Abstract
Cadmium (Cd) accumulation by benthic organisms poses a significant threat to aquatic environmental safety. Both vegetation and water velocity in rivers could influence this process, yet their coupled interaction mechanisms remain unclear. This study used laboratory flume experiments to simulate four scenarios: static water (C0), pure water velocity (C+H), vegetation-water velocity (V+H), and coexistence of vegetation-water velocity-Corbicula fluminea (C. fluminea) (C+V+H). The dynamics of Cd release from sediment to overlying water and its bioaccumulation within C. fluminea were investigated. A mathematical model coupling Cd release, diffusion, and C. fluminea bioaccumulation was developed based on the lattice Boltzmann method (LBM). The results showed that compared to the non-vegetation group (C+H), the presence of vegetation (V+H, C+V+H) initially reduced sediment resuspension and Cd release. However, the turbulence induced by vegetation significantly increased the Cd diffusion coefficient and equilibrium concentration in the water. Consequently, Cd accumulation in C. fluminea within the vegetation-water velocity group (C+V+H) was significantly higher than in the pure water velocity group (C+H). The established LBM model exhibited good simulation accuracy (for overlying water Cd concentration: R2 = 0.8201–0.942; for C. fluminea Cd concentration: R2 = 0.7604–0.8191) and successfully reproduced the processes of Cd release and bioaccumulation under varying vegetation-water velocity conditions. This study elucidates the mechanism by which vegetation promotes Cd accumulation in C. fluminea by altering water velocity structure and diffusion characteristics, providing crucial theoretical parameters for multi-media migration and transformation models of heavy metals in complex water velocity environments and for early warning systems concerning Cd accumulation risks in riverine organisms.
1. Introduction
With industrial development, an increasing amount of pollutants is being discharged into water bodies [1]. The accumulation of heavy metals in organisms is a significant concern that impacts food safety and, consequently, human health [2,3]. Heavy metals are ubiquitous in the natural environment and can be challenging to detect due to their low environmental concentrations and potential analytical interferences from complex matrices [4]. They diffuse with the water flow and are absorbed by aquatic organisms, affecting their growth and development. Therefore, it is extremely important to pay attention to the transport of heavy metals in rivers and their accumulation by organisms [5].
Some metals, such as copper (Cu), zinc (Zn), and iron (Fe), are toxic only when they exceed certain limits. In contrast, non-essential elements such as cadmium (Cd) are highly toxic even at low concentrations. Exposure to toxic metals can result in severe health issues, including renal dysfunction, bone demineralization, and potential carcinogenic effects [6,7]. The concentrations of heavy metals can significantly increase through the food chain due to bioaccumulation and biomagnification. Corbicula fluminea (C. fluminea) is widely recognized as a potential biological monitor for heavy metals. Its enrichment characteristics offer valuable insights into the biotoxicity of heavy metals in rivers [8]. Numerous studies have investigated the enrichment of heavy metals in C. fluminea. For instance, Sow [9] evaluated the heavy metal toxicity of Asian clams, including C. fluminea, in the Mekong, Pasak, and Huafuli rivers of Thailand. Graney [10] conducted a study on the potential of the Asian clam C. fluminea as a biological indicator of Cd, Cu, and Zn during 28 days of exposure to artificial streams in fields receiving river water, demonstrating that the Asian clam may be a reliable indicator of specific heavy metal intake.
Cadmium in water bodies is typically released from the sediment with changes in environmental conditions, such as pH and oxidation-reduction potential (ORP), and the physical processes, such as water velocity, which can resuspend settled sediment [11,12]. Geng [13] found that the equilibrium concentration of Cd in water increased with water velocity intensity under different flow conditions. Vegetation affects river flow dynamics by creating drag forces, thereby lowering the average water velocity [14,15]. However, due to the interaction between vegetation and water flow, turbulence in vegetated areas becomes more intense, resulting in changes to the diffusion coefficient of pollutants from sediment [16]. Zhang [17] studied the vertical distribution of flow velocity in the presence of flexible vegetation and found that from the riverbed to the water surface, flow velocity in vegetated zones first increases, then stabilizes, and increases again. Zong [18] demonstrated that vegetation roots enhance the diffusion coefficient of pollutants in vegetated areas.
Field observations and laboratory studies, such as those providing diffusion coefficient data, are crucial for understanding specific aspects of Cd transport and accumulation under vegetation-influenced flow. However, the inherent complexity arising from the coupled interactions of water velocity, vegetation-induced turbulence, sediment resuspension, and biological uptake demands a more integrated and predictive approach. Numerical models are essential for simulating pollutant transport and accumulation in organisms [19]. The diffusion of heavy metals involves key processes: adsorption/desorption at the sediment-water interface and transport within the water column. Adsorption refers to Cd2+ ions binding to sediment particles (e.g., clay minerals, organic matter), while desorption is their release back into water. Water velocity significantly impacts these processes by influencing shear stress, sediment resuspension, and mixing. Geng [13] used a lattice Boltzmann model to investigate the release patterns of Cd under different water velocity conditions and demonstrated the variation pattern of Cd concentration in water caused by the suspension of metal Cd with sediment. For bioaccumulation models, logarithmic curve models are generally employed. Lin [20] applied a single-chamber first-order toxicokinetic model to describe the bioaccumulation process of Cd in mussels, noting that the Cd content in mussels could reach a dynamic equilibrium through absorption and elimination in their tissues. This study revealed the absorption law of heavy metals by river clams, providing a basis for numerical model simulation. Wang [21] assessed the key processes (bioaccumulation, transportation, and toxicity) of metal ecotoxicology in aquatic systems by evaluating biokinetic models (BK), physiologically-based pharmacokinetic models (PBPK), and toxicokinetic models (TKTD). These models delve deeper into the complex mechanism of Cd absorption by clams, enhancing the accuracy of simulation results.
Though researchers have explored Cd release from sediments and its accumulation in C. fluminea under water velocity conditions, the role of vegetation in these processes and its impact on pollutant diffusion in rivers remain poorly understood. This study combines laboratory experiments with the lattice Boltzmann method to simulate Cd release and accumulation in C. fluminea across different water velocity scenarios. The findings offer valuable theoretical parameters for heavy metal migration and transformation models in multi-media environments and provide a reference for early warning systems monitoring Cd accumulation in riverine organisms.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experiment and Validation Data
To better approach the natural environment, the experimental setups were located in a glass house with natural ventilation and lighting conditions. This experiment was divided into four groups simultaneously (Table 1): three dynamic water treatment groups and one static water control group. To create a buffer zone for water flow, the collected sediment was evenly spread in the central area of the sediment tank, forming a layer approximately 150 cm in length and 8 cm in thickness. Both ends were sealed with baffles (Figure 1). The three dynamic water treatment groups were initialized with identical flow velocities. Specifically, 200 individuals of C. fluminea were placed in the sediment of group (C+H), submerged plants (Vallisneria natans L.) were planted in the sediment of group (V+H), and both Vallisneria natans L. and C. fluminea were placed in the sediment of group (C+V+H) (Figure 2). To match the sediment/water ratio of the dynamic water treatments, the control group C0 utilized a static water tank (200 cm × 100 cm × 30 cm) containing three parallel mud tanks (85 cm × 17 cm × 10 cm). Key sediment characteristics were as follows: pH 8.0 ± 0.3; ORP 263 ± 10 mV; cation exchange capacity (CEC) 0.96 ± 0.01 cmol/kg; electrical conductivity (EC) 137 ± 5 mS/m; acid volatile sulfides (AVS) 0.16 ± 0.02 μmol/g dw; total organic carbon (TOC) 0.67 ± 0.07%; clay content 10.6 ± 0.3%; water content 49.2 ± 2.1%. Dechlorinated tap water was employed for the experiment. Monitoring points for overlying water and sediment were strategically placed in the inflow, stable, and outflow zones. Prior to planting Vallisneria natans L., an ADV flow meter was used to calibrate the discharge rate.

Table 1.
Experimental parameters.
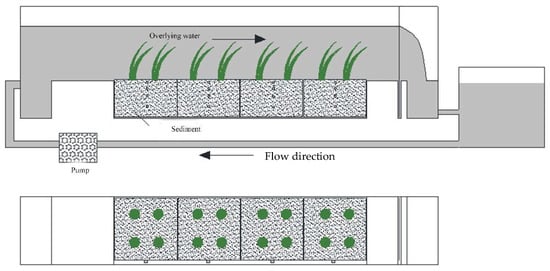
Figure 1.
Pictures of experimental equipment (made by Hubei Tuying S & T Equipment Co. LTD and located in Hangzhou, China).

Figure 2.
The picture of experimental C. fluminea, V. natans L, and the mechanism of Cd uptake.
Samples of 100 mL water, 20 individuals of C. fluminea, and 20 plants were collected at seven time points (0, 1, 3, 6, 12, 20, 30, and 40 days) to analyze the Cd content. Water samples were taken using an injector linked with a rubber pipe 5 cm below the water surface. For metal analysis in C. fluminea, samples were pretreated following Geng’s method [13]. Tissues were dried at 60 °C for 48 h until a constant weight was achieved, then homogenized and digested with a HNO3-H2O2 (4:1) mixture at 120 °C for 6 h. Cd quantification was performed using an inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometer (ICP-MS; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). All sampling equipment was rinsed with ultrapure water. Analytical-grade reagents were used, except for guaranteed-grade nitric acid. The instrument’s quantitation limit for Cd was >0.03 mg/L. Analytical accuracy was verified through blanks, triplicates, and standard reference materials (SRMs, recovery rates of 95–105%) from China’s Standardization Administration, including standards for trace elements in stream sediment (GBW07347) and mussel tissue (GBW08571).
2.2. Numerical Model
2.2.1. Cd Diffusion Process
For the detailed mathematical formulation of these diffusion processes under water velocity, refer to Geng [13]
where is the Cd concentration in water (μg/L); is time (s); is the porosity of the sediment; is the diffusion coefficient of Cd in the sediment (m2/s); is the first-order rate constant (s−1); is the equilibrium concentration of Cd in water under static water velocity conditions (μg/L); is the turbulent diffusion coefficient (m2 s−1).
After adding C. fluminea, the concentration of Cd in the overlying water also needs to consider the absorption of Cd by C. fluminea. Therefore, the formula becomes
where is the absorption rate coefficient of Cd by C. fluminea.
The most important aspect of Cd diffusion is the change in diffusion coefficient, which can be referenced in porous media, can be expressed as
where is the molecular diffusion coefficient in water (m2/s), which varies with the targeting solution; m = 3 is a constant [22].
In water bodies, it is mainly influenced by molecular diffusion and turbulent diffusion. The governing equation can be expressed as [23]
where is the area of the water-sediment interface (m2), is the kinematic viscosity of water (m2 s−1), and = 3 is a constant [24], and is the shear velocity
In vegetation water bodies, the diffusion of Cd is complex, involving turbulent and mechanical diffusion caused by vegetation. The diffusion coefficient has been changed to [25]
where and are constants used by Nepf [26] and Lu [25], is the drag coefficient of vegetation, is the diameter of vegetation, is the density of vegetation, and is the average velocity.
2.2.2. Cd Desorption from Resuspended Sediment
It is assumed that the sediment concentration in the overlying water is uniform. Here, the dynamic release caused by sediment suspension is much larger than the static release caused by diffusion [27,28]. Therefore, only the effects of sediment resuspension and sediment deposition are considered
where is the particle diameter and is the dimensionless particle diameter; , where and represent the density of particles and the density of the fluid, respectively; k = 9 × 10−3 (kg/m3); is shear velocity; is deposition flux; is re-suspension flux; is sediment critical velocity.
For a solute at equilibrium, the dimensionless ratio of the particulate concentration to the dissolved concentration is the product of a partition coefficient and the suspended sediment concentration [29]. When equilibrium is reached, the relationship between Cd and suspended sediment can be expressed by the following equation
where is the partition coefficient, (L/μg) is assumed to be a constant, and is the total concentration.
2.2.3. Cd Enrichment Model of C. fluminea
In much earlier studies, the kinetic model was developed in radioecological research with a rather simple equation [20]
where (t) is the accumulated concentration of Cd in the organisms (mg g−1) at time t (d); is the uptake rate constant (L g−1 d−1); and is the efflux rate constant (d−1).
2.2.4. The Lattice Boltzmann Method
The lattice Boltzmann method (LBM) includes two steps: migration and collision. In the migration step, the particles move in a certain direction and at a certain speed to the adjacent grid nodes. The equation of LBM can be described as follows [30]
where is the particle distribution function in terms of a discrete particle at direction k; is the equilibrium distribution function at direction k; and is the relaxation frequency.
The LBM function can be described as
where is the time step; is relaxation frequency; is the particle distribution function in terms of a discrete particle at direction k; is the equilibrium distribution function at direction k; and = = = = 0.25.
The LBM function for sediment in overlying water can be described as follows
A Cd concentration variation model for C. fluminea in the LBM Model:
To conclude the above contents, the 2-D sediment and Cd transport numerical model of LBM can be calculated as previously described.
2.3. Data Analysis
To verify whether the model results perform well, the root mean square error (RMSE) and coefficient () are calculated as follows:
where denotes the number of lateral measuring points, and and represent the calculated and measured values, respectively.
All data were presented as means, and the variabilities of the determinations of the replicates and the recoveries of the standard values were within 10%. The numerical simulation and data analysis in this article were conducted using MATLAB R2016a. As a mature numerical calculation software, MATLAB can efficiently simulate the transport of Cd and contains rich parameter calculation modules, which can quickly obtain the simulation accuracy of the numerical model.
3. Results
3.1. The Concentration Changes of Cd in Overlying Water and C. fluminea
In the static group, the Cd concentration in the overlying water showed a gradual decline (Figure 3), reaching 0.004 μg/L at the final sampling point. In the water velocity group with C. fluminea present, the Cd concentration initially rose rapidly, peaked, and then declined, eventually stabilizing at 0.032 μg/L. In the vegetation-water velocity groups (without or with C. fluminea present), the Cd concentrations exhibited rapid increases in the early stages, followed by slight decreases after reaching the peaks, and then stabilized, with final concentrations of 0.0089 μg/L and 0.0085 μg/L, respectively. The variation of Cd concentration within C. fluminea is illustrated in Figure 4. In the C. fluminea with water velocity group, the Cd concentration initially increased, then gradually decreased in the later stages, and finally stabilized at 5.78 μg/g. In the C. fluminea with vegetation-water velocity group, the Cd concentration rose rapidly in the early stage and continued to increase gradually in the later stages, reaching 9.54 μg/g after 40 days.
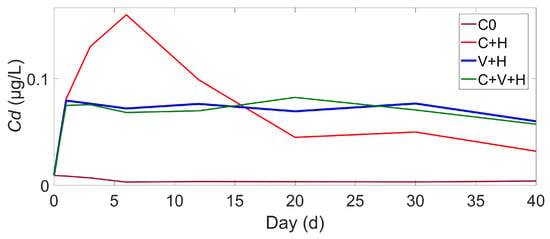
Figure 3.
Changes in Cd concentration in the overlying water of different treatment groups.

Figure 4.
Changes in Cd concentration in C. fluminea under different treatment groups.
3.2. Model Simulation Results
The simulation results for Cd concentration variations in the overlying water are presented in Figure 5, indicating a reliable model performance. The RMSE of the model ranged from 0.0009 μg/L and 0.0116 μg/L, with R2 values between 0.8201 and 0.942. As highlighted in Table 2, the model showed the highest simulation accuracy for the static water treatment group. Additionally, the simulation results for Cd concentration changes in C. fluminea are displayed in Figure 6, yielding a good simulation effect. The RMSE for this model ranged from 0.56 μg/g and 0.91 μg/g, with R2 values between 0.7604 and 0.8191.
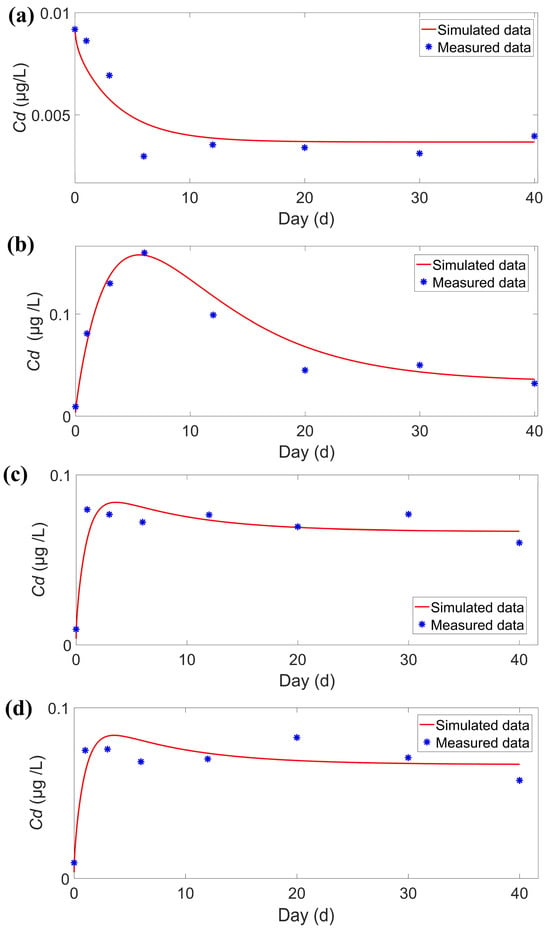
Figure 5.
Simulation results of Cd concentration in overlying water in C0 (a), C+H (b), V+H (c), and C+V+H (d) groups.

Table 2.
Simulation accuracy analysis table.
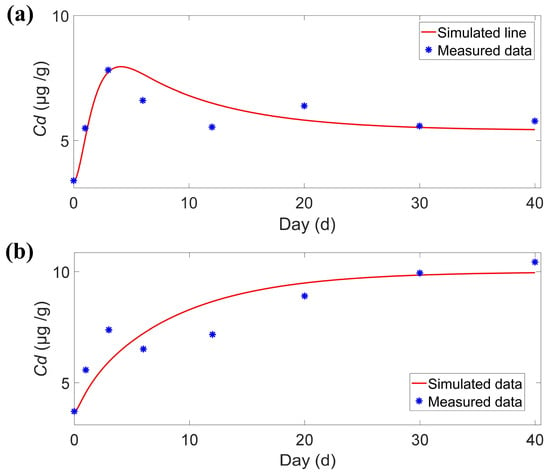
Figure 6.
Simulation results of Cd concentration in C. fluminea in C+H (a) and C+V+H (b) group.
4. Discussion
4.1. The Behavioral Mechanism of Cd in the Water Environment
The equilibrium Cd concentrations in the vegetation group (V+H/C+V+H) were significantly higher than in the non-vegetation group (C+H, 0.0032 μg/L), aligning with Zong’s [18] conclusion that vegetation roots enhance pollutant diffusion coefficients. However, the peak Cd concentration in the vegetated groups in this experiment (~0.07 μg/L) was higher than the value reported by Zhang [17] in flexible vegetation water flow (~0.03 μg/L). This discrepancy may arise from the stronger turbulence induced by the rigid vegetation used in this study.
In the C0 group, the water Cd concentration initially decreased gradually and then stabilized. The initial Cd concentration in the overlying water was higher than the equilibrium concentration due to experimental disturbance. As the experiment progressed, Cd2+ was reabsorbed by the sediments [31]. In contrast, in the C+H group, the Cd concentration increased rapidly in the early stages due to sediment resuspension caused by higher flow velocities. Subsequently, with the re-adsorption of fine particles like clay and the settlement of suspended particles, the water Cd concentration eventually reached equilibrium, consistent with our previous research [13]. Similar trends were noted in the V+H group and C+V+H group, where vegetation significantly reduced flow shear stress, stabilized sediments, and decreased sediment suspension [32,33]. Consequently, less Cd was released from the sediment to the water during the early stage of the experiment compared to the C+H group. However, the vortex formation caused by water flow through vegetation increased the Cd diffusion coefficient in the water, leading to higher equilibrium Cd concentrations than in the C+H group [13].
4.2. Cadmium Enrichment Characteristics of C. fluminea
The final Cd concentration in the C+V+H group of river clams was 9.54 μg/g, significantly exceeding the 5.78 μg/g in the C+H group. This confirms Wang’s [21] finding that benthic organisms in vegetation areas are more prone to accumulate heavy metals. However, unlike Lin’s [20] observation of mussels in fixed-concentration water, where Cd levels first rose and then fell, the river clams in this experiment maintained high Cd concentrations even after dynamic equilibrium. This suggests the significant role of suspended particulate Cd in long-term exposure.
Cd uptake in C. fluminea occurs via ingestion of Cd-containing food or particles (particle-phase uptake) and may also involve direct uptake through gill epithelial cells (water-phase uptake) or adsorption of dissolved or small particle-phase Cd onto the organism’s mucus layer (multiphase uptake) [34]. In the C+H group, increased water Cd concentrations initially enhanced uptake, primarily via surface adsorption. As water Cd levels rapidly declined, the uptake efficiency decreased, leading to a higher excretion rate and reduced Cd concentrations in C. fluminea. When water Cd levels stabilized, C. fluminea Cd concentrations showed a slight decrease. Wang [21] also observed a transient increase in C. fluminea Cd concentrations, followed by a slight decrease in fixed Cd environments, likely due to the absence of sediment and the dissolved form of Cd in experiments [13]. In the C+V+H group, the Cd concentration in C. fluminea initially rose with increasing water Cd level (Figure 4). The uptake rate exceeded the excretion rate, causing Cd content to gradually increase until equilibrium. The equilibrium water Cd concentration in the C+V+H group was higher than in the C+H group.
This study reveals that vegetation significantly enhances Cd diffusion by altering water velocity conditions (Equation (5)). Compared to the non-vegetated group (C+H), the diffusion coefficient Dt increased substantially in the vegetated groups (V+H, C+V+H), leading to higher Cd equilibrium concentrations in the water column (Figure 3). This effect stems from vegetation-induced turbulence enhancement [26], with intensity positively correlated to vegetation density. Vegetation also promoted Cd bioaccumulation in C. fluminea. The accumulation level in the C+V+H group (9.54 μg/g) was 1.7 times that of the C+H group (5.78 μg/g) (Figure 4). Beyond raising dissolved Cd concentrations, increased suspended particulate matter in vegetated areas may provide more bioavailable Cd [34], while the filter-feeding behavior of C. fluminea is more active in vegetated zones. This finding cautions that although vegetation stabilizes sediments, its intensified bioaccumulation effect may elevate the ecological risk for C. fluminea [18].
4.3. Meaning and Limitations of the Model
The model’s limitations and potential error sources mainly result from overly simplified assumptions, such as ignoring sediment heterogeneity, relying on empirical constants for vegetation, and simplifying clam uptake. Uncertainty in key parameters like porosity and adsorption coefficients, compounded by a lack of sensitivity analysis, further contributes to these limitations. Additionally, the model excludes critical ecological factors such as direct plant Cd uptake, clam bioturbation, and Cd speciation changes. Extrapolating lab-scale flume results to complex natural rivers also poses significant risks. Overall, these factors compromise the model’s reliability and predictive power in broader scenarios, and the original study does not sufficiently demonstrate the model’s claimed applicability across different water velocity conditions.
Results indicate that while vegetation can reduce sediment resuspension and Cd release into the water in the early stage, the turbulence caused by vegetation increases the equilibrium Cd concentration in the water and promotes Cd accumulation in C. fluminea. Therefore, in vegetated rivers, even if the Cd concentration in the water is not high, benthic organisms may still accumulate higher Cd levels, warranting further attention [16]. Unlike traditional models that simulate heavy metal accumulation and excretion in C. fluminea without considering environmental changes like water velocity, this model incorporates flow velocity and equilibrium Cd concentration in the overlying water [4]. This allows for a more accurate simulation of Cd concentration changes in C. fluminea under varying water velocity conditions. To better apply this model to natural water systems, future experiments should investigate Cd accumulation by C. fluminea across a range of flow velocities.
5. Conclusions
This study shows that vegetation in water velocity environments significantly alters Cd dynamics in rivers. Although vegetation reduces sediment resuspension and Cd release, it increases Cd diffusion and the equilibrium concentration in the water column due to turbulence. As a result, Cd accumulation in the C. fluminea is much higher under vegetated flow compared to non-vegetated flow. This highlights a greater long-term ecological risk for benthic organisms, even if initial water Cd concentrations are lower.
A LBM-based numerical model effectively simulated Cd release and C. fluminea bioaccumulation under static, water velocity, and vegetated-water velocity conditions. The model achieved high accuracy (R2: 0.7604–0.942, RMSE: 0.0009–0.0116 µg/L for water; R2: 0.7604–0.8191, RMSE: 0.56–0.91 µg/g for C. fluminea). By integrating key environmental factors like flow velocity, stones, and vegetation effects on diffusion, it overcomes limitations of traditional models.
This research provides crucial parameters and a reliable modeling tool for simulating multi-media heavy metal transport and transformation in complex aquatic systems. It supports better ecological risk assessment and early warning strategies. Future research will integrate Cd toxicity experiments on C. fluminea with a diffusion model to simulate river Cd distribution. Then, Life Cycle Assessment could be incorporated to evaluate different vegetation configurations, which would help quantify their net impact reduction for controlling river Cd pollution more effectively.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.S. and H.W.; methodology, H.W.; resources, N.G.; writing—original draft preparation, N.G.; writing—review and editing, L.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2022YFE0128600), Nanxun scholars program of ZJWEU (RC2022010817), and Central Guidance Funds for Science and Technology Local Development Projects (2025ZY01091).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
Thanks for the assistance from Yu Bai in establishing the mathematical model.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Zhao, J.; Rao, M.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Q.; Shen, Y.; Ye, J.; Feng, K.; Zhang, S. Evolution of Interspecific Interactions Underlying the Nonlinear Relationship between Active Biomass and Pollutant Degradation Capacity in Bioelectrochemical Systems. Water Res. 2025, 274, 123071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, J.; Cao, X.; Xiong, H.; Liu, F.; Xie, M.; Chen, R.; Tan, Q. Hidden Threat in Turbid Waters: Quantifying and Modeling the Bioaccumulation and Risks of Particulate Metals to Clams. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 368, 125746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, J.; Hu, T.; Xiong, H.; Cao, X.; Liu, F.; Gosnell, K.J.; Xie, M.; Chen, R.; Tan, Q. Turbid Waters and Clearer Standards: Refining Water Quality Criteria for Coastal Environments by Encompassing Metal Bioavailability from Suspended Particles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 5244–5254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.; Chen, S.; Li, Z.; Liu, P.; Xu, C.; Yang, X. Assessment of Heavy Metals in Water, Sediment and Shellfish Organisms in Typical Areas of the Yangtze River Estuary, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 151, 110864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baby, J.; Raj, J.; Biby, E.; Sankarganesh, P.; Jeevitha, M.; Ajisha, S.; Rajan, S. Toxic Effect of Heavy Metals on Aquatic Environment. Int. J. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2011, 4, 939–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, M.S.; Benci, J.L.; Selote, D.S.; Sharma, A.K.; Chen, A.G.Y.; Dang, H.; Fares, H.; Vatamaniuk, O.K. Detoxification of Multiple Heavy Metals by a Half-Molecule ABC Transporter, HMT-1, and Coelomocytes of Caenorhabditis Elegans. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Wang, W. Dynamics of Copper Regulation in a Marine Clam Sinonovacula Constricta at the Organ Level: Insight from a Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 336, 122421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.W.; Yap, C.K.; Nulit, R.; Hamzah, M.S.; Chen, S.K.; Cheng, W.H.; Karami, A.; Al-Shami, S.A. Effects of Anthropogenic Activities on the Heavy Metal Levels in the Clams and Sediments in a Tropical River. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 116–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sow, A.Y.; Dee, K.H.; Lee, S.W.; Eh Rak, A.A.L. An Assessment of Heavy Metals Toxicity in Asian Clam, Corbicula Fluminea, from Mekong River, Pa Sak River, and Lopburi River, Thailand. Sci. World J. 2019, 2019, 1615298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graney, R.L.; Cherry, D.S.; Cairns, J. Heavy Metal Indicator Potential of the Asiatic Clam (Corbicula fluminea) in Artificial Stream Systems. Hydrobiologia 1983, 102, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, M.; Zuo, Q.; Zhang, J.; Li, C.; Li, G. Influence of Changes in Hydrodynamic Conditions on Cadmium Transport in Tidal River Network of the Pearl River Delta, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 7501–7516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xie, D.; Dou, M.; Liu, D.; Li, X. Cadmium Transportation Modeling under Accident Release in Pearl River Delta Network. J. Coast. Res. 2008, 10052, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, N.; Bai, Y.; Pan, S. Research on Heavy Metal Release with Suspended Sediment in Taihu Lake under Hydrodynamic Condition. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 28588–28597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artini, G.; Calvani, G.; Francalanci, S.; Solari, L. Effects of Vegetation at a Bar Confluence on River Hydrodynamics: The Case Study of the Arno River at Greve Junction. River Res. Apps 2021, 37, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verschoren, V.; Meire, D.; Schoelynck, J.; Buis, K.; Bal, K.D.; Troch, P.; Meire, P.; Temmerman, S. Resistance and Reconfiguration of Natural Flexible Submerged Vegetation in Hydrodynamic River Modelling. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2016, 16, 245–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhuo, J.; Jia, F.; Deng, L.; Wang, H.; Han, Y. Simulation of Pollutant Diffusion in Vegetation Open Channel Based on LBM-CA Method. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 71252–71269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, Q.; Mi, Z. Evaluation of a Random Displacement Model for Scalar Mixing in Ecological Channels Partially Covered with Vegetation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 30, 31281–31293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, L.; Nepf, H. Flow and Deposition in and around a Finite Patch of Vegetation. Geomorphology 2010, 116, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalilzadeh Poshtegal, M.; Mirbagheri, S.A. Simulation and Modelling of Heavy Metals and Water Quality Parameters in the River. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Xu, X.; Xie, M.; Chen, R.; Tan, Q.-G. Measuring Metal Uptake and Loss in Individual Organisms: A Novel Double Stable Isotope Method and Its Application in Explaining Body Size Effects on Cadmium Concentration in Mussels. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 9979–9988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-X.; Tan, Q.-G. Applications of Dynamic Models in Predicting the Bioaccumulation, Transport and Toxicity of Trace Metals in Aquatic Organisms. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 1561–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullman, W.J.; Aller, R.C. Diffusion Coefficients in Nearshore Marine Sediments1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1982, 27, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Nakamura, Y. Effects of Hydrodynamic Conditions on DO Transfer at a Rough Sediment Surface. J. Environ. Eng. 2011, 137, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rijn, L.C. Sediment Transport, Part III: Bed Forms and Alluvial Roughness. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1984, 110, 1733–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepf, H.M.; Sullivan, J.A.; Zavistoski, R.A. A Model for Diffusion within Emergent Vegetation. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1997, 42, 1735–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepf, H.M. Drag, Turbulence, and Diffusion in Flow through Emergent Vegetation. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Cheng, P.; Zhong, B.; Wang, D. Hydrodynamic Effects on Contaminants Release Due to Rususpension and Diffusion from Sediments. J. Hydrodyn. 2013, 25, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Falconer, R.A.; Lin, B. Numerical Modelling Sediment-Bacteria Interaction Processes in the Severn Estuary. JWARP 2011, 03, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Wang, X.; Bockelmann-Evans, B.N.; Falconer, R.A. Study on Nutrient Distribution and Interaction with Sediments in a Macro-Tidal Estuary. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 52, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girimaji, S. Lattice Boltzmann Method: Fundamentals and Engineering Applications with Computer Codes. AIAA J. 2013, 51, 278–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Dai, J.; Teng, Z.; Yuan, J.; Wang, G.; Luo, W.; Ji, X.; Hu, W.; Li, M. Immobilization of Cadmium in River Sediment Using Phosphate Solubilizing Bacteria Coupled with Biochar-Supported Nano-Hydroxyapatite. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 348, 131221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Duan, Y. The Vertical Distribution of Suspended Sediment and Phosphorus in a Channel with Ice Cover. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 37953–37962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Shen, D.; Huang, D. Vertical Heterogeneity and Flexible Root Dynamics in Pollutant Transport: A Hybrid Lattice Boltzmann Method—Random Displacement Model Approach for Optimizing Artificial Floating Bed Design. Water Res. 2025, 280, 123536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Lv, L.; An, M.; Wang, T.; Li, M.; Yu, Y. Heavy Metals in Marine Food Web from Laizhou Bay, China: Levels, Trophic Magnification, and Health Risk Assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 841, 156818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).