Hydro-Meteorological Assessment of Three GPM Satellite Precipitation Products in the Kelantan River Basin, Malaysia
Abstract
1. Introduction
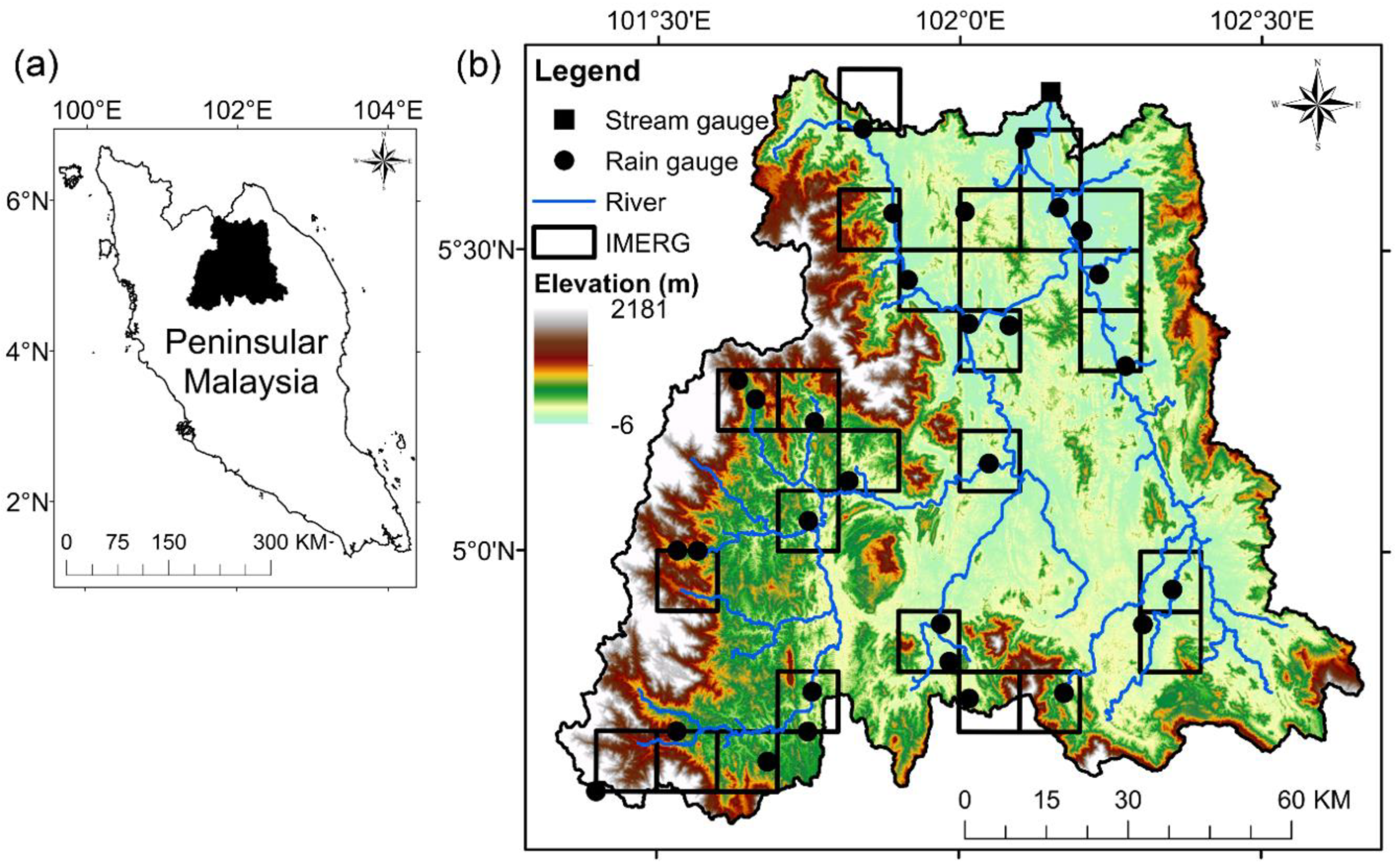
2. Study Area
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. GPM IMERG
3.2. Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) Model
3.3. Ground Data
3.4. Hydro-Meteorological Assessment
4. Results
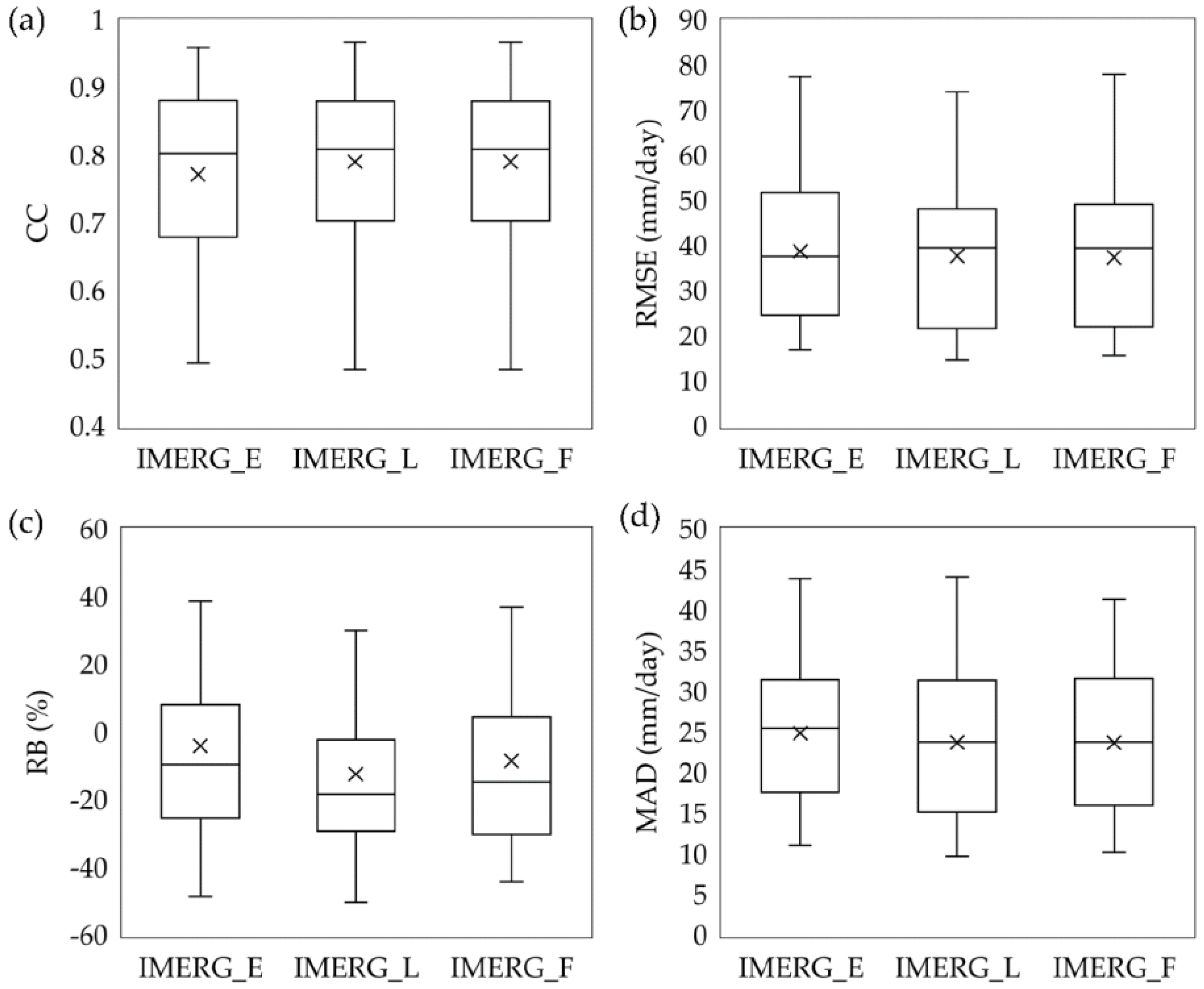
4.1. Meteorological Assessment
4.2. SWAT Model Calibration and Validation
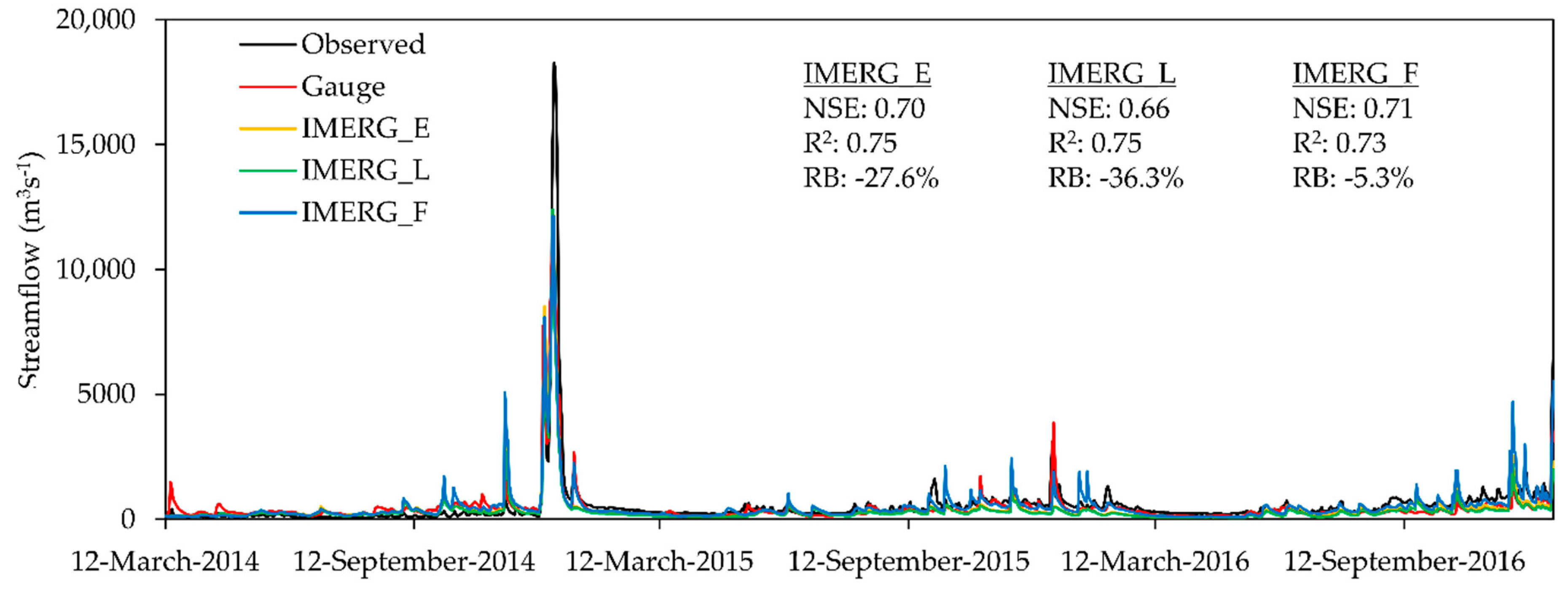
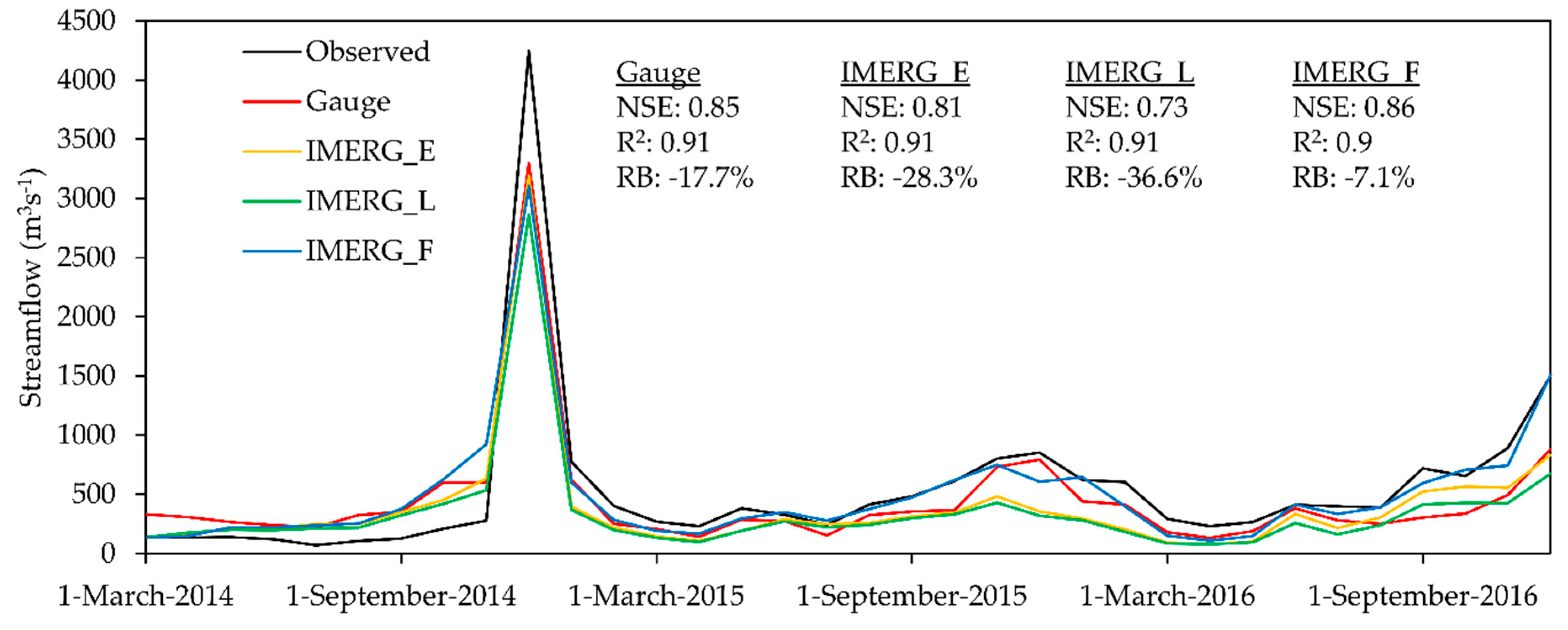
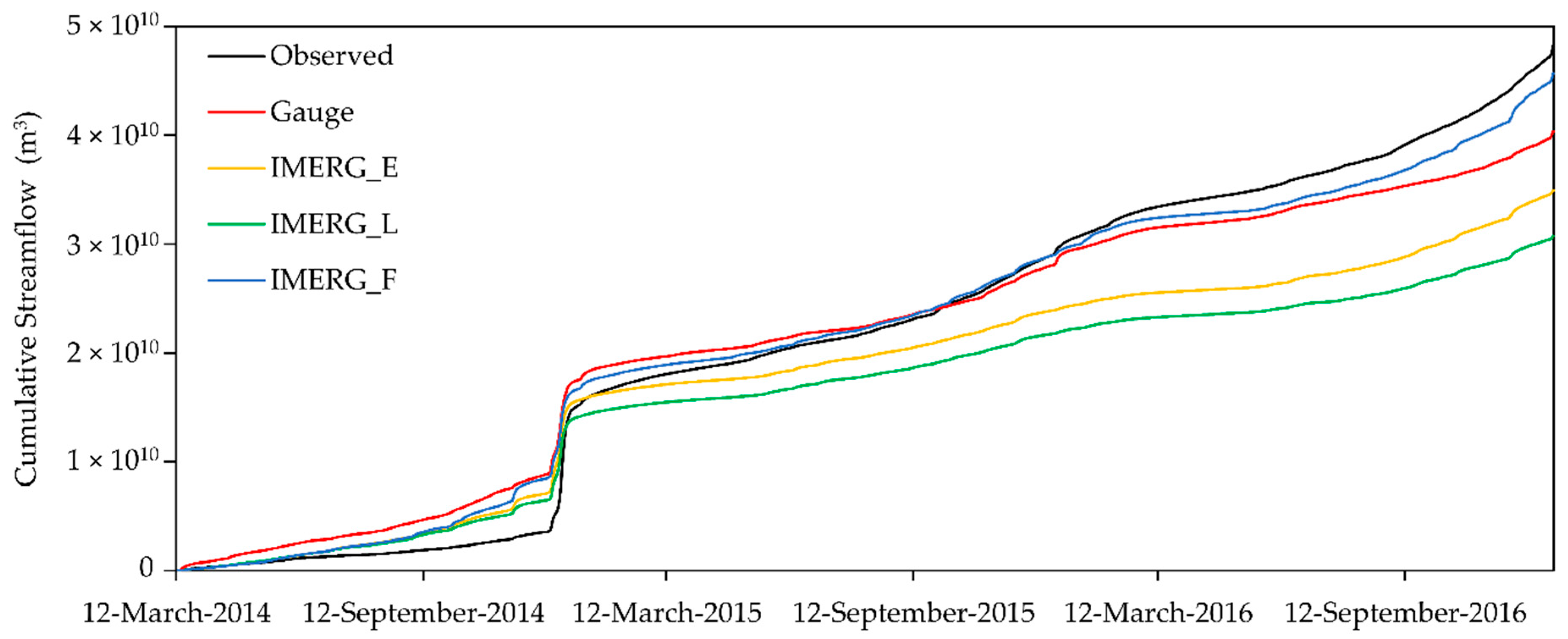
4.3. Hydrological Assessment
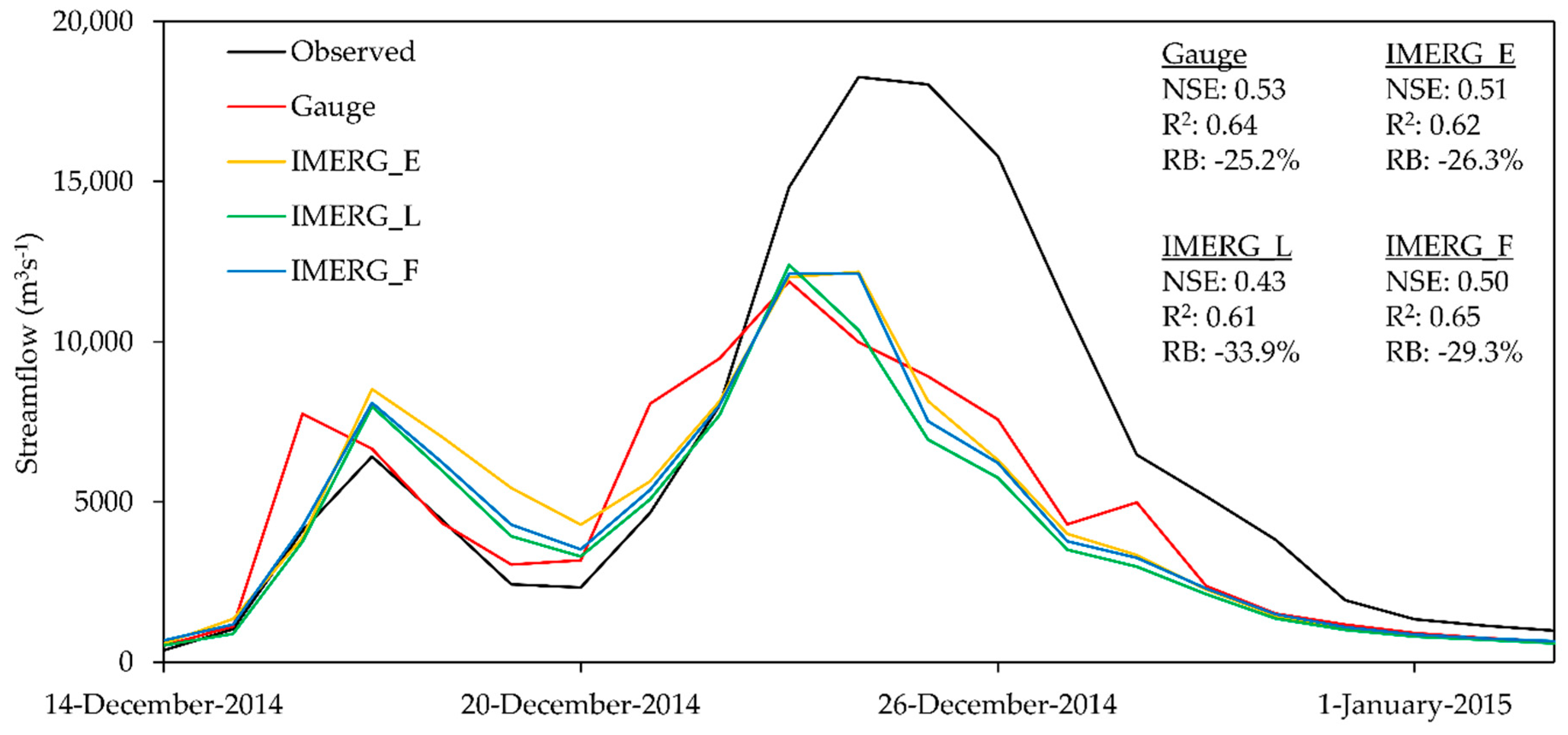
4.4. The 2014–2015 Flood Assessment
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- -
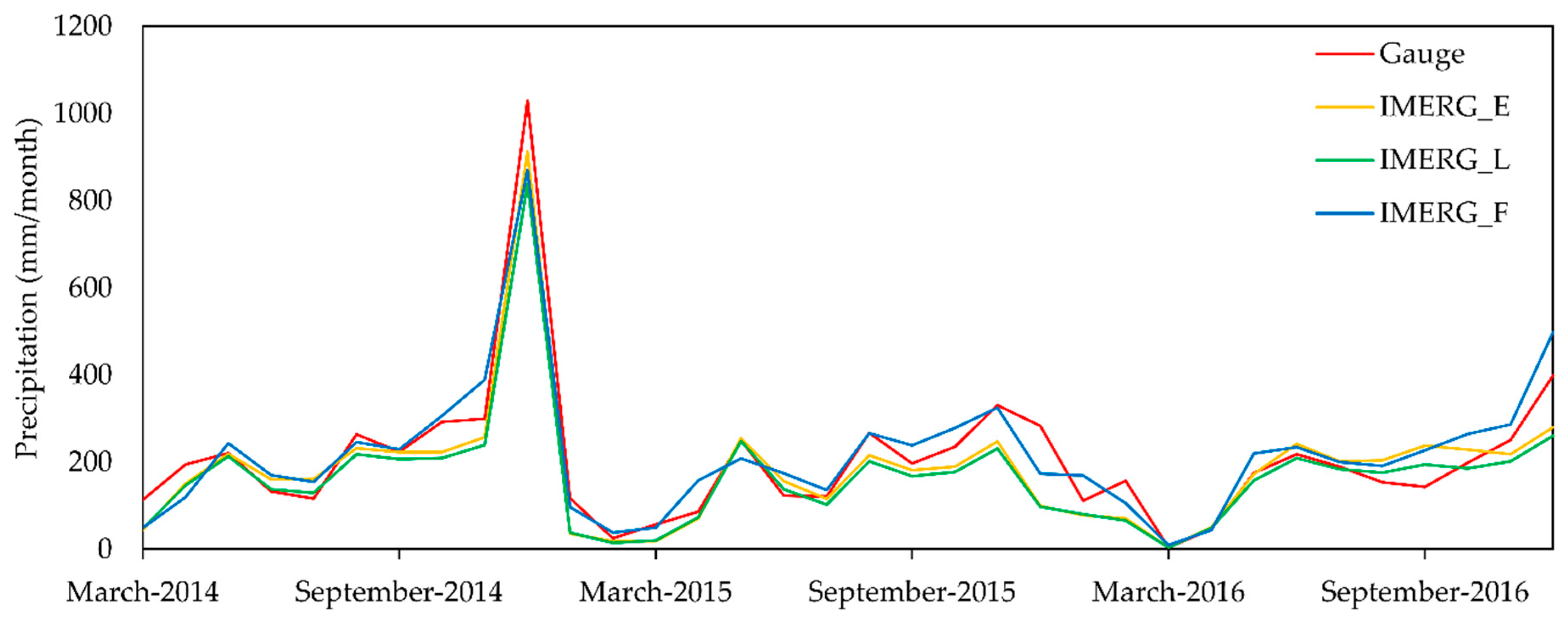
- The temporal variability of monthly precipitation was well captured by the IMERG products, with low precipitation amounts in February 2015 and March 2016, and high precipitation amounts in December 2014. The IMERG_F slightly outperformed the IMERG_E and IMERG_L in terms of systematic bias, with a RB value of 7.14%.
- -
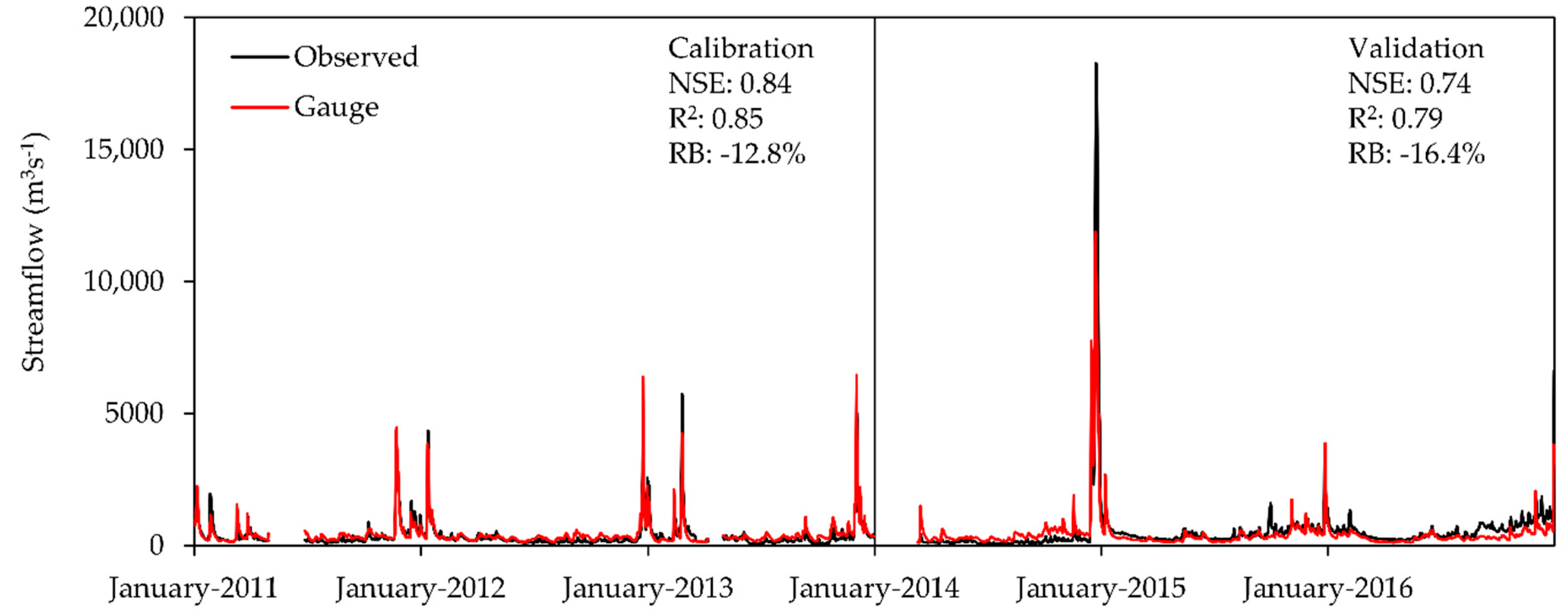
- The SWAT model performed “good” in daily streamflow simulations, with NSE and R2 values of 0.74 and 0.79, respectively. However, the model underestimated the daily streamflow by 16.4%, particularly during the peak flows. Because SWAT daily streamflow validation is relatively low in Malaysia, this study could act as a reference to those would like to study the daily scale of the Malaysian hydrological cycle. A modification of the oil palm module within the SWAT module is essential to improve the model’s capability in tropical regions.
- -
- The IMERG products performed comparable with precipitation gauges in streamflow simulations, indicating a great potential in tropical hydrology applications. Overall, the IMERG_F (NSE = 0.71~0.86, R2 = 0.73~0.9 and RB = −5.3%~−7.1%) performed the best in both daily and monthly streamflow simulations, followed by the IMERG_E (NSE = 0.7~0.81, R2 = 0.75~0.91 and RB = −27.6%~−28.3%), and IMERG_L (NSE = 0.66~0.73 and R2 = 0.75~0.91 and RB = −36.3%~−36.6%). The near real-time products underestimated the daily and monthly streamflow significantly, so a systematic bias correction is essential prior to applying them in any operational applications.
- -
- Similar to the findings reported by Tan and Santo [7], the IMERG products have better meteorological performance in the 2014–2015 flood period than the entire period. In contrast to the meteorological assessment, all three products have a poorer hydrological performance in the 2014–2015 flood period compared to the entire period. Nevertheless, the performance of the IMERG_E and IMERG_F was still regarded as “satisfactory” in the flood streamflow simulations based on the NSE and R2 values of 0.5~0.51 and 0.62~0.65, respectively. One thing to be considered is that the IMERG products underestimated the peak flow rate from 23 to 28 December 2014.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garcia, M.; Peters-Lidard, C.D.; Goodrich, D.C. Spatial interpolation of precipitation in a dense gauge network for monsoon storm events in the southwestern United States. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Xie, X.; Liu, D.L.; Ji, F.; Wang, L. Spatial interpolation of daily rainfall data for local climate impact assessment over greater sydney region. Adv. Meteorol. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Duan, Z. Assessment of GPM and TRMM precipitation products over Singapore. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, A.Y.; Kakar, R.K.; Neeck, S.; Azarbarzin, A.A.; Kummerow, C.D.; Kojima, M.; Oki, R.; Nakamura, K.; Iguchi, T. The global precipitation measurement mission. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 701–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Ma, Y.; Long, D.; Zhong, L.; Hong, Y. Evaluation of GPM day-1 IMERG and TMPA version-7 legacy products over mainland China at multiple spatiotemporal scales. J. Hydrol. 2016, 533, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, M.N.; Ding, Y.; Shangguan, D.; Ahmad, I.; Ijaz, M.W.; Farid, H.U.; Yagoub, Y.E.; Zaman, M.; Adnan, M. Performance evaluation of latest Integrated Multi-satellite Retrievals for Global Precipitation Measurement (IMERG) over the northern highlands of Pakistan. Atmos. Res. 2018, 205, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.L.; Santo, H. Comparison of GPM IMERG, TMPA 3B42 and PERSIANN-CDR satellite precipitation products over malaysia. Atmos. Res. 2018, 202, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asong, Z.E.; Razavi, S.; Wheater, H.S.; Wong, J.S. Evaluation of Integrated Multisatellite Retrievals for GPM (IMERG) over southern Canada against ground precipitation observations: A preliminary assessment. J. Hydrometeorol. 2017, 18, 1033–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.L.; Gassman, P.W.; Cracknell, A.P. Assessment of three long-term gridded climate products for hydro-climatic simulations in tropical river basins. Water 2017, 9, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Zhang, L.; Win, K.; Ren, L.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Y. Assessment of GPM and TRMM multi-satellite precipitation products in streamflow simulations in a data-sparse mountainous watershed in Myanmar. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakoksung, K.; Takagi, M. Effect of satellite based rainfall products on river basin responses of runoff simulation on flood event. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2016, 2, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhong, R.; Lai, C.; Chen, J. Evaluation of the GPM IMERG satellite-based precipitation products and the hydrological utility. Atmos. Res. 2017, 196, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Zeng, Z.; Long, D.; Guo, X.; Yong, B.; Zhang, W.; Hong, Y. Statistical and hydrological comparisons between trmm and gpm level-3 products over a midlatitude basin: Is day-1 IMERG a good successor for TMPA 3B42V7? J. Hydrometeorol. 2016, 17, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Tang, G.; Zhao, P.; Hong, Y.; Gou, Y.; Yang, K. Statistical assessment and hydrological utility of the latest multi-satellite precipitation analysis IMERG in Ganjiang River basin. Atmos. Res. 2017, 183, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubieta, R.; Getirana, A.; Espinoza, J.C.; Lavado-Casimiro, W.; Aragon, L. Hydrological modeling of the Peruvian—Ecuadorian Amazon basin using GPM-IMERG satellite-based precipitation dataset. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 3543–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Tan, K.; Chua, V.; Chan, N. Evaluation of TRMM product for monitoring drought in the Kelantan River Basin, Malaysia. Water 2017, 9, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J. Integrated Multi-Satellite Retrievals for GPM (IMERG) Technical Documentation; NASA/GSFC: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Precipitation Measurement Missions. Available online: https://pmm.Nasa.Gov/data-access/downloads/gpm (accessed on 3 April 2018).
- Arnold, J.G.; Srinivasan, R.; Muttiah, R.S.; Williams, J.R. Large area hydrologic modeling and assessment part I: Model development. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1998, 34, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannschatz, T.; Wolf, T.; Hülsmann, S. Nexus tools platform: Web-based comparison of modelling tools for analysis of water-soil-waste nexus. Environ. Model. Softw. 2016, 76, 137–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.G.; Kiniry, J.R.; Srinivasan, R.; Williams, J.R.; Haney, E.B.; Neitsch, S.L. Soil Andwater Assessment Tool Input/Tool File Documentation. Version 2012; Texas Water Resources Institute: College Station, TX, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Neitsch, S.L.; Arnold, J.G.; Kiniry, J.R.; Grassland, J.R.W. Soil and Water Assessment Tool Theoretical Documentation Version 2009; Agricultural Research Service Blackland Research Center: Temple, TX, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.L.; Ficklin, D.; Ibrahim, A.L.; Yusop, Z. Impacts and uncertainties of climate change on streamflow of the Johor River Basin, Malaysia using a CMIP5 general circulation model ensemble. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2014, 5, 676–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.L.; Ibrahim, A.L.; Yusop, Z.; Duan, Z.; Ling, L. Impacts of land-use and climate variability on hydrological components in the Johor River Basin, Malaysia. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2015, 60, 873–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dlamini, N.S.; Kamal, M.R.; Soom, M.A.B.M.; Mohd, M.S.F.b.; Abdullah, A.F.B.; Hin, L.S. Modeling potential impacts of climate change on streamflow using projections of the 5th assessment report for the Bernam River Basin, Malaysia. Water 2017, 9, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, Z.A.; Hamidon, N.; Yusof, M.S.; Ghani, A.A. Flow and sediment yield simulations for Bukit Merah Reservoir catchment, Malaysia: A case study. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 66, 2170–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memarian, H.; Balasundram, S.K.; Abbaspour, K.C.; Talib, J.B.; Boon Sung, C.T.; Sood, A.M. SWAT-based hydrological modelling of tropical land-use scenarios. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2014, 59, 1808–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.L.; Ibrahim, A.L.; Yusop, Z.; Chua, V.P.; Chan, N.W. Climate change impacts under CMIP5 RCP scenarios on water resources of the Kelantan River Basin, Malaysia. Atmos. Res. 2017, 189, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Ibrahim, A.; Duan, Z.; Cracknell, A.; Chaplot, V. Evaluation of six high-resolution satellite and ground-based precipitation products over Malaysia. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 1504–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.L.; Ficklin, D.L.; Dixon, B.; Ibrahim, A.L.; Yusop, Z.; Chaplot, V. Impacts of DEM resolution, source, and resampling technique on SWAT-simulated streamflow. Appl. Geogr. 2015, 63, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condom, T.; Rau, P.; Espinoza, J.C. Correction of TRMM 3B43 monthly precipitation data over the mountainous areas of Peru during the period. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 1924–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chokngamwong, R.; Chiu, L.S. Thailand daily rainfall and comparison with TRMM products. J. Hydrometeorol. 2008, 9, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feidas, H.; Porcu, F.; Puca, S.; Rinollo, A.; Lagouvardos, C.; Kotroni, V. Validation of the h-saf precipitation product H03 over Greece using rain gauge data. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 131, 377–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Gitau, M.W.; Pai, N.; Daggupati, P. Hydrologic and water quality models: Performance measures and evaluation criteria. Trans. ASABE 2015, 58, 1763–1785. [Google Scholar]
- Tam, N.V.; Jörg, D. Modification of the SWAT model to simulate regional groundwater flow using a multicell aquifer. Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 939–953. [Google Scholar]
- Krysanova, V.; White, M. Advances in water resources assessment with SWAT—An overview. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2015, 60, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.L.; Chua, V.P.; Tan, K.C.; Brindha, K. Evaluation of TMPA 3B43 and NCEP-CFSR precipitation products in drought monitoring over Singapore. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 2089–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, P.; Boyle, D.; Bäse, F. Comparison of different efficiency criteria for hydrological model assess. Adv. Geosci. 2005, 5, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, A.; Eguchi, S.; Kato, T.; Kasuya, M.; Ono, K.; Miyata, A.; Tase, N. Development and evaluation of a paddy module for improving hydrological simulation in SWAT. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 137, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, A.; Eguchi, S.; Kasuya, M. Examination of the water balance of irrigated paddy fields in SWAT 2009 using the curve number procedure and the pothole module. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2014, 60, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
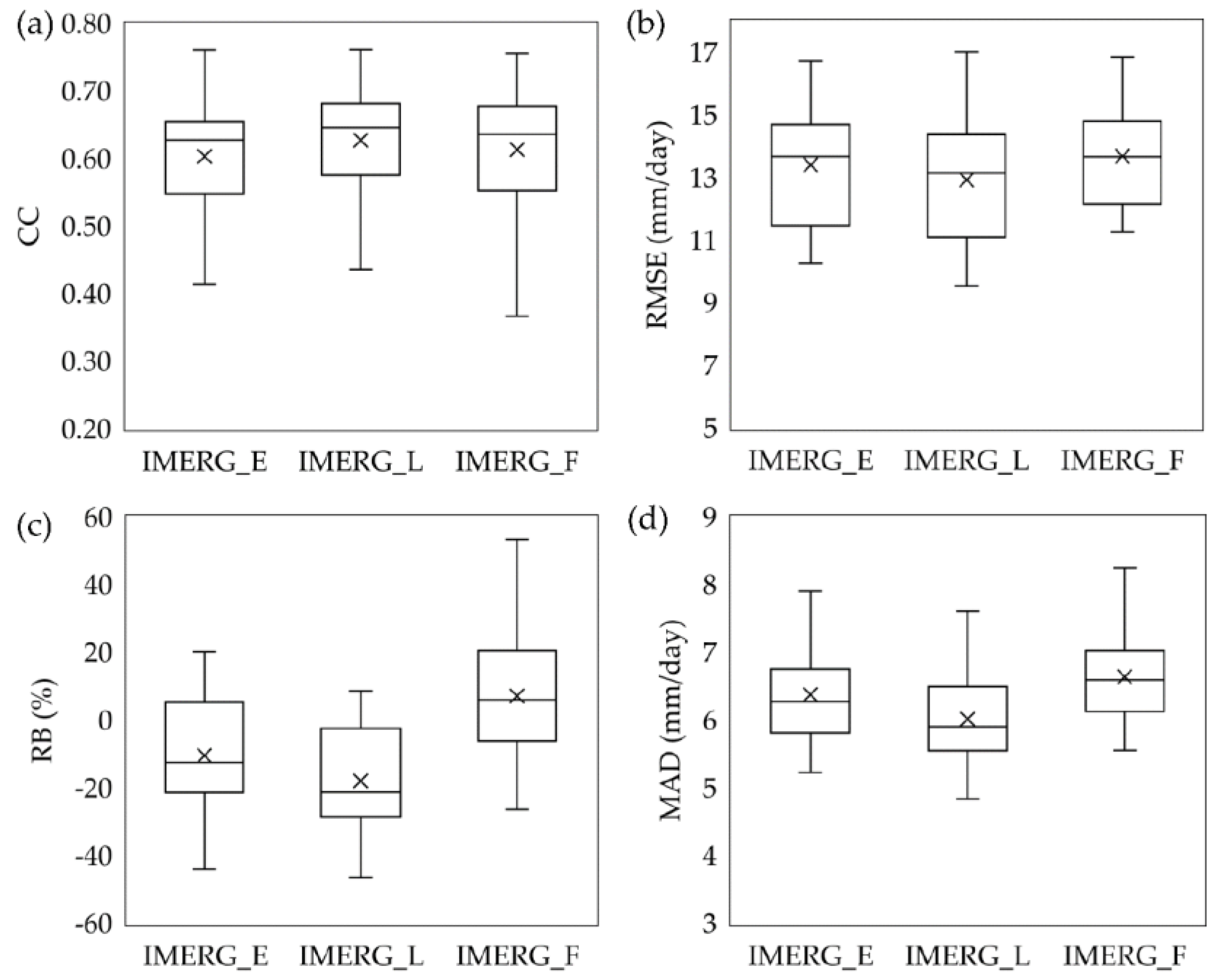
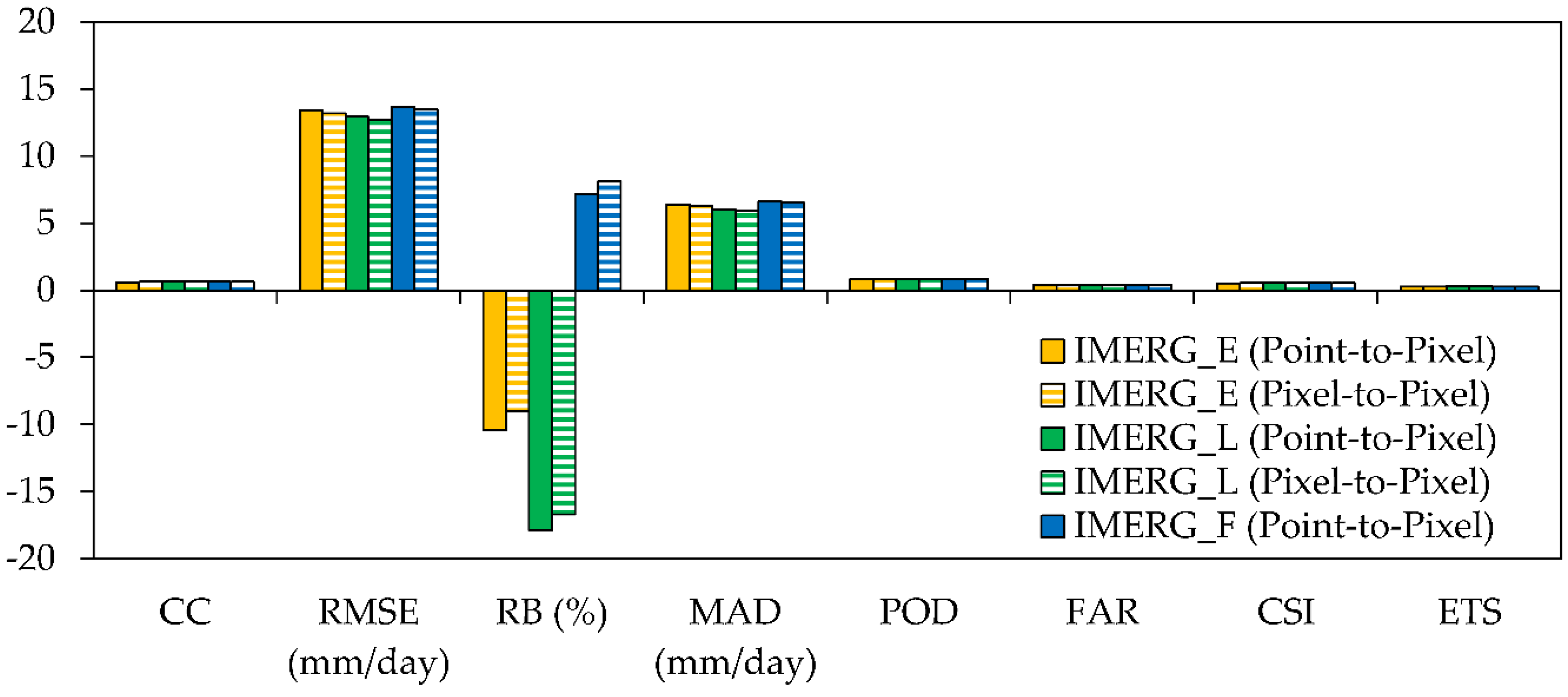
| IMERG_E | IMERG_L | IMERG_F | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Daily (1 January 2010–31 December 2016) | |||
| CC | 0.60 | 0.63 | 0.61 |
| RMSE (mm/day) | 13.41 | 12.93 | 13.69 |
| RB (%) | −10.42 | −17.92 | 7.14 |
| MAD (mm/day) | 6.38 | 6.02 | 6.64 |
| POD | 0.81 | 0.82 | 0.84 |
| FAR | 0.4 | 0.39 | 0.41 |
| CSI | 0.52 | 0.53 | 0.53 |
| ETS | 0.27 | 0.28 | 0.26 |
| ACC | 0.70 | 0.71 | 0.70 |
| Monthly (January 2010–December 2016) | |||
| CC | 0.86 | 0.87 | 0.86 |
| RMSE (mm/month) | 106.26 | 108.81 | 103.54 |
| RB (%) | −10.42 | −17.92 | 7.14 |
| MAD (mm/month) | 76.31 | 75.62 | 74.08 |
| The 2014–2015 flood (14 December 2014–3 January 2015) | |||
| CC | 0.77 | 0.79 | 0.79 |
| RMSE (mm/day) | 38.71 | 37.73 | 37.41 |
| RB (%) | −4.02 | −12.39 | −8.46 |
| MAD (mm/day) | 24.89 | 23.73 | 23.69 |
| POD | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.95 |
| FAR | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.06 |
| CSI | 0.89 | 0.90 | 0.89 |
| ETS | 0.64 | 0.67 | 0.65 |
| ACC | 0.91 | 0.92 | 0.91 |
| No | Parameter Name | Parameter | Original | Final | Fitted | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | manning’s value for main channel | CH_N2 | 0.00 | 0.30 | 0.00 | 0.16 | 0.01 |
| 2 | baseflow alpha factor | ALPHA_BF | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.46 | 1.00 | 0.97 |
| 3 | groundwater “revap” coefficient | GW_REVAP | 0.02 | 0.40 | 0.10 | 0.40 | 0.37 |
| 4 | channel effective hydraulic conductivity | CH_K2 | 0.00 | 500.00 | 234.00 | 500.00 | 483.77 |
| 5 | initial SCS CN II value | CN2 | 35.00 | 98.00 | 57.00 | 98.00 | 86.73 |
| 6 | threshold water depth in the shallow aquifer for flow | GWQMN | 0.00 | 5000.00 | 2276.00 | 5000.00 | 4757.56 |
| 7 | groundwater delay | GW_DELAY | 0.00 | 500.00 | 0.00 | 308.00 | 71.15 |
| 8 | available water capacity | SOL_AWC | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.64 | 0.17 |
| 9 | threshold depth of water in the shallow aquifer for “revap” to occur | REVAPMN | 0.00 | 500.00 | 0.00 | 296.00 | 54.17 |
| 10 | deep aquifer percolation faction | RCHRG_DP | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.65 | 0.19 |
| 11 | surface runoff lag time | SURLAG | 0.05 | 24.00 | 0.05 | 13.00 | 0.56 |
| 12 | soil evaporation compensation factor | ESCO | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.43 | 1.00 | 0.92 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, M.L.; Samat, N.; Chan, N.W.; Roy, R. Hydro-Meteorological Assessment of Three GPM Satellite Precipitation Products in the Kelantan River Basin, Malaysia. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1011. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10071011
Tan ML, Samat N, Chan NW, Roy R. Hydro-Meteorological Assessment of Three GPM Satellite Precipitation Products in the Kelantan River Basin, Malaysia. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(7):1011. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10071011
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Mou Leong, Narimah Samat, Ngai Weng Chan, and Ranjan Roy. 2018. "Hydro-Meteorological Assessment of Three GPM Satellite Precipitation Products in the Kelantan River Basin, Malaysia" Remote Sensing 10, no. 7: 1011. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10071011
APA StyleTan, M. L., Samat, N., Chan, N. W., & Roy, R. (2018). Hydro-Meteorological Assessment of Three GPM Satellite Precipitation Products in the Kelantan River Basin, Malaysia. Remote Sensing, 10(7), 1011. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10071011








