Abstract
The ever-increasing volumes of food waste generated and the associated environmental issues require the development of new processing methods for these difficult waste streams. One of the technologies that can treat these waste streams directly is hydrothermal carbonization. In this work, olive pomace and orange peels were treated via a mild hydrothermal carbonization process (TORWASH®) in a continuous-flow pilot plant. For olive pomace, a solid yield of 46 wt% and a dry matter content of 58% for the solid press cakes were obtained during continuous operation for 18 days. For orange peels, the values were lower with 31 wt% solid yield and a 42% dry matter content during 28 days of continuous operation. These values corresponded fully with initial laboratory-scale batch experiments, showing the successful transformation from batch to continuous processing. The obtained hydrochar from both feedstocks showed an increase in higher heating value (HHV) and a significant reduction in ash content. Pellets produced from the solids met the requirements for industrial use, demonstrating a large increase in the deformation temperature and a significant reduction in the potassium and chlorine content compared to the original feedstock. These results indicate the excellent potential of these pellets for combustion applications.
1. Introduction
The increasing world population and living standards result in an ever-increasing volume of food waste. Estimates of global food waste from citrus production and olive oil production are estimated at well over 50 Mt [1,2,3] and 15 Mt [4], respectively. The current disposal methods include incineration, composting and landfilling of the solid waste as well as direct reuse of contaminated process water on fields. These practices should be limited, as they result in significant greenhouse gas emissions, land and groundwater contamination and release of methane and acid gases [5]. Technical solutions for the valorization of these wet carbon-rich waste streams towards higher-value products, e.g., energy carriers, and targeted recovery of bioactive compounds should be further developed to establish sustainable and economically viable zero-waste biorefinery processes [6,7,8].
Hydrothermal carbonization (HTC) is a thermochemical process that is applied at mild reaction temperatures, typically ranging from 180 to 250 °C, with water as the reaction medium [9,10]. The major advantage of this process is the direct applicability of wet (biomass) streams, which excludes the use of an energy-intensive drying step [11]. During the HTC process, multiple reactions take place simultaneously, including hydrolysis, dehydration, decarboxylation, condensation and repolymerization [10,12,13,14]. The effect of these reactions is a decrease in both the atomic H/C and atomic O/C ratio, moving towards values that are typical for lignite [15,16]. The main products obtained during the process are a solid fraction (hydrochar) and a carbon-rich aqueous solution. The product distribution and characteristics are determined by the process conditions used and the type and composition of the feedstock. The most important process parameter is the reaction temperature. Higher temperatures result in more degradation reactions, lowering the solid yield [9,10,13]. The solid hydrochar product obtained at higher temperatures typically has better fuel properties, but the liquid stream becomes less suitable for digestion due to the formation of phytotoxic components [17,18,19,20]. Additionally, the dewaterability of the obtained product slurry into the solid and liquid products increases with a higher reaction temperature [21]. Another important parameter is the reaction time. A longer exposure at reaction conditions results in a higher carbon content in the hydrochar [19]. The solid yield decreases with extended reaction time, although an initial increase in yield can be observed due to secondary char formation, i.e., the repolymerization of the dissolved components in the aqueous phase to hydrochar [11,22,23]. The biomass to water ratio influences the product yield, as a higher water concentration results in more extensive hydrolysis reactions, resulting in a lower solid yield [10]. The type of applied feedstock has a high influence on both the solid yield and final properties. Lignin-rich feedstocks typically give high solid yields, whereas feedstocks that are rich in hemicellulose tend to give low hydrochar yields [24,25]. Another benefit of water as the reaction medium is the removal of many water-soluble alkali metals and salts from the solid phase. This significantly enhances the combustion behavior of the hydrochar solid product, according to reduced slagging and corrosion at an elevated temperature, due to the reduction in the potassium and chlorine content [11,26,27]. In the past years many application studies have been performed on hydrochar. The bulk of these papers focus on the use of hydrochar as an energy carrier [16,20,28,29,30,31]. Other applications that are commonly reported for hydrochar are the use as an adsorbent (e.g., CO2), for pollutant removal (like metals and dyes), as a soil amendment and as a carbon sequestration medium [13,32,33,34]. Recently, some more dedicated papers have focused on its use as a metallurgic reducing agent [35,36,37], as a source for nutrient recovery [38,39] and in the recovery of valuable compounds like fatty acids and phenols from the HTC products [40,41]. Additional research in these areas would be valuable, especially at a pilot scale, as recovery of valuable compounds can further improve the business case and feasibility of HTC processes in industry.
In recent years, there have been many reports on hydrothermal carbonization of olive pomace and orange peels at a wide range of temperatures. At the mildest processing temperatures (180–200 °C), solid yields of 55–75% have been reported for olive pomace [9,26,35,42,43,44,45,46], whereas with orange peel, the solid yield ranges from 34 to 45% at these temperatures [1,2,3,34]. These relatively low values clearly show that valorization of the liquid stream, e.g., as biogas, is essential for the economic feasibility of the process [8,47], complemented with the recovery of valuable bioactive compounds [6]. Additionally, these results clearly show the differences between feedstocks and highlight the requirement for a robust (reactor) process for treating a wide range of feedstocks.
One of the factors that is currently limiting the implementation of the HTC technology is the lack of knowledge on continuous pilot-scale operation. We have previously reported the successful hydrothermal treatment of biosludge from a paper mill in a continuous flow-through (TORWASH®) reactor [48] and a process model which showed a much more efficient feedstock utilization for the production of energy [49]. An overall block diagram of the continuous treatment of wet organic residue streams to solid hydrochar is shown in Figure 1. Based on this earlier work, the main objective of this study is to evaluate continuous, pilot-scale HTC testing with biogenic residue streams with a significantly higher dry matter content (e.g., 20 wt%), namely, olive pomace and orange peels. This ultimately contributes to the overall sustainability of these agrofood industries by demonstrating the feasibility of HTC for residue valorization. Initial work is performed at laboratory-scale to determine the optimal process conditions in terms of solid yield and dewaterability, and these results are used as a starting point to establish a continuous, pilot-scale hydrothermal carbonization process.
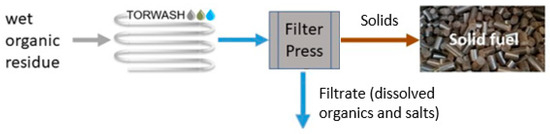
Figure 1.
Block diagram of the process steps from the initial wet organic residue stream to solid fuel (hydrochar).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Feedstock
Olive pomace was provided by APPO (Bari, Italy). Olive pomace is the olive pulp that remains after the mechanical extraction of oil from olives and an olive stone removal step and therefore contains some oil (approximately 3%) as well as some residual olive stones (smaller than 3 mm size). The feedstock was used as received. Orange peels were provided by Delafruit (La selva del Camp, Spain). This feedstock was diluted with water (2:1 water/feed ratio) and milled with an immersion blender to obtain a smooth paste suitable for processing. For the continuous-flow process, the orange peels were ground and filtered through a 5 mm sieve.
2.2. TORWASH Process
A mild hydrothermal carbonization treatment was applied to olive pomace and orange peels. This was performed via a patented process (TORWASH®) that applies HTC to wet biogenic residues via a unique reactor technology. During the process, an effluent is obtained that can be much more easily dewatered than the initial feedstock. Dewatering yields a solid product (hydrochar) and a liquid fraction in which part of the salts and organic material is dissolved. The liquid stream is biodegradable and can be applied for biogas production.
2.3. Lab-Scale Batch Experiments
The first experiments were carried out in small microclaves (125 mL) to determine the best temperature for an optimal balance between solid yield and dewaterability. A small temperature range (170–200 °C) was screened for both feedstocks. For olive pomace, every experiment was performed with 75 g of sample, while for orange peel, a 2:1 weight ratio water/orange peel was used to obtain a mixture that could be stirred, with a total volume of 75 g. The reactor was heated to the target temperature in a heating block and held for 30 min at this temperature while maintaining a constant stirring speed of 500 rpm.
Larger-scale laboratory experiments were performed at the optimal reaction temperature as determined by the small-scale reactions. A stainless-steel vessel (20 L, indirectly heated) was used for these experiments. For olive pomace, 15 kg was added to the reactor, while for orange peel, 5 kg of the feedstock and 10 kg of demineralized water were used for the experiment. The reactor was held for 30 min at the set reaction temperature after a relatively slow heating period of 3 h.
2.4. Pilot-Scale Continuous-Flow Experiments
Based on the results of the laboratory-scale experiments, continuous testing was conducted in a pilot-scale reactor, initially targeting the optimized temperature identified at laboratory-scale. The pilot-scale equipment has a maximum capacity of 50 kg/h throughput. A detailed description of the pilot reactor has been previously reported [48].
The pilot plant applies three different temperatures during the process. In the first part, the feedstock is heated to roughly 150 °C; in this stage, the reactivity is limited to some initial hydrolysis reactions. During the second part, the feedstock is heated to the optimal reaction temperature (190 °C for olive pomace, 195 °C for orange peel, ~1 h residence time). In the final part, the reaction mixture is cooled, followed by a depressurization step and collection of the product slurry in tanks. On average, 25 kg/h of diluted feedstock was processed, with an approximate total residence time of 2 h.
2.5. Dewatering Experiments
At laboratory-scale, the product produced after mild HTC was filtered (2.7 µm Whatman GF/D glass microfiber filter) to separate the solids. These solids were then dewatered mechanically via pressing in a 58 mm diameter carver die fitted with 20 µm pore size nylon filters. The press was operated for a period of 1 min at 65 bar pressure to create a solid cake. At pilot-scale, the effluent from the HTC reactor was dewatered using a pilot-scale membrane filter press (Limburg Filter, Maastricht, The Netherlands). The effluent was pumped into the filter press chambers, and the pressure was increased to mechanically separate the solid and liquid fractions. This was followed by a squeezing phase to further dewater the solids into solid press cakes.
2.6. Pellet Production and Mechanical Durability Determination
Pelleting of orange peel hydrochar was performed at CPM. The material was grounded with a hammer mill and fed to the ring die pelletizer. For olive pomace hydrochar, a different pelletizer was required (flat die pelletizer, top loaded) to obtain durable pellets. Mechanical durability of the pellets was determined with a tumbler, in which 500 g of pellets was tumbled for 10 min. The total weight of the remaining pellets was measured to determine the mechanical durability.
2.7. Analyses
The feed slurries, HTC effluent and dewatering products (solid press cakes and liquid filtrate) were analyzed for dry matter content via drying overnight at 105 °C and atmospheric pressure. This analysis was very important as it was used as the main indicator of dewaterability of the material after HTC.
Dried samples of each of these streams were also analyzed for elemental content (Element Analyser Flash 2000 from Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Specifically, C, H and N content was evaluated according to EN 15104 [50]. Ash content was measured according to EN 14775 [51] with a Nabertherm LV5/11/B180 oven (Nabertherm GmbH, Lilienthal, Germany). The higher heating value (HHV) of the materials was measured via EN 14918 [52], and volatile matter was analyzed according to method EN 15148 [53]. Inductively coupled plasma (ICP) was used to measure concentrations of inorganics (ICAP6300 ICP-OES, Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) following the NEN 6963 [54] and NEN 6966 [55] standards. The elements F, Br and Cl were assessed according to NEN-EN-ISO-10304-1 [56], and the mercury concentration was assessed via cold vapor atomic fluorescence spectroscopy.
For liquid samples, dissolved chemical oxygen demand (COD), phosphorus and nitrogen were measured via the Hach Lange cuvette testing method.
The ash melting behavior was determined according to EN ISO 21404:2020-06 [57] in an oxidizing atmosphere.
XRF analysis of the ashes was carried out at the Institute for Chemical Technologies and Analytics at the TU Wien. The ash was produced according to EN ISO 18122:2015-11 [58]. The measurement was performed with a Panalytical Axios Advanced system.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Feedstock Analysis
Analysis of olive pomace and orange peels showed that the two feedstocks are relatively similar in composition as can be seen in Table 1. Both feedstocks are acidic, the dry matter content of the two streams is very similar (~20 wt%) and both the ash content and volatile matter are very similar. The main differences between the feedstocks are the significantly higher carbon content of olive pomace and the associated higher heating value (also partially caused by residual oil). The conductivity of olive pomace is also significantly higher, as indicated by the higher sulfur and chloride content. The most striking characteristic of orange peel is the very high oxygen content. The reported values and differences between the feedstocks corresponded fully with literature values [46,59].

Table 1.
Characteristics of olive pomace and orange peels as received. db = dry basis; analysis of solids that were dried at 105 °C.
3.2. Batch Experiments
Initial small-scale screening experiments were performed on batch scale to gain more insight into the hydrothermal carbonization process of the two feedstocks. A small-scale temperature study using microclaves (75 g feed) and olive pomace showed similar values for temperatures ranging from 170 to 190 °C for both solid yield (46–49 wt%) and dry matter content of the obtained press cakes (61–63%) (Table 2). Increasing the temperature to 200 °C showed a relatively sharp decrease in solid yield. An indication for an effective carbonization process is a decrease in pH as a result of the formation of organic acids, which is supported by the obtained results. Furthermore, an increase in the conductivity of the product slurry is an indication of more dissolved salts, which is corroborated by a lower ash content in the solids obtained after dewatering. As the pH of the obtained product slurry at 190 °C (4.40) was a bit lower compared to lower temperatures (4.48–4.49) and the conductivity a bit higher, 190 °C was selected as the target temperature for subsequent experiments. Typically, the desired process temperature is selected based on a compromise between the highest solid yield and highest dry matter content. An experiment in an autoclave (15 kg feed) performed at 190 °C showed similar results with a solid yield well in line with the microclave experiment (47 wt%), a somewhat higher dry matter content for the obtained press cake (68%) and a slightly lower pH of 4.35 compared to the small-scale experiment at 190 °C. The small differences are likely an effect of the slower heating and cooling profile of the autoclave, effectively resulting in a slightly longer effective reaction time. These results clearly show that large increases in the reactor size and the amount of feed do not have an effect on the hydrothermal carbonization process. The obtained values are slightly lower than previously reported solid yields for the HTC of olive pomace (55–75%) [9,26,35,42,43,44,45,46], which could be a result of the high moisture content of the applied reaction mixture.

Table 2.
Solid yield and dry matter content of the obtained press cakes after hydrothermal carbonization of olive pomace.
The small-scale screening study with orange peels showed that the orange peels (milled into small pieces) could not be used as received, as this feedstock could not be stirred. Therefore, a 2:1 water/orange peel mixture was applied for these experiments to ensure proper mixing during the hydrothermal carbonization process, as this dilution allowed for good stirring (a 1:1 ratio was still difficult to stir). The small-scale experiments in the microclave at 170 °C and 180 °C showed similar results in terms of solid yield (33–35 wt%) and dry matter content (57–60%) as can be seen in Table 3. As the solid yield was already low at these temperatures, no experiments were performed at higher temperatures. The pH of the slurry after the carbonization process was slightly lower than that of the feedstock, but due to the acidic nature of the feed, this effect was rather limited. Performing the experiments at larger scale showed excellent reproducibility in terms of dry matter content of the press cake and a small improvement in the obtained solid yield. Based on these results, a process temperature of 170 °C was deemed as optimal. The obtained solid yields are in excellent agreement with reported literature values [1,2,3,34].

Table 3.
Obtained solid yield and dry matter content of the obtained press cakes after hydrothermal carbonization of orange peel.
3.3. Pilot-Scale Continuous-Flow Experiments
3.3.1. Optimization
As preparation for the hydrothermal carbonization experiments in a continuous-flow reactor for a prolonged time, the effect of feed concentration was tested. Previous experience with sludges has shown that feed concentrations up to 5 wt% can be processed without issues in a continuous-flow reactor [48]. The main effects analyzed in these tests were the pumpability of the feedstock and the effect of the feed concentration on the flow and temperature profile in the reactor. Direct addition of the olive pomace resulted in blocking of the pump. By reducing the feed concentration to 8 wt%, this issue was resolved for both olive pomace and orange peels. During prolonged operation with these feedstocks (6–8 h), an inconsistent flow and temperature profile were observed, with decreasing performance over time. Upon inspection of the flow reactor, it was noticed that for both feedstocks, some settling had occurred in the reactor. This was likely a combined effect of both feedstock concentration and low internal velocity of the reactor. With some reactor modifications to increase the internal velocity and by decreasing the feed to 4 wt%, consistent process performance was achieved.
With stable performance, the effect of the reactor temperature could be studied. For olive pomace, the established optimal temperature was 190 °C. At the initial starting settings, an average temperature of 185 °C was achieved. Analysis of the obtained press cakes showed a solid yield of 49 wt% and a dry matter content of 60% (Table 4), which corresponded fully with the batch reactor results at 180 °C (Table 2). Increasing the reactor temperature by 10 °C resulted in the expected small drop in solid yield to 44 wt% and increase in dry matter content of the obtained press cakes to 64% (average of three cakes, ranging from 63 to 65% dry matter content). Based on these results, it was concluded that during long-duration operation, the process temperature should remain below 190 °C in order to have the highest solid yield in combination with a high dry matter content.

Table 4.
Obtained solid yield and dry matter content of the obtained press cakes of olive pomace and orange peel after hydrothermal carbonization in the continuous-flow reactor. a feedstock as used (diluted), b accumulation of solid material observed in the reactor.
With orange peel, the obtained results were less in line with the corresponding batch experiments. The product slurry obtained at 180 °C was not pressable into a solid cake. At higher temperatures, the product slurry became pressable, with the slurries obtained at 190 °C and 200 °C being significantly easier and more consistent to dewater compared to the slurry obtained at 185 °C (Table 4). This can also be seen in the dry matter content of the obtained press cakes at 190 and 200 °C, with a 56–57% average dry matter content and values ranging from 52 to 60% compared to a 50% average dry matter content at 185 °C and values ranging from 41 to 55%. The pH also decreased with increasing temperature, indicating a better carbonization process. The results for the solid yield showed an unexpected increase in solid yield with increasing temperature. Closer analysis of the product slurry showed an increase in dry matter content over time of the continuous testing, which is caused by accumulation of solids in the reactor. As the higher temperatures were tested at the later stage of the test, the results at the lower temperatures are likely an underestimation, and longer process time is required to obtain a more reliable number. However, the obtained values for the solid yield are in the same range compared to the batch experiments at a somewhat lower temperature. This shows that for this feedstock, higher reactor temperatures are required for continuous-flow operation.
3.3.2. Long-Duration Operation
The performance of the pilot-scale reactor for an extended time period was performed onsite at the feedstock suppliers to ensure a constant and fresh supply of the feedstock. For olive pomace, the reactor was continuously operated for 18 days, with regular cleaning sessions every 3–4 days due to accumulation of olive stones in the reactor which decreased the reactor performance. The target temperature was set at 185 °C and ranged between 175 and 191 °C during the long-duration operation, with the lower values prior to reactor cleaning. Initial operation was performed with a 4 wt% feed concentration, which was successfully increased stepwise up to 5.8 wt% at the later stages of operation.
During the long-duration operation, approximately 8500 kg of diluted olive pomace was treated, which yielded 334 kg of wet press cake after dewatering with a membrane filter press (Figure 2). The obtained press cakes had an average dry matter content of 58% with very consistent values of 55–60% for over 50 press cakes produced. Some olive stones could be detected in the press cake, showing that the olive stones are not converted at the applied process conditions. The values for the dry matter content were very comparable to the press results during batch operation, despite using a different kind of filter equipment for the pilot plant, which applies a significantly lower pressure (16 bar compared to 65 bar), showing that the hydrochar can be dewatered easily. The total amount of obtained dry press cake corresponded to a total solid yield of 46 wt%, which corresponded fully with the results for the reactor optimization test and corresponding batch experiments.

Figure 2.
Wet press cake obtained after dewatering of the product slurry after carbonization of olive pomace.
Analysis of the product streams during continuous operation showed the same values for the solid yield (difference between product slurry and filtrate, Table 5). This analysis also showed a loss of solids during the reaction of the feedstock to the product slurry, which is a combined effect of gas formation and accumulation of solids in the reactor. Further analysis of the product streams showed a decrease in the pH and an increase in conductivity, which is in agreement with batch experiments. After hydrothermal carbonization, the COD and phosphate content did show an increase, and a significant increase in total nitrogen content was observed. This makes the filtrate not only an interesting stream for digestion but also a potential nutrient source.

Table 5.
Characteristics of the olive pomace feed, product slurry and filtrate obtained at 190 °C process temperature. Reported values for COD, total nitrogen and (PO4)3− correspond to the dissolved fraction.
The long-duration testing of orange peels was performed for 28 days, during which over 10,000 kg of feedstock was treated. The initial target temperature was set at 195 °C, which was later slightly increased to be in the range of 195–200 °C. After the feed size was reduced to 3 mm, the temperature could be maintained consistently between 190 and 200 °C. The 10,000 kg of treated orange peel yielded 281 kg of wet press cake after dewatering with a membrane filter press. The obtained press cakes had an average dry matter content of 42% but with a relatively wide deviation ranging between 33 and 47% for over 60 press cakes. This corresponds to a solid yield of 31 wt%, which is slightly lower compared to the values obtained for batch operation.
A sharp temperature effect on the dewaterability was observed during the long-duration test. Daily sample analysis showed that the product slurry was significantly harder to dewater if the operation temperature was below 195 °C. The lower temperatures were mainly during the first week of operation as a result of the larger particle size of the feed. Therefore, the average dry matter content of the first batch of press cakes was lower with an average dry matter content of 39% compared to the subsequent three batches with an average dry matter content of 43%. Another observation of the daily analysis was the improved process performance after 2 days of operation, yielding press cakes with a clearly higher dry matter content (~3% improvement) at the same process conditions. This is likely a result of the autocatalytic effect of the carbonization process, which takes relatively long to establish due to the constant addition of fresh feedstock and the removal of product slurry.
The results show a much lower dry matter content for the long-duration experiment (15% decrease) compared to the optimization experiments, but this is due to the use of a different dewatering technique at pilot-scale operation (membrane filter press, 16 bar squeezing pressure) compared to the optimization experiments (hydraulic lab press, 65 bar operating pressure). Comparing this with olive pomace shows a clear difference, as for olive pomace, this difference was only 2%. This indicates that orange peel is inherently more difficult to dewater, which is likely the reason for the higher temperature sensitivity of orange peel.
Analysis of the product streams (Table 6) showed a clear decrease in dry matter content after each process step. A significant decrease in dry matter content occurred during the carbonization process, which could be an effect of the high oxygen content of the feed resulting in gas formation. This could be seen in the higher gas production with orange peel (40–50 L/h) compared to olive pomace (15–20 L/h). Furthermore, it shows that over half of the dry matter content present in the product slurry ends up in the filtrate, explaining the low solid yield for orange peel as feedstock. The pH showed an unexpected increase in pH during the carbonization process. It should be noted that the pH of the fresh orange peel feedstock (3.63) was lower than the pH of the feed used during the optimization study (3.96), indicating that some acidic compounds present appear to be prone to degradation. The higher pH of the product slurry confirms that the carbonization reaction is not as effective for orange peel in a flow-through reactor compared to a batch reactor at the current conditions and that some process modifications are required. The conductivity shows an expected increase, showing the dissolution of salts in the product slurry.

Table 6.
Characteristics of the orange peel feed, product slurry and filtrate obtained at 195 °C process temperature. Reported values for COD, total nitrogen and (PO4)3− correspond to the dissolved fraction.
3.4. Hydrochar Quality and Combustion Potential
The obtained hydrochars from both olive pomace and orange peel were analyzed, and some notable changes were observed compared to the original feedstock (Table 7). Firstly, a clear increase in HHV was observed for both feedstocks, with the hydrochar from olive pomace showing particularly high values. The increase in fixed carbon and decrease in oxygen content corresponded with this increased value. For both hydrochars, a large reduction in ash content, up to 84% for olive pomace, was achieved by hydrothermal carbonization.

Table 7.
Characteristics of olive pomace and orange peel feedstock and the obtained hydrochar from both feedstocks. db = dry basis; analysis of solids that were dried at 105 °C.
Pelleting of the obtained hydrochars showed some clear differences between the obtained pellets. Pellets obtained from orange peel hydrochar were very robust, whereas pellets from olive pomace hydrochar, although they showed initially high durability, were more powdery upon storage and shipping (Figure 3). The latter is likely caused by the presence of some residual oil in the hydrochar, resulting in a lower integrity of the pellets.

Figure 3.
Robust orange peel pellets (left) and weak, powdery olive pomace pellets (right) obtained from pelleting the obtained press cakes.
A more detailed analysis of the pellets showed that apart from the high values for the heating value, the pellets derived from both treated olive pomace and orange peel also showed a high bulk density (approximately 600 kg/m3) and high mechanical durability (>95%) (Table 8). A comparison with pellet standards showed that the produced pellets are close to meeting the wood pellet standards (ENplus B [60]) and easily meet the biomass pellet standards (coal Illinois No. 6 [61]). With a proper selection of hydrochars obtained from different feedstocks, and potentially some blending with wood, the production of pellets that meet the wood pellet standard should be feasible.

Table 8.
Characteristics of the obtained pellets from treated olive pomace and orange peel and comparison with wood pellet (ENplus B) and industrial pellet (coal Illinois No. 6) standards.
In order to gain additional insight into the potential of the hydrochar for combustion and pyrolysis, both the ash melting behavior and ash composition were determined. For both olive pomace and orange peel, a significant increase in deformation temperature could be observed for the hydrochar compared to the initial feedstock (Table 9). The deformation temperature of 1380 °C of orange peel hydrochar indicates excellent applicability in high-temperature furnaces, as it is significantly higher than the 1200 °C requirement [60]. Analysis of the ash composition shows a very significant reduction in most elements. Most noticeable, the potassium and chlorine contents show a 200-fold reduction for olive pomace and a 30-fold reduction for orange peels (Table 9) when the total solid yield for both feedstocks is also taken into consideration. This is highly favorable for the combustion performance, clearly indicating the value of the TORWASH process as a pretreatment step for the production of an intermediate energy carrier from biogenic residues. The results show that most elements dissociate efficiently to the liquid phase, with the clear exception of calcium. The total mass of the ash consists primarily of CaO, with a 52% abundance in olive pomace hydrochar and a 69% abundance in orange peel hydrochar. These CaO-enriched ashes could be potentially valuable for other applications.

Table 9.
Ash melting behavior and elemental composition of the feedstock and obtained hydrochar for both olive pomace and hydrochar. Elemental composition is shown as a percentage of the ash content and as a percentage of the total solids.
4. Conclusions
This paper demonstrates the successful scale-up of hydrothermal carbonization of agricultural residues from a batch laboratory-scale process to a continuous-flow pilot process. This ultimately contributes to the sustainability of agrofood industries by demonstrating a feasible option for valorizing wet residue streams. For both olive pomace and orange peel, initial laboratory-scale experiments were performed to determine the optimal conditions. For olive pomace, 190 °C was found to be the optimal temperature, with a 47 wt% solid yield and a dry matter solid content of 68%. For orange peel, the optimal temperature was 170 °C, resulting in a 45 wt% yield with a 56% dry matter content. Based on these results and after some initial pilot-scale optimization, a successful long-duration test was performed for both olive pomace and orange peels for 18 days and 28 days, respectively. For olive pomace, a solid yield of 46 wt% was obtained with an average dry matter content of 58% for the obtained press cake. For orange peel, a solid yield of 31 wt% was obtained with an average dry matter content of 42%. The obtained values correspond with the batch experiments performed at laboratory-scale and with the reported literature values for both olive pomace and orange peel, although on the lower side of the reported range due to the required dilution for good pumpability, resulting in more hydrolysis reactions. The obtained hydrochar showed a clear increase in higher heating value due to an increased fixed carbon percentage and a significant decrease in the ash content. This work shows not only the important transition towards a continuous process but also that further improvements like feedstock preparation and a more concentrated feed are required to make the process suitable for direct use of biogenic residues. Follow-up studies on the combustion performance of hydrochar (pellets) compared to the initial feedstock would verify the expected increased performance based on the results for ash melting temperature and elemental composition. Additionally, the filtrate is rich in dissolved organics. The recovery of valuable products present in the stream and evaluation of the potential of aerobic digestion for biogas production should be investigated to allow for valorization of all obtained product streams.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization., P.N., J.R.P. and H.E.W.; methodology, E.C.-P., M.V. and D.J.S.; validation, P.N., J.R.P. and H.E.W.; investigation, E.C.-P., M.V. and D.J.S.; resources, P.N. and H.E.W.; data curation, D.S.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, D.S.Z. and M.V.; writing—review and editing, H.E.W., J.R.P. and P.N.; supervision, H.E.W. and P.N.; project administration, H.E.W.; funding acquisition, P.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under grant agreement No. 884226.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Frank Kruip and Marco Ugolini for their assistance during the onsite trials. The Test Laboratory for Combustion Systems at TU Wien is acknowledged for performing the ash melting measurements and Florian Benedikt and Florian J. Müller from TU Wien are acknowledged for interpretating the data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analysis or interpretation of data; in writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Deepak, K.R.; Mohan, S.; Dinesha, P.; Balasubramanian, R. CO2 uptake by activated hydrochar derived from orange peel (Citrus reticulata): Influence of carbonization temperature. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 342, 118350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Q.; Kannan, S.; Raghavan, V. Uncatalyzed and acid-aided microwave hydrothermal carbonization of orange peel waste. Waste Manag. 2021, 126, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satira, A.; Paone, E.; Bressi, V.; Iannazzo, D.; Marra, F.; Calabrò, P.S.; Mauriello, F.; Espro, C. Hydrothermal Carbonization as Sustainable Process for the Complete Upgrading of Orange Peel Waste into Value-Added Chemicals and Bio-Carbon Materials. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, M.; Wust, D.; Merzari, F.; Lucian, M.; Andreottola, G.; Kruse, A.; Fiori, L. One stage olive mill waste streams valorisation via hydrothermal carbonisation. Waste Manag. 2018, 80, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manhongo, T.T.; Chimphango, A.F.A.; Thornley, P.; Röder, M. Current status and opportunities for fruit processing waste biorefineries. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 155, 111823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paini, J.; Benedetti, V.; Ail, S.S.; Castaldi, M.J.; Baratieri, M.; Patuzzi, F. Valorization of Wastes from the Food Production Industry: A Review Towards an Integrated Agri-Food Processing Biorefinery. Waste Biomass Valorization 2021, 13, 31–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Sanchez, M.; Solarte-Toro, J.C.; Orrego-Alzate, C.E.; Acosta-Medina, C.D.; Cardona-Alzate, C.A. Integral use of orange peel waste through the biorefinery concept: An experimental, technical, energy, and economic assessment. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2020, 11, 645–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ipiales, R.P.; de la Rubia, M.A.; Diaz, E.; Mohedano, A.F.; Rodriguez, J.J. Integration of Hydrothermal Carbonization and Anaerobic Digestion for Energy Recovery of Biomass Waste: An Overview. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 17032–17050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedner, K.; Naisse, C.; Rumpel, C.; Pozzi, A.; Wieczorek, P.; Glaser, B. Chemical modification of biomass residues during hydrothermal carbonization—What makes the difference, temperature or feedstock? Org. Geochem. 2013, 54, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Hameed, B.H.; Siddiqui, M.R.; Alothman, Z.A.; Alsohaimi, I.H. Hydrothermal Conversion of Food Waste to Carbonaceous Solid Fuel-A Review of Recent Developments. Foods 2022, 11, 4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, M.; Fiori, L. From olive waste to solid biofuel through hydrothermal carbonisation: The role of temperature and solid load on secondary char formation and hydrochar energy properties. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2017, 124, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauline, A.L.; Joseph, K. Hydrothermal carbonization of organic wastes to carbonaceous solid fuel—A review of mechanisms and process parameters. Fuel 2020, 279, 118472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavali, M.; Libardi Junior, N.; de Sena, J.D.; Woiciechowski, A.L.; Soccol, C.R.; Belli Filho, P.; Bayard, R.; Benbelkacem, H.; de Castilhos Junior, A.B. A review on hydrothermal carbonization of potential biomass wastes, characterization and environmental applications of hydrochar, and biorefinery perspectives of the process. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, J.; Qian, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhai, Y. Biowaste hydrothermal carbonization for hydrochar valorization: Skeleton structure, conversion pathways and clean biofuel applications. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 324, 124686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Xiang, W.; Wang, R.; Ding, F.; Hong, P.; Gao, B. Straw and wood based biochar for CO2 capture: Adsorption performance and governing mechanisms. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 287, 120592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.B.; Sarmah, A.K.; Dubey, B. Hydrothermal carbonization of renewable waste biomass for solid biofuel production: A discussion on process mechanism, the influence of process parameters, environmental performance and fuel properties of hydrochar. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 123, 109761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhakta Sharma, H.; Panigrahi, S.; Dubey, B.K. Food waste hydrothermal carbonization: Study on the effects of reaction severities, pelletization and framework development using approaches of the circular economy. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 333, 125187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, D.; Stark, A.; Kammann, C.I.; Glaser, B. Genotoxic and phytotoxic risk assessment of fresh and treated hydrochar from hydrothermal carbonization compared to biochar from pyrolysis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 97, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Ma, X.; Lin, Y. Effects of hydrothermal treatment temperature and residence time on characteristics and combustion behaviors of green waste. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 104, 678–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saqib, N.U.; Baroutian, S.; Sarmah, A.K. Physicochemical, structural and combustion characterization of food waste hydrochar obtained by hydrothermal carbonization. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 266, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäkelä, M.; Benavente, V.; Fullana, A. Hydrothermal carbonization of lignocellulosic biomass: Effect of process conditions on hydrochar properties. Appl. Energy 2015, 155, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ischia, G.; Cutillo, M.; Guella, G.; Bazzanella, N.; Cazzanelli, M.; Orlandi, M.; Miotello, A.; Fiori, L. Hydrothermal carbonization of glucose: Secondary char properties, reaction pathways, and kinetics. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 449, 137827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, M.; Picone, A.; Luz, F.C.; Mosonik, M.C.a.; Volpe, R.; Messineo, A. Potential pitfalls on the scalability of laboratory-based research for hydrothermal carbonization. Fuel 2022, 315, 123189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Yi, L.; Zhang, X.; Hu, H.; Yao, H. Correlations between hydrochar properties and chemical constitution of orange peel waste during hydrothermal carbonization. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 265, 432–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Berge, N.D. Influence of feedstock chemical composition on product formation and characteristics derived from the hydrothermal carbonization of mixed feedstocks. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 166, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, L.J.; Fendt, S.; Spliethoff, H. Comparison of Fuels and Effluents Originating from Washing and Hydrothermal Carbonisation of Residual Biomass. Waste Biomass Valorization 2021, 13, 2321–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhai, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Gan, X.; Zheng, L.; Peng, C.; Wang, B.; Li, C.; Zeng, G. Evaluation of the clean characteristics and combustion behavior of hydrochar derived from food waste towards solid biofuel production. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 266, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djandja, O.S.; Liew, R.K.; Liu, C.; Liang, J.; Yuan, H.; He, W.; Feng, Y.; Lougou, B.G.; Duan, P.G.; Lu, X.; et al. Catalytic hydrothermal carbonization of wet organic solid waste: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 873, 162119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wang, Q.; Fang, M.; Wu, D.; Cui, D.; Pan, S.; Bai, J.; Xu, F.; Wang, Z. Hydrothermal carbonization of food waste for sustainable biofuel production: Advancements, challenges, and future prospects. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 897, 165327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavente, V.; Calabuig, E.; Fullana, A. Upgrading of moist agro-industrial wastes by hydrothermal carbonization. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2015, 113, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koçer, A.T.; Özçimen, D.; Gökalp, İ. An experimental study on the combustion behaviours of orange peel-based solid biofuels. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espro, C.; Satira, A.; Mauriello, F.; Anajafi, Z.; Moulaee, K.; Iannazzo, D.; Neri, G. Orange peels-derived hydrochar for chemical sensing applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 341, 130016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basakcilardan Kabakci, S.; Baran, S.S. Hydrothermal carbonization of various lignocellulosics: Fuel characteristics of hydrochars and surface characteristics of activated hydrochars. Waste Manag. 2019, 100, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, M.E.; Ledesma, B.; Roman, S.; Bonelli, P.R.; Cukierman, A.L. Development and characterization of activated hydrochars from orange peels as potential adsorbents for emerging organic contaminants. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 183, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surup, G.R.; Leahy, J.J.; Timko, M.T.; Trubetskaya, A. Hydrothermal carbonization of olive wastes to produce renewable, binder-free pellets for use as metallurgical reducing agents. Renew. Energy 2020, 155, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb Abhi, T.; Norouzi, O.; Macdermid-Watts, K.; Heidari, M.; Tasnim, S.; Dutta, A. Miscanthus to Biocarbon for Canadian Iron and Steel Industries: An Innovative Approach. Energies 2021, 14, 4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Nanou, P.; Wray, H.; Zhang, J.; Lundstrom, I.; Lundqvist, S.; Wang, C. Feasibility Study of Bio-Sludge Hydrochar as Blast Furnace Injectant. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaf, N.; Leahy, J.J.; Kwapinski, W. Phosphorus recovery from hydrothermal carbonization of organic waste: A review. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2023, 98, 2365–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragón-Briceño, C.I.; Pozarlik, A.K.; Bramer, E.A.; Niedzwiecki, L.; Pawlak-Kruczek, H.; Brem, G. Hydrothermal carbonization of wet biomass from nitrogen and phosphorus approach: A review. Renew. Energy 2021, 171, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimenez, M.; Rodríguez, M.; Montoro, L.; Sardella, F.; Rodríguez-Gutierrez, G.; Monetta, P.; Deiana, C. Two phase olive mill waste valorization. Hydrochar production and phenols extraction by hydrothermal carbonization. Biomass Bioenergy 2020, 143, 105875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motavaf, B.; Dean, R.A.; Nicolas, J.; Savage, P.E. Hydrothermal carbonization of simulated food waste for recovery of fatty acids and nutrients. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 341, 125872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzaz, A.A.; Jeguirim, M.; Kinigopoulou, V.; Doulgeris, C.; Goddard, M.L.; Jellali, S.; Matei Ghimbeu, C. Olive mill wastewater: From a pollutant to green fuels, agricultural and water source and bio-fertilizer—Hydrothermal carbonization. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 139314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missaoui, A.; Bostyn, S.; Belandria, V.; Cagnon, B.; Sarh, B.; Gökalp, I. Hydrothermal carbonization of dried olive pomace: Energy potential and process performances. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2017, 128, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzaz, A.A.; Matei Ghimbeu, C.; Jellai, S.; El-Bassi, L.; Jeguirim, M. Olive Mill by-Products Thermochemical Conversion via Hydrothermal Carbonization and Slow Pyrolysis: Detailed Comparison between the Generated Hydrochars and Biochars Characteristics. Processes 2022, 10, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donar, Y.O.; Çağlar, E.; Sınağ, A. Preparation and characterization of agricultural waste biomass based hydrochars. Fuel 2016, 183, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balmuk, G.; Cay, H.; Duman, G.; Kantarli, I.C.; Yanik, J. Hydrothermal carbonization of olive oil industry waste into solid fuel: Fuel characteristics and combustion performance. Energy 2023, 278, 127803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Arias, J.; Sánchez, M.E.; Cara-Jiménez, J.; Baena-Moreno, F.M.; Zhang, Z. Hydrothermal carbonization of biomass and waste: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 20, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zijlstra, D.S.; Cobussen-Pool, E.; Slort, D.J.; Visser, M.; Nanou, P.; Pels, J.R.; Wray, H.E. Development of a Continuous Hydrothermal Treatment Process for Efficient Dewatering of Industrial Wastewater Sludge. Processes 2022, 10, 2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.; Dijkstra, J.W.; Wray, H. Process evaluation of mild hydrothermal carbonization to convert wet biomass residue streams into intermediate bioenergy carriers. Biomass Bioenergy 2023, 181, 107036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 15104; Solid Biofuels—Determination of Total Content of Carbon, Hydrogen and Nitrogen—Instrumental Methods. Stichting Koninklijk Nederlands Normalisatie Insitituut: Delft, The Netherlands, 2011.
- EN 14775; Solid Biofuels—Determination of Ash Content. Stichting Koninklijk Nederlands Normalisatie Insitituut: Delft, The Netherlands, 2009.
- EN 14918; Solid Biofuels—Determination of Calorific Value. Stichting Koninklijk Nederlands Normalisatie Insitituut: Delft, The Netherlands, 2009.
- EN 15148; Solid Biofuels—Determination of the Content of Volatile Matter. Stichting Koninklijk Nederlands Normalisatie Insitituut: Delft, The Netherlands, 2010.
- NEN 6963; Milieu Ontsluiting voor de Bepaling van 30 Geselecteerde Elementen Met Salpeterzuur, Waterstoffluoride en Perchloorzuur. Stichting Koninklijk Nederlands Normalisatie Insitituut: Delft, The Netherlands, 2003.
- NEN 6966; Analyse Van Geselecteerde Elementen in Water, Eluaten en Destruaten—Atomaire-Emissie-Spectrometrie Met Inducatief Gekoppeld Plasma. Stichting Koninklijk Nederlands Normalisatie Insitituut: Delft, The Netherlands, 2005.
- NEN-EN-ISO-10304-1; Water Quality—Determination of Dissolved Anions by Liquid Chromatography of Ions. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023.
- EN-ISO-21404:2020-06; Solid Biofuels—Determination of Ash Melting Behaviour. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- EN-ISO-18122:2015-11; Solid Biofuels—Determination of Ash Content. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015.
- Kabadayi Catalkopru, A.; Kantarli, I.C.; Yanik, J. Effects of spent liquor recirculation in hydrothermal carbonization. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 226, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ENplus. ENplus Handbook, Quality Certification Scheme; ENplus: Brussels, Belgium, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- TNO. Phylis2, Database for (Treated) Biomass, Algae, Feedstocks for Biogas Production and Biochar; TNO Biobased and Circular Technologies: Brussels, Belgium, 2022. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).