Abstract
Waste-to-energy (WtE) incineration technology is widely used to solve the energy supply, greenhouse gas emissions, and waste generation problems in urban areas. In Taiwan, there are new laws and regulations that would affect greenhouse gas management of WtE incineration plants. This research aims to identify or raise key issues to be promoted for WtE incineration plants due to existing management systems and complex issues mixed with GHG, energy, and solid waste treatment. This study utilizes inventory analysis and social LCA (SLCA) approach on GHG management of WtE incineration plants in Taiwan to systematically identify materiality issues to be promoted. According to the results of materiality analysis for SLCA, this study generalizes four stakeholders, nine subcategories, and their 15 inventory indicators; and concludes that, among assessment results of 15 inventory indicators, three indicators are at a high level, four at a medium level, and eight at a low level. In total, 12 materiality issues are recognized. This study suggests WtE incineration plants should consider the following materiality issues with respect to priority: a systematic database and calculation methods, the goal and criteria of the laws and regulations, technology development toward circular economy and promotion activity or opportunity for local community and organization level.
1. Introduction
The phenomenon of urbanization is becoming more intense around the world. Population and economic activities have been concentrated in urban areas. Problems of water resource depletion, energy consumption, waste generation, and other pollution emissions commonly occur. As a result, urban areas are gradually becoming the centers of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and waste generation.
On the aspect of reducing GHG emissions and waste, waste-to-energy (WtE) incinerators are not only an alternative technology for solving municipal solid waste (MSW) generation problems, but also an option for mitigating GHG emissions and producing energy. Pan et al. [1] and Cucchiella et al. [2] considered that WtE incineration technology can supply renewable energy and solve climate change issues. It is an approach to achieve a circular economy through simultaneously solving problems of energy demand, waste management, and GHG emissions.
In fact, compositions of MSW are very complex. MSW consists of materials other than biomass, such as plastic, glass, and minerals. The incineration of non-biomass materials will release non-biogenic GHGs and, therefore, cause the atmospheric accumulation of GHGs. Thus, it is necessary to have systematic assessment on WtE incinerator strategies and their supporting measures to determine the effect of GHG mitigation.
To systematically assess and draw up appropriate policies and measures, life cycle assessment (LCA) has been widely applied to the study of WtE incinerator. Finnveden et al. [3] used LCA to compare results for energy use, and GHG emissions from different alternative waste treatment strategies. According to the total weighted results, the study shows that promoting incineration of paper materials may be successful in reducing GHG emissions if the waste can replace oil or coal as energy sources.
GHG emissions and carbon balance in WtE incinerators are often investigated by scholars. Tan et al. [4] utilized the 2006 Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories [5] (2006 IPCC Guidelines) to make scenario analyses through comparisons of energy conversion and GHG emissions derived from landfill gas recovery systems and waste incineration facilities for MSW in Malaysia. The study found an optimal scenario with acceptable performance of energy potential and GHG emissions and the best economical beneficial result. Lee et al. [6] constructed a framework for assessing the carbon balance of power generation from MSW incinerators with feedstock of vetiver and utilized life cycle inventory analysis to assess the balances of energy and carbon flow of the bio-power system.
Sustainable development is tightly linked with the mitigation of GHG emissions. With respect to sustainability assessment, Klopffer [7] recommended that binding the environment into LCA, social life cycle assessment (SLCA), and life cycle cost can be a way to assess the product under the premise of sustainability. Ripaldi [8] indicates that “in order to have a sustainable perspective it also would be necessary to introduce a social life cycle assessment and a life cycle cost assessment that would also consider the social and economic feasibility of the introduction of the incineration”. Achillasa et al. [9] conducted a survey in order to assess social acceptance for the development of a WtE facility in Thessaloniki, Greece. They found there was a significant information gap at the level of local communities. Hence, SLCA is an indispensable key approach to help draw up relative strategies of WtE incineration.
There were many changes on GHG legal management for the industry in Taiwan in the past two years. In July 2015, the Greenhouse Gas Reduction and Management Act (the GHG Act) entered into force. The government has a legal basis to manage GHG emissions from industrial sectors and promote policies and measures for their mitigation and adaptation. The GHG Act sets a long-term goal of GHG reduction and the sectors will have their reduction objectives in the near future. The Amendment of Electricity Act also entered into effect in January 2017. It opens up rights for renewable energy suppliers to sell power to consumers through various methods, instead of just one method through the Taiwan Power Company. The government can conduct monitoring and management based on carbon emission factors of power generation under request of this Amendment.
Taiwan has applied WtE incineration plants to combust MSW since the 1990s. Before any WtE incineration plant could be constructed in Taiwan, an environmental impact assessment (EIA) had to be made. The EIA has considered social and economic issues regarding environment pollutants. It is not necessary to cover GHG issues because the laws and regulations about GHG management were not ready at that time. Nowadays, GHG mitigation has become a sufficient and necessary condition for reaching sustainability. GHG reduction and management are legally-binding requirements for operating a corporation in Taiwan, and even around the world. It is necessary to explore and review how to apply SLCA to the conditions of WtE incineration plants.
Under the occasion and background mentioned above, this study utilizes the concepts of life cycle inventory analysis and SLCA to check the criteria, regulations, and management conditions for WtE incineration in Taiwan. It conducts materiality analysis under the subcategories and categories of SLCA. There are two main purposes in this research. The first is to raise materiality issues for enhancing GHG management of WtE incineration plants in Taiwan. The second is to determine possible issues for improving GHG management of WtE incineration plants by qualitatively analyzing domestic laws and regulations. This paper will begin with an introduction of WtE incineration in Taiwan. This work is comprised of the following sections: Waste-to-Energy Incineration in Taiwan (Section 2), Research Methods (Section 3), Results and Discussion (Section 4), and Conclusions and Recommendations (Section 5).
2. Waste-to-Energy Incineration in Taiwan
Taiwan is an island of 36,193 square kilometers and had a population of about 23.53 million in 2016. Due to limited land area, economy, and population growth, Taiwan faced an MSW generation problem in the 1980s. The government started to promote the Resource Recycling System in 1987, which emphasizes linkages with the community, recycling businesses, local government, and recycling foundations, and implemented the four-in-one resource recycling program. In the 1990s, waste management policies focused on MSW end-of-pipe treatment and proper disposal. Taiwan finished the construction of its first WtE incineration plant in 1992. Currently, there are 26 WtE incineration plants constructed in Taiwan.
Regarding the construction and operation of incinerators, five plants were constructed and operated by the government, while 16 were constructed by the government and operated by private firms. The remaining five plants, including two build-operate-transfer (BOT) plants and three build-operate-own (BOO) plants, were constructed and operated by private firms. Among these 26 plants, 24 plants are well under operation, but the two BOO plants are not due to protests against their operation. The designed capacity of incineration disposal per day of the 24 WtE incineration plants in Taiwan reached 24,650 tons/day in 2008. Thereafter, it maintained the designed capacity at the same level. These WtE incineration plants are called large-scale incinerators because their designed capacity of incineration disposal is higher than 300 tons/day. Taiwan also has many medium- or small-scale incineration plants with low designed capacity but without power generation facilities. Designed capacity of incineration disposal of each medium- or small-scale incinerator is lower than 300 tons/day. However, these incineration plants are beyond the scope of this study [10].
Waste received by WtE incineration plants comes from MSW and industrial waste. According to the Environmental Resources Database of the Taiwan Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) [11], the waste generated and the operation trends of WtE incineration plants in Taiwan are shown in Table 1. In 2008, about 4,535,133 tons of MSW generated were sent to WtE incineration plants. Approximately 1,648,950 tons of industrial generated waste were sent to WtE incineration plants. In 2015, approximately 4,329,863 tons of MSW generated were sent to WtE incineration plants, and approximately 2,292,207 tons of industrial generated waste were sent to WtE incineration plants. In 2016, the amount of MSW received for incineration decreased to 4,271,179 tons. The amount of industrial waste received for incineration decreased to 2,170,820 tons.

Table 1.
The waste treated and related operations of WtE incineration in Taiwan.
In 2008, WtE incineration plants received about 6,184,083 tons of waste, which contained 4,535,133 tons of MSW and 1,648,950 tons of industrial waste for incineration; incinerated 6,110,838 tons of waste; and generated 2,967,218 kWh of electric power. In 2016, WtE incineration plants received about 6,441,999 tons of waste, which contained 4,271,179 tons of MSW and 2,170,820 tons of industrial waste for incineration; incinerated 6,392,159 tons of waste; and generated 3,245,229 kWh of electric power. From 2008 to 2016, the average growth rate of MSW received was −0.75%. The amount of industrial waste received increased at a rate of 3.5%. The amount of total waste incinerated increases at a rate of 0.56%, and electric power generation increased at 1.13% [12].
In sum, Taiwan currently has 24 WtE incineration plants under operation with designed capacity of 24,650 tons disposal per day. Historical trends for waste incinerated show a slight increase contributed by growth of industrial waste received. MSW has shared about two thirds of the total waste incinerated and industrial waste has occupied about one third of total waste incinerated for the past three to four years. Electric power generation by WtE incineration plants and the amount of ash from incineration also has the same trend of a slight increase. According to the above analysis, it can be said that the operation condition of WtE incineration plants in Taiwan has remained stable. All parameters regarding WtE incineration plants, as shown in Table 1, show small changes.
3. Research Methods
This study draws up the research approach, referring to “Guidelines for Social Life Cycle Assessment of Products” [13] and “The Methodological Sheets for Subcategories in Social Life Cycle Assessment” by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) [14]. This study starts by reviewing documents and data. The following steps in pace with SLCA phases would be scope definition and data sources, inventory analysis, materiality analysis for SLCA, and results analysis and recommendations. Details of the steps are described in the following.
3.1. Scope Definition and Data Sources
This study conducts a survey on the relative documents, data, regulations and other reports to have a good and whole understanding of WtE incineration in Taiwan. The main documents and data sources are listed as below.
- ∙
- Greenhouse Gas Reduction and Management Act
- ∙
- Energy Management Act
- ∙
- Renewable Energy Development Act
- ∙
- Electricity Act
- ∙
- Environmental Resources Database by Taiwan EPA
- ∙
- Related information about GHG inventory of WtE incinerators
The system boundary for this study is shown in Figure 1, which indicates that a process for WtE incineration plants includes raw materials, manufacture, distribution, consumer use, and disposal/recycling. The text boxes with bold font in Figure 1 are units that this study mainly focuses on. The text boxes with italics font in Figure 1 are indirect process or units. The inputs for this system contain MSW, industrial waste and auxiliary fuel. The outputs for this system involve ashes, electricity/heat, and GHGs. This study does not consider electricity power purchased, air pollutants, wastewater, hazard organics, etc.
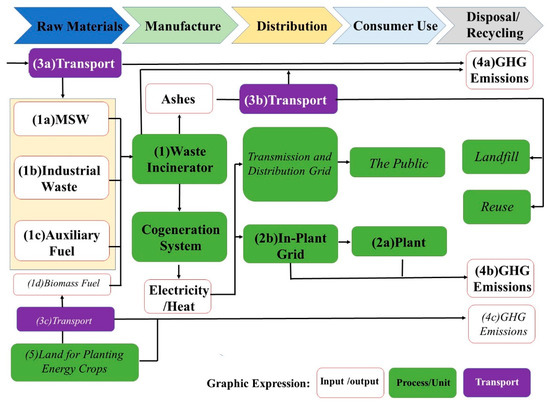
Figure 1.
Scope definition and system boundary for this study.
The input (raw materials) is burned in the incinerator. The incinerator utilizes heat to produce steam for generating electricity, emits flue gas, and produces ashes. The electricity generated by cogeneration systems would be divided into the transmission and distribution grid for the public use and in-plant grid for in-plant use. The (4a) GHG emissions (Figure 1, Item 4a) are derived from fuel combustion and the refrigerant of vehicles and flue gas by incineration. The (4b) GHG emissions (Figure 1, Item 4b) are derived from gas-insulated switchgears in in-plant grids, refrigerators, air conditioning, and septic tanks of office buildings and possible land use changes in incineration plants. All GHG emissions are composed of emissions from biomass and non-biomass. As shown in (1d), (3c), (4c), and (5) items in Figure 1, if biomass fuel becomes one of the raw materials in the future, it is required to extend the system boundary to land for planting energy crops and its transport.
3.2. Inventory Analysis
Based on the concept of lifecycle inventory analysis, this study plans to make inventory analyses of laws and regulations and GHGs for checking and figuring out the conditions and schemes for GHG management of the system. The results of analyses would offer useful and valuable information to the inputs for interpretation in the stage of SLCA. The inventory analyses used in this study are described as below.
3.2.1. Laws and Regulations
One of the important ways to have a comprehensive understanding of corporate social responsibility of a given issue is through exploring the relative laws and regulations. This study lists the goals, requests, standards, measures and the competent authorities in the relative laws and regulations of GHG management and power generation. An owner or operator needs to understand the detail of the relative regulations for having an effective and legally-binding operation on WtE incineration plants. Additionally, this analysis would help a decision-maker know if the effects and conflicts of response policies and measures derived from the relative regulations occur or exist in order to improve or draw up the executive approach.
This study reviews the four related Acts listed in Section 3.1 and conducts analyses of the contents of the relative criteria for GHG management, indicators concerning GHG management, and the competent authorities for each Act regarding WtE incineration plants. A scheme for GHG management on WtE incineration plants is illustrated in this study according to the result of inventory analysis of laws and regulations.
3.2.2. GHG Inventory Analysis
Approaches of GHG inventory analyses can be divided into three types, which are based on nation, city, and community; enterprise; and organization. This study adopts the concepts of two of them for discussing GHG management of WtE incineration plants. These two approaches are illustrated as follows.
The first one is the national GHG inventory, which aims to assess the total GHG emissions and the removal of a country based on sectors and categories of sources and sinks. The best practice in the world would be the calculation methods in the 2006 IPCC Guidelines, which is widely applied to the parties to the United Nations Framework Convention of Climate Change (UNFCCC). This study applies the logic concept and calculation methods from the 2006 IPCC Guidelines to GHG inventory analysis of this section. The calculation methods applied may belong to the waste sector, energy sector, industrial process, and product use sector, and agriculture, forestry, and other land use sector in the 2006 IPCC Guidelines. This study assesses the key GHG emissions per year on the basis of limited open and public data and default parameters in the 2006 IPCC Guidelines. Hence, decision-makers from the central and local governments can have a whole view with environmental integrity on the GHG inventory of WtE incineration plants.
The second is the organizational GHG inventory, which aims to assess the total GHG emissions and the removal of an enterprise or organization. ISO 14064-1:2006 is a common guidance at the organization level for quantification of GHG emissions and removals. This study applies the concept of the organizational boundary in ISO 14064-1:2006 to define the system boundary shown in Figure 1, which belongs to the GHG emissions and removals of Scope 1 illustrated in ISO 14064-1:2006. The owner and operator of WtE incineration plants can have an outlook on how to identify their own responsibility and accountability of GHG emissions and reduction according to the rules of ISO 14064-1:2006.
3.3. Social Life Cycle Assessment
The UNEP developed a category-systematic approach for conducting SLCA. The approach illustrated in the UNEP guidelines [13] and methodological sheets [14] is constructed on a tree structure formed by stakeholders, their subcategories and various indicators. These stakeholder categories include worker, consumer, local community, society, and value chain actors, not including consumers.
According to the UNEP guidelines and methodological sheets for subcategories for SLCA, this study raises subcategories under each stakeholder for SLCA toward GHG management of WtE incineration plants. GRI Sustainability Reporting Standards 2016 (Global Sustainability Initiative, GRI) [15] defines materiality in sustainability reporting as: “the principle that determines which relevant topics are sufficiently important that it is essential to report on them. Not all material topics are of equal importance, and the emphasis within a report is expected to reflect their relative priority”. As to the definition of material topics, GRI Sustainability Reporting Standards 2016 raises many factors that the reporting organization can take into account. Two of these factors, “Laws, regulations, international agreements, or voluntary agreements of strategic significance to the organization and its stakeholders” and “Key organizational values, policies, strategies, operational management systems, goals, and targets” [15], are very meaningful for this research. This study raises materiality issues to reflect the relative priority according to the results of qualitative analysis of domestic laws and regulations and the definitions of materiality and material topics in GRI Sustainability Reporting Standards 2016.
Materiality analysis for SLCA is conducted by this study as follows: Inventory indicators under each subcategory are raised and this study assesses each inventory indicator based on the degree of its current condition. Assessment results are be represented by three levels: high, medium, and low. If an assessment result for an inventory indicator is high, that means the indicator-related issue reaches a high degree of completeness or performance and its materiality is low. On the contrary, if an assessment result for an inventory indicator is low, that means the indicator-related issue reaches low degree of completeness or performance and its materiality is high. This study takes electricity power generated, renewable energy certification, and carbon reduction credit as products. WtE incineration plants are regarded as an organization affected by implementation of the GHG Act in Taiwan. The results of recognizing categories, subcategories, inventory indicators, assessment results, and materiality-related issues are shown in Section 4.
4. Results and Discussion
Based on the research approach described above and the SLCA thinking, this study generalizes results from the above information, regulations, and documents collected. In this section, the results will be illustrated in three parts: the GHG management under regulations and office systems, GHG inventory, and considerations for SLCA. In the end of this section, key aspects are raised for discussions. This study expects to add valuable considerations to GHG management of WtE incineration plants while conducting SLCA on them.
4.1. Regulations of GHG Management
The main and direct regulation for GHG management of WtE incineration plants is no doubt the GHG Act in Taiwan. Taiwan also has many indirect supporting regulations, among which are the Measures for the Implementation of Cogeneration System under Energy Management Act and the Renewable Energy Development Act, for enhancing low carbon development. It is necessary for this study to consider the indirect supporting regulations regarding electricity and renewable energy because incineration plants involve issues of waste, GHG emissions, and the former items.
The GHG Act sets a long-term national goal of GHG reduction to emit no more than 50% of 2005 GHG emissions by 2050. It authorizes all levels of the government to manage GHG emissions and removals and endows the government and the corporation with responsibility to reduce GHG emissions. The GHG Act develops a scheme with periodical regulation on a five-year basis. It asks that the Action Guideline shall be reviewed and the government, which is divided into energy, manufacture, transportation, residential and commercial, agriculture, and environment sectors, shall set periodical and sectoral regulatory goals every five years. Periodical reduction responsibility is also allocated to WtE incineration plants. Additionally, the GHG Act draws up a three-stage measure to move GHG reduction of the corporation forward. These measures, which WtE incineration plants in Taiwan shall obey, are annual accounting and registration of GHG inventories at the first stage, GHG emission performance standards and incentives at the second stage, and a cap-and-trade scheme at the third stage.
Other related regulations for WtE incineration plants are about energy issues. Measures for the Implementation of Cogeneration Systems under Article 10 of the Energy Management Act are developed to manage various cogeneration systems in the industry. Of course, cogeneration systems of WtE incineration plants are under its supervision. Energy use derived from incineration of MSW and industrial waste is defined as renewable energy by the Renewable Energy Development Act. This Act offers supporting measures for promoting renewable energy usage. Subsidies for renewable energy facilitation and its power price and Feed-In-Tariff scheme are examples of supporting measures. A pilot measure of renewable energy certification was launched for volunteers in May 2017. WtE incineration plants, as power suppliers, shall obey the criterion of the monitory and management based on the carbon emission factor of power generation according to Article 28 of the Electricity Act.
In sum, the relative criteria and indicators concerned for GHG management of WtE incineration plants in Taiwan are shown in Table 2. This may help the owners and operators of WtE incineration plants manage and reduce GHG emissions for fulfilling domestic laws and regulations. Table 2 also represents the relative criteria as a whole and may be helpful in terms of reviewing SLCA for WtE incineration plants in Taiwan.

Table 2.
Relative criteria and indicators concerning GHG management of WtE incineration in Taiwan.
4.2. GHG Inventory Analysis
As mentioned above, this study makes a plan for conducting GHG inventory on WtE incineration plants, referring to the methods and rules from the 2006 IPCC Guidelines and ISO 14064-1:2006. According to the scopes of sources and sinks categorized by ISO 14064-1:2006, explanations for the sources and sinks, which belong to Scope 1 and 2 of emissions and removals, are made as follows.
4.2.1. Incineration of MSW and Industry Waste
Recalling the system boundary shown in Figure 1, the GHG emissions from incineration of MSW and industrial waste are the key direct emission sources. This study checks collected data, and finds there is information on the amount of waste, physical composition, chemical analysis, and heating values for MSW in Taiwan. However, there is no available information on the physical composition, chemical analysis, and heating values for industrial waste incinerated in Taiwan. Hence, this study selects the calculation of GHG emissions from MSW as the case study to show the following calculation approaches.
According to Volume 5: Waste of the 2006 IPCC Guidelines, there are two main methods for calculating CO2 emissions from incineration. The first one is based on the total amount of waste combusted and the second is based on MSW composition. This study considers the methods and information collected, and uses the second method to calculate CO2 emissions from incineration. A series of data sources for calculating CO2 emissions from MSW incineration is collected, as shown in Table 3. According to data sources and method type classified by the 2006 IPCC Guidelines, the method utilized here are Tier 1.

Table 3.
Data sources for calculating CO2 emissions from MSW incineration.
Calculation method of CH4 and N2O emissions is cited from Equations (5.4) and (5.5) in Volume 5: Waste of the 2006 IPCC Guidelines [5] based on the amount of MSW combusted. This method belongs to Tier 1 in the 2006 IPCC Guidelines.
WtE incineration in Taiwan belongs to the continuous type with fluidized bed. CH4 emission factor for continuous incineration with fluidized bed is zero given by the 2006 IPCC Guidelines. Default N2O emission factor for continuous incineration with fluidized bed is 50 g N2O/ton waste on wet base given by the 2006 IPCC Guidelines. 2006 IPCC Guidelines do not explain if CH4 and N2O emission factors contain biogenic emissions or not. CH4 and N2O emissions from fossil or biomass materials should be included in a GHG inventory except the CO2 emissions from combustion of biomass materials. Thus, this study takes CH4 and N2O emissions as emissions from both fossil and biomass materials.
According to the data sources and methods mentioned above, results of calculating GHG emissions from MSW incinerated in 2015 in Taiwan are shown in the following. CO2 emission from non-biomass fraction amounts to 1,945,465.0 tons CO2 eq. calculated by the Tier 1 method of the waste sector based on the MSW composition and biogenic CO2 emission dose of 3,557,914.0 tons CO2 eq. CH4 emission is zero due to consideration of incineration technology. N2O emission amounts to 64,515.0 tons CO2 eq. based on consideration of incineration technology. In this case study, not all GHG emissions from MSW incinerated are biogenic emissions. Biogenic CO2 emission is 1.8 times the CO2 emission from the non-biomass fraction.
4.2.2. Other Direct Emission Sources
Other direct emission sources under the system boundary may include incineration of auxiliary fossil fuel, incineration of auxiliary biomass fuel, vehicles, refrigerators, air conditioners, electric equipment, septic tanks, etc. The relative GHGs that these sources emit are CO2, CH4, N2O, HFCs, and SF6. Emission sources include incineration of auxiliary fossil fuel, incineration of auxiliary biomass fuel, and vehicles belonging to energy sector, refrigerators, and air conditioners and electric equipment belonging to industrial process and product use sector, and septic tanks belonging to waste sector. Energy for vehicles may cover fossil fuel, biodiesel, and electrical power from renewable energy, power generated by incineration plants, or bought from the other power company. Every type of energy for vehicles should be recorded as well. Details of calculating GHG emissions from these secondary and direct emission sources are not discussed here.
4.2.3. LULUCF and HWP
If an incineration plant changes its own land use, GHG emissions, or removals of land use, land-use change and forestry (LULUCF) should be considered under the system boundary. For example, if a plant owner builds a parking lot on a piece of grassland where vegetation was removed, grassland use is changed. If the plant owner plants biomass crops on some given land and harvests it for incineration input, it will cause GHG emissions or removals from the land use. Harvested wood products (HWP) can be wood or wood products combusted in incinerators. It may derive biogenic CO2 emissions, which are not included in the GHG inventory, and CH4 and N2O emissions, which are included in GHG inventory.
4.2.4. Indirect Emissions of Scope 2
Generally speaking, indirect emissions of Scope 2 refer to GHG emissions derived from energy bought from outside of the system boundary, such as electrical power, steam, or heat from other companies. To collect emission factors or emission data from the outside is a way to calculate indirect emissions. For example, the MOEA publishes the CO2 emission factor of electricity power every year, offering to calculate CO2 emissions caused by power usage which is generated by the Taiwan Power Company, private power companies, and cogeneration systems. For Taiwan, the CO2 emission factor of electricity power was 0.528 kg CO2/kWh in 2015 [17].
4.3. Social Life Cycle Assessment
As mentioned above, this study generalizes the results of GHGs, laws and regulations inventory to raise suggestions for considerations for SLCA. Materiality analysis for SLCA is made in this section. Interpretations for stakeholders, subcategories, inventory indicators, assessment results, and materiality-related issues are illustrated in the following.
4.3.1. Stakeholder of Local Community
Community engagement, access to immaterial resources, and access to material resources are selected to be subcategories in stakeholders of the local community due to the features of the products from WtE incineration plants. With respect to community engagement, transparency of government policy-making and promotion of the GHG relative laws and regulations are important ways for local community to understand the legal-binding GHG management for WtE incineration plants. Support from local community and organizations is a key indicator for assessing impact of the products from WtE incineration plants. If the degree of transparency, promotion, and support is getting higher, community engagement is getting deeper, thus the impact is decreasing, in principle. With respect to access to immaterial resources, awareness of climate change, and GHG emissions and presence/strength of community education, they are regarded as two indicators for assessing the impact toward the local community. If the degree of awareness, presence, and strength is increasing, community engagement is getting deeper, and then the impact might be reduced. Regarding access to material resources, a certified environmental and energy management system and local waste incineration are suggested as two indicators. Of course, if an incineration plant has a certified environmental and energy management system and has priority to combust waste generated by the local area/community, the impact would be regarded as low.
For community engagement, assessment results for its inventory indicators are from low to medium. On the aspect of transparency of government policymaking, the government held many public hearings or meetings to explain the GHG Act and its enforcement rules in the past two years. Currently, operators of WtE incineration plants need to know what their roles are and what they can, or may, do under relative rules and measures across various Acts. This study suggests an integrated explanation of relative rules and measures across various Acts, which is regarded as a materiality issue. The other two indicators, which are scored as low, are about the promotion of the GHG relative laws and regulations to the local community and organizations and their support. “Promotion activity for local community and organization level” and “activity or opportunity to show if local community and organization level support what WtE incineration plants do under relative Acts” are regarded as materiality issues which the government may face.
For access to immaterial resources, assessment results for awareness are scored as high due to promotion of national policies and measures for tackling climate change. Assessment results for presence/strength of community education are ranged at low level. This study considers that the local community has to have comprehensive and strong understanding of the relationship between GHG emissions and WtE incineration and its importance on the waste recycle.
For access to material resources, WtE incineration plants in Taiwan already obtained ISO-certified environmental management systems, but not energy management systems. This study gives a medium level to this indicator. To have certification of energy management systems is a materiality issue for WtE incineration plants. An incineration plant has priority to combust waste generated by the local area/community so that the score for this indicator can be high. Anyway, incineration of waste from the other counties gradually becomes an environmental and political issue in Taiwan.
4.3.2. Stakeholder of Value Chain Actors
Promoting social responsibility is a suitable and applicable subcategory for assessing the impact of the products from WtE incineration plants with respect to the stakeholders of the value chain actors. If an incineration plant meets the goals and criteria of the laws and regulations on GHG management, it is regarded as promoting or meeting its social responsibility. National goals and criteria of the laws and regulations on GHG management are shown in Table 2.
For promoting social responsibility, the indicator determining whether an incineration plant meets the goal and criteria of the laws and regulations on GHG management is scored at a low level. This does not mean incineration plant does not meet the goals and criteria, but that the goals for incineration plants remain unclear. For example, GHG reduction goals and emission performance standards for WtE incineration plants are not formulated by the central and industry-competent authorities. This study raises the goal and criteria of the laws and regulations for WtE incineration plants as a materiality issue.
4.3.3. Stakeholders of Worker
Social benefit/social security and operation patterns are recognized as subcategories in the stakeholders of worker. The UNEP methodological sheets define “the hours of work comply with applicable laws and industry standards” [14], whereas social benefits that may be provided include education and training. This study suggests “hours of education and training on relative knowledge and regulations of GHG management for the officer and the employment” and “licenses about ISO 14064 and ISO 50001 which the officer and the employment obtain” are two key indicators in the stakeholder of social benefit/social security. Operation patterns in WtE incineration plants may be changed due to the criteria of GHG laws and regulations. For identifying the impact of worker, operation patterns are raised to be a subcategory by this study and records for calculating GHG emissions are regarded as its inventory indicator.
On the aspect of social benefit/social security, two indicators for hours of education, and training and licenses are ranked at a medium level. “Courses and mechanism of education and training for the officer and the employment” and “encouraging the officer and the employment to have relative ISO licenses” are raised as materiality issues.
For operation patterns, assessment results of records for calculating GHG emissions are at a low level. In order to get accurate emissions, a WtE incineration plant has to carefully select GHG calculation methods in the light of MSW and industrial waste incinerated. It is necessary for WtE incineration plants to change operation patterns and keep good records on MSW and industrial waste incinerated. “GHG calculation methods and detail data about MSW and industrial waste incinerated” is recognized as a materiality issue.
4.3.4. Stakeholders of Society
In the stakeholders of society, this study identifies three subcategories: public commitment to sustainability issues, contribution to economic development, and technology development. Engagement of the sector regarding sustainability, GHG reduction, and renewable energy certification as an indicator could be reviewed in the subcategory of public commitment to sustainability issues. Contributions to GHG reduction credits, power generation, and renewable energy certification could be indicators for circular economy. Both involvement in WtE-related research and development projects and investments in the technologies of GHG reduction and energy efficiency could be regarded as two key indicators.
For public commitment to sustainability issues, the indicator for engagement of the sector is assessed as low level because what the goal for incineration plant seems to be unclear. The goal and criteria of the laws and regulations for WtE incineration plants is regarded as a materiality issue. For contribution to economic development, assessment results are ranked at high level because WtE incineration plants have contributed to circular economy. For technology development, two indicators for involvement and investments are ranked at low level. The best available technology (BAT) for WtE incineration under the GHG Act is a materiality issue.
To sum up, materiality analysis for SLCA of the products of GHG reduction credits, electricity power, and renewable energy certification from WtE incineration plants is shown in Table 4. This study generalizes four stakeholders, nine subcategories, and their 15 inventory indicators for conducting materiality analysis for SLCA of the products of WtE incineration plants. Among assessment results of 15 inventory indicators, three indicators are at a high level, four at a medium level, and eight at a low level. In total, 13 materiality issues are recognized in this study. Among them, the goal and criteria of the laws and regulations and BAT for WtE incineration plants promotion, GHG calculation methods and detail data, and activity for the local community and organization level are the most important issues.

Table 4.
Materiality analysis for social life cycle assessment regarding the WtE incineration as products.
4.4. Discussions
Listed here are four key issues for discussions with respect to the results.
4.4.1. Renewable Energy and GHG Emissions
According to traditional opinions in the MSW field, WtE incineration is, without doubt, a type of renewable energy due to recycling and reuse of MSW and industrial waste. Thus, WtE incineration belongs to the supervision of Renewable Energy Development Act. WtE incineration plants can obtain subsidies for renewable energy facilitation and its power price from the MOEA.
However, GHG emissions from WtE incineration plants can be divided into biogenic CO2 emissions and GHG emissions from non-biomass fraction according to methodology of the 2006 IPCC Guidelines. Biogenic CO2 emissions are not accounted in national GHG inventory because they are regarded as neutral carbon and part of the global carbon cycle. That means not all electricity power generated by WtE incineration plants derives from renewable materials. In Taiwan, WtE incineration plants obtain subsidies based on all electricity power generated. This seems unreasonable with respect to the opinion of GHG emissions.
4.4.2. Subsidies, Tariff Rate, Incentive, Reduction Credits, and Renewable Energy Certification
WtE incineration plants can utilize different measures, including subsidies, tariff rate, incentive, reduction credits, and renewable energy certification as shown in Table 2, to promote low carbon development. Of course, there are three-stage measures for the industry based on the GHG Act. Currently, WtE incineration plants can apply for subsidies and certification under the Renewable Energy Development Act and incentives based on the GHG emission performance standards in the near future. Additionally, a WtE incineration plant can implement GHG reduction projects to obtain reduction credits.
The government does not allow the industry to apply for all measures to avoid double counting of “reduction”. Anyway, an integrated rule to bridge different laws and regulations is in demand.
4.4.3. Energy Sector and Environment Sector
Since energy from waste combustion is utilized for energy use for power generation, GHG emissions from WtE incineration plants are classified as energy sector based on sectors and categories of the 2006 IPCC Guidelines. However, WtE incineration plants are under the administrative supervision of the environmental agencies in local governments in Taiwan. The cogeneration systems in WtE incineration plants are under the administrative supervision of the MOEA.
It is reasonable that there are different competent authorities for different administrative purposes. Under the GHG Act, the central competent authority for them is the EPA. However, what is the central industry competent authority for them? This issue implies which competent authority shall raise GHG emission control action programs for WtE incineration plants. Otherwise, are they only covered in GHG control implementation plans by local governments?
Do WtE incineration plants belong to the energy sector or the environment sector under the GHG Act? Here are three main reasons for consideration: First, they are not responsible for domestic power dispatch and are not main power suppliers. Second, the environmental protection office system is in charge of and familiar with WtE incineration plants. GHG control implementation plans and GHG emission control action programs raised by the environmental protection office system seem more suitable for WtE incineration plants than those raised by the MOEA. Third, in the opinion of LCA, an integrated GHG reduction approach with MSW and industrial waste disposal policies is better for them than that without waste disposal policies, and the MOEA is not in charge of waste disposal. Obviously, this study suggests WtE incineration plants should be classified as environment sector under the GHG Act in Taiwan when they need to meet the reduction goal and conduct reduction projects.
4.4.4. Materiality Pathway
This study makes inventory analysis and SLCA of GHG emissions and energy generated from WtE incineration in Taiwan. In fact, stressors or concerns of MSW are not limited to GHG emissions and energy generated for governmental authorities, community, and society. Waste treatment, pollution, and nuisances are also issues concerned by stakeholders. The levels described below for materiality are based on the relative priority. In the opinion of materiality pathway, at the beginning, governmental authorities have stressors on waste treatment. The importance of waste treatment is at a high level. Secondly, governmental authorities pay attention to energy and GHG issues for meeting national or international goals. The importance of energy and GHG is at medium level. Then, pollution and nuisances are noticed by governmental authorities. Thus, pollution and nuisances are issues regarded at a low level for governmental authorities.
Conversely, community and society pay attention to pollution and nuisances derived from WtE incineration first because these issues directly affect them. The importance of pollution and nuisances is at a high level. Secondly, community and society might have stressors on waste treatment because arguments on combustion of MSW from localities or other places might arises one day. The importance of waste treatment is at medium level. Then, energy and GHG issues are noticed by community and society. Energy and GHG are issues regarded at a low level for community and society.
In sum, waste treatment is regarded as a local issue and scored at a high level as a whole. Pollution and nuisances are regarded as local/regional issues and scored at a medium level. Energy and GHG are regarded as national/global issues and scored at low level. Materiality pathway for stressors and concerns of MSW is shown in Table 5. Stressors and concerns of MSW are complicated because of different stakeholders and spatial scales. Although this study raises 13 materiality issues for improving GHG management of WtE incineration in Taiwan, decision-makers should have a better overall view on MSW to moderate issues for solving energy and GHG issues, even for circular economics and sustainability development.

Table 5.
Materiality pathway for stressor and concerns of WtE incineration.
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
WtE incineration plants, which have operated for over 20 years, have played the very important role of solid waste treatment in Taiwan. Facing a new domestic regulation of GHG management, it is difficult for WtE incineration plants to identify or raise key issues to be promoted due to the existing management system and complex issues mixed with GHG, energy, and solid waste treatment. As described in Section 1, many researchers utilized the LCA approaches to solve various issues. This study utilizes the inventory analysis and SLCA approach on GHG management of WtE incineration plants in Taiwan to systematically identify materiality issues to be promoted. According to the results of materiality analysis for SLCA, this study generalizes four stakeholders, nine subcategories, and their 15 inventory indicators; and concludes that, among the assessment results of 15 inventory indicators, three indicators are at a high level, four are at a medium level, and eight are at a low level. In total, 12 materiality issues are recognized.
Two materiality issues about detail activity data and calculation methods for GHG emissions are indicated in stakeholder local community and by workers. A systematic database and calculation methods with consistency are critical and essential. Operation pattern needs to be improved for keeping records of detailed data. These can help in clarifying biogenic CO2 emissions and GHG emissions from non-biomass fraction emitted by WtE incineration. Then, WtE incineration could have reasonable and equal reduction goals or commitment during negotiation of the GHG Act. Followed by this, measures of subsidies, tariff rate, incentive, reduction credits, and renewable energy certification may efficiently support WtE incineration for enhancing GHG reduction.
The goal and criteria of the laws and regulations for WtE incineration plants are regarded as materiality issues for stakeholder value chain actors and society. Although the GHG Act already has a national goal of GHG reduction, and relative policy and measures, the goal and detailed rules for WtE incineration plants are not clear and need to be imperatively formulated. BAT is a materiality issue in stakeholder society. Technology development toward a circular economy may contain technologies for the recycling of waste, high-efficiency incinerators, high-efficiency cogeneration systems, and other GHG reduction. BAT would be a key instrument of GHG reduction for WtE incineration plants. Additionally, promotional activity or opportunities at the local community and organization levels are materiality issues to promoting community engagement in the stakeholder local community. This study suggests WtE incineration plants should consider the above materiality issues, which include a systematic database and calculation methods, the goal and criteria of the laws and regulations, BAT, and promotional activity or opportunities for the local community and organization level, with respect to priority.
However, this study found that conflict exists between the concept of the 2006 IPCC Guidelines and the definition of the Renewable Energy Development Act. WtE incineration plants also need to pay attention to this conflict. This study recommends that it is necessary to adjust the definition and rule of the Renewable Energy Development Act because non-neutral GHG emissions are not “renewable” or sustainable in the opinion of the GHG Act. Subsidies or tariff rates for WtE incineration should be modified according to biogenic GHG emissions.
The approach utilized by this study is applicable to GHG management of WtE incineration for identifying materiality topics. It is also applicable to cross issues based on the relative priority. For example, it could be helpful and useful for making decisions on newly-constituted or extended urban development, public construction, affairs and regulation impact, etc., which involve environmental, social, and economic issues.
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported in part by the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan under the grant number of MOST105-2621-M-305-005.
Author Contributions
Yu-Tsang Lu and Yuh-Ming Lee conceived and designed the experiments; Yu-Tsang Lu performed the experiments; Yu-Tsang Lu and Yuh-Ming Lee analyzed the data; Chien-Yu Hong contributed materials for analysis; and Yu-Tsang Lu wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cucchiella, F.; D’Adamo, I.; Gastaldi, M. Sustainable waste management: Waste to energy plant as an alternative to landfill. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 131, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.-Y.; Du, M.A.; Huang, I.T.; Liu, I.H.; Chang, E.E.; Chiang, P.C. Strategies on implementation of waste-to-energy (WtE) supply chain for circular economy system: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 108, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnveden, G.; Johansson, J.; Lind, P.; Moberg, G. Life cycle assessment of energy from solid waste—Part 1: General methodology and results. J. Clean. Prod. 2005, 13, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.T.; Hashim, H.; Lim, J.S.; Ho, W.S.; Lee, C.T.; Yan, J.Y. Energy and emissions benefits of renewable energy derived from municipal solid waste: Analysis of a low carbon scenario in Malaysia. Appl. Energy 2014, 136, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories; IGES: Hayama, Japan, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.M.; Su, C.L.; Tsao, H.J. Assessing Carbon Balance of Power Generation by Municipal Solid Waste Incinerators with Feedstock of Vetiver. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Sustainable Energy and Environment (SEE 2009), Bangkok, Thailand, 18–23 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kloepffer, W. Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment of Products. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2008, 13, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripaldi, G. Life Cycle Assessment of Waste Management System. The case of Avezzano, Italy. Master’s Thesis, Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm, Sweden, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Achillasa, Ch.; Vlachokostas, Ch.; Moussiopoulos, N.; Banias, G.; Kafetzopoulos, G.; Karagiannidis, A. Social acceptance for the development of a waste-to-energy plant in an urban area. Res. Conserv. Recycl. 2011, 55, 857–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taiwan Environmental Protection Agency. Assessment Report of Waste Disposal Policy: Part 1: Transforming to Biomass Energy Center from Incineration Plant; Taiwan Environmental Protection Agency: Taipei, Taiwan, 2012. Available online: https://www.epa.gov.tw/public/Data/46915375171.PDF (accessed on 28 March 2017).
- Taiwan Environmental Protection Agency. Environmental Resources Database. Available online: https://erdb.epa.gov.tw/DataRepository/PollutionProtection/LargeIncinOperateInfo.aspx (accessed on 5 July 2017).
- Taiwan Environmental Protection Agency. Information System for Operation and Management of Incineration Plants. Available online: https://swims.epa.gov.tw/swims/swims_net/index.aspx (accessed on 5 July 2017).
- United Nations Environment Programme. Guidelines for Social Life Cycle Assessment of Products; UNEP; SETAC; Life-Cycle Initiative: Paris, France, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Environment Programme. The Methodological Sheets for Subcategories in Social Life Cycle Assessment (S-LCA); UNEP; SETAC; Life-Cycle Initiative: Paris, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Global Sustainability Initiative. Consolidated Set of GRI Sustainability Reporting Standards 2016; GRI: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Taiwan Environmental Protection Agency. Annual Statistic Report of Environment Protection 2016; Taiwan Environmental Protection Agency: Taipei, Taiwan, 2016.
- Bureau of Energy, Ministry of Economic Affairs. The CO2 Emission Factor of Electricity Power in 2016. Available online: http://web3.moeaboe.gov.tw/ECW/populace/content/wHandMenuFile.ashx?menu_id=5426&file_id=3962 (accessed on 5 July 2017).
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).