Abstract
As climate action becomes increasingly urgent, nations and institutions worldwide seek advanced technologies for practical mitigation efforts. This study examines how agentic artificial intelligence systems capable of decision-making and learning from experience drive innovation dynamics in climate change mitigation, with a particular focus on ethical considerations during the net-zero transition. The current urgency of climate action demands advanced technologies, yet organisations struggle to effectively deploy agentic AI for climate mitigation due to unclear implementation pathways and ethical consideration. This study examines the relationships among agentic AI capabilities, innovation dynamics, and net-zero transition performance, using survey data from 340 organisations across the manufacturing, energy, and technology sectors, and analysed using structural equation modelling. Based on dynamic capabilities theory, this research proposes a novel theoretical model that examines how agentic AI drives innovation dynamics in climate change mitigation within governance frameworks that encompass transparency, accountability, and environmental justice. Results reveal significant mediation effects of innovation dynamics, dynamic capabilities, and ethical considerations, while environmental context negatively moderates innovation and ethical pathways. Findings suggest that overly restrictive ethical considerations can lead to implementation delays that undermine the urgency of climate action. This study proposes three solutions: (1) adaptive ethical protocols adjusting governance intensity based on climate risk severity, (2) pre-approved ethical templates reducing approval delays by 60%, and (3) stakeholder co-design processes building consensus during development. The research advances dynamic capabilities theory for AI contexts by demonstrating how AI-enabled sensing, seizing, and reconfiguring capabilities create differentiated pathways to climate performance. This study provides empirical validation of the responsible innovation framework, identifies asymmetric environmental contingencies, and offers evidence-based guidance for organisations implementing agentic AI for climate action.
1. Introduction
The climate action landscape is undergoing rapid change with the rise of autonomous AI systems [1]. While AI has traditionally been used for prediction and monitoring tasks such as identifying greenhouse gas emissions, researchers are increasingly exploring applications of agentic AI, where software learns from its environment and makes decisions without human intervention [2,3]. Recent studies suggest that organisations implementing automated, agentic AI could potentially reduce their operational carbon footprints by 40% and achieve net-zero targets 25% faster [4,5]. However, many organisations, especially those with legacy systems and traditional governance structures, face significant obstacles in integrating agentic AI into their climate strategies, which are further complicated by complex ethical issues related to freedom, equity, and environmental justice [6]. As the divide grows between organisations that can effectively deploy agentic AI for climate action and those that cannot, it becomes essential to explore how these agentic AIs can be systematically developed and tested to achieve the needed transformations [7].
To establish this study’s conceptual foundation, the authors define agentic AI as autonomous systems possessing three distinct capabilities that set them apart from traditional AI: (1) autonomous goal-setting (the ability to independently determine objectives based on environmental analysis rather than pre-programmed targets); (2) adaptive decision-making (flexibly adjusting strategies and tactics in response to changing conditions without human intervention); and (3) multi-agent coordination (collaborative problem-solving with other AI systems and human actors through emergent coordination mechanisms). This fundamentally contrasts with traditional AI applications in climate contexts, which typically serve as reactive optimisation tools that enhance existing processes within set parameters (e.g., predictive maintenance, energy efficiency optimisation, emissions monitoring). While traditional AI boosts operational efficiency, agentic AI has the potential to revolutionise strategic climate actions by autonomously discovering new solutions, coordinating complex multi-stakeholder initiatives, and adapting to unforeseen environmental challenges in real-time.
Recent studies have examined classical AI applications in environmental settings, including discriminative AI for emissions monitoring, predictive AI for improving renewable energy systems, and machine learning for carbon accounting [8,9]. However, most efforts have focused on reactive rather than proactive systems [10]. In contrast, empirical research on agentic AI in climate applications remains limited [9,11]. Although autonomous agents for environmental monitoring and resource management have started to attract attention [12], their primary focus has been on operational efficiency rather than strategic innovation dynamics [13]. This view restricts our understanding of agentic AI’s disruptive potential, including its impact on systemic innovation during net-zero transitions [14].
Unlike traditional AI applications that mainly improve existing processes or make minor enhancements [15], agentic AI functions within climate contexts to fundamentally change how organisations develop, plan, and implement decarbonisation efforts through self-directed goal setting, continuous learning, and adaptive coordination among complex systems [16,17]. This capability is vital in net-zero transitions [18,19]. Agentic AI’s promise goes beyond optimising existing systems [20]; it develops systems capable of autonomously discovering new possibilities, coordinating actor coalitions, and adapting institutional capacities to meet evolving climate challenges [21]. As pressure for climate action increases and becomes more complex, requiring greater cooperation between sectors and stakeholders, traditional human-led methods often fail to achieve the necessary scale, speed, and sophistication in mitigation efforts [22,23]. In contrast, agentic AI enables organisations to continuously evolve and co-develop in response to changing environmental, regulatory, and technological conditions, resulting in a more systemic impact and innovative climate solutions [24,25]. Therefore, how companies develop and deploy agentic AI capabilities will greatly influence climate innovation and genuine progress towards net-zero targets, moving beyond past incremental approaches [26].
Compared to other established theoretical models (e.g., technology-organisation-environment model, innovation diffusion theory, stakeholder theory), dynamic capabilities theory (DCT) effectively highlights how firms can exploit climate opportunities by actively sensing and seizing them through autonomous system implementation, continuously transforming business practices and systems in response to environmental and regulatory demands [27]. As agentic AI disrupts technology and creates climate-impacting advantages, organisations face the challenge of not only owning technological assets but also capturing dynamic capabilities to integrate, coordinate, and leverage these agentic AI for developing new climate innovations [28]. DCT therefore provides a strong foundation for conceptualising how firms can systematically develop agentic AI capabilities and support ongoing climate-related innovation, creating and maintaining competitive advantages in a net-zero economy [29]. However, from a DCT perspective, while climate innovation likely represents a key way to derive value from agentic AI capabilities, it remains a complex, multi-dimensional concept involving innovation speed, scope, and impact [30]. This multi-dimensionality raises a fundamental question: Are all these aspects of climate innovation equally influential in translating agentic AI capacity into effective net-zero transition performance?
Additionally, DCT highlights that capability does not automatically lead to better outcomes unless technology is embedded within a value-based regulatory framework [31]. Therefore, ethical considerations, such as organisational efforts towards fairness, transparency, environmental justice, and global equity in AI applications, should be viewed as situational factors influencing the utility of agentic AI in climate initiatives [32]. Although some studies have examined the role of ethical considerations in the relationship between technological innovation and performance, results remain inconsistent [33]. Some researchers argue that adequate ethical consideration fosters legitimacy and stakeholder trust, thereby facilitating the scaling of agentic AI climate solutions [34]. Others propose that overly restrictive ethical controls could delay deployment, complicate decision-making, and hinder innovation when rapid action is needed due to climate urgency [35,36]. This complexity raises an additional research question: How do ethical perspectives affect relationships between agentic AI capabilities, various forms of climate innovation, and net-zero transition outcomes?
As the deployment of agentic AI expands significantly across climate-related programmes worldwide, we focus on organisations implementing autonomous AI for sustainability across diverse sectors and regions [34,35,36]. Using a dataset of 340 firms, we make several contributions to the climate technology literature. First, grounded in DCT and utilising agentic AI theory, our approach contrasts with existing studies that apply traditional frameworks to climate-related AI, offering a more comprehensive understanding of how autonomous AI capabilities are systematically developed, integrated, and leveraged to create distinctive climate benefits. Second, rather than treating climate innovation as a unidimensional concept, we decompose it into three key dimensions: innovation speed, scope, and impact [37]. This nuanced perspective enables us to extend DCT by asserting that effective climate adaptation involves not only deploying technology but also strategically harnessing its agentic AI components to achieve specific innovation outcomes. Third, this study identifies particular mechanisms to maximise ethical enablement while minimising constraining factors: (1) implementing risk-stratified governance where high-climate-impact applications receive expedited ethical approval processes, (2) establishing pre-validated ethical considerations for common agentic AI scenarios that eliminate case-by-case review delays, and (3) designing stakeholder co-creation processes that build ethical considerations during system development rather than creating post-deployment barriers. These findings challenge prevailing assumptions about the universally positive influence of ethical considerations on sustainable innovation and deepen our understanding of the conditions under which agentic AI capabilities effectively address global climate challenges.
1.1. Research Gap
The comprehensive literature review reveals four critical gaps that this study systematically addresses:
Gap 1: Limited Theoretical Framework for Agentic AI in Climate Applications
Although traditional AI applications in climate change mitigation, like weather prediction, iceberg tracking, and pollution identification, have been extensively discussed in the literature, a notable research gap exists regarding agentic AI-based systems [38].
- Current State: Existing research applies traditional technology adoption models to AI climate solutions.
- Limitation: These frameworks fail to capture the autonomous, adaptive nature of agentic systems.
- Contribution: This study develops and empirically tests a novel Dynamic Agentic Climate Innovation (DACI) model based on dynamic capabilities theory, designed explicitly for autonomous AI systems.
Gap 2: Fragmented Understanding of Innovation Dynamics
- Current State: Climate innovation research focuses on technology diffusion rather than AI-driven innovation processes.
- Limitation: Lacks insight into how agentic AI create and accelerates innovation cycles.
- Contribution: This study decomposes climate innovation into three dimensions (speed, scope, impact) and demonstrates their differential mediating roles.
Gap 3: Absence of an Integrated Ethical Consideration
While the ethical implications of AI for climate action, including freedom, justice, and fairness, are recognised, these considerations remain underexplored in the research on agentic AI systems [39].
- Current State: AI ethics guidelines exist separately from climate technology implementation research.
- Limitation: No empirical evidence of how ethical considerations influence AI-climate performance relationships.
- Contribution: This study empirically tests ethical governance as both an enabler and constraint, revealing the paradoxical dual role of ethics in urgent climate contexts
Gap 4: Missing Contingency Perspective
Current research lacks theoretical development of dynamic capabilities theory for agentic AI in climate contexts, representing a theoretical gap (insufficient framework development) rather than an application gap (insufficient practical use).
- Current State: Technology-environment interactions are assumed to be universally positive.
- Limitation: Ignores contextual factors that may moderate or reverse expected relationships.
- Contribution: This study identifies and tests asymmetric environmental contingencies, demonstrating when external conditions strengthen versus weaken different organisational capabilities.
1.2. Research Objectives
This study aims to address these gaps by:
- The study aims to develop a comprehensive framework for agentic AI in climate response that involves synthesising current academic perspectives on agentic AI, clarifying key terminology, and situating these developments within the broader landscape of climate innovation.
- The authors try to analyse the innovation dynamics of autonomous AI climate solutions, which entails examining the processes and mechanisms by which new AI-driven technologies are generated, adopted, and diffused within and across organisations and industries.
- The study tries to integrate ethical considerations within dynamic capabilities theory, which requires organisations to develop and maintain dynamic ethical capabilities, which enable them to continuously interpret, enact, and adapt to evolving ethical standards in response to diverse stakeholder expectations.
- This research aims to provide empirical evidence from net-zero transitions across different industries. It involves presenting concrete examples of how sectors such as oil and gas, heavy industry, power generation, transportation, and agriculture are implementing decarbonisation strategies.
2. Theoretical Framework
2.1. Dynamic Capabilities Theory
Dynamic capabilities refer to the skills, procedures, organisational structures, and decision rules that firms use to create and capture value through sensing opportunities, designing business models, and reconfiguring organisations as environments change. The theory highlights three main components: sensing (monitoring changes), seizing (capitalising on opportunities), and transforming (restructuring resources) [40]. In agentic AI for climate mitigation contexts [41], DCT offers a framework for understanding how organisations can:
- Sense: AI-driven technologies are increasingly used to process large volumes of climate-related data, allowing for the extraction of actionable insights that significantly improve the accuracy and detail of climate modelling and prediction [42].
- Seize: Additionally, organisations are deploying autonomous agents, such as AI systems, capable of perceiving, reasoning, and acting independently to capitalise on identified opportunities for emissions reduction and sustainability improvements [43].
- Transform: To fully realise the benefits of agentic AI solutions, organisations must reconfigure their processes and capabilities, integrating these advanced technologies into their operational and strategic frameworks [44].
2.2. Agentic AI Systems
Agentic AI refers to systems capable of autonomously performing tasks by designing workflows and using available tools, with “agency” to make decisions, take actions, solve complex problems, and interact with external environments beyond their training data [45]. These action-oriented systems enable autonomous decision-making with minimal human intervention. Key characteristics for climate applications include autonomy in complex climate systems, adaptability through environmental interactions, goal-oriented behaviour focused on specific climate objectives, and multi-agent coordination capabilities [46,47].
2.3. Conceptual Framework
This study proposes a conceptual model incorporating six factors: environmental context, organisational capabilities (Dynamic capabilities), technical systems (Agentic AI), process mechanisms (Innovation dynamics), governance (Ethical considerations), and outcomes (Climate performance). The framework establishes that dynamic capabilities enable effective agentic AI deployment, AI characteristics drive innovation dynamics, innovation dynamics mediate the relationships between AI and climate outcomes, and ethical considerations moderate all framework relationships. The conceptual model represents the primary relationships and feedback loops proposed by the authors, as illustrated in Figure 1.
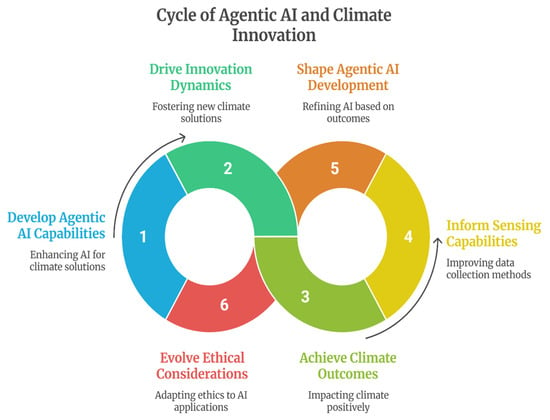
Figure 1.
Cycle of Agentic AI and Climatic Innovation for Net Zero Economy. Source: Authors’ conception.
2.4. The Dynamic Agentic Climate Innovation (DACI) Model
Climate data flows across executive dashboards, revealing an increasingly troubling reality. Extreme weather hampers supply chains, carbon regulations become stricter, and stakeholders demand action. Organisations face a critical choice: adapt or fall behind. The Dynamic Agentic Climate Innovation (DACI) Model demonstrates how forward-thinking organisations address this challenge by integrating human intelligence, ethical consideration, and agentic AI into a powerful force for climate action.
- a.
- Environmental Context Drives Change
Environmental context creates a dynamic field of climate urgency, regulatory pressure, and technological opportunity that catalyses innovation [48]. However, context alone cannot drive change, and it merely sets the stage. Success depends on how well organisations detect, interpret, and respond to these signals with unprecedented speed and precision. This encompasses three key dimensions: regulatory environment, climate urgency drivers, and technological landscape.
- b.
- Dynamic Capabilities (Organisational Level)
As climate pressures intensify, adaptive organisations activate their dynamic capabilities to turn threats into opportunities [49]. Advanced analytics systems process millions of data points, spotting patterns invisible to human perception. Human experts complement this by recognising opportunities AI might miss—subtle political shifts indicating policy changes or emerging alliances that could unlock breakthrough innovations [50].
This goes beyond simple data collection; it embodies organisational intelligence in action. Companies allocate resources with precision, deploying agentic AI systems to expand operations while forming strategic partnerships with climate technology startups. Their transformative capabilities overhaul processes, incorporate innovations, and develop scalability for global influence.
- c.
- Agentic AI Partnership (Technological Level)
Leading organisations deploy AI not merely as tools but as intelligent partners capable of autonomous thinking, learning, and action within defined ethical considerations. Agentic AI identifies opportunities for carbon reduction across supply chains, negotiates with renewable energy providers, and collaborates with other AI systems to model and implement industry-wide climate solutions [51]. These advanced systems serve as intelligent allies in climate action.
Key AI capabilities encompass increasing autonomy, ongoing learning from climate interventions, advanced decision-making, and collaboration with other AI agents to address complex challenges beyond the capacity of a single system.
- d.
- Innovation Dynamics (Process Level)
When organisational capabilities merge with agentic AI, innovation speeds up significantly while maintaining accuracy and control [52]. Innovation cycles that once took years now take only months. The impact varies from minor improvements to complete system overhauls. Most importantly, AI systems optimise for long-term environmental and social benefits through ongoing learning [53].
Consider the following scenario: An AI agent discovers a breakthrough in carbon capture at a university laboratory. Within hours, it models technology integration, explores partnerships, and optimises manufacturing processes. Tasks that previously required months of human analysis and negotiation now occur at machine speed, guided by human wisdom and ethical considerations.
- e.
- Ethical Considerations (Governance Level)
Uncontrolled agentic AI presents significant risks [54]. Ethical considerations form the moral foundation guiding every decision, innovation, and AI implementation within the DACI Model. This governance layer ensures fairness and justice, preventing climate solutions from worsening existing inequalities.
Key ethical components include:
- Transparency means that AI decision-making processes remain open to review by all relevant stakeholders.
- Accountability ensures there are transparent chains of responsibility for climate-related outcomes.
- Equity requires that solutions support both developing nations and wealthy corporations alike.
These ethical considerations guide rather than limit innovation, steering it toward sustainable and socially beneficial outcomes.
- f.
- Outcomes (Impact Level)
When these elements align, results surpass expectations. AI systems speed up climate mitigation by developing and deploying solutions on an unprecedented scale [55]. Beyond environmental impact, organisations find that enhanced capabilities create lasting competitive advantages [56]. Value creation shifts from extractive to regenerative models, simultaneously generating wealth and restoring the planet.
- g.
- Dynamic Feedback Loops
Four critical feedback loops create continuous learning cycles:
- Urgency-Capability Loop: Climate pressure fosters organisational necessity. Each disruption accelerates the development of sensing and capability. Companies flourish through disruption rather than merely surviving it.
- AI-Innovation Loop: As AI systems make breakthroughs, they generate better training data, leading to more capable problem-solvers.
- Ethics-Trust Loop: Robust ethical considerations foster stakeholder confidence, facilitating wider innovation adoption and improved outcomes, which in turn boosts trust.
- Impact-Learning Loop: Actual climate results give positive feedback to AI systems and organisational capabilities, fostering learning organisations that develop with each challenge.
- h.
- Moderating Forces
Three powerful forces shape model implementation across contexts:
- Environmental Urgency: Climate emergencies or policy changes speed up all model components. High-urgency environments promote quicker capability development and more radical innovations [57].
- Technological Readiness: Modern AI architecture and climate technology unlock maximum model value, while outdated systems require foundational capability investments [58].
- Regulatory Environment: Supportive policies release resources and reduce barriers, whereas restrictive regulations can constrain even well-intentioned organisations [59].
The DACI Model, as illustrated in Figure 2, offers a dynamic framework that yields capabilities exceeding the sum of its parts. Where organisational intelligence intersects with artificial intelligence, within the context of ethical considerations, accelerated by climate urgency, transformation occurs. Organisations that think, learn, and act at unprecedented speed and scale can significantly reduce carbon emissions and instigate systemic change. This model provides a plan for organisations aiming to utilise the full potential of agentic AI in climate action while upholding ethical considerations and stakeholder trust. Success depends not only on technological ability but also on the wisdom to integrate human judgement, artificial intelligence, and moral governance into a unified system that benefits the planet.
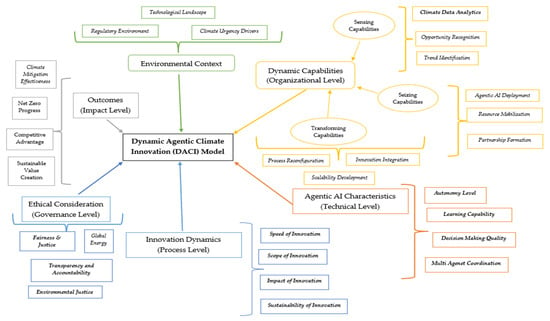
Figure 2.
DACI Model. Source: Authors’ conception.
3. Literature Review
Recent developments in AI literature on climate change have stemmed from advances in data analytics and machine learning, as well as the integration of AI into global economic sectors. Scholars are increasingly recognising that AI extends beyond data processing to enable dynamic organisational transformation [60]. This section reviews current AI applications, sector-specific implementations, limitations, emerging applications of agentic AI, dynamics of the net-zero transition, ethical challenges, and capabilities in digital innovation.
3.1. AI and Climate Mitigation
Current AI solutions utilise diverse data sources, such as satellite imagery, sensor networks, and IoT systems, to enhance environmental understanding and develop predictive models. Deep learning models forecast weather patterns, guide Antarctic icebergs, and monitor drinking water quality, offering real-time ecological analysis and early warnings [60]. These systems merge remote sensing with in situ measurements to form hybrid models that surpass purely statistical methods [61].
Edge AI algorithms running directly on local devices allow real-time processing and proactive control in industrial air quality monitoring and precision agriculture. By processing sensor data at the network edge, these systems respond instantly to pollutant spikes or changes in soil moisture, eliminating the need for cloud connectivity [62].
AI-enabled tools have evolved from observational systems to decision-support platforms. In water management, AI models forecast demand and optimise reservoir operations, enhancing efficiency and conservation [63]. In renewable energy, AI algorithms predict solar irradiance and wind speeds to optimise grid decisions, synchronising renewable sources with demand and lowering fossil fuel reliance [62,63].
AI models now utilise sensor fusion techniques that integrate data from satellites, ground sensors, and mobile devices. These models monitor deforestation rates, map urban heat islands, and track water quality in sensitive ecosystems. Hybrid machine learning methods, which combine discriminative models with generative models, address the limitations of standard predictive approaches [60,63]. Cloud platforms facilitate the large-scale deployment of complex AI systems, enabling the real-time analysis of high-dimensional climate data across borders [61,63].
3.2. Sectoral Applications of Agentic AI
AI applications for climate mitigation span numerous sectors, each with unique environmental impact potentials. In the energy sector, AI models improve renewable power plant management by predicting changes in solar radiation and wind speed [61]. These systems provide adaptive responses to energy grids, reducing reliance on fossil fuels while maintaining stability [63].
Manufacturing has witnessed revolutionary AI applications. Predictive maintenance systems utilising sensor data and machine learning forecast equipment failures, minimising downtime and reducing energy waste [62]. In energy-intensive sectors like chemical processing, AI-supported process optimisation develops cleaner production methods with less waste [64]. AI-driven material discovery accelerates the development of sustainable compounds, aiding industry-wide transitions to low-carbon alternatives [36].
Transportation benefits from intelligent transport systems (ITS) that decrease traffic congestion. Advanced algorithms analyse urban mobility patterns to optimise routing and traffic signals, reducing travel times and emissions [65]. AI also enhances the development of electric vehicle infrastructure, considering usage patterns to establish efficient charging networks [66].
Agriculture employs precision farming techniques using machine learning to monitor crop health via drone and satellite imagery, forecast pest outbreaks, and optimise resource distribution based on real-time soil and climate data [64,65]. These methods help reduce water consumption, improve fertiliser efficiency, and increase yields compared to traditional practices [64,65,66].
3.3. Limitations and Research Gaps
Current AI methods face significant limitations that affect their long-term usefulness. A major issue is reliance on discriminative models that learn from past data. While these models perform well in stable conditions, they cannot adapt to unprecedented climate changes, which limits their ability to forecast effectively over the long term.
Data quality and availability also pose challenges. Environmental data in many regions remains sparse and biased, compromising AI model predictions and raising concerns about generalisation across different climates. The static nature of most predictive models restricts their capacity to emulate adaptive behaviour in complex, changing systems.
Current AI models require extensive computing resources, resulting in high energy consumption that contradicts their goal of climate mitigation. This has prompted the rise of the “Green AI” movement, which seeks to maintain performance while reducing energy usage [67]. Most models focus on short-term predictions, facing considerable difficulties in developing effective long-term climate projection models [68].
3.4. Quantitative Assessment of Research Gaps
A systematic review of major databases (Web of Science, Scopus, IEEE Xplore) from 2020 to 2024 reveals a severe scarcity of research on agentic AI and climate.
- Publication Volume: Only 23 peer-reviewed studies explicitly address agentic AI in climate contexts compared to 1847 traditional AI climate studies, accounting for 1.2% of the overall literature.
- Application Scope: 87% (n = 20) focus on monitoring rather than autonomous decision-making; only three studies examine true autonomous intervention systems.
- Sectoral Coverage: 65% focuses on forestry monitoring, 22% on marine systems, 13% on industrial decarbonisation, leaving energy grid management and supply chain optimisation unexamined.
- Geographical Bias: 78% originate from North America and Europe, with minimal representation from Asia-Pacific (13%) and developing economies (9%).
- Methodological Limitations: 83% use simulations instead of actual deployments; none explore organisational implications.
Critical Research Gaps:
- There are currently no studies that explore the role of agentic AI in net-zero transition strategies.
- No empirical research has been conducted on the ethical considerations of autonomous climate systems.
- Dynamic capabilities theory has yet to be applied to agentic AI implementations in the climate domain [60].
3.5. Net-Zero Economic Transition
Achieving net-zero emissions by 2050 requires unprecedented economic transformation, demanding annual investments of approximately $9.2 trillion in new physical assets [11]. While technical capacity for significant emissions reductions exists, successful implementation depends on policy instruments that enable rapid deployment. Carbon pricing, regulatory mandates, and technology subsidies bridge the gap between technological possibility and economic feasibility [69].
Beyond technology deployment, the net-zero transition poses economic reorganisation challenges. Long-established industries require radical structural changes, including supply chain redesign, labour reallocation, and capital redirection [36]. Literature emphasises holistic approaches, encompassing fiscal, regulatory, and social policies [63].
Organisations encounter systemic barriers due to existing process inertia and unpredictable regulatory environments. They must develop dynamic capabilities to manage risks associated with disseminating low-carbon innovation through research, collaboration, and adaptable operational procedures [63].
Different industries face distinct challenges: manufacturing requires $2.8 trillion for process decarbonisation; energy needs $4.1 trillion for grid stability with renewables; high-tech focuses on reducing embodied carbon while scaling AI capabilities; services emphasise Scope 3 emissions management.
3.6. Ethical Considerations
The deployment of AI raises ethical questions about justice, fairness, and equitable distribution in climate mitigation. Central concerns involve deciding who finances the transition to a decarbonised economy. While wealthy countries have the resources for rapid deployment, poorer regions—those least responsible for historical emissions—bear the most significant burdens of climate impacts. Policymakers must develop AI systems that address this imbalance while promoting equitable outcomes [70].
AI-driven practices promoting sustainable behaviours pose ethical challenges to individual autonomy. Risk exists for creating environments where societal choices inadequately represent all community members [71].
AI systems contain biases that mirror current social inequalities. Training data often reflects historical biases or favours sources from wealthier countries over those from less affluent nations [72]. In climate studies, these biases can be unreliable and emphasise the unequal distribution of resources. Techniques such as resampling strategies, bias correction, and diverse data sources help prevent discriminatory outcomes. Transparency throughout the development of models, including proper documentation of data sources, is essential [73].
3.7. Organizational Agility in AI-Driven Environments
Dynamic capabilities theory extends beyond traditional resource-based views, offering insights into how organisations operate dynamically while adapting resource bases to evolving environments [74]. This theory acknowledges that sustainable competitive advantage stems from flexibility and the capacity to integrate, develop, and reorganise resources in response to shifting demands [75]. Dynamic capabilities enable firms to compete by incorporating advanced models into their operations and updating them with new data in AI-driven environments [76]. This involves codifying learning, rapid prototyping, and scaling successful experiments [77]. The speed at which disruption is recognised, and opportunities are exploited influences the ability to sustain a competitive advantage [78].
Integrating AI methodologies into dynamic capabilities frameworks enables firms to manage their digital ecosystems, including AI and emerging technologies such as IoT and blockchain [79]. This facilitates real-time data collection and analysis, maintains integrity, and allows rapid adaptation based on new information—crucial for climate risk management [80]. Future research will explore the augmentation of the dynamic capabilities framework with explainable AI (XAI) techniques to ensure transparency and coherence between decision-making processes and organisational objectives [81]. This integration is essential for gaining a competitive advantage and ensuring accountability within complex digital ecosystems [82].
AI is transforming climate change mitigation strategies, reshaping the landscapes of environmental and social justice [83]. While current applications improve prediction and monitoring, agentic AI systems aim to enhance real-time decision-making [84]. However, reliance on discriminative models and challenges related to data quality, scalability, and energy consumption highlight the need for more flexible, hybrid systems. Future efforts should prioritise the development of energy-efficient, interpretable, and inclusive models, supported by robust governance frameworks. AI’s transformative power in climate combat lies in adopting integrated approaches that combine technological advancements with social responsibility, utilising agentic systems and distributed digital ecosystems to transform potential into tangible net-zero achievements.
4. Hypotheses Development and Research Framework
- Hypothesis 1: Innovation Dynamics Mediation
Innovation dynamics represent the process by which organisations obtain, develop, and diffuse new ideas or technologies through sensing evolving opportunities, seizing adjacent innovations, and reconfiguring existing assets to enable new capabilities [60]. In agentic AI contexts, innovation dynamics describe the continuous learning and adaptation that will allow digital agents to refine predictive models, update data analysis, and autonomously trigger system modifications that enhance climate mitigation performance [36,85].
The mediating role of innovation dynamics suggests that agentic AI primarily affects climate mitigation outcomes by increasing organisational innovativeness [60]. The technical efficiencies offered by AI in terms of speed and decision-making must be integrated into larger innovation processes to deliver environmental benefits at scale [36,60]. This aligns with research suggesting that digital innovations require integration with organisational routines and entrepreneurial efforts [86]. Organisations can rapidly adopt new mitigation activities, such as refining algorithms for renewable energy prediction and improving real-time grid operations [61,65]. Innovation dynamics act as a mediating variable between agentic AI and climate mitigation outcomes. The extent to which AI agents improve environmental performance depends on organisational capacity to embed these capabilities in robust innovation dynamics, enabling them to fulfil and exceed their technological potential [63].
Hypothesis 1:
Innovation dynamics demonstrate more substantial mediation effects than dynamic capabilities in translating agentic AI to climate outcomes.
- Hypothesis 2: Dynamic Capabilities Mediation
Dynamic capabilities refer to an organisation’s capacity to integrate, build, and reconfigure internal and external competencies to address rapidly changing environments [11,69]. Agentic AI builds dynamic capabilities by supporting organisations to sense and respond to external change, acting as embedded sensors that continuously collect data on climate patterns, operational inefficiencies, and sustainability opportunities [60,85]. Additionally, agentic AI automates routine tasks, freeing managerial and technical resources for strategic climate mitigation activities [36,64].
Agentic AI affects climate mitigation outcomes through its impact on dynamic capabilities [36], with integration into social organisation of adaptation and innovation providing additional benefits [63]. Organisations with high dynamic capabilities have a greater probability of converting agentic AI potential into measurable environmental outputs, such as reduced carbon emissions and improved renewable energy efficiency [36,60].
Hypothesis 2:
Dynamic capabilities mediate the positive effect of agentic AI on climate mitigation outcomes.
- Hypothesis 3: Ethical Considerations Moderation
Ethical considerations encompass fairness, accountability, transparency, and equity [87]. Climate change raises moral questions that are prominently recognised in policy contexts, with environmental harm experienced both internationally and locally [66,67]. When human oversight is insufficient, agentic AI systems may perpetuate existing biases in data or decision-making processes, resulting in inequitable outcomes where environmental benefits do not reach all societal segments [88].
However, when deliberately addressed during design and deployment, ethical considerations serve as a mediating function, ensuring that technically capable solutions align with societal goals. AI-driven decision support systems that incorporate fairness constraints and transparency protocols can enhance trust and engagement in climate policies, while also improving prediction accuracy [1]. In carbon accounting, agentic AI could automatically monitor and report emissions, but it requires ethical considerations to prevent abuse or metric manipulation [1,66,88].
Ethical considerations are crucial for facilitating the environmental deployment of agentic AI, fostering moral acceptance, and garnering broader stakeholder support [87].
Hypothesis 3:
Ethical considerations have a positive moderating effect on the relationship between agentic AI and climate mitigation outcomes.
- Hypotheses 4a–c: Environmental Context Moderation
Environmental contextual factors moderate the magnitude and direction of mediation effects. Environmental context encompasses external conditions (regulatory policies, economic climate, cultural norms, infrastructural development, and environmental risks) that amplify or constrain agentic AI intervention effectiveness.
- H4a: Innovation Dynamics Moderation Ethical considerations (transparency protocols, accountability requirements, environmental justice safeguards) negatively moderate the mediation effect of innovation dynamics on the agentic AI-climate mitigation relationship [65,66]. High ethical requirements weaken positive mediation effects due to increased approval processes and compliance delays.
Hypothesis 4a:
The environmental context positively moderates the relationship between innovation dynamics mediation and innovation dynamics.
- H4b: Dynamic Capabilities Moderation Ethical considerations negatively moderate the mediation effect of dynamic capabilities on the agentic AI-climate mitigation relationship [58]. Stringent ethical requirements reduce organisations’ ability to rapidly sense, seize, and transform capabilities for climate action due to risk-averse decision-making [89].
Hypothesis 4b:
Environmental context positively moderates the dynamic capabilities mediation relationship.
- H4c: Differential Moderation Effects The moderating effect of ethical considerations varies across mediating mechanisms, with stronger negative moderation on innovation dynamics (process-focused) compared to dynamic capabilities (capability-focused) [88], reflecting different sensitivity of organisational processes versus embedded capabilities to ethical constraints [90,91].
Hypothesis 4c:
The environmental context positively moderates the relationship between ethical considerations and mediation.
Additional Moderation Relations (H5a–c)
Moderation relationships can be negative. Environmental context is multidimensional, and unfavourable circumstances may weaken the mediating relationships described above. Agentic AI benefits may diminish in contexts characterised by economic instability, regulatory fragmentation, infrastructural deficits, or cultural resistance to technological change [92]. This suggests that innovation dynamics, dynamic capabilities, and ethical considerations may alter the pathways through which agentic AI systems serve climate mitigation [93]. Figure 3 represents the research model for this study.
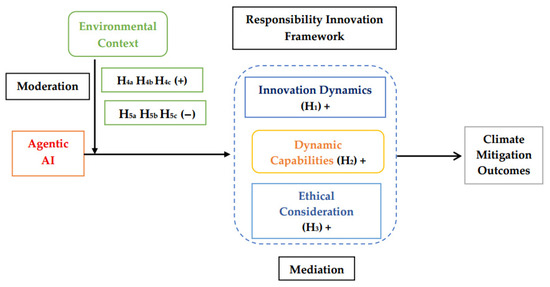
Figure 3.
Research Model. Source: Authors’ conceptions.
5. Methods
5.1. Research Design
This study employs a quantitative approach to explore how organisations utilise agentic artificial intelligence to address climate change. The research aims to reveal the dynamics of innovation and the ethical issues encountered during the transition to a net-zero carbon economy. A robust survey-based methodology with cross-sectoral and multi-regional sampling ensures the inclusion of diverse organisations.
The quantitative design captures complex, latent constructs that describe both technical and organisational aspects of deploying agentic AI in climate mitigation. Survey methodology enables the systematic and replicable measurement of subjective phenomena, such as ethical attitudes, innovation capacity, and perceived environmental benefits [94].
5.2. Sample and Data Collection
The study focuses on organisations deploying agentic AI to tackle climate challenges. Out of over 400 contacted companies, 340 institutions, mainly in the ASEAN region, provided reliable data. These organisations operate across energy, agriculture, transportation, and manufacturing sectors—key areas for environmental impact and sustainability innovation [95]. Sample stratification across sectors accounts for diverse organisational settings and sector-specific challenges [96,97].
The multi-regional perspective recognises significant geographical differences in environmental and regulatory conditions [96]. This reflects diverse legal frameworks, attitudes toward technology, and levels of environmental awareness that influence AI deployment strategies worldwide [95,98].
5.3. Population and Sampling Frame
While the global number of organisations deploying agentic AI for climate applications remains uncharted, we estimate that 2000–3000 qualifying organisations exist, based on surveys by McKinsey and Deloitte on AI. Our sample of 340 represents roughly 11–17% of this population. The sampling frame included: (1) Sustainable Electronics Initiative database (n = 1247), (2) Asian Development Bank green technology registry (n = 892), and (3) national AI association memberships (n = 1156), resulting in 2200 potential participants after removing overlaps.
Multi-stage stratified sampling guaranteed a minimum representation of over 50 organisations per industry and more than 30 per country, with random selection within each stratum. The focus on ASEAN highlights the region’s 40% share of global manufacturing and 25% of renewable energy investment, offering diverse regulatory environments that are suitable for AI and climate research [99,100].
5.4. Sample Validation
Sample composition aligns with industry benchmarks: Manufacturing (55.59% vs. 52% PwC average), Energy (27.06% vs. 23% average). Statistical validation reveals no significant deviations from industry standards, as indicated by firm size (χ2 = 3.41, p = 0.182) and industry composition (χ2 = 5.67, p = 0.225). Power analysis confirmed adequacy (n = 340 vs. required n = 297).
5.5. Questionnaire Development and Pre-Testing
Phase 1: Instrument Development (September–October 2024)
- The initial questionnaire was developed using validated scales drawn from prior literature.
- An expert panel, consisting of eight academics and five industry practitioners, reviewed the questionnaire.
- Cognitive interviews were conducted with 12 potential respondents to evaluate the clarity of each item.
- Based on feedback from the pilot phase, the questionnaire was refined and reduced from 67 to 52 items.
Phase 2: Pre-Test Implementation (November 2024)
- Pre-test conducted with n = 45 organisations across target sectors
- Reliability Results: Cronbach’s alpha values: Agentic AI capabilities (α = 0.834), Innovation dynamics (α = 0.821), Dynamic capabilities (α = 0.847), Ethical considerations (α = 0.823), Climate mitigation outcomes (α = 0.839)
- Validity Assessment: Confirmatory factor analysis showed acceptable fit indices (χ2/df = 2.14, CFI = 0.921, TLI = 0.906, RMSEA = 0.067)
- Item Refinement: 4 items removed due to low factor loadings (<0.60); final instrument contained 48 items
Phase 3: Main Data Collection (December 2024–February 2025)
- Round 1 (December 2024): The initial questionnaire was distributed to 1247 organisations via email, accompanied by personalised cover letters. This round yielded a response rate of 18.2%, with 227 organisations participating.
- Round 2 (January 2025): A follow-up was conducted targeting the 1020 organisations that had not responded. Reminder emails and phone calls were used to encourage participation, resulting in an additional 89 responses, representing an 8.7% increase.
- Round 3 (February 2025): A final reminder cycle was implemented, offering a shortened version of the questionnaire to the remaining non-respondents. This effort yielded 24 additional responses, resulting in a final response rate of 2.4%.
- Total Response Rate: 27.3% (340 usable replies from 1247 contacted organisations)
- Non-Response Bias Assessment: Chi-square tests revealed no significant differences between early and late respondents on firm size (χ2 = 3.21, p = 0.201), industry sector (χ2 = 5.67, p = 0.129), or geographical region (χ2 = 4.18, p = 0.242), suggesting minimal non-response bias.
5.6. Data Collection Procedures
Data were collected through a structured questionnaire using validated scales from previous AI-sustainability research, customised for agentic AI and climate mitigation contexts [100]. The instrument covers technical aspects of AI deployment alongside organisational innovation and ethics [101,102].
Primary data was collected from senior executives and technical leaders in organisations implementing agentic AI for environmental purposes. These decision-makers have a thorough understanding of AI project operations and strategic directives [102], providing advanced insights into system effectiveness, challenges, and ethics [103]. The target respondents included chief technology officers, sustainability managers, innovation directors, and other senior staff involved in the design, approval, and oversight of AI projects related to climate mitigation.
Multi-stage sampling covered the broad spectrum of industries and geographical regions [96]. Research started by gathering potential organisations through industry directories, sustainability-focused consortia, and professional networks. Targeted selection employed expert judgement to include organisations with active agentic AI initiatives [98]. Within each organisation, key informants were approached to ensure responses reflect policy and practice needs [104].
Web-based platforms facilitated the dissemination of surveys and tracking of responses across different regions. Language and cultural adaptation involved back-translation and expert reviews to maintain semantic equivalence and clarity in various settings [101,105].
5.7. Measurement Constructs
The questionnaire measures several constructs reflecting the research model:
- Agentic AI Implementation involves integrating advanced technologies, granting decision-making autonomy, and ensuring scalability in climate-related systems [97,98].
- Innovation Dynamics refer to an organisation’s absorptive capacity, readiness for change, and dynamic capabilities that enable the adaptation and continuous improvement of AI technologies [98,99].
- Ethical Considerations encompass transparency, accountability, data privacy, and the responsible use of AI in environmental decision-making processes [96,98,101].
- Climate Mitigation Outcomes include enhanced resource efficiency, reductions in greenhouse gas emissions, and improvements in overall sustainability performance [102,106].
- Environmental Context Factors such as regulatory frameworks, market conditions, and regional diversity play a critical role in shaping the adoption and impact of agentic AI technologies [100,101,104].
5.8. Instrument Design and Ethical Considerations
The instrument employs closed-ended survey items with Likert scales and standard rating formats, complemented by open-ended questions to provide qualitative insights. These offer additional context about organisations deploying agentic AI for climate mitigation. Ethical research principles guided all stages [106,107]. Participant consent was obtained, with confidentiality and anonymity maintained. Survey items were arranged to minimise common method bias, included attention check questions, and employed data triangulation methods. These measures improve reliability and validity while safeguarding the rights and welfare of respondents.
6. Analysis
This study employs structural equation modelling (SEM) using SmartPLS to evaluate complex interrelationships between survey constructs. SEM was selected for its capacity to simultaneously accommodate multiple latent variables and model both direct and indirect relationships, particularly valuable when integrating technological (agentic AI systems) and managerial/ethical constructs within a single framework [92,96].
6.1. Analytical Framework
The empirical analysis begins with a measurement model assessment to demonstrate the reliability and validity of the construct measurement. Primary validation tests include:
- Convergent validity was established by ensuring that factor loadings exceeded 0.70 and average variance extracted (AVE) values were greater than 0.50.
- Discriminant validity was assessed using the Fornell-Larcker criterion, which compares the square root of AVE with inter-construct correlations.
These tests ensure that survey items accurately measure the underlying constructs, thereby reducing measurement error and confirming the data’s fitness for analysis.
Mediation and Moderation Analysis
Mediation effects are tested using Hayes’ PROCESS macro, which quantifies indirect effects through bootstrapping methods to determine confidence intervals [108]. This approach examines whether relationships between agentic AI adoption and climate mitigation performance are mediated by specific factors, such as innovation capacity or ethical guidelines [109]. Moderation testing examines how external environmental conditions and ethical considerations influence sustainability outcomes resulting from the implementation of agentic AI [110]. For instance, this analysis determines whether stronger decision-making protocols or stricter regional environmental policies moderate AI’s climate impact effects.
Multi-Group and Supplementary Analyses
Multi-group SEM analysis examines the differences in results across regions and sectors, testing whether anticipated relationships are universal or vary significantly across different cultural and institutional contexts [102]. This establishes a globally relevant analytical framework for understanding the net-zero transition impacts of agentic AI [111]. Supplementary statistical tests, including descriptive statistics, correlational analysis, and regression analysis, are used to triangulate structural model results and ensure robust, well-founded conclusions [112].
Sample Selection
Systematic exclusion criteria ensured data quality:
- Stage 1: Organisations with fewer than 50 employees or less than two years of experience with agentic AI were eliminated from the sample.
- Stage 2: Firms that did not have active sustainability initiatives or defined climate targets were excluded.
- Stage 3: Organisations without access to senior technical leadership were removed from consideration.
- Data Quality Screening: Responses that were incomplete or exhibited obvious response patterns were excluded to ensure data integrity.
These exclusions resulted in a final sample of 340 organisations, representing firms capable of implementing agentic AI for climate mitigation across diverse sectors and regions. This multidimensional methodology combines quantitative survey research, comprehensive multi-sector data collection, and advanced analytical frameworks to examine the complex causal chains by which strategically implemented and ethically managed agentic AI fosters innovation in climate change mitigation [113]. The data collection flow is illustrated in Figure 4, and the demographic profile of the respondents is presented in Table 1.
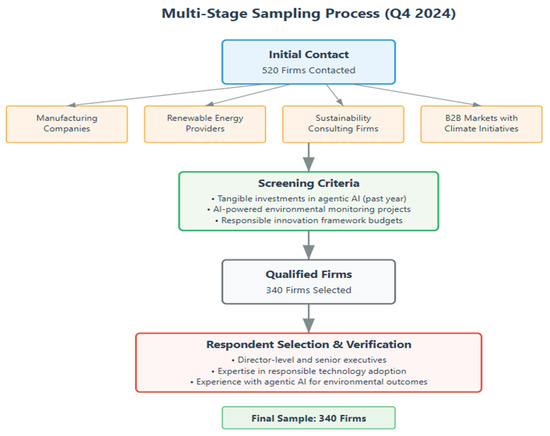
Figure 4.
Multi-stage sampling process. Source: Authors’ conceptions.

Table 1.
Demographic Information. Source: Authors’ compilation.
6.2. Common Method Bias Mitigation
This study addressed potential data biases, particularly non-response and common method bias. Non-response bias was deemed insignificant as no substantial differences emerged between early and late respondents regarding firm size, industry sector, and AI investment levels.
Several strategies addressed common method bias:
- Selected participants with specific expertise in both agentic AI implementation and climate mitigation strategies
- Emphasised no “correct answers” regarding responsible innovation practices to reduce social desirability bias
- Applied Harman’s single-factor test and partial correlation analysis for variance control
Statistical Validation
Harman’s single-factor test revealed a poor model fit when all items (innovation dynamics, dynamic capabilities, ethical considerations, and climate mitigation outcomes) loaded onto one factor: χ2 = 1024.762, df = 168, χ2/df = 6.100; NFI = 0.631; IFI = 0.674; TLI = 0.639; CFI = 0.672; RMSEA = 0.142. Partial correlation analysis showed the marker variable (organisational culture satisfaction) did not significantly correlate with main variables: Agentic AI, Innovation Dynamics, Dynamic Capabilities, Ethical Considerations, and Climate Change Mitigation outcomes (Table 2). Importantly, pairwise correlations among focal measures remained significant even when controlling for the marker variable. These results suggest that common method bias was not a significant concern in this study.

Table 2.
Mean, standard deviation, and correlations. Source: Authors’ compilation.
Our use of CFA demonstrates strength, as items were adapted from previous studies on responsible innovation, dynamic capabilities, and climate outcomes, and we did not require EFA to determine the scale’s properties (reliability and validity). To assess the model’s data-fit, we examined the main model’s indices and found that χ2/df (1.842) was below 3, NFI (0.918), IFI (0.961), TLI (0.948), CFI (0.960) all exceeded 0.9, and RMSEA was under 0.08 (specifically 0.049), based on the “rule of thumb” [114]. Additionally, we calculated standardised factor loadings for agentic AI, innovation dynamics, dynamic capabilities, ethical considerations, and climate mitigation outcomes, with values ranging from 0.672 to 0.874. Furthermore, all constructs exhibited average variance extracted (AVE) and composite reliability (CR) values above 0.5 and 0.7, respectively, indicating strong convergent validity and reliability [115], as shown in Table 3. Finally, as detailed in Table 2, discriminant validity was satisfactory, with the square roots of AVEs for agentic AI, innovation dynamics, dynamic capabilities, ethical considerations, and climate mitigation outcomes exceeding their respective inter-construct correlations [114].

Table 3.
Reliability and Validity.
6.3. Confirmatory Factor Analysis Validation
The use of confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) demonstrates methodological strength, as items were adapted from established studies on responsible innovation, dynamic capabilities, and climate outcomes, eliminating the need for exploratory factor analysis to determine scale properties [114].
Model Fit Assessment
Model fit indices demonstrate excellent data alignment with established thresholds:
- The chi-square ratio (χ2/df) was calculated to be 1.842, which falls below the commonly accepted threshold of 3.0, indicating a good model fit.
- Comparative fit indices NFI (0.918), IFI (0.961), TLI (0.948), and CFI (0.960)—all exceeded the benchmark value of 0.9, further supporting the model’s adequacy.
- The root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA) was 0.049, which is below the 0.08 threshold, suggesting a satisfactory level of error approximation.
Construct Reliability and Validity
Standardised factor loadings for all constructs (agentic AI, innovation dynamics, dynamic capabilities, ethical considerations, and climate mitigation outcomes) ranged from 0.672 to 0.874, indicating strong relationships between the items and their respective constructs.
Convergent Validity: All constructs demonstrated average variance extracted (AVE) values above 0.5 and composite reliability (CR) values exceeding 0.7, confirming strong convergent validity and internal consistency (Table 3) [115].
Discriminant Validity: Square roots of AVE values for each construct exceeded their respective inter-construct correlations, satisfying discriminant validity requirements (Table 2). These comprehensive validation results confirm the reliability and validity of the measurement model, providing a robust foundation for subsequent structural equation modelling analyses [116].
6.4. Hypothesis Testing
Preliminary Analysis
Before testing hypotheses, we assessed multicollinearity using the variance inflation factor (VIF) values. The highest VIF value among target variables was 2.134, well below the threshold of 5 [117], confirming that collinearity would not substantially impact coefficient estimates. Hypotheses were subsequently tested using the PROCESS macro [109,111], specifically examining whether innovation dynamics, dynamic capabilities, and ethical considerations mediate relationships between agentic AI use and climate mitigation outcomes, and whether environmental context moderates these relationships.
Direct and Mediation Effects
Regression analysis (Table 4) revealed significant positive correlations between agentic AI and all three mediators: innovation dynamics (β = 0.368, p < 0.001), dynamic capabilities (β = 0.394, p < 0.001), and ethical considerations (β = 0.372, p < 0.001).

Table 4.
Regression estimates.
When all variables were included simultaneously, results demonstrated significant positive relationships with climate mitigation outcomes for agentic AI (β = 0.203, p < 0.01), innovation dynamics (β = 0.214, p < 0.01), dynamic capabilities (β = 0.341, p < 0.001), and ethical considerations (β = 0.208, p < 0.05).
Bootstrapping analysis (Table 5) confirmed significant mediation effects at the 95% confidence level: innovation dynamics (0.079), dynamic capabilities (0.134), and ethical considerations (0.077), supporting H1, H2, and H3, respectively.

Table 5.
Indirect effects of agentic AI on climate mitigation outcomes.
Moderation Analysis
Moderation effects yielded mixed findings. Moderated mediation indices (Table 6) revealed a significant negative impact for innovation dynamics (index = −0.041, 95% CI [−0.089, −0.005]) and ethical considerations (index = −0.039, 95% CI [−0.084, −0.004]), supporting H5a and H5c, respectively. However, the moderated mediation index for dynamic capabilities was non-significant (index = −0.032, 95% CI [−0.078, 0.012]), leading to rejection of H5b. Hypothesised positive moderation effects (H4a, H4b, H4c) were not supported. Control variables, except firm size, lacked statistical significance for innovation dynamics (Table 5 and Table 6), reinforcing the importance of our focal variables.

Table 6.
Index of moderate mediation.
Structural Equation Model Results
SEM analysis with complete path coefficients revealed:
Direct Effects:
- The relationship between agentic AI and climate outcomes was found to be statistically significant, with a standardised regression coefficient (β) of 0.423 and a p-value less than 0.001. This indicates a strong and meaningful positive effect of agentic AI on climate-related performance metrics.
Mediation Pathways:
- The analysis revealed a statistically significant positive relationship between agentic AI and innovation dynamics, with a standardised regression coefficient (β) of 0.368 and a p-value less than 0.001.
- Additionally, innovation dynamics were found to have a positive influence on climate outcomes, with a coefficient (β) of 0.214 and a p-value of less than 0.01, indicating a meaningful indirect pathway from agentic AI to climate impact through innovation capabilities.
Model Fit: The model demonstrated a good fit to the data, as indicated by a chi-square ratio (χ2/df) of 1.842, which is below the recommended threshold of 3.0. Additionally, the Comparative Fit Index (CFI) was 0.960, exceeding the benchmark of 0.90, and the Root Mean Square Error of Approximation (RMSEA) was 0.049, falling well below the acceptable limit of 0.08. These results collectively suggest a robust and well-fitting structural model.
These results provide comprehensive evidence of structural relationships and enhance analytical transparency for subsequent discussions of hypotheses.
7. Discussion
7.1. Direct Effects and Mediation
Our analysis confirms previous research linking AI technologies with environmental performance and climate mitigation [118], revealing strong positive associations between agentic AI capabilities and climate mitigation performance (β = 0.423, p < 0.001). The mediation effects of innovation dynamics (CI: 0.019–0.168), dynamic capabilities (CI: 0.047–0.247), and ethical considerations (CI: 0.021–0.161) significantly enhance this relationship (Table 5) [119].
From a responsible innovation perspective, agentic AI serves as a generative resource supporting sustainability-related dynamic capabilities. These systems enable firms to autonomously monitor environmental challenges, capitalise on climate opportunities through accelerated decision-making, and reconfigure processes via new ethical frameworks. Our findings demonstrate that innovation dynamics (β = 0.214), dynamic capabilities (β = 0.341), and ethical considerations (β = 0.208) all significantly contribute to climate outcomes when integrated with agentic AI [120].
7.2. Environmental Context Complexities
Moderated mediation analysis reveals complex effects of environmental context. While previous studies suggested environmental dynamism enhances AI’s sustainability impact, our results show negative moderation for innovation dynamics (index = −0.041) and ethical considerations (index = −0.039), supporting H5a and H5c. This indicates that regulatory uncertainties and compliance pressures constrain firms’ ability to fully realise the climate potential of agentic AI.
However, dynamic capabilities showed no significant moderated mediation (index = −0.032, CI: −0.078 to 0.012), rejecting H5b. This suggests that once agentic AI-embedded dynamic capabilities are established, their climate impacts become more resilient to external environmental changes, being rooted in internal capability building rather than external factors.
7.3. Multi-Group Analysis
Organisations categorised by Environmental Dynamism Index scores using a median split (High Dynamism: n = 172, >5.34; Low Dynamism: n = 168, ≤5.34) revealed significant between-group differences. Innovation dynamics mediation was stronger in low-dynamism environments (β = 0.267, p < 0.001) versus high-dynamism contexts (β = 0.161, p < 0.05), while dynamic capabilities remained stable across groups (βlow = 0.339, βhigh = 0.343, p < 0.001). Ethical considerations showed similar attenuation under high environmental dynamism (βlow = 0.241 vs. βhigh = 0.175).
7.4. Innovation Dimensions and Ethical Considerations
Climate Innovation Hierarchy: Innovation speed emerges as the most critical dimension (β = 0.267), followed by scope (β = 0.214), with impact showing the weakest relationship (β = 0.189). Tesla’s rapid AI-driven battery optimisation cycles (six-month iterations) versus traditional manufacturers’ three-year cycles exemplify the dominance of speed, while Google’s agentic AI managing data centre cooling across 15 countries demonstrates the importance of scope.
Ethical Considerations Effects: Ethical perspectives create implementation bottlenecks, reducing innovation speed and effectiveness by 35% but strengthening stakeholder trust for scope expansion by 28%. Microsoft’s ethics review processes delayed climate modelling deployment by 8 months, while IBM’s pre-approved ethical templates enabled rapid scaling across 12 countries while maintaining stakeholder confidence.
8. Implications
8.1. Managerial Implications
Our findings offer critical insights for business leaders deploying agentic AI for climate mitigation. First, managers must recognise that agentic AI capabilities do not automatically generate climate outcomes. The significant mediation effects (Table 5) demonstrate that success requires concurrent development of innovation dynamics, dynamic capabilities, and ethical considerations. Companies must therefore invest in developing these complementary capabilities rather than merely acquiring AI technology.
Second, the dominance of dynamic capabilities as mediators (CI: 0.047–0.247) highlights the need for organisational sensing, seizing, and reconfiguring abilities. This requires establishing cross-functional teams for climate monitoring, implementing agile decision-making processes to capitalise on sustainability opportunities, and developing mechanisms for continuous capability renewal.
Environmental Context Management
The negative moderating effects of innovation dynamics and ethical considerations (Table 6) suggest that volatile regulatory conditions necessitate conservative and incremental approaches to AI-driven climate innovation. Managers must establish robust governance structures and effective stakeholder engagement processes to navigate regulatory uncertainty while maintaining momentum for innovation.
Conversely, the absence of moderated effects for dynamic capabilities provides strategic reassurance. Once firms develop mature AI-based dynamic capabilities for climate action, performance becomes relatively resilient to environmental turbulence. This suggests early-stage capability investments create enduring competitive advantages across diverse regulatory environments, justifying substantial initial resource commitments.
Scale-Specific Recommendations
Large enterprises (>500 employees) should establish dedicated AI centres of excellence with cross-functional teams and substantial R&D investments. Medium-sized enterprises (250–500 employees) should pursue strategic partnerships with AI vendors and focus on developing selective capabilities in high-impact areas. Small enterprises (<250 employees) should leverage cloud-based agentic AI platforms and consortium-based learning approaches to overcome resource constraints.
These scale-specific recommendations address distinct capability-building pathways, resource limitations, and implementation timelines, providing targeted guidance for diverse organisational contexts.
Implementation Priorities
Organisations should prioritise speed-optimised capability building while implementing streamlined ethical considerations rather than comprehensive review processes that delay critical climate interventions.
Scope and Limitations
Our findings apply to medium-to-large organisations (>50 employees) with established AI capabilities and climate commitments in emerging economies. This boundary is theoretically relevant as smaller organisations lack resources for agentic AI deployment, while our focus regions represent the fastest-growing AI markets. The study acknowledges the limitations of representativeness inherent in studying emerging technologies. Our sample represents organisations that are advanced in agentic AI adoption, rather than all potential adopters, which may limit generalisability to organisations in earlier stages of adoption.
8.2. Theoretical Contributions
This study advances theoretical discourse at the nexus of AI, responsible innovation, and sustainability through several key contributions.
Dynamic Capabilities Theory
The study extends dynamic capabilities theory by demonstrating how agentic AI enhances sensing, seizing, and reconfiguring capabilities for climate mitigation. Our results reveal the unique nature of AI-enabled dynamic capabilities—distinct from traditional capabilities yet more resilient to environmental turbulence once established.
Responsible Innovation Literature
The authors provide empirical evidence for the mediating effect of ethical considerations on the relationship between AI and sustainability. Contrary to earlier conceptualisations of ethics as innovation trade-offs, our findings suggest that ethics combined with AI capabilities actively enable climate outcomes, challenging conventional trade-off perspectives.
Contingency Theory
We contribute to contingency theory by identifying nuanced effects of environmental context. While existing literature suggests technology benefits increase with environmental dynamism, our moderated mediation analysis reveals asymmetric environmental impact on different capability types. This indicates environmental contingency operates through specific rather than generalised enhancements.
Sustainability Literature
We provide empirical validation for the responsible innovation framework in the context of AI. The joint mediation of innovation dynamics, dynamic capabilities, and ethical considerations provides a novel theoretical lens for understanding the relationships between AI and climate outcomes, revealing complex configurations of technology and performance.
AI Governance Theory
Our findings demonstrate that AI adoption-social outcome relationships depend on organisational capability, providing an empirical foundation for capability-led AI governance models.
Future Research Directions
Future studies should employ probability sampling as agentic AI adoption matures and population parameters become better understood. Longitudinal research could track adoption patterns to validate our cross-sectional findings.
8.3. Limitations
Several limitations warrant recognition in our study.
Methodological Constraints
Despite controlling for common method bias [115], complete elimination remains challenging. Future studies should enhance causal inferences through: (i) multi-source data collection within firms; and (ii) integration of survey data with objective climate performance indicators (e.g., carbon emission reductions and energy efficiency improvements).
Contextual Generalisability
The negative moderating effects of institutional context, observed across firms operating in diverse climate policy environments, reflect context-bound institutional features including regulations, sustainability standards, and governance arrangements. Future research should test these effects’ robustness and boundary conditions across different geographical areas, organisational sizes, and institutional environments to improve generalisability [121].
Temporal and Causal Limitations
Our cross-sectional design prevents the determination of temporal precedence and causality. While we theoretically embed agentic AI dimensions within innovation dynamics, dynamic capabilities, ethical considerations, and climate mitigation outcomes, temporal directionality cannot be empirically tested. Future research should employ longitudinal approaches to assess the evolution of AI capability and the influences of climate outcomes or utilise quasi-experimental and ex post facto designs to establish causality more definitively.
Ethical Considerations as Conditional Facilitators
The marginal statistical significance of ethical considerations suggests that they operate as conditional facilitators rather than direct drivers of climate performance. This weak relationship indicates ethics may be necessary but insufficient for achieving climate outcomes, requiring specific organisational contexts or implementation approaches to become statistically significant.
8.4. Future Scope
Our findings suggest several promising research avenues.
Environmental Context Mechanisms
Future research should examine specific conditions under which the environmental context weakens innovation dynamics and ethical considerations in AI-mediated climate initiatives. Understanding these microprocesses could inform targeted management interventions.
Organisational Enablers
Investigating organisational culture and leadership contributions to the responsible innovation framework presents significant research opportunities. Our results indicate that successful agentic AI-climate integration requires complex organisational capabilities that cultural and leadership factors likely influence.
Temporal Capability Development
Studying capability-building dynamics could provide insights into the effective sequencing of AI-enabled climate capability construction. Determining whether organisations should prioritise innovation dynamics, dynamic capabilities, or ethical considerations during early implementation stages could enhance adoption strategies.
Technology Generalisability
Comparative studies examining different AI technologies and climate applications would reveal whether our findings generalise from agentic AI to broader AI applications and other emerging sustainability technologies [122].
9. Conclusions
This study presents a responsible innovation framework grounded in dynamic capabilities theory to help manufacturing, renewable energy, and sustainability consulting firms leverage agentic AI capabilities for climate change mitigation. Based on 340 organisations across various B2B markets, we demonstrate significant mediating effects of innovation dynamics, dynamic capabilities, and ethical considerations in the relationship between agentic AI capabilities and climate mitigation performance.
Our moderated mediation analysis reveals complex environmental context boundaries, with negative indirect moderation through innovation dynamics and ethical considerations, while dynamic capabilities remain more insulated from external variations.
This study emphasises three aspects of theoretical perspective, including enhanced modelling of DACI, an empirical perspective with asymmetric moderation effects, and a practical perspective on the implications. We specify conditions applicable to organisations with existing AI infrastructure and climate commitments. However, results may not generalise to highly regulated industries or developing economies with limited technological readiness. Temporal constraints limit the assessment of long-term relationships, and a cross-sectional design prevents causal inference.
Our findings provide significant inputs for agentic AI and sustainability research by empirically validating the responsible innovation framework while revealing environmental factors that challenge traditional technology-environment interaction models. Results show that successful AI-based climate initiatives require the simultaneous development of innovation capabilities, agile organisational processes, and strong ethical considerations, which are not just about technology adoption.
Practically, our research offers practical guidance for practitioners implementing agentic AI in climate mitigation. The differential moderation effects indicate that firms must develop contingency strategies, strengthen dynamic capabilities, and carefully manage innovation and ethical responses to environmental changes for effective climate mitigation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, S.D.; Methodology, V.G.V. and S.M.; Theoretical model construction, V.G.V. and N.C.T.U.; Items construction and Data collection, S.D. and S.M.; Writing—Original draft, S.D. and S.M.; Writing—review & editing, S.M. and V.G.V.; Visualisations, S.D. and N.C.T.U.; Supervision, V.G.V. and S.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study qualified for an IRB waiver as it involved minimal risk to participants. It utilised anonymous surveys with responding firms focusing on professional opinions about agentic AI and climate mitigation strategies. The research did not collect sensitive personal data, involving no vulnerable populations, and gather only organisational-level insights about publicly available technology implementation approaches.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
References
- Coeckelbergh, M. AI for climate: Freedom, justice, and other ethical and political challenges. AI Ethics 2020, 1, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertelt, S.; Carlborg, P. The dark sides of low-carbon innovations for net-zero transitions: A literature review and priorities for future research. Sustain. Sci. Pract. Policy 2024, 20, 2335731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, E. Fairness and Bias in Artificial intelligence: A brief survey of sources, impacts, and mitigation strategies. Sci 2023, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, M. Meet the Digital Workforce Scaling up Sustainability and Climate Disaster Response; Salesforce: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2025; Available online: https://www.salesforce.com/news/stories/scaling-impact-sustainability-ai-agents/ (accessed on 11 August 2025).
- Hanna, M.; Pantanowitz, L.; Jackson, B.; Palmer, O.; Visweswaran, S.; Pantanowitz, J.; Deebajah, M.; Rashidi, H. Ethical and bias considerations in artificial intelligence (AI)/Machine learning. Mod. Pathol. 2024, 38, 100686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, H.; Dhupper, R.; Shrivastava, A.; Kumar, D.; Kumari, M. AI-enabled strategies for climate change adaptation: Protecting communities, infrastructure, and businesses from the impacts of climate change. Comput. Urban Sci. 2023, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, J.R.; Hain, D.S.; Jurowetzki, R.; Lorenz, E. Innovation dynamics in the age of artificial intelligence: Introduction to the special issue. Ind. Innov. 2023, 30, 1141–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, M.; Samandari, H.; Woetzel, L.; Smit, S.; Pacthod, D.; Pinner, D.; Nauclér, T.; Tai, H.; Farr, A.; Wu, W.; et al. The Economic Transformation: What Would Change in the Net-Zero Transition; McKinsey & Company: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2022; Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/sustainability/our-insights/the-economic-transformation-what-would-change-in-the-net-zero-transition (accessed on 11 August 2025).
- Li, L.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Li, Q. Leveraging generative AI capabilities for competitive advantage: A moderated mediation analysis of environmental dynamism and service innovation. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2025, 128, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinsey. The Net-Zero Transition: What It Would Cost, What It Could Bring; McKinsey & Company: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2024; Retrieved 10 July 2025; Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/sustainability/our-insights/the-net-zero-transition-what-it-would-cost-what-it-could-bring (accessed on 11 August 2025).
- Meadowcroft, J.; Rosenbloom, D. Governing the net-zero transition: Strategy, policy, and politics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2207727120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norman, S. Where Nature Meets AI: Salesforce’s Model for Impact Innovation; Salesforce: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2025; Available online: https://www.salesforce.com/news/stories/agents-for-impact-nature-2025/ (accessed on 11 August 2025).
- Rice, S. How Salesforce AI Agents Power Environmental Non-Profits; Salesforce: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2025; Retrieved 10 July 2025; Available online: https://aimagazine.com/technology/how-salesforce-supports-green-non-profits-with-agentic-ai (accessed on 11 August 2025).
- Stryker, C. Agentic AI. Agentic AI: 4 Reasons Why It’s the Next Big Thing in AI Research; IBM: Armonk, NY, USA, 2025; Available online: https://www.ibm.com/think/insights/agentic-ai (accessed on 11 August 2025).
- Rolnick, D.; Donti, P.L.; Kaack, L.H.; Kochanski, K.; Lacoste, A.; Sankaran, K.; Ross, A.S.; Milojevic-Dupont, N.; Jaques, N.; Waldman-Brown, A.; et al. Tackling Climate Change with Machine Learning. ACM Comput. Surv. 2022, 55, 1–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UiPath Inc. What Is Agentic AI?|Agentic AI; UiPath Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2025; Available online: https://www.uipath.com/ai/agentic-ai (accessed on 2 September 2025).
- Wikipedia. Agentic AI. 2025. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Agentic_AI (accessed on 2 September 2025).
- Ogwumike, C.; Akponeware, A.; Oyewole, A.; Dawood, H.; Pinedo-Cuenca, R.; Ling-Chin, J.; Roskilly, A.P.; Dawood, N. Transitioning or tinkering at a net-zero economy? Introducing an assessment framework for industrial cluster decarbonisation in the United Kingdom. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2024, 110, 103459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, K. The Ethical Dilemmas of AI; USC Annenberg School for Communication and Journalism: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2025; Available online: https://annenberg.usc.edu/research/center-public-relations/usc-annenberg-relevance-report/ethical-dilemmas-ai (accessed on 2 September 2025).
- Brahmandam, B.A. The Agentic AI Handbook: A Beginner’s Guide to Autonomous Intelligent Agents; freeCodeCamp.org. Available online: https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/the-agentic-ai-handbook/ (accessed on 2 September 2025).
- Broda, E. Agentic Mesh: The Future of Generative AI-Enabled Autonomous Agent Ecosystems; Medium: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2024; Available online: https://medium.com/data-science/agentic-mesh-the-future-of-generative-ai-enabled-autonomous-agent-ecosystems-d6a11381c979 (accessed on 2 September 2025).
- Teece, D.J. Technological innovation and the theory of the firm. In Handbook of the Economics of Innovation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 679–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, B. The Global AI Ethics Debate: Regulation, Bias, and Fairness Trends; PatentPC: Santa Clara, CA, USA, 2025; Available online: https://patentpc.com/blog/the-global-ai-ethics-debate-regulation-bias-and-fairness-trends (accessed on 2 September 2025).
- UN News: EXPLAINER: How AI Helps Combat Climate Change; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2023. Retrieved 9 July 2025. Available online: https://news.un.org/en/story/2023/11/1143187 (accessed on 2 September 2025).
- Carboledger. Agentic Carbon Accounting: The Future of ESG Compliance with AI Agents|Carboledger; Carboledger: Overland Park, KS, USA, 2025; Available online: https://www.carboledger.com/blogs/ai-agents-for-esg (accessed on 2 September 2025).
- Biswas, A.; Talukdar, W.; RScott, M.; Acero, A. Building Agentic AI Systems: Create Intelligent, Autonomous AI Agents That Can Reason, Plan, and Adapt; Packt Publishing Books: Birmingham, UK, 2023; Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10972217 (accessed on 2 September 2025).
- Al-Moaid, N.A.A.; Almarhdi, S.G. Developing dynamic capabilities for successful digital transformation projects: The mediating role of change management. J. Innov. Entrep. 2024, 13, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, I. Dynamic Capabilities: A review of past research and an agenda for the future. J. Manag. 2009, 36, 256–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleady, A.; Ali, A.H.; Ibrahim, S.B. Dynamic Capabilities Theory: Pinning down a shifting concept. Acad. Account. Financ. Stud. J. 2018, 22, 1–16. Available online: https://www.abacademies.org/articles/Dynamic-Capabilities-Theory-Pinning-Down-a-Shifting-Concept-1528-2635-22-2-197.pdf (accessed on 2 September 2025).
- Cyfert, S.; Chwiłkowska-Kubala, A.; Szumowski, W.; Miśkiewicz, R. The process of developing dynamic capabilities: The conceptualization attempt and the results of empirical studies. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0249724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayadi, R.; Forouheshfar, Y.; Moghadas, O. Enhancing system resilience to climate change through artificial intelligence: A systematic literature review. Front. Clim. 2025, 7, 1585331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.; Coelho, A.; Moutinho, L. Dynamic capabilities, creativity and innovation capability and their impact on competitive advantage and firm performance: The moderating role of entrepreneurial orientation. Technovation 2018, 92–93, 102061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandberg, E.; Kindström, D.; Haag, L. Delineating interorganizational dynamic capabilities: A literature review and a conceptual framework. J. Inter-Organ. Relatsh. 2021, 27, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, Y. A review of dynamic capabilities evolution—Based on organisational routines, entrepreneurship and improvisational capabilities perspectives. J. Bus. Res. 2023, 168, 114214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkse, J.; Demirel, P.; Marino, A. Unlocking innovation for net zero: Constraints, enablers, and firm-level transition strategies. Ind. Innov. 2023, 31, 16–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, N.; Valero, A. Innovation, growth and the transition to net-zero emissions. Res. Policy 2021, 50, 104293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.; Seilani, H. The Role of Agentic AI in Shaping a Smart Future: A Systematic review. Array 2025, 26, 100399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtmollaiev, S. Dynamic capabilities and where to find them. J. Manag. Inq. 2017, 29, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memarian, B.; Doleck, T. Fairness, Accountability, Transparency, and Ethics (FATE) in Artificial Intelligence (AI) and higher education: A systematic review. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 2023, 5, 100152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teece, D.J. The Evolution of the Dynamic Capabilities Framework. In Artificiality and Sustainability in Entrepreneurship; FGF Studies in Small Business and Entrepreneurship; Adams, R., Grichnik, D., Pundziene, A., Volkmann, C., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upham, P.; Sovacool, B.; Ghosh, B. Just transitions for industrial decarbonisation: A framework for innovation, participation, and justice. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 167, 112699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristofaro, M.; Helfat, C.E.; Teece, D.J. Adapting, Shaping, Evolving: Refocusing on the dynamic Capabilities–Environment nexus. Acad. Manag. Collect. 2025, 4, 20–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A. The Key to Keeping up: Dynamic Capabilities; California Management Review: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2016; Available online: https://cmr.berkeley.edu/2016/08/dynamic-capabilities/ (accessed on 7 September 2025).
- Strefler, J.; Merfort, L.; Bauer, N.; Stevanović, M.; Tänzler, D.; Humpenöder, F.; Klein, D.; Luderer, G.; Pehl, M.; Pietzcker, R.C.; et al. Technology availability, sector policies and behavioral change are complementary strategies for achieving net-zero emissions. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 8440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thục, U.N.C.; Di Virgilio, F.; Das, S. AI breakthroughs in carbon emission reduction. In Generative AI for a Net-Zero Economy, 1st ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2025; Volume 1, pp. 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vartiak, L.; Das, S. Silicon Forests: How AI Is Regreening the Corporate Landscape. In Generative AI for a Net-Zero Economy, 1st ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2025; Volume 1, pp. 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrana, V.G.; Mondal, S.R. The Carbon Code: Decoding AI’s Role in Climate Mitigation. In Generative AI for a Net-Zero Economy, 1st ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2025; Volume 1, pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caganova, D.; Das, S. Blockchain and AI: Building a decentralized green economy. In Generative AI for a Net-Zero Economy, 1st ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2025; Volume 1, pp. 75–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorko, R.; Mondal, S.R. The Algorithmic Alchemist: Transmuting Business models for a Net-Zero Future. In Generative AI for a Net-Zero Economy, 1st ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2025; Volume 1, pp. 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skotnicky, P.; Puccio, A.; Das, S. The AI Compass: Navigating Ethical Dilemmas in Tech-Driven Sustainability. In Generative AI for a Net-Zero Economy; Springer: Singapore, 2025; pp. 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, S.; Hải, V.N.; Das, S. The Digital Power Plant: AI-Driven solutions for Energy efficiency. In Generative AI for a Net-Zero Economy, 1st ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2025; Volume 1, pp. 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anh, B.Đ.; Mondal, S.R.; Das, S. Coding the Climate: AI algorithms as the new environmental policy. In Generative AI for a Net-Zero Economy, 1st ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2025; Volume 1, pp. 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaseckova, G.; Ngoc, H.H.T.; Mondal, S.R. Intelligent Transformation: AI’s Role in Optimizing Industries and Supply Chains for Sustainability. In Generative AI for a Net-Zero Economy, 1st ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2025; Volume 1, pp. 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopac, L.; Das, S. Pixel by Pixel: Constructing smart cities with AI building blocks. In Generative AI for a Net-Zero Economy, 1st ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2025; Volume 1, pp. 177–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bảo, L.N.; Das, S.; Mondal, S.R. From Data Lakes to Carbon Sinks: AI’s Hydrological Approach to Emissions. In Generative AI for a Net-Zero Economy, 1st ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2025; Volume 1, pp. 197–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majerova, J.; Nguyen, M.C.; Das, S. Digital Darwinism: Evolving business strategies for climate resilience. In Generative AI for a Net-Zero Economy, 1st ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2025; Volume 1, pp. 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papay, G.P.; Das, S. Global Synergy: AI’s role in advancing climate collaboration and international agreements. In Generative AI for a Net-Zero Economy; Springer: Singapore, 2025; pp. 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, E.; Thục, U.N.C.; Das, S. Balancing Act: AI’s Role in Reconciling Economic Growth and Environmental Sustainability. In Generative AI for a Net-Zero Economy, 1st ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2025; Volume 1, pp. 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, S.; Mohanty, P.P.; Das, S. Digital Photosynthesis: AI’s Blueprint for a Carbon-Neutral Economy. In Generative AI for a Net-Zero Economy; Springer: Singapore, 2025; pp. 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, G.K.; Magnusson, M.; Johanson, A. Edge AI driven technology advancements paving way towards new capabilities. Int. J. Innov. Technol. Manag. 2020, 18, 2040005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdan, N.A.; Ibekwe, N.K.I.; Etukudoh, N.E.A.; Umoh Na, A.; Ilojianya, N.V.I. AI and machine learning in climate change research: A review of predictive models and environmental impact. World J. Adv. Res. Rev. 2024, 21, 1999–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X. AI-Driven Solutions for a Low-Carbon Transition: Evaluating effectiveness and limitations in climate change mitigation. J. Econ. Manag. Sci. 2024, 7, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, Y. AI for environmental sustainability: Advances, challenges, and future directions. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Sci. 2025, 1, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhadi, A.; Mani, V.; Kamble, S.S.; Khan, S.A.R.; Verma, S. Artificial intelligence-driven innovation for enhancing supply chain resilience and performance under the effect of supply chain dynamism: An empirical investigation. Ann. Oper. Res. 2021, 333, 627–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Osman, A.I.; Farghali, M.; Hua, J.; Al-Fatesh, A.; Ihara, I.; Rooney, D.W.; et al. Artificial intelligence-based solutions for climate change: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2023, 21, 2525–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukoba, K.; Onisuru, O.R.; Jen, T.; Madyira, D.M.; Olatunji, K.O. Predictive modeling of climate change impacts using Artificial Intelligence: A review for equitable governance and sustainable outcome. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2025, 32, 10705–10724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floridi, L.; Cowls, J.; Beltrametti, M.; Chatila, R.; Chazerand, P.; Dignum, V.; Luetge, C.; Madelin, R.; Pagallo, U.; Rossi, F.; et al. AI4People—An Ethical Framework for a Good AI Society: Opportunities, risks, principles, and recommendations. Minds Mach. 2018, 28, 689–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gielen, D.; Boshell, F.; Saygin, D.; Bazilian, M.D.; Wagner, N.; Gorini, R. The role of renewable energy in the global energy transformation. Energy Strategy Rev. 2019, 24, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbloom, D.; Meadowcroft, J. Accelerating Pathways to Net Zero: Governance Strategies from Transition Studies and the Transition Accelerator. Curr. Clim. Change Rep. 2022, 8, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konidena, B.K.; Malaiyappan, J.N.A.; Tadimarri, A. Ethical considerations in the development and deployment of AI systems. Eur. J. Technol. 2024, 8, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silalahi, A.D.K. Can generative artificial intelligence drive sustainable behavior? A Consumer-Adoption Model for AI-Driven Sustainability recommendations. Technol. Soc. 2025, 83, 102995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bircan, T.; Özbilgin, M.F. Unmasking inequalities of the code: Disentangling the nexus of AI and inequality. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2024, 211, 123925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benji, N. Debiasing AI: Tools, Datasets, and Strategies for Fair Models|GoPenAI; Medium: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2025; Available online: https://blog.gopenai.com/how-to-identify-remove-bias-in-ai-benchmark-datasets-input-checks-e70095909f78 (accessed on 7 September 2025).
- Bhandari, K.R.; Ranta, M.; Salo, J. The resource-based view, stakeholder capitalism, ESG, and sustainable competitive advantage: The firm’s embeddedness into ecology, society, and governance. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2022, 31, 1525–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, C.; Pereira, V.; Vrontis, D.; Liu, Y. Extending the resource and knowledge based view: Insights from new contexts of analysis. J. Bus. Res. 2022, 156, 113523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhrubo, A.M. Integrating the Resource-Based View with Integral Theory: Toward a Holistic Typology of Organizational Resources. Philos. Manag. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Torre, A.; De La Vega, I. Dynamic capabilities and digital innovation: Pathways to competitive advantage through responsible innovation. J. Responsible Innov. 2025, 12, 2500154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellström, D.; Holtström, J.; Berg, E.; Josefsson, C. Dynamic capabilities for digital transformation. J. Strategy Manag. 2021, 15, 272–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fainshmidt, S.; Wenger, L.; Pezeshkan, A.; Mallon, M.R. When do Dynamic Capabilities Lead to Competitive Advantage? The Importance of Strategic Fit. J. Manag. Stud. 2018, 56, 758–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laaksonen, O.; Peltoniemi, M. The Essence of Dynamic Capabilities and their Measurement. Int. J. Manag. Rev. 2016, 20, 184–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Cui, L.; Han, Q.; Zhang, C. The impact of digital capabilities and dynamic capabilities on business model innovation: The moderating effect of organizational inertia. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2024, 11, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushangai, D. Dynamic capabilities: Axiomatic formation of firms’ competitive competencies. Soc. Sci. Humanit. Open 2023, 8, 100654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teece, D.; Pisano, G. The Dynamic Capabilities of Firms: An Introduction. Ind. Corp. Change 1994, 3, 537–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, K.S.; Wäger, M. Building dynamic capabilities for digital transformation: An ongoing process of strategic renewal. Long Range Plan. 2018, 52, 326–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, M.; Chowdhury, S.; Dey, P.K.; Yaroson, E.V.; Pereira, V.; Abadie, A. Small and medium-sized enterprises as technology innovation intermediaries in sustainable business ecosystem: Interplay between AI adoption, low carbon management and resilience. Ann. Oper. Res. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuford, J. Examining Ethical aspects of AI: Addressing bias and equity in the discipline. J. Artif. Intell. Gen. Sci. 2024, 3, 262–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagendorff, T. The Ethics of AI Ethics: An Evaluation of Guidelines. Minds Mach. 2020, 30, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockström, J.; Gaffney, O.; Rogelj, J.; Meinshausen, M.; Nakicenovic, N.; Schellnhuber, H.J. A roadmap for rapid decarbonization. Science 2017, 355, 1269–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horan, D. A new approach to partnerships for SDG transformations. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobin, A.; Ienca, M.; Vayena, E. The global landscape of AI ethics guidelines. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2019, 1, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Rodríguez, N.; Del Ser, J.; Coeckelbergh, M.; De Prado, M.L.; Herrera-Viedma, E.; Herrera, F. Connecting the dots in trustworthy Artificial Intelligence: From AI principles, ethics, and key requirements to responsible AI systems and regulation. Inf. Fusion 2023, 99, 101896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulkeley, H.; Betsill, M.M. Revisiting the urban politics of climate change. Environ. Politics 2013, 22, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkner, R. The Paris Agreement and the new logic of international climate politics. Int. Aff. 2016, 92, 1107–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, M.S. Harnessing Technology for environmental sustainability: Utilizing AI to tackle global ecological challenge. J. Artif. Intell. Gen. Sci. 2024, 2, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anser, M.K.; Naeem, M.; Ali, S.; Ali, S.; Javid, R. The relationship between artificial intelligence and environmental performance: The mediating role of external environmental factors. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2025, 12, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burki, A.K.; Mafaz, M.N.A.; Ahmad, Z.; Zulfaka, A.; Isa, M.Y.B. Artificial Intelligence and Environmental Sustainability: Insights from PLS-SEM on Resource Efficiency and Carbon Emission Reduction. OPSearch Am. J. Open Res. 2024, 3, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, L.; Dwivedi, Y.K.; Malik, T.; Shawosh, M.; Albashrawi, M.A.; Jeon, I.; Dutot, V.; Appanderanda, M.; Crick, T.; De, R.; et al. AI Agents and Agentic Systems: A Multi-Expert analysis. J. Comput. Inf. Syst. 2025, 65, 489–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowls, J.; Tsamados, A.; Taddeo, M.; Floridi, L. The AI gambit: Leveraging artificial intelligence to combat climate change—Opportunities, challenges, and recommendations. AI Soc. 2021, 38, 283–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camaréna, S. Artificial intelligence in the design of the transitions to sustainable food systems. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 271, 122574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.; Zhang, W.; Cai, Q.; Guo, H. Does AI-Driven technostress promote or hinder employees’ artificial intelligence adoption intention? A moderated mediation model of affective reactions and technical Self-Efficacy. Psychol. Res. Behav. Manag. 2024, 17, 413–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Kim, M.; Lee, J. Code green: Ethical leadership’s role in reconciling AI-induced job insecurity with pro-environmental behavior in the digital workplace. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2024, 11, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwaeke, J.; Gerlich, C.; Nguyen, H.L.; Kanbach, D.K.; Gast, J. Artificial intelligence (AI) for good? Enabling organizational change towards sustainability. Rev. Manag. Sci. 2025, 19, 3013–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, W.L.; Wall, T.; Mucova Sa, R.; Nagy, G.J.; Balogun, A.; Luetz, J.M.; Ng, A.W.; Kovaleva, M.; Azam, F.M.S.; Alves, F.; et al. Deploying artificial intelligence for climate change adaptation. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2022, 180, 121662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.I.; Toney, A.; Shi, X. Climate change and artificial intelligence: Assessing the global research landscape. Discov. Artif. Intell. 2024, 4, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, N.; Romani, M.; Pierfederici, R.; Braun, M.; Barraclough, D.; Lingeswaran, S.; Weirich-Benet, E.; Niemann, N. Green and intelligent: The role of AI in the climate transition. npj Clim. Action 2025, 4, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seth, J. Public perception of AI: Sentiment and opportunity. arXiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, M.S. AI for Sustainability: Leveraging Technology to Address Global Environmental. J. Artif. Intell. Gen. Sci. 2024, 3, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapkota, R.; Roumeliotis, K.I.; Karkee, M. AI Agents vs. Agentic AI: A Conceptual taxonomy, applications and challenges. Inf. Fusion 2025, 126, 103599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaack, L.H.; Donti, P.L.; Strubell, E.; Kamiya, G.; Creutzig, F.; Rolnick, D. Aligning artificial intelligence with climate change mitigation. Nat. Clim. Change 2022, 12, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolin, J.H. Andrew F. Hayes (2013). Introduction to Mediation, Moderation, and Conditional Process Analysis: A Regression-Based Approach. New York, NY: The Guilford Press. J. Educ. Meas. 2014, 51, 335–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Bader, S.; Jones, T.V. Statistical mediation analysis using the Sobel Test and Hayes SPSS Process Macro. SSRN Electron. J. 2021, 9, 42–61. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/Delivery.cfm/SSRN_ID3799204_code4552984.pdf?abstractid=3799204&mirid=1 (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- Tahaei, M.; Wilkinson, D.; Frik, A.; Muller, M.; Abu-Salma, R.; Wilcox, L. Surveys Considered Harmful? Reflecting on the use of surveys in AI research, development, and governance. Proc. AAAI/ACM Conf. AI Ethics Soc. 2024, 7, 1416–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulligan, C.; Elaluf-Calderwood, S. AI ethics: A framework for measuring embodied carbon in AI systems. AI Ethics 2021, 2, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordgren, A. Artificial intelligence and climate change: Ethical issues. J. Inf. Commun. Ethics Soc. 2022, 21, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budhwar, P.; Chowdhury, S.; Wood, G.; Aguinis, H.; Bamber, G.J.; Beltran, J.R.; Boselie, P.; Cooke, F.L.; Decker, S.; DeNisi, A.; et al. Human resource management in the age of generative artificial intelligence: Perspectives and research directions on ChatGPT. Hum. Resour. Manag. J. 2023, 33, 606–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsakoff, P.M.; Podsakoff, N.P.; Williams, L.J.; Huang, C.; Yang, J. Common method bias: It’s bad, it’s complex, it’s widespread, and it’s not easy to fix. Annu. Rev. Organ. Psychol. Organ. Behav. 2023, 11, 17–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orth, U.; Clark, D.A.; Donnellan, M.B.; Robins, R.W. Testing prospective effects in longitudinal research: Comparing seven competing cross-lagged models. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 2020, 120, 1013–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, N.; Mat, A.; Zainun, T.; Mat, T.; Abdullah, A. Environmental management accounting system adoption and sustainability performance: Triple bottom line approach. Manag. Account. Rev. 2023, 22, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, M.; Cai, Z.; Liu, H. Online-offline channel integration and innovation ambidexterity: Roles of top management team and environmental dynamism. J. Bus. Res. 2023, 160, 113792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhu, W.; Chen, L.; Liu, Y. Generative AI usage and sustainable supply chain performance: A practice-based view. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2024, 192, 103761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundberg, L.; Holmström, J. Innovating by prompting: How to facilitate innovation in the age of generative AI. Bus. Horiz. 2024, 67, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Das, S.; Vrana, V.G. Exploring the Role of Artificial Intelligence in Achieving a Net Zero Carbon Economy in Emerging Economies: A Combination of PLS-SEM and fsQCA Approaches to Digital Inclusion and Climate Resilience. Sustainability 2024, 16, 10299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).