Spatial-Temporal Evolution and Influencing Mechanism of Traffic Dominance in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data Sources and Research Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Research Methods
2.3.1. Road Density
2.3.2. Influence Degree of Trunk Lines
2.3.3. Spatial Accessibility
2.3.4. Ordinary Least Squares (OLS)
2.3.5. Geographically Weighted Regression (GWR)
3. Results
3.1. Spatial and Temporal Evolution Characteristics of Traffic Dominance
3.1.1. Road Density
3.1.2. Influence Degree of Trunk Lines
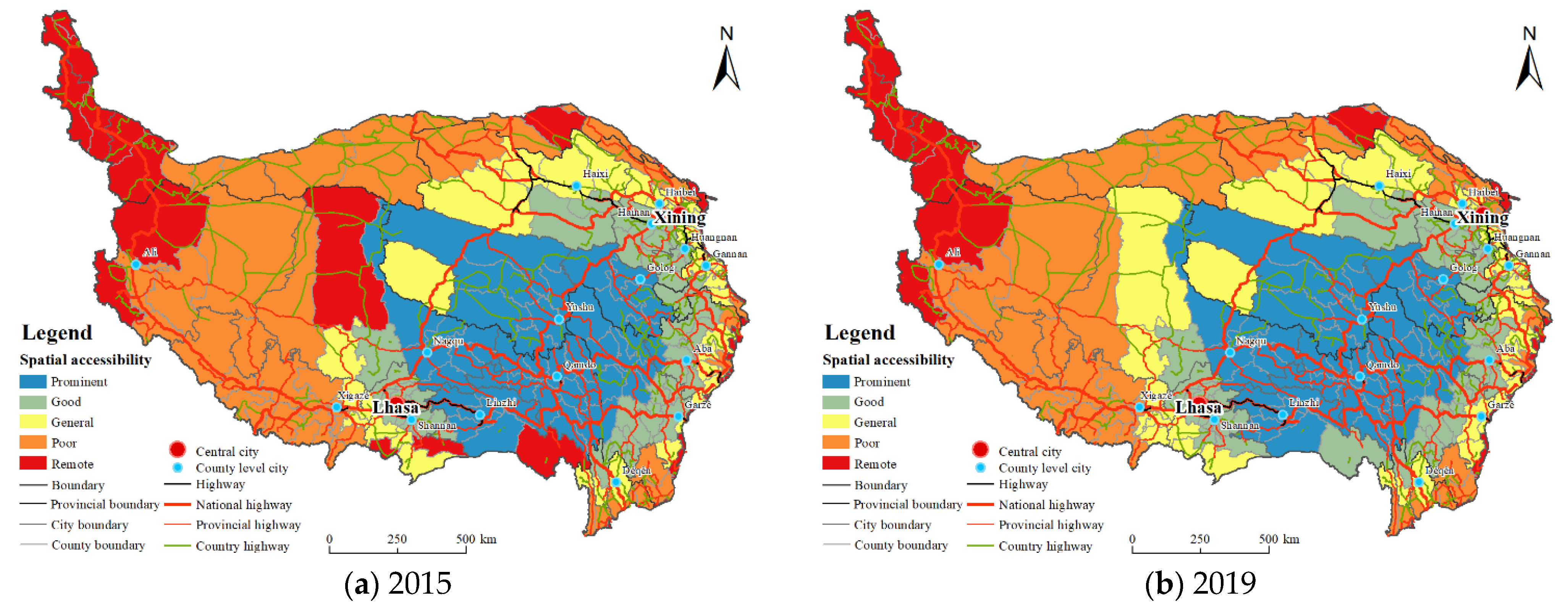
3.1.3. Spatial Accessibility
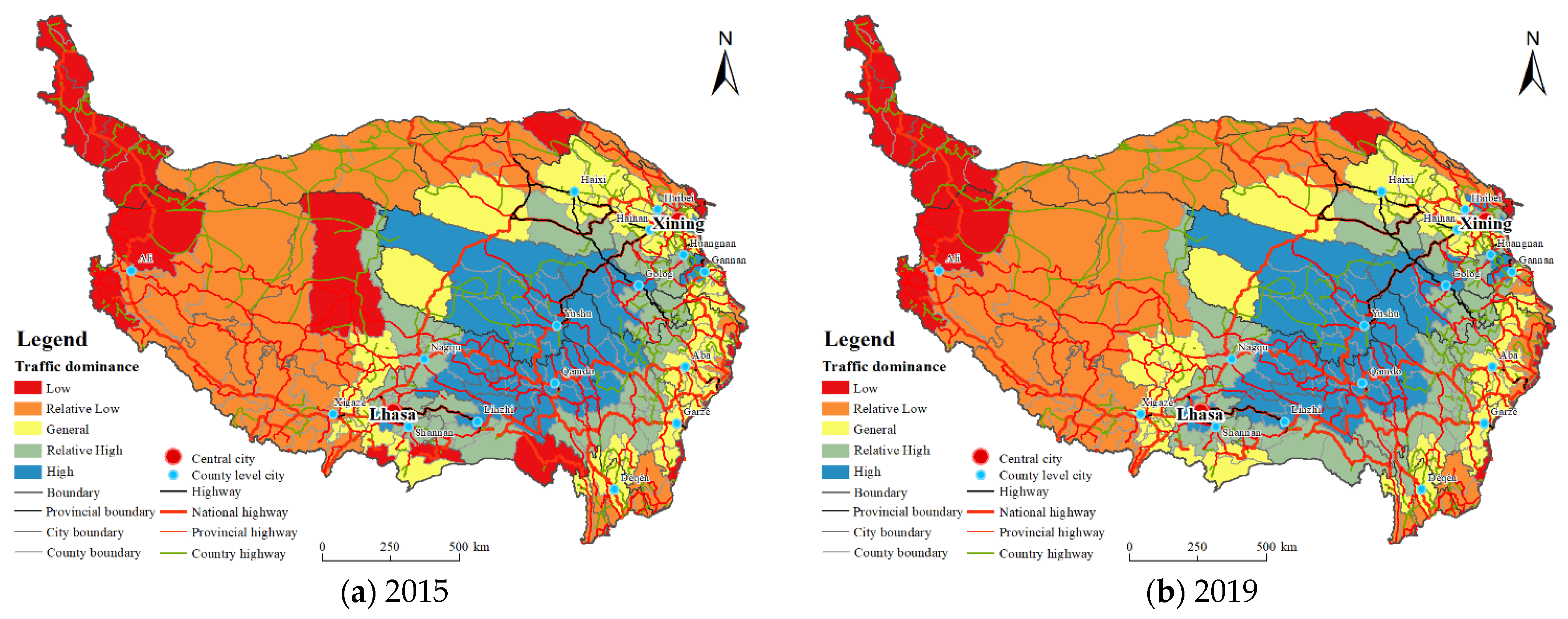
3.1.4. Traffic Dominance
3.2. Influencing Factors of the Spatial and Temporal Pattern Differentiation of Traffic Dominance
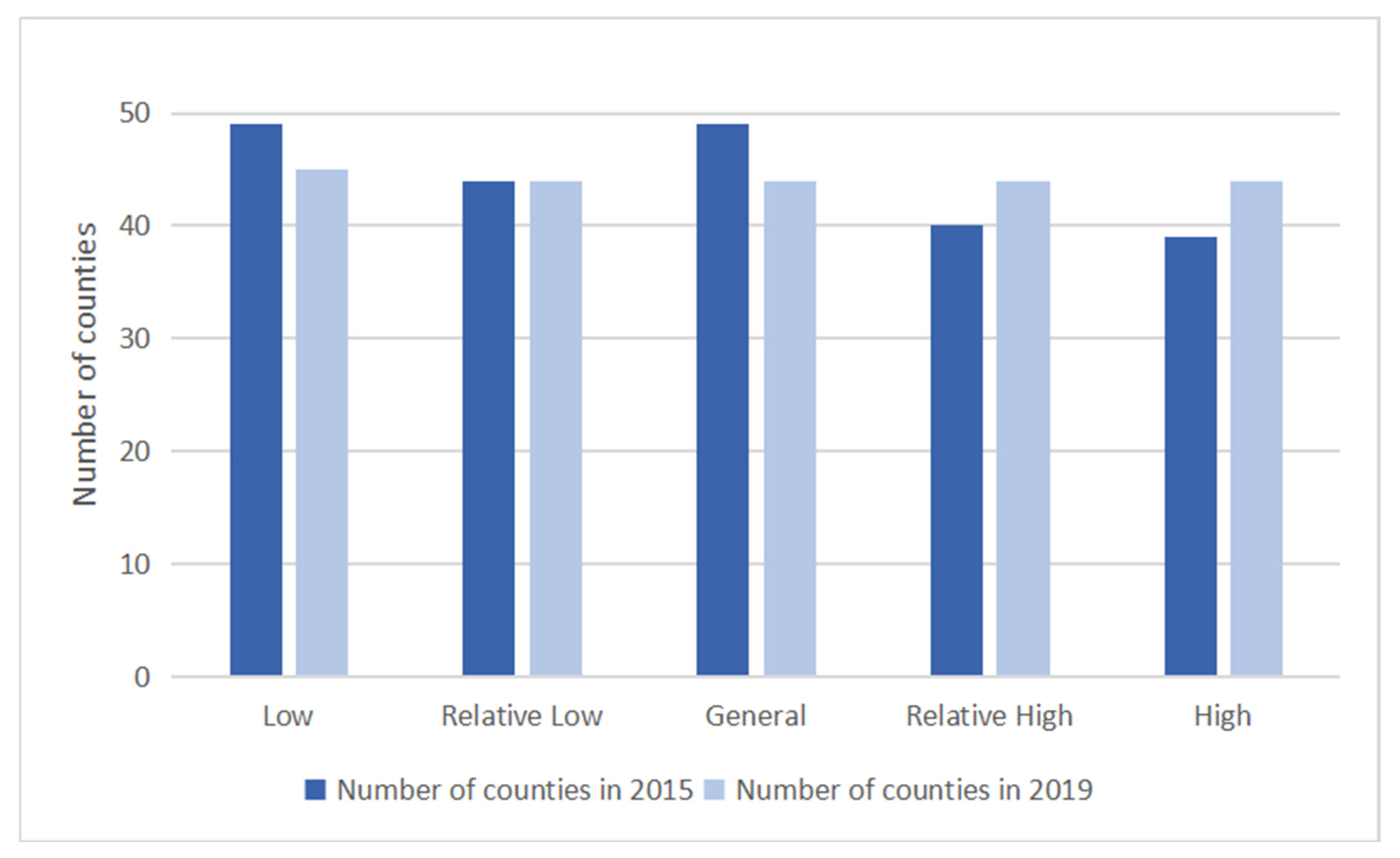
3.2.1. Analysis of Influencing Factors
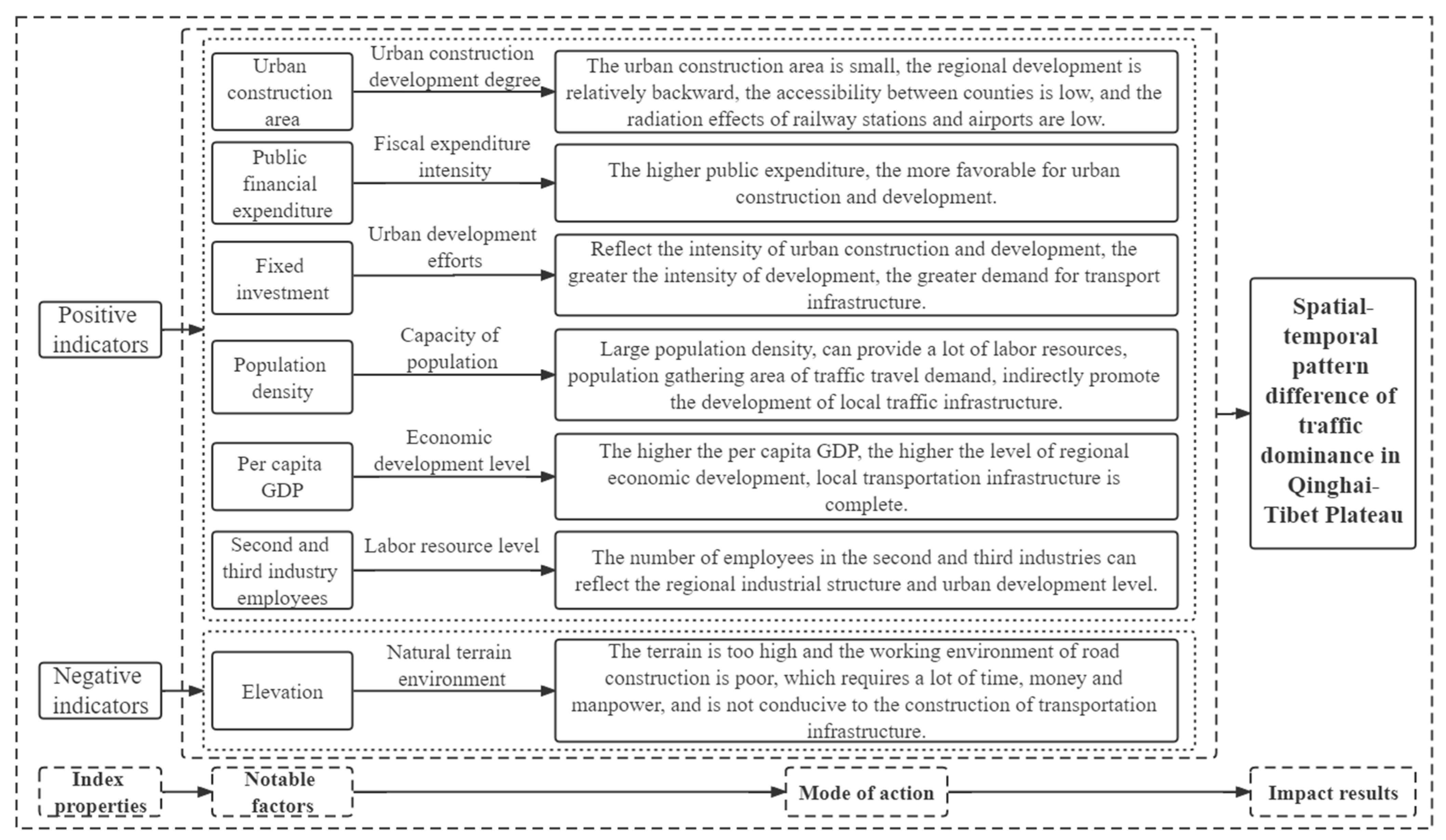
3.2.2. Analysis of Influencing Mechanisms
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, C.; Cheng, J. Spatial pattern of expressway network accessibility and evolution in China. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2016, 36, 803–812. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Jin, F.; Lu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Yang, Y. Development history and accessibility evolution of land transportation network in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 2252–2264. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, J. China: The third pole. Nature 2008, 454, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Immerzeel, W.W.; Lutz, A.F.; Andrade, M.; Bahl, A.; Biemans, H.; Bolch, T.; Hyde, S.; Brumby, S.; Davies, B.J.; Elmore, A.C.; et al. Importance and vulnerability of the world’s water towers. Nature 2020, 577, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, T.; Chen, F.; Cui, P.; Ma, Y.; Xu, B.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, F.; Wang, W.; Ai, L.; Yang, X. From Tibetan Plateau to Third Pole and Pan-Third Pole. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2017, 32, 924–931. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, Y.; Lu, W.; Dai, T.; Song, J. Comprehensive traffic advantage degree and its spatial characteristics at the prefecture level on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: A case study of Linzhi City. Prog. Geogr. 2021, 40, 1332–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Liu, S.; Zhou, L. Regional differentiation of population in Tibetan Plateau: Insight from the “Hu Line”. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2020, 75, 255–267. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X. Impact of Transport Accessibility on Land Use Change in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Ph.D. Thesis, Shanxi Normal University, Xi’an, China, 25 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Cao, X.; Li, T.; Lv, M. Evolution of accessibility spatial pattern of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau in 1976–2016. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2019, 74, 1190–1204. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, Y.; Liu, H.; Song, J.; Dai, T. Research progress of transportation facilities construction and their impact assessment in the Qinghai Tibet Plateau. Adv. Earth Sci. 2020, 35, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Mu, Y.; Xie, S.; Mao, Y.; Chen, D. Thermal-mechanical intluences and environmental effects of expressway construction on the Qinghai-Tibet Permafrost Engineering Corridor. Adv. Earth Sci. 2017, 32, 459–464. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, S. Impact assessment the effect of Qinghai-Tibet Railway construction on ecological environment. Mod. Agric. Sci. 2008, 15, 41–42. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, B.; Yu, Z.; Yang, S.; Huai, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, W. Effects of Qinghai-Tibetan Highway on the activities of Pantholops hodgsoni, Procapra picticaudata and Equus kung. Chin. J. Ecol. 2007, 26, 810–816. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.; Wang, J.; Jin, F.; Ding, N. Evolution of regional transport dominance in China 1910–2012. J. Geogr. Sci. 2015, 25, 723–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, Y.; Pan, W.; Wang, W.; Jin, F. Evolution of China’s overland transportation dominance and its economic effect: A county-level analysis. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2022, 77, 1937–1952. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, F.; Wang, C.; Li, X. Discrimination Method and Its Application Analysis of Regional Transport Superiority. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2008, 63, 787–798. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, G. The spatiotemporal differentiation and mechanisms of traffic dominance in Northeast China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2021, 76, 444–458. [Google Scholar]
- Kwok, R.C.W.; Yeh, A.G.O. The use of modal accessibility gap as an indicator for sustainable transport development. Environ. Plann. A. 2004, 36, 921–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, G.; Liu, R.; Yao, S. Empirical research on evaluation model of transport superiority degree—A Case study of Shandong Province. Hum. Geogr. 2010, 25, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.; Sheng, J.; Lu, Y. Evolvement of spatial pattern of county level traffic dominance in Henan, China. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2014, 34, 280–287. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, X.; Jiang, L.; Chen, F. Spatio-temporal cooperative evolution analysis of traffic dominance and county urbanization in Yunnan province. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2017, 37, 1875–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Li, J.; Liu, L.; Yin, S. Coupling evaluation of transportation advantage and economic development in Liaoning province from 2000 to 2018. Geogr. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2021, 37, 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Lee, K.; Anderson, W.P.; Lakshmanan, T.R. Industrial agglomeration and transport accessibility in metropolitan Seoul. J. Geogr. Syst. 2012, 14, 299–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Xu, Q.; Yu, C. Spatial coupling cooperative analysis of transport superiority and rural development in China. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2016, 36, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Xue, D. Study on temporal and spatial variation characteristics and influencing factors of land use efficiency in Xi’an, China. Sustain. 2019, 11, 6649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, A. Evaluation of transport dominance and delimitation of land suitability for construction in the Yushu earthquake region. Resour. Sci. 2012, 34, 1688–1697. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Loo, B.P.Y.; Vickerman, R. High-speed rail networks, economic integration and regional specialisation in China and Europe. Travel Behav. Soc. 2015, 2, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Zhou, C.; Qin, C. No difference in effect of high-speed rail on regional economic growth based on match effect perspective? Transport Res. A-Pol. 2017, 106, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Xie, J.; Che, Y. Based on grey correlation analysis for the correlation between transportation network and the development of tourism in Qinghai province. J. Qinghai Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2017, 33, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Zhang, X.; Gui, D.; Lei, J.; Dong, W.; Wang, B. The relationship between urban development and transport accessibility in Xinjiang. Prog. Geogr. 2010, 29, 1239–1248. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, X.; Fang, C.; Zhang, Q. Spatial relationship between high-speed transport superiority degree and land-use efficiency in Shandong Peninsula urban agglomeration. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2018, 73, 1149–1161. [Google Scholar]
- Pokharel, R.; Bertolini, L.; Brommelstroet, M.; Acharya, S. Spatio-temporal evolution of cities and regional economic development in Nepal: Does transport infrastructure matter? J. Transp. Geogr. 2021, 90, 102904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castella, J.; Manh, P.; Kam, S.; Villano, L.; Tronche, N. Analysis of village accessibility and its impact on land use dynamics in a mountainous province of northern Vietnam. Appl. Geogr. 2005, 25, 308–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Liu, C. A New Method to Visualise the Time-space Compression Effect in Road Network: A Case Study of Beijing-Tianjing-Hebei Region. Econ. Geogr. 2016, 62–69. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Shen, Y.; Meng, D.; Xue, J. The city network centrality and spatial structure in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei metropolitan region. Econ. Geogr. 2013, 33, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lu, F. Location advantage and accessibility evaluation on Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei metropolitan area. Geogr. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2008, 24, 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Ye, Y.; Su, Y. The impact of Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao bridge on the traffic pattern of Pearl Piver Delta. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2012, 67, 723–732. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Cao, X.; Huang, X. The relationship between spatial structure of accessibility and population change in Pearl River Delta. Geogr. Res. 2012, 31, 1661–1672. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Cao, X. The road network accessibility and spatial pattern of Guangzhou-Foshan Metropolitan Area. Econ. Geogr. 2011, 31, 371–378. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Hu, B.; Lu, Q. Appraisal of transport superiority degree in Changsha-Zhuzhou-Xiangtan Urban group based on major function regionalization. Econ. Geogr. 2014, 34, 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y. Research on the spatio-temporal evolution pattern and influence mechanism of traffic dominance in Chengdu-Chongqing economic circle. J. Xi’an Univ. Technol. 2021, 37, 478–487. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Zheng, D. A discussion on the boundary and area of the Tibetan Plateau in China. Geogr. Res. 2002, 21, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Dong, B. Influence of the Tibetan Plateau uplift on the Asian monsoon-arid environment evolution. Chin. Sci. B-Chin. 2013, 58, 4277–4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.; Liu, Y. Threshold study on transportation and industrial development in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Nat. Resour. 2000, 15, 363–368. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Yang, W.; Cao, X. Research on coordination degree between road transport superiority degree and county economic level in Wuling Mountain Area. Hum. Geogr. 2019, 34, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Du, D.; Jin, F. Comparison of spatial structure and linkage systems and geographic constraints: A perspective of multiple traffic flows. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2019, 74, 2482–2494. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, D.; Lu, Y. Evaluation of Henan County Transportation Dominance and Regional Economic Coordination Based on PPM. Available online: https://kdocs.cn/l/cosFvpY2nfHY (accessed on 26 June 2022).
- Wei, D. Research on the Coupling and Coordination Relationship Between Traffic dominance and Economic Level in Shaanxi Province. Master’s Thesis, Chang’an University, Xi’an, China, June 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fan, H.; Wang, D.; Xin, T.; Wang, D.; Guo, Q.; Xiu, L. Spatial Pattern of Highway Transport Dominance in Qinghai–Tibet Plateau at the County Scale. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-inf. 2021, 10, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Chen, S.; Yao, S.; Xiong, C. Traffic dominance degree and its spatial differentiation pattern in Kenya. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2020, 40, 956–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Y. Research on the Influence of Transportation Dominance on Regional Economic Growth—A Case study of Guanzhong Plain City Cluster. Spatial Governance for High-Quality Development-Proceedings of the 2021 China Urban Planning Annual Conference (06 Urban Transportation Planning), Chengdu, China, 25 September, 2021. Available online: https://kdocs.cn/l/cuBb6oltvQ05 (accessed on 26 June 2022).
- Tong, X.; He, Y.; Wei, Y. Analysis of Spatial-temporal Distribution Pattern and Influence Mechanism of Poverty in Guangxi. Areal Res. Dev. 2020, 39, 32–38. [Google Scholar]
- Brunsdon, C.; Fotheringham, A.S.; Charlton, M.E. Geographically Weighted Regression: A Method for Exploring Spatial Nonstationarity. Geogr. Anal. 2010, 28, 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, H. Poverty differentiation and influence mechanism in mountainous counties Songxian county in—A case study of Henan province. Master’s Thesis, Henan University, Kaifeng, China, June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, C. Path selection of ecological environment protection and harmonious economic development in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Developing 2007, 157–158. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Gao, P.; Song, C.; Wang, Y. Connotation and evaluation of high-quality development in counties of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Beijing Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2022, 58, 328–336. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; Wei, X. Dynamic total factor carbon emissions performance changes in the Chinese transportation industry. Appl. Energy 2015, 146, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Hao, J.; Liu, H.; Wu, X.; Hu, J.; Walsh, M.P.; Wallington, T.J.; Zhang, K.M.; Stevanovic, S. On-road vehicle emissions and their control in China: A review and outlook. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 332–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C. Special thinking and green development path of urbanization in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2022, 77, 1907–1919. [Google Scholar]
- Stefaniec, A.; Hosseini, K.; Xie, J.; Li, Y. Sustainability assessment of inland transportation in China: A triple bottom line-based network DEA approach. Transport Res. D-Tr. E. 2020, 80, 102258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
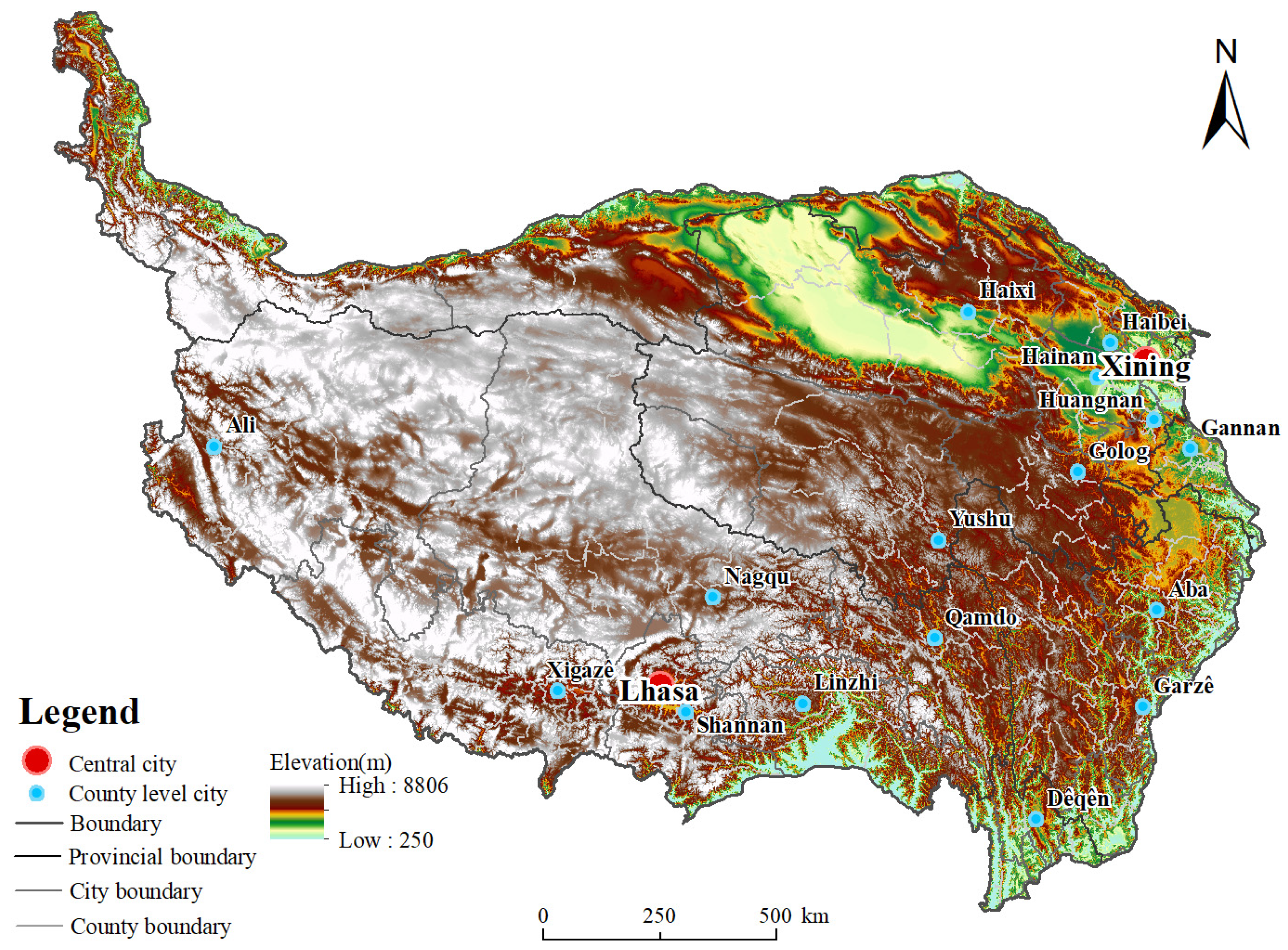
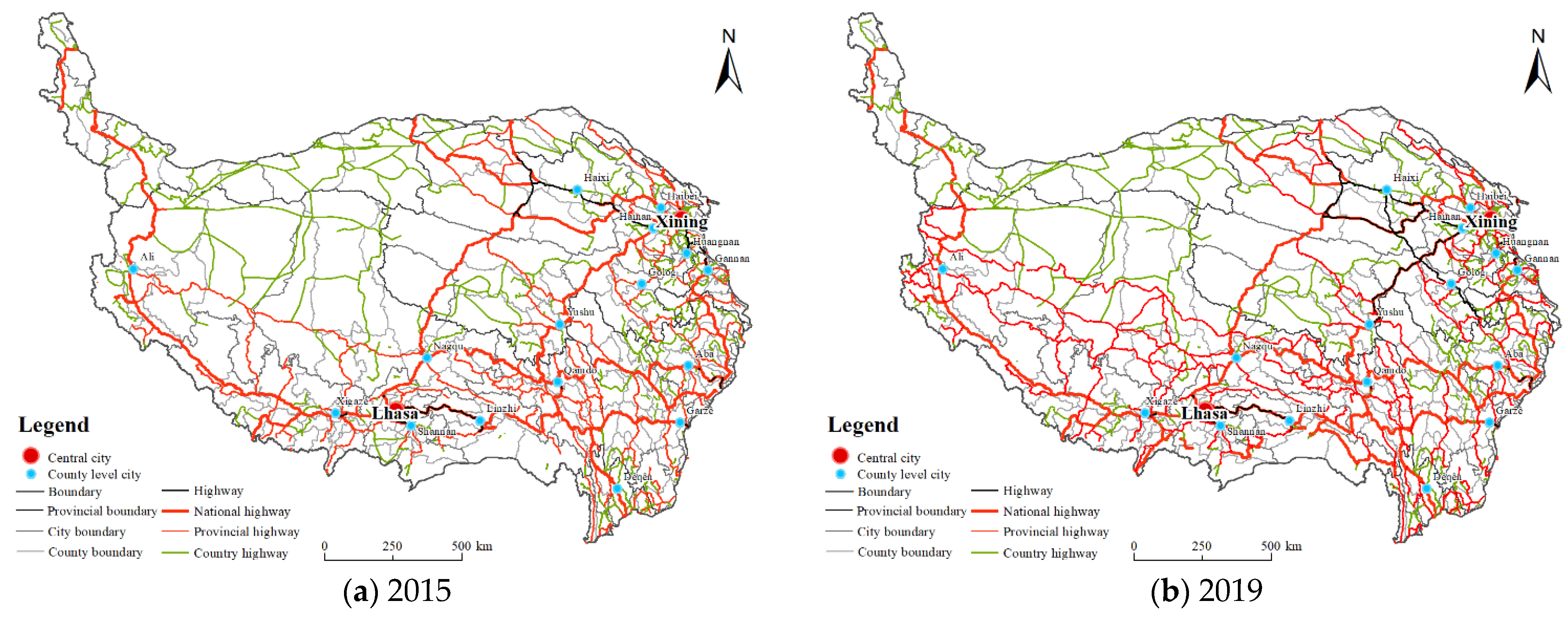

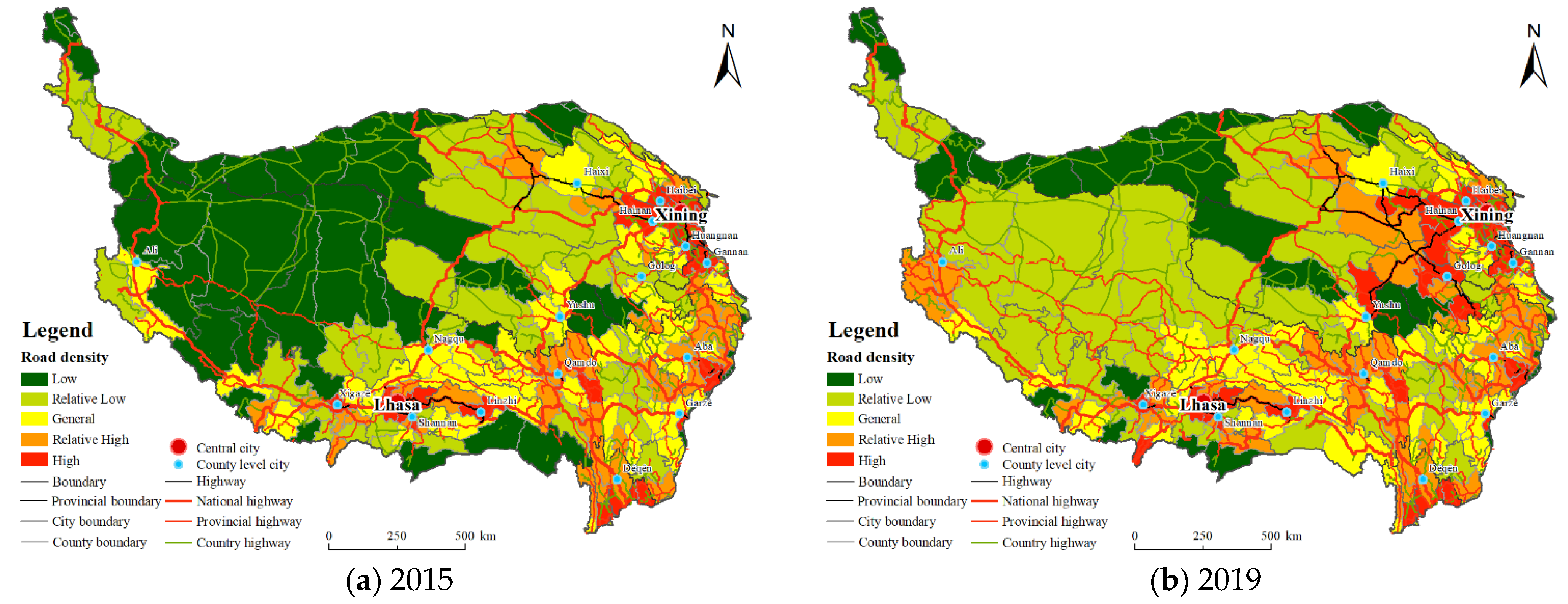
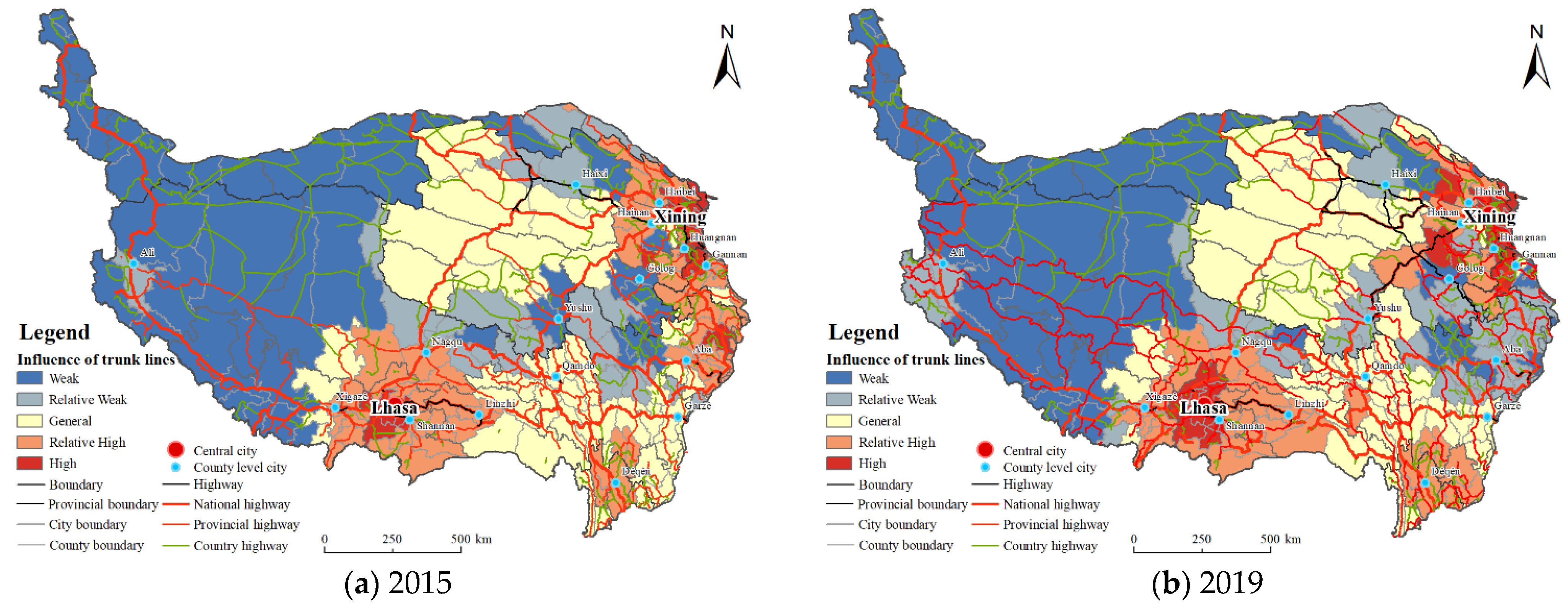
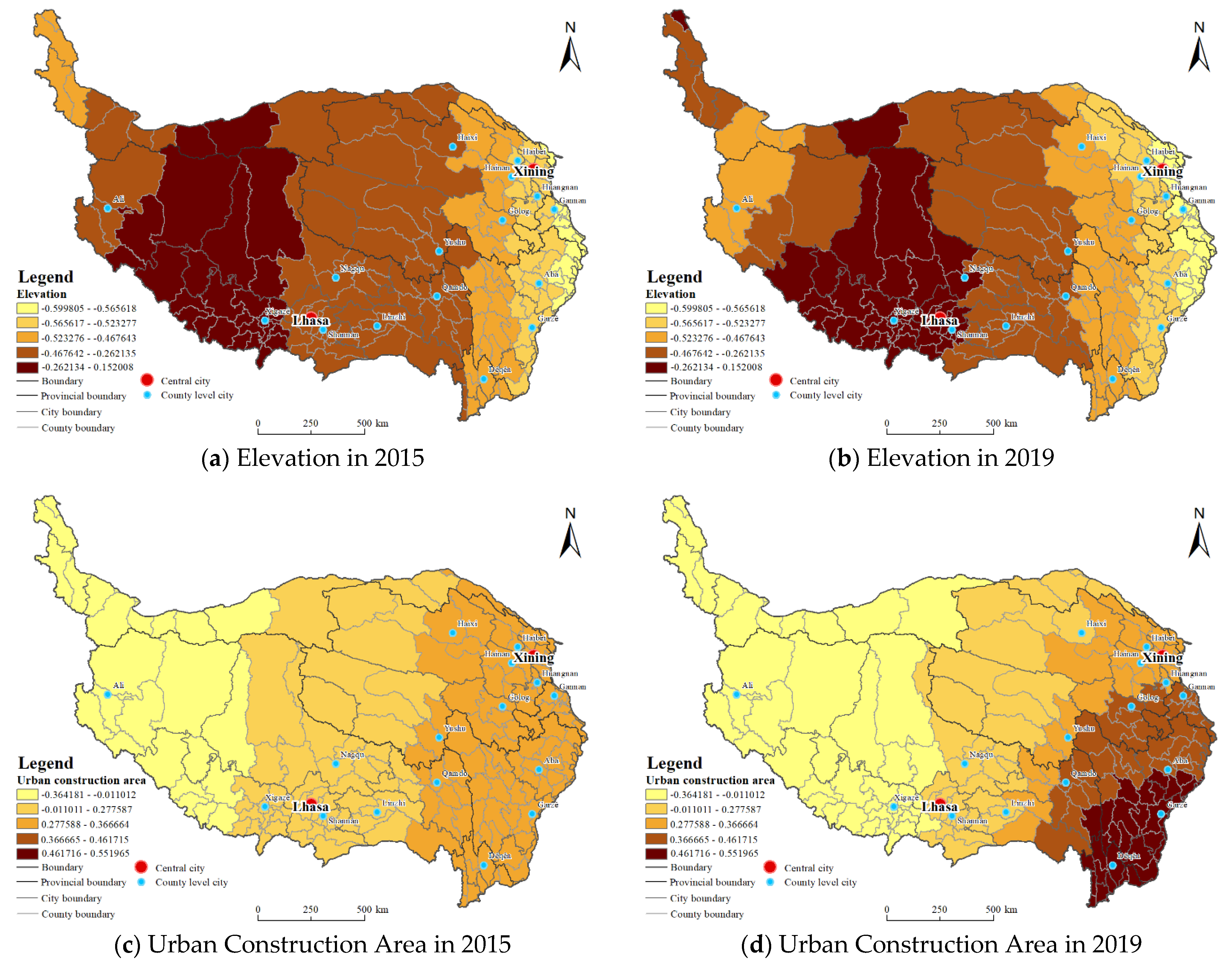
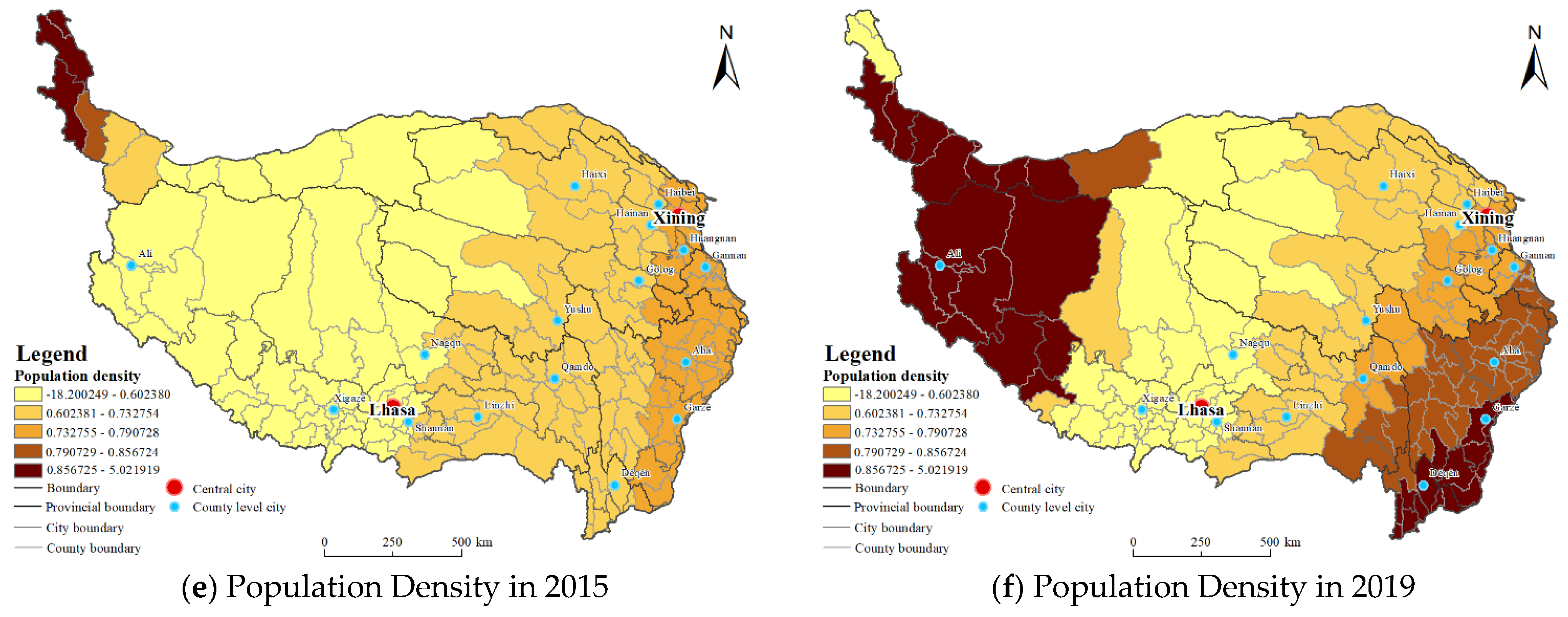
| Data Type | Data Sources | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| National highway/Provincial/Country highway/Highway | Open Street Map (OSM) database | - |
| Passenger station/Railway station /Highway intersection/Airport | Baidu Map POI | - |
| Elevation | Geospatial Data Cloud http://www.gscloud.cn/ (accessed on 18 June 2020) | DEM extraction from Qinghai-Tibet Plateau based on SRTM DEM 30 m resolution digital elevation data. |
| Population density | World Pop https://www.worldpop.org/ (accessed on 11 May 2022) | Based on the downloaded 1 km population density grid data of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau in 2015 and 2019; the population density data at the county unit scale are obtained by zoning statistics. |
| Socio-economic indicators | China Statistical Yearbook (County-Level) (2016, 2020)1 China City Statistical Yearbook (2016, 2020)2 | Urban construction area, public fiscal expenditure, fixed asset investment, regional GDP, and employees of secondary and tertiary industries in each county unit. |
| Type | Standard | Weight Assignment | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Road | Highway | Contains highway exits | 2.5 |
| Lh* ≤ 30 km | 2.0 | ||
| 30 km < Lh ≤ 60 km | 1.0 | ||
| Lh > 60 km | 0 | ||
| Ordinary highway | 1st | 2.5 | |
| 2nd | 2.0 | ||
| 3rd | 1.5 | ||
| Others | 1.0 | ||
| Railway | Railway station | 2.5 | |
| Lh ≤ 30 km | 2.0 | ||
| 30 km < Lh ≤ 60 km | 1.0 | ||
| Lh > 60 km | 0 | ||
| Airport | Airport | 2.0 | |
| Lh ≤ 30 km | 1.0 | ||
| 30 km ≤ Lh ≤ 60 km | 0.5 | ||
| Lh > 60 km | 0 | ||
| Years | Dimension | Index | Regression Coefficients | Standard Deviation | t-Statistic | Significance ρ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | Natural Environment | Elevation | −0.317 | 0.066 | −4.817 | 0.00001 |
| Land Resources | Urban Construction Area | 0.254 | 0.083 | 3.062 | 0.00250 | |
| Social Development | Population Density | 0.662 | 0.163 | 4.059 | 0.00000 | |
| 2019 | Natural Environment | Elevation | −0.305 | 0.063 | −4.834 | 0.00002 |
| Land Resources | Urban Construction Area | 0.335 | 0.076 | 4.377 | 0.00003 | |
| Social Development | Population Density | 0.716 | 0.144 | 4.968 | 0.00000 |
| Years | Dimension | Regression Coefficients | Adjusted R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | Elevation | −0.441 | 0.414 |
| Urban Construction Area | 0.203 | ||
| Population Density | 0.677 | ||
| 2019 | Elevation | −0.421 | 0.556 |
| Urban Construction Area | 0.241 | ||
| Population Density | 0.790 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, D.; Wang, K.; Wang, Z.; Fan, H.; Chai, H.; Wang, H.; Long, H.; Gao, J.; Xu, J. Spatial-Temporal Evolution and Influencing Mechanism of Traffic Dominance in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11031. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141711031
Wang D, Wang K, Wang Z, Fan H, Chai H, Wang H, Long H, Gao J, Xu J. Spatial-Temporal Evolution and Influencing Mechanism of Traffic Dominance in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sustainability. 2022; 14(17):11031. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141711031
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Dongchuan, Kangjian Wang, Zhiheng Wang, Hongkui Fan, Hua Chai, Hongyi Wang, Hui Long, Jianshe Gao, and Jiacheng Xu. 2022. "Spatial-Temporal Evolution and Influencing Mechanism of Traffic Dominance in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau" Sustainability 14, no. 17: 11031. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141711031
APA StyleWang, D., Wang, K., Wang, Z., Fan, H., Chai, H., Wang, H., Long, H., Gao, J., & Xu, J. (2022). Spatial-Temporal Evolution and Influencing Mechanism of Traffic Dominance in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sustainability, 14(17), 11031. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141711031








