Abstract
The purpose of this paper is to determine which factors influence the willingness of Italian wine consumers to purchase and pay a premium for sustainably produced wine. Data from 522 Italian consumers were collected using an online convenience sampling method to capture their attitudes and knowledge towards sustainably produced wine. Respondent socio-demographic characteristics were analysed using descriptive statistics. Multivariate logistic regression was used to examine whether the willingness to pay a premium for sustainably produced wines differs significantly based on past environmental related purchasing behaviour and socio-demographic characteristics. The main determinants of Italian consumers’ purchases of sustainably produced wine are wine knowledge, age, previously having bought sustainably produced goods, previously having bought sustainably produced wine, and the price of wine. Income, education, or gender did not positively influence willingness to pay a premium value for sustainably produced wines. This study produced surprising results. Consumers in Italy are buying foods that are sustainably certified and over 60% would be willing to buy a sustainable wine, in theory.
1. Introduction
The Italian wine industry dates to the Roman Empire more than 2000 years ago. It has an important role in the Italian economy and, as the largest producer of wine in the world, contributes significantly to GDP, employment, and exports. Many Italian wine-producing regions are on the UNESCO World Heritage List. These regions showcase terroir and culture and have been declared as having universal value for humanity and future generations. These designations, along with the natural beauty of many of the wine regions, help make Italy the second most popular tourist destination in the world, contributing significantly to national economic output [1].
Unsurprisingly the consumption of wine in Italy is high both in absolute and per capita terms (Statista, 2024). Italy is the third highest country consumer of wine (24 million hL) after France (25 million hL) and the USA (33 million hL) [2]. It is also the third highest per capita consumer of wine (46 L per year), behind France (47 L per year) and Portugal (52 L per year) [2]. However, due to increased consumer concerns about the negative impacts of conventional agriculture on both human health and the environment, wine consumption has undergone a significant transformation in recent years [3]. The production of organic, biodynamic, and natural wines has significantly increased because of these changes [4], with 16.6% of Italy’s vineyards now being farmed organically [5].
To better understand the changes in consumption, it could be useful to observe the different signals on wine packaging. Labels and many different eco-certifications signal green and sustainable practices in the vineyard and winery [6]. Sustainably produced wines encompass a range of production methods both in the vineyard and the winery and include organic, biodynamic, sustainable, natural, and fairtrade designations. Sustainably produced wines refer to wine that focuses on environmental stewardship, economic profitability, and social and economic equity [7]. Winemakers do this by ensuring healthy and productive vines for current and future generations, taking care of their workforce and giving back to the community, all while furthering business goals [8].
In Italy, the national VIVA wine certification scheme was established in 2014 and is managed by the Ministry of the Environment and Energy Security. VIVA seeks to improve sustainability performance with respect to air, water, vineyard, and territory. To date, 138 farms have been certified [9]. Another wine certification scheme in Italy is Equalitas, which is a “Made in Italy for the World of Wine” sustainability standard/system across the supply chain. It also has a focus on the social, environmental, and economic dimensions of sustainability. There are five certification bodies that Equalitas recognises (CSQA, Valoritalia, Agroqualita, DNV, SGS). There are currently 310 wine producers certified under the auspices of Equalitas. Overall, the industry is increasingly incorporating sustainability concepts into business operations [10].
The consumption of natural and organic products has a long history in Italy [4]. Wine consumers in Italy are very influenced in their purchasing behaviour if a wine bottle’s label includes information about the country of origin [11]. Globally, consumers, in general, support the concept of sustainably produced and certified wines. However, prior research indicates that they are not aware of the definition or processes for accreditation of such labelled wine [7]. The primary factors influencing consumer wine purchases are still price and quality, but a significant and growing number of consumers are now prepared to pay a premium for wine if it is sustainably produced. However, consumers must first be aware of the sustainability claim, then comprehend, believe, and use the label or certification as a tool for buying decisions, to choose a sustainable wine. Investigating their reasons for purchasing sustainably produced wines is crucial, especially as Italy moves towards more vineyards and wines eligible for the various certification schemes.
The aim of this paper is to elicit the factors that influence preferences (willingness to purchase and pay a premium value) for sustainably produced wine by Italian consumers. This is to understand what their most important considerations are when buying wine, whether past behaviours with sustainable certification influences their purchases, whether socio-demographics have an influence, and specifically whether consumers have a willingness to pay (WTP) a premium to pay for sustainable wines. Five hundred and twenty-two Italian wine drinkers were surveyed. Their socio-demographic characteristics were also captured to test whether their attitudes and/or other factors influence their purchase of sustainably produced wines.
Literature Review
Global results are inconsistent when it comes to customers’ WTP for eco certified products. French organic wine drinkers asserted that wines made sustainably are valued on par with other uncertified wines [12]. Alonso Ugaglia et al. [13] shows that for French consumers, the WTP a premium value for any eco certified wine is influenced by the importance each consumer gives to the individual certification. However, American customers are unwilling to spend extra for ecologically friendly wines because of the perceived difference in quality [14]. In contrast, in Chile, consumers were found to be prepared to pay more for wines that are organic and eco certified [15]. Similar results were found in a more recent United States study [16]. Among European countries, Spain has a similar outcome, with customers preferring to pay more for wine that has received eco certification [17], where they are influenced by their income, ages, and gender when it comes to paying more for sustainable wine [18].
Around the world there are divergent results with respect to environmental consciousness and wine. Sustainable attributes in wine production are positively valued by wine consumers [19]. Barber et al. [20] found that consumers who had pro-environment attitudes also had a WTP a premium value for environmentally produced wines. Wine is such a sensory good (taste and aromatics); therefore, unless the consumer’s environmental consciousness is very high, eco certification is unlikely to outperform such variables [21].
It is also important to understand whether any socio-demographic factors, such as gender, age, education attainment, income, and marital status, could have an indirect effect on purchasing behaviour [18,21].
Global research has found that the relationship between gender and WTP is ambiguous. One study found that women have a higher WTP for eco certified wines when exposed to different labels that document the sustainability benefits [22,23]. Similarly, other studies [24,25,26] have also found that women are more likely to pay a premium for sustainable wine. However, Di Vita et al. [27] found the opposite—that men are significantly more willing to pay a premium for eco certified wines. Interestingly, there could be a link between gender and age.
There have been many studies conducted which attempt to discern what is in the minds of the youngest wine consumers [22,23,28,29]. It seems that the youngest generations are more readily influenced by the environment than their elders. This often translates into their willingness to pay more for sustainable wines than those their senior [22,28,30]. However, this youngest generation is still learning and experimenting with alcohol and is drinking less of it overall. Therefore, it is no surprise that there are contrasting results with the relationship between age and wine purchasing behaviour. Lanfranchi et al. [25] found that older customers would pay a higher premium than millennials for eco certified wine. It is possible that age could be influenced by income and general education levels.
Most of the literature shows that income is positively correlated with a positive WTP for sustainably produced wine [3,18,27]. Conversely, education was not found to have any significance in consumer willingness to pay for eco certified wines in the United States [31] and Switzerland [32].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Survey Instrument
An online survey was developed to capture socio-demographic, attitudinal, and price payment data from 522 Italian wine consumers. The survey took between 5 and 10 min to complete and was open during 2020.
The survey had four sections. First, consumers were asked about their wine purchasing behaviour. This included questions about the number of bottles purchased per month, the average spent on a bottle, the number of times in a year they visit a winery, the primary and secondary reasons they drink wine, their favourite varietal, where they buy wine, and their important considerations when buying wine. Second, respondents’ opinions and views on eco certified food and wines and their attitudes towards purchasing these types of goods were collected. In the third section, consumers were asked about their willingness to purchase, and pay additional value for eco certified wine. Respondents could choose zero or nonzero answers, and for the latter, they were presented with choices from a range of price brackets which were (EUR 0, EUR 1–5; EUR 6–10; and greater than EUR 10). Their responses indicated their WTP a premium price value. Fourth, data on the following socio-demographic characteristics of the respondents were requested: income, age, education, and gender.
2.2. Study Population
The study population was accessed using convenience sampling. The aim was to a capture data from more than 500 wine-drinking respondents in Italy. The provided information was identical, and respondents could click on an embedded link to access the survey, which was hosted on the Qualtrics survey platform. The survey was completely anonymous, and only those who volunteered participated. Responses were counted only if a survey was fully completed. A total of 522 complete and usable responses out of 552 surveys submitted were eligible for use in the analysis. The spatial distribution of the respondents, determined using their IP address’s latitude/longitude stamp, can be seen in Figure 1. It is generally a well-represented geographic distribution across the country.
Figure 1.
Italy and the distribution of the respondents.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
A descriptive analysis was performed to identify the socio-demographic details of the participants. Multivariate logistic regression [33] was used to examine whether the WTP a premium for sustainably produced wines differs significantly based on past environmental-related purchasing behaviour and socio-demographic characteristics. The survey data were analysed using STATA, Statistical Software for Data Science (Version 18) [34].
In the survey, respondents were asked, “How much more, in addition to the current price, would you be willing to pay for a bottle if it was certified as sustainably produced?” Respondents could choose whether they wanted to pay EUR 0, EUR 1–5, EUR 6–10, or greater than EUR 10. EUR 1–5, EUR 6–10, and greater than EUR 10 were converted to 1 and WTP EUR 0 was converted to 0. The dependent variable “WTP a premium value for sustainably produced wines” was converted into a binary variable during the logistic regression analysis. This study employed a logistic model because they offer a more straightforward and less complex analytical process, which facilitates ease of execution and interpretation. Furthermore, logistic models necessitate fewer assumptions to be rigorously tested, streamlining the modelling process and enhancing its robustness. Finally, in the survey dataset, a notable issue emerged because of the limited number of responses in one or more categorical variables, potentially leading to challenges in the estimation and stability of the statistical model. Consequently, to address this concern and enhance the model’s reliability, this study opted to consolidate certain adjacent categories within the variables of interest. Consequently, the results derived from a logistic model are inherently more accessible for explanation when compared to the intricacies of interpreting findings from an ordinal model.
The responded values of several other categorical predictors were used as explanatory variables. Age and education level included seven categories. In contrast, wine knowledge and the likelihood of buying eco certified wine had six categories each.
2.4. Logistic Regression Model
Multivariate logistic regression analysis is a formula used to predict the relationships between dependent and independent variables. When there is a dichotomous outcome dependent variable, logistic regression is a powerful empirical method to use [35]. The model can be used to model and explain a dichotomous single dependent variable (Y), which represents the occurrence or non-occurrence of an event, using several independent variables (X).
In the model, the dependent variable was the WTP (Yes = nonzero value; No = none or not sure) a premium value for sustainably produced wine. The independent variables were the socio-economic characteristics of the respondents (gender, age, education, and income), their past behaviour in purchasing wine and sustainably produced goods, and the six most important considerations when buying wine (age, origin, price, certification, expert rating, and taste).
The variables identified were used in the logistic regression multivariate model. Logistic regression provides coefficients for both continuous and categorical independent variables, while the dependent variable is a binary categorical variable. Further, logistic regression can also describe the combined effects of several factors.
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Analysis and Results
Most commonly, wine was bought in a regular retail store (supermarket) (41%) (Table 1). Very few respondents thought that they had expert level knowledge of wine (4%). Many considered that they had an adequate level of knowledge to pair wine with food (21%) or purchase wine in a restaurant with some confidence (20%). A total of 28% considered that they had a basic knowledge of wine, but 16% thought that they had very little knowledge about it.

Table 1.
Descriptive analysis: purchasing sustainable products (n = 522).
Many respondents had previously purchased sustainably produced products (88%), but only just under one-third (32%) had previously purchased sustainably purchased wine. A total of 74% of respondents were willing to buy it, and only 4% were not likely to buy it at all.
Table 2 outlines the descriptive characteristics of the respondents who successfully completed all components of the questionnaire. The survey respondents were 55% men and 45% women, with a median income level of EUR 35,000 to EUR 50,000. A total of 67% were married or in a de facto relationship. In addition, the median age was 35 to 54 years, and the median education attainment was completion of a bachelor’s degree. Respondents often buy biodynamic, fairtrade, organic, natural, and sustainable goods.

Table 2.
Characteristics of respondents (n = 522).
On a Likert scale, respondents were asked to rank from extremely important to not at all important what the most significant considerations were for them when they purchased (any) wine. The options were age; region/country of region; price; certification; expert rating; and taste. Some very interesting results can be observed. Only the region/country of origin of the wine (40%) was considered extremely important by more than 7% of respondents. Sustainable certification (32%) and expert rating (24%) were considered not to be important at all by respondents (Figure 2).
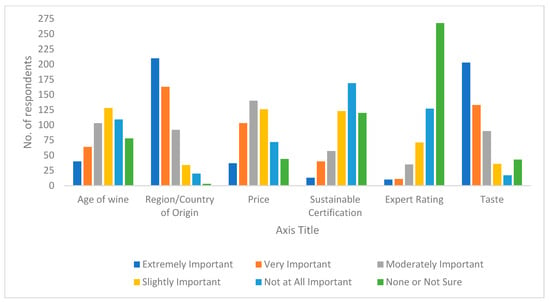
Figure 2.
Most important considerations when buying wine (n = 522).
The WTP a premium value for sustainably produced wine results contrasted with the earlier reported responses about the same topic. The response of WTP = EUR 0 was the most predominant response at n = 201 (38%). For WTP = up to EUR 1, there were 201 responses (38%); WTP = EUR 1 to 5 had 71 (13%); EUR 6 to 10 had 26 (5%); and EUR 11 and more had 23 (4%) (Table 3). Over 60% of the respondents indicated a positive WTP a premium for sustainable wine.

Table 3.
Willingness to pay a premium value for sustainably produced wine (n = 522).
3.2. Logistic Regression Results
Table 4 demonstrates the key factors that determine respondent WTP for sustainably produced wines. This is denoted by their statistical significance in the logical regression estimation procedure. The regression analysis indicated that wine knowledge is significantly related to willingness to pay a premium for sustainably produced wines (odds ratio [95% CI]: 1.33 [1.12, 1.58]). Respondents with greater wine knowledge showed a positive WTP a premium price. In contrast, older respondents were less likely to pay a premium for wines with sustainable certification (Odds ratio [95% CI]: 0.81 [0.65, 0.99]) compared to the younger respondents. No significant differences were observed in WTP for gender, education, and income. Noticeably, respondents who previously purchased sustainable products showed significantly higher likely to pay a premium price (odds ratio [95% CI]: 2.35 [1.23, 4.48]) than those who did not. Respondents who previously purchased sustainable produced wines had significantly lower WTP a premium value for sustainably produced wines (odds ratio [95% CI]: 0.53 [0.34, 0.82]). The price of wine was significant in the analysis with a higher WTP a premium value evidenced (odds ratio [95% CI]: 1.289 [1.04, 1.59]).

Table 4.
Logistic regression of attributes influencing the willingness to pay a premium value for sustainable wine (n = 522).
4. Discussion
Italy has an enormous domestic wine market and is one of the major producers and distributors of wine in the world. Therefore, it is in a unique position to have an equally large impact on the sustainability of wine with their production and purchasing behaviours. If this impact is multiplied with the Italian’s government goal of certification under the various sustainability schemes, it is likely that Italy will be extremely influential with respect to the production and consumption of sustainably produced wine.
Individual traits play a significant role in affecting consumer preferences and their WTP a premium value for sustainably produced wine. From the statistical results, it is evident that the main factors influencing Italian consumers’ purchase of sustainably produced wine are wine knowledge, age, previously having bought sustainably produced goods, previously having bought sustainably produced wine, and the price of wine. Income, education, or gender did not positively influence WTP for sustainably produced wines.
While there has been significant research analysing the link between wine knowledge and WTP, there has been limited analysis concerning wine eco certification and specifically sustainability in Italy. [18] believe that there is an indirect correlation between wine knowledge and the likelihood that a wine consumer will pay a premium for a sustainable wine and similarly. Their findings indicate that those with less wine knowledge would be willing to pay more. Yet the findings indicate a strong and positive effect of self-reported wine knowledge and a higher WTP a premium value.
Knowledge about the sustainable practices themselves could be a more significant motivation for purchasing sustainable wines. An earlier Italian study found that consumers environmental knowledge did not affect their WTP for an environmentally certified wine [36]. Even with the national sustainability plan in place, Italian consumers do not know much about sustainability, rather the focus for Italian consumers when making purchasing decisions is on the varietal and terroir [37]. Other studies have found the opposite with respect to sustainable practices, the environmental effect has an important influence in the decision as to whether to pay a premium in Italy [18,22].
Age is significant in the study with younger people willing to pay more for environmentally friendly wines which is the converse result found by [23,38] found that Italian millennials have a slightly higher WTP to pay and prefer carbon neutral wines over traditionally produced wines. In France it was also found that younger consumers have a higher WTP for eco certified wines [13].
Prior Italian studies revealed that customers are more likely to spend more when they have a favourable attitude towards environmentally friendly wines and a stronger commitment to environmental protection [23,39,40]. Some consumers prefer sustainably produced wine because of the issue of added sulphites in traditional production methods which can lead to headaches [41,42], ref. [43] shows that, on average, Italian consumers do not prefer certified organic wine; only 19% of them are willing to purchase organic wine.
A recent study revealed that the priority given to the label’s information on ingredient amounts and sensory qualities is positively correlated with customer WTP for natural wine [30]. Another study demonstrated that attitudes towards a wine with a sustainable label are influenced by both environmental and qualitative views about sustainable wine but are unaffected by the sustainability’s economic component [44]. According to a recent investigation into the factors affecting consumer preference and WTP in the Italian market, drinking frequency and occasion, organic production practices, sulphite level, income, and attitudes towards healthy food and the environment are all positively correlated with a higher WTP for natural wine [3]. According to other surveys, men and those with better incomes are more likely to purchase organic wines in Italy [27,45].
The results suggest that consumers have a more favourable opinion of such wine if they see sustainable accreditation as an assurance of high-quality standards [44,46]. Additionally, it appears that attitude is slightly influenced by age because younger customers appear to be more concerned about the sustainability of food goods than older consumers [44]. Even with all of these different characteristics, it seems that sustainable wine is currently only a niche market and is likely to remain that way, even as the overall percentage of vineyards that are sustainable increases [47].
Given that the survey captured a diverse range of geographies around the country, was balanced between males and females, captured a good median range of ages, and was not disproportionately biased based on income, the study results suggest that the surveyed Italian consumers are not very interested or motivated by sustainability and wine.
These results are surprising, nonetheless. Consumers in Italy are buying foods that have eco certification, and over 60% of those surveyed indicated a willingness to buy a sustainable wine, in theory.
The results are potentially influenced by the following three major motivations: history, geography, and domestic pride. Sustainability in the country, for wine, is very new. However, there are thousands of years of wine experience in the country. Italy has made an excellent product for generations and tradition is important for many consumers.
Given the impressive geography of Italy (further emphasised by the many UNESCO-designated wine regions), it could be that the general geographic isolation could be encouraging Italians to drink mainly Italian wines. With mountains to the north and surrounded by water on three sides, Italy has an isolated geography, even though they have been exporting wine for a long time. Also, the different regions of the country and the amazing soils have allowed the industry to prosper and thrive.
There are two United Nations Sustainable Development Goals [48] which are relevant to the topic at hand, as follows: SDG 2: End hunger, achieve food security, and promote sustainable agriculture and SDG 12: Ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns. SDGs 2 and 12 identify the urgent need to move wine production and consumption towards a more sustainable basis, and [49] outline the difficulties of achieving these goals without a transformation in thinking about the issues to adopt a multidisciplinary approach to economic development.
Limitations
There are some limitations of this study. Most studies in the literature use stated preference experiments to elicit WTP, and these are valuable exercises as they can provide an indication of consumer preferences for potential certifications before they are introduced to the market. Conversely, the hedonic price models employed by [50] do not have this ability; instead, they provide information on the revealed preferences of consumers based on market data. In the case of certification, this provided an important comparison to the rest of the literature analysed, revealing that many of the stated preference experiments may overestimate WTP for eco certification. A potential reason for this overestimation is the hypothetical nature of the experiments.
In this study, an ordinal dependent variable was used in the logistic regression instead of a continuous variable (because of data limitations). Using ordinal dependent variables provides information on the probability or likelihood of an event occurring rather than a precise WTP estimate. This study did not use an outcome variable (e.g., ranked) suitable for the rank-ordered probit model, which fits respondents’ program choices into a utility-theoretic framework, which is used to estimate WTP. The aim of the study was to examine the factors that influence additional WTP for sustainable wine.
It would be possible to explore this result with experiential economics techniques (like [12]) with consumers in an auction situation to reveal their WTP. This is a costly but efficient method because consumers are positioned in a real-life wine purchase situation.
The survey population of 500 Italian wine drinkers in this study may not be representative of the wider Italian population, and as such, the results and conclusions drawn should be considered in that light.
5. Conclusions
This study identified several key factors, including age, wine knowledge, and price, that influence Italian consumers’ willingness to pay a premium for sustainably produced wine. Since Italian consumers predominantly buy Italian wine and are motivated by tradition and regionalism, it is recommended that the VIVA and Equalitas programs work harder to expand their vineyard and winery participation rates. Given the number of certified sustainable wineries only measures in the hundreds out of the approximately 38,000 wineries in Italy [2], there is more education needed from wine producers to inform consumers about sustainability. Also, the government should separately work to promote sustainable consumption and not only sustainable production. If sustainability does not gain traction in Italy, the potential influence of this important wine country, and of these consumers, will limit the possibility for growth in sustainability in the wine industry worldwide.
However, it is highly likely that there will be a change in the coming decades, and there remains opportunity for hope. The findings indicate that younger Italian consumers are interested in buying and paying a premium value for sustainable wines. As these demographics gain a more significant voice in society and government in the coming years and decades, there could be a significant shift towards sustainability.
As sustainability certifications become more prevalent and mature, and as this newest generation becomes the loudest voice in the country, it is highly likely that sustainability and wine will become synonymous in Italy. However, for the sustainability of wine to permeate across all of Italy, it will need to be merged with the history, geography, and pride in Italian wine.
Future Research
The study results confirm some a priori expectations that are supported by the literature, whilst some other important factors in the purchasing decisions of consumers towards eco certified goods like wine were not borne out by the data and results.
Author Contributions
J.G., D.M., A.R., A.A.U., L.V. and R.M. were involved in the conceptualisation of the study, survey design, data collection, data analysis, and writing of the manuscript. R.R. undertook the data analysis. R.H. undertook the literature review. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Approval was received from Stockton University IRB 11/19/2018.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Deidentified data is available from the authors upon request.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge that this manuscript has not previously been published nor is it under consideration for publication at other journals concurrently. We acknowledge the contribution to Azzurra Rinaldi to data collection and Rezwanul Haque to the literature search.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this manuscript.
References
- World Travel and Tourism Council. Travel and Tourism Economic Impact 2022; WTTC: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Statista. Wine Consumption Worldwide in 2023, by Country. 2024. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/858743/global-wine-consumption-by-country/ (accessed on 17 July 2024).
- Migliore, G.; Thrassou, A.; Crescimanno, M.; Schifani, G.; Galati, A. Factors affecting consumer preferences for “natural wine” An exploratory study in the Italian market. Br. Food J. 2020, 122, 2463–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbrizzi, S.; Alampi Sottini, V.; Cipollaro, M.; Menghini, S. Sustainability and Natural Wines: An Exploratory Analysis on Consumers. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eurostat. Organic Crop Area by Agricultural Production Methods and Crop. 2024. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/databrowser/view/org_cropar/default/table?lang=en (accessed on 8 June 2024).
- Delmas, M.; Gergaud, O. Sustainable practices and product quality: Is there value in eco-label certification? The case of wine. Ecol. Econ. 2021, 183, 106953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscovici, D.; Reed, A. Comparing Wine Sustainability Certifications around the World: History, Status, and Opportunity. J. Wine Res. 2018, 29, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gow, J.; Rezwanul, R.; Moscovici, D.; Alonso Ugaglia, A.; Valenzuela, L.; Mihailescu, R.; Coelli, R. Australian consumers and environmental characteristics of wine: Price premium indications. Int. J. Wine Bus. Res. 2022, 34, 542–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VIVA. VIVA La Sostenibilita Nella Vitivinicoltura In Italia. 2024. Available online: https://viticolturasostenibile.org/programma-viva/ (accessed on 15 June 2024).
- Equalitas. Equalitas Sustainable Wineries. 2024. Available online: https://www.equalitas.it/en/equalitas-sustainable-wineries/ (accessed on 18 March 2024).
- Malorgio, G.; Hertzberg, A.; Grazia, C. Italian wine consumer behaviour and wineries responsive capacity. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Congress, Ghent, Belgium, 26–29 August 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bazoche, P.; Deola, C.; Soler, L.-G. An experimental study of wine consumers’ willingness to pay for environmental characteristics. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Congress, Ghent, Belgium, 26–29 August 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso Ugaglia, A.; Niklas, B.; Rinke, W.; Moscovici, D.; Gow, J. Consumer preferences for Certified Wines in France: A Comparison of Sustainable Labels. Wine Econ. Policy 2021, 10, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loureiro, M.; Hine, S. Discovering niche markets: A comparison of consumer willingness to pay for local (Colorado grown), organic, and GMO-Free Products. J. Agric. Appl. Econ. 2002, 34, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, L.; Ortega, R.; Moscovici, D.; Gow, J.; Alonso Ugaglia, A.; Mihailescu, R. Consumer willingness to pay for sustainable wine—The Chilean case. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscovici, D.; Rezwanul, R.; Mihailescu, R.; Gow, J.; Ugaglia, A.; Valenzuela, L.; Rinaldi, A. Preferences for eco certified wines in the United States. Int. J. Wine Bus. Res. 2021, 33, 153–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellers, R. Would you pay a price premium for a sustainable wine? The voice of the Spanish consumer. Agric. Agric. Sci. Procedia 2016, 8, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellers-Rubio, R.; Nicolau-Gonzalbez, J. Estimating the willingness to pay for a sustainable wine using a Heckit model. Wine Econ. Policy 2016, 5, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tait, P.; Saunders, C.; Dalziel, P.; Rutherford, P.; Driver, T.; Guenther, M. Estimating wine consumer preferences for sustainability attributes: A discrete choice experiment of Californian Sauvignon blanc purchasers. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 233, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, N.; Taylor, C.; Remar, D. Desirability bias and perceived effectiveness influence on willingness-to-pay for pro-environmental wine products. Int. J. Wine Bus. Res. 2016, 28, 206–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäufele, I.; Hamm, U. Consumers’ perceptions, preferences and willingness-to-pay for wine with sustainability characteristics: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 147, 379–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomarici, E.; Asioli, D.; Vecchio, R.; Næs, T. Young consumers’ preferences for water-saving wines: An experimental study. Wine Econ. Policy 2018, 7, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomarici, E.; Vecchio, R. Millennial generation attitudes to sustainable wine: An exploratory study on Italian consumers. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 66, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscovici, D.; Gow, J.; Alonso Ugaglia, A.; Rezwanul Valenzuela, L.; Mihailescu, R. Consumer preferences for organic wine—Global analysis of people and place. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 368, 133215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanfranchi, M.; Schimmenti, E.; Campolo, M.; Giannetto, C. The willingness to pay of Sicilian consumers for a wine obtained with sustainable production method: An estimate through an ordered probit sample-selection model. Wine Econ. Policy 2019, 8, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchio, R. Determinants of Willingness-to-Pay for Sustainable Wine: Evidence from Experimental Auctions. Wine Econ. Policy 2013, 2, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vita, G.; Pappalardo, G.; Chinnici, G.; La Via, G.; D’Amico, M. Not everything has been still explored: Further thoughts on additional price for the organic wine. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 231, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkin, T.; Thach, L. Millennial wine consumers: Risk perception and information search. Wine Econ. Policy 2012, 1, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellini, A.; Samoggia, A. Millennial consumers’ wine consumption and purchasing habits and attitude towards wine innovation. Wine Econ. Policy 2018, 7, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galati, A.; Schifani, G.; Crescimanno, M.; Migliore, G. “Natural wine” consumers and interest in label information: An analysis of willingness to pay in a new Italian wine market segment. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 227, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loureiro, M. Rethinking new wines: Implications of local and environmentally friendly labels. Food Policy 2003, 28, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, S.; Ferjani, A.; Reissig, L. What matters to consumers of organic wine? Br. Food J. 2012, 11, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooldridge, J. Introductory Econometrics: A Modern Approach; Nelson Education: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Stata Corp. Stata Statistical Software, Release 18; StataCorp LLC: College Station, TX, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, C.; Lee, K.; Ingersoll, G. An introduction to logistic regression analysis and reporting. J. Educ. Res. 2002, 96, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzocchi, C.; Ruggeri, G.; Corsi, S. Consumers’ preferences for biodiversity in vineyards: A choice experiment on wine. Wine Econ. Policy 2019, 8, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastroberardino, P.; Calabrese, G.; Cortese, F.; Petracca, M. Sustainability in the wine sector An empirical analysis of the level of awareness and perception among the Italian consumers. Br. Food J. 2020, 122, 2497–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassivera, F.; Gallenti, G.; Troiano, S.; Marangon, F.; Cosmina, M.; Bogoni, P.; Campisi, B.; Carzedda, M. Italian millennials’ preferences for wine: An exploratory study. Br. Food J. 2020, 122, 2403–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogari, G.; Mora, C.; Menozzi, D. Factors driving sustainable choice: The case of wine. Br. Food J. 2016, 118, 632–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caracciolo, F.; Furno, M.; D’Amico, M.; Califano, G.; Di Vita, G. Variety seeking behavior in the wine domain: A consumers segmentation using big data. Food Qual. Prefer. 2022, 97, 104481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, M.; Ballco, P.; López-Galán, B.; De Magistris, T.; Verneau, F. Exploring consumers’ perception and willingness to pay for “Non-Added Sulphite” wines through experimental auctions: A case study in Italy and Spain. Wine Econ. Policy 2017, 6, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanigro, M.; Appleby, C.; Menke, S. The wine headache: Consumer perceptions of sulfites and willingness to pay for non sulfited wines. Food Qual. Prefer. 2014, 31, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boncinelli, F.; Dominici, A.; Gerini, F.; Marone, E. Insights into organic wine consumption: Behaviour, segmentation and attribute non-attendance. Agric. Food Econ. 2021, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogari, G.; Corbo, C.; Macconi, M.; Menozzi, D.; Mora, C. Consumer attitude towards sustainable-labelled wine: An exploratory approach. Int. J. Wine Bus. Res. 2015, 27, 312–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maesano, G.; Carra, G.; Peri, I. How Do Consumers Perceive Sustainable Wine? A Review. Qual. Access Success 2019, 20, 351–357. [Google Scholar]
- Maesano, G.; Di Vita, G.; Chinnici, G.; Pappalardo, G.; D’Amico, M. What’s in organic wine consumer mind? A review on purchasing drivers of organic wines. Wine Econ. Policy 2021, 10, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzola, P.; Grechi, D.; Pavione, E.; Gilardoni, G. Italian wine sustainability: New trends in consumer behaviours for the millennial generation. Br. Food J. 2022, 124, 4103–4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Sustainable Development Goals: 17 Goals to Transform Our World. 2015. Available online: https://www.un.org/en/exhibits/page/sdgs-17-goals-transform-world (accessed on 29 July 2024).
- Meramveliotakis, G.; Manioudis, M. History, Knowledge, and Sustainable Economic Development: The Contribution of John Stuart Mill’s Grand Stage Theory. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanasch, P.; Frick, B. The value of signals: Do self-declaration and certification generate price premiums for organic and biodynamic wines? J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 249, 119415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).