Abstract
This study evaluated regional and seasonal variations in cobalt (Co), cadmium (Cd), and lead (Pb) concentrations in the serum and milk of she-camels and their calves across five regions of Saudi Arabia to evaluate their potential as bioindicators of environmental contamination. A total of 450 biological and environmental samples (serum, milk, soil, water, and feed) were analyzed using inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP–OES). Regional, seasonal, and physiological effects were assessed by analysis of variance and Pearson correlation. Serum Co varied significantly (p < 0.05) by region and season, with the highest values in the Eastern region during spring. She-camel cadmium showed significant regional differences, particularly higher concentrations in the Southern region, while Pb displayed pronounced seasonal variation, peaking in spring serum and milk of she-camel. In she-camel milk, Co, Cd, and Pb were significantly influenced by region and season interactions (p < 0.05). Correlation analysis revealed strong positive associations between Cd and Pb (r = 0.85, p < 0.001) and between Co and Pb (r = 0.70, p < 0.01), indicating shared exposure pathways. In conclusions, although all metal concentrations remained below FAO/WHO permissible limits, the observed variability highlights the camel’s value as a bioindicator of environmental contamination. Continued monitoring is recommended to safeguard food safety and support Saudi Vision 2030 sustainability goals.
1. Introduction
Heavy metals are naturally occurring elements with high atomic weights and densities, some of which are essential in trace amounts for normal metabolic functions, while others pose toxicity risks even at low concentrations [1,2,3]. Non-essential metals such as cadmium (Cd), lead (Pb), and cobalt (Co) have no known biological role and can cause oxidative stress, organ dysfunction, and growth impairment upon accumulation [4,5,6,7]. These metals enter ecosystems through both natural processes, such as rock weathering and volcanic activity, and anthropogenic sources, including industrial effluents, agricultural runoff, and waste disposal [8,9]. Arid and semi-arid regions, such as Saudi Arabia, are particularly vulnerable to heavy metals contamination due to limited rainfall, high evaporation rates, and slow soil leaching, which favor metal persistence in soil and water [10,11,12].
The dromedary camels (Camelus dromedarius) are a keystone species in desert ecosystems and a major source of food and livelihood for pastoral communities. Its wide-ranging grazing, long lifespan, and physiological tolerance to heat and water scarcity make it a suitable bioindicator of environmental contamination, especially by heavy metals [13,14]. Metal accumulation in camel serum and milk can reflect regional pollution levels and potential food safety risks [15,16].
Previous studies in the Middle East have documented the presence of Cd and Pb in camel tissues, linking their distribution to industrial, traffic, and agricultural emissions [17,18]; however, regional and seasonal dynamics in Saudi Arabia remain poorly understood. This study focuses on Co, Cd, and Pb because they represent metals of contrasting biological importance and environmental relevance in the Arabian regions [19,20,21]. Some heavy metals are essential in trace amounts for biological processes such as enzyme function, immune defense, and reproductive efficiency [22]. Cobalt is essential for vitamin B12 synthesis and enzymatic functions, but can become toxic at elevated levels [23,24]. Cadmium and lead, in contrast, are toxic even at trace concentrations and have been associated with industrial and atmospheric contamination in several Saudi regions [10,25,26]. Recent monitoring reports highlight persistent Co, Cd, and Pb residues in soil, feed, and groundwater near agricultural and urban zones, underscoring the need for integrated environmental surveillance [27].
However, excessive accumulation, along with exposure to non-essential metals such as Cd, Pb, and Co-induces oxidative stress, cellular damage, and metabolic dysfunction, resulting in reduced growth, impaired fertility, and organ toxicity [7,28]. Cadmium exposure, for example, is linked to nephrotoxicity, hepatotoxicity, and bone demineralization, whereas Pb interferes with the nervous and hematopoietic systems, inhibiting heme synthesis and impairing cognitive and motor functions [4,17]. Humans may be exposed to these metals through consumption of contaminated camel milk, meat, and offal, particularly in pastoral communities that rely heavily on camel products for nutrition [29,30]. Chronic exposure, even at sublethal levels, can lead to serious health consequences, including carcinogenic, mutagenic, and neurotoxic effects [4,31,32]. To mitigate such risks, the WHO and FAO have established permissible limits for heavy metals in food products [33]. Polluted soils and vegetation represent continuous sources of exposure for grazing animals, perpetuating contamination cycles in arid ecosystems [13]. Moreover, atmospheric transport of dust can carry industrial and urban-derived metals across long distances, affecting even remote and previously uncontaminated areas [34,35].
Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030, reinforced by the National Transformation Program (NTP 2020), sets a comprehensive framework for balanced socio-economic growth and environmental sustainability. It prioritizes sustainable livestock production, food security, and the protection and restoration of natural ecosystems while promoting measures to minimize industrial environmental impacts [36,37,38,39,40]. Despite growing awareness, comprehensive assessments of heavy metal transfer from environmental sources to camel biological systems remain limited. This knowledge gap hampers the ability to establish contamination baselines, assess food, safety, and guide policy interventions consistent with Saudi Vision 2030s environmental and public health priorities. Therefore, this study aimed to determine regional and seasonal variations in Co, Cd, and Pb concentrations in camel serum and milk across Saudi Arabia, evaluate relationships among these metals and environmental matrices, and assess the camel’s role as a bioindicator for monitoring ecosystem health and food safety in arid environments.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of King Saud University (Ethical NO: KSU-SE-22-21).
2.2. Study Area and Climatic Conditions
The study was carried out across five representative regions of Saudi Arabia: the Central region (Riyadh), the Western (Mecca), the Eastern (Dammam), the Southern (Najran), and the Northern (Al-Jouf) regions, during the summer, winter, and spring seasons. A total of 450 samples were collected, comprising 150 calf serum, 150 she-camel serum, and 150 she-camel milk samples, each representing five regions, three seasons, and ten animals per group (Figure 1).
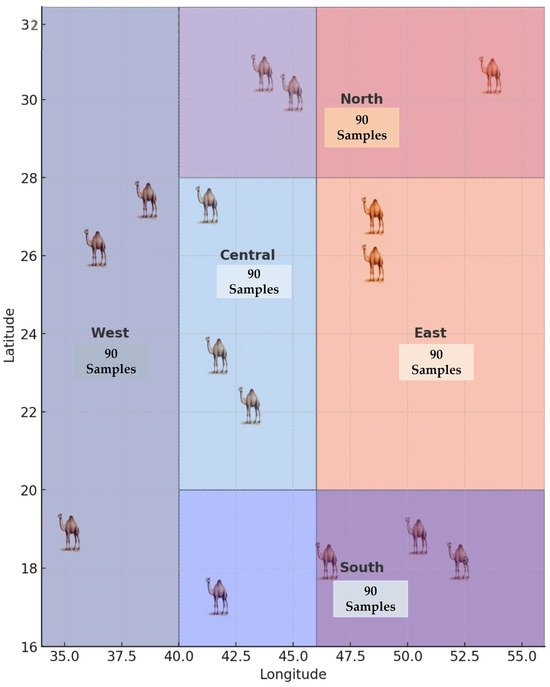
Figure 1.
Geographical distribution of camel sampling sites across the five regions of Saudi Arabia.
Meteorological data show a gradual increase in ambient temperatures across all five regions throughout the three sampling seasons (Figure 2).
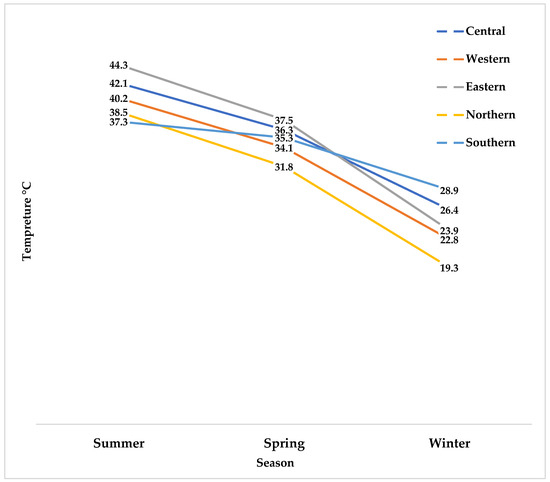
Figure 2.
Seasonal temperature variation across the five study regions.
2.3. Environmental Sample Collection
In each region, five representative soil samples were collected from a depth of 100 cm, placed in sterile labeled plastic bags, and transported and stored for laboratory analysis (Figure 3). Drinking water samples were also collected in sterilized containers from each region and transferred for laboratory analysis for heavy metal concentrations. Additionally, representative feed samples were collected from grazing sites and feed storage facilities (Figure 4). During the study period, natural grazing plants were widely available across all regions, reducing the supplementation of alfalfa hay, Rhodes grass, and barley (Figure 5).
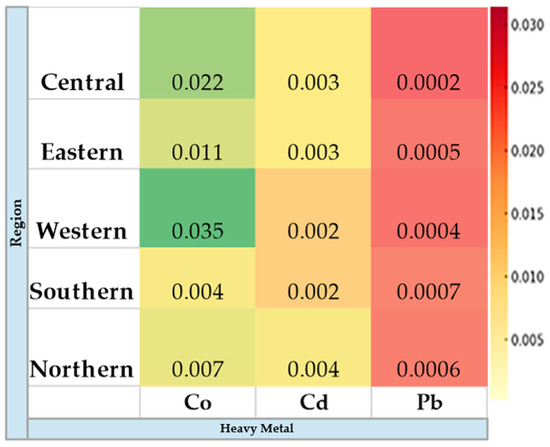
Figure 3.
Heavy metal concentrations (µg/L) in soil samples collected from the study regions.
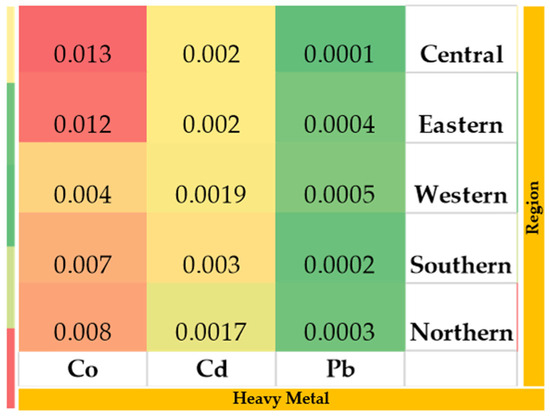
Figure 4.
Heavy metal concentrations in water (µg/L) samples collected from the study regions. The colors represent relative concentration levels (red = higher, yellow = moderate, green = lower).
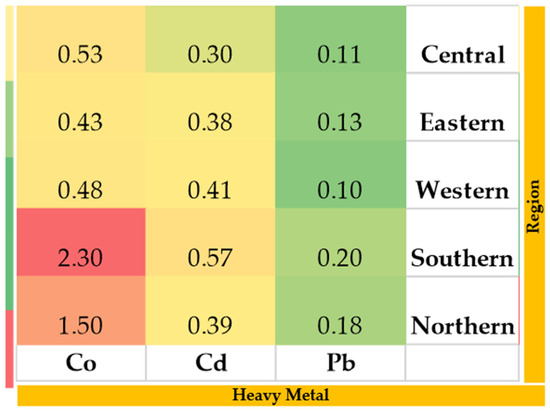
Figure 5.
Heavy metal concentrations (µg/L) in feed samples collected from the study regions. Color intensity represents concentration levels, with green indicating lower values, yellow indicating moderate values, and red indicating higher values. Color gradient (green to red) reflects increasing concentration levels.
2.4. Handling and Preservation of Biological Samples
All biological samples were collected by a licensed veterinary specialist using sterile equipment. Blood and milk samples were transferred immediately to sterile containers, kept on ice, and transported under controlled conditions to the laboratory. Upon arrival, samples were stored at −20 °C until further processing.
2.5. Sample Digestion Procedure
Feed, water, and soil samples were wet digested using a PerkinElmer Multiwave GO microwave digestion system (Hanna Instruments, Woonsocket, RI, USA) fitted with Teflon vessels under controlled temperature and pressure, following the protocol of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists [41] and analyzed for trace minerals using ICP–OES as described by Abdelrahman et al. [22] and Harris et al. [42]. The digestion program consisted of a temperature ramp to 180 °C over 10 min, held for 20 min, followed by automatic cooling to room temperature. The digested solutions were then diluted to a final volume of 25 mL with ultrapure water before analysis. Blank and certified reference materials were processed simultaneously to verify digestion efficiency and contamination control.
For liquid samples (serum and milk), 1 mL of each sample was placed in digestion tubes, followed by the addition of 3 mL nitric acid (HNO3; 65%), 1 mL hydrochloric acid (HCl), 1 mL hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and 1 mL deionized water. Digestion was performed on a hot plate at 122 °C, continuing until the solution became clear.
For solid samples (feed and soil), 0.50 g was accurately weighed and digested using the same reagent composition and protocol. After complete digestion, the clear solution was diluted with 0.1 N HCl to a final volume of 25 mL, mixed thoroughly, and analyzed immediately by ICP–OES.
2.6. Mineral Analysis by ICP–OES
Trace mineral concentrations were determined using a Meinhard nebulizer (type A2) coupled to an ICP–OES system (Thermo Scientific iCAP 7000 Series, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Argon gas was used as both carrier and plasma-maintaining gas. Instrumental operating parameters were as follows: RF power: 1300 W, plasma flow: 15 L/min; auxiliary flow: 0.2 L/min; nebulizer flow: 0.8 L/min; and sample uptake rate: 1.5 mL/min. Analytical signals were measured in peak-area mode with two-point background correction and three replicates per sample. Minerals were quantified using both axial and radial views to minimize spectral interference. Calibration standards were prepared by diluting a stock multi-mineral standard solution (1000 mg/L) in 0.5% (v/v) nitric acid to obtain working standards ranging from 1 to 1000 µg/L. Calibration curves for all minerals exhibited excellent linearity across the working range (0.001–10 µg/L), with determination coefficients (R2) of 0.9992 for Co, 0.9994 for Cd, and 0.9996 for Pb. Calibration standards were prepared using multi-element ICP standards (PerkinElmer, USA), and linearity was verified prior to each analytical run.
Instrumental performance was validated by determining detection and quantification limits for all analyzed elements (instrumental limit of detection (LOD) = 0.001–0.005 µg/L; limit of quantification (LOQ) = 0.003–0.015 µg/L). Analytical quality assurance/quality control (QA/QC) was assured through routine use of certified reference material (NIST-1643f, National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg, MD, USA), with recovery rates ranging from 92% to 106%. Measured concentrations were within ±8% of certified values, confirming the validity of the calibration and analytical performance. Calibration external standard solutions were freshly prepared in pre-cleaned polypropylene vessels treated with 10% HNO3 and rinsed with ultra-pure water (18.2 Ω cm) from a Millipore Milli-Q system. All calibration solutions shared the same acid matrix as the samples and blanks to minimize variability and analytical bias. Calibration was verified after every ten samples, and reagent blanks were periodically analyzed to check for contamination. These quality control procedures confirmed the accuracy, precision, and stability of the ICP–OES measurements [43,44].
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using the PROC GLM procedure in SAS software (version 9.4; SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA). Cadmium, Pb, and Co concentrations were treated as dependent variables, while the five study districts (Central, Western, Eastern, Southern, and Northern) were considered as independent variables. Samples from different regions and seasons were treated as independent observations within a completely randomized design (CRD). Each biological matrix was analyzed in 10 replicates per region and season, resulting in a total of 150 serum samples from she-camels, 150 serum samples from their calves, and 150 milk samples from she-camels. All measurements were performed in duplicate for analytical confirmation, and mean values were used for statistical evaluation. For repeated seasonal measurements, each sampling event was considered a distinct temporal replicate, and data were analyzed using a two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) to test the main effects of region and season, as well as their interaction. Values below the LOD were replaced with half the LOD value (LOD/2) to minimize bias while maintaining dataset integrity. Missing values due to analytical or sampling constraints were excluded from the analysis under the assumption of randomness. Statistical significance was evaluated for all analyzed metals, with differences considered significant at p ≤ 0.05. Pearson’s correlation coefficients (r) were calculated to evaluate relationships among heavy metal concentrations in camel tissues. The strength of Pearson’s correlation coefficients (r) was interpreted according to standard criteria, where |r| < 0.3 indicates a weak correlation, 0.3 ≤ |r| ≤ 0.7 indicates a moderate correlation, and |r| > 0.7 indicates a strong correlation.
3. Results
3.1. Soil, Water, and Feed Heavy Metals
The concentrations of Co, Cd, and Pb in soil, water, and feed samples collected from the five study regions are shown in Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5. Heavy metal levels in soil, water, and feed samples were generally low and remained within internationally acceptable limits. Soil samples exhibited moderate regional variation, likely reflecting natural geochemical differences and the influence of fertilizer use. Water samples showed minimal contamination across all regions, although Pb concentrations were slightly higher in the Western region, suggesting localized anthropogenic inputs such as traffic emissions or dust deposition. Feed samples followed a similar trend, with modest regional variation and the highest Co concentrations observed in the Southern region, indicating potential trace-element enrichment from soil or forage composition.
3.2. Serum Heavy Metals
Regional and seasonal variations in serum Co, Cd, and Pb concentrations of she-camels and their calves are summarized in Table 1, Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4. Cobalt showed significant regional (p < 0.05) and seasonal (p < 0.01) differences, with higher concentrations in the Eastern and Western regions and during spring. Cadmium exhibited marked regional variation in she-camels (p < 0.001), peaking in the Southern region, but remaining relatively stable across seasons and in calves. Lead showed modest seasonal variation in she-camels (p < 0.01), increasing during spring, while regional effects were non-significant (p > 0.001).

Table 1.
Mean concentrations of heavy metals (µg/L) in serum of she-camels and their calves across regions.

Table 2.
Mean concentrations of heavy metals (µg/L) in serum of she-camels and their calves across seasons.

Table 3.
Mean concentrations of heavy metals (µg/L) in she-camel serum by seasons and regions interaction.

Table 4.
Mean concentrations of heavy metals (µg/L) in calf serum by seasons and regions interaction.
Overall, Co ranged between 0.011 and 0.016 µg/L, Cd between 0.019 and 0.027 µg/L, and Pb between 0.004 and 0.014 µg/L in she-camels’ serum. In calves’ serum, Co varied from 0.011 to 0.017 µg/L, Cd from 0.021 to 0.059 µg/L, and Pb from 0.004 to 0.023 µg/L, confirming low but variable exposure levels.
3.3. Milk Heavy Metals
As shown in Table 5 and Table 6, Co, Cd, and Pb concentrations in milk demonstrated region- and season-dependent patterns. Cobalt varied significantly across region*season interaction (p < 0.001), with peak values in the Eastern region during summer. Cadmium showed significant interactive effects (p < 0.05), with higher levels in the Western region during winter. Lead exhibited both regional (p = 0.016) and seasonal variation (p < 0.05), reaching its highest mean in milk from the central region during spring. Across all samples, Co, Cd, and Pb in milk ranged from 0.15 to 3.81 µg/L, 0.03–0.19 µg/L, and 0.13–0.97 µg/L, respectively, values well below FAO/WHO permissible limits, indicating no immediate food-safety concern.

Table 5.
Mean concentrations of heavy metals (µg/L) in she-camel milk across regions and seasons.

Table 6.
Mean concentrations of heavy metals (µg/L) in she-camel milk by regions and seasons interaction.
3.4. Correlation Analysis
Correlation matrices (Figure 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8) revealed positive associations among several metals. In she-camels, Co correlated strongly with Pb (r = 0.70, p < 0.01). In calves, Co and Pb were positively correlated (r = 0.65, p < 0.01), and Cd showed a strong association with Pb (r = 0.85, p < 0.001). In milk, Co weakly correlated with Cd (r = 0.41), while Pb showed weak negative or nonsignificant relationships with other metals. Cross-correlations between serum and milk were generally weak, suggesting partial but limited transfer of metals between these biological matrices.
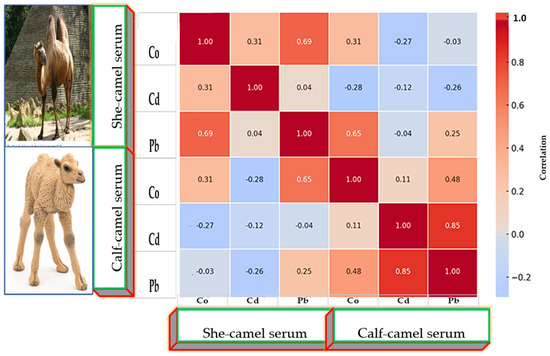
Figure 6.
Correlation coefficients matrix between heavy metals, µg/L concentrations in serum she- and calf camels.
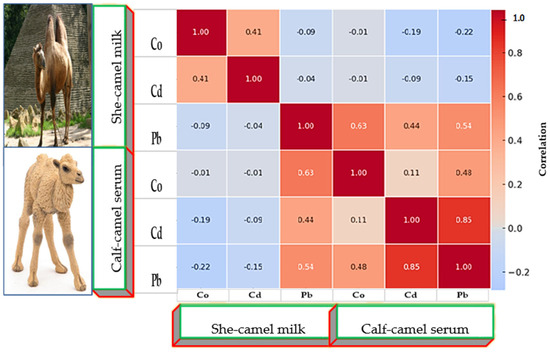
Figure 7.
Correlation coefficients matrix between heavy metals, µg/L concentrations in milk of she- and calf camels.
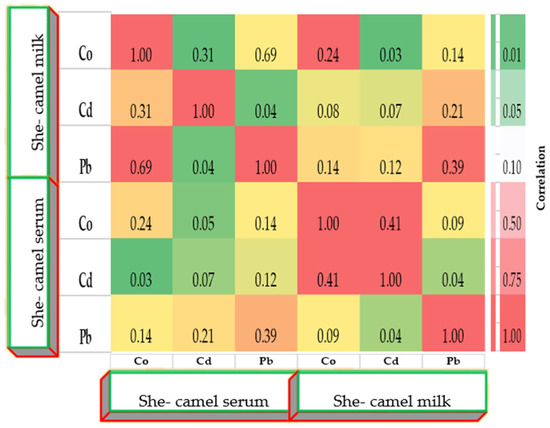
Figure 8.
Correlation coefficients matrix between heavy metals, µg/L concentrations in serum and milk of the she-camels. Correlation matrix of heavy metals between serum and milk. Color gradient (green to red) represents increasing correlation strength.
4. Discussion
The present results reveal both consistencies and divergences with previous studies on heavy metals in camels. Cobalt showed clear regional variation, with higher levels in the Eastern region. This pattern aligns with reports linking trace element levels in camels to environmental factors such as soil and forage composition. Here, serum Co concentrations (approximately 0.012–0.015 µg/L) were considerably lower than those reported by B. Reference [45] and Khan et al. [46], who documented around 0.8 µg/L in healthy camels. This discrepancy may reflect differences in analytical methods, unit conversions, or genuine environmental changes over time. Similar, Ajarem et al. [13] reported elevated heavy metals in camels from industrial zones, reinforcing the influence of local environmental factors. Cadmium was significantly higher in Southern she-camels, suggesting localized exposure through soil or water. In contrast, calves showed no significant differences, likely due to shorter exposure period and limited bioaccumulation. Previous work in Egypt reported higher serum Cd values, around 7 µg/L, [47], while Saudi studies also documented spatial variation [48]. The comparatively low serum Cd values in this study may reflect regional environmental differences or improved analytical sensitivity. Lead concentrations were relatively uniform Pb across regions, differing from previous reports of regional variation in Saudi camel tissues [48]. In this study, Pb levels (0.006–0.012 µg/L) were substantially lower than those reported in Egyptian camels (14 µg/L; [47]), suggesting minimal and evenly distributed Pb exposure in study areas. Since serum levels reflect short-term exposure; however, tissue analysis remains a better indicator of long-term Pb accumulation [13]. Overall, Co showed the strongest regional signal, Cd was elevated in Southern adults, and Pb remained stable across locations. The differences emphasize the need to consider analytical techniques, biological matrix, and environmental context when interpreting heavy metal exposure in camels.
The seasonal variation revealed dynamic environmental influences on heavy metal exposure in camels. Both adult and calf camels had significantly higher Co levels in spring, likely reflecting improved forage availability and quality during that period. Comparable seasonal trends in serum heavy minerals have been reported by Faye, B. [45]. The parallel response in adults and calves indicates that Co bioavailability is environmentally, rather than age, driven. In contrast, Cd showed no significant seasonal variation in either age group, suggesting that exposure arises from stable environmental sources rather than seasonal changes in forage. These agree with Abdelrahman et al. [48], who reported relatively stable Cd levels in camel tissues year-round. Lead exhibited higher levels in spring among adult she-camels, possibly due to increased ingestion of dust and contaminated forage, when camels consume larger amounts of fresh forage. Calves again showed little seasonal fluctuation, consistent with their lower exposure time. Seasonal Pb increases have also been observed in other grazing livestock under dusty, arid conditions [13]. Collectively, these results indicate that Co and Pb exposure in camels are influenced by season, especially in spring, while Cd remains relatively stable, emphasizing the role of forage quality, soil ingestion, and dust in shaping heavy metal dynamics.
In this study, serum Co varied significantly by both region and season, with the highest levels in spring and in Eastern camels (0.014–0.015 µg/L). This confirms earlier findings that mineral bioavailability is shaped by soil and forage composition [48,49]. Cadmium displayed modest regional differences, particularly elevated levels in the South, but minimal seasonal variation consistent with Meligy et al. [50] and lower than older reports [47]. Lead remains low and relatively uniform across regions but increases during spring, contrasting with studies conducted near industrial zones [13,47].
This study shows that age influences accumulation. Calves exhibited fewer regional differences and weaker metal interaction, indicating that shorter exposure duration limits heavy metal bioaccumulation. Seasonal Co peaks persisted in serum calves, while Cd and Pb remained stable, confirming that essential elements (Co) are more sensitive to environmental shifts than toxic metals such as Cd and Pb. Here, both serum and milk Co were highest in spring and in Eastern regions, reinforcing the nutritional and environmental determinants of Co availability. These findings are consistent with Faye, B. [45], who showed variation in serum Co linked to nutrition, and more recent work by Acosta–Dacal et al. [51], which emphasized the role of background mineral status in camel trace element profiles.
Serum and milk Cd concentrations remained generally low and stable, but were slightly elevated in Southern camels, in agreement with Abdelrahman et al. [48] and Meligy et al. [50]. Lead; however, showed significant regional and seasonal increases, highest in Western regions and in spring milk samples, likely reflecting enhanced dust ingestion and forage contamination. Similar Pb elevations were reported in Saudi camels near industrial areas and in milk contamination studies [13,52,53]. Compared with older Egyptian data [47] Pb concentrations here were lower, suggesting reduced but still notable environmental exposure in Saudi Arabia.
In this study, heavy metal concentrations in she-camel milk are influenced mainly by region and, to a lesser extent, season. Milk Co levels peaked in the Eastern region during summer (3.813 µg/L), Cd in the Western region during winter (0.194 µg/L), and Pb in the central region during spring (0.966 µg/L), patterns likely influenced by soil and forage mineral composition, dust ingestion, and contamination of fresh forage, indicating localized environmental pollution. The present findings align with those of Abdelrahman et al. [48], who also reported regional, but not seasonal, variation in Cd in camels. Comparable geographic differences in camel trace elements were observed by Acosta–Dacal et al. [51] and Faye, B. [45]. Similarly, Ajarem et al. [13], Zakaria et al. [52], and Kerdoun et al. [53] emphasized Pb in camel milk as a potential food safety concern. The positive correlations among Co, Cd, and Pb indicate shared exposure routes, primarily via soil, water, and forage ingestion. Strong correlations between serum and milk metals suggest co-accumulation and overlapping absorption mechanisms in the gastrointestinal tract. Similar multi-element associations were described by Acosta–Dacal et al. [51] and Abdelrahman et al. [48]. In this study, Pb showed the strongest cross-element correlation, clustering with Co and Cd, particularly in calves, indicating common exposure pathways and a higher susceptibility of young animals. The association between Co and Cd concentrations in she-camel milk highlights the possibility of concurrent transfer of essential and toxic elements, which may pose risks to milk safety and consumer health. Also, there were observed weak but significant serum–milk correlations, especially between Co and Pb (r = 0.69) and Co and Cd (r = 0.41), supporting evidence of overlapping absorption and secretion mechanisms. The Pb link between serum and milk (r = 0.39) suggests partial transfer from blood into milk, consistent with Faye, B. [45]. Pb’s role as a bridge element underscores its mobility and significance in one health risk assessment [53,54,55]. The spatial and seasonal variations in heavy metal levels likely result from combined environmental, physiological, and anthropogenic factors. Elevated Co in spring may reflect enhanced forage mineral uptake after rainfall, whereas higher Pb and Cd indicate inputs from vehicle emissions, fertilizers, or industrial activity. Dust deposition and physiological factors such as lactation also influence metal distribution. Overall, variability in Co, Cd, and Pb arises from both geogenic and anthropogenic sources, yet all concentrations remained below international safety limits, confirming the camel’s role as a sensitive bioindicator in arid ecosystems.
The present findings confirm that environmental and seasonal factors influence heavy-metal dynamics in camels. Cobalt primarily reflects nutritional status, cadmium indicates localized environmental exposure, and lead represents a broader contamination risk. Despite regional and temporal variation, all concentrations remained below international safety thresholds, reinforcing the camel’s role as a reliable bioindicator in arid ecosystems. In this study, combined serum concentrations of Co, Cd, and Pb in she-camels and their calves ranged from 0.011 to 0.017 µg/L, 0.020–0.043 µg/L, and 0.004–0.019 µg/L. In milk, Co, Cd, and Pb levels varied between 0.15 and 3.81 µg/L, 0.03–0.19 µg/L, and 0.13–0.97 µg/L. These values are substantially lower than the FAO/WHO maximum permissible limits for milk and edible animal products (Cd: 0.05 mg/kg; Pb: 0.1 mg/kg), suggesting no immediate food safety concern.
The environmental matrices (soil, water, and feed) exhibited trace concentrations of Co, Cd, and Pb that correspond closely with the biological accumulation patterns observed in camels. Slightly higher Co and Cd levels in soils and feeds from the Southern and Eastern regions suggest a soil–plant–animal transfer mechanism influenced by local geochemical composition and fertilizer use. The marginally elevated Pb concentrations in water from the Western region likely reflect localized anthropogenic contributions, such as vehicular emissions, atmospheric dust, or proximity to urban activity. Overall, these environmental findings reinforce that the studied areas experience low-level, diffuse exposure to heavy metals rather than acute contamination, supporting the interpretation that observed regional and seasonal variations in camel serum and milk primarily result from background environmental inputs.
When compared with regional reports, these concentrations are consistent with those of Abdelrahman, M. M., I. A. Alhidary, R. S. Aljumaah, and B. Faye [22], who described similar low-to-moderate heavy-metal burdens in Saudi camels under non-industrial conditions. By contrast, Meligy, A. M., W. R. El-Ghareeb, S. M. Abdel-Raheem, H. A. Ismail, W. S. Darwish, M. Kandeel, A. E. Alfifi, S. S. Al-Shokair, and M. A. Hussein [50] and Abdou, A., and F. Mohamed [47] reported higher Cd and Pb levels in Egyptian camels, likely due to greater industrial and agricultural emissions. Elevated Cu and Al concentrations in milk from camels grazing near industrial zones, as observed by Zakaria, A. M., Y. A. Amin, H. M. Zakaria, F. Farrag, L. Fericean, I. Banatean-Dunea, M. Abdo, A. Hafez, and R. H. Mohamed [52], further highlight the role of anthropogenic influence. Similarly, Meligy, A. M., W. R. El-Ghareeb, S. M. Abdel-Raheem, H. A. Ismail, W. S. Darwish, M. Kandeel, A. E. Alfifi, S. S. Al-Shokair and M. A. Hussein [50] and Abdelrahman, M. M., I. A. Alhidary, M. M. Alobre, A. M. Matar, M. A. Al-Badwi, M. M. Qaid and R. S. Aljumaah [15] emphasized spatial variability of trace elements across camel tissues in semi-arid regions, driven by soil–plant–animal transfer. In contrast Ajarem et al. [13] documented oxidative stress and tissue injury in camels near petroleum-industry zones, effects not detected in the present study, indicating comparatively lower industrial exposure in the surveyed areas.
Although contamination levels were low, the observed regional and seasonal variability, particularly higher Pb concentrations in milk during spring, suggests fluctuating environmental exposure, possibly linked to dust deposition or feed contamination. Some limitations should be acknowledged, including the modest sample size per region, potential environmental heterogeneity among sampling sites, and minor analytical uncertainty near the detection limits of ICP–OES. Future studies incorporating larger, stratified sampling designs and isotopic tracing techniques would enhance the precision of exposure assessment. Overall, this study provides essential baseline data on Co, Cd, and Pb in Saudi camels and demonstrates their potential as bioindicators of environmental quality—supporting Saudi Vision 2030 objectives for sustainable livestock production, environmental protection, and food-safety assurance.
5. Conclusions
This study demonstrated clear regional and seasonal variation in Co, Cd, and Pb concentrations in dromedary camels, confirming their utility as bioindicators of environmental quality in arid ecosystems. Although all measured values remained below FAO/WHO permissible limits, the observed fluctuations, particularly elevated Pb levels in milk during spring, indicate a potential food safety concern and the need for proactive environmental and food-safety monitoring.
From a policy perspective, these findings highlight the importance of integrating camel-based bioindicator surveillance into national environmental monitoring frameworks. Establishing reference thresholds for trace metals in camel serum and milk would enhance early detection of contamination and guide evidence-based mitigation strategies. Moreover, harmonizing heavy-metal surveillance with Saudi Vision 2030 initiatives could strengthen sustainable livestock management and promote public health protection in pastoral communities.
Future research should focus on longitudinal monitoring across broader geographic gradients to capture temporal exposure trends and identify contaminant sources using isotopic or geospatial approaches. Risk assessment models linking environmental concentrations to human dietary intake from camel products are also recommended to refine safety standards and inform targeted environmental regulations. Collectively, these measures will support ecosystem resilience, food safety, and sustainable agricultural development in Saudi Arabia.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.M.A. (Mutassim M. Abdelrahman), A.M.M., M.M.Q. and R.S.A.; data curation, A.M.M., M.A.A.-B., and M.M.A. (Mohsen M. Alobre); formal analysis, M.A.A.-B. and M.M.A. (Mohsen M. Alobre); funding acquisition, M.M.A. (Mutassim M. Abdelrahman); investigation, A.M.M. and M.M.Q.; methodology, M.M.A. (Mohsen M. Alobre), A.M.M. and M.M.A. (Mutassim M. Abdelrahman); project administration, M.M.A. (Mutassim M. Abdelrahman) and R.S.A.; resources, M.M.A. (Mutassim M. Abdelrahman) and A.A.A.; software, R.A.A., M.M.A. (Mutassim M. Abdelrahman) and M.A.A.-B.; supervision, R.S.A. and M.M.A. (Mutassim M. Abdelrahman); validation, R.S.A., M.M.A. (Mutassim M. Abdelrahman) and A.A.A.; visualization, R.S.A., M.M.Q. and A.A.A.; writing—original draft, M.M.A. (Mohsen M. Alobre) and M.M.Q. All authors have writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Ongoing Research Funding Program (ORF-2025-1071), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Research Ethics Committee (REC), King Saud University (protocol code No KSU-SE-22-21 and date of approval 24 March 2022).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their appreciation to the Ongoing Research Funding Program (ORF-2025-1071), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia for financial support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Yedjou, C.G.; Patlolla, A.K.; Sutton, D.J. Heavy metal toxicity and the environment. In Molecular, Clinical and Environmental Toxicology: Volume 3: Environmental Toxicology; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2012; Volume 101, pp. 133–164. [Google Scholar]
- Jadaa, W.; Mohammed, H. Heavy metals–definition, natural and anthropogenic sources of releasing into ecosystems, toxicity, and removal methods–an overview study. J. Ecol. Eng. 2023, 24, 249–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maglas, N.N.; Turki, S.A.; Qiang, Z.; Ali, M.M.; Osta, A.A.; Alwarqi, M.S.; Najar, M. Assessment of radioactive nuclides and heavy metals in soil and drink water in lahij city, yemen. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2025, 215, 111566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaishankar, M.; Tseten, T.; Anbalagan, N.; Mathew, B.B.; Beeregowda, K.N. Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2014, 7, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobojonov, K.S.; Umataliyevna, U.K.; Asanaliyevna, S.Z.; Muxsimovna, A.M.; Mamadjanovna, T.F.; Shavkatovna, A.M.; G’ulom o’gli, A.U.B.; Abdujalol o’g’li, G.A. Priority toxic metals arsenic, cadmium, mercury, and lead in ecosystems: A review of sources, toxicity, and regulatory approaches. Chem. Rev. Lett. 2025, 8, 883–902. [Google Scholar]
- Generalova, A.; Davidova, S.; Satchanska, G. The mechanisms of lead toxicity in living organisms. J. Xenobiotics 2025, 15, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghribi, F.; Bejaoui, S.; Chetoui, I.; Trabelsi, W.; Belhassen, D.; Ben Fayala, C.; Boubaker, S.; Mili, S.; Soudani, N. Toxicological effects of cobalt on common carp: Oxidative stress, ionic imbalance, fatty acid disruption, and gill histopathology. Environ. Geochem. Health 2025, 47, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alloway, B.J. Heavy Metals in Soils: Trace Metals and Metalloids in Soils and Their Bioavailability; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Di Bella, G.; El-Sorogy, A.S.; Giacobbe, S.; Nava, V.; Al-Kahtany, K.; Nour, H.E. Risk assessment of potentially toxic elements in intermittent rivers, “fiumara”, flowing in the gulf of milazzo (Sicily, Italy). Environ. Earth Sci. 2024, 83, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulaziz, M.; Alshehri, A.; Yadav, I.C.; Badri, H. Pollution level and health risk assessment of heavy metals in ambient air and surface dust from saudi arabia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2022, 15, 799–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gantayat, R.R.; Elumalai, V. Salinity-induced changes in heavy metal behavior and mobility in semi-arid coastal aquifers: A comprehensive review. Water 2024, 16, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kenawy, A.M. Hydroclimatic extremes in arid and semi-arid regions: Status, challenges, and future outlook. In Hydroclimatic Extremes in the Middle East and North Africa; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Ajarem, J.S.; Hegazy, A.K.; Allam, G.A.; Allam, A.A.; Maodaa, S.N.; Mahmoud, A.M. Heavy metal accumulation, tissue injury, oxidative stress, and inflammation in dromedary camels living near petroleum industry sites in saudi arabia. Animals 2022, 12, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, T.; Nour, H.E.; Al-Kahtany, K.; Zumlot, T.; El-Sorogy, A.S. Health risk assessment and contamination of lead and cadmium levels in sediments of the northwestern arabian gulf coast. Heliyon 2024, 10, e36447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelrahman, M.M.; Alhidary, I.A.; Alobre, M.M.; Matar, A.M.; Al-Badwi, M.A.; Qaid, M.M.; Aljumaah, R.S. Trace elements levels in growing camels’(camelus dromedarius) biological tissues from semi-arid areas. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2025, 53, 2452506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, M.M.; Alhidary, I.A.; Alobre, M.M.; Matar, A.M.; Alharthi, A.S.; Faye, B.; Aljumaah, R.S. Regional and seasonal variability of mineral patterns in some organs of slaughtered one-humped camels [Camelus dromedarius] from saudi arabia. Animals 2022, 12, 3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, S.; Ennab, W.; Wei, Q.; Wang, C.; Quddus, A.; Mustafa, S.; Hadi, T.; Mao, D.; Shi, F. Impact of cadmium and lead exposure on camel testicular function: Environmental contamination and reproductive health. Animals 2023, 13, 2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustapha, A.; Zainab, K.R.; Musa, H. Determination of heavy metals in some organs of ruminants slaughtered at funtua central abattoir, katsina state, nigeria. Niger. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. NJAST 2025, 8, 125–135. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Kahtany, K.; El-Sorogy, A.S.; Alharbi, T. Ecological risk assessment and potential source of as, cd, co, and ni in al qunfudhah seawater, red sea coast, saudi arabia. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2024, 36, 103560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sorogy, A.S.; Nour, H.E.; Al-Kahtany, K.; Youssef, M.; Alharbi, T.; Yakubu, M.A. Potential health and ecological risk assessment of selected heavy metals in dammam coastal sediments, arabian gulf. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2025, 89, 104354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazzal, Y.; Bărbulescu, A.; Sharma, M.; Howari, F.; Ben Salem, I.; Dghaim, R.; Kumbhar, P.; Xavier, C.M.; Alghafli, S.; Al-Taani, A.A.; et al. Heavy metal pollution in arid urban environments: Anthropogenic and geogenic insights from road dust in the united arab emirates. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2025, 89, 313–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, M.M.; Alhidary, I.A.; Aljumaah, R.S.; Faye, B. Blood trace element status in camels: A review. Animals 2022, 12, 2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyat, M.S.; Monem, U.M.A.; Mostafa, T.H.; Thabet, R.M.; El-Latif, K.M.A.; Al-Sagheer, A.A. Influence of long-term dietary cobalt supplementation on lactation performance and reproductive efficiency in maghrabi she-camels. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2025, 203, 5183–5194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genchi, G.; Lauria, G.; Catalano, A.; Carocci, A.; Sinicropi, M.S. Prevalence of cobalt in the environment and its role in biological processes. Biology 2023, 12, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouida, L.; Rafatullah, M.; Kerrouche, A.; Qutob, M.; Alosaimi, A.M.; Alorfi, H.S.; Hussein, M.A. A review on cadmium and lead contamination: Sources, fate, mechanism, health effects and remediation methods. Water 2022, 14, 3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, A.G.; El-Saeid, M.H.; Alzahrani, A.J.; Ibrahim, H.M. Heavy metal pollution and associated health risk assessment of urban dust in riyadh, saudi arabia. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0261957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuznietsov, P.; Biedunkova, O. Application of multivariate statistical techniques for assessing spatiotemporal variations of heavy metal pollution in freshwater ecosystems. Water Conserv. Sci. Eng. 2025, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, A.; Mahreen, N. Emerging insights into the impacts of heavy metals exposure on health, reproductive and productive performance of livestock. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1375137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.; Saleem, M.; Yap, C.; Zaib, M.; Khan, Q.; Ibrahim, M.; Sakandar, H. Estimation of heavy metals in milk of different areas of sialkot (pakistan) and its possible health impact on consumer. J. Food Qual. Hazards Control 2025, 12, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, M.R.S.; Pimenta, A.M.; Catarino, R.I.L.; Leal, M.F.C.; Simões, E.T.R. Heavy metals in milk and dairy products: Safety and analysis. Pollutants 2025, 5, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, G.; Raza, A.M.; Dhole, P. Heavy metal exposure and its health implications: A comprehensive review. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2025, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomova, K.; Alomar, S.Y.; Nepovimova, E.; Kuca, K.; Valko, M. Heavy metals: Toxicity and human health effects. Arch. Toxicol. 2025, 99, 153–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codex Stan 193-1995; Codex General Standard for Contaminants and Toxins in Food and Feed. FAO: Rome, Italy, 2024.
- Al Nadhairi, R.; Al Kalbani, M.; Al Khazami, S.; Al Hashmi, M.; Al Zadai, S.; Al-Rumhi, Y.; Al-Kindi, K.M. Air quality and health risk assessment during middle eastern dust storms: A study of particulate matter. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2025, 18, 587–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budakoti, S.; Singh, C.; Choudhury, A. Transport of a severe dust storm from middle east to indian region and its impact on surrounding environment. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 10345–10366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almotairy, H.M.; Alshehri, K.A.; Almutairi, O.A.; Alenizi, H.O.; Bokheder, S. Enhancing agricultural biosecurity: Strategies for food safety and environmental sustainability in saudi arabia. In Worldwide Megatrends in Food Safety and Food Security; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almulhim, A.I. Toward a greener future: Applying circular economy principles to saudi arabia’s food sector for environmental sustainability. Sustainability 2024, 16, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharthi, S.; Alharthi, A.; Alharthi, M. Sustainable development goals in the kingdom of saudi arabia’s 2030 vision. Sustain. City XIII 2019, 238, 455. [Google Scholar]
- Altouma, A.; Bashir, B.; Ata, B.; Ocwa, A.; Alsalman, A.; Harsányi, E.; Mohammed, S. An environmental impact assessment of saudi arabia’s vision 2030 for sustainable urban development: A policy perspective on greenhouse gas emissions. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2024, 21, 100323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshuwaikhat, H.M.; Mohammed, I. Sustainability matters in national development visions—Evidence from saudi arabia’s vision for 2030. Sustainability 2017, 9, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemists. AOAC: Official Methods of Analysis, 20th ed.; Latimer, G.W., Ed.; AOAC International: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, A.; Xanthos, S.J.; Galiotos, J.K.; Douvris, C. Investigation of the metal content of sediments around the historically polluted potomac river basin in washington dc, united states by inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectroscopy (icp-oes). Microchem. J. 2018, 142, 140–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzawi, B.; Qadah, D.; Mubiana, V.K.; Bervoets, L.; Al Zabadi, H.; Blust, R. Exposure assessment of as, cd, hg, and pb in fish and canned fish collected from local markets at ramallah city using high-resolution inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2025, 9, 1591035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häßler, M.; Wetzel, K.; Warnecke, L.; Niedenthal, T.; Montero, L.; Ayala-Cabrera, J.F.; Schmitz, O.J. Assessment of the differentiation of sambucus nigra plant parts using a multi-target and suspect screening by lc-hrms and icp-oes. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2025, 417, 6209–6220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faye, B. Camel. In Encyclopedia of Dairy Sciences; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, Z.I.; Liu, W.; Mubeen, I.; Alrefaei, A.F.; Alharbi, S.N.; Muhammad, F.G.; Ejaz, A.; Ahmad, K.; Nadeem, M.; Shoukat, J.; et al. Cobalt availability in the soil plant and animal food chain: A study under a peri-urban environment. Braz. J. Biol. 2023, 83, e270256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdou, A.; Mohamed, F. Estimation of some heavy metals residues in blood serum and tissues of camels. Assiut Vet. Med. J. 2015, 61, 221–229. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelrahman, M.M.; Alhidary, I.A.; Matar, A.M.; Alobre, M.M.; Ayadi, M.; Aljumaah, R.S. Heavy metals levels in soil, water and feed and relation to slaughtered camels’ tissues (Camelus dromedarius) from five districts in saudi arabia during spring. Life 2023, 13, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, W.H.; Sherkawy, H.S.; Mohamed, R.H.; Noseer, E.A. Assessment of trace elements and metals status in imported camels. J. Adv. Vet. Res. 2024, 14, 113–116. [Google Scholar]
- Meligy, A.; Ghareeb, W.; Raheem, S.; Ismail, H.; Darwish, W.; Kandeel, M.; Alfifi, A.; Shokair, S.; Hussein, M. Assessment of some toxic elements (co, cr, mn, se, and as) in muscle, offal, hair, and blood of camels (Camelus dromedaries) and their risk assessment. Open Vet. J. 2024, 14, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Dacal, A.; Henríquez, A.M.; Corbera, J.A.; Macías-Montes, A.; Zumbado, M.; Ruiz-Suárez, N.; Martín-Barrasa, J.L.; Luzardo, O.P.; Tejedor-Junco, M.T. Comprehensive profiling of essential elements and organic and inorganic contaminants in dromedary camels from the canary islands: A baseline for nutritional and environmental assessment. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, A.M.; Amin, Y.A.; Zakaria, H.M.; Farrag, F.; Fericean, L.; Banatean-Dunea, I.; Abdo, M.; Hafez, A.; Mohamed, R.H. Impact of grazing around industrial areas on milk heavy metals contamination and reproductive ovarian hormones of she-camel with assessment of some technological processes on reduction of toxic residue concentrations. BMC Vet. Res. 2024, 20, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerdoun, M.A.; Djafer, R. Heavy metal levels in camel milk and health risk assessment: A global systematic review. J. Trace Elem. Miner. 2024, 8, 100131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.S.I.; Hafez, A.-E.E.; El Bayomi, R.M.; Mahmoud, A.F.A. Review on camel meat: Health benefits, chemical contaminants, health risks, and mitigation strategies. Egypt. J. Vet. Sci. 2025, 56, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elafify, M.; El-Toukhy, M.; Sallam, K.I.; Sadoma, N.M.; Abd-Elghany, S.M.; Abdelkhalek, A.; El-Baz, A.H. Heavy metal residues in milk and some dairy products with insight into their health risk assessment and the role of lactobacillus rhamnosus in reducing the lead and cadmium load in cheese. Food Chem. Adv. 2023, 2, 100261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).