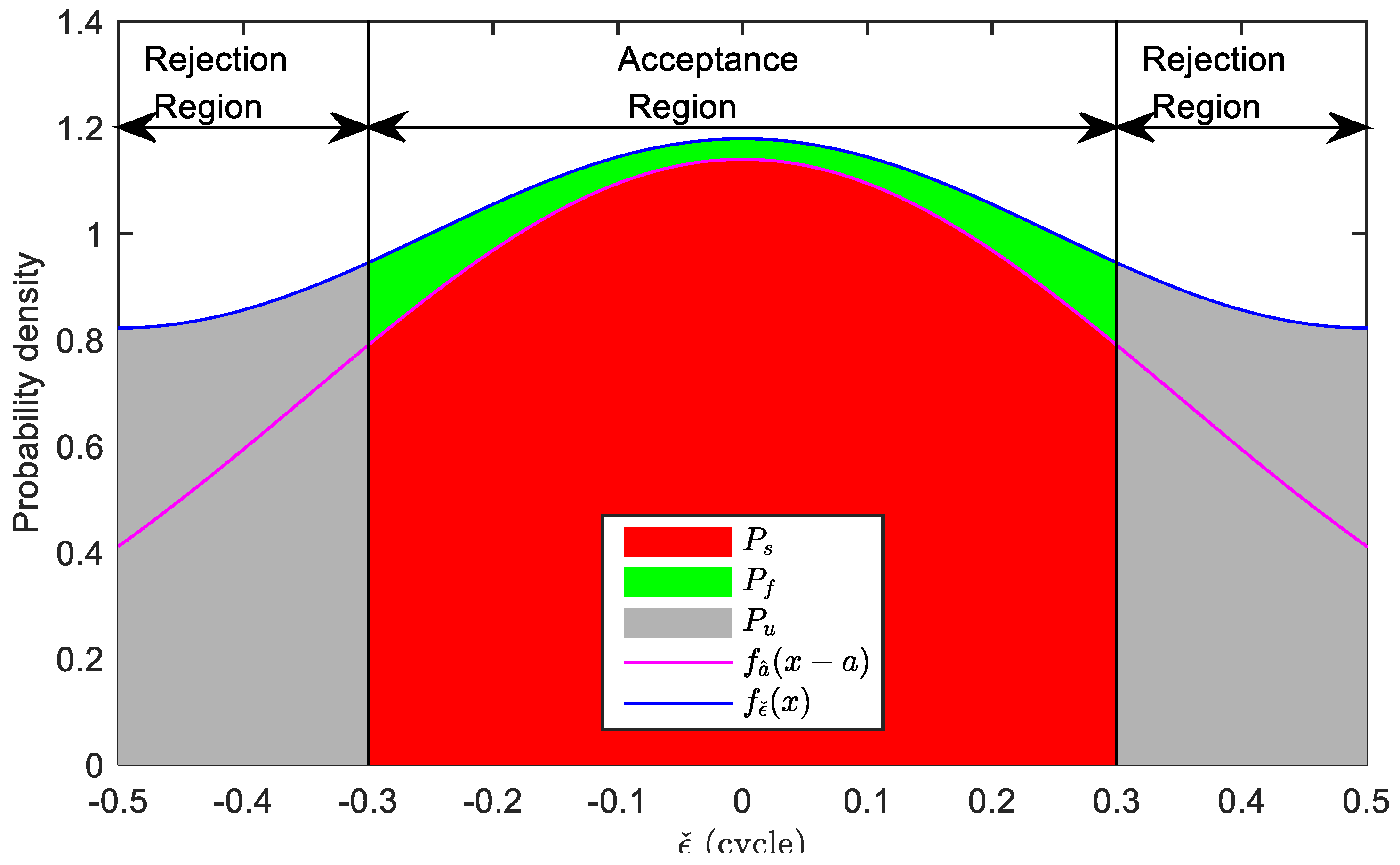
2.3. Properties of LRIA
2.3.1. The Success Fix Rate Property
2.3.2. The Local Failure Rate Property
2.3.3. Computational Complexity
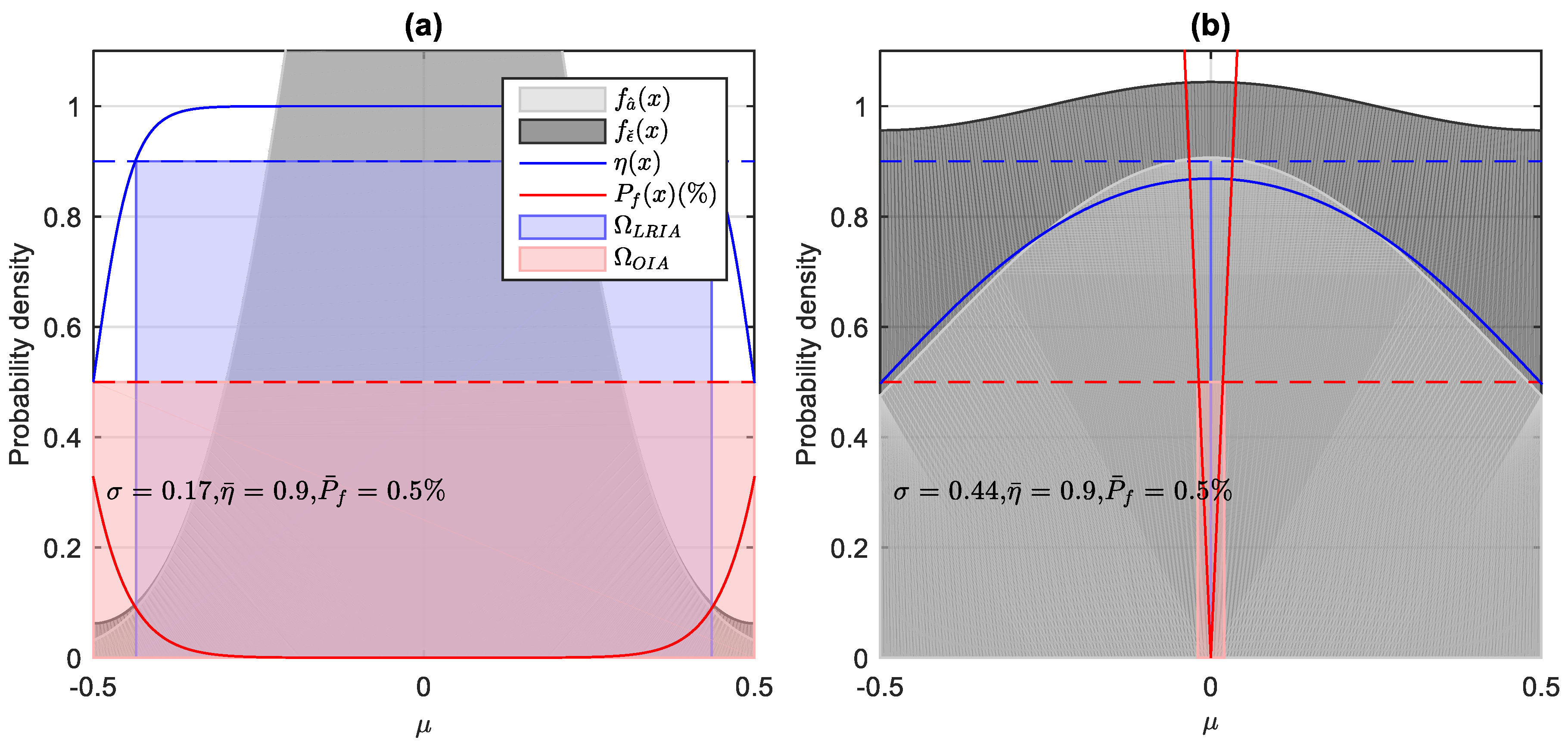
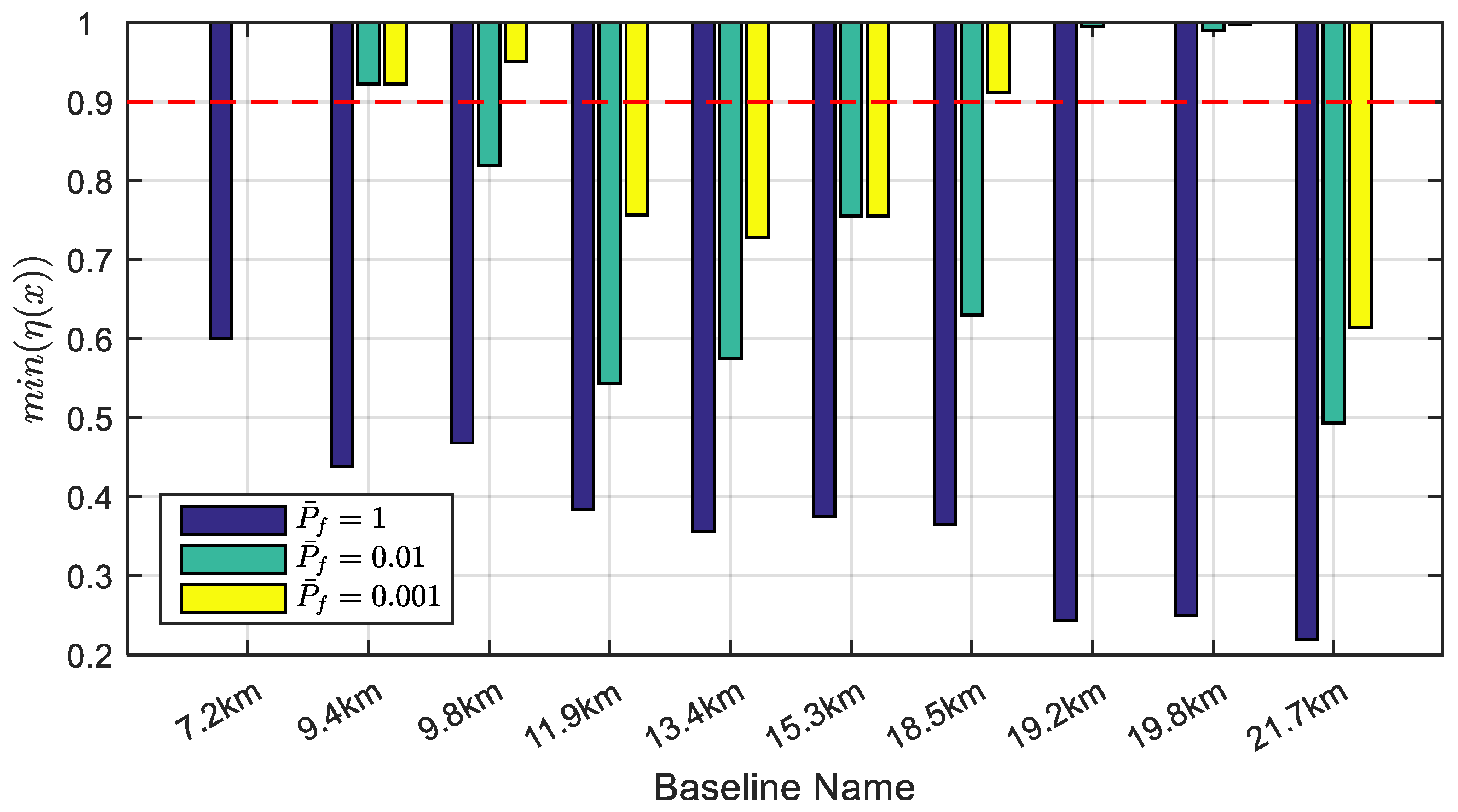
2.4. The Relationship between the FL-Threshold and the Model Strength
3. Numerical Analysis
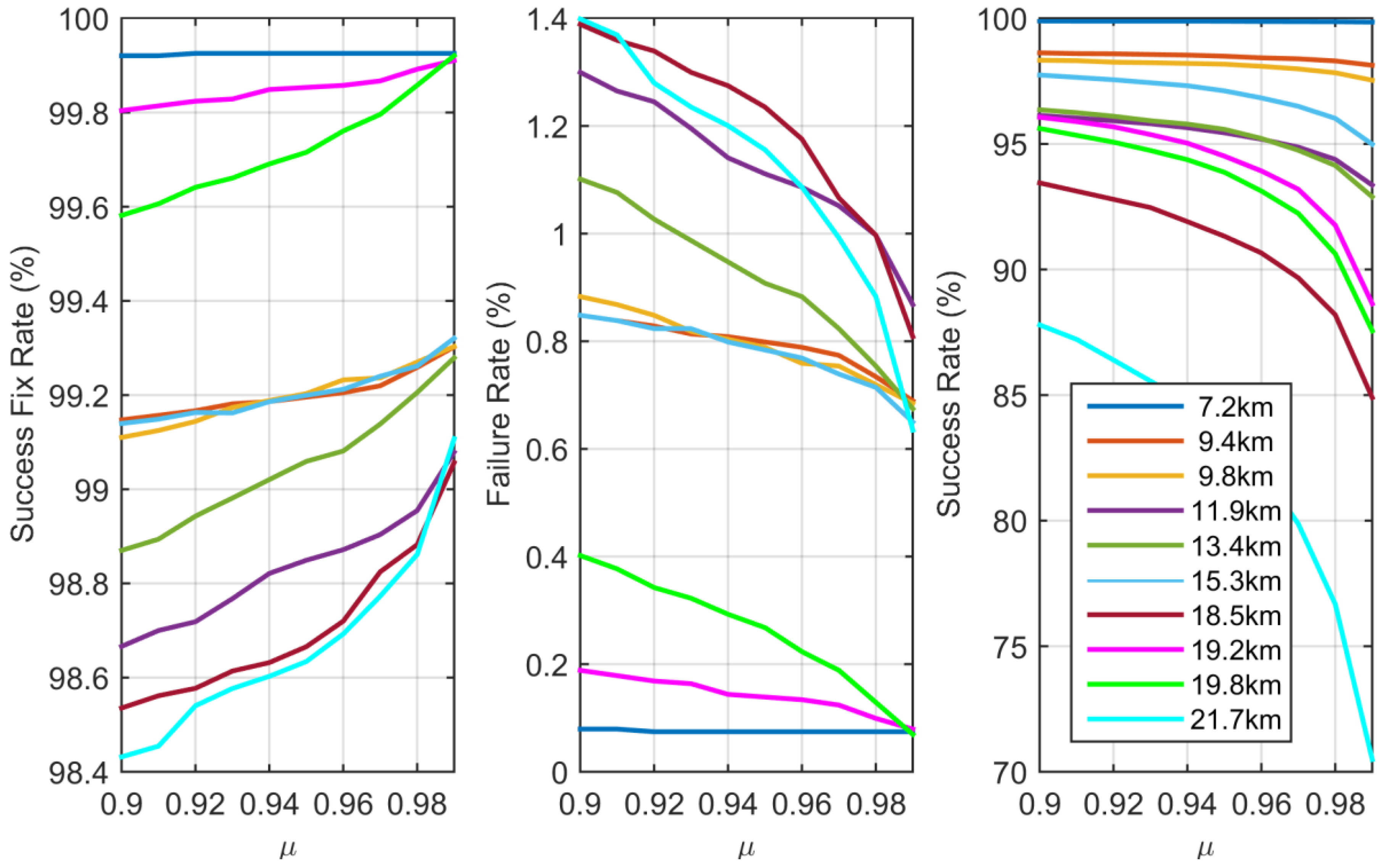
3.1. Failure Fate Assessment of the FL-approach
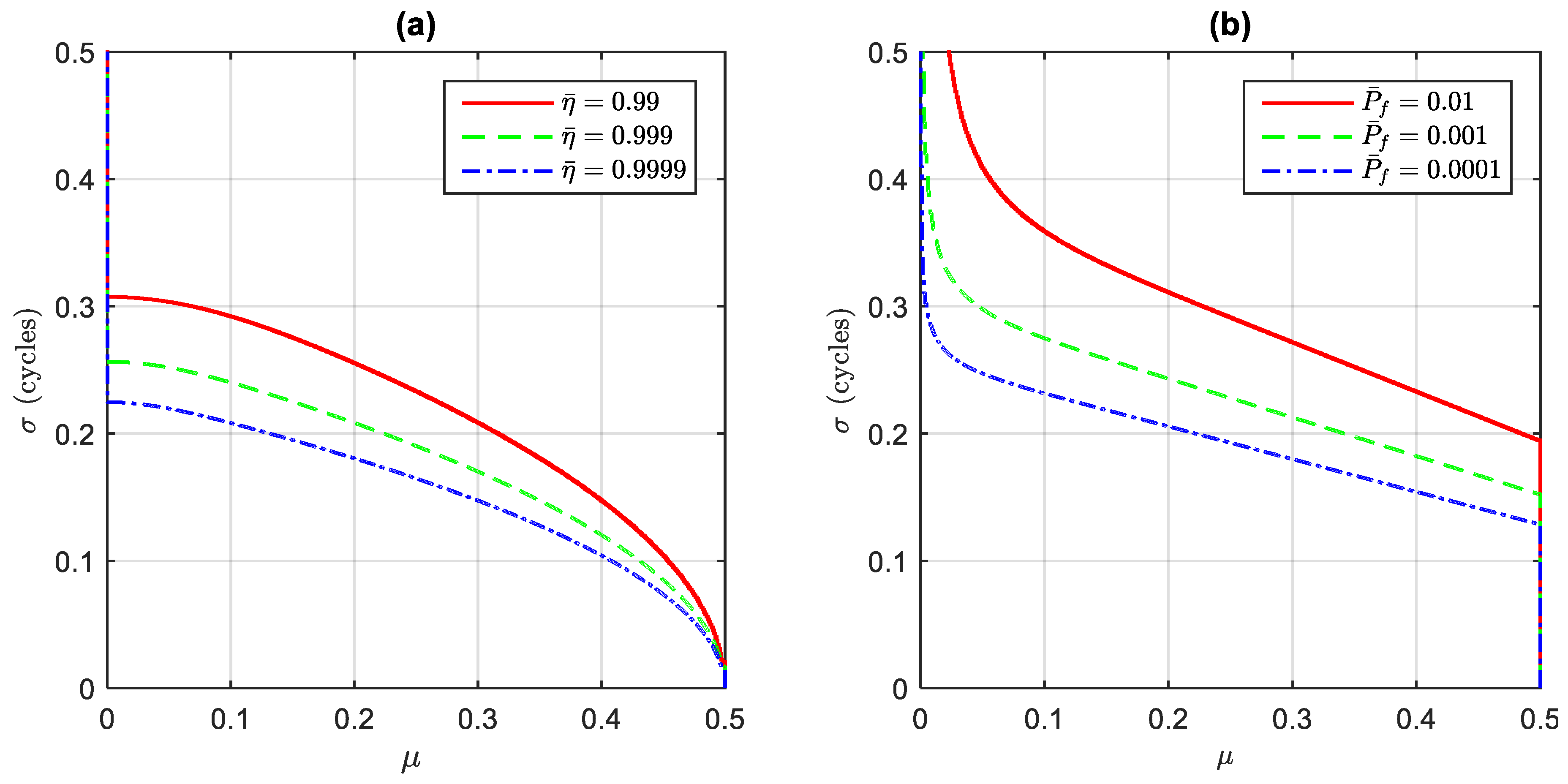
3.2. Success Rate Assessment of the FL-Approach
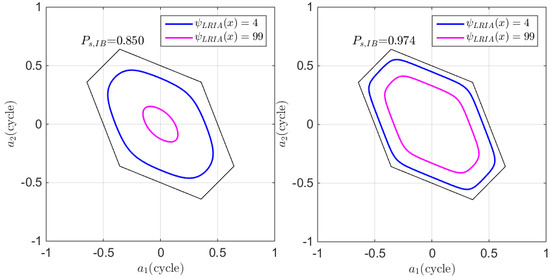
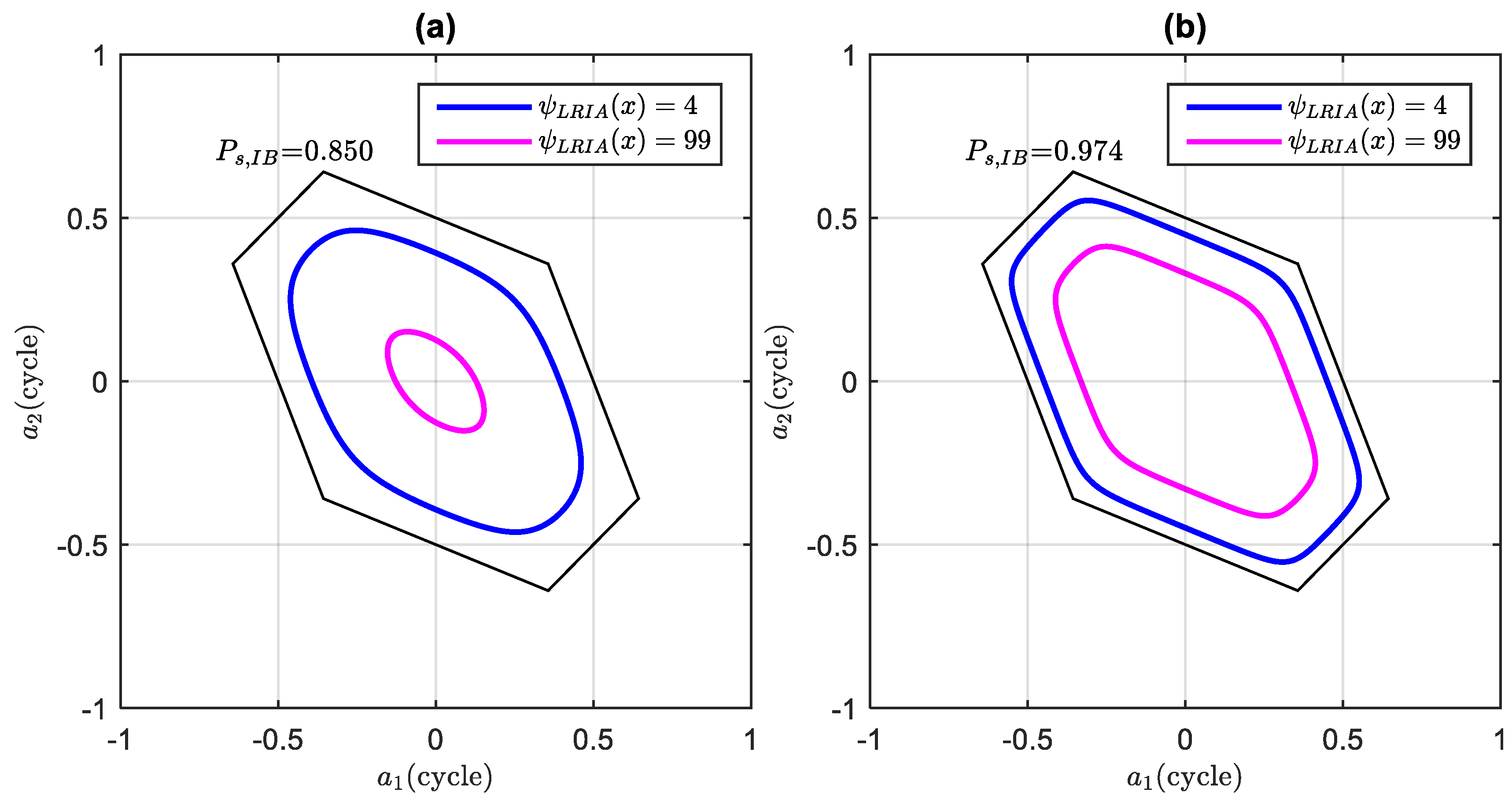
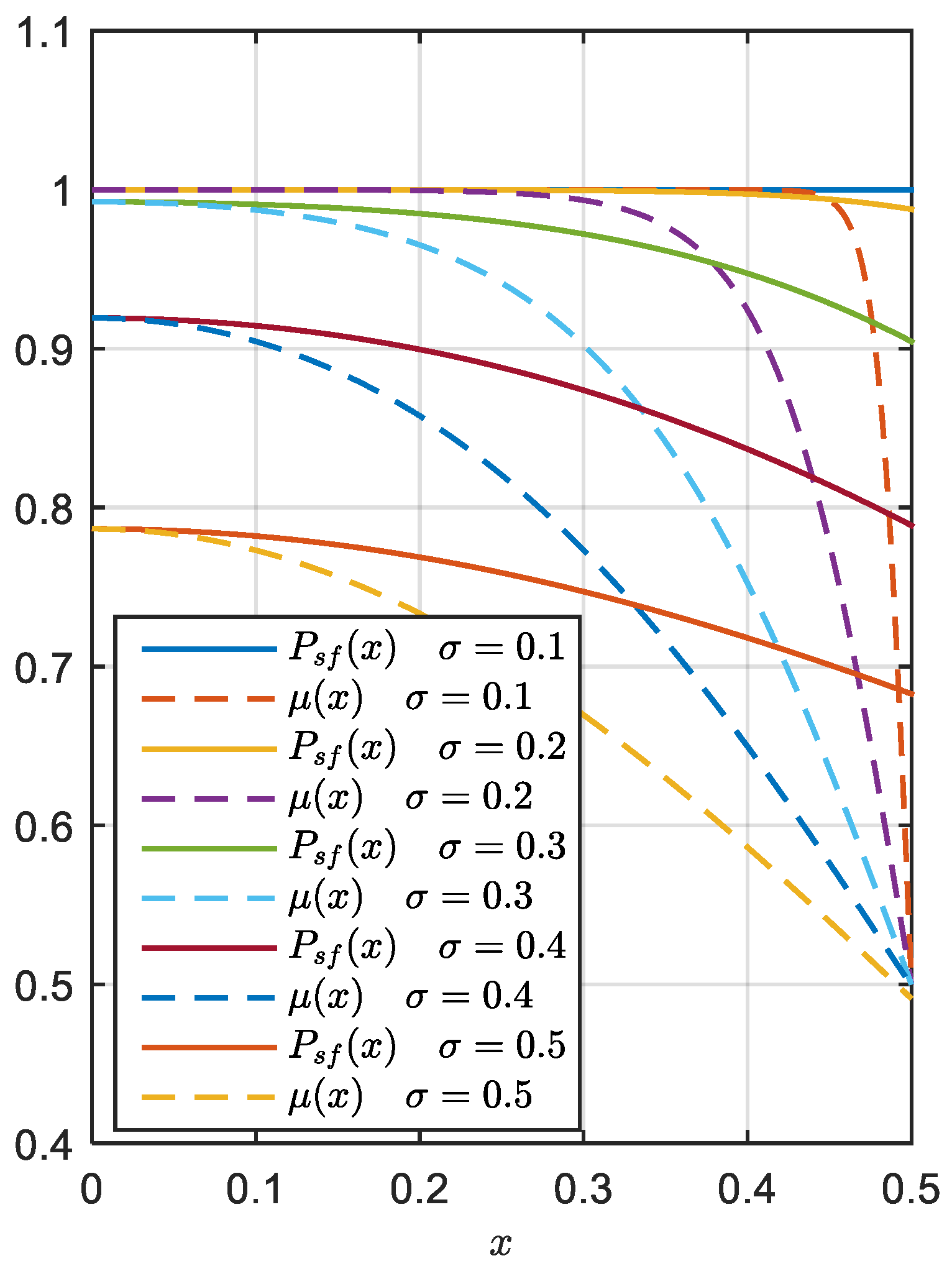
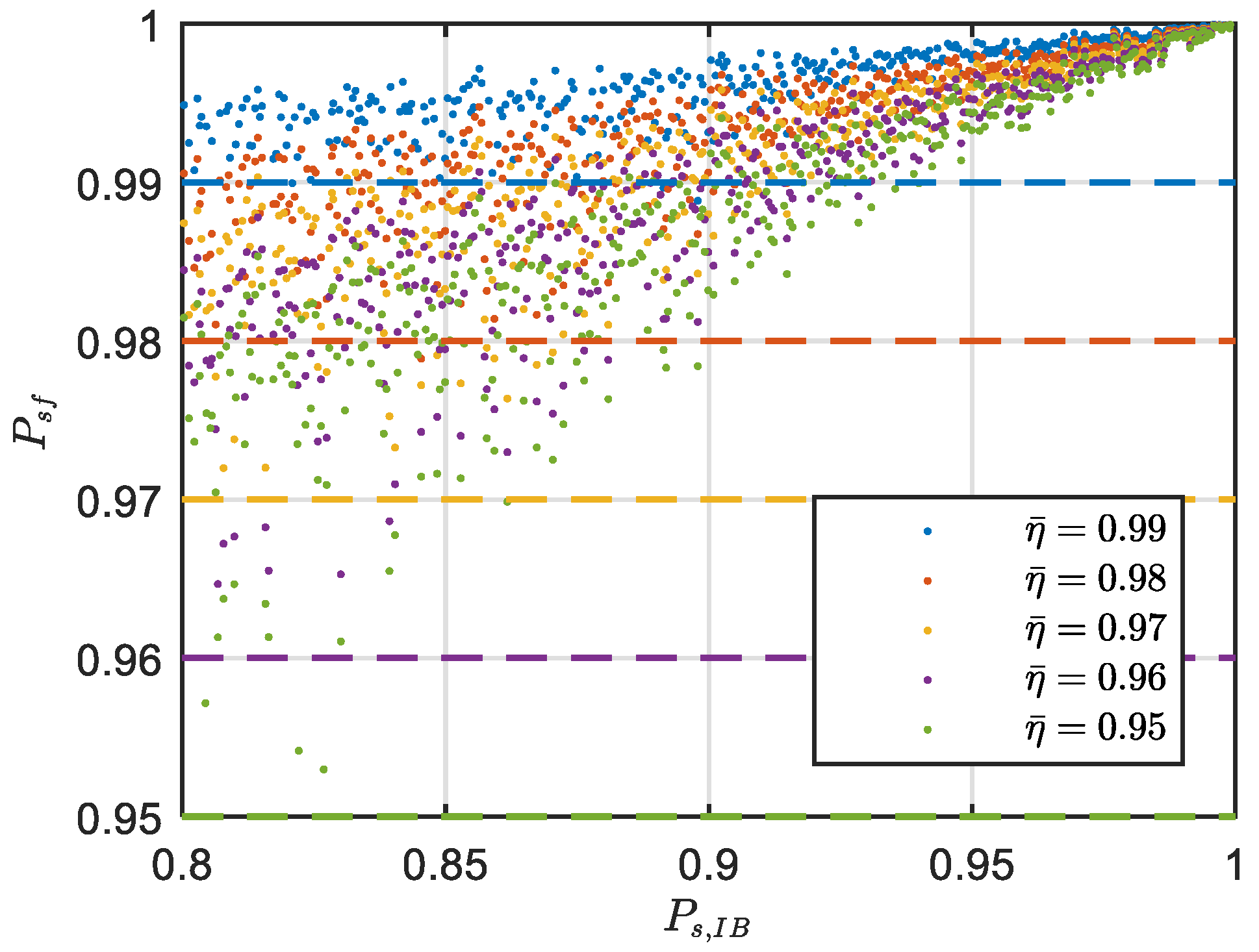
3.3. Success Fix Rate Assessment of the FL-Approach.
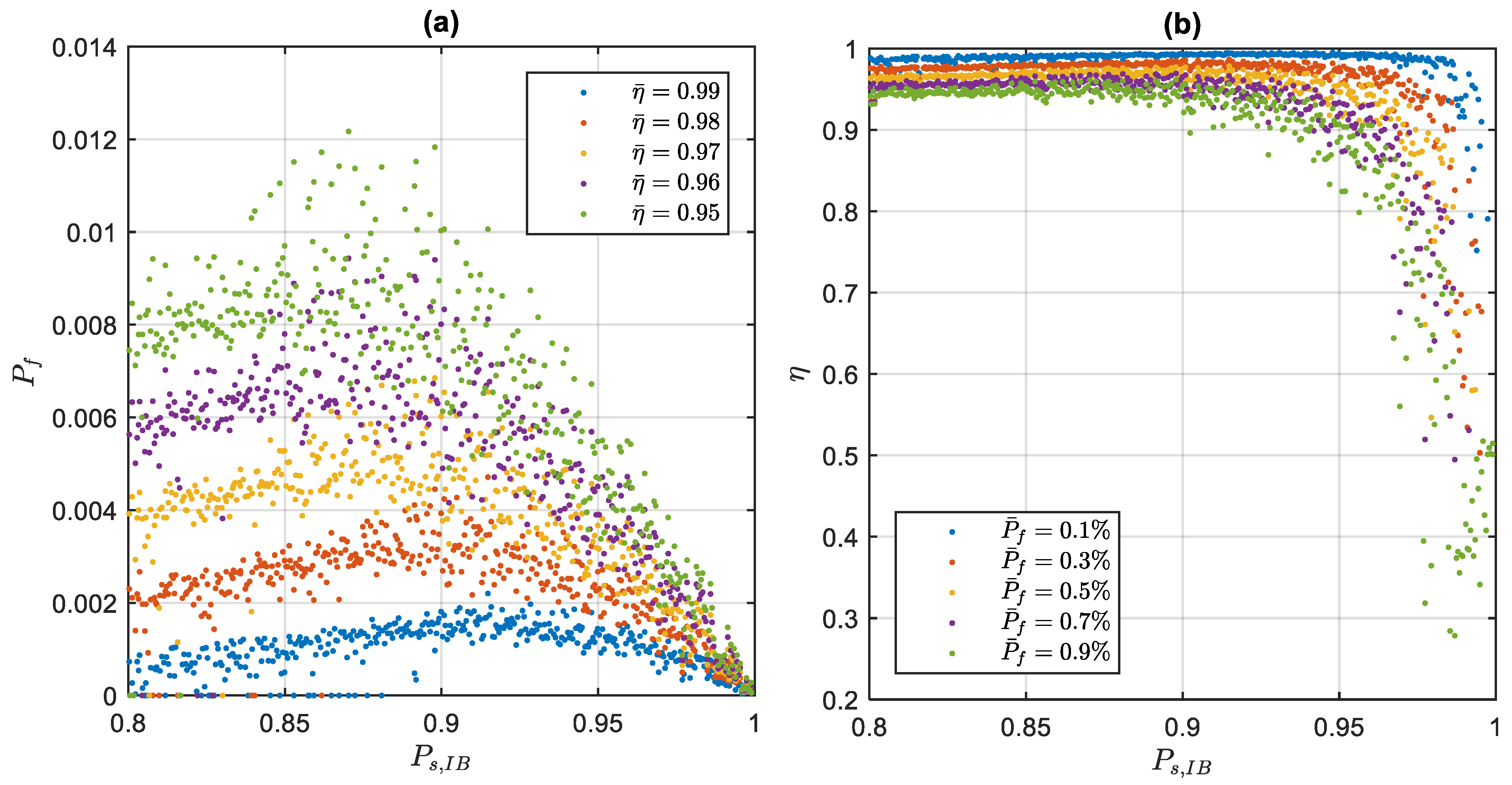
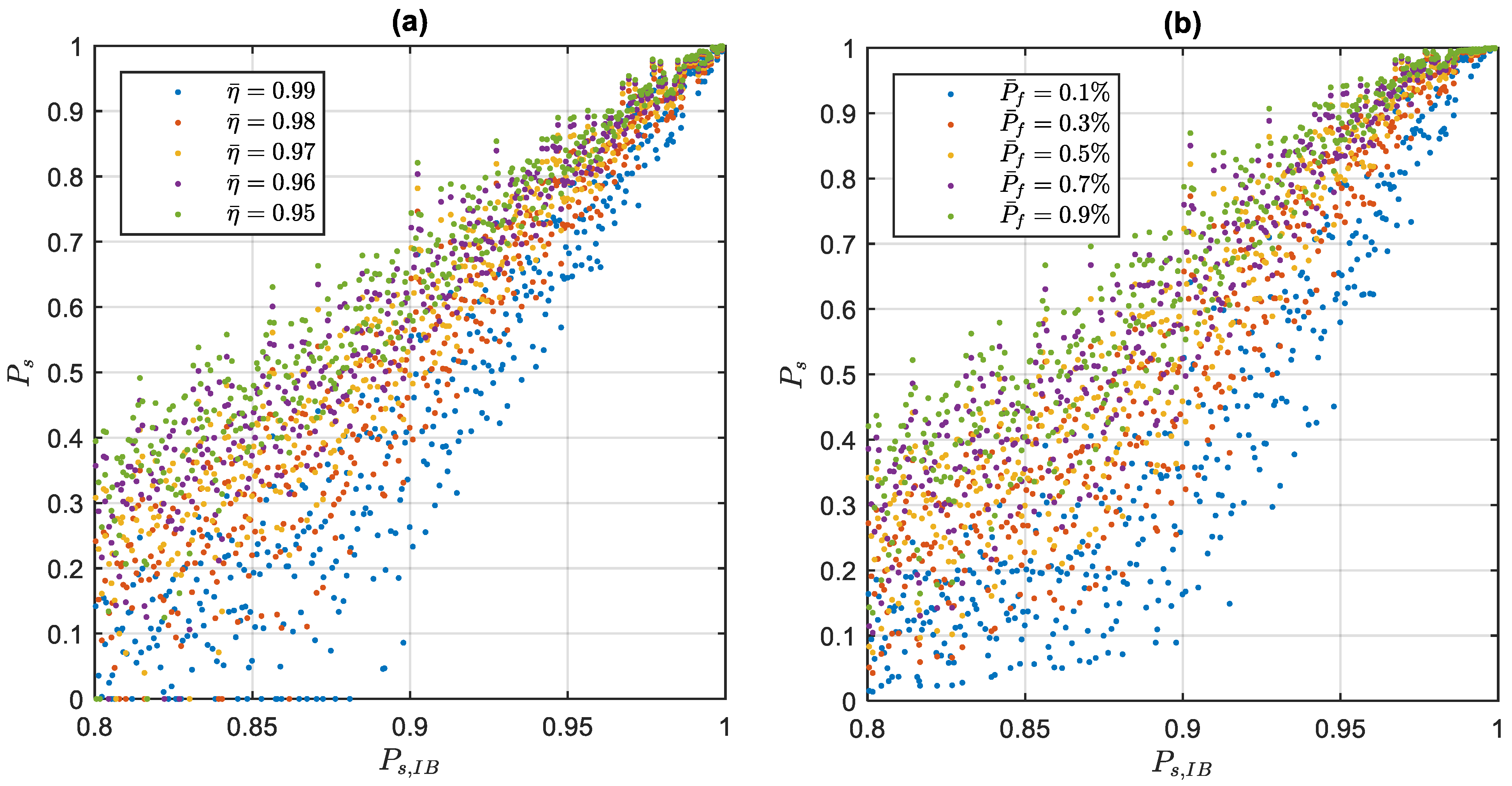
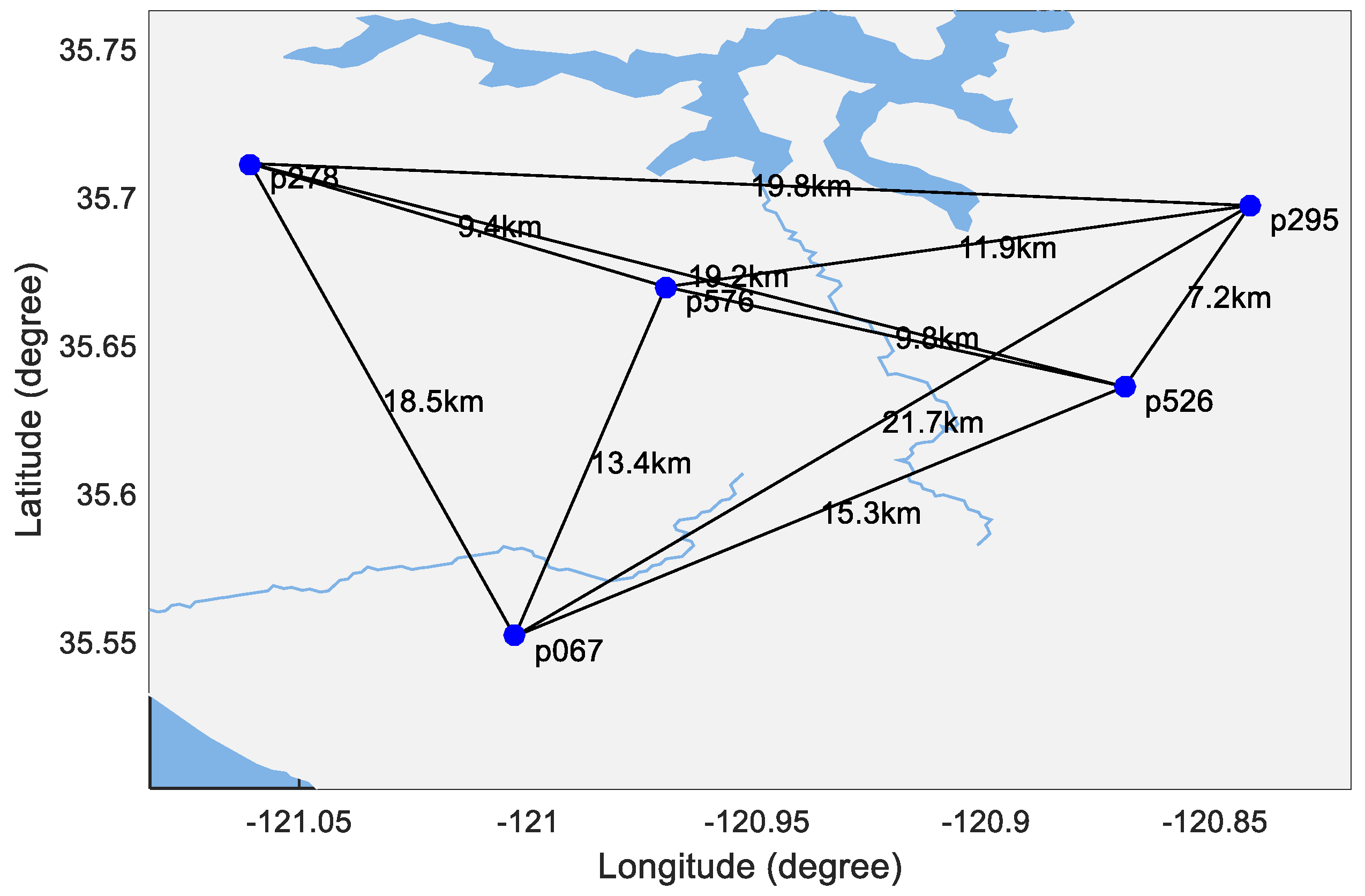
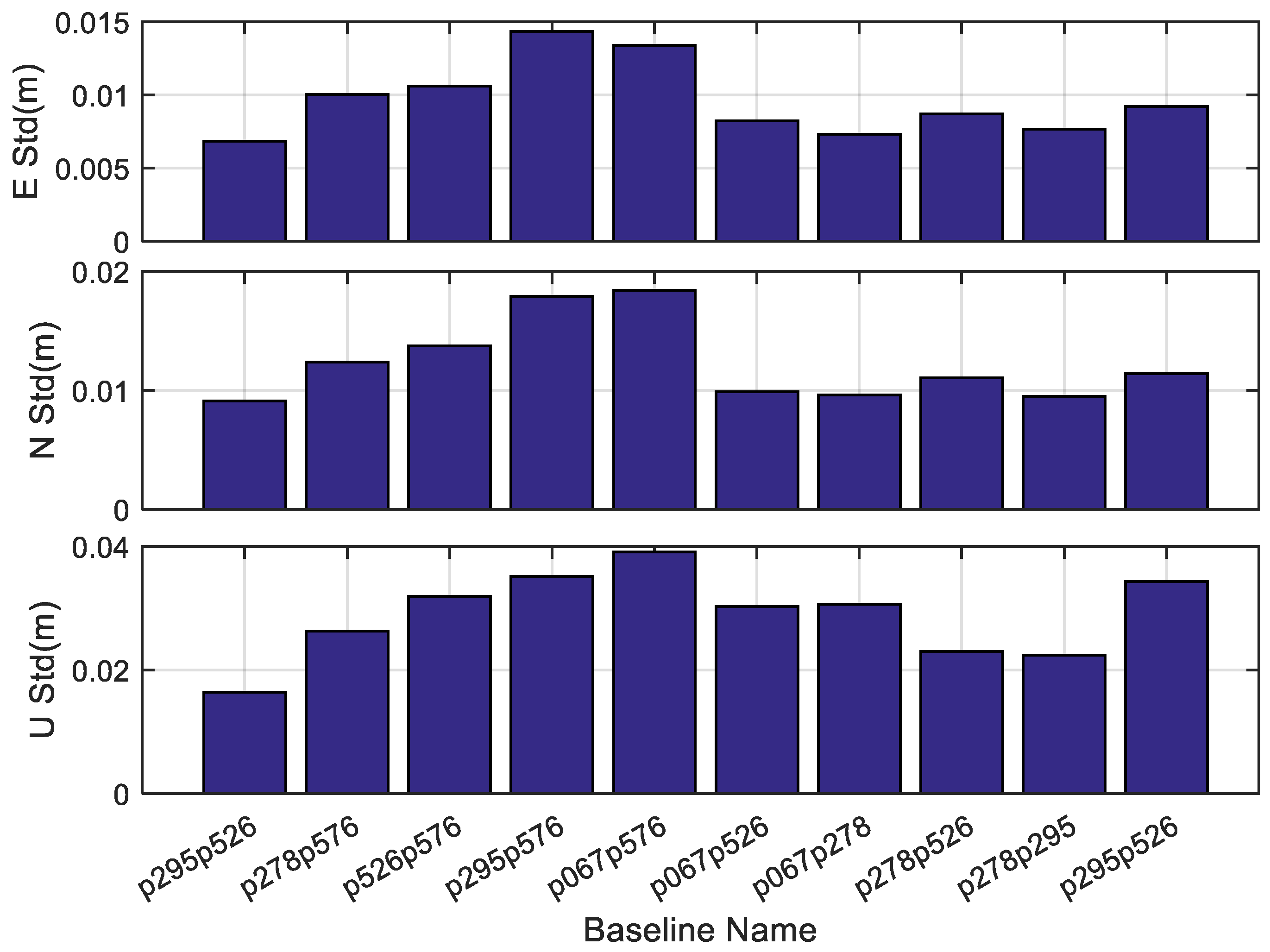
3.4. Performance Assessment with the Real GNSS Data
3.5. The Likelihood Ratio Analysis in Real Data Processing
3.6. Computational Efficiency of the FL-Approach
3.7. Positioning Precision with the LRIA Estimator
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A Proof of Equation Success Fix Rate Property
Appendix B Proof of Local Failure Rate Property
References
- Verhagen, S. Integer ambiguity validation: An open problem? GPS Solut. 2004, 8, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Feng, Y. Reliability of partial ambiguity fixing with multiple GNSS constellations. J. Geod. 2013, 87, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhagen, S. The GNSS Integer Ambiguities: Estimation and Validation; Delft University of Technology: Delft, The Netherland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Verhagen, S.; Teunissen, P.J.G. On the probability density function of the GNSS ambiguity residuals. GPS Solut. 2006, 10, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. A carrier phase ambiguity estimator with easy-to-evaluate fail-rate. Artif. Satell. 2003, 38, 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. Integer aperture GNSS ambiguity resolution. Artif. Satell. 2003, 38, 79–88. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Feng, Y. Fixed failure rate ambiguity validation methods for GPS and COMPASS. In Proceedings of the China Satellite Navigation Conference (CSNC), Wuhan, China, 15–17 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Verhagen, S. A new ambiguity acceptance test threshold determination method with controllable failure rate. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landau, H.; Euler, H.-J. On-the-fly ambiguity resolution for precise differential positioning. In Proceedings of the ION GPS, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 16–18 September 1992; pp. 607–613. [Google Scholar]
- Abidin, H.Z. Computational and Geometrical Aspects of on-the-Fly Ambiguity Resolution; University of New Brunswick: New Brunswick, CA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Euler, H.-J.; Schaffrin, B. On a measure for the discernibility between different ambiguity solutions in the static-kinematic GPS-mode. In Proceedings of the International Association of Geodesy Symposia, Banff, AB, Canada, 10–13 September 1990; pp. 285–295. [Google Scholar]
- Tiberius, C.C.; De Jonge, P. Fast positioning using the LAMBDA method. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Differential Satellite Navigation Systems, Bergen, Norway, 24–28 April 1995; pp. 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S. Quality-control issues relating to instantaneous ambiguity resolution for real-time GPS kinematic positioning. J. Geod. 1997, 71, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Stewart, M.P.; Tsakiri, M. A discrimination test procedure for ambiguity resolution on-the-fly. J. Geod. 1998, 72, 644–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. Some Remarks on GPS Ambiguity Resolution. Artif. Satell. 1998, 32, 119–130. [Google Scholar]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. Integer aperture bootstrapping: A new GNSS ambiguity estimator with controllable fail-rate. J. Geod. 2005, 79, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. Integer aperture least-squares estimation. Artif. Satell. 2005, 40, 219–227. [Google Scholar]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. Penalized GNSS Ambiguity Resolution. J. Geod. 2004, 78, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. GNSS ambiguity resolution with optimally controlled failure-rate. Artif. Satell. 2005, 40, 219–227. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L. Reliability Control of GNSS Carrier-Phase Integer Ambiguity Resolution; Queensland University of Technology: Brisbane, Australia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Verhagen, S.; Feng, Y. Ambiguity Acceptance Testing: A Comparison of the Ratio Test and Difference Test. In Proceedings of the China Satellite Navigation Conference (CSNC), Nanjing, China, 21–23 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Teunissen, P.J.G.; Verhagen, S. The GNSS ambiguity ratio-test revisited: A better way of using it. Surv. Rev. 2009, 41, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhagen, S.; Teunissen, P.J.G. The ratio test for future GNSS ambiguity resolution. GPS Solut. 2013, 17, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Verhagen, S.; Feng, Y. A Novel Ambiguity Acceptance Test Threshold Determination Method with Controllable Failure Rate. In Proceedings of the ION GNSS+, Tampa, FL, USA, 8–12 September 2014; pp. 2494–2502. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Y.; Verhagen, S.; Wu, J. An Efficient Implementation of Fixed Failure-Rate Ratio Test for GNSS Ambiguity Resolution. Sensors 2016, 16, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, M.; Schwarz, K.-P. Fast Ambiguity Resolution Using an Integer Nonlinear Programming Method. In Proceedings of the ION GPS, Palm Springs, CA, USA, 12–15 September 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Euler, H.-J.; Landau, H. Fast GPS Ambiguity Resolution On-The-Fly for Real Time Applications. In Proceedings of the 6th International Geodetic Symposium on Satellite Positioning, Columbus, OH, USA, 17–20 March 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, K.-R. Parameter Estimation and Hypothesis Testing in Linear Models; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Feng, Y.; Guo, J.; Wang, C. Impact of Decorrelation on Success Rate Bounds of Ambiguity Estimation. J. Navig. 2016, 69, 1061–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blewitt, G. Carrier phase ambiguity resolution for the Global Positioning System applied to geodetic baselines up to 2000 km. J. Geophys. Res. 1989, 94, 10.187–110.203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jonge, P.J.; Tiberius, C.C. The Lambda Method for Integer Ambiguity Estimation: Implementation Aspects; Delft University of Technology: Delft, The Netherlands, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Chen, R.; Shen, L.; Feng, Y.; Pan, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, P. Improving GNSS Ambiguity Acceptance Test Performance with the Generalized Difference Test Approach. Sensors 2018, 18, 3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, S.; Zhang, S.; Lahaye, F.O.; Héroux, P. A comparison between GPS-only and combined GPS+GLONASS Precise Point Positioning. J. Spat. Sci. 2013, 58, 169–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Feng, Y.; Guo, J. Reliability control of single-epoch RTK ambiguity resolution. GPS Solut. 2016, 21, 591–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Truth | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| H0 | Ha | ||
| Decision | Accept | Correctly Accept | Miss detection |
| Reject | False Alarm | Correctly Reject | |
| Baseline | Length (km) | Mean | Mean Time Consumption (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|
| p295–p526 | 7.2 | 99.97 | 27.53 |
| p278–p576 | 9.4 | 99.80 | 25.39 |
| p526–p576 | 9.8 | 99.74 | 25.27 |
| p295–p576 | 11.9 | 99.26 | 25.07 |
| p067–p576 | 13.4 | 98.64 | 25.17 |
| p067–p526 | 15.3 | 97.83 | 27.04 |
| p067–p278 | 18.5 | 94.73 | 27.79 |
| p278–p526 | 19.2 | 93.67 | 27.84 |
| p278–p295 | 19.8 | 92.91 | 28.19 |
| p067–p295 | 21.7 | 90.01 | 29.29 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Chen, R.; Shen, L.; Zheng, F.; Feng, Y.; Guo, J. A Controllable Success Fix Rate Threshold Determination Method for GNSS Ambiguity Acceptance Tests. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11070804
Wang L, Chen R, Shen L, Zheng F, Feng Y, Guo J. A Controllable Success Fix Rate Threshold Determination Method for GNSS Ambiguity Acceptance Tests. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(7):804. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11070804
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lei, Ruizhi Chen, Lili Shen, Fu Zheng, Yanming Feng, and Jiming Guo. 2019. "A Controllable Success Fix Rate Threshold Determination Method for GNSS Ambiguity Acceptance Tests" Remote Sensing 11, no. 7: 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11070804
APA StyleWang, L., Chen, R., Shen, L., Zheng, F., Feng, Y., & Guo, J. (2019). A Controllable Success Fix Rate Threshold Determination Method for GNSS Ambiguity Acceptance Tests. Remote Sensing, 11(7), 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11070804