Abstract
This narrative review examines adolescents’ perceptions of sustainable dietary characteristics, including local eating, plant-based diets, organic food, and food waste, and how these influence their understanding and behavior. Evidence indicates that adolescents often have simplified conceptions of these practices, which leads to misconceptions. Local food is frequently perceived as inherently more sustainable despite complex factors such as seasonality, production methods, and transportation. Although reducing meat consumption is crucial for environmental impact, adolescents may struggle to understand sustainable protein sources and animal-based foods in various contexts. Although viewed positively, the benefits and limitations of organic food remain poorly understood. Food waste is recognized as significant; however, adolescents often focus on individuals rather than on systemic drivers. Schools play a pivotal role in the promotion of food literacy and sustainable dietary habits. Educational interventions that integrate sustainability into curricula, provide hands-on learning, and engage families can help adolescents to develop critical thinking skills and make informed food choices. Strategies such as promoting a plant-based diet, sourcing local produce, incorporating organic options, and implementing waste reduction programs can create environments that support sustainable eating habits. These efforts must be context-sensitive, culturally relevant, and grounded in understanding food systems. By empowering adolescents to question assumptions, recognize complexities, and take action, schools can cultivate a generation capable of leading the transition towards healthier and more sustainable diets.
1. Introduction
Sustainable diets have low environmental impacts that contribute to food and nutrition security and to a healthy life for present and future generations. Sustainable diets are protective and respectful of biodiversity and ecosystems; culturally acceptable, accessible, economically fair, and affordable; nutritionally adequate, safe, and healthy; and optimize natural and human resources [1]. By adopting dietary habits that emphasize plant-based foods, reduce meat consumption, and prioritize locally sourced seasonal produce, individuals can significantly decrease their carbon footprint, while contributing to biodiversity conservation. These choices not only help to mitigate the environmental impacts of industrial agriculture, such as deforestation, water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions, but also support improved health outcomes by reducing the risk of chronic diseases associated with excessive consumption of meat and ultra-processed foods [2]. For animals, a shift in demand towards more ethical food systems may ultimately result in enhanced welfare standards [3]. Thus, a sustainable diet represents more than a personal lifestyle choice; it is a collective strategy for fostering a healthier planet and more equitable food system. Introducing principles of sustainable eating at an early age is crucial. In particular, adolescents are at a critical developmental stage, in which their values, habits, and worldviews are still being shaped. Engaging them in an open, balanced dialogue on food choices provides a foundation for informed decision-making and a deeper understanding of the broader implications of these choices [4]. However, the growing complexity of food-related information, shaped by social media, peer influence, and commercial interests, can easily lead to confusion and the spread of misinformation. Misconceptions about topics such as the benefits of organic food, plant-based diets, the meaning of eating locally, and the causes and consequences of food waste are common, often resulting in polarized views or simplistic interpretations that do not reflect the nuanced reality of sustainable food practices [5].
Adolescents are at a critical developmental stage where food preferences and eating behaviors are actively being formed, rendering this demographic particularly significant for interventions aimed at promoting food literacy and sustainable dietary habits. Increasing evidence indicates that nutritional literacy acquired during adolescence is linked to healthier food choices and heightened awareness of dietary quality, which may influence long-term health outcomes and prevent chronic diseases. A strong correlation has been identified between higher levels of nutrition literacy and improved food habits in adolescents, underscoring the importance of early education in this domain [6]. The social environment surrounding young individuals, particularly their families and schools, plays a pivotal role in facilitating or hindering this learning process. Family dynamics and school-based education have been demonstrated to significantly impact adolescents’ understanding of nutrition and their ability to apply it in daily life [7]. This narrative review aimed to investigate adolescents’ perceptions of the key characteristics of sustainable diets, specifically local eating, plant-based diets, organic food, and food waste, and how these perceptions influence their understanding and behavior. By synthesizing the available evidence, this review aimed to identify prevalent misconceptions and sources of confusion, and to propose school-based interventions that can effectively elucidate these topics. Promoting critical thinking and encouraging dialogue in educational settings may serve as a potent means of countering misinformation, clarifying complex concepts, and inspiring young individuals to become agents of change within their communities. Ultimately, equipping adolescents with tools to navigate the discourse on sustainable food not only benefits their own health and well-being but also contributes to a broader cultural shift towards more conscious and responsible consumption patterns. Focusing on adolescents reflects a commitment to early context-sensitive interventions, acknowledging that lifelong sustainable and health-conscious food behaviors are most effectively established during youth.
2. Understanding Food, Diet, and Sustainability: Foundations for Transformative Education
The terms food and diet, although seemingly straightforward, encompass complex and layered meanings. Food is essential for human survival and provides nutrients necessary for health and development. However, its significance extends beyond human needs; it is part of a vast web of interconnections involving plants, animals, insects, and climate. In this ecological context, food is a shared element within the broader web of life. The concept of diet extends beyond that of eating. It has rich social and cultural connotations shaped by individual preferences, cultural norms, accessibility, affordability, and moral values. What is considered desirable or acceptable may be rejected by another person. Diet does not refer to a single meal but rather to a long-term pattern of food intake spanning days, years, and even a lifetime. It reflects ingrained habits, social conventions, and cultural understandings of what is “normal” to eat. It is important to note that food and diet are not synonymous. Food refers to tangible items (ingredients or products consumed for nourishment), whereas diet refers to the way food is selected, combined, and consumed over time. In other words, food is what we eat and diet is how, when, and why we eat it. This distinction helps to frame broader discussions about nutrition, culture, sustainability, and health [8,9].
The food system is an interconnected network of processes and actors involved in food production, processing, distribution, consumption, and disposal. It is shaped by a wide array of economic, sociocultural, environmental, and political factors at both local and global levels. When these systems are structured to minimize environmental impacts, support livelihoods, and ensure food and nutrition security for both current and future generations, they are referred to as sustainable food systems [10]. Within this broader context, the concept of a sustainable diet has emerged as a more specific, outcome-oriented component. Sustainable diets are characterized by their low environmental impact and ability to promote health and well-being over time. They are culturally acceptable, accessible, affordable, and nutritionally adequate, while also optimizing the use of natural and human resources [11]. Although closely interconnected, sustainable food systems and diets are not synonymous. A sustainable diet refers to an individual or a collective pattern of food consumption. By contrast, a sustainable food system encompasses the structures, policies, and practices that enable and support these dietary choices. In essence, sustainable diets are the goal, whereas sustainable food systems are the means through which that goal can be achieved [12].
As consumers, our attention should be focused on embracing sustainable diets that not only support our health and well-being, but also respect the limits of the planet. The choices we make daily, from the food we buy to the way we prepare and consume it, have a direct impact on environmental sustainability, biodiversity, and social equity. By prioritizing seasonal, local, minimally processed, and plant-rich foods and reducing food waste, we contribute to a food system that is fairer, more resilient, and better equipped to nourish both people and the planet now and in the future [2,13]. Schools play a crucial role in empowering young people with the knowledge, skills, and values required to adopt and advocate a sustainable diet. As foundational spaces for learning and socialization, schools have a unique opportunity to integrate food literacy into their curricula, promote healthy and sustainable eating habits, and create food environments that align with ecological and social responsibilities. Education has become a key driver in shaping a generation capable of leading the transition towards more sustainable food systems by equipping students with the ability to make informed food choices and understand the broader impact of their diets [14,15].
3. Sustainable Diet: Myth or Reality Among Adolescents?
3.1. Eat Local
Local eating is a dietary approach that prioritizes the consumption of food produced in close proximity to the location where it is consumed. Although the concept of “eat local” or “local food” has gained significant attention in recent decades, it remains a complex and multifaceted notion with varied interpretations. Traditionally, local eating has been associated with geographical proximity, promoting the consumption of food that is grown or produced within a specified distance from the point of purchase or consumption. It often involves strengthening social connections between producers and consumers with the aim of shortening the food supply chain and fostering a sense of community [16]. Environmental motivations are also central, as local food systems are perceived as reducing food miles and carbon footprints [16,17]. Additionally, eating locally is viewed as a means of supporting local economies and sustaining regional agricultural practices [18,19]. Health is frequently linked to the availability of fresher, less processed foods, which are assumed to be more nutritious [20].
In the context of a sustainable diet, the consumption of locally sourced food has emerged as the most frequently cited practice, with young adults offering both specific recommendations—such as “purchase food from local farmers” or “shop at farmers’ markets”—and more general suggestions like “eat local” [21]. The acquisition of regional food represents the second-most prevalent sustainable food consumption practice among Generation Z students attending Greek universities [22]. Consuming local food significantly contributes to social sustainability by generating new employment opportunities, particularly for young individuals, enhancing farmers’ self-esteem, and fostering stronger connections between rural and urban communities [16]. Moreover, direct interactions between farmers and consumers can cultivate trust and social capital, thereby contributing to a stronger sense of local identity and community. Given that young adults already recognize the importance of consuming local food within the framework of sustainable diets, targeted messaging that aids them in identifying and accessing local food options may be particularly effective [21].
While many adolescents and young adults acknowledge the significance of consuming locally sourced food, their interpretations often reflect simplified or idealized conceptions of this practice. Examining more nuanced scenarios can uncover underlying uncertainties and encourage critical reflection. The notion of local food prompts several questions regarding its definition and implications. Is the classification of food as local primarily determined by the distance it travels or the identity of its producer? For example, can food grown nearby by a large industrial entity be considered local in the same manner as that produced by a smallholder farm in the area? Furthermore, if products are bought directly from a trusted producer at a farmers’ market but are consumed at home after a long drive, do they still qualify as local? Conversely, if the same product is available in a nearby supermarket that lacks personal interaction, but maintains geographic proximity, does this enhance its local status? Additionally, if a product is processed locally but contains imported ingredients, can it be labelled as local? Should food produced in a nearby region using energy-intensive greenhouses during the off season be considered sustainable? Does a multinational corporation’s involvement in the local processing of a product affect its classification as local? Moreover, if a local farm engages in unsustainable or exploitative practices, does it align with ethical principles of consumption? These simple questions reveal the complexity of the concept and highlight the need to foster a deeper and more critical understanding among young individuals, as they navigate increasingly intricate food systems (Figure 1). Consumers frequently overestimate the environmental advantages of consuming regional food compared with scientific evidence. Although regional food is often regarded as an environmentally friendly option, its actual environmental impact is relatively limited, particularly when compared to more significant dietary changes such as adopting a meat-free diet [23]. In certain cases, regional food production may even elevate greenhouse gas emissions owing to less efficient land use, increased soil emissions, or reduced agricultural productivity [24]. Transportation, a common focal point in discussions on local food, generally constitutes only a minor portion of a food product’s total life-cycle emissions [25]. Most environmental impacts occur during the agricultural production phase [26,27]. Moreover, the environmental benefits of regional foods are heavily contingent on seasonality. For instance, consuming local produce out of season cultivated in heated greenhouses may result in a greater carbon footprint than importing the same product from a region where it grows naturally [28]. Ultimately, the type of food consumed, particularly the distinction between plant- and animal-based products, exerts a more substantial influence on the environmental impact than geographic origin [29]. This underscores the necessity of aligning consumer perceptions with scientific evidence, emphasizing that, while supporting regional food has its merits, it should not overshadow more effective strategies for reducing the environmental footprint of our diets.
The concept of seasonality in food consumption is complex and open to various interpretations, particularly within the framework of a sustainable diet (Figure 1). According to the UK’s Department for Environment, Food, and Rural Affairs (DEFRA), two primary forms of seasonality are identified: global seasonality, which pertains to food cultivated outdoors during its natural season regardless of its consumption location, and local seasonality, which requires that food is both produced and consumed within the same climatic zone, without reliance on high-energy inputs for storage or climate control [30]. A third perspective further refines this understanding by introducing local seasonal food, which connects outdoor and natural-season production with geographical proximity between production and consumption [31]. These distinctions are not merely semantic but also have significant implications for the environmental, nutritional, economic, and cultural aspects of sustainable eating. Promoting seasonal food consumption, particularly that of locally produced items, is increasingly recognized as a crucial component of sustainable healthy diets [31,32]. Locally, seasonal food is often associated with reduced greenhouse gas emissions owing to lower transportation demands and avoidance of energy-intensive production methods [31,33,34]. It may also enhance biodiversity by encouraging diverse crop rotations and preserving regional food variety [35,36]. In addition, by supporting regional producers, seasonal consumption can contribute to local economies and strengthen community-based food systems [37]. Seasonal food is frequently perceived as fresher and more flavorful, which can further motivate consumption and support healthier eating habits [38,39]. However, these benefits must be weighed against potential limitations. Strict adherence to local seasonality may lead to a reduced availability of fresh fruits and vegetables during the winter months, potentially decreasing their overall intake and compromising dietary diversity and nutritional adequacy [40,41]. Furthermore, reliance on local production may reduce the resilience of food systems to extreme weather events and global supply shocks [42,43].
Thus, the concept of eating locally necessitates a more comprehensive and inclusive redefinition that fully accounts for the intricate relationships among food, place, and identity. A more robust framework would embrace the ontological complexity of food, expanding the definition of local beyond all ingredients to include multi-ingredient foods, recipes, menus, and dietary patterns. This perspective also calls for acknowledging multiple dimensions of locality, including not only physical distance but also geographical origins and social relationships embedded in food systems (Figure 1). Importantly, the concept should allow for gradability, recognizing that “localness” is not a binary attribute, but exists along a spectrum. It should also accommodate a wide range of food types and cultural expressions. Moreover, the meaning of local food must be negotiable, shaped by individual or collective values, and context-sensitive. This redefinition should also embrace fallibility, remaining open to ongoing revision and critique as informed by empirical evidence and theoretical insights. Finally, a reimagined understanding of eating local must accommodate heterogeneity, reflecting the reality of multi-ethnic societies and the diverse, often deeply personal connections between food, culture, and identity. By incorporating these elements, the concept of eating local becomes more nuanced, flexible, and better suited to the complexities of contemporary food systems and the cultural diversity of the modern world (Figure 1) [44,45,46].
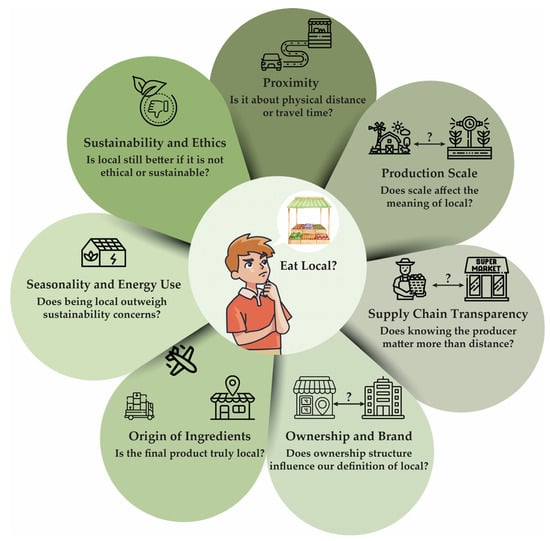
Figure 1.
Multiple questions surrounding the concept of “local food.” The diagram highlights key dimensions, such as proximity, production scale, ingredient origin, sustainability, and ethics, that challenge a simplistic definition of localness and encourage deeper reflection on food choices [16,47,48,49,50,51,52,53].
Schools can play a pivotal role in helping adolescents to understand the meaning of eating locally and make informed food choices. Educational interventions may include integrating food system literacy into subjects such as science, geography, or citizenship education, where students can explore how food is produced, transported, and consumed and what impact these processes have on the environment and society. Experiential learning activities, such as visits to local farms, farmers’ markets, or school gardens, allow students to connect theoretical knowledge with real-world experiences. Classroom discussions and project-based learning can encourage critical thinking about what “local” really means, considering factors such as seasonality, sustainability, and social justice. Involving students in school meal planning or local food promotion campaigns can further empower them to apply their knowledge to practical settings. By embedding these interventions in the school context, adolescents can develop the awareness, skills, and values necessary to make conscious and context-sensitive food choices aligned with the principles of a sustainable diet [54,55].
3.2. Plant-Based Diet
Meat consumption is associated with a range of positive and negative factors that shape individual and societal perceptions of the dietary role of meat (Figure 2). Meat is a rich source of protein, iron, and zinc, which play important roles in muscle development and other physiological processes [56]. Additionally, many individuals appreciate the distinct taste of meat, particularly its umami flavor, which enhances its appeal in various cuisines [57]. Meats also have cultural significance, playing a vital role in culinary traditions, religious rituals, and social gatherings worldwide. For some, it is considered a necessary component of a balanced diet that reinforces its presence in daily eating habits [58]. Livestock farming plays a crucial role in many economies, particularly in developing regions. Ruminants often graze on marginal lands that are unsuitable for crops, thereby supporting food production in unproductive areas. Eliminating these systems could lead to socioeconomic disruption, inefficient land use, and an increased demand for crop production, potentially negating environmental benefits. Additionally, animal-based foods have cultural and traditional significance and can contribute to circular food systems when sustainably managed [59]. However, meat consumption is also associated with several other factors. A primary issue is its environmental impact, as meat production contributes significantly to climate change [60], water and air pollution [3], and biodiversity loss [60] due to deforestation [61] and intensive farming practices [62]. From a health perspective, frequent consumption of meat, especially processed red meat, is associated with an increased risk of various diseases and higher mortality rates [63]. Ethical concerns regarding animal welfare are also prevalent, particularly in the context of industrial-scale livestock farming, where animals are often raised in conditions that raise serious moral questions [2,3]. Furthermore, meat production is highly resource-intensive and requires substantial amounts of land, water, and feed, rendering it a less sustainable option than plant-based alternatives [29]. Considering the multifaceted concerns encompassing nutritional, cultural, environmental, ethical, and economic dimensions, a gradual reduction in meat consumption and transition towards plant-based diets are identified as necessary strategies to promote sustainable health and environmental outcomes (Figure 2).
The increasing variation in the global climate, primarily driven by carbon emissions, poses a serious threat to both environmental and human health. High-population-density regions are responsible for 70–80% of global energy consumption and are thus key contributors to CO2 emissions [64]. Agriculture further intensifies the problem, accounting for approximately 14% of global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, with emissions from agriculture, forestry, and land use nearly doubling in recent decades and projected to continue rising [65,66]. Among the food sources, meat production contributes disproportionately to environmental degradation. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), meat accounts for over 20% of total food waste owing to its high carbon footprint, which is considerably greater than that of fruits and vegetables [66,67]. The global demand for animal-source foods, especially beef, is expected to grow sharply by 2050, particularly in urbanizing regions, such as China and India [68,69]. This shift may lead to a 30–80% increase in food-related GHG emissions, affecting food prices, availability, and access to diverse nutritious diets [70]. A diet high in meat, such as that of a heavy meat-eater in the United States, emits approximately 3.3 tons of CO2 equivalent annually, whereas a vegan diet emits only 1.5 tons [71]. Substituting even a portion of the daily meat intake with plant-based alternatives could reduce emissions by up to 19%. Studies have shown that adopting Mediterranean, pescatarian, or vegetarian diets can reduce emissions by 30%, 45%, and 55%, respectively [72]. Animal proteins vary widely in terms of their environmental impacts. Beef is the most carbon-intensive, mainly because of methane emissions from enteric fermentation. This accounts for 37% of the climate change impacts per kilogram of meat, compared to 10.1% for pork and 9.8% for poultry. In addition, the packaging of meat and poultry products often involves non-biodegradable plastics that add to their carbon footprint [73]. Meanwhile, the fisheries sector contributes 4–5% of global GHG emissions annually, although its environmental impact varies by species and production method [74,75,76]. For example, shellfish farming has a much lower footprint, partly because of the carbon-trapping properties of their shells. Mussel production using low-impact methods can generate less than 500 kg of CO2 equivalent per metric ton, making it one of the most sustainable animal protein sources [77].
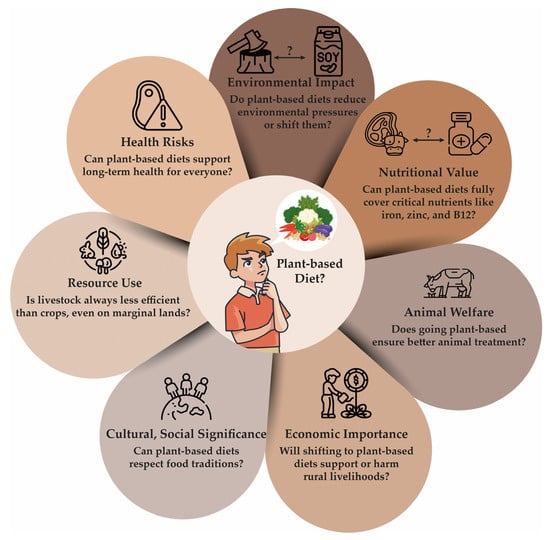
Figure 2.
Multiple questions regarding the concept of a plant-based diet. The diagram highlights key dimensions such as environmental impact, nutritional adequacy, cultural traditions, animal welfare, economic resilience, and resource use, which challenge simplistic narratives and invite deeper reflection on sustainable, ethical, and health-conscious dietary choices. These questions underscore the importance of context-specific, inclusive, and evidence-based approaches for promoting plant-based eating [78,79,80,81,82,83,84].
Although the environmental benefits of shifting to plant-based or low-impact animal proteins are well established, changes in meat consumption patterns are influenced by the complex interplay of individual, social, and economic factors. A recent study examining meat consumption in the United States found that, although a significant proportion of individuals reported reducing their intake of red (70%) and processed meat (64%) over the previous year, overall consumption remained above the recommended levels for both health and sustainability. The study revealed that health concerns and food prices were the primary drivers of meat reduction, whereas environmental sustainability and animal welfare were less influential in shaping consumer behavior. This highlights a critical gap between environmental awareness and dietary choices, suggesting that communication strategies aimed at reducing meat consumption may be more effective if they emphasize personal health benefits and economic savings. The findings also indicate marked sociodemographic differences in consumption patterns, underlining the importance of tailoring interventions to diverse population groups. Given the considerable environmental burden of ruminant meat production, including greenhouse gas emissions, water use, and biodiversity loss, policy measures and public health campaigns must prioritize accessible and culturally sensitive approaches that resonate with consumer motivation [85].
A substantial body of evidence underscores the health, environmental, and economic benefits of whole-food, plant-based (WFPB) diets. These dietary patterns, which prioritize minimally processed plant foods while reducing or eliminating animal products, have been associated with weight loss, enhanced cardiovascular and metabolic health, and potential contributions to climate-change mitigation. In clinical settings, the WFPB diet has shown remarkable efficacy for the management and prevention of chronic diseases. The BROAD study, a randomized controlled trial involving participants with obesity, ischemic heart disease, or type 2 diabetes, reported significant reductions in body mass index (BMI), waist circumference, and HbA1c levels in the intervention group adhering to a WFPB diet, even without calorie restriction or mandatory physical activity [86]. These findings were accompanied by improvements in cholesterol levels, medication usage, and self-reported quality of life [86]. Another 12-week WFPB nutrition program demonstrated similar benefits, including reductions in low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and total cholesterol levels comparable to those achieved through pharmacological interventions [87]. Cardiovascular outcomes associated with plant-based diets are consistently favorable. Such dietary patterns are linked to lower BMI, reduced blood pressure, improved glycemic control in diabetes, and significantly decreased LDL cholesterol [88]. Furthermore, prospective studies and randomized trials have indicated that plant-based diets reduce atherosclerosis and mortality due to ischemic heart disease. For instance, vegetarians were found to have a 24% lower risk of death from ischemic heart disease, even after adjusting for confounding variables, such as age and smoking status [88]. These benefits may arise from reduced dietary cholesterol intake, increased fiber consumption, and improved weight management, all of which are inherent characteristics of WFPB diets [88]. In addition to improving cardiovascular health, plant-based diets show promise in neurological contexts. A recent randomized controlled trial demonstrated that comprehensive lifestyle changes centered on a plant-based diet can significantly enhance cognition and functional outcomes in individuals with mild cognitive impairment or early Alzheimer’s disease [89]. Biomarkers such as the Aβ42/40 ratio improved and favorable shifts in gut microbiota composition were observed, suggesting a multifactorial mechanism involving inflammation, metabolism, and the microbiome [89]. The degree of adherence is positively correlated with the magnitude of clinical and biomarker improvements, further highlighting the therapeutic potential of lifestyle interventions [89]. However, the transition to plant-based diets raises important questions regarding their effectiveness in addressing obesity and chronic disease risks [90]. Evidence suggests that plant-based diets alone do not significantly reduce obesity risk. The lower obesity rates among vegetarians and vegans observed in some studies are likely influenced by lifestyle factors beyond dietary intake [69]. Vegan diets, which exclude all animal-derived foods, pose a greater risk of nutritional deficiencies than vegetarian diets that include dairy or eggs [90]. This distinction underscores the need for nuanced dietary recommendations, rather than a one-size-fits-all approach.
Although the health benefits of WFPB diets are compelling, their impact extends beyond individual well-being. Environmental and ethical considerations are powerful motivators for dietary change and may support long-term adherence. Research indicates that motivations rooted in environmental sustainability and animal welfare are strongly associated with the development of a plant-based dietary identity and greater dietary persistence over time [87]. Participants in WFPB programs often transition from health-centered to altruistic motives, reinforcing the behavioral transformation necessary for sustained dietary change [87]. However, such shifts may lead to social tensions as individuals navigate environments in which plant-based eating diverges from prevailing cultural norms [87]. Climate implications for reducing animal agriculture are profound. Modeling studies estimate that a global phaseout of animal agriculture could offset up to 68% of carbon dioxide emissions in this century, primarily by decreasing methane and nitrous oxide emissions and allowing for extensive carbon sequestration via reforestation on former grazing and feed crop lands [91]. Partial dietary transition can yield substantial environmental benefits. Despite these advantages, the feasibility of large-scale change is constrained by social and economic realities, including the livelihoods of over a billion people dependent on animal agriculture and the nutritional needs of populations with limited access to plant-based foods [91]. Nevertheless, these challenges must be weighed against the escalating threat posed by climate change. The safety and nutritional adequacy of WFPB diets have also been well-documented. When appropriately planned, such diets provide sufficient protein from legumes, whole grains, and other plant sources and are rich in fiber and phytonutrients [88]. While potential risks, such as vitamin B12 deficiency, exist, they are easily mitigated through supplementation or fortified foods. Although some studies have raised concerns about the increased risk of fractures or hemorrhagic stroke among vegetarians, these findings remain inconclusive and may be influenced by confounding factors such as BMI or insufficient differentiation among dietary subgroups [88]. In summary, WFPB diets present a holistic and evidence-based strategy to address some of the most pressing health and environmental challenges of the time. Their proven efficacy in managing obesity, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes coupled with promising cognitive and microbiome-related outcomes suggests a strong clinical rationale for their promotion. Furthermore, the ethical and ecological dimensions of WFPB diets not only enhance individual motivation but also align with global sustainability goals. Continued research and investment are essential to optimize accessibility, improve adherence, and ensure that transitions towards plant-based eating are equitable and inclusive. Promoting WFPB requires a balanced approach that considers individual nutritional needs, cultural practices, food preparation methods, and environmental considerations [34,90]. Further research is crucial to better align health promotion with sustainability objectives through informed dietary choice. A recent systematic review examined the barriers to adopting plant-based diets in high-income countries, highlighting both the potential benefits of these dietary patterns and the complex challenges associated with their implementation [92]. Although plant-based diets have been associated with improved health outcomes and reduced environmental impacts, thereby contributing to the achievement of developmental goals, their adoption remains limited. The review identified 40 distinct barriers, categorized into 11 thematic groups. The most frequently cited obstacles include lack of knowledge about appropriate food choices within plant-based diets, concerns about nutritional adequacy, and persistence of established dietary habits and routines [92]. This review recommends targeted educational interventions and communication strategies to facilitate informed dietary change. Importantly, the authors emphasized the necessity of context-specific solutions and acknowledged that cultural norms, socioeconomic factors, and individual lifestyles influence the relevance and strength of these barriers. To support the broader adoption of plant-based diets, future research should not only continue to explore barriers but also investigate facilitators and consider differences across plant-based dietary subtypes such as vegan, vegetarian, and flexitarian patterns [92].
Encouraging adolescents to reduce meat consumption requires more than just individual awareness; it must begin at home within the family unit [2]. Families are pivotal in shaping dietary habits, and the dynamics of family life can both facilitate and challenge the shift towards more sustainable eating. Research indicates that efforts to decrease meat consumption among adolescents aged 15–20 years often involve negotiating a balance between maintaining family cohesion and shared mealtime routines. While adolescents may show an interest in adopting plant-based diets, their preferences need to be harmonized with the family’s collective practices and values. Notably, mothers often bear the burden of adapting their meal plans and preparations, translating abstract sustainability goals into everyday food choices. This gendered distribution of responsibilities underscores the need to support caregivers, particularly women, during this transition. Promoting a collaborative approach to dietary change in which adolescents actively participate in suggesting and co-creating plant-based meals can enhance both environmental awareness and family unity. Therefore, effective strategies to promote sustainable diets in this age group must extend beyond individual messaging to address the family as a whole and acknowledge the shared responsibilities and emotional bonds that influence what is eaten around the dinner table [93,94].
Schools are pivotal in shaping children’s dietary habits and are ideally positioned to advocate sustainable food choices such as reducing meat consumption. A recent study on the incorporation of meat substitutes into Swedish school meals underscores both the potential and challenges of integrating these alternatives into daily menus [95]. While most substitutes are high in fiber and low in saturated fats and free sugars, they often contain high levels of salt and are classified as ultra-processed foods. Despite these drawbacks, their taste and texture closely resemble conventional meat, making them attractive to meal-planners, who view them as effective tools for gradually transitioning students to more sustainable diets. However, ensuring nutritional adequacy remains a concern because of the variability in protein content and limited fortification with essential micronutrients, such as iron and vitamin B12 [95]. Additionally, domestic production faces logistical challenges, including the lack of large-scale processing infrastructure. To enhance student acceptance, meal planners have employed various strategies: training kitchen staff, clearly communicating food choices to students, gradually introducing vegetarian meals, using neutral terminology to avoid polarization, and offering taste tests. Although the effectiveness of these strategies is yet to be fully quantified, early observations suggest that they hold promise in balancing student preferences with the nutritional and environmental goals of school meal programs [95]. Similarly, a study on school meal strategies in France explored ways to improve sustainability while maintaining nutritional quality [96]. Four key interventions were examined: reducing the number of meal components, adhering to national nutritional guidelines, increasing the number of vegetarian meals, and avoiding ruminant meat. The most significant environmental benefits were achieved by increasing the consumption of vegetarian meals and eliminating ruminant meat. A 20-meal cycle that included 12 vegetarian meals, 4 fish-based meals, and 4 meals with pork or poultry reduced greenhouse gas emissions by 50% without sacrificing nutritional adequacy [96]. However, the success of these changes depends largely on student acceptance and community involvement. Sudden shifts or poorly communicated changes, such as removing ruminant meat or introducing unfamiliar plant-based dishes, can lead to decreased acceptability and increased food waste, particularly in regions with strong meat-eating traditions [96]. To address these challenges, this study suggests training catering staff to prepare appealing vegetarian meals, involving children, parents, and school staff in the transition, and clearly communicating the health and environmental benefits of new menus [96]. Food education plays a crucial role in supporting these efforts, although it is often underutilized. By raising awareness of the environmental impact of dietary choices and the nutritional value of plant-based meals, schools can help normalize vegetarian options and foster more positive attitudes towards them [96]. Activities such as cooking classes, tasting sessions, and discussions on sustainable diets can familiarize students with new food and encourage them to try it. These initiatives also help to build a broader understanding of sustainable food systems, which are not only environmentally sound but also culturally relevant, affordable, and nutritionally adequate [96]. Although further research is needed to assess the long-term impact of these strategies on dietary intake, health outcomes, and environmental sustainability, the current evidence supports the view that schools are key agents of change. Through a combination of educational initiatives, thoughtful menu planning, and community engagement, schools can lead the transition towards more sustainable food systems and foster lifelong healthy eating habits.
3.3. Organic Food
Organic food systems are increasingly acknowledged for their potential to significantly advance sustainable diets. Organic foods are defined as being produced without the use of synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, or genetically modified organisms. Central to the organic food system is a codified set of principles supported by government-regulated standards and control mechanisms throughout the food chain. These principles promote biodiversity, enhance soil fertility, encourage agricultural diversification, and boost ecological resilience. This system shares numerous values with agroecological approaches, including the application of ecological science to agricultural development and climate adaptation [1,97,98].
The alignment of organic agriculture with FAO’s definition of sustainable diets is corroborated by a growing body of evidence. Organic food systems provide a framework integrating health, environmental protection, and ethical values. The health implications of organic food consumption continue to be a subject of ongoing scientific research. One of the most consistently reported advantages of organic food is reduced exposure to pesticide residues and synthetic chemicals. Organic farming standards prohibit the use of many conventional pesticides and fertilizers, resulting in organic foods that typically contain significantly fewer residues [98,99,100,101,102]. This reduced chemical load may be particularly pertinent for vulnerable populations, such as pregnant women and children [103,104,105]. Furthermore, some studies have identified higher levels of certain nutrients and bioactive compounds, including antioxidants, polyphenols, and secondary metabolites in organic crops [101,106,107,108]. Lower levels of heavy metals such as cadmium have also been reported in some organic foods [101]. There is limited but increasing evidence linking organic food consumption to improved health outcomes [102]. Some studies have suggested associations with lower rates of overweight, obesity, and metabolic syndrome, as well as a possible reduction in the risk of specific conditions [102,109,110,111,112]. Animal studies have indicated potential immune benefits, although these findings have yet to be validated in humans [113,114]. Despite these results, it is important to highlight that many investigations are observational in nature and susceptible to confounding by lifestyle factors. Consumers of organic food often adhere to healthier diets, engage in more physical activity, and exhibit greater health consciousness than the general population, thus complicating the isolation of the specific effects of organic food consumption [115]. Moreover, the current body of evidence does not permit definitive conclusions regarding the superior nutritional quality or long-term health benefits of organic food. Potential concerns have also been identified. Some studies have suggested that organic foods may present a higher risk of microbiological contamination, such as Escherichia coli or naturally occurring mycotoxins, although these findings have not been consistently observed [116]. Additionally, organic crops may exhibit lower protein and nitrogen content, which, while not inherently detrimental, could affect nutritional balance if not compensated for elsewhere in the diet [117]. Importantly, no specific harmful effects of consuming organic foods have been reported. However, organic farming does not eliminate all food safety risks and further research is necessary to fully understand its implications for public health (Figure 3).
From an environmental perspective, diets rich in organic products may be associated with reduced GHG emissions and lower cumulative energy demands, particularly when organic consumption is combined with predominantly plant-based dietary patterns. In these cases, a higher plant-to-animal protein ratio contributed to more favorable sustainability outcomes. However, the consumption of organic food alone does not necessarily lead to environmental benefits. When the diet remains rich in animal-based foods, switching to organic products may increase the environmental pressure. Specifically, organic agriculture requires more land per unit of food produced than conventional systems do, which can lead to increased land occupation. Additionally, the impact of organic farming on GHG emissions is often comparable to that of conventional farming when assessed per kg of food. Therefore, the environmental advantages of organic diets appear to be most significant when accompanied by a dietary shift towards more plant-based consumption, rather than through organic food substitution alone (Figure 3) [118].
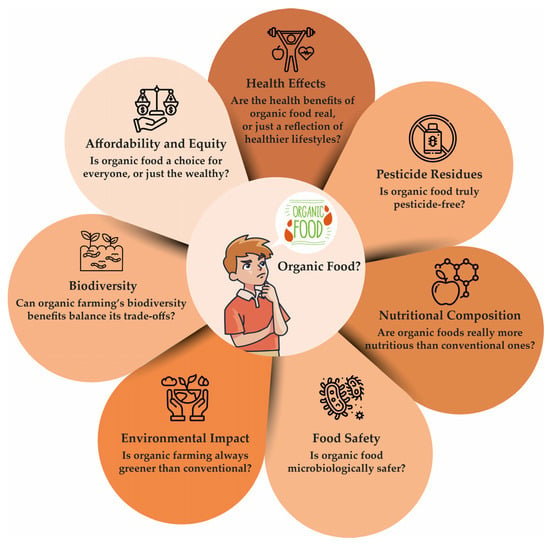
Figure 3.
Multiple questions regarding the concept of organic food. The diagram highlights key dimensions, such as health effects, nutritional composition, food safety, environmental impact, biodiversity, pesticide residues, and affordability, which challenge the simplistic perception of organic food as inherently superior. These questions encourage a deeper understanding of the complexities of organic agriculture, its potential trade-offs, and its role in promoting sustainable, ethical, and health-conscious food systems [119,120,121,122,123,124,125].
Organic food systems play a crucial role in the conservation of biodiversity. Organic farms generally support greater plant, faunal, and microbial diversity than conventional farms [126]. Despite these strengths, organic food systems have encountered significant challenges. Lower yields, particularly in high-input cropping systems, are of major concern. Although diversification strategies can help to mitigate the yield gap, organic farming typically produces a lower yield per hectare than conventional farming systems. Lower yields associated with organic agriculture may necessitate the conversion of natural ecosystems into farmland, and the resulting biodiversity gains from organic practices are unlikely to offset the losses incurred through such land-use changes [117]. Additionally, organic food tends to be more expensive, owing to labor-intensive practices and limited market share. These higher costs coupled with time constraints and limited accessibility may deter low-income households from adopting organic diets [127,128,129]. This complexity necessitates further investigation of the nuanced contributions of organic systems (Figure 3).
Adolescents’ engagement with organic food is influenced by a combination of perceptions, behaviors, structural limitations, and socio-demographic factors. Young individuals often hold positive views regarding organic food, particularly its association with animal welfare, environmental protection, and health benefits [130,131]. These favorable attitudes do not consistently lead to regular consumption. Studies conducted in Flanders and the Netherlands have demonstrated that, while adolescents express interest in organic food, actual consumption remains low, especially within the school context. In Flanders, research conducted as part of the Human Biomonitoring Program (FLEHS IV) on adolescents aged 14–15 years has revealed infrequent consumption of organic products. Contrary to expectations, those reporting regular consumption of organic foods did not exhibit a reduced internal exposure to environmental pollutants. In fact, slightly elevated levels of substances, such as organochlorine compounds, lead, and arsenic derivatives, were observed, suggesting that organic food consumption alone may not be sufficient to reduce the body’s burden of pollutants. These findings highlight the complexity of exposure pathways and the necessity of considering overall dietary patterns and environmental contexts rather than focusing solely on organic labels [132]. A study conducted in the Netherlands surveyed approximately 700 adolescents aged 15–16 years to evaluate their knowledge, attitudes, and purchase intentions regarding organic food. While most students expressed favorable views towards organic products and indicated a willingness to purchase them in adulthood, significantly fewer were inclined to buy such items within their school environment. Their responses highlighted a disconnect between long-term values and short-term choices, particularly when confronted with practical constraints, such as price, taste, and limited availability. Organic food is generally perceived as expensive and, in some instances, less palatable, an opinion that is potentially influenced by misconceptions or associations with other dietary trends such as vegetarianism. These perceptions were not uniform: female students tended to place a higher value on animal welfare and held more positive attitudes overall, whereas students from higher educational tracks demonstrated greater knowledge and acceptance than their peers in lower educational tracks [133]. A recent study explored the factors influencing intention to purchase organic food among Millennial and Gen Z consumers, offering both theoretical insights and market segmentation based on consumption motivation. The findings reveal that environmental concern and health consciousness are key drivers of green attitudes, subjective knowledge, and, ultimately, purchasing behavior. Interestingly, environmental concerns had a more significant impact than health-related motives did. This study identifies subjective knowledge as a crucial predictor of intention, suggesting that a perceived understanding of organic products boosts consumer confidence and decision-making. By segmenting consumers into preventive and therapeutic categories, this study uncovered significant demographic and behavioral differences, including variations in age, gender, income, education, and marital status. Using a multi-theoretical framework that incorporates the Health Belief Model, Knowledge–Attitude–Behavior Model, and Value–Belief–Norm Theory, this study offers a nuanced perspective on how values and beliefs translate into sustainable food choices. Furthermore, it highlights the importance of digital platforms in shaping attitudes and promoting health-conscious consumption, particularly through family-centered messaging. Overall, this study advocates tailored marketing and public health strategies that acknowledge the complex interplay between altruistic and egoistic motivations, especially within the socioeconomic context of emerging economies [134]. The findings indicate that adolescents’ engagement with organic food is influenced not only by their values and beliefs, but also by social context, perceived knowledge, and structural barriers. Therefore, it is crucial to reflect critically on the broader implications of organic and local food consumption. Notably, the notion of superiority of local food, often advocated as inherently more sustainable or ethical, warrants careful examination. Concepts such as proximity, ownership, transparency in supply chains, and the true origins of ingredients are complex and may not consistently align with sustainability objectives. Encouraging adolescents to explore these complexities aids in transcending binary thinking and developing a more informed perspective on the concept of eating “locally”. By engaging young individuals in open discussions that challenge assumptions and invite consideration of economic, environmental, and social dimensions, we can enhance food literacy and empower the next generation to make thoughtful and responsible food choices (Figure 3).
School influence extends beyond food provision and is pivotal in shaping eating habits. Educational interventions that integrate the principles of organic farming and sustainable consumption into the curriculum can enhance students’ understanding of the food systems and their health and environmental implications. This type of integrated learning not only raises awareness but also has the potential to maintain long-term health and sustainability values and behaviors. The integration of organic food into school meal programs often requires a comprehensive menu redesign. Additionally, the influence of school-based organic food initiatives may extend beyond the confines of educational settings. By shaping students’ food preferences and enhancing their nutritional knowledge, these programs may indirectly influence the dietary habits of their families and broader communities. This ripple effect underscores the significant societal potential of incorporating organic food into school systems [135]. However, schools face several challenges in promoting the consumption of organic foods. In many schools, particularly in the Netherlands, students bring packed lunches and warm meals are rarely provided, limiting opportunities for exposure to organic products [133,135]. Furthermore, where organic food is available, such as in some Italian schools, communication regarding its availability and benefits is often lacking [136]. This gap in visibility undermines the potential of school meals as an effective entry point for fostering sustainable eating habits. Therefore, promoting organic food in schools requires a systemic multifaceted approach. Integrating organic products into publicly funded school meals allows students to become familiar with these foods through direct experience, which is essential for normalizing consumption and countering negative stereotypes. Embedding themes of sustainable agriculture and food systems into the curriculum, particularly through hands-on activities such as cooking, tasting, and menu planning, can enhance ecoliteracy and food literacy [137,138].
Efforts to promote food education should extend beyond the classroom to include both families and communities. Encouraging family involvement in school-based food education can reinforce behaviors learned at school and ensure continuity at home. Research on Italian households indicates that families with children and higher education levels are more inclined to purchase organic and local products. Engagement in cultural activities and environmental initiatives further enhances the likelihood of sustainable food purchase. Family structures, dietary patterns (e.g., adherence to the Mediterranean diet), and economic conditions play pivotal roles in shaping organic food consumption [139]. In summary, although adolescents generally view organic food positively, their consumption patterns remain limited due to perceptual, economic, and institutional barriers. Schools are positioned uniquely to promote organic food through education, availability, and experiential learning. A comprehensive strategy that combines curriculum development, improved communication, family and community engagement, and policy support can foster sustainable dietary habits and empower adolescents to make informed food choices throughout their lives.
3.4. Food Waste
Food waste is defined as food intended for human consumption that is ultimately discarded irrespective of its edibility. This encompasses the food discarded during preparation, storage, service, and after service. It includes a broad spectrum of wasteful practices throughout the food supply chain, with significant prevalence in the household, retail, and food service sectors. A distinct category of food waste is plate waste, which refers to the edible portion of food served to a consumer, but left uneaten. In contrast to food loss, which occurs earlier in the supply chain owing to factors such as inadequate harvesting or spoilage, plate waste is directly associated with consumer behavior, including decisions based on taste preferences, portion sizes, satiety, or unfamiliarity with served food [140,141,142].
Globally, approximately one-third of all food produced for human consumption is lost or wasted, amounting to an estimated 1.05 billion tons in 2022. Of this total, the majority (approximately 60%) occurs within households, followed by 28% in food service environments, such as restaurants and canteens, and 12% in retail settings. Within the European Union, households represent the largest contributors, accounting for 54% of the total food waste, with processing and manufacturing responsible for 21.2%, food services for 9.2%, primary production for 8.7%, and retail for 7.2%. These statistics indicate that the final stages of the food supply chain, where consumers make decisions regarding the purchase, preparation, and consumption of food, are critical points for implementing interventions aimed at significantly reducing waste [143,144].
The adverse effects of food waste are extensive, encompassing significant environmental, economic, and social ramifications. From an environmental perspective, food waste entails the misuse of resources employed in its production, including land, water, energy, and labor. It is estimated that approximately 20% of global freshwater, cropland, and fertilizer usage is allocated to food that remains uneaten [145]. When food waste is deposited in landfills, it decomposes and emits methane, a greenhouse gas with global warming potential that exceeds that of carbon dioxide by more than 25 times [146]. Food waste accounts for approximately 8–10% of global GHG [141,147]. Economically, food waste leads to considerable financial losses throughout the supply chain. At the consumer level, it is estimated that each individual discards approximately 132 kg of food annually, contributing billions of euros to losses each year in Europe [145]. Socially, food waste exacerbates inequality and food insecurity, as edible food is discarded and millions of individuals worldwide lack access to adequate nutrition [148].
Adolescents’ perceptions of food waste are influenced not only by personal values, habits, and food preferences but also by broader cultural and systemic factors. Although many young individuals recognize the ethical and environmental ramifications of food waste, often associating it with feelings of guilt or personal failure, this awareness does not consistently lead to behavioral changes [149,150]. Research conducted in university settings indicates that sensory attributes, such as appearance, taste, and texture, along with portion size and familiarity, significantly affect whether meals are consumed or discarded. For instance, vegetables are frequently wasted, even when students report high levels of vegetable consumption, highlighting the disconnection between stated intentions and actual practices [150,151]. Beyond individual choices, deeper and more complex questions arise concerning the structural and cultural dimensions of food waste. Students may discard food not merely due to preference but also because of inflexible portioning systems or production norms that fail to accommodate varied appetites or cultural expectations. In certain contexts, generous services are linked to notions of hospitality and care, yet they may inadvertently reinforce wasteful practices [152]. The type of food wasted is also significant; while all waste has consequences, discarding resource-intensive foods such as meat or dairy can have far greater environmental impacts than discarding leftover bread or fruit [29]. Nevertheless, many reduction strategies treat all waste equally, overlooking these critical distinctions. Moreover, efforts to minimize waste can entail unintended trade-offs; for example, smaller portions may reduce leftovers but could also result in inadequate nutritional intake, particularly among adolescents with high energy needs [153,154,155]. Another essential consideration is the tendency to place responsibility squarely on individual consumers, particularly adolescents, without adequately addressing the food systems that shape their choice. This focus risks obscuring structural factors, such as overproduction, aggressive marketing, and supply chain inefficiencies. Although many adolescents are motivated to adopt more sustainable behaviors, their capacity to do so is shaped by availability, affordability, and how food is presented in daily contexts. Economic motivations to reduce waste may also at times conflict with institutional priorities such as operational efficiency or the need to offer variety [156,157]. In this context, it is vital not only to raise awareness but also to foster critical engagement. Reflective questions such as whether reducing food waste always leads to better outcomes or whether emphasizing food waste shifts blame unfairly for individuals should be actively discussed with adolescents. These questions are not meant to discourage action but to help young people understand the complexity of the issue, recognize contradictions, and develop informed, nuanced perspectives. Encouraging open dialogue about what is wasted, why it is wasted, and under what circumstances can promote a deeper understanding and empower adolescents to become thoughtfully informed participants in the transition to more sustainable food systems (Figure 4).
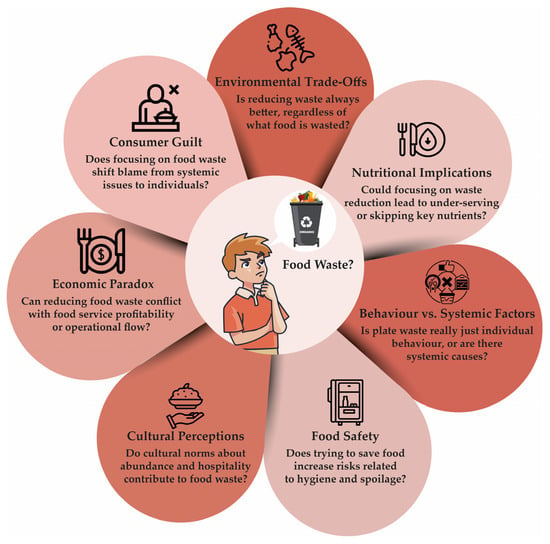
Figure 4.
Multiple questions surrounding the concept of food waste. The diagram highlights key dimensions, such as consumer guilt, environmental trade-offs, nutritional implications, systemic versus behavioral drivers, food safety, cultural perceptions, and economic tensions. These questions challenge the notion that all food waste can be resolved through individual responsibility, encouraging broader reflection on structural constraints, unintended consequences, and the need for more holistic and context-sensitive strategies in waste reduction efforts [156,158,159,160,161,162].
Educational institutions play a pivotal role in advancing food waste reduction by shaping dietary habits, fostering awareness, and cultivating environments conducive to sustainable behaviors. As venues where numerous children and adolescents consume meals daily, schools are uniquely positioned to influence food-related attitudes and practices at an early age. Effective strategies extend beyond merely providing nutritious meals; they actively engage students, families, and school personnel in comprehending the value of food and the repercussions of waste. Educational interventions that integrate information with active participation have demonstrated particular efficacy. For instance, campaigns employing posters, videos, or interactive activities to raise awareness of food waste have resulted in measurable reductions in plate waste [163,164]. In one instance, the implementation of a “plate waste tracker” in schools, where students could weigh and observe their uneaten food, facilitated reflection on portion sizes and food choices, culminating in a behavioral shift [163]. Other successful interventions include menu modifications based on student feedback, reducing the availability of less popular options, and offering flexible portion sizes [165,166]. Engaging families through take-home materials, social media, and school events has also been shown to reinforce learning and extend awareness beyond the classroom [167]. Schools that implement these measures not only reduce waste, but also contribute to food literacy, empower students to make informed choices, and support broader environmental objectives.
4. Conclusions
This review examined adolescents’ perceptions and responses to critical elements of sustainable diets, including local consumption, plant-based diets, organic food, and food waste. Across these areas, prevalent misconceptions endure, such as the belief that local food is invariably more sustainable or that plant-based diets and organic food are inherently healthier. These oversimplified narratives often obscure intricate environmental, nutritional, cultural, and ethical dimensions. Table 1 provides a structured synthesis of the myths and realities identified in the literature alongside concrete school-based interventions designed to clarify these issues and facilitate the translation of knowledge into action. Several recommendations under “School-Based Interventions to Debunk the Myth” exhibit overlap across various sustainability characteristics. This overlap primarily arises from the necessity of implementing interventions that do not concentrate solely on individual aspects such as local eating, reduced meat consumption, organic food choices, or food waste in isolation. Instead, these interventions should adopt integrated approaches that combine multiple elements within broader programs. Evidence indicates that school-based interventions targeting sustainable food behaviors among adolescents tend to adopt integrated approaches. These interventions commonly focus on broad concepts of food literacy, often combining themes such as healthy eating, food waste, and environmental awareness within the same program, making it difficult to assess their impact on individual behaviors like local food consumption or reduced meat intake. Although certain components, such as preference for plant-based foods or reduced waste, may show improvement, these outcomes typically result from multifaceted interventions rather than isolated actions [168,169,170]. By presenting evidence in this manner, the table functions not only as a pedagogical tool but also as a practical framework for developing educational strategies tailored to adolescents. This demonstrates how schools can progress beyond mere information delivery towards deeper engagement, promoting critical thinking, experiential learning, and value-driven decision-making. Whether through tracking food miles, engaging in debates on sustainable protein sources, participating in gardening projects, or conducting food waste audits, the interventions outlined offer a roadmap for integrating sustainability into school curricula and daily routines. Empowering adolescents with the capacity to question assumptions, comprehend trade-offs, and reflect on their food choices is essential for cultivating a generation capable of addressing interconnected challenges of human and planetary health. As highlighted in the table, sustainable dietary behaviors are not merely about selecting the “right” foods but about understanding systems, recognizing complexity, and taking informed, context-sensitive action.

Table 1.
Myths and realities of sustainable diets: a framework for school interventions.
Funding
This work is funded by the European Union through the NextGeneration EU mechanism under the Recovery and Resilience Plan—PRR (www.recuperarportugal.gov.pt, accessed on 5 February 2025), within the scope of the project Integrated Training Network for the Modernization of Agricultural Sciences—Agro@TecVerde (through the Impulso Mais Digital investment and operation code—10/C06-i07/2024.P11729), currently underway at the Institute of Biomedical Sciences Abel Salazar of the University of Porto (ICBAS-UP).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- FAO. Sustainable diets and biodiversity: Directions and solutions for policy, research and action. In Proceedings of the International Scientific Symposium on Biodiversity and Sustainable Diets: United Against Hunger, Rome, Italy, 3–5 November 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Willett, W.; Rockström, J.; Loken, B.; Springmann, M.; Lang, T.; Vermeulen, S.; Garnett, T.; Tilman, D.; Declerck, F.; Wood, A.; et al. Food in the Anthropocene: The EAT–Lancet Commission on healthy diets from sustainable food systems. Lancet 2019, 393, 447–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godfray, H.C.J.; Aveyard, P.; Garnett, T.; Hall, J.W.; Key, T.J.; Lorimer, J.; Pierrehumbert, R.T.; Scarborough, P.; Springmann, M.; Jebb, S.A. Meat consumption, health, and the environment. Science 2018, 361, eaam5324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Story, M.; Neumark-Sztainer, D.; French, S. Individual and Environmental Influences on Adolescent Eating Behaviors. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2002, 102, S40–S51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Bussel, L.M.; Kuijsten, A.; Mars, M.; van ‘t Veer, P. Consumers’ perceptions on food-related sustainability: A systematic review. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 341, 130904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koca, B.; Arkan, G. The relationship between adolescents’ nutrition literacy and food habits, and affecting factors. Public Health Nutr. 2021, 24, 717–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delbosq, S.; Velasco, V.; Vercesi, C.; Vecchio, L.P. Adolescents’ Nutrition: The Role of Health Literacy, Family and Socio-Demographic Variables. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, J.L.; Fanzo, J.C.; Cogill, B. Understanding Sustainable Diets: A Descriptive Analysis of the Determinants and Processes That Influence Diets and Their Impact on Health, Food Security, and Environmental Sustainability. Adv. Nutr. 2014, 5, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. The State of Food and Agriculture 2021: Making Agrifood Systems More Resilient to Shocks and Stresses; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Von Braun, J.; Afsana, K.; Fresco, L.O.; Hassan, M.H.A.; Torero, M. Food System Concepts and Definitions for Science and Political Action. In Science and Innovations for Food Systems Transformation; von Braun, J., Afsana, K., Fresco, L.O., Hassan, M.H.A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Sustainable Healthy Diets: Guiding Principles; Food & Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Meybeck, A.; Gitz, V. Highlighting interlinkages between sustainable diets and sustainable food systems. In Sustainable Diets: Linking Nutrition and Food Systems; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2019; pp. 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Laine, J.E.; Huybrechts, I.; Gunter, M.J.; Ferrari, P.; Weiderpass, E.; Tsilidis, K.; Aune, D.; Schulze, M.B.; Bergmann, M.; Temme, E.H.M.; et al. Co-benefits from sustainable dietary shifts for population and environmental health: An assessment from a large European cohort study. Lancet Planet. Health 2021, 5, e786–e796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ares, G.; De Rosso, S.; Mueller, C.; Philippe, K.; Pickard, A.; Nicklaus, S.; Van Kleef, E.; Varela, P. Development of food literacy in children and adolescents: Implications for the design of strategies to promote healthier and more sustainable diets. Nutr. Rev. 2024, 82, 536–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.; Araújo, R.; Lopes, F.; Ray, S. Nutrition and Food Literacy: Framing the Challenges to Health Communication. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, A.J.; Santini, F. The sustainability of “local” food: A review for policy-makers. Rev. Agric. Food Environ. Stud. 2022, 103, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, K.A.; Michelsen, M.K.; Carpenter, C.L. Modern Diets and the Health of Our Planet: An Investigation into the Environmental Impacts of Food Choices. Nutrients 2023, 15, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunori, G.; Galli, F.; Barjolle, D.; Van Broekhuizen, R.; Colombo, L.; Giampietro, M.; Kirwan, J.; Lang, T.; Mathijs, E.; Maye, D.; et al. Are Local Food Chains More Sustainable than Global Food Chains? Considerations for Assessment. Sustainability 2016, 8, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terlau, W.; Hirsch, D.; Blanke, M. Smallholder farmers as a backbone for the implementation of the Sustainable Development Goals. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 27, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiffoleau, Y.; Dourian, T. Sustainable Food Supply Chains: Is Shortening the Answer? A Literature Review for a Research and Innovation Agenda. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzgys, S.; Pickering, G.J. Perceptions of a sustainable diet among young adults. Environ. Educ. Res. 2025, 31, 512–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamenidou, I.C.; Mamalis, S.A.; Pavlidis, S.; Bara, E.-Z.G. Segmenting the Generation Z Cohort University Students Based on Sustainable Food Consumption Behavior: A Preliminary Study. Sustainability 2019, 11, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polleau, A.; Biermann, G. Eat local to save the planet? Contrasting scientific evidence and consumers’ perceptions of healthy and environmentally friendly diets. Curr. Res. Environ. Sustain. 2021, 3, 100054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, E.; Galli, F.; Menozzi, D.; Maye, D.; Touzard, J.-M.; Marescotti, A.; Six, J.; Brunori, G. Comparing the sustainability of local and global food products in Europe. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 165, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards-Jones, G.; Milà i Canals, L.; Hounsome, N.; Truninger, M.; Koerber, G.; Hounsome, B.; Cross, P.; York, E.H.; Hospido, A.; Plassmann, K.; et al. Testing the assertion that ‘local food is best’: The challenges of an evidence-based approach. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 19, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhashim, R.; Deepa, R.; Anandhi, A. Environmental Impact Assessment of Agricultural Production Using LCA: A Review. Climate 2021, 9, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemecek, T.; Jungbluth, N.; Canals, L.M.I.; Schenck, R. Environmental impacts of food consumption and nutrition: Where are we and what is next? Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2016, 21, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdiarmid, J.I. Seasonality and dietary requirements: Will eating seasonal food contribute to health and environmental sustainability? Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2014, 73, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poore, J.; Nemecek, T. Reducing food’s environmental impacts through producers and consumers. Science 2018, 360, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DEFRA. Understanding the Environmental Impacts of Consuming Foods That Are Produced Locally in Season; DEFRA: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Vargas, A.M.; De Moura, A.P.; Deliza, R.; Cunha, L.M. The Role of Local Seasonal Foods in Enhancing Sustainable Food Consumption: A Systematic Literature Review. Foods 2021, 10, 2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillaumie, L.; Vézina-Im, L.-A.; Boiral, O.; Prescott, J.; Bergeron, A.; Yuriev, A. Promoting local food products for sustainability: Developing a taxonomy of best practices. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 32, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röös, E.; Karlsson, H. Effect of eating seasonal on the carbon footprint of Swedish vegetable consumption. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 59, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viroli, G.; Kalmpourtzidou, A.; Cena, H. Exploring Benefits and Barriers of Plant-Based Diets: Health, Environmental Impact, Food Accessibility and Acceptability. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Xiong, J.; Du, T.; Ju, X.; Gan, Y.; Li, S.; Xia, L.; Shen, Y.; Pacenka, S.; Steenhuis, T.S.; et al. Diversifying crop rotation increases food production, reduces net greenhouse gas emissions and improves soil health. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Li, T.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Sui, P. Changes in soil microbial biomass, diversity, and activity with crop rotation in cropping systems: A global synthesis. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 186, 104815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deller, S.C.; Lamie, D.; Stickel, M. Local foods systems and community economic development. In Local Food Systems and Community Economic Development; Routledge: London, UK, 2020; pp. 4–30. [Google Scholar]
- Régnier, F.; Dalstein, A.-L.; Rouballay, C.; Chauvel, L. Eating in Season—A Lever of Sustainability? An Interview Study on the Social Perception of Seasonal Consumption. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallnoefer, L.M.; Riefler, P.; Meixner, O. What Drives the Choice of Local Seasonal Food? Analysis of the Importance of Different Key Motives. Foods 2021, 10, 2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locke, E.; Coronado, G.D.; Thompson, B.; Kuniyuki, A. Seasonal Variation in Fruit and Vegetable Consumption in a Rural Agricultural Community. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2009, 109, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waswa, L.M.; Jordan, I.; Krawinkel, M.B.; Keding, G.B. Seasonal Variations in Dietary Diversity and Nutrient Intakes of Women and Their Children (6–23 Months) in Western Kenya. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 636872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karan, E.P.; Asgari, S.; Asadi, S. Resilience assessment of centralized and distributed food systems. Food Secur. 2023, 15, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, I.Y.; Forero, O.A.; Wagner-Medina, E.V.; Florez Diaz, H.; Tremma, O.; Fargetton, X.; Lowenberg-DeBoer, J. Resilience of food supply systems to sudden shocks: A global review and narrative synthesis. Glob. Food Secur. 2025, 44, 100842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brune, S.; Knollenberg, W.; Barbieri, C.; Stevenson, K. Towards a unified definition of local food. J. Rural Stud. 2023, 103, 103135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feagan, R. The place of food: Mapping out the ‘local’ in local food systems. Prog. Hum. Geogr. 2007, 31, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delind, L.B. Are local food and the local food movement taking us where we want to go? Or are we hitching our wagons to the wrong stars? Agric. Hum. Values 2011, 28, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards-Jones, G. Does eating local food reduce the environmental impact of food production and enhance consumer health? Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2010, 69, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, D.R.; Chávez, N.; Allen, E.; Ramirez, D. Food sovereignty, urban food access, and food activism: Contemplating the connections through examples from Chicago. Agric. Hum. Values 2012, 29, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Born, B.; Purcell, M. Avoiding the Local Trap:Scale and Food Systems in Planning Research. J. Plan. Educ. Res. 2006, 26, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- László, V.; Wahlen, S. Exploring young consumer’s understanding of local food through proximity and social representations. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2024, 8, 1464548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gega, M.; Höhler, J.; Bijman, J.; Oude Lansink, A.G. The relationship of firm ownership structure and sustainability performance in agri-food chains: A systematic literature review. Clean. Logist. Supply Chain. 2024, 13, 100193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeag, L.; Kruszewski, S. Defining Local Food: An Analysis of State Approaches and Challenges; Vermont Law and Graduate School: South Royalton, VT, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie, H. You want to reduce the carbon footprint of your food? Focus on what you eat, not whether your food is local. In Our World in Data; Global Change Data Lab: Oxford, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz, L.D.; Radtke, M.D.; Scherr, R.E. Development and Pilot Testing of a Food Literacy Curriculum for High School-Aged Adolescents. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, P. Enhancing Adolescent Food Literacy Through Mediterranean Diet Principles: From Evidence to Practice. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, F.; Nick; Adegbola; Beal, T.; Iannotti, L.; Paul; Mann, N. The role of meat in the human diet: Evolutionary aspects and nutritional value. Anim. Front. 2023, 13, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffioen-Roose, S.; Mars, M.; Siebelink, E.; Finlayson, G.; Tomé, D.; de Graaf, C. Protein status elicits compensatory changes in food intake and food preferences. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 95, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, F.; Praet, I. Meat traditions. The co-evolution of humans and meat. Appetite 2015, 90, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, P.T.; Carson, B.P.; Witard, O.C. Dietary protein considerations in a sustainable and ageing world: A narrative review with a focus on greenhouse gas emissions and skeletal muscle remodelling and maintenance. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2024, 25, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoll-Kleemann, S.; Schmidt, U.J. Reducing meat consumption in developed and transition countries to counter climate change and biodiversity loss: A review of influence factors. Reg. Environ. Change 2017, 17, 1261–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recanati, F.; Allievi, F.; Scaccabarozzi, G.; Espinosa, T.; Dotelli, G.; Saini, M. Global Meat Consumption Trends and Local Deforestation in Madre de Dios: Assessing Land Use Changes and other Environmental Impacts. Procedia Eng. 2015, 118, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gržinić, G.; Piotrowicz-Cieślak, A.; Klimkowicz-Pawlas, A.; Górny, R.L.; Ławniczek-Wałczyk, A.; Piechowicz, L.; Olkowska, E.; Potrykus, M.; Tankiewicz, M.; Krupka, M.; et al. Intensive poultry farming: A review of the impact on the environment and human health. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 160014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, N.; Marquès, M.; Nadal, M.; Domingo, J.L. Meat consumption: Which are the current global risks? A review of recent (2010–2020) evidences. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragkias, M.; Lobo, J.; Strumsky, D.; Seto, K.C. Does Size Matter? Scaling of CO2 Emissions and U.S. Urban Areas. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beach, R.H.; Deangelo, B.J.; Rose, S.; Li, C.; Salas, W.; Delgrosso, S.J. Mitigation potential and costs for global agricultural greenhouse gas emissions. Agric. Econ. 2008, 38, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbow, H.-O.P.; Reisinger, A.; Canadell, J.; O’Brien, P. Special Report on Climate Change, Desertification, Land Degradation, Sustainable Land Management, Food Security, and Greenhouse Gas Fluxes in Terrestrial Ecosystems (SR2); IPCC: Ginevra, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 650. [Google Scholar]
- Food Wastage Footprint. Food Wastage Footprint: Impacts on Natural Resources: Summary Report; Food & Agriculture Organization of the UN (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ranganathan, J.; Vennard, D.; Waite, R.; Lipinski, B.; Searchinger, T.; Dumas, P. Shifting Diets for a Sustainable Food Future; World Resources Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Pathways Towards Lower Emissions: A Global Assessment of the Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Mitigation Options from Livestock Agrifood Systems; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Friel, S.; Dangour, A.D.; Garnett, T.; Lock, K.; Chalabi, Z.; Roberts, I.; Butler, A.; Butler, C.D.; Waage, J.; McMichael, A.J.; et al. Public health benefits of strategies to reduce greenhouse-gas emissions: Food and agriculture. Lancet 2009, 374, 2016–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsson-Kanyama, A.; Ekström, M.P.; Shanahan, H. Food and life cycle energy inputs: Consequences of diet and ways to increase efficiency. Ecol. Econ. 2003, 44, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilman, D.; Clark, M. Global diets link environmental sustainability and human health. Nature 2014, 515, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uysal-Unalan, I.; Sogut, E.; Realini, C.E.; Cakmak, H.; Oz, E.; Espinosa, E.; Morcillo-Martín, R.; Oz, F.; Nurmi, M.; Cerqueira, M.A.; et al. Bioplastic packaging for fresh meat and fish: Current status and future direction on mitigating food and packaging waste. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 152, 104660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, H.T.; Reg, W.; Daniel, P. Fueling Global Fishing Fleets. AMBIO J. Hum. Environ. 2005, 34, 635–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, R.W.; Blanchard, J.L.; Gardner, C.; Green, B.S.; Hartmann, K.; Tyedmers, P.H.; Watson, R.A. Fuel use and greenhouse gas emissions of world fisheries. Nat. Clim. Change 2018, 8, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, K.; Zeller, D.; Woroniak, J.; Coulter, A.; Winchester, M.; Palomares, M.L.D.; Pauly, D. Global trends in carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from fuel combustion in marine fisheries from 1950 to 2016. Mar. Policy 2019, 107, 103382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, A.A.; Álvarez-Salgado, X.A.; Antelo, L.T. Assessing the impact of bivalve aquaculture on the carbon circular economy. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdiarmid, J.I.; Douglas, F.; Campbell, J. Eating like there’s no tomorrow: Public awareness of the environmental impact of food and reluctance to eat less meat as part of a sustainable diet. Appetite 2016, 96, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lea, E.J.; Crawford, D.; Worsley, A. Public views of the benefits and barriers to the consumption of a plant-based diet. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 60, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raptou, E.; Tsiami, A.; Negro, G.; Ghuriani, V.; Baweja, P.; Smaoui, S.; Varzakas, T. Gen Z’s Willingness to Adopt Plant-Based Diets: Empirical Evidence from Greece, India, and the UK. Foods 2024, 13, 2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venter De Villiers, M.; Cheng, J.; Truter, L. The Shift Towards Plant-Based Lifestyles: Factors Driving Young Consumers’ Decisions to Choose Plant-Based Food Products. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnes, C.; Carstairs, S.A.; Cecil, J.E. A qualitative study of young peoples’ thoughts and attitudes to follow a more plant-based diet. Front. Psychol. 2023, 14, 1196142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Zanten, H.H.; Herrero, M.; Van Hal, O.; Röös, E.; Muller, A.; Garnett, T.; Gerber, P.J.; Schader, C.; De Boer, I.J. Defining a land boundary for sustainable livestock consumption. Glob. Change Biol. 2018, 24, 4185–4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havermans, R.C.; Rutten, G.; Bartelet, D. Adolescent’s willingness to adopt a more plant-based diet: A theory-based interview study. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 688131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downs, S.M.; Merchant, E.V.; Sackey, J.; Fox, E.L.; Davis, C.; Fanzo, J. Sustainability considerations are not influencing meat consumption in the US. Appetite 2024, 203, 107667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, N.; Wilson, L.; Smith, M.; Duncan, B.; McHugh, P. The BROAD study: A randomised controlled trial using a whole food plant-based diet in the community for obesity, ischaemic heart disease or diabetes. Nutr. Diabetes 2017, 7, e256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, É.; Michaud-Létourneau, I.; Couturier, Y.; Roy, M. A whole-food, plant-based nutrition program: Evaluation of cardiovascular outcomes and exploration of food choices determinants. Nutrition 2019, 66, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clem, J.; Barthel, B. A look at plant-based diets. Mo. Med. 2021, 118, 233–238. [Google Scholar]
- Ornish, D.; Madison, C.; Kivipelto, M.; Kemp, C.; McCulloch, C.E.; Galasko, D.; Artz, J.; Rentz, D.; Lin, J.; Norman, K.; et al. Effects of intensive lifestyle changes on the progression of mild cognitive impairment or early dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: A randomized, controlled clinical trial. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2024, 16, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magkos, F.; Tetens, I.; Bügel, S.G.; Felby, C.; Schacht, S.R.; Hill, J.O.; Ravussin, E.; Astrup, A. A Perspective on the Transition to Plant-Based Diets: A Diet Change May Attenuate Climate Change, but Can It Also Attenuate Obesity and Chronic Disease Risk? Adv. Nutr. 2020, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisen, M.B.; Brown, P.O. Rapid global phaseout of animal agriculture has the potential to stabilize greenhouse gas levels for 30 years and offset 68 percent of CO2 emissions this century. PLoS Clim. 2022, 1, e0000010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickerby, A.; Green, R. Barriers to Adopting a Plant-Based Diet in High-Income Countries: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2024, 16, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesselberg, J.; Pedersen, S.; Grønhøj, A. Meat reduction meets family reality: Negotiating sustainable diets in households with adolescents. Appetite 2024, 195, 107213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata, J.; Knobl, V.; Takezawa, M. Exploring the role of adolescents in healthier, more sustainable family meals: A decision study on meat consumption. Appetite 2025, 208, 107916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, J.; Post, A.; Elf, M.; Wollmar, M.; Sjoberg, A. Meat substitutes in Swedish school meals: Nutritional quality, ingredients, and insights from meal planners. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 75, 637–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poinsot, R.; Vieux, F.; Maillot, M.; Darmon, N. Number of meal components, nutritional guidelines, vegetarian meals, avoiding ruminant meat: What is the best trade-off for improving school meal sustainability? Eur. J. Nutr. 2022, 61, 3003–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reganold, J.P.; Wachter, J.M. Organic agriculture in the twenty-first century. Nat. Plants 2016, 2, 15221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahanta, D.; Bisht, J.K.; Kant, L. Chapter 1—Concept and global scenario of organic farming. In Advances in Organic Farming; Meena, V.S., Meena, S.K., Rakshit, A., Stanley, J., Srinivasarao, C., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2021; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Möhring, N.; Ingold, K.; Kudsk, P.; Martin-Laurent, F.; Niggli, U.; Siegrist, M.; Studer, B.; Walter, A.; Finger, R. Pathways for advancing pesticide policies. Nat. Food 2020, 1, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Union. Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Barański, M.; Średnicka-Tober, D.; Volakakis, N.; Seal, C.; Sanderson, R.; Stewart, G.B.; Benbrook, C.; Biavati, B.; Markellou, E.; Giotis, C.; et al. Higher antioxidant and lower cadmium concentrations and lower incidence of pesticide residues in organically grown crops: A systematic literature review and meta-analyses. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 112, 794–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulia, K.-A.; Bakaloudi, D.R.; Alevizou, M.; Papakonstantinou, E.; Zampelas, A.; Chourdakis, M. Impact of organic foods on chronic diseases and health perception: A systematic review of the evidence. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2025, 79, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, L.G.; Philippat, C.; Nakayama, S.F.; Slama, R.; Trasande, L. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals: Implications for human health. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 703–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.d.B.; Carvalho, D.S.d.; Chong-Silva, D.C.; Urrutia-Pereira, M.; Albuquerque, G.S.C.d.; Cieslak, F.; Chong-Neto, H.J. Association between exposure to pesticides and allergic diseases in children and adolescents: A systematic review with meta-analysis. J. Pediatr. 2022, 98, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Dries, M.A.; Guxens, M.; Pronk, A.; Spaan, S.; El Marroun, H.; Jusko, T.A.; Longnecker, M.P.; Ferguson, K.K.; Tiemeier, H. Organophosphate pesticide metabolite concentrations in urine during pregnancy and offspring attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder and autistic traits. Environ. Int. 2019, 131, 105002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima, D.P.; dos Santos Pinto Júnior, E.; de Menezes, A.V.; de Souza, D.A.; de São José, V.P.B.; da Silva, B.P.; de Almeida, A.Q.; de Carvalho, I.M.M. Chemical composition, minerals concentration, total phenolic compounds, flavonoids content and antioxidant capacity in organic and conventional vegetables. Food Res. Int. 2024, 175, 113684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czech, A.; Szmigielski, M.; Sembratowicz, I. Nutritional value and antioxidant capacity of organic and conventional vegetables of the genus Allium. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chausali, N.; Saxena, J. Chapter 15—Conventional versus organic farming: Nutrient status. In Advances in Organic Farming; Meena, V.S., Meena, S.K., Rakshit, A., Stanley, J., Srinivasarao, C., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2021; pp. 241–254. [Google Scholar]
- Kesse-Guyot, E.; Baudry, J.; Assmann, K.E.; Galan, P.; Hercberg, S.; Lairon, D. Prospective association between consumption frequency of organic food and body weight change, risk of overweight or obesity: Results from the NutriNet-Santé Study. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 117, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, B.; Du, Y.; Snetselaar, L.G.; Sun, Q.; Hu, F.B.; Bao, W. Inverse Association between Organic Food Purchase and Diabetes Mellitus in US Adults. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudry, J.; Lelong, H.; Adriouch, S.; Julia, C.; Allès, B.; Hercberg, S.; Touvier, M.; Lairon, D.; Galan, P.; Kesse-Guyot, E. Association between organic food consumption and metabolic syndrome: Cross-sectional results from the NutriNet-Santé study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 2477–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagavathula, A.S.; Vidyasagar, K.; Khubchandani, J. Organic Food Consumption and Risk of Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Healthcare 2022, 10, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finamore, A.; Britti, M.S.; Roselli, M.; Bellovino, D.; Gaetani, S.; Mengheri, E. Novel Approach for Food Safety Evaluation. Results of a Pilot Experiment to Evaluate Organic and Conventional Foods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 7425–7431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauridsen, C.; Jørgensen, H.; Halekoh, U.; Christensen, L.P.; Brandt, K. Organic diet enhanced the health of rats. DARCOFenews 2005, 1–2. Available online: https://pure.au.dk/portal/en/publications/organic-diet-enhanced-the-health-of-rats (accessed on 6 June 2025).
- Lo Dato, E.; Gostoli, S.; Tomba, E. Psychological Theoretical Frameworks of Healthy and Sustainable Food Choices: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, A.P.; Trząskowska, M.; Trafialek, J. Microorganisms in Organic Food-Issues to Be Addressed. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giampieri, F.; Mazzoni, L.; Cianciosi, D.; Alvarez-Suarez, J.M.; Regolo, L.; Sánchez-González, C.; Capocasa, F.; Xiao, J.; Mezzetti, B.; Battino, M. Organic vs conventional plant-based foods: A review. Food Chem. 2022, 383, 132352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, M.S.; Stoessel, F.; Jungbluth, N.; Juraske, R.; Schader, C.; Stolze, M. Environmental impacts of organic and conventional agricultural products—Are the differences captured by life cycle assessment? J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 149, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, C.; Tong, C. Organic or local? Investigating consumer preference for fresh produce using a choice experiment with real economic incentives. HortScience 2009, 44, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesse-Guyot, E.; Péneau, S.; Méjean, C.; Szabo de Edelenyi, F.; Galan, P.; Hercberg, S.; Lairon, D. Profiles of organic food consumers in a large sample of French adults: Results from the Nutrinet-Sante cohort study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughner, R.S.; McDonagh, P.; Prothero, A.; Shultz, C.J.; Stanton, J. Who are organic food consumers? A compilation and review of why people purchase organic food. J. Consum. Behav. Int. Res. Rev. 2007, 6, 94–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aertsens, J.; Verbeke, W.; Mondelaers, K.; Van Huylenbroeck, G. Personal determinants of organic food consumption: A review. Br. Food J. 2009, 111, 1140–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padel, S.; Foster, C. Exploring the gap between attitudes and behaviour: Understanding why consumers buy or do not buy organic food. Br. Food J. 2005, 107, 606–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslihan Nasir, V.; Karakaya, F. Consumer segments in organic foods market. J. Consum. Mark. 2014, 31, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.C.; Salois, M.J. Local versus organic: A turn in consumer preferences and willingness-to-pay. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2010, 25, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomiero, T.; Pimentel, D.; Paoletti, M.G. Environmental Impact of Different Agricultural Management Practices: Conventional vs. Organic Agriculture. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2011, 30, 95–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durham, T.C.; Mizik, T. Comparative Economics of Conventional, Organic, and Alternative Agricultural Production Systems. Economies 2021, 9, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalke, A.; Köhler, S.; Messmann, L.; Thorenz, A.; Tuma, A.; Gaugler, T. True cost accounting of organic and conventional food production. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 408, 137134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hough, G.; Contarini, A. Can low-income consumers choose food from sustainable production methods? Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2023, 51, 101035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, J.E.; Laska, M.N.; Neumark-Sztainer, D.; Story, M. Positive Attitudes towards Organic, Local, and Sustainable Foods Are Associated with Higher Dietary Quality among Young Adults. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2013, 113, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenoy, K.R.; Ranjith, V.K.; Nayak, S.; Anirvinna, C. Conceptualizing organic food consumption: A consumer motive perspective. Cogent Soc. Sci. 2024, 10, 2338864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Larebeke, N.; Colles, A.; Leermakers, M.; Den Hond, E.; Voorspoels, S.; Goderis, L.; Schoeters, G. Organic food and internal exposure to pollutants among Flemish adolescents. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2024, 41, 1315–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stobbelaar, D.J.; Casimir, G.; Borghuis, J.; Marks, I.; Meijer, L.; Zebeda, S. Adolescents’ attitudes towards organic food: A survey of 15- to 16-year old school children. Int. J. Consum. Stud. 2007, 31, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munaqib, P.; Darzi, M.A.; Bhat, S.A.; Islam, S.B.; Mushtaq, N. Understanding Millennials and Gen Z’s organic food buying intentions: A mediation and segmentation study. Clean. Waste Syst. 2025, 11, 100294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Mikkelsen, B.E. The association between organic school food policy and school food environment: Results from an observational study in Danish schools. Perspect. Public Health 2014, 134, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkola, M.; Roos, G. Tracing Food Education for Sustainable Development in iPOPY countries. Recommendations for learning about sustainability and organic food within educational contexts. In Organic Food for Youth in Public Settings: Potentials and Challenges. Preliminary Recommendations from a European Study. Proceedings of the iPOPY session held at BioFach Congress 2010.; CORE Organic Project Series Report; ICROFS: Tjele, Denmark, 2010; pp. 29–35. [Google Scholar]
- Strassner, C.; Cavoski, I.; Di Cagno, R.; Kahl, J.; Kesse-Guyot, E.; Lairon, D.; Lampkin, N.; Løes, A.-K.; Matt, D.; Niggli, U.; et al. How the Organic Food System Supports Sustainable Diets and Translates These into Practice. Front. Nutr. 2015, 2, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, E.B.; Da Costa Maynard, D.; Zandonadi, R.P.; Raposo, A.; Botelho, R.B.A. Sustainability Recommendations and Practices in School Feeding: A Systematic Review. Foods 2022, 11, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annunziata, A.; Agovino, M.; Mariani, A. Sustainability of Italian families’ food practices: Mediterranean diet adherence combined with organic and local food consumption. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 206, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Global food losses and food waste–Extent, causes and prevention. In SAVE FOOD: An Initiative on Food Loss and Waste Reduction; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Forbes, H. Food Waste Index Report 2021; United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Parfitt, J.; Barthel, M.; Macnaughton, S. Food waste within food supply chains: Quantification and potential for change to 2050. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 3065–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forbes, H.; Peacock, E.; Abbott, A.; Jones, M. Think Eat Save. Tracking progress to halve global food waste. In Food Waste Index Report; United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Eurostat. Food Waste and Food Waste Prevention—Estimates; Eurostat: Luxembourg, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kummu, M.; de Moel, H.; Porkka, M.; Siebert, S.; Varis, O.; Ward, P.J. Lost food, wasted resources: Global food supply chain losses and their impacts on freshwater, cropland, and fertiliser use. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 438, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S.; Qin, D.; Manning, M.; Chen, Z.; Marquis, M.; Averyt, K.B.; Tignor, M.; Miller, H.L. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Mbow, C.; Rosenzweig, C.; Barioni, L.G.; Benton, T.G.; Herrero, M.; Krishnapillai, M.; Waha, K. Chapter 5: Food security. In IPCC Special Report on Climate Change and Land; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 437–550. [Google Scholar]
- Seberini, A. Economic, social and environmental world impacts of food waste on society and Zero waste as a global approach to their elimination. SHS Web Conf. 2020, 74, 03010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, A.N.; Kearney, J.M.; O’Sullivan, E.J. The underlying role of food guilt in adolescent food choice: A potential conceptual model for adolescent food choice negotiations under circumstances of conscious internal conflict. Appetite 2024, 192, 107094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, J.; Alenčikienė, G.; Riipi, I.; Starkutė, U.; Čepytė, K.; Buraitytė, A.; Zabulionė, A.; Šalaševičienė, A. Exploring Causes and Potential Solutions for Food Waste among Young Consumers. Foods 2023, 12, 2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiriyaphanich, T.; Guinard, J.-X.; Spang, E.; Amsler Challamel, G.; Valgenti, R.T.; Sinclair, D.; Lubow, S.; Putnam-Farr, E. Food Choice and Waste in University Dining Commons—A Menus of Change University Research Collaborative Study. Foods 2021, 10, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebrok, M.; Boks, C. Household food waste: Drivers and potential intervention points for design—An extensive review. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 151, 380–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; van den Berg, M.; Nguyen, M. Food waste in primary schools: Evidence from peri-urban Viet Nam. Appetite 2023, 183, 106485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetherington, M.M.; Blundell-Birtill, P. The portion size effect and overconsumption—Towards downsizing solutions for children and adolescents. Nutr. Bull. 2018, 43, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermote, M.; Versele, V.; Stok, M.; Mullie, P.; D’Hondt, E.; Deforche, B.; Clarys, P.; Deliens, T. The effect of a portion size intervention on French fries consumption, plate waste, satiety and compensatory caloric intake: An on-campus restaurant experiment. Nutr. J. 2018, 17, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schanes, K.; Dobernig, K.; Gözet, B. Food waste matters—A systematic review of household food waste practices and their policy implications. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 182, 978–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravi, L.; Francioni, B.; Murmura, F.; Savelli, E. Factors affecting household food waste among young consumers and actions to prevent it. A comparison among UK, Spain and Italy. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 153, 104586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschemann-Witzel, J.; De Hooge, I.; Amani, P.; Bech-Larsen, T.; Oostindjer, M. Consumer-Related Food Waste: Causes and Potential for Action. Sustainability 2015, 7, 6457–6477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, M.; Meah, A. Food, waste and safety: Negotiating conflicting social anxieties into the practices of domestic provisioning. Sociol. Rev. 2012, 60, 102–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neff, R.A.; Kanter, R.; Vandevijvere, S. Reducing food loss and waste while improving the public’s health. Health Aff. 2015, 34, 1821–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betz, A.; Buchli, J.; Göbel, C.; Müller, C. Food waste in the Swiss food service industry–Magnitude and potential for reduction. Waste Manag. 2015, 35, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D. Blaming the consumer–once again: The social and material contexts of everyday food waste practices in some English households. Crit. Public Health 2011, 21, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonska, J.; Kodors, S.; Deksne, J.; Litavniece, L.; Zvaigzne, A.; Silicka, I.; Kotane, I. Reducing Plate Waste in Latvian Schools: Evaluating Interventions to Promote Sustainable Food Consumption Practices. Foods 2025, 14, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, M.P.; Burg, X.; Metcalfe, J.J.; Lipka, A.E.; Herritt, C.; Cunningham-Sabo, L. Healthy Planet, Healthy Youth: A Food Systems Education and Promotion Intervention to Improve Adolescent Diet Quality and Reduce Food Waste. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mingay, E.; Hart, M.; Yoong, S.; Palazzi, K.; D’Arcy, E.; Pursey, K.M.; Hure, A. The Impact of Modifying Food Service Practices in Secondary Schools Providing a Routine Meal Service on Student’s Food Behaviours, Health and Dining Experience: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malefors, C.; Sundin, N.; Tromp, M.; Eriksson, M. Testing interventions to reduce food waste in school catering. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 177, 105997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laila, A.; Gallant, M.; Bain, M.; Alexander, C.; Reis, L.; Welboren, A.; Von Massow, M.; Parizeau, K.; Walton, K.; Ma, D.W.L.; et al. Household Food Waste Intervention Is Feasible, Acceptable, and Effective. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2024, 56, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, G.C.B.S.D.; Azevedo, K.P.M.D.; Garcia, D.; Oliveira Segundo, V.H.; Mata, Á.N.D.S.; Fernandes, A.K.P.; Santos, R.P.D.; Trindade, D.D.B.D.B.; Moreno, I.M.; Guillén Martínez, D.; et al. Effect of School-Based Food and Nutrition Education Interventions on the Food Consumption of Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, G.; Burton, W.; Sinclair, M.; Bryant, M. Interventions to Strengthen Environmental Sustainability of School Food Systems: Narrative Scoping Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 5916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samad, N.; Bearne, L.; Noor, F.M.; Akter, F.; Parmar, D. School-based healthy eating interventions for adolescents aged 10–19 years: An umbrella review. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2024, 21, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri, A.R.; Larrick, R.P.; Hossain, S.; Patino-Echeverri, D. Consumers underestimate the emissions associated with food but are aided by labels. Nat. Clim. Change 2019, 9, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobronnikov, E.; Boyle, M.; Grosz, M.; Lipton, I.; Nutter, R.; Velez, M.; Yadav, L. Farm to School Literature Review; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Guffey, A.; Stewardson, D. Sowing Agricultural Literacy: The National Agriculture in the Classroom Organization. J. Agric. Food Inf. 2023, 24, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theurl, M.C.; Haberl, H.; Erb, K.-H.; Lindenthal, T. Contrasted greenhouse gas emissions from local versus long-range tomato production. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2014, 34, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.L.; Tan, P.Y.; Gong, Y.Y. Evaluating the impacts of school garden-based programmes on diet and nutrition-related knowledge, attitudes and practices among the school children: A systematic review. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monterrosa, E.C.; Frongillo, E.A.; Drewnowski, A.; De Pee, S.; Vandevijvere, S. Sociocultural Influences on Food Choices and Implications for Sustainable Healthy Diets. Food Nutr. Bull. 2020, 41, 59S–73S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Boer, J.; Schösler, H.; Aiking, H. Towards a reduced meat diet: Mindset and motivation of young vegetarians, low, medium and high meat-eaters. Appetite 2017, 113, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melina, V.; Craig, W.; Levin, S. Position of the academy of nutrition and dietetics: Vegetarian diets. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2016, 116, 1970–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, M.; Boeing, H.; Grünewald-Funk, D.; Heseker, H.; Kroke, A.; Leschik-Bonnet, E.; Oberritter, H.; Strohm, D.; Watzl, B. Vegan diet. Position of the German nutrition society (DGE). Ernahr. Umsch. 2016, 63, 92–102. [Google Scholar]
- Fedde, S.; Wießner, M.; Hägele, F.A.; Müller, M.J.; Bosy-Westphal, A. Ultra-processed foods and plant-based alternatives impair nutritional quality of omnivorous and plant-forward dietary patterns in college students. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 4233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, C.E.; Christian, M.S.; Cleghorn, C.L.; Greenwood, D.C.; Cade, J.E. Systematic review and meta-analysis of school-based interventions to improve daily fruit and vegetable intake in children aged 5 to 12 y. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 96, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, W.J.; Mangels, A.R. Position of the American Dietetic Association: Vegetarian diets. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2009, 109, 1266–1282. [Google Scholar]
- Seufert, V.; Ramankutty, N.; Foley, J.A. Comparing the yields of organic and conventional agriculture. Nature 2012, 485, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuck, S.L.; Winqvist, C.; Mota, F.; Ahnström, J.; Turnbull, L.A.; Bengtsson, J. Land-use intensity and the effects of organic farming on biodiversity: A hierarchical meta-analysis. J. Appl. Ecol. 2014, 51, 746–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.; Tilman, D. Comparative analysis of environmental impacts of agricultural production systems, agricultural input efficiency, and food choice. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 064016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Breiting, S.; Perez-Cueto, F.J.A. Effect of organic school meals to promote healthy diet in 11–13 year old children. A mixed methods study in four Danish public schools. Appetite 2012, 59, 866–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maini, E.; De Rosa, M.; Vecchio, Y. The Role of Education in the Transition towards Sustainable Agriculture: A Family Farm Learning Perspective. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeans, M.R.; Landry, M.J.; Vandyousefi, S.; Hudson, E.A.; Burgermaster, M.; Bray, M.S.; Chandra, J.; Davis, J.N. Effects of a school-based gardening, cooking, and nutrition cluster randomized controlled trial on unprocessed and ultra-processed food consumption. J. Nutr. 2023, 153, 2073–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McManus, S.; Pendergast, D.; Kanasa, H. The Intersection Between Food Literacy and Sustainability: A Systematic Quantitative Literature Review. Sustainability 2025, 17, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, S.L.; Barnes, S.P.; Wilkins, N.J. Scoping review of family and community engagement strategies used in school-based interventions to promote healthy behaviors. J. Sch. Health 2023, 93, 828–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, M.P.; Cleary, R.; Bonanno, A.; Costanigro, M.; Jablonski, B.B.R.; Long, A.B. Farm to School Activities and Student Outcomes: A Systematic Review. Adv. Nutr. 2020, 11, 357–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, B.; Costa Leite, J.; Rayner, M.; Stoffel, S.; Van Rijn, E.; Wollgast, J. Consumer interaction with sustainability labelling on food products: A narrative literature review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanks, C.B.; Banna, J.; Serrano, E.L. Food waste in the National School Lunch Program 1978-2015: A systematic review. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2017, 117, 1792–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.F.W.; Richardson, S.; Parker, E.; Catalano, P.J.; Rimm, E.B. Impact of the New U.S. Department of Agriculture School Meal Standards on Food Selection, Consumption, and Waste. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2014, 46, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eustachio Colombo, P.; Elinder, L.S.; Patterson, E.; Parlesak, A.; Lindroos, A.K.; Andermo, S. Barriers and facilitators to successful implementation of sustainable school meals: A qualitative study of the OPTIMAT™-intervention. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2021, 18, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bretter, C.; Unsworth, K.L.; Russell, S.V.; Quested, T.E.; Kaptan, G.; Doriza, A. Food waste interventions: Experimental evidence of the effectiveness of environmental messages. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 414, 137596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).