Abstract
Pastirma is an ethnic meat product derived from dry curing, drying, and pressing the whole muscles of cattle and buffalo and coating them with a special paste containing fenugreek seed flour, garlic, milled red capia pepper, and water. In this narrative literature review, the history of pastirma, its definition and classification, detailed production steps, composition and yield, chemical and microbiological properties, pastirma fraud, and customer concerns are mentioned. In this narrative review, relevant studies were identified by searching Scopus, Science Direct, Web of Science, Trdizin, and Google Scholar, including articles, online reports, books, and electronic books in English or Turkish. The keywords “pastirma, cemen, cemening, cemen paste, fenugreek” were used. The results of this review indicate that future studies on pastirma may focus on the related cultural aspects, the elimination of unpleasant odor from fenugreek, providing a detailed grading guide, the histological and chemical effects of pressing meat parts, the kinetics of drying, osmotic dehydration, and developing new starter combinations. Additionally, this is the first article to provide information on grading and food fraud in pastirma.
1. Introduction
The percentage of ethnic diversity in developed countries is continuously increasing [1]. Global population movement has changed the demographics of many countries, leading to culturally diverse societies. Food is known to be linked to an individual’s personality, cultural identity, social practices, and religious beliefs. Ethnic foods express history, memory, feelings, and social status [2]. For example, in the United States, ethnic food is highly accessible and popular, with over fifty percent of the population consuming ethnic foods, such as Italian cuisine and Mexican tacos, which have become staples in the American diet. This blending of culinary traditions not only enriches the food landscape but also fosters a greater appreciation for the cultural narratives that accompany these dishes [3,4]. Traditionally, culturally, and commercially, ethnic meat products are considered precious foods in different nations worldwide. The meat products prepared by Eastern Mediterranean people and Middle Easterners are typically cured or cooked and occasionally smoked or sun dried [5]. Many ethnic food products with animal origins are still in demand today and sold under various brands due to their traditional, nutritional, and sensory properties. One example of these products is pastirma, which is commonly consumed in the Anatolian region. It is also consumed in the Middle East, Central Asia, the Mediterranean, Balkans, and Europe [6,7,8]. Pastirma is a dried product that is categorized among medium-moisture foods. Also, pastirma manufacturing involves the following five stages: animal supply, meat preparation, processing, spice paste coating, and packing. So, pastirma is a meat product produced without heating or smoking and can be consumed without cooking. It is an ethnic meat product produced by dry curing, drying, and pressing the whole muscles of cattle and buffalo and coating them with a paste called “cemen”, made with special spices [7,9,10]. Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.) seed flour, garlic (Allium sativum L.), milled red capia pepper (Capsicum annuum L.), and water are the primary ingredients used in the preparation of cemen (Figure 1). Among ethnic meat products, pastirma is similar to dry-cured meat products such as jerky, kaddid, cecina, and carne de sol [11,12].
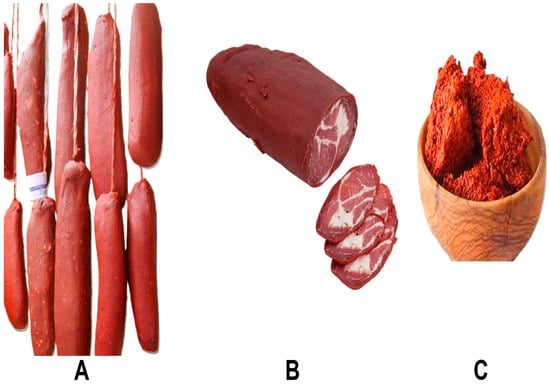
Figure 1.
Appearance of pastirma (A), pastirma slice (B), and cemen paste (C). ((A): https://www.kulturportali.gov.tr/medya/fotograf/fotodokuman/8986, accessed on 3 March 2025; (B): https://www.islamogluvakfikebir.com/urun/pastirma, accessed on 3 March 2025; (C): https://www.amazon.com/Turkish-Breakfast-Paste-Fenugreek-Approx/dp/B0791ST9JN, accessed on 3 March 2025).
Pastirma contains high amounts of meat protein and is a rich source of essential amino acids. These nutritional benefits make pastirma an excellent high-quality protein source. In addition, cemen paste not only adds flavor and aroma to the product but may also provide health benefits due to the phenolic compounds it contains. However, pastirma’s high salt content may increase daily sodium intake. This may pose a health risk to consumers [7,9,10,12].
The growth of international businesses and the significant influx of visitors have resulted in a multicultural civilization characterized by an increasing diversity of ethnic foods. A growing number of consumers have developed an interest in ethnic cuisines as a means to immerse themselves in different cultures [13]. Scientific research on ethnic food products is essential, not only for those who create scientific knowledge but also for the food policymaker sector, producers, and consumers. Furthermore, it is crucial to provide researchers with fresh perspectives, innovative ideas, and aspects requiring more attention. This comprehensive approach will enable a deeper understanding of pastirma, fostering collaboration among researchers and industry stakeholders. By synthesizing existing research and incorporating diverse viewpoints, this collaborative effort will promote sustainable practices within the industry, benefiting all parties involved. To this end, this narrative literature review aimed to comprehensively address the presentation and definition of pastirma, together with its historical, technological, biochemical, microbiological, safety legislation, and food fraud properties.
2. Methods
This narrative review was executed in the following three stages: performing the search, analyzing abstracts and whole documents, and synthesizing and discussing the results. In this review, relevant studies were identified by searching Scopus, Science Direct, Web of Science, Trdizin, and Google Scholar. The final search was conducted in May 2024 and included articles, online reports, books, and electronic books written in English or Turkish. The keywords “pastirma, pastirma, çemen, cemen, cemening, cemen paste, fenugreek” were used. The inclusion criteria were studies that explored the production methods, health benefits, and cultural significance of pastirma. This comprehensive approach ensured a thorough understanding of the topic, leading to a robust discussion of the findings in the context of both culinary practices and nutritional implications. After the search, the abstracts were reviewed to confirm that they addressed the subject of interest. All duplicates were deleted, and the remaining publications’ abstracts were evaluated. Since it is a narrative review, it was not necessary to document the literature search on specific platforms. Nevertheless, a Prisma diagram is given in the Supplementary Material. Consequently, the studies of interest focusing on the historical, technological, biochemical, and microbiological properties of pastirma were analyzed and synthesized to compose this narrative literature review [14].
3. Historical Aspects
Food consumption patterns are seen as a cultural attribute and, as such, vary in accordance with the societal culture. As it is known, food culture is a result of the accumulation of years of knowledge transferred from generation to generation. Nomads, who mostly salted, pressed, and dried their meat, tried alternative methods for storing food at ambient temperature to safely consume it over an extended period of time [15]. According to historians and archeologists [16,17], Hun and Oghuz Turks, who led a nomadic and militant life in Central Asia, used to carry out their alimentation activities with salted meat and meat pieces of animals they hunted in order to advance on horseback without wasting time. They carried these pieces of meat in their saddles or saddlebags, which they placed on their mounts, and during their journeys that often lasted for weeks, the pieces of meat turned into pastirma by being stuck and pressed between horse and saddle [16,18,19,20]. Pastirma, a Turkish name, is derived from the verb “bastırma”, which means to apply pressure [21]. The primary ancestral territory of Hun and Oghuz Turks was in Central Asia, with the Khingan Mountains in the east, the Caspian Sea in the west, Siberia in the north, and the Himalayas in the south. Hun and Oghuz Turks have been migrating for thousands of years and have spread out from the mainland to various parts of the world [15]. Thus, pastirma culture has been reshaped as a consequence of migration to different geographical areas and its interaction with different cultures (Figure 2).
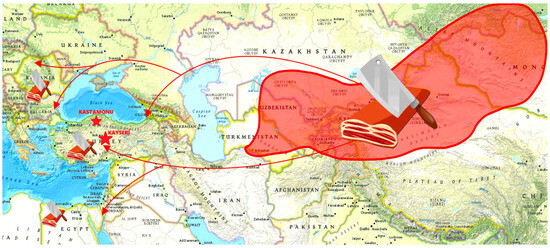
Figure 2.
Migration map of pastirma via Turkic tribes from east to west throughout history.
The cultural interaction between nomads and agricultural societies has shaped pastirma into its current form over time. To prevent the surface of the pastirma from becoming moldy, ancient people covered meat with a thin spice paste called cemen, the main ingredient of which is fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.). Greek hayseed, commonly known as fenugreek, was considered the best stabilizer and preservative by ancient people due to its easily obtainable and fibrous, sticky texture [10,22,23].
The earliest documented evidence indicates that pastirma entered Anatolia from Central Asia during the Seljuk era from the 11th to 12th century. One work from the Seljuk period, “Divanü Lugati-t Türk (in English: Compendium of Turkic Languages)”, mentions pastirma, and a lot of ethnic products were described. This work was prepared as a comprehensive dictionary by Mahmud of Kashgar in 1073, in order to teach Turkish to Arabs [10,22]. During the era of the Ottoman Empire, pastirma had spread from Anatolia to North Africa (Egypt, Algeria, Libya, and Tunisia) and Southeast Europe (Rumelia and the Balkans) [5,24]. The manuscripts that described social functions in 16th century Ottoman Empire mentioned that pastirma served as an appetizer in private bars at a point in time. On the other hand, it is estimated that the commercial production of pastirma started in the 17th century [19,25].
Today, pastirma, known as pasterma or basṭarma in Egypt and consumed in high demand, especially by Egyptians, is no different from Turkish-style pastirma. Unfortunately, pastirma is called pastrami in some publications from Turkey and Egypt [6,21,26,27,28]. However, pastrami, which is considered a word of Jewish origin in America, refers to a different delicatessen product made by brining and smoking. This could potentially be a mere instance of an English translation error.
The name seems to originate from closely related words in Romanian, Russian, Turkish, Greek, and Armenian, namely pastram, pastromá, pastirma, pastramis, and basturma, which all convey the meaning of “pressed”. Also, an etymologist, identified a more extended version of the term, pastramagiu, in the Romanian language, which describes meat that is salty, smoky, and reddish in color [16,21,29,30].
The geographical and climatic conditions of a region shape the traditional products that reflect its culture. These products often utilize local resources and techniques, highlighting the original identity of the region. Nowadays, the province of Kayseri, located in the middle of the Anatolia region, serves as a widely centralized hub for pastirma manufacturing, primarily its industrial production. Although not very well known, Kastamonu, in the Black Sea region to the north of Turkey, is a unique and important place for consumers of traditional pastirma (Figure 2). The essential factor distinguishing Kastamonu pastirma from other pastirma is that it is produced in small enterprises, under natural conditions, using traditional methods based on the experience and talents of the master chefs. These artisanal producers prioritize quality and authenticity, ensuring that each piece of pastirma captures the rich flavors and heritage of the region. This dedication to craftsmanship not only preserves the culinary traditions of Kastamonu but also supports the local economy, allowing these small businesses to thrive. Generally, conventional production occurs under natural conditions, depending on the annual climate and weather conditions, in late September, October, and November. The local community in Anatolia also refers to these months as “pastirma summer” [10]. Nowadays, people consume pastirma either raw or cooked with fried eggs for breakfast. Additionally, it serves as the primary ingredient in numerous dishes such as paçanga, which involves frying pastirma, kashar, and pepper wrapped in ready-made phyllo dough, or haricot with pastirma. Researchers are still investigating the common eating practices of pastirma and the related sociocultural and historical aspects. These studies aim to uncover how pastirma has influenced regional culinary traditions and its role in social gatherings. By examining recipes passed down through generations, researchers hope to highlight the enduring significance of this delicacy in Anatolian culture.
4. Definition and Classification
Pastirma is defined as dry-cured, pressed, washed, dried, coated with cemen paste, and re-dried whole muscles of beef or buffalo, classified as a ready-to-eat (RTE) product that does not require heat treatment. The different parts of the carcass produce different grades of pastirma, and up to 20 different types of pastirma can be made from mature cattle (Bos Taurus) or buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) carcass [9,31]. The chuck and neck (Mehle, omuz, ortabez, kanlıbez), shank (bacak, kürek), rib, short plate, short loin, sirloin and flank (sırt, kuşgömü, ortaetek, kenaretek, arkabaş, döş, kavram), and the round and part of sirloin (şekerpare, dilme, bohça, bohçagömü, kapak, kenar) are prepared to make different kinds of pastirma. Pastirma can be divided into three grades according to quality (Figure 3). Moreover, the figure also shows the parts of the animals from which specific pastirma types are made, and the anatomical names of the major muscle groups that make up these pastirma types are given in Table 1.
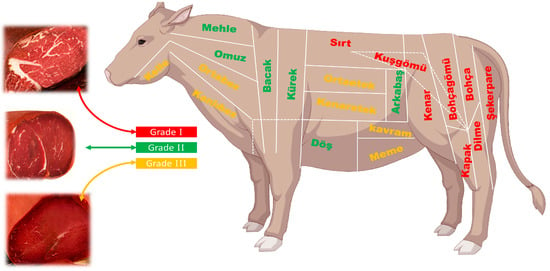
Figure 3.
Infographic diagram of pastirma types and quality classification.

Table 1.
Pastirma types, anatomic location, and Latin names of major muscle groups.
The Turkish Standards Institute standard no. TS-1071 specifies the grading of pastirma. Briefly, Grade 1 pastirma types have a highly marbled, low-fat, and soft texture and a pinky-red color. Grade 1 pastirma can only be made from Sırt, kuşgömü, bohça, kenar, kapak, dilme, and şekerpare. Additionally, the thickness of the cemen paste should be no more than 6 mm. However, grade 2 pastirma types have medium-marbled, medium-fat, and moderate texture; red color; and cemen paste thinner than 8 mm. Also, grade 2 pastirma can only be made from Arkabaş, döş, kürek, bacak, mehle, and omuz parts. On the other hand, grade 3 pastirma types have a non-marbled, rich-fat, and hard texture; a dark red color; and cemen paste thinner than 10 mm. In addition, grade 3 pastirma can only be made from kelle, ortabez, kanlıbez, ortaetek, kenaretek, kavram, and meme parts [31,32]. According to the TS-1071 standard, the color, structure, texture, fatness, and intramuscular fat distribution of pastirma are determined organoleptically. A specific examination method is given only for the fatness status. Accordingly, fatness is determined by the cross-sectional area of a slice cut from the middle of one of the pastirma types, excluding the cemen paste. If the fat ratio is more than 1/3, it is considered fatty; if it is between 1/3 and 1/5, it is regarded as medium fat; and if it is less than 1/5, it is considered low fat [32]. Interestingly, Turkey (Türkiye) does not legally require pastirma grading, despite the standard’s mention of it. Grading of pastirma is voluntary, and the Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry is responsible for grading. Unfortunately, the Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry does not specify who or what qualified people can perform this organoleptic examination. The number of establishments where pastirma is sold with quality grading is very limited. Many commercial companies do not indicate the grade or type of pastirma sold on their packaging. This makes it very difficult to acquire quality and delicious pastirma. To address this issue, it would be beneficial for the ministry to establish clear guidelines and training programs for graders, ensuring that consumers can make informed choices. Enhanced labeling practices could also help elevate pastirma standards and promote transparency within the market.
5. Manufacture of Pastirma
5.1. Animal Selection
Despite experimental attempts to make pastirma from horses, chicken, and fish, consumers remain unfamiliar with these [31,33,34]. The animal chosen to produce pastirma is usually a cow (Bos Taurus), bull (Bos Taurus), or male buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) between 3 and 6 years of age. Meat from young animals is not preferred because of its exudative appearance. Poor water-holding capacity or PSE (Pale, soft, and exudative) meat complicates the drying and salting processes. In addition, heifers (Bos Taurus), oxen (Bos Taurus), and female buffaloes (Bubalus bubalis) are not preferred because of their meat quality, due it being tougher and less chewable, with strong flavor and unfavorable fat content. Also, due to its higher pH, DFD (Dark, Firm, and Dry) beef exhibits deterioration during the salting and drying stages of pastirma manufacturing. Consequently, DFD beef is unsuitable for pastirma. Instead, it is processed into sausages [31].
5.2. Definition and Preparation of Cemen Paste (Fenugreek Paste)
Cemen, the edible covering used for paste seasoning and cementing, is a tremendous source of nutrients, antioxidants, and flavor that are very important to the pastirma industry [35]. Fenugreek seeds are the main ingredient in cemen paste. Crude fenugreek seeds are brownish-yellow in color and rectangular-shaped, hard, pleasantly bitter, and have a maple flavor [23]. Seeds are composed of carbohydrates, accounting for approximately 45 to 60% of their composition. These carbohydrates include mucilaginous fiber, specifically galactomannans. These galactomannans play an important role in making fenugreek paste an excellent coating material. The seeds also contain protein, making up around 20 to 30% of their composition, and they are notably high in tryptophan and lysine. Various flavonoids such as apigenin, orientin, luteolin, quercetin, vitexin, and isovitexin are present, as well as free amino acids including 4-hydroxyisoleucine (0.09%), arginine, lysine, and histidine [23,36,37]. In addition to its consumption as food, fenugreek has a wide range of pharmacological uses and therapeutic effects. Fenugreek was used as a medicine in ancient Egypt. The Ebers papyrus, one of the earliest therapeutic manuscripts, contains reports on the advantages and medicinal applications that have been associated with it. The effects of fenugreek (T. foenum-graecum) on dealing with many health issues have been demonstrated by a multitude of in vitro, in vivo, and clinical studies. Fenugreek has been shown to have anti-hyperglycemic, hypocholesterolemic, immunomodulator, anticancer, anti-obesity, phytoestrogenic, neuroprotective, antimicrobial, and antioxidant effects [38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45].
Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.) seed flour, garlic (Allium sativum L.), and milled red capia pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) are used to produce a semi-solid paste that consists of natural flavors and is known as cemen or fenugreek paste. Cemen is an ethnic food product in and of itself. And cemen’s use is not limited to the preparation of pastirma alone. It can also be consumed on toast for breakfast or as a fresh snack. There is no standard for the composition of cemen paste. Manufacturers use various formulations of paste, provided its the main ingredients remain consistent. The common composition of cemen paste used for pastirma production is 22.5% fenugreek seed flour, 15% garlic, 3.75% paprika, 3.75% red pepper powder, and 55% water [7,31,46].
Applying a layer of cemen paste over the pastirma results in a distinctive appearance, color, flavor, and aroma. Also, it prevents oxidation, microbial contamination, and supports the prevention of over-drying the pastirma [7,47,48]. Kritsi et al. [30] reported that the moisture content decreased and the hardness values increased for both sliced lamb, beef, and buffalo pastirma under refrigerator conditions. The parts of the sliced pastirma that do not interact with the cemen paste are more susceptible to moisture loss. Aside from their benefits, many customers enjoy the unique and strong odor of cemen paste, while some do not. In pastirma, the activity of organosulfur compounds, mainly solotone in fenugreek and allicin in garlic, causes an unpleasant odor in human sweat, breath, and urine [35,49]. Notwithstanding this unpleasant odor, pastirma continues to be enjoyed with great satisfaction, particularly among those residing in the Anatolian region. This preference for pastirma, despite its odor, highlights cultural ties and the dish’s significance within local culinary traditions. Many consumers value its taste and heritage over the sensory drawbacks associated with its ingredients [18,25]. For customers bothered by the odor, cemen paste-scraped pastirma has also been sold in recent years.
5.3. Production Steps
Pastirma masters have their own terminology. The terminology used for the production of pastirma has been passed down from masters to apprentices from past to present. Even customers or suppliers may have never heard of the terms used in production. Production can use a different range of temperature and time combinations. Below is an example.
The selection and slaughter of the processed animals is the first step in pastirma production. After rigor mortis and carcass aging occur, the meat is deboned and cut off as muscle blocks. This process is called “söküm”, which means dissection [31]. The chuck and neck (Mehle, omuz, ortabez, kanlıbez), shank (bacak, kürek), rib, short plate, short loin, sirloin and flank (sırt, kuşgömü, ortaetek, kenaretek, arkabaş, döş, kavram), and round and part of sirloin (şekerpare, dilme, bohça, bohçagömü, kapak, kenar) [31,32] are prepared to make different kinds of pastirma (Figure 3).
After that, excess parts are trimmed, like lymph nodes, fascia, tendons, and ligaments. Furthermore, muscles are given a rectangular shape. This process is called “açım”, which means trimming. Then, a rope is tied to one end of the meat blocks and prepared for salting. For this purpose, a process called “şaklama”, which means gashing, is performed. Sometimes, punctures are created in meat using the sharp point of a knife, while at other times, slices are formed. The meat is sliced into sections from its vast surface, often ranging from five to eight sections. These sections are cut at an angle of 45 degrees, ensuring that they do not exceed half of the overall thickness of the meat itself [50]. Each section is called “şak”. After şaklama, the first salting process is performed at 6 ± 1 °C for 20–24 h. Generally, rock salt with sodium nitrite (NaNO2) or rock salt with potassium nitrate (KNO3) are used. Rock salt with a size of 2.0–2.8 mm is used for dry salting [50]. The large particle size of rock salt leads to salt burns on the meat. Conversely, tiny salt particles can lead to oxidation, darkening, and overly salted products. Relatively cold environments that do not receive sunlight are preferred in the salting process. Dry-salted meat blocks are stacked to a height of 20–25 cm. After the first salting, the second salting process is performed at 6 ± 1 °C for 6–12 h. At this stage, parts of the meat that have yet to be treated are salted and turned over. Meat chunks stacked on top of each other is turned upside down. The recommended quantity of salt to be used in the first and second salting processes should be between 5 and 10% of the total meat weight. When the salt concentration exceeds 10%, it leads to yield loss in the final product. Then, salted meat is washed and rinsed to remove excess salt. This washing and rinsing process takes 1–3 min [31,50]. The washed meat is taken to the first drying process, called “sergileme”, which means exhibition. The meat parts are hung on special hangers to avoid contact with other objects. This drying process can be performed under natural conditions or in air-conditioned rooms. The conventional method of natural drying takes place in late September, October, and November for 3–5 days on windy and sunny days, when the weather is not too hot, or 12–15 days in cloudy and mildly cold weather. On the other hand, the commercial drying method is carried out in climate rooms with 80–85% relative humidity at 15 ± 1 °C and 15–30 m/min airflow for 5 days. After that, the first press, called the “soğuk denkleme”, which means cold pressure, is performed. At this stage, 0.9–1 kg/cm2 pressure is applied to the dried meats at 7–8 °C for 10–17 h [50]. Meat loses some water at this time and appears flattened. Also, the sections called “şak” are closed. The next step is the second drying. The surfaces of the pressed meats are moist. Therefore, a drying process is applied to the meats from 3 to 5 days, depending on the temperature and relative humidity. At the end of this process, the moisture in the meat can be below 34%. In addition, the fat on the surface of the meat melts and gives it a white appearance. This is referred to as “ağarma”, which means bleaching, among manufacturers. After that, the second press, called “sıcak denkleme”, which means hot pressure, is performed. Hot pressure is applied to 0.9–1 kg/cm2 at 20–25 °C for 1–7 h [50]. Finally, the meat coming out of the hot pressure process is covered with cemen paste and hung from 4 to 7 days to dry. Actually, the meat is kept covered in cemen paste for 16–36 h, and then, it is covered with cemen paste with a maximum thickness of 4 mm and left to dry for 7–11 days [31,50,51,52,53]. It is crucial to remember that the cemen paste dough does not contain salt, and the cemen paste absorbs salt from the meat during the cemen paste process. A flow-sheet of the manufacturing process of pastirma is shown in Figure 4.
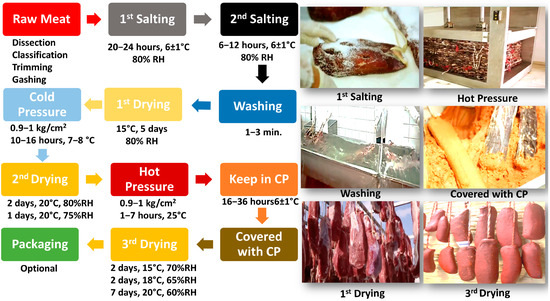
Figure 4.
Flow-sheet of the manufacture of pastirma (CP: cemen paste; RH: relative humidity).
6. Composition and Yield of Pastirma
In general, meat is a rich source of macronutrients, as well as micronutrients, and it provides essential amino acids, essential fatty acids, minerals, and vitamins essential for human growth. The quality of the final product is directly proportional to the quality of the raw meat. The meat used in the production of pastirma is sourced from carcasses that are in excellent condition, follow beef-cut standards, and are well maturated. Raw meat loses weight as a result of the pressing and drying processes used in accordance with pastirma manufacturing method. There may be differences in terms of yield loss in modern and conventional production. However, the literature provides limited data on the relationship between production methods and yield in pastirma. When producing pastirma, raw meat typically loses 30–35% of its weight, until it reaches the stage where cemen paste covers it. After cemen application and the third drying, the wastage is between 20 and 35% [31]. Akçay et al. [26] indicated that, as the weight of the piece of meat used in producing pastirma increases, total income also increases, depending on the sale price, despite the rise in production costs such as the ripening time and yield decrease in the pastirma.
The reported chemical composition of pastirma differs considerably (Table 2). A 100 g serving of pastirma typically contains 5–7 g of fat, 2–3 g of carbohydrates, and approximately 20–35 g of protein [31]. However, these rates vary depending on the specific manufacturing procedure used, as well as the type of meat from which pastirma is made.

Table 2.
Mean basic composition of experimental pastirma, as reported by different studies and commercially labeled pastirma (manufacturer’s declaration).
7. Chemical Properties of Pastirma
The Turkish Food Codex regulation specifies the upper limits for moisture, salt (in dry matter), and pH in pastirma, an ethnic dry-cured meat product, at 50%, 8.5%, and 5.8, respectively. Additionally, the final product can contain cemen up to a maximum of 10% of its total mass [58]. The moisture content of pastirma plays an important part in determining its qualitative characteristics. The initial moisture content of the raw material, about 75%, undergoes a reduction of up to 50% via the processes of curing, first and second drying, and pressure processing. It then increases again during the keeping and covering with cemen paste process. The insufficient drying of the meat and poor reduction in water activity (aw) will lead to product deterioration during the ripening process. Spoilage microorganisms that increase swiftly on the meat surface lead to the deterioration of the product prior to its formation. Akköse et al. [59] found aw values between 0.84 and 0.92 in five different types of pastirma. Similarly, İnat [60] found aw values between 0.84 and 0.89 after the cemen process in pastirma.
It is well recognized that NaCl plays a crucial role in the composition of pastirma, affecting the degree of customer acceptance. The suggested amount of salt for the curing process of pastirma manufacture is 50–60 g of salt per kilogram of meat [53]. In the production of pastirma, salt, nitrite, or nitrates are used together for the curing stage. Firstly, NaCl gives meat a salty taste and brings out its own flavor by affecting many biological reactions during the curing process, such as proteolysis, lipolysis, and lipid oxidation. The second thing that NaCl can do is prevent the growth of pathogenic bacteria by reducing water activity and suppressing the formation of biogenic amines. This can help ensure safety and enhance the stability of the product’s shelf life [59,60,61]. High salt consumption may lead to hypertension, which can then trigger and result in cardiovascular disease. In addition, stroke, left ventricular hypertrophy, nephrolithiasis, gastric cancer, and other diseases are associated with elevated salt consumption [62]. The World Health Organization (WHO) advises adults to consume less than 5 g of NaCl daily; at this point, the worldwide average daily consumption is over 10.8 g, more than the recommended consumption limit [63]. Pastirma, like other dry-cured meat products, is a food product that significantly increases daily sodium intake. Recently, strategies have been developed to decrease sodium levels in dry-cured meats. It is worth noting that reducing NaCl content in foods can lead to a series of quality changes and a decrease in the consumer acceptance of products, especially in dry-cured meat products. However, the effects of novel salt reduction technologies and methods, such as ultrasonic-assisted curing technologies, basic electrolyzed water, sodium chloride with an altered physical structure, etc., on the quality and taste of pastirma are unknown.
Nitrates and nitrites enhance the color quality of pastirma and provide additional benefits, including antioxidant and antibacterial properties. The visual aspect of pastirma, as influenced by the outer surface or sliced surface color, plays a significant role in shaping customers’ preferences for this product. The color of pastirma is influenced not only by the quantity of salt and nitrite or nitrates included but also by the quality of the raw meat, the muscle block type, and the composition and thickness of the cemen paste used [47,48,51]. A study has found that nitrate levels had significant effects on pH and thiobarbituric acid reactive substance (TBARS) levels in final products [64]. On the other hand, another study has shown that nitrite level had an effect on the composition and amount of free amino acids (FAAs) in the final product [65]. Researchers report that using nitrite in production increases the amount of lysine amino acids. The authors stated that between the second drying and pastirma stages, the FAA amounts in samples containing 150 ppm nitrite were lower than in samples containing 50 and 100 ppm nitrite [65]. It is known that residual nitrite can interact with free amino acids and amines, resulting in the formation of nitrosamines in cured beef products. There is strong evidence that nitrosamines are associated with multiple types of cancer, Alzheimer’s, and Parkinson’s disease [66]. Although the authors do not state this, it can be assumed that this is related to the antimicrobial effect of nitrite against proteolytic microorganisms. It is well known that lipolysis and proteolysis take place during the manufacturing process and shelf life of pastirma. There are many factors that affect proteolysis and lipolysis, such as raw meat quality and composition, proteolytic and lipolytic microorganisms’ quantity and activity, the production steps, curing agents, etc. Most of these reactions are known to be due to endo- or exo-peptidases and lipases [65,67,68,69,70]. There are studies reporting that there is a relationship between the degree of proteolysis in pastirma and the flavor of pastirma [68,69]. After the first drying, non-protein nitrogenous substances and free amino acids increase in pastirma samples. Additionally, researchers observed that the density of high molecular weight proteins decreased after the second drying stage, and new protein bands with molecular weights of 85 and 56 kDa appeared as a result of myofibrillar proteolysis during the production of pastirma. This means that proteolysis and lipolysis are accelerated during the drying phase, as in many dry-cured meat products [68].
The pH of pastirma is an important quality criterion that is influenced by several factors, including the post-rigor state of the meat used, the amount of salt, the degree of drying, the pH level of the cemen paste, the usage of starter culture, and the degree of fermentation [71]. According to Turkish standards, the pH of pastirma should be between 4.5 and 5.8 [32].
During the production of raw-consumed products and dry-cured meat products such as pastirma, the increase in the amount of lipid oxidation is a critical quality concern. The TBARS value is a lipid oxidation index that quantifies the amount of malondialdehyde (MDA). Hydroperoxides, the first products of polyunsaturated fatty acids interacting with oxygen, form MDA. As mentioned in the manufacturing steps, during the second drying stage of pastirma production, the fat drops that form on the outer surface of the meat leach into the product due to hot pressure, and the pastirma gains sufficient flavor. Then, the oxidation of the lipids is slowed down, taking advantage of the antioxidant properties of the cemen paste [47,51]. Additionally, cemen paste interrupts the meat block’s contact with oxygen and acts as a barrier to prevent fat oxidation. Researchers have generally tried to prevent lipid oxidation in pastirma by making modifications to the coating material or cemen paste [47,51,52,57,72]. In addition, Aksu and Erdemir [73] reported that potassium lactate (PL, Potassium-L-2-hydroxy-propionate, Potassium-L-Lactate) usage in curing mixtures decreased lipid oxidation in pastirma. While the majority of salt balance occurs between the cemen paste and the salted meat during the keep and covered in cemen paste stage, additional chemical substances, including some amino acids and bioactive compounds, also permeate the meat [51,73]. Aksu et al. [47] reported that cemen paste has a 3.73 mg/g total phenolic content, 237 µmol/g ferric reducing antioxidant power activity, 40.40% DPPH radical scavenging activity, 11.86% metal chelating activity, and 31.78% total antioxidant activity. Also, Deniz et al. [74] have indicated that pastirma represents a good source of natural bioactive peptides capable of reducing free radicals and inhibiting ACE activity. Also, cemen paste contributes to the high bioactivity of pastirma. It can be said that there is definitely a negative correlation between the total antioxidant activity of the cemen paste and the lipid oxidation of pastirma during the storage period. As mentioned above, cemen paste has antioxidant properties, a high phenolic content, oxygen barrier properties, and an edible and biodegradable structure, making it a suitable packaging material for pastirma. This makes cemen paste an active, green packaging material. Also, fenugreek seed flour can be thought of as an edible film, coating polymers like chitosan, gelatin, whey protein, and guar gum.
8. Microbiological Properties of Pastirma
8.1. Natural Flora of Pastirma
The natural flora of pastirma consists of lactic acid bacteria (LAB), catalase-positive cocci, and halotolerant yeast or mold. Researchers have shown that LAB dominate pastirma in some samples, whereas catalase-positive cocci represent the dominant flora in other samples [71,75,76,77]. Due to the use of traditional techniques in pastirma manufacturing, the microflora of pastirma may differ across manufacturers. In fabricated production, starter cultures (Latilactobacillus sakei + Staphylococcus xylosus, Lactiplantibacillus pentosus + Staphylococcus carnosus, etc.) may be used [75]. Also, researchers have investigated the possible use of commercial starter culture preparations for pastirma manufacture [78]. Fettahoglu et al. [79] examined the effect of autochthonous coagulase-negative staphylococci species on pastirma and found that these species increased the redness value and decreased lipid oxidation in pastirma. Currently, there is no specific commercial starter culture combination for pastirma that encompasses its complete sensory, chemical, and microbiological effects. Research on this subject is mostly limited to the biochemical field.
Dincer and Kivanc [80] detected Lactiplantibacillus plantarum as the dominant species in pastirma samples. Çinar et al. [81] identified the dominant flora in pastirma, experimentally and under controlled conditions, as Pediococcus pentosaceus. Researchers have also noted that P. acidilactici, Latilactobacillus sakei, and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum came after that microorganism. Öz et al. [76] identified LAB isolated from pastirma through 16S rDNA sequence analysis and found that their main population consisted of Latilactobacillus sakei, Weisella cibaria, and Weisella confusa, respectively. It has been observed that LAB strains isolated from pastirma can be homofermentative, such as Latilactobacillus sakei, Pediococcus pentosaceus, or heterofermentative, such as Weisella cibaria. The primary function of LAB in pastirma is not to undergo lactic acid fermentation but to contribute to forming sensory characteristics. The pH of pastirma confirms this phenomenon. Briefly, the optimal pH level for pastirma is below 6.0. However, it often stands at 5.5 and does not decrease further below that point [53]. It is known that fermented meat products are suitable carriers for probiotics and can potentially induce health benefits [82]. Topçu et al. [83] found that six strains (P. pentosaceus K7, K41, K44, K51, K81, and P. acidilactici K99), chosen from LAB strains taken from pastirma, had probiotic properties.
In a study where they isolated and identified coagulase-negative staphylococci in pastirma samples, Fettahoğlu et al. [84] genetically identified Staphylococcus vitulinus, S. saprophyticus, S. equorum, and S. xylosus in pastirma samples. Moreover, the researchers stated that the dominant species in the samples was S. vitulius. On the other hand, Kaban [10] reported that S. saprophyticus and S. xylosus were the predominant species in pastirma. Coagulase-negative staphylococci (CNS) are technologically important microorganisms for pastirma. Briefly, CNS are involved in the occurrence and stability of coloring through nitrate reductase activity, causing nitroso myoglobin (NO-Mb) formation in pastirma. Nitrite, formed by reducing nitrate, can also limit lipid oxidation. Also, nitrite in pastirma turns into nitric oxide and prevents the growth of pathogens such as Clostridium botulinum, Listeria monocytogenes, etc., providing microbial safety [75,84,85,86]. Moreover, CNS are essential in controlling lipid oxidation by breaking down hydrogen peroxide through catalase and superoxide dismutase activities. On the other hand, CNS play a role in flavor development by forming low molecular weight compounds through their proteolytic and lipolytic activities [84,85].
Due to the tolerance of yeast to high-osmotic and low-pH conditions, it is capable of causing the spoilage of cured meat products. At the same time, it may lead to economic losses throughout the food manufacturing or storage stages [87,88]. In different pastirma samples, Ozturk’s [77] study found a total of eight species from five different genera. These organisms include Candida, Yarrowia, Trichosporon, Cryptococcus, and Debaryomyces. According to the researcher’s results, Candida zeylanoides (58% of all samples and in all stages of pastirma processing) was the predominant yeast species, followed by Candida deformans (12%) and Candida galli (11%).
8.2. Pathogens in Pastirma
In pastirma production, dry curing, drying, pressing, and coating the meat with a cemen paste significantly suppresses the development of foodborne pathogens. However, it has been indicated that pathogens such as Listeria monocytogenes, Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus cereus, Salmonella spp., Escherichia coli O157:H7, and other enterohemorrhagic species such as E. coli, Clostridium perfringens, and Clostridium botulinum can be found in dry-cured meat products due to unsuitable production or conservation [10,28,89,90,91].
It is known that the elimination of pathogens cannot be wholly guaranteed if no thermal processing is applied. Therefore, in the production of pastirma, pH, water activity, or changes associated with other inhibiting factors such as salt concentration and the presence of nitrite are extremely important. Nitrite plays an essential role in the inhibition of several pathogens, especially Clostridium botulinum [92,93].
Parasites can also be present in pastirma. The presence of parasites in the raw meat used in making pastirma, such as Sarcocystis hominis, Sarcocystis heydorni, Cysticercus bovis, Toxoplasma gondii, and Echinococcus granulosus, should be considered a biological hazard [28,75,93,94]. As is known, Cysticercus bovis, which occurs in the muscles of cattle, is the larval form of the cestode parasite Taenia saginata, which causes tapeworm infection in humans. If a small amount of Cysticercus bovis is detected in the carcass as a result of an inspection performed by the veterinarian in the slaughterhouse, the vet may decide to use these meats in making pastirma to prevent economic loss. It is reported that cysticerci lose their pathogenicity 14 days after the production of pastirma [50,95].
9. Food Fraud and Customer Concerns Regarding Pastirma
One of the products that food fraudsters frequently abuse to endanger public health is pastirma. Examples of fraud in pastirma include the use of meat from unlicensed butchering and without veterinary inspection, adding malicious contamination chemicals to extend shelf life, dealing grade 3 or 2 pastirma under the name of grade 1, and labeling pastirma made from different animals as cattle pastirma [31,50].
Pastirma can be stored for nine months, depending on its oxidation parameters [76]. The main reason for the stability and safety of pastirma is its low water activity. In addition, paste containing garlic has a protective effect on mold growth and excess drying in the final product. Overall, these factors contribute to the extended shelf life of pastirma while maintaining its flavor and nutritional value. Therefore, adhering to proper storage practices and quality control measures is essential for both producers and consumers.
Again, the marketing of improperly stored and spoiled products is also a concern for consumers. Because cemen can effective mask deterioration, reapplying cemen on spoiled pastirma may effectively mask unpleasant smells and evidence of deterioration. It is the industry’s responsibility to introduce safe products into the market. This includes implementing strict storage protocols and ensuring transparency in labeling practices. By prioritizing quality and safety, producers can build consumer trust and promote the long-term viability of their products in the market. This can be achieved by correctly following the Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) procedure. El-Mougy et al. [27] have introduced the HACCP procedure for pastirma produced in Egypt and have determined four critical control points (first pressing, second pressing, applying the cemen paste, and final drying). The research team observed that all parts of the HACCP procedure used in producing pastirma, including the pre-requisite programs (Good Manufacturing Practices, GMPs), were key to success of the HACCP plan. The effective implementation of these critical control points not only ensures the safety and quality of pastirma but also enhances consumer confidence in the product. Furthermore, continuous monitoring and regular training for the staff involved in the production process play a vital role in maintaining compliance with HACCP standards. Codex Alimentarius states that a food hygiene system should be reviewed periodically, and legislation should be prescriptive and practicable [96].
10. Conclusions and Future Aspects
The current research focuses on increasing the health benefits, efficiency, and quality properties of pastirma. Nevertheless, there are still unresolved questions. Firstly, the histological and histochemical impacts of pressing and cemen coating meat blocks are not sufficiently understood. Secondly, researchers should investigate the kinetics of drying and osmotic processing. The osmotic process, such as salt absorption and adsorption during production, is affected by several factors related to the product structure, shape, temperature, process duration, etc. In recent years, strategies for reducing sodium in dry-cured meat products have been developed. The effects of novel salt reduction technologies on the quality and taste of pastirma are unknown. The third point pertains to the necessity of using a starter culture, the type of the starter, and the ratio of microorganisms. As mentioned, LAB and some yeasts contribute to the formation of the sensory properties of pastirma, but their action is limited because of the cemen paste and the final product’s low water activity. It may be useful to develop new starter combinations based on the microorganisms isolated from traditional pastirma, which have already been identified, their salt tolerance, and their symbiosis with CNS. Finally, no alternative has been provided for the unpleasant odor in people’s sweat and urine coming from fenugreek paste solotone. Preventing unpleasant odors without affecting the characteristic and sensory properties of the product could be a good research topic.
This review reveals a rich tapestry woven from the historical roots, technological advancements, and intricate biochemical and microbiological properties of pastirma. This review may help pastirma producers improve the quality of pastirma and may encourage further research to evaluate the overall characteristics of the pastirma at all stages of production and storage.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/su17072801/s1, PRISMA 2020 flow diagram for Pastirma review.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Bennett, G.; Bardon, L.A.; Gibney, E.R. A Comparison of Dietary Patterns and Factors Influencing Food Choice among Ethnic Groups Living in One Locality: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillekroken, D.; Bye, A.; Halvorsrud, L.; Terragni, L.; Debesay, J. Food for Soul—Older Immigrants’ Food Habits and Meal Preferences After Immigration: A Systematic Literature Review. J. Immigr. Minor. Health 2024, 26, 775–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Li, H.; DiPietro, R.B.; Levitt, J.A. The Role of Authenticity in Mainstream Ethnic Restaurants. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2018, 30, 1035–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arviv, B.; Shani, A.; Poria, Y. Delicious—But Is It Authentic: Consumer Perceptions of Ethnic Food and Ethnic Restaurants. J. Hosp. Tour. Insights 2024, 7, 1934–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagaoua, M.; Boudechicha, H.R. Ethnic Meat Products of the North African and Mediterranean Countries: An Overview. J. Ethn. Foods 2018, 5, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elghany, S.M.; El-Makhzangy, A.M.; El-Shawaf, A.-G.M.; El-Mougy, R.M.; Sallam, K.I. Improving Safety and Quality of Egyptian Pastrami through Alteration of Its Microbial Community. LWT 2020, 118, 108872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksu, M.İ.; Turan, E.; Şat, İ.G. Effects of Lyophilized Red Cabbage Water Extract and pH Levels on the Quality Properties of Pastırma Cemen Paste during Chilled Storage. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2020, 89, 101696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, S.; Aksu, M.İ. Free Amino Acids Profile and Quantities of ‘Sırt’, ‘Bohca’ and ‘Sekerpare’ Pastirma, Dry Cured Meat Products. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 956–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakıcı, N.; Aksu, M.İ.; Erdemir, E. A Survey of the Physico-Chemical and Microbiological Quality of Different Pastırma Types: A Dry-Cured Meat Product. CyTA—J. Food 2015, 13, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaban, G. Sucuk and Pastırma: Microbiological Changes and Formation of Volatile Compounds. Meat Sci. 2013, 95, 912–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aykın Dinçer, E. Dried Meat Products Obtained by Different Methods from Past to Present. Food Rev. Int. 2023, 39, 2457–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mediani, A.; Hamezah, H.S.; Jam, F.A.; Mahadi, N.F.; Chan, S.X.Y.; Rohani, E.R.; Che Lah, N.H.; Azlan, U.K.; Khairul Annuar, N.A.; Azman, N.A.F.; et al. A Comprehensive Review of Drying Meat Products and the Associated Effects and Changes. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1057366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilmore, J.H.; Pine, B.J. Authenticity: What Consumers Really Want; Harvard Business Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2007; ISBN 978-1-59139-145-6. [Google Scholar]
- Lins, M.; Puppin Zandonadi, R.; Raposo, A.; Ginani, V.C. Food Waste on Foodservice: An Overview Through the Perspective of Sustainable Dimensions. Foods 2021, 10, 1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batu, A.; Batu, H.S. Historical Background of Turkish Gastronomy from Ancient Times until Today. J. Ethn. Foods 2018, 5, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merwin, T. Pastrami on Rye: An Overstuffed History of the Jewish Deli. In Pastrami on Rye; New York University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-0-8147-6274-5. [Google Scholar]
- Oboturova, N.; Evdokimov, I.; Kulikova, I.; Bratsikhin, A.; Bogueva, D. Chapter 4—Traditional Foods of the North Caucasus Region. In Nutritional and Health Aspects of Traditional and Ethnic Foods of Eastern Europe; Bogueva, D., Golikova, T., Shamtsyan, M., Jākobsone, I., Jakobsons, M., Eds.; Elsevier Traditional and Ethnic Food Series: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 69–91. ISBN 978-0-12-811734-7. [Google Scholar]
- Çılgınoğlu, H.; Mutlu, S. Gastronomi Turizmi Kapsamında Yöresel Ürünlerin Geliştirilmesi: Kastamonu Pastırması Örneği. J. Tour. Gastron. Stud. 2022, 10, 3034–3054. [Google Scholar]
- Erdinçli, İ. 16. Yüzyıldan 20. Yüzyıla İstanbul Meyhane Âlemlerine Eşlik Eden Mezeler ve Yiyecekler. TAD 2023, 42, 151–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, G. Iznik, the Pottery of Ottoman Turkey. By Nurhan Atasoy and Julian Raby. pp. 784, 991 Illus. Including 303 in Colour. London, Alexandra Press, under the Auspices of the Institute of Social Sciences, Istanbul University and the Patronage of the Türk Ekonomi Bankasi, Istanbul, 1989. £120.00. J. R. Asiat. Soc. 1990, 122, 162–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özkan, N. Pastırma Sözü Üzerine. Dil Araştırmaları 2013, 13, 45–55. [Google Scholar]
- Batu, A. Konya (Turkey) Gastronomy Culture Extending to Seljuk Empire. J. Ethn. Foods 2018, 5, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visuvanathan, T.; Than, L.T.L.; Stanslas, J.; Chew, S.Y.; Vellasamy, S. Revisiting Trigonella Foenum-Graecum L.: Pharmacology and Therapeutic Potentialities. Plants 2022, 11, 1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güney, S. Foods Spreading from Turkish Cuisine to the World. J. Multidiscip. Acad. Tour. 2023, 8, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türker, N.; Türkmen, M.; Caymaz, E. Geleneksel bir Ürün Olarak Kastamonu Pastirmasi. Gastroia J. Gastron. And. Travel. Res. 2019, 3, 264–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akçay, A.; Sariözkan, S.; Al, S.; Dïnç, F. Pastırma Üretim ve Satışının Kullanılan Karkas Parçasına Göre Ekonomik Analizi: Economic Analysis of Production and Marketing of Turkish Pastrami According to Carcass Cuts. Vet. J. Ank. Univ. Ank. Univ. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2015, 62, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mougy, R.M.; Abd-Elghany, S.M.; Imre, K.; Morar, A.; Herman, V.; Sallam, K.I. Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) Application to Dry-Cured Pastrami in Egyptian Pastrami Factories. Foods 2023, 12, 2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildirim, Y.; Ertas Onmaz, N.; Gonulalan, Z.; Al, S.; Yildirim, A.; Karadal, F.; Hizlisoy, H.; Pamuk, Ş. Microbiological Quality of Pastrami and Associated Surfaces at the Point of Sale in Kayseri, Turkey. Public Health 2017, 146, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, P.d.S.; Fagundes, J.M.; Couto, D.S.; de Marchi Pires, E.; Guimarães, C.E.D.; Ribeiro, C.D.F.; Otero, D.M. From Curing to Smoking: Processes and Techniques for the Production of Pastrami/Da Cura à Defumação: Processos e Técnicas Para a Produção de Pastrami. Braz. J. Dev. 2020, 6, 61511–61520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kritsi, E.; Ladika, G.; Stavropoulou, N.A.; Oikonomakou, M.; Ioannou, A.-G.; Christodoulou, P.; Konteles, S.J.; Cavouras, D.; Sinanoglou, V.J. Evaluation of the Quality Changes in Three Commercial Pastourma Samples during Refrigerated Storage Using Physicochemical, Microbiological, and Image Analyses Combined with Chemometrics. Foods 2024, 13, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anar, Ş. Et ve Et Ürünleri Teknolojisi (4. Basım); Dora Basım-Yayın Ve Dağıtım Ltd.: Bursa, Türkiye, 2017; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Turkish Standards Institution. Standard No: TS-1071-Pastırma. Available online: https://intweb.tse.org.tr/standard/standard/Standard.aspx?081118051115108051104119110104055047105102120088111043113104073089100111057111098111085079067109 (accessed on 15 October 2024).
- Kök, F.; Arslan, A. The Effect of Different Storage Time Periods in Cumin Paste on the Quality of Barbus Esocinus Pastırma. Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2003, 27, 181–188. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, W.-W.; Bekhit, A.E.-D.A.; Li, F.; Yang, H.-Y.; Jiang, X.-F.; Zhang, W.; Kong, L.-M. Physicochemical Properties of Pastirma from Horse Meat, Beef, Mutton and Pork. J. Food Qual. 2015, 38, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahhmed, A.; Özcan, C.; Karaman, S.; Öztürk, İ.; Çam, M.; Fayemi, P.O.; Kaneko, G.; Muguruma, M.; Sakata, R.; Yetim, H. Utilization of Fermented Soybeans Paste as Flavoring Lamination for Turkish Dry-Cured Meat. Meat Sci. 2017, 127, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Garg, A.N. Availability of Essential Trace Elements in Indian Cereals, Vegetables and Spices Using INAA and the Contribution of Spices to Daily Dietary Intake. Food Chem. 2006, 94, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, S.A.; Kumar, P. Fenugreek: A Review on Its Nutraceutical Properties and Utilization in Various Food Products. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2018, 17, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achari, A.E.; Jain, S.K. Adiponectin, a Therapeutic Target for Obesity, Diabetes, and Endothelial Dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbari, S.; Abdurahman, N.H.; Yunus, R.M.; Alara, O.R.; Abayomi, O.O. Extraction, Characterization and Antioxidant Activity of Fenugreek (Trigonella-Foenum Graecum) Seed Oil. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 2019, 2, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almalki, D.A.; Naguib, D.M. Anticancer Activity of Aqueous Fenugreek Seed Extract Against Pancreatic Cancer, Histological Evidence. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2022, 53, 683–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geberemeskel, G.A.; Debebe, Y.G.; Nguse, N.A. Antidiabetic Effect of Fenugreek Seed Powder Solution (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.) on Hyperlipidemia in Diabetic Patients. J. Diabetes Res. 2019, 2019, e8507453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelwahab, N.S.; Morsi, A.; Ahmed, Y.M.; Hassan, H.M.; AboulMagd, A.M. Ecological HPLC Method for Analyzing an Antidiabetic Drug in Real Rat Plasma Samples and Studying the Effects of Concurrently Administered Fenugreek Extract on Its Pharmacokinetics. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 4740–4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevrin, T.; Alexandre-Gouabau, M.-C.; Castellano, B.; Aguesse, A.; Ouguerram, K.; Ngyuen, P.; Darmaun, D.; Boquien, C.-Y. Impact of Fenugreek on Milk Production in Rodent Models of Lactation Challenge. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shesharao, K.P.; Manjunatha, K.P.; Suguna Rao Sathyanarayana, M.L.; Shridhar, N.; Byregowda, S.M.; Ramachandra, G. Evaluation of Immunomodulatory Cells CD4+and CD8+and Their Ratio Using Alcoholic Seed Extract of Trigonella Foenum Graecum and Alcoholic Leaves Extract of Coccinia Indica by Flow Cytometry in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2020, 9, 2943–2947. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, N.; Yadav, S.S.; Kumar, S.; Narashiman, B. Ethnopharmacological, Phytochemical and Clinical Studies on Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.). Food Biosci. 2022, 46, 101546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastaoglu, E.; Vural, H. New Approaches to Production of Turkish-Type Dry-Cured Meat Product “Pastirma”: Salt Reduction and Different Drying Techniques. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2018, 38, 224–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksu, M.I.; Turan, E.; Sat, I.G.; Erdemir, E.; Oz, F.; Gürses, M. Improvement of Quality Properties of Cemen Paste of Pastirma by Lyophilized Red Cabbage Water Extract. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2020, 44, e14714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksu, M.I.; Konar, N.; Turan, E.; Tamtürk, F.; Serpen, A. Properties of Encapsulated Raspberry Powder and Its Efficacy for Improving the Color Stability and Amino Acid Composition of Pastırma Cemen Pastes with Different pH during Long Term Cold-Storage. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 62, 310–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mebazaa, R.; Mahmoudi, A.; Fouchet, M.; Santos, M.D.; Kamissoko, F.; Nafti, A.; Cheikh, R.B.; Rega, B.; Camel, V. Characterisation of Volatile Compounds in Tunisian Fenugreek Seeds. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 1326–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, A. Et Muayenesi ve et Ürünleri Teknolojisi; Medipres: Catania, Italy, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Aksu, M.İ.; Erdemir, E.; Turan, E.; Öz, F. Chemical, Microbial, Color, Oxidative and Sensory Properties of Clean-Label Pastırma Produced with Raspberry Water Extracts as a Novel Ingredient. Meat Sci. 2022, 186, 108737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksu, M.I.; Turan, E.; Erdemir, E.; Öz, F. Freeze-Dried Pomegranate Extract as a Natural and Novel Ingredient in Cemen Paste and Pastırma Quality During Refrigerated Storage. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2023, 249, 1329–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, M.; Oral, Z.F.Y.; Kaban, G. Pastırma. In Production of Traditional Mediterranean Meat Products; Lorenzo, J.M., Domínguez, R., Pateiro, M., Munekata, P.E.S., Eds.; Methods and Protocols in Food Science; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 143–152. ISBN 978-1-07-162103-5. [Google Scholar]
- Biringen Löker, G.; Amoutzopoulos, B.; Özge Özkoç, S.; Özer, H.; Şatir, G.; Bakan, A. A Pilot Study on Food Composition of Five Turkish Traditional Foods. Br. Food J. 2013, 115, 394–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göğüş, F.; Ötles, S.; Erdoğdu, F.; Özçelik, B. Functional and Nutritional Properties of Some Turkish Traditional Foods. In Functional Properties of Traditional Foods; Kristbergsson, K., Ötles, S., Eds.; Integrating Food Science and Engineering Knowledge into the Food Chain; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 87–104. ISBN 978-1-4899-7662-8. [Google Scholar]
- Gençcelep, H.; İhtïyar, B.; Yüzer, M.O. Determination of Quality Properties of Kastamonu Pastırma: A Dry-Cured Meat Product. Harran Tarım Ve Gıda Bilim. Derg. 2022, 26, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, M.R.S.; Mohamed, M.A.; Mohamed, H.M.H.; Emara, M.M.T. Improving the Sensory, Physicochemical and Microbiological Quality of Pastirma (A Traditional Dry Cured Meat Product) Using Chitosan Coating. LWT 2017, 86, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkish Food Codex. Turkish Food Codex Regulation; Official Gazette: Ankara, Turkey, 2002; Volume 23. [Google Scholar]
- Akköse, A.; Kaban, G.; Karaoğlu, M.M.; Kaya, M. Characteristics of Pastırma Types Produced from Water Buffalo Meat. Kafkas Univ. Veter Fak. Derg. 2018, 24, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İnat, G. Pastırma Üretiminde Kontaminasyon Kaynaklarının Belirlenmesi ve Đyileştirme Koşullarının Araştırılması. Uludağ Üniversitesi Vet. Fakültesi Derg. 2008, 27, 53–59. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, S.; Shen, H.; Wang, D.; Liu, S.; Ding, Y.; Zhou, X. Novel NaCl Reduction Technologies for Dry-Cured Meat Products and Their Mechanisms: A Comprehensive Review. Food Chem. 2024, 431, 137142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.J.; Tan, M.; MacGregor, G.A. 1—Salt and Health. In Reducing Salt in Foods, 2nd ed.; Beeren, C., Groves, K., Titoria, P.M., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Food Science, Technology and Nutrition; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2019; pp. 3–43. ISBN 978-0-08-100890-4. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Global Action Plan for the Prevention and Control of Noncommunicable Diseases 2013–2020; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013; ISBN 978-92-4-150623-6. [Google Scholar]
- Akköse, A.; Ünal, N.; Yalınkılıç, B.; Kaban, G.; Kaya, M. Volatile Compounds and Some Physico-Chemical Properties of Pastırma Produced with Different Nitrate Levels. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 30, 1168–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdemir, E.; Aksu, M.İ. Changes in the Composition of Free Amino Acid During Production of Pastirma Cured with Different Levels of Sodium Nitrite. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2017, 41, e12801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoica, M.; Antohi, V.M.; Alexe, P.; Ivan, A.S.; Stanciu, S.; Stoica, D.; Zlati, M.L.; Stuparu-Cretu, M. New Strategies for the Total/Partial Replacement of Conventional Sodium Nitrite in Meat Products: A Review. Food Bioprocess. Technol. 2022, 15, 514–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oz, E.; Kabil, E.; Kaya, M. The Effects of Curing Agents on the Proteolysis and Lipid Oxidation of Pastırma Produced by the Traditional Method. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 2806–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oz, E.; Kaya, M. The Proteolytic Changes in Two Different Types of Pastırma during the Production. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2019, 43, e14042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyer, A.; Uğuz, Ş.; Dalmiş, Ü. Proteolytic Changes During Processing in Turkish Dry-Cured Meat Product (Pastirma) with Different Salt Levels. J. Food Qual. 2011, 34, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toldra, F. Proteolysis and Lipolysis in Flavour Development of Dry-Cured Meat Products. Meat Sci. 1998, 49, S101–S110. [Google Scholar]
- Aksu, M.; Kaya, M. Some Microbiological, Chemical and Physical Characteristics of Pastirma Marketed in Erzurum (Erzurum Piyasasında Tüketime Sunulan Pastırmaların Bazı Fiziksel, Kimyasal ve Mikrobiyolojik Özellikleri). Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2001, 25, 319–326. [Google Scholar]
- Abdallah, M.R.; Mohamed, M.A.; Mohamed, H.; Emara, M.T. Application of Alginate and Gelatin-Based Edible Coating Materials as Alternatives to Traditional Coating for Improving the Quality of Pastirma. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 27, 1589–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksu, M.İ.; Erdemir, E. The Effect of Potassium Lactate on the Free Amino Acid Composition, Lipid Oxidation, Colour, Microbiological, and Sensory Properties of Ready-to-Eat Pastırma, a Dry-Cured and Dried Meat Product. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 59, 1288–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deniz, E.; Mora, L.; Aristoy, M.-C.; Candoğan, K.; Toldrá, F. Free Amino Acids and Bioactive Peptides Profile of Pastırma during Its Processing. Food Res. Int. 2016, 89, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dişhan, A.; Yetïm, H.; Gönülalan, Z. Pastırma Mikrobiyatası. Bozok Vet. Sci. 2021, 2, 115–125. [Google Scholar]
- Öz, E.; Kaban, G.; Barış, Ö.; Kaya, M. Isolation and Identification of Lactic Acid Bacteria from Pastırma. Food Control 2017, 77, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, I. Presence, Changes and Technological Properties of Yeast Species During Processing of Pastirma, a Turkish Dry-Cured Meat Product. Food Control 2015, 50, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksu, M.I.; Kaya, M. Effect of Commercial Starter Cultures on the Fatty Acid Composition of Pastirma (Turkish Dry Meat Product). J. Food Sci. 2002, 67, 2342–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landeta, G.; Curiel, J.A.; Carrascosa, A.V.; Muñoz, R.; de las Rivas, B. Characterization of coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from Spanish dry cured meat products. Meat Sci. 2013, 93, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dincer, E.; Kivanc, M. Characterization of Lactic Acid Bacteria from Turkish Pastirma. Ann. Microbiol. 2012, 62, 1155–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çïnar, K.; Fettahoğlu, K.; Kaban, G. Genotypic Identification of Lactic Acid Bacteria in Pastirma Produced with Different Curing Processing. Kafkas Univ. Veter Fak. Derg. 2018, 25, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munekata, P.E.S.; Pateiro, M.; Tomasevic, I.; Domínguez, R.; da Silva Barretto, A.C.; Santos, E.M.; Lorenzo, J.M. Functional Fermented Meat Products with Probiotics—A Review. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 133, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topçu, K.C.; Kaya, M.; Kaban, G. Probiotic Properties of Lactic Acid Bacteria Strains Isolated from Pastırma. LWT 2020, 134, 110216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fettahoğlu, K.; Çinar, K.; Kaya, M.; Kaban, G. Biodiversity and Characterization of Gram-Positive, Catalase-Positive Cocci Isolated from Pastırma Produced under Different Curing Processes. Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2019, 43, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fettahoğlu, K.; Kaya, M.; Kaban, G. Evaluation of Autochthonous Coagulase—Negative Staphylococci as Starter Cultures for the Production of Pastırma. Foods 2023, 12, 2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; Xu, B.; Shao, X.; Chen, C.; Wang, W.; Li, P. Theoretical Basis of Nitrosomyoglobin Formation in a Dry Sausage Model by Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci: Behavior and Expression of Nitric Oxide Synthase. Meat Sci. 2020, 161, 108022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güngören, A.; Patir, B.; Özpolat, E. The Effect of Propolis Application on Quality Properties of Vacuum-Packed Hot Smoked Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus Mykiss, Walbaum 1792) Fillets During Cold Storage. LWT 2023, 184, 115084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone, G.; Rodriguez, A.; Magistà, D.; Magan, N. Insights into Existing and Future Fungal and Mycotoxin Contamination of Cured Meats. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2019, 29, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büyükünal, S.K.; Şakar, F.Ş.; Turhan, İ.; Erginbaş, Ç.; Sandıkçı Altunatmaz, S.; Yılmaz Aksu, F.; Yılmaz Eker, F.; Kahraman, T. Presence of Salmonella Spp., Listeria Monocytogenes, Escherichia coli 0157 and Nitrate-Nitrite Residue Levels in Turkish Traditional Fermented Meat Products (Sucuk and Pastirma). Kafkas Univ. Veter Fak. Derg. 2015, 22, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gök, V.; Aktop, S.; Özkan, M.; Tomar, O. The Effects of Atmospheric Cold Plasma on Inactivation of Listeria Monocytogenes and Staphylococcus aureus and Some Quality Characteristics of Pastırma—A Dry-Cured Beef Product. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2019, 56, 102188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gungor, C.; Barel, M.; Dishan, A.; Burak Disli, H.; Koskeroglu, K.; Onmaz, N.E. From Cattle to Pastirma: Contamination Source of Methicillin Susceptible and Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) along the Pastirma Production Chain. LWT 2021, 151, 112130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraqueza, M.J.; Laranjo, M.; Elias, M.; Patarata, L. Microbiological Hazards Associated with Salt and Nitrite Reduction in Cured Meat Products: Control Strategies Based on Antimicrobial Effect of Natural Ingredients and Protective Microbiota. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 38, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majou, D.; Christieans, S. Mechanisms of the Bactericidal Effects of Nitrate and Nitrite in Cured Meats. Meat Sci. 2018, 145, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenthal, B.M. Zoonotic Sarcocystis. Res. Vet. Sci. 2021, 136, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gürbüz, Ü. Mezbaha Bilgisi ve Pratik et Muayenesi; Selçuk Üniversitesi Basımevi Konya: Konya, Turkey, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Codex Alimentarus Alimentarius: General Principles of Food Hygiene CXC 1-1969—Google Akademik. Available online: https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?title=General%20principles%20of%20food%20hygiene%20CXC%201-1969&publication_year=2020&author=C.%20Alimentarius (accessed on 6 January 2024).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).