Abstract
This paper aims to find the relationship between PM10 (particulate matter) concentrations in Seoul and Beijing for a sustainable environment. The influence of Beijing’s PM10 concentrations on those of Korea has been extensively discussed since 2019. Previous studies have presented conflicting opinions on the origin of particulate matter in Korea. Some argued that the particulate matter in Korea had its origin in foreign countries, while others emphasized that particulate matter concentrations in Korea were affected by Korean domestic factors. Thus, we try to answer this controversial question based on actual data. For this, we analyze the correlation between concentrations of particulate matter (PM10) in Seoul and Beijing using hourly data for Shunyi, Beijing and Jung-gu, Seoul from March 2014 to February 2017 and examine how particulate matter in Seoul has been affected by particulate matter in Beijing, taking into consideration wind speed and wind direction, through regression analysis. We hypothesize that particulate matter concentrations in Beijing have affected concentrations in Seoul, and that this would be confirmed if there were a correlation between concentrations of particulate matter in Beijing and concentrations in Seoul when the wind blew from China to Korea. The results of this paper are as follows: (i) When considering the 42-h delay and wind direction, the correlation between Seoul_PM10 and Beijing_PM10 becomes more pronounced. (ii) Regression analysis confirms the influence of Beijing’s factors on Seoul’s PM10 concentrations. (iii) Interaction effects between Beijing PM10 concentration and Beijing wind speed are also identified, indicating a stronger impact when the wind blows more strongly from Beijing. This paper contributes to understanding the dynamics of fine dust in Korea, emphasizing the importance of considering external factors, especially from China.
1. Introduction
The presence of particulate matter (PM2.5, PM10) in Korea may be due to internal factors within Korea itself, but some Korean people think that other factors are Asian sand dust and particulate matter (PM2.5, PM10) of Chinese origin. This view was reflected in a recent report by the National Institute of Environmental Research [1], which predicts particulate matter (PM10) and fine particulate matter (PM2.5) concentrations in Korea using aerosol concentrations in China’s Shandong, Beijing, and Hebei provinces. The report stated that when the wind blew from China and the aerosol concentrations in Chinese provinces such as Shandong, Shaanxi, Beijing, and Hebei were very high, particulate matter concentration in Korea was also high [2]. The influence of China’s particulate matter concentrations on those of Korea has been extensively discussed since 2019. Some reported that when concentrations of particulate matter in Beijing, Tianjin, and Shijiazhuang increased, particulate matter levels in Korea increased 1 to 2 days later [3,4]. Others said that 51% of the particulate matter in Korea had its origin in foreign countries and that particulate matter concentrations in Korea were not affected by the influence of China [5,6,7,8].
The divergent opinions reported above suggest a need for objective analysis based on adequate data. A significant number of fine-dust-related studies focus on measuring and reporting fine dust concentrations by region. Most studies report the status of fine dust generation in the short term or track trends in fine dust concentration from a long-term perspective [9]. Summarizing most of the research results so far, we can tentatively conclude that Korea’s fine dust is caused by a combination of factors originating in Korea, China, and other regions. However, it will be very difficult to exactly know where and how the fine dust in Korea occurs.
The majority of those studies revolve around PM2.5 levels, and studies on PM10 are relatively rare. Also, inflated estimates have been obtained in studies that generally focus on short time periods, use older emissions inventories, and have little or no international collaboration. Thus, they seem to produce diverse research results due to errors in data collection, bias in the selection of variables used in analysis, and failure to properly consider the direction and speed of the wind. In addition, there is still a lack of research on where and why fine dust is generated.
Thus, we analyze a correlation between concentrations of particulate matter (PM10) in Seoul and Beijing using hourly data for Shunyi, Beijing and Jung-gu, Seoul from March 2014 to February 2017. If the correlation between PM10 concentrations in Beijing and Seoul is high when wind blows from China, then we may hypothesize that PM10 concentrations in China affect PM10 concentrations in Korea.
2. Literature Review
There have been many studies about Chinese influence on particulate matter levels in Korea. However, controversy continues as to whether the concentration of fine dust in Korea originates within Korea or from other regions. According to the National Institute of Environmental Research [1], China exerts a large influence on particulate matter levels in Incheon. They found that when the wind blew from China and the aerosol concentration in the eastern part of China (Shandong, Shaanxi, Beijing, Hebei) was high, then particulate matter concentration in Incheon was also high. However, their research had the limitation that particulate matter concentrations in inland China were not sufficiently analyzed, and they analyzed only the relationship between Incheon and Shandong Province, which is very close to Incheon. Park and Shin [9] separated Korean and Chinese variables to identify factors affecting concentrations of ultraparticulate matter (PM2.5) in Korea using 16 metropolitan cities’ data for the period February 2015 to May 2016. The data covered regional diesel consumption, coal-fired power generation transaction volumes, indexes of chemical and cement manufacturing production, and measurements of wind direction data for Korea, but only PM2.5 data were used for China. They found that, when the wind blew from China, the concentration of PM2.5 in Shandong, China had a positive effect on the concentration of PM2.5 in Korea, but the Korean factors had no significant effect. Kim et al. [10] analyzed the effect of particulate matter in Shandong on air quality in Korea. According to satellite observations, from 2012 to 2016, the concentration of NOx and SO2 in China decreased overall. It is indicated that PM2.5 concentration in Korea decreased as Chinese emissions decreased. Joo et al. [11] analyzed the relationship between particulate matter (PM10) concentrations in seven cities in China and Seoul in Korea using daily data from 2014 to 2017. They used particulate matter concentration in Seoul and seven Chinese cities and showed that the correlation coefficient of a 1-day lag is higher than that of a 0-day lag (same day) across all regions of China. Kim et al. [12] analyzed whether the concentration of PM10 in Beijing and Tianjin affects the concentration of PM10 in Seoul and showed that Seoul is affected by PM10 occurring in Seoul itself and PM10 the day before in Beijing and Tianjin. Chun et al. [13] examined how particulate matter from China affected Korea before and after COVID-19 and analyzed how changes in China’s manufacturing index are related to the level of particulate matter in Korea, based on analysis of data on the number of COVID-19 patients. However, their study did not involve sufficient statistical verification. Choi and Jung [14] comparatively analyzed factors affecting particulate matter concentrations before and after COVID-19 using particulate matter concentration as a dependent variable and meteorological factors and air pollutants as independent variables. They concluded that the main factor affecting both PM10 and PM2.5 levels is CO, and that the foreign air pollutant factor is not significantly higher due to the impact of COVID-19 containment policies. Liu et al. [15] analyzed the literature in the field related to fine dust and found that eastern, northern, and northeastern China had the greatest influence on fine dust pollution in Korea, Japan, and China.
In response to the claim that a large amount of fine dust is flowing into Korea from China via westerly winds, Park et al. [16] showed that more than 70% of PM2.5 observed in Seoul originated domestically. They said that the Korean government had announced that overseas influence was 50–70%, but domestic influence was overwhelming. Their study was conducted by analyzing all domestic measurements related to ultrafine dust over two years and deriving the contribution rate of each pollutant source. Although foreign factors may have more influence at certain times, overall, much more ultrafine dust is generated domestically, and foreign factors are reported to account for about 27% of the total [17]. Hwang et al. [18] hypothesized that the main cause of the problem was fine dust generated from Korea, rather than viewing China as the only cause of the problem. They claimed that fine dust in Korea is also generated domestically in an equally large amount at least. In particular, large cities such as Seoul consume a lot of energy due to the concentration of population and economic activities, and, as a result, direct emissions of air pollutants are high. Data on traffic volume, the biggest factor with respect to fine dust, and the amount of fine dust generation were collected and analyzed. The results of the analysis did not show that traffic volume and atmospheric fine and ultrafine dust were proportional. In theory, areas with a large amount of traffic should have had a high amount of fine and ultrafine dust, but the results were not sufficient to support the proposed hypothesis. These results are partly due to the insufficient reliability of the measured data, given the fact that the locations of fine dust measurement stations are installed at a higher level than the living area and are also outdated. Additionally, the dust that is emitted directly into the atmosphere without going through a designated outlet at construction sites, etc. is assumed to be another cause. Lim et al. [19] analyzed PM2.5 in Seoul and Baekryeong Island according to the airflow inflow path based on fine dust measurement data for about a month from 19 May 2015 to 13 June 2015. The analysis results showed high levels of frequency and PM2.5 concentration in areas which can be affected by China and Seoul metropolitan area. Additionally, upon further investigation of cases of dust flowing into Seoul via Baengnyeong Island, PM2.5 was found to be higher in Seoul than in Baengnyeong Island. It was estimated that NO3s, which showed the largest increase rate of 5.81 times, were caused by the influence of high NOx emissions due to automobile exhaust gases and energy use as they flowed into the metropolitan area. Nam et al. [20] analyzed seasonal PM2.5 characteristics in the Northeast Asia region. PM2.5 ground measurement data, weather map data, and meteorological and air quality models were used to analyze seasonal PM2.5 in Northeast Asia, including Korea, focusing on the research period of 2015. As a result of evaluating the domestic and foreign contributions to PM2.5 concentration at six main measurement stations in Korea, the foreign contribution to PM2.5 concentration in the Baengnyeong Island area was over 90% in all periods, and the influence from overseas was dominant. This can be interpreted as the dominant influence of contributions from overseas due to its geographical proximity to China. Conversely, in regions with high self-emission characteristics, such as Seoul and Ulsan, overseas contributions to PM2.5 were relatively low compared to other regions, at 48.2% and 50.8%, respectively. This can be seen to be consistent with the research results of Lim et al. [19]. Lee and Kang [21] examined the changes in the number of visitors to regions during periods of PM2.5 concentrations in Seoul and analyzed the regional differences of these changes.
The majority of studies revolve around PM2.5 levels, and studies around PM10 are relatively rare. Also, inflated estimates have been obtained in studies that generally focus on short time periods, use older emissions inventories, and have little or no international collaboration. Thus, they seem to produce diverse research results due to errors in data collection, bias in the selection of variables used in analysis, and failure to properly consider the direction and speed of the wind. In addition, there is a lack of research on where and why fine dust is generated.
3. Data and Research Methods
This study analyzes the correlation between particulate matter levels in Beijing and Seoul, using hourly data of wind direction, wind speed, and PM10 concentration from March 2013 to February 2017.
3.1. Data Preprocessing for Hourly Data of Beijing, China
We downloaded hourly particulate matter data for Beijing, China from the UCI database [22]. Among many variables, we selected PM10 concentration, wind direction, and wind speed data for the Shunyi district of Beijing.
3.2. Data Preprocessing for Hourly Data of Seoul, Korea
The data format for particulate matter of Seoul, Korea was different from that of Beijing. The data sources for particulate matter levels and wind direction were also different. To obtain wind directions and speeds for Seoul, we downloaded data on Seoul Jung-gu district from the Korea National Climate Data Center [23]; for particulate matter levels, we downloaded data from Air Korea [24].
- (1)
- Preprocessing of wind direction and wind speed data
For the wind direction and wind speed data for Seoul, we selected data for Seoul Jung-gu district and extracted wind direction and wind speed from the downloaded ‘OBS*.csv’ files. We converted multi-column Chinese date information into a single-column Korean form, i.e., a string in the form of yyyyMMddHH. Then, we changed the wind direction in Seoul which was represented by a number into azimuth angle data in string format, which was used for the wind direction data in Beijing.
- (2)
- Particulate matter data for Seoul
Particulate matter data for Seoul were restricted to Jung-gu. We downloaded the particulate matter data from the Air Korea database [24]. The downloaded files were CSV and Excel files, with data for years and quarters, respectively. From these files, we extracted the PM10 concentration for the 111121 code corresponding to Jung-gu.
3.3. Data Merge
We merged files of the Chinese and Korean data into one file in the same data format. We used the Python language to extract PM10 information for Jung-gu, Seoul (111121 inspection station) from the CSV files downloaded from Air Korea and merged this with data for particulate matter levels, wind directions, and wind speeds for Beijing, along with particulate matter levels, wind directions, and wind speeds for Seoul, into a merged.csv file. After deleting records with null columns, we obtained a total of 33,982 records in our final merged datafile, as shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Merged file of Korean and Chinese data.
Figure 1 compares Beijing_PM10 and Seoul_PM10 in a graph from March 2023 to March 2017. Beijing_PM10 is shown in blue and Seoul_PM10 is shown in red. As shown in Figure 1, PM10 concentration in the two neighboring countries seems to be related, and Beijing_PM10 is almost higher than Seoul_PM10.
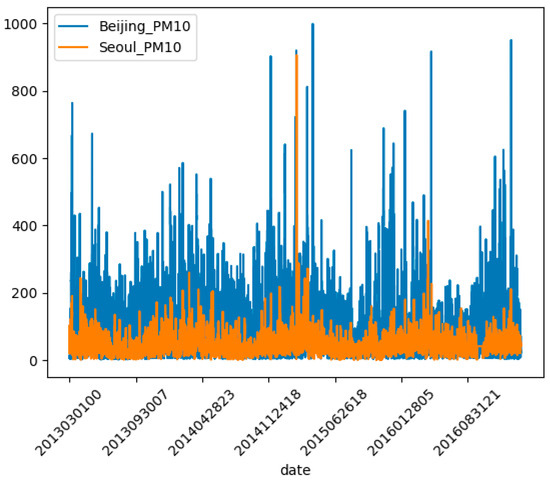
Figure 1.
Beijing_PM10 vs. Seoul_PM10.
3.4. Correlation and Regression Analysis
We performed a correlation analysis to find a relationship between the two countries. First, we performed a correlation analysis for all 33,982 data records. Secondly, we performed a correlation analysis for the 42-h delayed data. To obtain the 42-h delayed data, we calculated the average wind speed (6.07 m/s) and the average arrival time (42 h) when the wind from Beijing arrives in Seoul approximately 42 h later using the distance between Seoul and Beijing (about 952 km). Thus, the total 33,940 data records were used for correlation and regression analysis. Thirdly, we performed a regression analysis using the following regression model:
where Seoul_PM10_42 is particulate matter in Seoul with a time difference of 42 h from Beijing, Seoul_WS is wind speed in Seoul, Beijing_PM10 is particulate matter in Beijing, and Beijing_WS is wind speed in Beijing.
Seoul_PM10_42 = α + β1 × Seoul_WS + β2 × Beijing_PM10 + β3 × Beijing_WS + ε
α: constant β: coefficient ε: residuals
α: constant β: coefficient ε: residuals
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Descriptive Statistics
Prior to empirical analysis, the descriptive statistics of variables used in this paper were confirmed. The values of independent and dependent variables are shown in Table 2. Table 2 indicates that Beijing_PM10 is higher than Seoul_PM10 in terms of average and standard deviation.

Table 2.
Descriptive statistics.
4.2. Correlation Analysis
- (1)
- Results of the model without time lag
We performed a correlation analysis for all 33,982 data records. Table 3 shows that the particulate matter concentration in Seoul (Seoul_PM10) is positively related to particulate matter concentration in Beijing (Beijing_PM10) and wind speed in Beijing (Beijing_WS). However, it is negatively related to wind speed in Seoul (Seoul_WS).

Table 3.
Correlation coefficient matrix without time lag.
Also, Figure 2 shows the correlation results using a heat map.
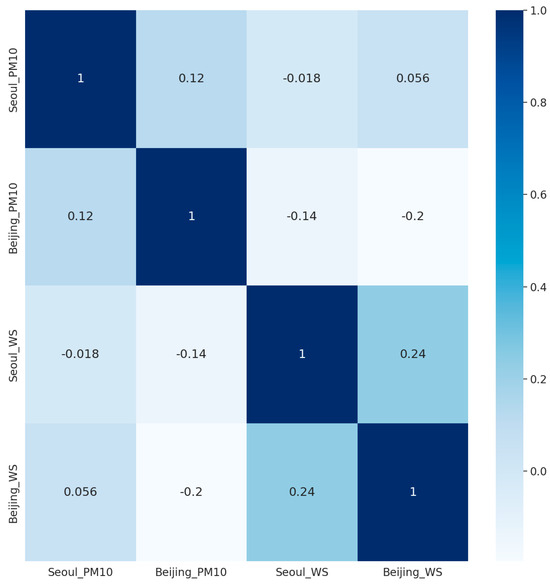
Figure 2.
Correlation heatmap.
- (2)
- Results of the 42-h time lag model 1: when a westerly wind blows in Beijing
We analyzed the 42-h delayed data when a westerly wind blows in Beijing. For this, we selected 1160 records from among the 33,982 data records and carried out correlation analysis. Table 4 shows the results of correlation analysis when the new variable, Seoul_PM10_42, was added.

Table 4.
Correlation coefficient matrix with the 42-h time lag model 1.
When time lag was not considered, the correlation coefficient between Seoul_PM10 and Beijing_PM10 was 0.121, as shown in Table 3. However, when we consider the 42-h time lag data, the correlation coefficient between Seoul_PM10_42 and Beijing_PM10 increased from 0.121 to 0.216, shown in Table 4. This is somewhat supported by the result of Joo et al. [11] that the correlation coefficient of a 1-day lag is higher than that of a 0-day lag (same day) across all regions of China. Also, Table 4 shows that Seoul_PM10_42 has a positive relationship with Beijing_WS, which implies that Seoul_PM10_42 was affected by Beijing factors. Also, Seoul_PM10 and Seoul_PM10_42 were more correlated with Beijing_WS than with Seoul_WS, further confirming that when the wind speed from Beijing was strong, Seoul_PM10_42 and Seoul_PM10 were higher.
- (3)
- Results of the 42-h time lag model 2: when a westerly wind blows in Seoul and Beijing at the same time
Next, we analyzed the 42-h time lag model when westerly winds blew in Seoul and Beijing at the same time. For this, we obtained 202 cases among 1160 cases when the wind direction was west in Beijing. Table 5 shows the results of the correlation analysis.

Table 5.
Correlation coefficient matrix with the 42-h time lag model 2: the case of westerly winds blowing in both Seoul and Beijing at the same time.
When westerly winds blew in Seoul and Beijing at the same time, the correlation coefficient between Seoul_PM10_42 and Beijing_PM10 increased from 0.216 to 0.354, as shown in Table 5. Also, Seoul_PM10_42 has a positive relationship with Beijing_PM10 and Beijing_WS, which implies that Seoul_PM10_42 was affected by Chinese factors. Giving the same result as in the previous section, Seoul_PM10 and Seoul_PM10_42 were more correlated with Beijing_WS than Seoul_WS, further confirming that when the wind speed from Beijing was strong, Seoul_PM10_42 and Seoul_PM10 were higher.
- (4)
- Results of the 42-h time lag model 3: when the wind speed in Seoul is over 4 m/s.
Next, we performed a correlation analysis when wind speed was strong because Seoul_PM10 was statistically significant in relation to wind speed when the wind blows from Beijing. So, we selected 52 records when wind speed in Seoul was over 4 m/s among 202 cases when wind direction was west from both Seoul and Beijing at the same time. Table 6 shows the results of the correlation analysis.

Table 6.
Correlation coefficient matrix with the 42-h time lag model 3: the case when wind speed in Seoul is over 4 m/s.
When the wind speed is above 4 and the westerly wind blows in Seoul and Beijing at the same time, the correlation coefficient between Seoul_PM10_42 and Beijing_PM10 increased from 0.354 to 0.412, which shows that wind speed is aggravating particulate matter concentration in Seoul. If only Korea’s own particulate matter was a factor, the particulate matter concentration should be high when the wind is stagnant. Thus, when the wind speed is high and the wind blows from China, the correlation coefficient between Beijing and Seoul is high, which means that the particulate matter concentration in Seoul is largely influenced by Beijing. The fact is that the correlation coefficient (0.407) between the Seoul particulate matter concentration (Seoul_PM10) and the wind speed in Beijing (Beijing_WS) is higher than the correlation coefficient (0.174) between the Seoul particulate matter concentration (Seoul_PM10) and the wind speed in Seoul (Seoul_WS). If there were only Korean factors involved, the Seoul particulate matter concentration (Seoul_PM10) should be negatively correlated to the wind speed in Seoul. However, as shown in Table 6, the Seoul particulate matter concentration (Seoul_PM10) is more significantly affected by the wind speed of Beijing (Beijing_WS), while it was not correlated with the wind speed in Seoul (Seoul_WS).
4.3. Regression Analysis
- (1)
- Regression model 1: 42-h delayed data
To examine how PM10 in Seoul (Seoul_PM10) was affected by PM10 in Beijing (Beijing_PM10), we performed a regression analysis for 33,940 occasions using as a dependent variable the 42-h delayed Seoul’s particulate matter concentration data (Seoul_PM10_42), considering wind speed. The regression model is as follows:
where Seoul_PM10_42 is 42-h delayed particulate matter data in Seoul, Beijing_PM10 is particulate matter in Beijing, Seoul_WS is wind speed in Seoul, and Beijing_WS is wind speed in Beijing.
Seoul_PM10_42 = α + β1 × Beijing_PM10 + β2 × Seoul_WS + β3 × Beijing_WS + ε
α: constant β: coefficient ε: residuals
α: constant β: coefficient ε: residuals
Table 7 shows that the particulate matter concentrations in Korea were caused by Chinese factors such as particulate matter in Beijing, China (Beijing_PM10) and wind speed in Beijing (Beijing_WS). Particulate matter in Beijing, China (Beijing_PM10) has a p-value of 0.000, indicating a statistically positive effect on particulate matter in Seoul (Seoul_PM10_42). The wind speed in Beijing (Beijing_WS) is also a significant variable, with a p-value of 0.002. However, the wind speed in Seoul is not significantly related to Korea’s particulate matter although it is negatively related to it. It can be seen that, in general, Korea’s fine dust is influenced by China’s fine dust and China’s wind speed.

Table 7.
Regression model 1 for particulate matter in Seoul (dependent variable: Seoul_PM10_42).
- (2)
- Regression model 2: the case of westerly winds in Beijing and Seoul at the same time
In this section, in order to see how the wind direction changes the results of the regression analysis, we selected 202 occasions from among the total 33,940 records and analyzed the cases where there were simultaneous westerly winds in Beijing and Seoul. The regression model is the same as in the previous section.
Table 8 shows that the particulate matter concentrations in Korea were caused by Chinese factors such as particulate matter in Beijing (Beijing_PM10) and wind speed in China (Beijing_WS). Particulate matter in Beijing (Beijing_PM10) has a p-value of 0.000, indicating a statistically positive effect on particulate matter in Seoul (Seoul_PM10). The wind speed in Beijing (Beijing_WS) is also a significant variable, with a p-value of 0.039. Because this analysis covered occasions when the wind blew from China, it can be assumed that particulate matter also moved from China to Korea. Thus, when the wind blows strongly from Beijing, the particulate matter concentrations in Beijing and Seoul are very closely related, and so Chinese factors do affect particulate matter concentrations in Korea.

Table 8.
Regression model 2 for particulate matter in Seoul (dependent variable: Seoul_PM10_42).
- (3)
- Regression model 3: moderated regression analysis
We investigate an interaction effect of Beijing_PM10 and Beijing_WS on Seoul_PM10_42. Thus, we performed a moderated regression analysis to identify interaction effects of Beijing_PM10 and Beijing_WS on Seoul_PM10_42. The moderated regression model was as follows.
where Beijing_PM10_WS represents an interaction effect variable.
Seoul_PM10_42 = α + β1 × Beijing_PM10 + β2 × Seoul_WS + β3 × Beijing_WS
+ β4 × Beijing_PM10_Beijing_WS + ε
α: constant β: coefficient ε: residuals
+ β4 × Beijing_PM10_Beijing_WS + ε
α: constant β: coefficient ε: residuals
Table 9 shows that Beijing_PM10_Beijing_WS has a p-value of 0.013, indicating that when the wind blows strongly from Beijing, Beijing_PM10 has more influence on Seoul_PM10_42, which supports the hypothesis that when the wind blows more strongly from Beijing, Chinese factors affect particulate matter concentrations in Korea even more.

Table 9.
Regression model 3 for the moderated regression analysis (dependent variable: Seoul_PM10_42).
4.4. Discussion
We tested the divergent opinions about factors related to Korea’s particulate matter using PM10 and wind speed and direction data for Seoul and Beijing. When we did not consider the time lag, the correlation coefficient between Seoul_PM10 and Beijing_PM10 was 0.121. However, when we considered the time lag, the correlation coefficient between Seoul_PM10_42 and Beijing_PM10 increased from 0.121 to 0.216. When wind direction in Beijing and Seoul was considered simultaneously, the correlation coefficient between Seoul_PM10_42 and Beijing_PM10 increased from 0.216 to 0.354. Lastly, when we took into consideration the wind speed, the correlation coefficient between Seoul_PM10_42 and Beijing_PM10 increased from 0.354 to 0.412.
If there were only Korean factors involved, Seoul’s particulate matter concentration (Seoul_PM10) should be lower when the wind speed in Seoul is high. However, Seoul_PM10 was higher when the wind speed in Seoul was high, which implies that the particulate matter concentration in Seoul is closely related to particulate matter from Beijing (Beijing_PM10). Also, regression results show that the particulate matter concentrations in Seoul were affected by Beijing (Beijing _PM10) and wind speed in Beijing (Beijing_WS). Since environmental problems such as air pollution are not caused by factors within a specific country but are significantly influenced by neighboring countries, thus, cooperation and efforts between countries are very necessary for sustainable development.
5. Concluding Remarks and Future Work
In this paper, we analyzed the correlation between particulate matter concentrations in Seoul and Beijing using hourly data. We selected the Jung-gu district of Seoul in Korea and obtained data from the websites of the Korea Meteorological Administration and Air Korea. In addition, we obtained data for the Shunyi district of Beijing in China from the UCI database. We calculated the average wind arrival time from Beijing to Seoul, then used 42-h-delayed data for a correlation and regression analysis.
We examined how particulate matter in Seoul was affected by particulate matter in Beijing, taking into consideration the 42-h-time lag PM10 data, wind speed, and wind direction. We hypothesized that particulate matter concentrations in Beijing affected concentrations in Seoul, and that this would be confirmed if there were a correlation between concentrations of particulate matter in Beijing and concentrations in Seoul when the wind blew from Beijing to Seoul. Regression results revealed that there is indeed an interaction effect of particulate matter and wind speed in Beijing, confirming that when the wind blows strongly from Beijing, the level of particulate matter in Beijing significantly affects the level in Seoul.
This study can help to predict concentrations of particulate matter in Seoul using wind speed, wind direction, and particulate matter concentration data from Beijing by analyzing the time difference according to wind speed.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.-H.C.; methodology, S.-H.C.; software, S.-H.C.; validation, S.-H.C. and J.-W.K.; formal analysis, S.-H.C. and J.-W.K.; investigation, S.-H.C. and J.-W.K.; resources, S.-H.C. and J.-W.K.; data curation, S.-H.C.; writing—original draft preparation, S.-H.C.; writing—review and editing, S.-H.C. and J.-W.K.; visualization, S.-H.C.; supervision, S.-H.C.; project administration, S.-H.C. and J.-W.K.; funding acquisition, J.-W.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by Hankuk University of Foreign Studies Research Fund of 2024.
Data Availability Statement
https://github.com/sehakflower/data/blob/main/merged.csv (accessed on 30 May 2024).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- National Institute of Environmental Research, A Study on the Characteristics of PM2.5 in Major Cities of South Korea and China (I). 2020. Available online: https://www.nirs.go.kr/ (accessed on 30 May 2024).
- Ministry of the Interior and Safety. Available online: https://www.mois.go.kr/frt/bbs/type010/commonSelectBoardArticle.do?bbsId=BBSMSTR_000000000008&nttId=68536 (accessed on 30 May 2024).
- The Chosun Media. The Particulate Matter Is Made by the ‘Jing Jin Ji’ in China, Hits Seoul One or Two Days Later. Available online: https://www.chosun.com/national/transport-environment/2020/11/16/VD54A7D5KRF4JA52BVCTZOKLCM/ (accessed on 30 May 2024).
- The Kyung Hyang Shinmun. Available online: https://www.khan.co.kr/national/national-general/article/201911202139015 (accessed on 30 May 2024).
- The Hankyoreh. Available online: https://www.hani.co.kr/arti/society/environment/970232.html (accessed on 30 May 2024).
- DongA.com. Available online: https://www.donga.com/news/Opinion/article/all/20201116/104000215/1 (accessed on 30 May 2024).
- KBS.co.kr. Available online: https://news.kbs.co.kr/news/view.do?ncd=5049081 (accessed on 30 May 2024).
- Nocutnews.co.kr. Available online: https://www.nocutnews.co.kr/news/5448047 (accessed on 30 May 2024).
- Park, S.; Shin, H. Analysis of the Factors Influencing PM2.5 in Korea: Focusing on Seasonal Factors. J. Environ. Policy Adm. 2017, 25, 227–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.C.; Kwon, S.; Kim, B.U.; Kim, S. Review of Shandong Peninsular Emissions Change and South Korean Air Quality. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 34, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, H.S.; Lee, S.M.; Choi, J.W.; Kim, C.Y.; Choi, M.W.; Kim, K.H. A Study on Concentration Trends of Particulate Matter in China and Correlation between Air Pollution Levels in Korea and China. Korean Environ. Inst. 2019, 219. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.; Kim, O.S. Analyzing Transboundary Particulate Matters of Korea and China Using Time-series Analyses. J. Assoc. Korean Geogr. 2019, 8, 33–46. [Google Scholar]
- Chun, S.-H.; Lee, K.W.; Jang, J.W. Correlation Analysis between China and Korea for PM2.5 and PM10 using Big Data: Comparison of Before and After COVID-19. In Proceedings of the Korean Energy Society Conference, Daegu, Republic of Korea, 28–30 April 2021; p. 154. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, W.-C.; Cheong, K.-S. Analysis of the Factors Affecting Fine Dust Concentration Before and After COVID-19. J. Korean Soc. Hazard Mitig. 2021, 21, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, J.; Yao, F. Source-receptor relationship of transboundary particulate matter pollution between China, South Korea and Japan: Approaches, current understanding and limitations. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 52, 3896–3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.B.; Lee, T.J.; Lee, E.S.; Kim, D.S. Enhancing source identification of hourly PM2.5 data in Seoul based on a dataset segmentation scheme by positive matrix factorization (PMF). Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 1042–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Kukminilbo. Seoul’s Ultrafine Dust a Greater Domestic Impact … Foreign Factors Account for 27%. Available online: http://news.kmib.co.kr/article/view.asp?arcid=0924061242 (accessed on 30 May 2024).
- Hwang, S.Y.; Moon, J.Y.; Kim, J.J. Relationship Analysis between Fine Dust and Traffic in Seoul using R. J. Inst. Internet Broadcast. Commun. 2019, 19, 139–149. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, J.-H.; Han, S.-W.; Lim, Y.-J.; Shin, H.-J.; Ahn, J.-Y.; Han, J.-S. The Characteristics of PM2.5 Corresponding to Inflow Pathway of Seoul and Baengnyeong Island. J. Korean Soc. Urban Environ. 2016, 16, 313–322. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, K.P.; Lee, D.G.; Jang, L.S. Analysis of PM 2.5 Concentration and Contribution Characteristics in South Korea according to Seasonal Weather Patterns in East Asia: Focusing on the Intensive Measurement Periods in 2015. J. Environ. Impact Assess. 2019, 28, 183–200. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.H.; Kang, J.E. Spatial Disparity of Visitors Changes during Particulate Matter Warning Using Big Data Focused on Seoul, Korea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UCI Machine Learning Repository. Available online: https://archive.ics.uci.edu/dataset/501/beijing+multi+site+air+quality+data (accessed on 30 May 2024).
- KMA National Climate Data Center. Available online: https://data.kma.go.kr/data/grnd/selectAsosRltmList.do?pgmNo=36 (accessed on 30 May 2024).
- Air Korea, Korea Environment Corporation. Available online: https://www.airkorea.or.kr/ (accessed on 30 May 2024).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).