Codon Usage Bias for Fatty Acid Genes FAE1 and FAD2 in Oilseed Brassica Species
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sequence Data Source
2.2. Analysis of Base Composition and Codon Preference
2.3. Relative Synonymous Codon Usage (RSCU)
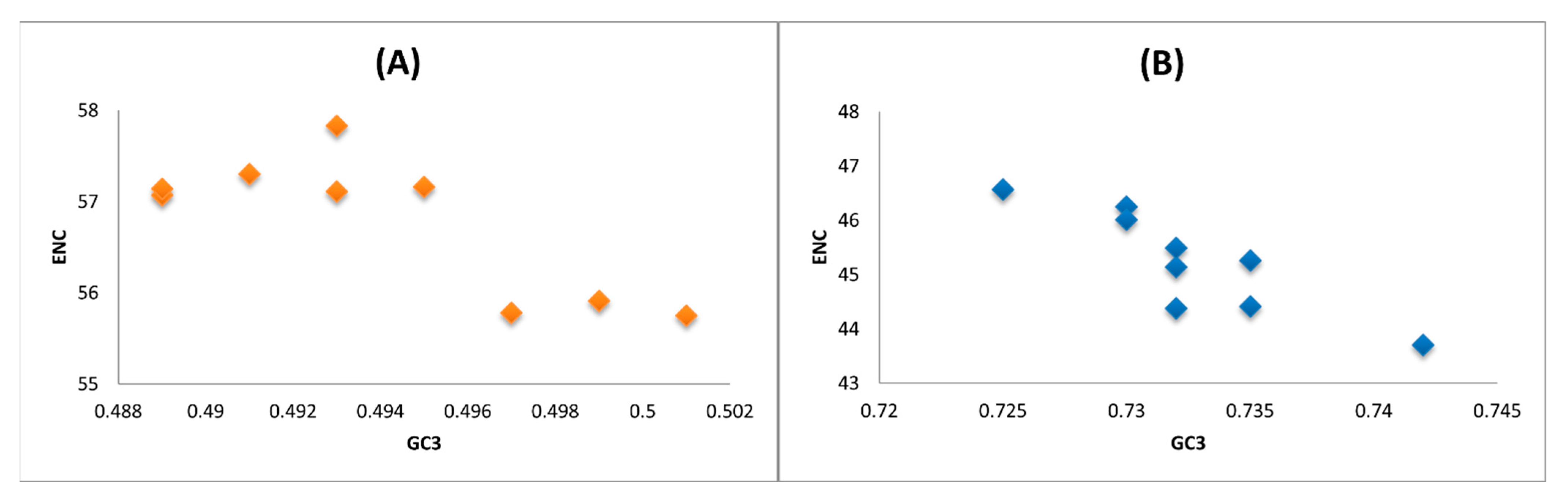
2.4. ENC-GC3 Plot Analysis
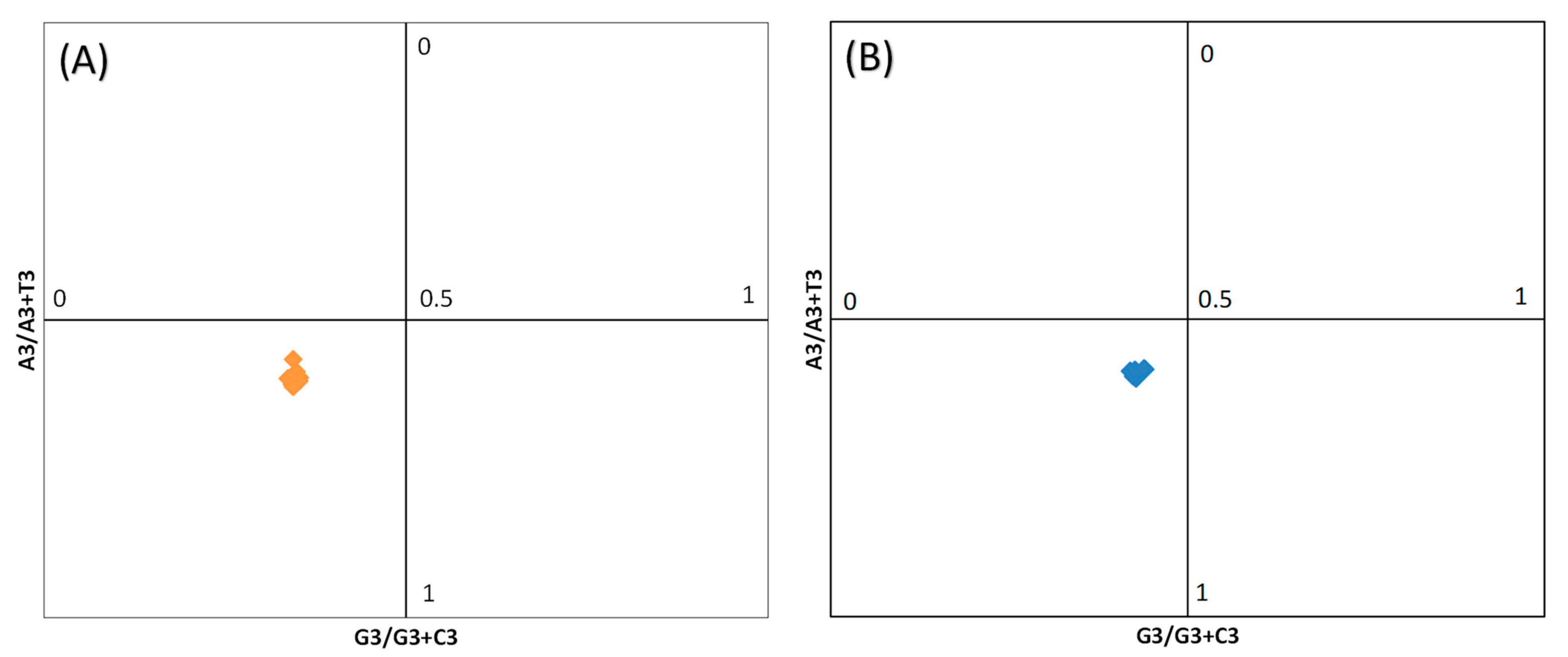
2.5. PR2-Bias Plot
2.6. Neutrality Plot
2.7. Frequency of Optimal Codon (Fop)
2.8. Evaluation and Analysis of Gene Expression
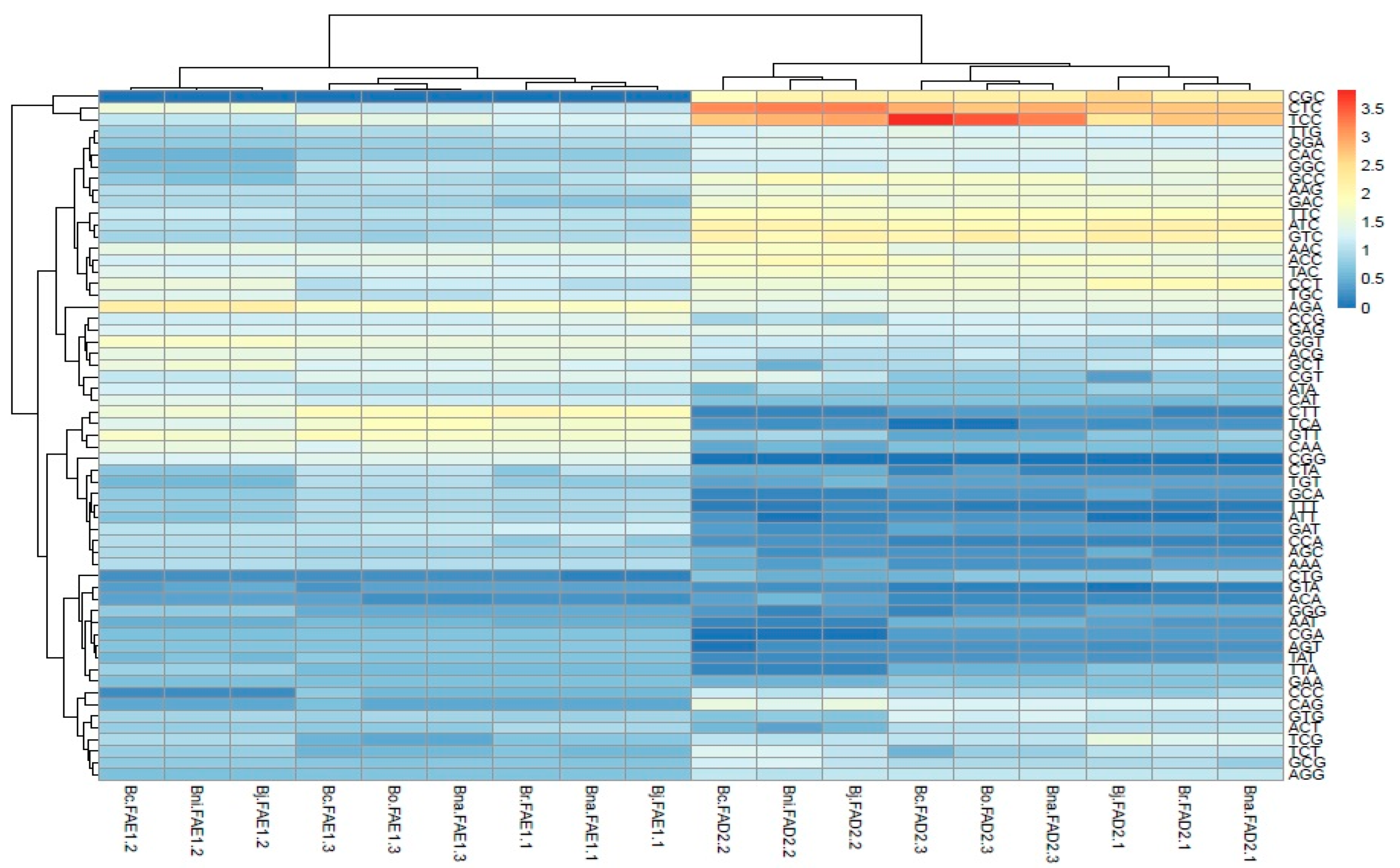
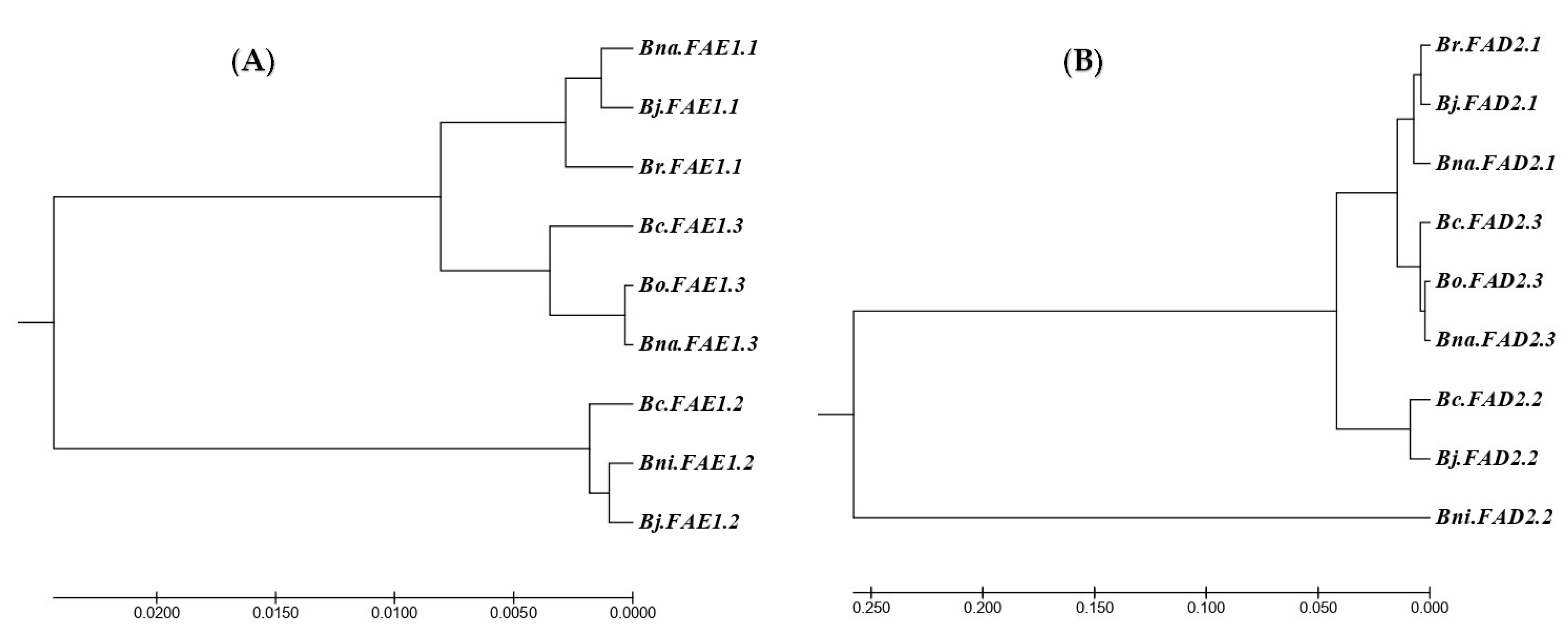
2.9. Clustering Based on Codon Usage Bias
2.10. Codon Adaptation Index (CAI)
2.11. Correspondence Analysis (COA)
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
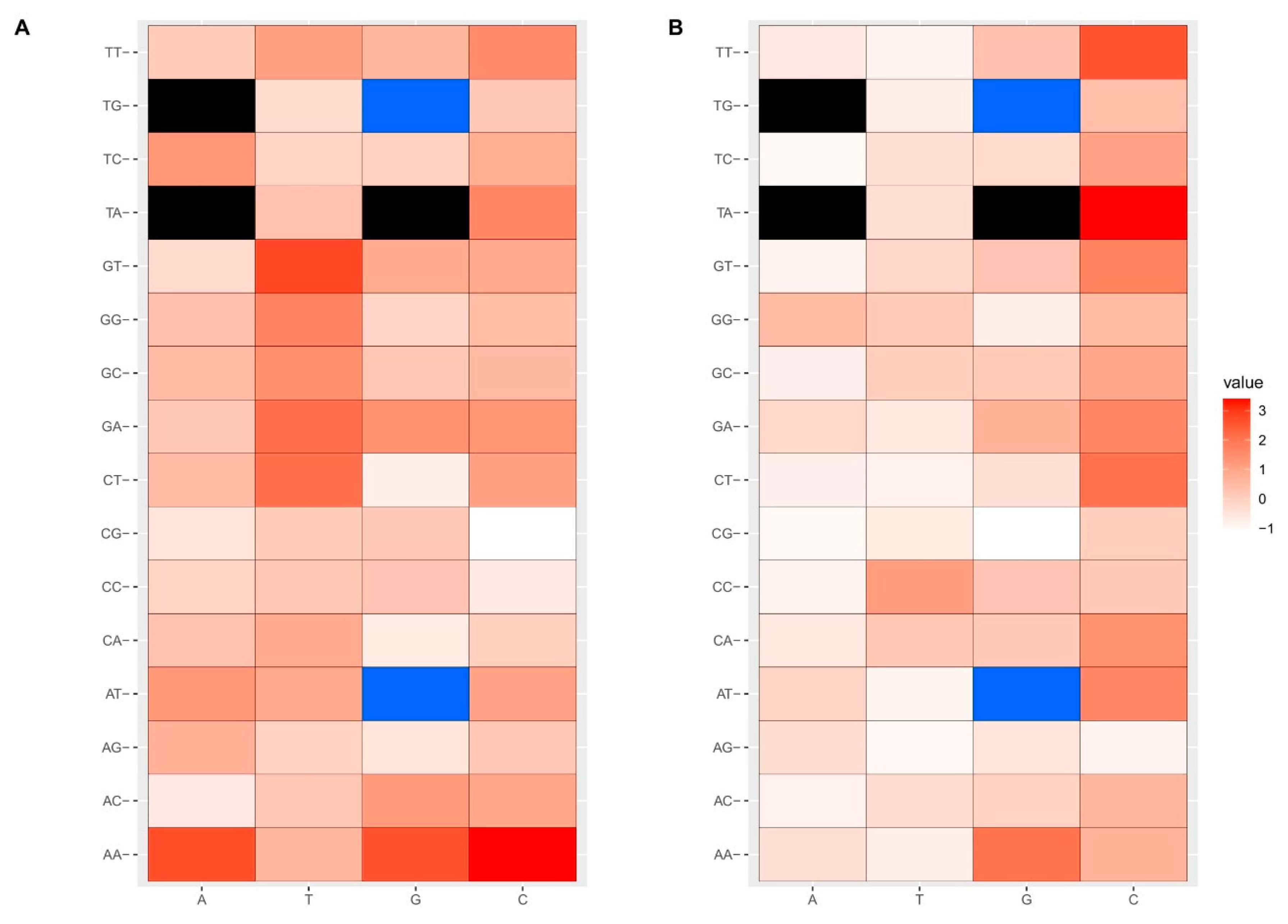
3.1. SNPs and Amino Acid Alterations in the Conserved Regions of FAE1 and FAD2 Genes
3.2. Analysis of Codon Bias of FAE1 and FAD2 Genes in Different Brassica Species
3.3. Preference of FAE1 and FAD2 Gene Codon Ended with G/C in Different Brassica Species
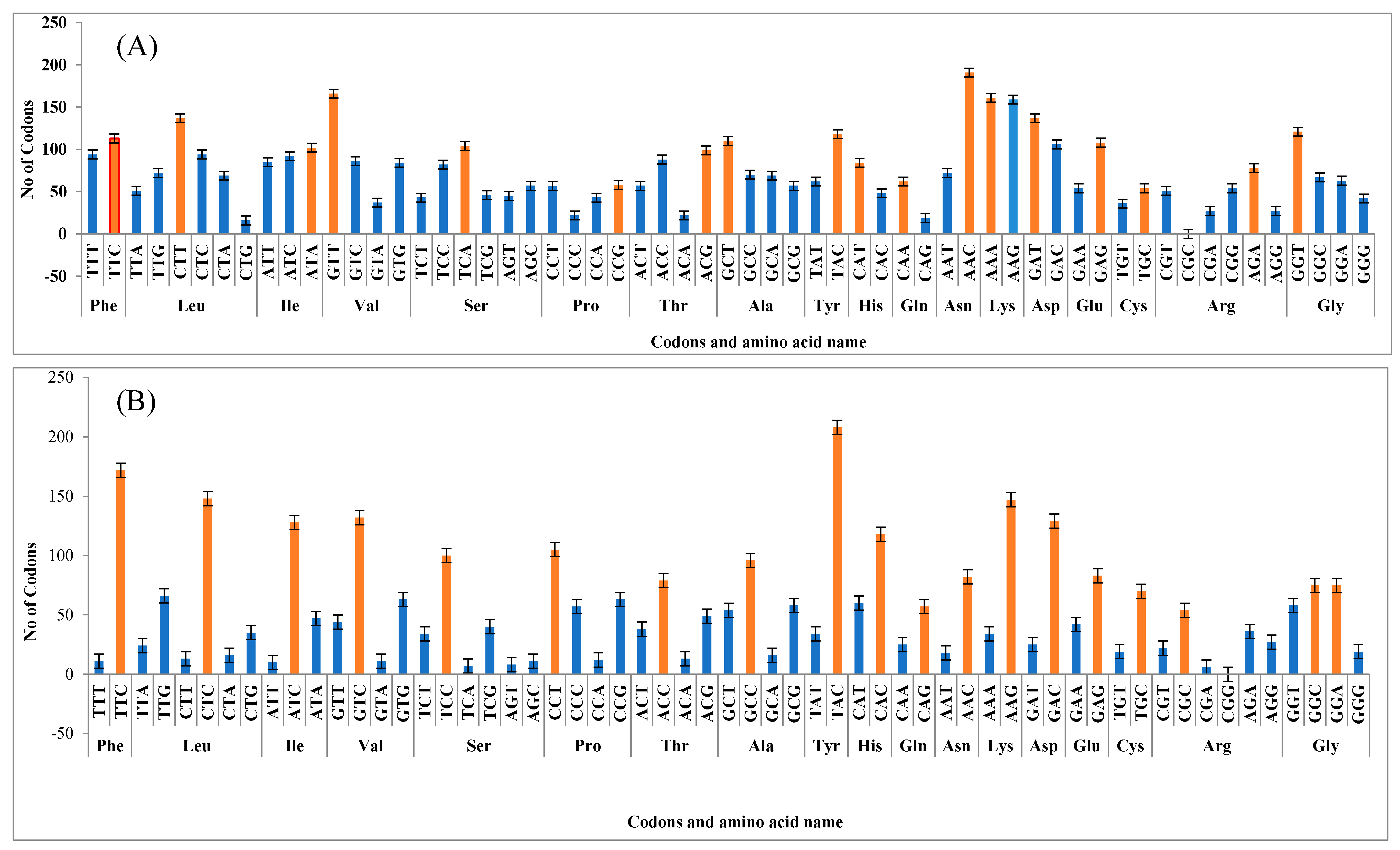
3.4. Relative Synonymous Codon Usage of FAE1 and FAD2 Genes
3.5. System Relationship of Codon Usage Patterns of FAE1 and FAD2 Genes
3.6. Influence from Selection Pressure of FAE1 and FAD2 Genes in Different Brassica Species
3.7. Neutrality Plot
3.8. PR-2 Bias Plot
3.9. Correspondence Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lateef, O.M.; Akintubosun, M.O.; Olaoba, O.T.; Samson, S.O.; Adamczyk, M. Making Sense of “Nonsense” and More: Challenges and Opportunities in the Genetic Code Expansion, in the World of TRNA Modifications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.F.; Alonso Morales, L.A.; Kassen, R. Effects of Synonymous Mutations beyond Codon Bias: The Evidence for Adaptive Synonymous Substitutions from Microbial Evolution Experiments. Genome Biol. Evol. 2021, 13, evab141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolskaya, S.; Andreev, Y.A. Site-Specific Incorporation of Unnatural Amino Acids into Escherichia coli Recombinant Protein: Methodology Development and Recent Achievement. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, J. Nucleosides, Nucleotides, Polynucleotides (RNA and DNA) and the Genetic Code. In Inventive Geniuses Who Changed the World; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; ISBN 9783030813802. [Google Scholar]
- Iriarte, A.; Lamolle, G.; Musto, H. Codon Usage Bias: An Endless Tale. J. Mol. Evol. 2021, 89, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jou, W.; Haegeman, G.Y.; Sebaert, M.; Fiers, W. Nucleotide Sequence of the Gene Coding for the Bacteriophage MS2 Coat Protein. Nature 1972, 237, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begum, N.S.; Chakraborty, S. Influencing Elements of Codon Usage Bias in Birnaviridae and Its Evolutionary Analysis. Virus Res. 2022, 310, 198672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotkin, J.B.; Robins, H.; Levine, A.J. Tissue-Specific Codon Usage and the Expression of Human Genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 12588–12591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grantham, R.; Gautier, C.; Gouy, M.; Jacobzone, M.; Mercier, R. Codon Catalog Usage Is a Genome Strategy Modulated for Gene Expressivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981, 9, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershberg, R.; Petrov, D.A. Selection on Codon Bias. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2008, 42, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Cui, P.; Ding, F.; Li, A.; Townsend, J.P.; Yu, J. Codon Deviation Coefficient: A Novel Measure for Estimating Codon Usage Bias and Its Statistical Significance. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kane, J.F. Effects of Rare Codon Clusters on High-Level Expression of Heterologous Proteins in Escherichia coli. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 1995, 6, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, I.; Jeong, B.J.; Bae, S.E.; Jung, J.; Son, H.S. Genomic Analysis of Influenza A Viruses, Including Avian Flu (H5N1) Strains. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 21, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.; Kuang, Y.; Joseph, J.S.; Kolatkar, P.R. Conserved Codon Composition of Ribosomal Protein Coding Genes in Escherichia coli, Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Saccharomyces cerevisiae: Lessons from Supervised Machine Learning in Functional Genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 2599–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.h.; Li, X.r.; Lan, X.; Han, S.Y.; Wang, Y.n; Hu, Y.; Pan, Q. The Genetic Divergences of Codon Usage Shed New Lights on Transmission of Hepatitis E Virus from Swine to Human. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 68, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Guo, J.; Cha, J.; Chae, M.; Chen, S.; Barral, J.M.; Sachs, M.S.; Liu, Y. Non-Optimal Codon Usage Affects Expression, Structure and Function of Clock Protein FRQ. Nature 2013, 494, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiapello, H.; Lisacek, F.; Caboche, M.; Hénaut, A. Codon Usage and Gene Function Are Related in Sequences of Arabidopsis thaliana. Gene 1998, 209, GC1–GC38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Chanyal, S.; Dubey, A.; Tewari, A.K.; Taj, G. Patterns of Codon Usage Bias in WRKY Genes of Brassica rapa and Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 11, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Deng, P.; Feng, K.; Liu, P.; Du, X.; You, F.M.; Weining, S. Comparative Analysis of Codon Usage Patterns in Chloroplast Genomes of the Asteraceae Family. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 32, 828–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chand, S.; Patidar, O.P.; Chaudhary, R.; Saroj, R.; Chandra, K.; Meena, V.K.; Limbalkar, O.M.; Patel, M.K.; Pardeshi, P.P.; Vasisth, P. Rapeseed-Mustard Breeding in India: Scenario, Achievements and Research Needs. In Brassica Breeding and Biotechnology; Islam, A.K.M.A., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021; p. 22. ISBN 978-1-83968-697-9. [Google Scholar]
- Saroj, R.; Soumya, S.L.; Singh, S.; Sankar, S.M.; Chaudhary, R.; Yashpal, R.; Saini, N.; Vasudev, S.; Yadava, D.K. Unraveling the Relationship Between Seed Yield and Yield-Related Traits in a Diversity Panel of Brassica juncea Using Multi-Traits Mixed Model. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 651936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, V.K.; Taak, Y.; Chaudhary, R.; Chand, S.; Patel, M.K.; Muthusamy, V.; Yadav, S.; Saini, N.; Vasudev, S.; Yadava, D.K. Deciphering the Genetic Inheritance of Tocopherols in Indian mustard (Brassica juncea L. Czern and Coss). Plants 2022, 11, 1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, S.S.; Babu, S.; Shekhawat, K.; Singh, V.K.; Upadhyay, P.K.; Singh, R.K.; Raj, R.; Singh, H.; Zaki, F.M. Oilseed Brassica Species Diversification and Crop Geometry Influence the Productivity, Economics, and Environmental Footprints under Semi-Arid Regions. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Seepaul, R.; Small, I.M.; George, S.; Kelly O’brien, G.; Marois, J.J.; Wright, D.L.; Huchzermeyer, B.; Florida, N. Interactive Effects of Nitrogen and Sulfur Nutrition on Growth, Development, and Physiology of Brassica carinata A. Braun and Brassica napus L. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesi, N.; Delourme, R.; Brégeon, M.; Falentin, C.; Renard, M. Genetic and Molecular Approaches to Improve Nutritional Value of Brassica napus L. Seed. Comptes Rendus-Biol. 2008, 331, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutzon, D.S.; Thompson, G.A.; Radke, S.E.; Johnson, W.B.; Knauf, V.C.; Kridl, J.C. Modification of Brassica Seed Oil by Antisense Expression of a Stearoyl- Acyl Carrier Protein Desaturase Gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 2624–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, D.C.; Barton, D.L.; Michael Giblin, E.; Mackenzie, S.L.; Van Den Berg, C.G.J.; McVetty, P.B.E. Microsomal Lyso-Phosphatidic Acid Acyltransferase from a Brassica oleracea Cultivar Incorporates Erucic Acid into the Sn-2 Position of Seed Triacylglycerols. Plant Physiol. 1995, 109, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, I.H.; Atta, B.; Ahmed, W.M. Biochemical and Toxicological Studies on the Effect of High and Low Erucic Acid Rapeseed Oil on Rats. Food/Nahrung 1994, 38, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Lang, C.; Wang, F.; Wu, X.; Liu, R.; Zheng, T.; Zhang, D.; Chen, J.; Wu, G. Depressed Expression of FAE1 and FAD2 Genes Modifies Fatty Acid Profiles and Storage Compounds Accumulation in Brassica napus Seeds. Plant Sci. 2017, 263, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Töpfer, R.; Martini, N.; Schell, J. Modification of Plant Lipid Synthesis. Science 1995, 268, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardin-Fanning, F. The Effects of a Mediterranean-Style Dietary Pattern on Cardiovascular Disease Risk. Nurs. Clin. N. Am. 2008, 43, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beisson, F.; Koo, A.J.K.; Ruuska, S.; Schwender, J.; Pollard, M.; Thelen, J.J.; Paddock, T.; Salas, J.J.; Savage, L.; Milcamps, A.; et al. Arabidopsis Genes Involved in Acyl Lipid Metabolism. A 2003 Census of the Candidates, a Study of the Distribution of Expressed Sequence Tags in Organs, and a Web-Based Database 1. Plant Physiol. 2003, 132, 681–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, W.; Lu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Huang, B.; Lu, X.; Sheteiwy, M.S.A.; Kuang, S.; Shao, H. Oil Crop Genetic Modification for Producing Added Value Lipids. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2020, 40, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, P.; Longden, L.; Bleasby, A. EMBOSS: The European Molecular Biology Open Software Suite. Trends Genet. 2000, 16, 276–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peden, J.F. Analysis of Codon Usage. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Nottingham, Nottingham, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Sharp, P.M.; Li, W.H. An Evolutionary Perspective on Synonymous Codon Usage in Unicellular Organisms. J. Mol. Evol. 1986, 24, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, F. The ‘Effective Number of Codons’ Used in a Gene. Gene 1990, 87, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, A.; Kaur, H.; Bhardwaj, P. Selection Constraints Determine Preference for A/U-Ending Codons in Taxus contorta. Genome 2020, 63, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueoka, N. Intrastrand Parity Rules of DNA Base Composition and Usage Biases of Synonymous Codons. J. Mol. Evol. 1996, 42, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueoka, N. Translation-Coupled Violation of Parity Rule 2 in Human Genes Is Not the Cause of Heterogeneity of the DNA G+C Content of Third Codon Position. Gene 1999, 238, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueoka, N.; Kawanishi, Y. DNA G + C Content of the Third Codon Position and Codon Usage Biases of Human Genes. Gene 2000, 261, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueoka, N. Directional Mutation Pressure and Neutral Molecular Evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 2653–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikemura, T. Codon Usage and TRNA Content in Unicellular and Multicellular Organisms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1985, 2, 13–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenico, M.; Lloyd, A.T.; Sharp, P.M. Codon Usage in Caenorhabditis elegans: Delineation of Translational Selection and Mutational Biases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 2437–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavner, Y.; Kotlar, D. Codon Bias as a Factor in Regulating Expression via Translation Rate in the Human Genome. Gene 2005, 345, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlin, S.; Mrázek, J. What Drives Codon Choices in Human Genes? J. Mol. Biol. 1996, 262, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, J.M.; Erill, I. Relative Codon Adaptation: A Generic Codon Bias Index for Prediction of Gene Expression. DNA Res. 2010, 17, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Paul, S.; Dutta, C. Synonymous Codon Usage in Adenoviruses: Influence of Mutation, Selection and Protein Hydropathy. Virus Res. 2006, 117, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Du, H.; Qu, Z.; Li, X.Q.; Xiang, H. Differences in Codon Usage Bias between Photosynthesis-Related Genes and Genetic System-Related Genes of Chloroplast Genomes in Cultivated and Wild Solanum Species. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andargie, M.; Congyi, Z. Genome-Wide Analysis of Codon Usage in Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.). Heliyon 2022, 8, e08687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Puigbò, P.; Bravo, I.G.; Garcia-Vallve, S. CAIcal: A Combined Set of Tools to Assess Codon Usage Adaptation. Biol. Direct 2008, 3, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, S.; Mahalingam, V.; Kumar, V. Synonymous Codon Usage Analysis of Thirty Two Mycobacteriophage Genomes. Adv. Bioinformatics 2009, 2009, 316936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatarinova, T.V.; Alexandrov, N.N.; Bouck, J.B.; Feldmann, K.A. GC3 biology in Corn, Rice, Sorghum and Other Grasses. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- WU, Y.q; LI, Z.y; Zhao, D.q; Tao, J. Comparative Analysis of Flower-Meristem-Identity Gene APETALA2 (AP2) Codon in Different Plant Species. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 867–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gun, L.; Yumiao, R.; Haixian, P.; Liang, Z. Comprehensive Analysis and Comparison on the Codon Usage Pattern of Whole Mycobacterium tuberculosis Coding Genome from Different Area. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 3574976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Błazej, P.; Mackiewicz, D.; Wnetrzak, M.; Mackiewicz, P. The Impact of Selection at the Amino Acid Level on the Usage of Synonymous Codons. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2017, 7, 967–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palidwor, G.A.; Perkins, T.J.; Xia, X. A General Model of Codon Bias Due to GC Mutational Bias. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, A.M.; Nasrullah, I.; Tong, Y. Genome-Wide Analysis of Codon Usage and Influencing Factors in Chikungunya Viruses. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouy, M.; Gautier, C. Codon Usage in Bacteria: Correlation with Gene Expressivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982, 10, 7055–7074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragg, J.G.; Quigg, A.; Raven, J.A.; Wagner, A. Protein Elemental Sparing and Codon Usage Bias are Correlated among Bacteria. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 2480–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicario, S.; Moriyama, E.N.; Powell, J.R. Codon Usage in Twelve Species of Drosophila. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.L.; Jiang, Y.R.; Liu, Y.Q.; Xia, R.X.; Qin, L. Selective Pressure Dominates the Synonymous Codon Usage in Parvoviridae. Virus Genes 2013, 46, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, G.K.S.; Wang, J.; Tao, L.; Tan, J.; Zhang, J.; Passey, D.A.; Yu, J. Compositional Gradients in Gramineae Genes. Genome Res. 2002, 12, 851–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Cai, X.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, H.; Cai, Y.; Ben, A. Factors Affecting Synonymous Codon Usage Bias in Chloroplast Genome of Oncidium Gower Ramsey. Evol. Bioinforma. 2011, 7, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Zhao, D.; Tao, J. Analysis of Codon Usage Patterns in Herbaceous Peony (Paeonia lactiflora Pall.) Based on Transcriptome Data. Genes 2015, 6, 1125–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Nielsen, R. Mutation-Selection Models of Codon Substitution and Their Use to Estimate Selective Strengths on Codon Usage. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2008, 25, 568–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennetzen, J.L.; Hall, B.D. Codon Selection in Yeast. J. Biol. Chem. 1982, 257, 3026–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R. Analysis of Synonymous Codon Usage Bias in Ancylostoma ceylanicum. Gene Rep. 2021, 24, 101290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, K.C. Comparative Study on Factors Influencing the Codon and Amino Acid Usage in Lactobacillus sakei 23K and 13 Other Lactobacilli. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, M.N.; Uddin, A.; Chakraborty, S. Nucleotide Composition and Codon Usage Bias of SRY Gene. Andrologia 2018, 50, e12787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, B.; Uddin, A.; Mazumder, G.A.; Chakraborty, S. Analysis of Codon Usage Pattern of Mitochondrial Protein-Coding Genes in Different Hookworms. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2018, 219, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, G.; Cai, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, C.; Xia, H.; Wu, Z.; Li, J.; Ou, Z.; Xu, Z.; et al. Genomewide Comparative Analysis of Codon Usage Bias in Three Sequenced Jatropha curcas. J. Genet. 2021, 100, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| S.N. | Brassica Species | Erucic Acid (FAE1) | Oleic Acid (FAD2) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene ID | Accession No. | Length (bp) | Chromosome | Amino Acid | Gene ID | Accession No. | Length (bp) | Chromosome | Amino Acid | ||
| 1 | B. rapa | Br.FAE1.1 | KF999626.1 | 1521 | A08 | 384 | Br.FAD2.1 | JN859550.1 | 1155 | A05 | 506 |
| 2 | B. nigra | Bni.FAE1.2 | MH745118.1 | 1521 | B07 | 384 | Bni.FAD2.2 | HM138369.1 | 1152 | B05 | 506 |
| 3 | B. oleracea | Bo.FAE1.3 | AF490460.1 | 1521 | C03 | 384 | Bo.FAD2.3 | JN859552.1 | 1155 | C05 | 506 |
| 4 | B. carinata | Bc.FAE1.2 | KF664167.1 | 1521 | B03 | 384 | Bc.FAD2.2 | AF124360.2 | 1155 | B06 | 506 |
| 5 | B. carinata | Bc.FAE1.3 | KF664166.1 | 1521 | C03 | 384 | Bc.FAD2.3 | JAAMPC010000013.1 | 1155 | C05 | 506 |
| 6 | B. napus | Bna.FAE1.1 | GU325717.1 | 1521 | A08 | 384 | Bna.FAD2.1 | JN992606.1 | 1155 | A05 | 506 |
| 7 | B. napus | Bna.FAE1.3 | GU325719.1 | 1521 | C03 | 384 | Bna.FAD2.3 | JN992607.1 | 1155 | C05 | 506 |
| 8 | B. juncea | Bj.FAE1.1 | AJ558197.1 | 1521 | A08 | 384 | Bj.FAD2.1 | MN585117.1 | 1155 | A05 | 506 |
| 9 | B. juncea | Bj.FAE1.2 | AJ558198.1 | 1521 | B07 | 384 | Bj.FAD2.2 | MN585120.1 | 1155 | B05 | 506 |
| S. N #. | A | T | G | C | A3 | T3 | G3 | C3 | AT (%) | GC (%) | GC1 (%) | GC2 (%) | AT3 (%) | GC3 (%) | GC12 (%) 2^ | AT12 (%) 2^ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Erucic acid (FAE1) | ||||||||||||||||
| 1. | 415 | 410 | 346 | 350 | 103 | 154 | 107 | 143 | 0.542 | 0.458 | 0.487 | 0.393 | 0.507 | 0.493 | 0.440 | 0.560 |
| 2. | 415 | 407 | 351 | 348 | 106 | 149 | 111 | 141 | 0.540 | 0.460 | 0.487 | 0.394 | 0.503 | 0.497 | 0.441 | 0.559 |
| 3. | 422 | 406 | 340 | 353 | 107 | 152 | 104 | 144 | 0.544 | 0.456 | 0.485 | 0.393 | 0.511 | 0.489 | 0.439 | 0.561 |
| 4. | 414 | 407 | 351 | 349 | 105 | 148 | 111 | 143 | 0.540 | 0.460 | 0.485 | 0.394 | 0.499 | 0.501 | 0.440 | 0.560 |
| 5. | 415 | 407 | 345 | 354 | 104 | 153 | 106 | 144 | 0.540 | 0.460 | 0.489 | 0.396 | 0.507 | 0.493 | 0.443 | 0.557 |
| 6. | 419 | 408 | 344 | 350 | 107 | 151 | 106 | 143 | 0.544 | 0.456 | 0.487 | 0.391 | 0.509 | 0.491 | 0.439 | 0.561 |
| 7. | 422 | 407 | 340 | 352 | 107 | 152 | 104 | 144 | 0.545 | 0.455 | 0.485 | 0.391 | 0.511 | 0.489 | 0.438 | 0.562 |
| 8. | 419 | 406 | 344 | 352 | 106 | 150 | 107 | 144 | 0.542 | 0.458 | 0.485 | 0.393 | 0.505 | 0.495 | 0.439 | 0.561 |
| 9. | 416 | 407 | 350 | 348 | 106 | 148 | 111 | 142 | 0.541 | 0.459 | 0.483 | 0.394 | 0.501 | 0.499 | 0.439 | 0.561 |
| Mean | 417.44 | 407.22 | 345.66 | 350.66 | 105.66 | 150.77 | 107.44 | 143.11 | 0.542 | 0.458 | 0.486 | 0.393 | 0.506 | 0.494 | 0.440 | 0.560 |
| SD1^ | 2.9481 | 1.1331 | 4.0276 | 2.0548 | 1.3333 | 2.0427 | 2.7125 | 0.9938 | 0.0018 | 0.0018 | 0.0016 | 0.0014 | 0.0040 | 0.0040 | 0.0013 | 0.001 |
| Oleic acid (FAD2) | ||||||||||||||||
| 1. | 250 | 359 | 272 | 274 | 43 | 61 | 98 | 183 | 0.411 | 0.548 | 0.506 | 0.408 | 0.270 | 0.730 | 0.457 | 0.543 |
| 2. | 248 | 370 | 263 | 271 | 43 | 56 | 98 | 187 | 0.403 | 0.556 | 0.518 | 0.409 | 0.258 | 0.742 | 0.464 | 0.536 |
| 3. | 247 | 361 | 272 | 275 | 41 | 62 | 99 | 183 | 0.409 | 0.551 | 0.509 | 0.410 | 0.268 | 0.732 | 0.460 | 0.540 |
| 4. | 245 | 370 | 268 | 272 | 40 | 62 | 97 | 186 | 0.404 | 0.556 | 0.519 | 0.413 | 0.265 | 0.735 | 0.466 | 0.534 |
| 5. | 246 | 362 | 274 | 273 | 40 | 63 | 97 | 185 | 0.409 | 0.550 | 0.506 | 0.410 | 0.268 | 0.732 | 0.458 | 0.542 |
| 6. | 249 | 357 | 276 | 273 | 42 | 64 | 97 | 182 | 0.413 | 0.545 | 0.506 | 0.405 | 0.275 | 0.725 | 0.456 | 0.544 |
| 7. | 246 | 361 | 273 | 275 | 41 | 62 | 99 | 183 | 0.409 | 0.551 | 0.509 | 0.410 | 0.268 | 0.732 | 0.460 | 0.540 |
| 8. | 247 | 359 | 273 | 276 | 42 | 62 | 99 | 182 | 0.409 | 0.550 | 0.506 | 0.413 | 0.270 | 0.730 | 0.460 | 0.540 |
| 9. | 245 | 372 | 268 | 270 | 41 | 61 | 95 | 188 | 0.404 | 0.556 | 0.519 | 0.413 | 0.265 | 0.735 | 0.466 | 0.534 |
| Mean | 247 | 271 | 273.22 | 363.44 | 41.44 | 61.44 | 97.67 | 184.33 | 0.449 | 0.551 | 0.511 | 0.410 | 0.267 | 0.733 | 0.461 | 0.539 |
| SD1^ | 1.633 | 3.742 | 1.872 | 5.315 | 1.066 | 2.114 | 1.247 | 2.108 | 0.0037 | 0.0037 | 0.0056 | 0.0025 | 0.0044 | 0.0045 | 0.0035 | 0.004 |
| Erucic Acid (FAE1) | Oleic Acid (FAD2) | Erucic Acid (FAE1) | Oleic Acid (FAD2) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amino Acid | Codon | No. (1) | RSCU (2) | No (1) | RSCU (2) | Amino Acid | Codon | No. (1) | RSCU (2) | No. (1) | RSCU (2) |
| Phe | TTT | 94 | 0.910 | 11 | 0.121 | Ala | GCT | 110 | 1.435 * | 54 | 0.964 |
| TTC | 113 | 1.090 * | 172 | 1.879 * | GCC | 70 | 0.917 | 96 | 1.714 * | ||
| Leu | TTA | 51 | 0.698 | 24 | 0.482 | GCA | 69 | 0.904 | 16 | 0.287 | |
| TTG | 72 | 0.984 | 66 | 1.311 * | GCG | 57 | 0.744 | 58 | 1.035 * | ||
| CTT | 137 | 1.871 * | 13 | 0.260 | Tyr | TAT | 62 | 0.689 | 34 | 0.281 | |
| CTC | 94 | 1.286 * | 148 | 2.935 * | TAC | 118 | 1.311 * | 208 | 1.719 * | ||
| CTA | 69 | 0.942 | 16 | 0.315 | His | CAT | 84 | 1.276 * | 60 | 0.674 | |
| CTG | 16 | 0.219 | 35 | 0.698 | CAC | 48 | 0.724 | 118 | 1.326 * | ||
| Ile | ATT | 85 | 0.909 | 10 | 0.162 | Gln | CAA | 62 | 1.531 * | 25 | 0.610 |
| ATC | 92 | 0.990 | 128 | 2.076 * | CAG | 19 | 0.469 | 57 | 1.390 * | ||
| ATA | 102 | 1.100 * | 47 | 0.762 | Asn | AAT | 72 | 0.547 | 18 | 0.361 | |
| Val | GTT | 166 | 1.781 * | 44 | 0.699 | AAC | 191 | 1.453 * | 82 | 1.639 * | |
| GTC | 86 | 0.922 | 132 | 2.113 * | Lys | AAA | 161 | 1.006 * | 34 | 0.376 | |
| GTA | 37 | 0.396 | 11 | 0.174 | AAG | 159 | 0.994 | 147 | 1.624 * | ||
| GTG | 84 | 0.901 | 63 | 1.013 * | Asp | GAT | 137 | 1.127 * | 25 | 0.324 | |
| Ser | TCT | 43 | 0.682 | 34 | 1.018 * | GAC | 106 | 0.873 | 129 | 1.676 * | |
| TCC | 82 | 1.307 * | 100 | 3.004 * | Glu | GAA | 54 | 0.667 | 42 | 0.672 | |
| TCA | 104 | 1.659 * | 7 | 0.210 | GAG | 108 | 1.333 * | 83 | 1.328 * | ||
| TCG | 46 | 0.729 | 40 | 1.199 * | Cys | TGT | 36 | 0.800 | 19 | 0.427 | |
| AGT | 45 | 0.717 | 8 | 0.240 | TGC | 54 | 1.200 * | 70 | 1.573 * | ||
| AGC | 57 | 0.906 | 11 | 0.330 | Arg | CGT | 51 | 1.294 * | 22 | 0.907 | |
| Pro | CCT | 57 | 1.267 * | 105 | 1.774 * | CGC | 0 | 0.000 | 54 | 2.235 * | |
| CCC | 22 | 0.489 | 57 | 0.960 | CGA | 27 | 0.684 | 6 | 0.250 | ||
| CCA | 43 | 0.956 | 12 | 0.201 | CGG | 54 | 1.368 * | 0 | 0.000 | ||
| CCG | 58 | 1.289 * | 63 | 1.065 * | AGA | 78 | 1.971 * | 36 | 1.490 * | ||
| Thr | ACT | 57 | 0.858 | 38 | 0.850 | AGG | 27 | 0.684 | 27 | 1.118 * | |
| ACC | 88 | 1.321 * | 79 | 1.764 * | Gly | GGT | 121 | 1.655 * | 58 | 1.027 * | |
| ACA | 22 | 0.331 | 13 | 0.290 | GGC | 67 | 0.908 | 75 | 1.318 * | ||
| ACG | 99 | 1.489 * | 49 | 1.096 * | GGA | 63 | 0.858 | 75 | 1.323 * | ||
| GGG | 42 | 0.578 | 19 | 0.333 | |||||||
| Brassica | RCBS | RCA | CAI | CBI | Fop | ENC | GC3 | L_sym | L_aa | The Highest RSCU | GRAVY | Aromo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Erucic acid (FAE1) | ||||||||||||
| Br.FAE1.1 | 0.124 | 0.506 | 0.121 | 0.083 | 0.451 | 57.11 | 0.493 | 492 | 506 | CTC (L) | −0.119 | 0.093 |
| Bni.FAE1.2 | 0.134 | 0.499 | 0.120 | 0.095 | 0.457 | 55.78 | 0.497 | 492 | 506 | AGA (R) | −0.103 | 0.095 |
| Bo.FAE1.3 | 0.126 | 0.505 | 0.125 | 0.086 | 0.453 | 57.07 | 0.489 | 492 | 506 | CTC (L) | −0.133 | 0.095 |
| Bc.FAE1.2 | 0.135 | 0.501 | 0.123 | 0.098 | 0.459 | 55.75 | 0.501 | 492 | 506 | AGA (R) | −0.105 | 0.097 |
| Bc.FAE1.3 | 0.119 | 0.500 | 0.124 | 0.090 | 0.455 | 57.83 | 0.493 | 492 | 506 | CTC (L) | −0.123 | 0.093 |
| Bna.FAE1.1 | 0.127 | 0.495 | 0.123 | 0.079 | 0.449 | 57.30 | 0.491 | 492 | 506 | CTC (L) | −0.107 | 0.095 |
| Bna.FAE1.3 | 0.125 | 0.504 | 0.125 | 0.088 | 0.455 | 57.14 | 0.489 | 492 | 506 | CTC (L) | −0.128 | 0.095 |
| Bj.FAE1.1 | 0.128 | 0.493 | 0.121 | 0.072 | 0.445 | 57.16 | 0.495 | 492 | 506 | CTC (L) | −0.117 | 0.095 |
| Bj.FAE1.2 | 0.132 | 0.501 | 0.121 | 0.097 | 0.459 | 55.91 | 0.499 | 492 | 506 | AGA (R) | −0.105 | 0.097 |
| Oleic acid (FAD2) | ||||||||||||
| Br.FAD2.1 | 0.194 | 0.581 | 0.131 | 0.208 | 0.527 | 46.25 | 0.730 | 366 | 384 | CTC (L); TCC(S) | −0.129 | 0.156 |
| Bni.FAD2.2 | 0.213 | 0.566 | 0.128 | 0.212 | 0.527 | 43.70 | 0.742 | 364 | 383 | CTC (L) | −0.139 | 0.151 |
| Bo.FAD2.3 | 0.188 | 0.572 | 0.133 | 0.212 | 0.529 | 45.14 | 0.732 | 365 | 384 | TCC(S) | −0.121 | 0.156 |
| Bc.FAD2.2 | 0.189 | 0.582 | 0.133 | 0.212 | 0.527 | 45.26 | 0.735 | 364 | 384 | CTC (L) | −0.127 | 0.154 |
| Bc.FAD2.3 | 0.192 | 0.577 | 0.135 | 0.212 | 0.529 | 44.38 | 0.732 | 365 | 384 | TCC(S) | −0.121 | 0.156 |
| Bna.FAD2.1 | 0.184 | 0.579 | 0.134 | 0.206 | 0.526 | 46.57 | 0.725 | 365 | 384 | CTC (L); TCC | −0.122 | 0.156 |
| Bna.FAD2.3 | 0.184 | 0.576 | 0.131 | 0.207 | 0.526 | 45.49 | 0.732 | 365 | 384 | TCC(S) | −0.111 | 0.156 |
| Bj.FAD2.1 | 0.201 | 0.571 | 0.131 | 0.213 | 0.529 | 46.01 | 0.730 | 365 | 384 | CTC (L) | −0.114 | 0.156 |
| Bj.FAD2.2 | 0.189 | 0.562 | 0.133 | 0.218 | 0.530 | 44.41 | 0.735 | 364 | 384 | CTC (L) | −0.128 | 0.154 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chaudhary, R.; Chand, S.; Alam, B.K.; Yadav, P.; Meena, V.K.; Patel, M.K.; Pardeshi, P.; Rathore, S.S.; Taak, Y.; Saini, N.; et al. Codon Usage Bias for Fatty Acid Genes FAE1 and FAD2 in Oilseed Brassica Species. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11035. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141711035
Chaudhary R, Chand S, Alam BK, Yadav P, Meena VK, Patel MK, Pardeshi P, Rathore SS, Taak Y, Saini N, et al. Codon Usage Bias for Fatty Acid Genes FAE1 and FAD2 in Oilseed Brassica Species. Sustainability. 2022; 14(17):11035. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141711035
Chicago/Turabian StyleChaudhary, Rajat, Subhash Chand, Bharath Kumar Alam, Prashant Yadav, Vijay Kamal Meena, Manoj Kumar Patel, Priya Pardeshi, Sanjay Singh Rathore, Yashpal Taak, Navinder Saini, and et al. 2022. "Codon Usage Bias for Fatty Acid Genes FAE1 and FAD2 in Oilseed Brassica Species" Sustainability 14, no. 17: 11035. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141711035
APA StyleChaudhary, R., Chand, S., Alam, B. K., Yadav, P., Meena, V. K., Patel, M. K., Pardeshi, P., Rathore, S. S., Taak, Y., Saini, N., Yadava, D. K., & Vasudev, S. (2022). Codon Usage Bias for Fatty Acid Genes FAE1 and FAD2 in Oilseed Brassica Species. Sustainability, 14(17), 11035. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141711035









