Abstract
This study aimed to examine the conceptual development, trends, and intellectual structures in the literature on revenue management in the tourism and hospitality industry. This study applied the bibliometric review method to analyze 1165 Scopus-indexed documents. Descriptive analyses, citation analysis, co-citation analysis, and keyword co-occurrence analysis were used to investigate the intellectual structure of the revenue management literature. The concept of revenue management literature has been globally examined since 2008 with greater interest over time. According to co-citation analysis, three schools of thought are identified, including customer orientation, operational performance, and revenue management technique. Most highly influential documents are conceptual papers. Six dominant topics in the research field of revenue management, including dynamic pricing, tourism, hotel, hospitality, machine learning, and consumer behavior, have recently been examined in the literature. As research in the revenue management literature has shifted to consumer orientation, applying consumer behavior theories to explain revenue management practices is beneficial to provide more significant insights for researchers. In addition, the literature has expanded to include different types of businesses, making it imperative to examine the application of revenue management in each type of business.
1. Introduction
Revenue management is crucial for companies in the tourism and hospitality industry to maximize revenue from their fixed and perishable capacity [1,2]. With a fixed capacity, it is nearly impossible for businesses in this field to increase their capacity quickly for high-demand periods. This challenge applies across the tourism and hospitality industry, in which fluctuations in customer demand are an ongoing constraint that impacts pricing and profitability [1,3,4,5,6]. Furthermore, companies in this industry must also contend with the perishability of their inventories, whether that consists of hotel rooms, airline seats, restaurant dining hours, or tee times on golf courses [1,4,5,6]. In all of these cases, there is a limited “shelf-life” in which the unsold inventory cannot be resold in the future.
With these particular industry characteristics, tourism and hospitality enterprises face an ongoing challenge to balance the sales price and inventory to minimize unused resources and maximize revenue [7]. Effective revenue management is vital for companies in this industry to attain year-round profitability despite fluctuating demand [1]. Indeed, differences in the capacity of companies to effectively manage revenue can explain differences in the financial performance of tourism and hospitality companies operating in the same marketplace [8,9,10].
Revenue management is recognized as a multidisciplinary topic. Its practices cut across multiple subject areas, including marketing, strategy, and consumer behavior [11]. However, research reviews that have examined the theoretical and empirical literature on revenue management in the tourism and hospitality industry tend to focus on specific business types. For example, Binesh and Belarmino reviewed research on revenue management in hotels [7], and Raza et al. examined studies of revenue management among airlines [12]. Multi-business reviews of revenue in tourism and hospitality that have been conducted have excluded airlines [2,11].
Furthermore, the reviews not only focused on specific business types (such as hotels), but each review limited its search scope in many ways. For instance, one of the review papers searched three online databases, including EBSCO, ScienceDirect, and ProQuest Business, and also limited the search to only selected journals in the hospitality and tourism field [11]; 158 documents were analyzed. In another bibliometric review of hospitality revenue management with similar search criteria, 343 documents were analyzed [2]. In another meta-analysis in the hotel industry, only four databases were used, EBSCO, ScienceDirect, Tourism and Hospitality Complete, and ProQuest [7]; 134 articles were identified, but only 76 articles were eligible for further analysis. While the bibliometric review of Reza et al. has a broader search criterion, it only reviews articles on airline revenue management [12].
Thus, the authors attempted to investigate more literature on a holistic multi-business review of research on revenue management in the tourism and hospitality industry that also encompasses airlines, hotels, restaurants, and other tourism enterprises, and revenue management is a multidisciplinary topic that cuts across various subject areas of business and management [11]. This approach offers another crucial perspective on the intellectual structure of the revenue management literature in the tourism and hospitality industry.
This systematic review of research used the bibliometrics method to review the literature on revenue management in the tourism and hospitality industry. This review addresses the following research questions:
- What do the breadth, growth trajectory and geographic distribution of the literature on revenue management in the tourism and hospitality industry look like?
- What are the existing schools of thought in the literature on revenue management in tourism and hospitality?
- What are the most frequently examined research topics in the revenue management literature in the tourism and hospitality industry and how has the trend of topical focus shifted over time?
This review analyzed 1165 Scopus-indexed documents using the bibliometric review method. As this study aimed to review the literature on revenue management across the tourism and hospitality industry published in both journals inside and outside of the tourism and hospitality field, the bibliometric review method was selected as it allowed for a large number of documents to be reviewed [13]. Bibliometric analyses included descriptive statistics, citation, co-citation, and keyword co-occurrence analysis. Software programs, including VOSviewer 1.6.18 [14], Microsoft Excel 16.77.1 [15], and Tableau Desktop Public Edition [16], were used for data analysis.
This review provides an overview of the landscape of 32 years of literature on revenue management across the tourism and hospitality industry. Unlike many recently published reviews, this paper included documents from journals inside and outside the tourism and hospitality field to understand revenue management from a multidisciplinary perspective. In addition, while many recent reviews excluded airlines in their review, this study also included documents on revenue management in airlines for review along with other businesses in the tourism and hospitality industry. Therefore, this review gives scholars in this field a broader view of the literature on revenue management in the tourism and hospitality industry in the aspects of growth trajectory, geographic distribution, intellectual domains, themes and linkages among top-cited authors, and the trend of frequently examined topics relating to revenue management.
2. Method
This paper applied the bibliometric review method to review the literature on tourism and hospitality industry revenue management. The main aim of this study was to examine the trends, intellectual structures, and frequently discussed topics associated with revenue management in this industry. Therefore, the bibliometric method was suitable for this review. Moreover, the bibliometric review method can handle many documents [13], enabling this review to examine the entire body of literature on the chosen subject.
2.1. Identification of Sources
Previous reviews on revenue management in the tourism and hospitality industry limited document collection to articles published in top journals in tourism and hospitality [2,11]. However, as noted above, revenue management is a multidisciplinary topic [11]. Thus, a broader search strategy is required to examine this literature comprehensively. For this reason, the author used a keyword search strategy. Scopus was selected as a database for the document search as Scopus is known to have more comprehensive coverage of social science literature than the Web of Science [13,17].
In terms of conceptual definition, revenue management is popularly defined as the process of selling the right capacity to the right customer for the right price at the right time through the right channel [2]. Another definition of revenue management is the combination of the art and science of demand forecasting while at the same time configuring the rate and availability of the inventory in regard to a particular demand group [18]. The United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) refers to tourism as the activity of visitors, who travel to places outside of their usual environment for personal or business purposes for less than a year [19]. Regarding hospitality, Brotherton has defined hospitality as a human exchange that is contemporary, voluntary, and mutually beneficial based on specific products or services [20].
In line with the conceptual definitions, two sets of keywords were used in the search. The first set was “revenue management” and the closely related terms “yield management” and “dynamic pricing”. The second set of keywords reflects the context of this study: “tourism” and “hospitality”. Moreover, given the goals of this review detailed above, “airline”, “hotel”, and “restaurant” were also included in the second set of keywords. Unlike previous reviews [2,11], the airline industry was included in this review as the nature of the airline business is related to the definition of tourism established by UNWTO [19].
Regarding search criteria, journal articles, conference papers, books, and book chapters were included in this search. As this paper aimed to examine a broad range of documents in the tourism and hospitality industry, books and book chapters were included in the search. Conference papers were included to identify any recent shift in the publication trend after the COVID-19 pandemic. Regarding document limitation, the author excluded documents that were not published in English. The search period was open-ended and spanned from 1989 to 2021.
This review adopted the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) guidelines [21] to conduct a systematic review of research. The initial search on the Scopus database with the two sets of keywords resulted in 1577 documents (see Figure 1). These 1577 documents were screened with the previously mentioned search criteria using the Scopus filters, and 159 documents were excluded from this study. After the screening process, there were 1418 documents eligible for further assessment. After the assessment, 253 duplicates or irrelevant documents were removed from this review. In the end, 1165 journal articles, conference papers, books, and book chapters on revenue management in the tourism and hospitality industry that were published in the English language from 1989 to 2021 were included in this review.
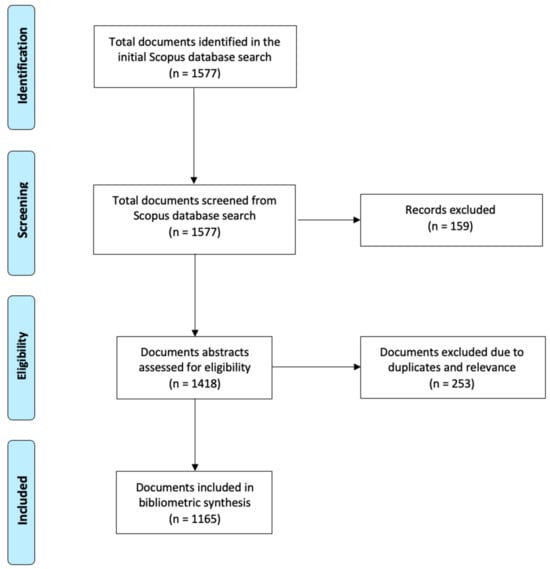
Figure 1.
PRISMA flow chart of document identification procedures.
2.2. Data Analysis
The metadata of 1165 Scopus-indexed documents were exported. The metadata include author names, titles, year of publication, authors’ affiliations, abstracts, journal names, keywords, and citation information. The exported metadata might contain text discrepancies that could mislead the result of data analysis. For instance, an author who published his or her work under two initial names might have fewer citations as his or her citations are cited under two different names. Also, keywords with similar meanings, such as “hotel” and “hotels”, could mislead the keyword co-occurrence analysis as keywords with similar meanings are counted separately. Therefore, thesaurus files were created to combine all the text discrepancies for authors and keywords as a data-cleansing process to ensure the quality of the metadata.
Descriptive analyses were used to examine the breadth, growth trajectory, and geographic distribution of the literature. Scopus analytical tools were used to identify the literature’s size and growth trajectory. For geographic distribution, the data were exported from Scopus and imported to Tableau [16] to create a geographic map of document distribution.
Other than descriptive analyses, science mapping is used to illustrate the results of the intellectual body of literature. Science mapping creates visuals that help describe relationship features in many data analysis techniques, such as citation analysis, co-citation analysis, and keyword co-occurrence analysis [13].
To identify the existing schools of thought, themes, and linkages among top-cited authors and documents and frequently examined research topics, VOSviewer software [14] was used. This software can be used to conduct citation analyses, co-citation analyses, and keyword co-occurrence analyses.
Author co-citation analysis was used to identify the existing schools of thought in the literature. Author co-citation analysis measured the number of times an author has been cited in the reference list of the reviewed documents [13]. This means that results from the author’s co-citation analysis go beyond the database of 1165 documents in this review. To be more specific, author co-citation analysis recognizes the influence of frequently cited authors on revenue management in the tourism and hospitality industry, even though their studies are not in the database searched in this review.
Citation and co-citation analyses on authors and documents were employed to identify themes and linkages among the top-cited authors and documents in the literature. Similar to identifying existing schools of thought, author and document co-citation analyses could be used to identify themes and linkages among authors and documents that strongly influence this topic. In addition, author and document citation analyses were also used to find the themes and linkages among top-cited authors and documents.
Citation analysis measures the number of times each author or document has been cited within a specific database [13]. In the case of this paper, it measures how many times other studies on Scopus have cited each of the 1165 documents and its author. Hallinger and Kovacevic have mentioned that it is best to understand the result of citation analysis together with other metrics, such as co-citation analysis [13]. Therefore, this review employed citation and co-citation analyses on authors and documents to identify themes and linkages among the top-cited authors and documents.
Keyword co-occurrence analysis is used to identify frequently examined research topics and shifts in trends over time. Keyword co-occurrence analysis is a text-mining technique that tracks the frequency of keywords in the title, keywords, and abstract of each document in the database [13]. The authors further explain that keyword co-occurrence analysis could be used to identify topics frequently studied in the literature. In addition, using VOSviewer [14], a temporal co-word map was generated to identify the trend of change in topics in the field over time [13].
3. Results
3.1. Growth Trajectory and Geographical Distribution of the Literature
There were 1165 Scopus-indexed publications on revenue management in the tourism and hospitality industry published between 1989 and 2021. Figure 2 illustrates the annual publication trend in that period. It could be inferred that there is a difference between the number of annual publications before and after 2008. More specifically, during the pre-2008 period, annual publications were never higher than 30, while from 2008 onwards, the lowest number of annual publications was 49. In addition, annual publications of revenue management literature in the tourism and hospitality industry significantly increased between 2007 and 2008, and the figure nearly doubled from 25 to 49 publications within just one year.
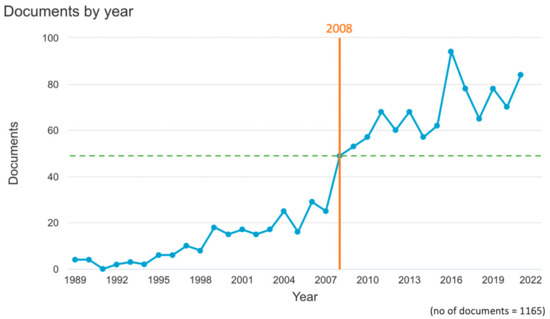
Figure 2.
Annual publication volume of revenue management literature between 1989 and 2021.
A similar trend of annual publication was also found by Denizci-Guillet [2]. A dramatic increase in the annual publications from 2007 to 2008 and the trend of the post-2008 period, during which the number of publications was tremendously higher than the pre-2008 period, were also noticed. The author has concluded that the increase in publication trends is the result of IT advances and the significance of online distribution channels [2].
Regarding geographical distribution, Figure 3 illustrates the number of published documents by territories between 1989 and 2007. It could be inferred that the United States is the only key contributor in terms of the number of publications, with 136 publications in 18 years. Other than Canada, the United Kingdom and China, which hold 15 publications, other countries only have a single-digit number of publications. Furthermore, Figure 3 shows that the topic of revenue management in the tourism and hospitality industry has not yet been of interest to scholars in various regions, such as Southeast Asia, the Middle East, Western Europe, Africa, and South America.
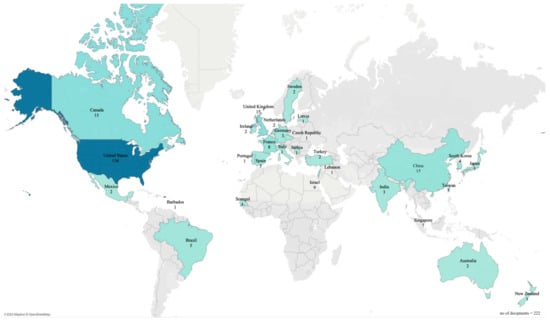
Figure 3.
Number of published studies on revenue management by territory, 1989–2007.
However, from 2018 onwards, the literature became more global in nature. Figure 4 shows the number of published studies by territory between 2008 and 2021. There was an increase in the number of publications from the territories that had already published studies before 2018. Comparing the number of publications within 13 years from 2008 to 2021 and 18 years from 1989 to 2007, some territories drastically increased this number. For instance, China increased its publications from 15 to 158, the United Kingdom from 15 to 77, and Germany from 3 to 54.
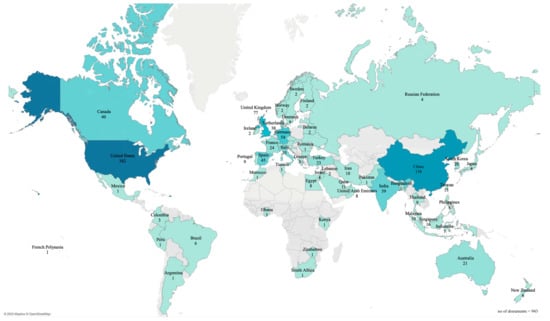
Figure 4.
Number of published studies on revenue management by territory, 2008–2021.
In addition, new territories started to publish studies from 2008 onwards. Clear examples are the Middle East, Southeast Asia, and Eastern Europe territories, where publications significantly increased from 1989 to 2007. Also, authors in South America and Africa started to examine this topic, but the number of studies in this field is still limited.
Looking into the Southeast Asia region, the economics of this region strongly relies on tourism. In 2018, EUR 121 billion was generated from tourism receipts in Southeast Asia, which accounted for 12.6% of its economy and created 38.1 million jobs or 12.2% of the total employment in the region [22]. Even though there were publications from 2018 onwards, the number was still low, with fewer than 50 studies being published from 1989 to 2021. Specifically, in the Greater Mekong Subregion, only Thailand has examined this topic, and only nine studies have been published. Revenue management applications could help companies in the tourism and hospitality industry drive their profit [9,10]. However, this field seems to not get much attention from scholars in this region.
3.2. Schools of Thought in the Revenue Management Literature
The authors’ co-citation analysis via VOSviewer [14] shows three schools of thought in the literature on revenue management in the tourism and hospitality industry, as shown in Figure 5. Schools of thought are classified by the topical focus of studies published by the authors in each cluster. The three schools of thought identified in this review are “Customer Orientation”, “Operational Performance”, and “Revenue Management Technique”.
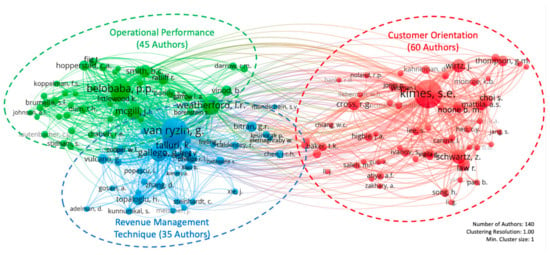
Figure 5.
Schools of thought in the revenue management literature.
Figure 5 presents important schools of thought in the revenue management literature. The size of the nodes reflects the frequency of citations of each author being cited by other studies on revenue management in the tourism and hospitality industry. In this review, the smaller nodes reflect 50–60 citations, while the bigger nodes represent 600–1400 citations. The link between nodes shows the co-citation frequency of two authors that other studies within this field have cited together. The density of the link indicates the number of co-citations between the two authors; a denser link means a more significant number of co-citations. The proximity between each author indicates the frequency of co-citations as well. Closer proximity reflects that the authors are cited together more often, which could imply a similar topical focus. Scholars are grouped into different colors based on the relatability of their studies. Each color represents a school of thought.
The customer orientation school of thought has 60 authors in total. The author’s co-citation analysis shows that the authors in the customer orientation school of thought tend to publish studies related to customers. For instance, Kimes came up with a list of acceptable and unacceptable practices in the view of customers [23]. Kimes and Wirtz tested acceptability for demand-based pricing in terms of different rate fences in the restaurant context and discovered that different rate fences could lead to different levels of customer perception of fairness [24]. Mattila and Choi explored the customer perception of fairness regarding pricing and confirmed that the level of information that customers receive influences their perception of fairness [25]. Noone et al. explored the possibility of integrating revenue management with customer relationship management and came up with crucial issues to be addressed [26]. From another angle, the publications in this school of thought are frequently associated with applying revenue management in the hospitality context, which is heavily focused on hotels and restaurants.
Kimes is the author with the most prominent node in this school of thought. This could imply that she is the most influential author in this school of thought. Her influence was also highlighted by Denizci-Guillet [2], who explained that Kimes’ seminal work had defined the definition of revenue management in the hospitality industry [1], which further studies used as a foundation to develop a more robust definition [27,28].
For the operational performance school of thought, there are 45 authors. Unlike the customer orientation school of thought, where one author stands out from the others in terms of influence, there are a few authors with large-sized nodes, including Belobaba, Weatherford, and McGill. The topical focus of this school of thought is mainly associated with the operational aspects of revenue management.
While the customer orientation school of thought tends to focus more on the customer side, studies from authors in the operational performance school of thought tend to focus more on the organization side, which is associated with revenue optimization, inventory management, and pricing models. In addition, studies in this school of thought are frequently discussed in the context of the airline business. For instance, Szymański and others developed a continuous pricing algorithm that helps airlines generate around one- to two-percent-higher revenue gain [29]. Van Ryzin and Mcgill introduced an adaptive algorithm for airline seat protection levels, which is suitable for small airlines that do not have a full revenue management system [30]. Tavana and Weatherford enhanced the expected revenue maximization formulation for airline seat allocation to make it more effective in an unrestricted fare environment [31].
Regarding the revenue management technique school of thought, there are 35 authors. A few authors have a strong influence on this school of thought, including Van Ryzin, Talluki, and Gallego. However, the nodes of these highly influential authors are plotted next to each other, which means they tend to have a similar topical focus as they are frequently cited together.
The revenue management technique school of thought tends to focus on the mathematical calculation of the models and algorithms with less application in any specific business, unlike the other two schools of thought. For instance, Davis and others designed a study to tackle optimization problems with the nested logit model [32]. Feng and Xiao presented a revenue maximization pricing model for perishable inventory and fixed capacity assets with the inclusion of risk factors [33]. Vulcano et al. provided a guideline on how an optimal dynamic auction should be conducted in a dynamic pricing environment [34].
It should be noted that the study on revenue management in the tourism and hospitality industry with the highest citation count on Scopus is a collaboration between two leading authors in this school of thought [35]. The document is a conceptual paper on optimal dynamic pricing which examines the problem of perishable inventory in a stochastic demand environment.
The most co-cited document was written together by two highly influential authors in the operational performance and revenue management technique schools of thought [36]. The document is a review paper containing a glossary of revenue management terminologies and topics such as information systems in revenue management and the development of revenue management [36]. This could be one of the explanations for the proximity between these two schools of thought.
It is reflected in Figure 5 that the customer orientation school of thought is distanced and contains fewer links compared to the other two schools of thought. This could be explained by the fact that revenue management concepts were first introduced in the airline industry, and then hotels adopted and applied the concept [11]. Also, the nodes between the operational performance and revenue management technique schools of thought are in close proximity, which reflects the fact that these two schools of thought both examine the operational aspect of revenue management, including topics such as pricing models and revenue optimization techniques. At the same time, the customer orientation school of thought tends to focus more on the customer aspect of revenue management.
3.3. Themes and Linkages among Top-Cited and Co-Cited Authors and Documents
Table 1 shows the top 20 authors in the revenue management field with the highest Scopus citation count. In detail, Table 1 indicates the author’s name, nation based on the author’s most recent affiliation, school of thought, number of documents published, Scopus citation count, and citations per document (CPDs).

Table 1.
Top 20 authors in revenue management with the highest number of Scopus citations.
In line with the finding on geographical distribution that a huge number of publications came from the United States, author citation analysis also shows that more than half of the top 20 authors have an affiliation in the United States. Regarding schools of thought, one important pattern was spotted in the author citation analysis. From the top half of Table 1, it could be inferred that authors in the revenue management technique school of thought only published a few studies, but they tended to have higher citations per document. On the other hand, authors in the customer orientation and operational performance schools of thought published a more significant number of documents, but their citations per document were much lower. This could be explained by the fact that both the customer orientation and operational performance schools of thought have published papers in many industry-specific research areas.
On the other hand, studies from the revenue management technique school of thought are more general, so they have a greater possibility of being cited in various fields of study. McGill is the only author that does not fit with this assumption. Still, the author co-citation map in Figure 5 shows that this author has a close relationship with key authors in the dynamic pricing model school of thought.
The results of the author co-citation analysis are displayed in Table 2, including the author’s name, nation based on a recent affiliation, school of thought, and number of co-citation counts. In line with the science map in Figure 5, Kimes stands out from the other authors in the customer orientation school of thought as the most influential author. For the other two schools of thought, even though there is one leading author with the greatest influence in the field, there tend to be two more authors with a high co-citation count in each school of thought.

Table 2.
Top 20 co-cited authors in the revenue management literature.
The results of the document citation analysis are shown in Table 3. The table provides information on the top 20 most cited documents in the literature, including document title, the location where the document was published, topical focus, type of research paper, number of Scopus citations, and number of citations per year. The document citation analysis results show that the geographical location trend is similar to the descriptive statistic, author citation analysis, and author co-citation analysis, where the United States dominated the top-cited publications list.

Table 3.
Top 20 documents in the revenue management literature with the highest number of Scopus citations.
Regarding topical focus, most studies on the top 20 list are associated with either pricing or capacity management. One important finding highlighted by the document citation analysis is that more than half of the studies on the top 20 highest number of Scopus citations list are conceptual papers. Only two review papers are listed on the top 20 highest number of Scopus citations list, and in a further analysis of the whole database, only around 25 research reviews were identified from 1165 documents. This implies a lack of reviews of research on the topic of revenue management in the tourism and hospitality industry.
The findings from the document citation analysis are also similar to the results from the document co-citation analysis. Table 4 shows the top 20 most co-cited documents in the literature. More than half of the documents on the top 20 co-citation list are conceptual papers. In addition, there are only three review papers on the list, which highlights the need for more reviews of research.

Table 4.
Top 20 co-cited documents in the revenue management literature.
McGill and Van Ryzin should be highlighted as their paper has the highest number of co-citations and the third highest number of Scopus citations [36]. This study is a review of research that summarizes the history of research on yield management in the transportation sector. This review covers various topics, ranging from a glossary of revenue management terminology, the development of revenue management techniques, critical factors to implement in revenue management along with information systems, and future research directions in revenue management [36].
From both document citation and document co-citation analyses, it could be inferred that the most influential documents are associated with pricing management or capacity management. This implies that documents on the top-cited and co-cited papers list focused on traditional revenue management, a more tactical approach [18]. Erdem and Jiang mentioned that the revenue management literature, especially in the hotel sector, has shifted focus to a more strategic approach that incorporates other functions [18]. Even though new studies on revenue management in the tourism and hospitality industry are focusing more on a strategic approach, the most influential studies are still the ones from the traditional side of revenue management.
3.4. Frequently Examined Topics and Trends in the Revenue Management Literature
The results of the keyword co-occurrence analysis are reflected in the temporal co-word map in Figure 6. The smallest node reflects 15 studies that contain the keywords in the title, keywords, or abstract.
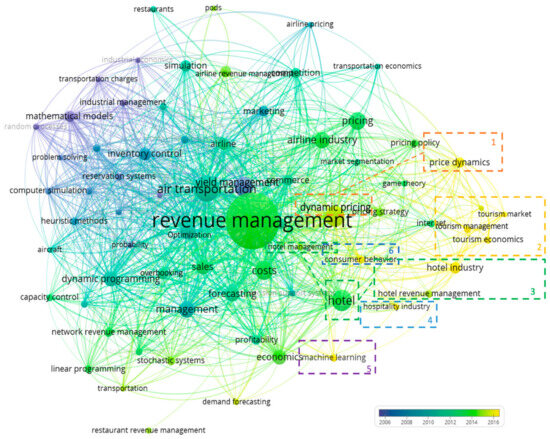
Figure 6.
Temporal co-word map on topics in the revenue management literature.
In terms of frequently examined topics, this review has categorized them into three groups: context, content, and disciplinary. In terms of context, airlines and hotels are the two key businesses that have been most frequently examined. Restaurant and tourism businesses also appear in the literature but with less frequency. In terms of content, there are four main themes that are frequently examined, including pricing, capacity management, optimization models, and forecasting. In line with previous reviews [63,64], these four topics were also identified to be frequently examined topics in the revenue management literature. In terms of discipline, economics, marketing, and consumer behavior are highlighted as the fields most frequently examined together with revenue management. This finding is in line with Binesh and others’ paper, which found that many economic theories are being used in revenue management [7]. In addition, this study confirmed the findings of Denizci-Guillet and Mohammed, who stated that revenue management is a multidisciplinary topic [11].
In addition, the temporal co-word map also reflects the time frame in which each keyword was mostly examined. Darker-colored nodes indicate that the topic has been frequently examined in the past, while the lighter-colored nodes mean that the topics have been frequently examined in more recent years [13].
It is clear from the map that the literature on revenue management has shifted the focus from yield management, industry management, and reservation systems toward the concepts of price dynamics, consumer behaviors, and tourism markets. Furthermore, a trend could also be seen in how the schools of thought are formed. The literature started with the application of revenue management in airlines, which is mostly related to optimization on the organization side. It was heavily influenced by dynamic pricing model concepts. Later, the hospitality businesses adopted the concept of revenue management from airlines but shifted the focus toward the customer side. Hence, both the author co-citation map in Figure 5 and the temporal co-word map in Figure 6 display the same result of a closer relationship between the revenue management technique and operational performance school of thought, while the customer orientation school of thought is independent.
This review has also identified six topics frequently examined in the past years. These six topics include dynamic pricing, tourism, hotel, hospitality, machine learning, and consumer behavior. These six topics could be categorized into three themes, content, context, and disciplinary, for further interpretation.
Regarding the content theme, machine learning in dynamic pricing is highlighted as a promising theme in the revenue management literature. The introduction of machine learning could impact the operation side of revenue management as machine learning can assist revenue managers with demand forecasting [65]. For instance, Schwartz and others explored machine learning and its effect on demand forecasting accuracy [66]. Sánchez-Medina and C-Sánchez also focused on using machine learning and big data to forecast hotel cancellations [67].
In terms of context, the interest of scholars in the revenue management field is beginning to shift from hotels toward other business types in the tourism and hospitality industry. Restaurant revenue management is also displayed on the temporal co-word map in Figure 6, even though the node is still small. Hence, more research on revenue management in restaurants and tourism destinations can be expected in the future. For instance, Thompson discussed models on demand timing flexibility to improve restaurant revenue [68]. Tang and others explored the perception of fairness in different revenue management practices in the restaurant business [69]. Meanwhile, regarding tourism destinations, Kuokkanen and Bouchon used behavioral game theory to explain how cooperation can lead to competitiveness in pricing and demand creation [3].
In terms of related disciplines, it could be implied that recent literature is more focused on the consumer side as the trend has shifted from traditional marketing to a consumer behavior perspective. For instance, Masiero and others used a discrete choice experiment to explore customer behavior regarding hotel booking decisions and found different behaviors among four customer segments [70]. Ettl and others developed a model for personalized discounts, which are expected to help increase revenue by two to seven percent [71].
4. Discussion and Conclusions
This bibliometric review was conducted to identify key themes in the revenue management literature in tourism and hospitality research from a broader perspective than previous reviews. In this section, an interpretation of this review’s main findings, conclusions, implications, and limitations are discussed.
4.1. Interpretation of the Findings
This review has obviously shown that the revenue management literature in the tourism and hospitality industry has become more popular, as reflected by both the increasing number of publications and the increasing number of regions publishing related studies since 2008. The findings from this review are in line with Denizci-Guillet [2], who also spotted a similar increasing trend in the revenue management literature from 2008 onwards. The author explains this phenomenon as an effect of IT advances and the increasing significance of online distribution channels.
Even though the results from citation and co-citation analyses point out that the revenue management literature is strongly influenced by publications from the United States, contributions from other regions worldwide are becoming more significant. For instance, regions such as the Middle East, Southeast Asia, and Eastern Europe began publishing revenue management studies from 2008 onwards. The documents reviewed by Binesh and others also show a mixture of articles from different regions of the world [7]. However, considering the importance of tourism in the Southeast Asia region [22], more studies on revenue management are expected from scholars in this region.
Three schools of thought were identified in the author’s co-citation analysis. The three schools of thought are customer orientation, operational performance, and revenue management technique. While the operational performance and the revenue management technique schools of thought have a close relationship, the customer orientation school of thought is more independent and distanced from the others. This study’s findings provide a broader perspective than the work of Denizci-Guillet [2], as this paper identified the schools of thought across different businesses. Their review focuses on identifying intellectual knowledge, specifically in the hospitality industry [2].
Further findings from the author citation analysis point out that authors from customer orientation and operational performance schools of thought published more studies than those from the revenue management technique school of thought. However, authors from the revenue management technique school of thought have a much higher number of citations per document. This could be explained by the fact that most of the studies from the revenue management technique school of thought are concepts that could be applied in various businesses, while studies in the customer orientation school of thought, which are frequently examined in the hospitality context, and those in the operational performance school of thought, which are frequently examined in the airline context, might receive citations within their field.
Findings from document citation analysis and co-citation analysis suggest a lack of reviews of the revenue management literature in the tourism and hospitality industry. Only around 25 reviews were identified from 1165 documents in the review database. In addition, the most influential papers in this field according to both citation and co-citation lists are conceptual papers, and only a few reviews were identified. The lack of reviews is also evidenced in Binesh and others’ paper [7], where there are only 2 reviews of research out of all the 76 reviewed articles. Denizci-Guillet and Mohammed have also called for more review papers for the revenue management literature [11].
Six topics were identified as emerging topics in the revenue management literature in the tourism and hospitality industry. This review categorized them into three themes, content, context, and disciplinary. In terms of content, recent attention has been given to enhancing demand forecasting with machine learning in a dynamic pricing environment. In terms of context, the focus has shifted from the airline to the hospitality industry, including hotels, restaurants, and tourism destinations. Denizci-Guillet also spotted the transition of revenue management literature from airlines to hotels and expansion of its scope to other business types in the hospitality industry [2]. In terms of disciplines relating to revenue management, the focus has shifted from traditional marketing toward consumer behavior. However, even though there are many studies that directly examine revenue management in the aspect of consumer behavior, Binesh and others found out that consumer behavior theories still need to be utilized by the revenue management literature [7].
Our review has demonstrated that revenue management is becoming more sustainable in terms of the business perspective. Previous studies point out that revenue management is shifting to become more long-term-oriented and customer-centric to sustain long-term revenue rather than focusing on short-term revenue gain from setting price in regard to the inventory level [18,72,73]. The findings of this study also provide a broad perspective of this shift. First, our analysis identified consumer behavior as one of the most frequently examined topics in the revenue management literature in recent years. Second, hotel and hospitality businesses have also been identified as a more recent topic, which is linked to our identification of the school of thought that studies in the hospitality context are frequently associated with the customer orientation school of thought. The findings also point out studies on customer perception of fairness in pricing and its possible integration with customer relationship management [23,24,25,26], which implies that revenue management is becoming more customer-centric. These findings explain the shift of revenue management toward a more sustainable business approach by becoming more customer-centric and long-term-oriented to sustain long-term revenue gain rather than focusing on short-term profit from inventory optimization.
4.2. Conclusions
This paper achieved its three objectives. Firstly, this paper indicated continuous growth in the breadth and trends in academic output from 1989 to 2022, and the growth trajectory has clearly and significantly increased in terms of the number of academic studies. The United States dominated in this field, but a significant increase in publications was found in Europe and Asia. Secondly, this paper found three schools of thought in the revenue management research in tourism and hospitality, namely “customer orientation”, “operational performance”, and “revenue management technique”’ Thirdly, the topical focus has shifted from yield management, industry management, and reservation systems toward consumer behaviors, price dynamics, and tourism markets.
4.3. Implications
The revenue management literature has been significantly investigated and expanded into the hospitality industry in recent years. Traditionally, hotels were the only main type of business that applied revenue management practices, but currently, it can be seen that practices of revenue management are also applicable to a variety of businesses, including restaurants. In addition, there have been several recent studies on revenue management in the context of tourism destinations. This implies that the application of revenue management is becoming broader and more relevant for different types of businesses in the tourism and hospitality industry. Hence, as the literature is expanding, future research could examine revenue management in non-traditional types of businesses.
Furthermore, even though this study points out that consumer behavior is the discipline that is most closely examined together with revenue management, there is still no evidence of the usage of consumer behavior theories in attempting to explain revenue management practices [7]. Therefore, future research on revenue management may utilize consumer behavior theories to explain the customer’s actions or reactions towards revenue management practices.
Moreover, this review’s findings indicate an increasing number of academic studies on revenue management in the tourism and hospitality industry. However, there are a limited number of systematic review papers on this topic. Therefore, future research in the form of reviews of research is highly crucial for highlighting or indicating the growth and trends of the literature on revenue management approaches in the tourism and hospitality industry.
The growth of the revenue management literature is not only highlighted in the number of publications but also in terms of regions. To be more specific, our findings show that revenue management has become more globally examined. In addition, our findings also identified the customer orientation school of thought; authors in this cluster tend to publish studies relating to customers. Future studies could take into account the cultural factors of customers in different regions and examine the topic of cultural differences relating to revenue management.
Although the revenue management literature in the tourism and hospitality industry has been globally examined since 2008, Southeast Asia, as a fast-growing and important tourism destination area, still only produces a small number of research and review studies, especially in the Greater Mekong Subregion, where Thailand is the only territory that has examined this topic. Therefore, scholars in this region are encouraged to publish more research on revenue management in the tourism and hospitality industry.
4.4. Limitations of this Review
First, this review used the bibliometric review method to analyze the literature on revenue management in the tourism and hospitality industry. Even though the bibliometric review method allows for many documents to be analyzed [13], it only provides the broad features of the knowledge base and does not explore substantive findings of documents in the database. Future research could further investigate the literature with different methodologies to examine more in-depth findings of particular domains or topics in the literature.
Second, this review only used Scopus as a single database for the document search. Scopus has more coverage of social science literature than the Web of Science [13,17]. However, it still did not include all potential sources. Future research could include other databases to review a higher number of documents.
Third, only documents published in the English language were included in this review due to the language capability of the author. The results of this study point out that the revenue management literature in the tourism and hospitality industry has been globally examined since 2008, especially in China, where the number of documents has increased significantly. Therefore, with the inclusion of documents that are published in other languages, it could be possible to analyze the revenue management literature in other aspects. Future research could include documents in other languages and compare the findings with this study.
Fourth, even though our contextual keywords consisted of two general keywords, “tourism” and “hospitality”, our business-specific keywords only included “airline”, “hotel”, and “restaurant”. Hence, some papers on other types of businesses that did not include the words “tourism” and “hospitality” in their title, keywords, or abstract were not included in this study. Future research could include more business-specific keywords in their search and compare the findings to this study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.S.; Methodology, C.S.; Formal Analysis, C.S. and C.Y.; Resources, C.S.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, C.S.; Writing—Review and Editing, C.Y.; Visualization, C.S.; Supervision, C.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research project is supported by National Research Council of Thailand (NRCT): (Contact No. N41A661112).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Correction Statement
This article has been republished with a minor correction to the Funding statement. This change does not affect the scientific content of the article.
References
- Kimes, S.E. Yield Management: A Tool for Capacity-Considered Service Firms. J. Oper. Manag. 1989, 8, 348–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denizci-Guillet, B. An Evolutionary Analysis of Revenue Management Research in Hospitality and Tourism: Is There a Paradigm Shift? Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2020, 32, 560–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuokkanen, H.; Bouchon, F. When Team Play Matters: Building Revenue Management in Tourism Destinations. Tour. Econ. 2021, 27, 379–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimes, S.E. Revenue Management on the Links: Applying Yield Management to the Golf-Course Industry. Cornell Hotel Restaur. Adm. Q. 2000, 41, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimes, S.E. Restaurant Revenue Management: Implementation at Chevys Arrowhead. Cornell Hotel Restaur. Adm. Q. 2004, 45, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimes, S.E.; Chase, R.B.; Choi, S.; Lee, P.Y.; Ngonzi, E.N. Restaurant Revenue Management: Applying Yield Management to the Restaurant Industry. Cornell Hotel Restaur. Adm. Q. 1998, 39, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binesh, F.; Belarmino, A.; Raab, C. A Meta-Analysis of Hotel Revenue Management. J. Revenue Pricing Manag. 2021, 20, 546–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remy, D.; Boo, H.C.; Tee, S. From Traditional to New Hotel Revenue Management Metrics: An Exploratory Study on the Potential of Nrevpar and Revpac. Tour. Hosp. Manag. 2023, 29, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanks, R.D.; Cross, R.G.; Noland, R.P. Discounting in the Hotel Industry: A New Approach. Cornell Hotel Restaur. Adm. Q. 2002, 43, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.C.; Leimkuhler, J.F.; Darrow, R.M. Yield Management at American Airlines. Interfaces 1992, 22, 8–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denizci Guillet, B.; Mohammed, I. Revenue Management Research in Hospitality and Tourism: A Critical Review of Current Literature and Suggestions for Future Research. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2015, 27, 526–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, S.A.; Ashrafi, R.; Akgunduz, A. A Bibliometric Analysis of Revenue Management in Airline Industry. J. Revenue Pricing Manag. 2020, 19, 436–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallinger, P.; Kovačević, J. Applying Bibliometric Review Methods in Education: Rationale, Definitions, Analytical Techniques, and Illustrations. In International Encyclopedia of Education, 4th ed.; Tierney, R.J., Rizvi, F., Ercikan, K., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2023; pp. 546–556. ISBN 9780128186299. [Google Scholar]
- van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software Survey: VOSviewer, a Computer Program for Bibliometric Mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Microsoft. Microsoft Excel 16.77.1; Microsoft: Redmond, WA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Tableau. Tableau Desktop Public Edition; Tableau: Seattle, WA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Mongeon, P.; Paul-Hus, A. The Journal Coverage of Web of Science and Scopus: A Comparative Analysis. Scientometrics 2016, 106, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, M.; Jiang, L. An Overview of Hotel Revenue Management Research and Emerging Key Patterns in the Third Millennium. J. Hosp. Tour. Technol. 2016, 7, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations World Tourism Organization. International Recommendations for Tourism Statistics 2008; Statistical Papers (Ser. M); Department of Economic and Social Affairs: New York, NY, USA, 2010.
- Brotherton, B. Towards a Definitive View of the Nature of Hospitality and Hospitality Management. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 1999, 11, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; PRISMA Group. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. Int. J. Surg. 2010, 8, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trupp, A.; Dolezal, C. Tourism and the Sustainable Development Goals in Southeast Asia. Österr. Z. Südostasienwiss. 2020, 13, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Kimes, S.E. Perceived Fairness of Yield Management. Cornell Hotel Restaur. Adm. Q. 2002, 43, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimes, S.E.; Wirtz, J. Has Revenue Management Become Acceptable? Findings from an International Study on the Perceived Fairness of Rate Fences. J. Serv. Res. 2003, 6, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattila, A.S.; Choi, S. The Impact of Hotel Pricing Policies on Perceived Fairness and Satisfaction with the Reservation Process. J. Hosp. Leis. Mark. 2005, 13, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noone, B.M.; Kimes, S.E.; Renaghan, L.M. Integrating Customer Relationship Management and Revenue Management: A Hotel Perspective. J. Revenue Pricing Manag. 2003, 2, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, D.K.; Miller, A. Revenue Management for the Hospitality Industry; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; ISBN 9780470393086. [Google Scholar]
- Kimes, S.E. A Strategic Approach to Yield Management. In Yield Management: Strategies for the Service Industries; Ingold, A., McMahon-Beattie, U., Yeoman, I., Eds.; Continuum: London, UK, 2000; pp. 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Szymański, B.; Belobaba, P.P.; Papen, A. Continuous Pricing Algorithms for Airline RM: Revenue Gains and Competitive Impacts. J. Revenue Pricing Manag. 2021, 20, 669–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Ryzin, G.; McGill, J. Revenue Management Without Forecasting or Optimization: An Adaptive Algorithm for Determining Airline Seat Protection Levels. Manag. Sci. 2000, 46, 760–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavana, H.; Weatherford, L. Application of an Alternative Expected Marginal Seat Revenue Method (EMSRc) in Unrestricted Fare Environments. J. Air Transp. Manag. 2017, 62, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.M.; Gallego, G.; Topaloglu, H. Assortment Optimization Under Variants of the Nested Logit Model. Oper. Res. 2014, 62, 250–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Xiao, B. Maximizing Revenues of Perishable Assets with a Risk Factor. Oper. Res. 1999, 47, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vulcano, G.; van Ryzin, G.; Maglaras, C. Optimal Dynamic Auctions for Revenue Management. Manag. Sci. 2002, 48, 1388–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego, G.; van Ryzin, G. Optimal Dynamic Pricing of Inventories with Stochastic Demand over Finite Horizons. Manag. Sci. 1994, 40, 999–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGill, J.I.; van Ryzin, G.J. Revenue Management: Research Overview and Prospects. Transp. Sci. 1999, 33, 233–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmaghraby, W.; Keskinocak, P. Dynamic Pricing in the Presence of Inventory Considerations: Research Overview, Current Practices, and Future Directions. Manag. Sci. 2003, 49, 1287–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talluri, K.; van Ryzin, G. An Analysis of Bid-Price Controls for Network Revenue Management. Manag. Sci. 1998, 44, 1577–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, J.; Stidham, S.; Lautenbacher, C.J. Airline Yield Management with Overbooking, Cancellations, and No-Shows. Transp. Sci. 1999, 33, 147–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Gallego, G. Optimal Starting Times for End-of-Season Sales and Optimal Stopping Times for Promotional Fares. Manag. Sci. 1995, 41, 1371–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerath, K.; Netessine, S.; Veeraraghavan, S.K. Revenue Management with Strategic Customers: Last-Minute Selling and Opaque Selling. Manag. Sci. 2010, 56, 430–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curry, R.E. Optimal Airline Seat Allocation with Fare Classes Nested by Origins and Destinations. Transp. Sci. 1990, 24, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weatherford, L.R.; Kimes, S.E. A Comparison of Forecasting Methods for Hotel Revenue Management. Int. J. Forecast. 2003, 19, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertsimas, D.; Popescu, I. Revenue Management in a Dynamic Network Environment. Transp. Sci. 2003, 37, 257–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Cooper, W.L. Revenue Management for Parallel Flights with Customer-Choice Behavior. Oper. Res. 2005, 53, 415–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, E.A.; Bilegan, I.C. Revenue Management and E-Commerce. Manag. Sci. 2003, 49, 1363–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrate, G.; Fraquelli, G.; Viglia, G. Dynamic Pricing Strategies: Evidence from European Hotels. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2012, 31, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, R.G.; Higbie, J.A.; Cross, D.Q.D. Revenue Management’s Renaissance: A Rebirth of the Art and Science of Profitable Revenue Generation. Cornell Hosp. Q. 2009, 50, 56–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, S.; Higle, J.L. An Introductory Tutorial on Stochastic Linear Programming Models. Interfaces 1999, 29, 33–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrate, G.; Viglia, G. Strategic and Tactical Price Decisions in Hotel Revenue Management. Tour. Manag. 2016, 55, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netessine, S.; Shumsky, R.A. Revenue Management Games: Horizontal and Vertical Competition. Manag. Sci. 2005, 51, 813–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lautenbacher, C.J.; Stidham, S. The Underlying Markov Decision Process in the Single-Leg Airline Yield-Management Problem. Transp. Sci. 1999, 33, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belobaba, P.P. OR Practice—Application of a Probabilistic Decision Model to Airline Seat Inventory Control. Oper. Res. 1989, 37, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brumelle, S.L.; McGill, J.I. Airline Seat Allocation with Multiple Nested Fare Classes. Oper. Res. 1993, 41, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talluri, K.; van Ryzin, G. Revenue Management Under a General Discrete Choice Model of Consumer Behavior. Manag. Sci. 2004, 50, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weatherford, L.R.; Bodily, S.E. A Taxonomy and Research Overview of Perishable-Asset Revenue Management: Yield Management, Overbooking, and Pricing. Oper. Res. 1992, 40, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollmer, R.D. An Airline Seat Management Model for a Single Leg Route When Lower Fare Classes Book First. Oper. Res. 1992, 40, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.C.; Hersh, M. A Model for Dynamic Airline Seat Inventory Control with Multiple Seat Bookings. Transp. Sci. 1993, 27, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belobaba, P.P. Survey Paper—Airline Yield Management an Overview of Seat Inventory Control. Transp. Sci. 1987, 21, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glover, F.; Glover, R.; Lorenzo, J.; McMillan, C. The Passenger-Mix Problem in the Scheduled Airlines. Interfaces 1982, 12, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y. Solution to the Continuous Time Dynamic Yield Management Model. Transp. Sci. 1999, 33, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.K.; Xie, X. Improving Hospitality Industry Sales: Twenty-Five Years of Revenue Management. Cornell Hosp. Q. 2010, 51, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, W.-C.; Chen, J.C.H.; Xu, X. An Overview of Research on Revenue Management: Current Issues and Future Research. Int. J. Revenue Manag. 2007, 1, 97–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo-Carrillo, M.Á.; Chávez-Miranda, E.; Escobar-Pérez, B. Scientific Production on Revenue Management in Tourism on Web of Science and SCOPUS. Curr. Issues Tour. 2020, 23, 880–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.N.; Cerqueira, V. Forecasting Hotel Demand for Revenue Management Using Machine Learning Regression Methods. Curr. Issues Tour. 2022, 25, 2733–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, Z.; Webb, T.; van der Rest, J.-P.I.; Koupriouchina, L. Enhancing the Accuracy of Revenue Management System Forecasts: The Impact of Machine and Human Learning on the Effectiveness of Hotel Occupancy Forecast Combinations across Multiple Forecasting Horizons. Tour. Econ. 2021, 27, 273–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Medina, A.J.; C-Sánchez, E. Using Machine Learning and Big Data for Efficient Forecasting of Hotel Booking Cancellations. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2020, 89, 102546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, G.M. The Value of Timing Flexibility in Restaurant Reservations. Cornell Hosp. Q. 2019, 60, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Repetti, T.; Raab, C. Perceived Fairness of Revenue Management Practices in Casual and Fine-Dining Restaurants. J. Hosp. Tour. Insights 2019, 2, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masiero, L.; Viglia, G.; Nieto-Garcia, M. Strategic Consumer Behavior in Online Hotel Booking. Ann. Tour. Res. 2020, 83, 102947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettl, M.; Harsha, P.; Papush, A.; Perakis, G. A Data-Driven Approach to Personalized Bundle Pricing and Recommendation. MSOM 2020, 22, 461–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noone, B.M.; McGuire, K.A.; Rohlfs, K.V. Social Media Meets Hotel Revenue Management: Opportunities, Issues and Unanswered Questions. J. Revenue Pricing Manag. 2011, 10, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Yoonjoung Heo, C.; Schwartz, Z.; Legohérel, P.; Specklin, F. Revenue Management: Progress, Challenges, and Research Prospects. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 2015, 32, 797–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).