Abstract
(1) Background: AI technology has been deeply applied to online shopping platforms to provide more accurate and personalized services for consumers. It is of great significance to study the different functional experiences of AI for consumers to improve the current application status of AI technology. (2) Method: Based on the “SOR” model, this study divides the AI technology experienced by the consumers of online shopping platforms into three dimensions: accuracy, insight, and interaction experience. The perceived value is taken as the mediating variable from the prospect of perceived utility value and perceived hedonic value. This article uses empirical research methods to analyze the effect of the three dimensions of online shopping AI experience to research the internal influence mechanism of consumers’ purchase intention. (3) Results: 1. The accuracy, insight, and interaction experience of AI marketing technology each have a significant positive impact on consumers’ perceived utility value and hedonic value; 2. Both the perceived utility value and perceived hedonic value obtained by an AI technology experience can promote the formation of consumers’ purchase intention; 3. The perceived hedonic value was better than perceived utility value at promoting the consumers’ purchase intention.
1. Introduction
As an important branch of computer science, artificial intelligence (AI) makes use of artificial methods and technologies to make automatic machines and computers simulate, extend, and expand human intelligence, so that some machines and equipment can have human thinking abilities—like self-learning, self-programming, and automatic mental labor [1]. After its birth and industrialization stage, AI has ushered in a stage of explosive development in the world with the application of big data after 2000. With the rapid development of the new generation of information technology and the popularization of marketing applications, marketing has developed from the one-way marketing of Web 1.0, to the interactive marketing of Web 2.0, then to precision marketing based on big data, and the smart marketing stage supported by AI technology [2]. AI technology can enhance the interactions not only among customers, products, or services, but also in interactive environments, and it can match demands quickly [3]. AI chat robots, content recommendation systems, and consumer feature recognition have become artificial agents for AI marketing activities [4]. Amazon takes the lead in using artificial intelligence technology to achieve the retail relocation of people, goods, and stores, and extends its artificial intelligence framework DSSTNE from dialogue, language understanding, and object recognition, to the field of search and recommendation. This makes the recommendation of related products and complementary products more personalized and real-time, improves the conversion rate of product purchases, and realizes precision marketing [5].
Capgemini Digital Transformation Research Institute released the report “Secrets of Artificial Intelligence Winning Consumers: Enabling Human Intelligence”. According to this research report, 38% of consumers have a good AI experience, and their purchase volume is increased significantly. In the study of AI marketing, some research has discussed AI service adoption willingness, AI personalized recommendations [6,7], AI pricing [8], and AI consumer assistants [9] in different marketing scenarios like service delivery [10] and information delivery [11]. Some studies have found that consumer perceived value [12], perceived trust, and perceived risk [13] can be the mediating variables of consumer experience and AI service.
However, there are few studies that explore AI technology in online shopping scenarios, especially the impact mechanism on consumer purchase intention, and that consider all the AI technology application experiences in the background of online shopping. In particular, the questions of whether perceived value can be an effective mediator between AI technology and consumer purchase intention have not been answered, as well as which mediator plays a more important role in online shopping platforms.
Therefore, in this study, we establish a structural equation model to explore the relationship between the AI technology of online shopping platforms and consumers’ purchase intention, analyzing the mediating role of perceived hedonic value and perceived utilitarian value. At the same time, we aim to discover the different effects between perceived hedonic value and perceived utilitarian value as mediators. The results provide a realistic basis for platform enterprises to explore a clearly researched direction of AI technology, and to optimize consumer shopping perceived value to make the online shopping services much more sustainable.
2. Review of Related Research
2.1. SOR Model
The Stimulus-Organism-Response (SOR) model was first proposed by Mehrabian and Russell in 1974 [14]. It considers that the assessment process of the human body is different from that of a machine. Various stimuli in the environment (S), such as auditory, visual, and olfactory stimuli, will cause changes in the state of internal emotion and in cognitive mechanisms (O), and then cause the response (R) (Figure 1).

Figure 1.
Mehrabian–Russell SOR model.
Donovan and Rossiter [15] first applied the SOR model to the shopping field. Eroglua et al. [16] introduced the SOR model into online shopping platforms for the first time to explore the influence of preference and cognitive state on online shopping consumption behavior in the atmosphere of online stores.
The research on purchase intention in online shopping platforms using the SOR model mainly includes the following points. Some scholars have shown the atmosphere of the website had an impact on the consumers’ approach or avoidance behavior [17]. The website image (security, convenience, entertainment) will affect the perceived quality and purchase intention in online stores [18]. The state of consumers’ feelings (pleasure and impulse) can affect consumers’ consumption impulse and expenditure [19]. Website navigation structure affects purchase intention through consumer participation, website atmosphere acceptance, and risk acceptance [20]. Sanjeev Prasha et al. [21] maintain that the website atmosphere is composed of internal factors (hedonic shopping value and utilitarian shopping value), external factors (website information, website entertainment and effectiveness of information content), and that the satisfaction brought by websites to consumers will directly affect consumers’ consumption behavior. From the perspective of e-commerce services, Zhang Beijia [22] takes the ease of online return policy as a stimulus variable that has a positive impact on consumers’ purchase intention through the intermediary effect of perceived commodity quality, while perceived shopping risk cannot be used as an intermediary variable to influence consumers’ purchase intention. From the perspective of e-commerce platform reputation and image, it is found that reputation has a positive correlation with online repurchase intention, perceived risk has a negative impact on online repurchase behavior, and subjective norms have a positive impact on consumers’ purchase intention [23]. Online store image can influence consumers’ online purchasing behavior through consumer interest [24], perceived value, and flow experience [25].
The current research on technology as stimulus is mainly reflected in the navigation structure of the website, the implementation of platform-assisted business technology, and the effectiveness of the network [26]. At present, AI technology, which has industry empowerment significance, has little research on its impact, as a kind of stimulation, on consumers’ internal mechanism of purchase intention. This study will creatively fill the gaps of SOR theory in the field of AI technology’s applications in online shopping.
2.2. AI technology Experience of Online Shopping Platform
Based on a large amount of existing literature on AI marketing at home and abroad, and the practice of industrial workers, this study concludes that consumers’ AI technology experiences of online shopping platforms can bring consumers intuitive AI experiences through intelligent identification and search, intelligent recommendation, and virtual customer service assistants. Therefore, this study innovatively takes the above three types of AI applications for online consumers’ corresponding experience effects—accuracy experience, insight experience, and interactive experience.
2.2.1. Accuracy Experience
The integration of artificial intelligence, information technology, and systems-engineering-related technologies forms an intelligent decision support system, which can change the potential of human decision-making [27]. Intelligent recognition and search refers to the use of big data and AI technology by the marketing engine of e-commerce platforms to help consumers realize rapid screening in massive data. When consumers input keywords, voice, or pictures in the search bar, AI can use text, voice, and image analysis technology to identify problems and search to find and prioritize possible targeted commodities [28]. Autonomous learning neural networks have reduced the error rate of image recognition from 30% in 2010 to 4% in 2016 [29]. In 2019, iFLYTEK’s speech recognition rate reached 98%, and it is predicted that AI speech recognition will reach the same level as human beings in 2021. An increase of data volume leads to the complexity of individual decision-making, and makes the decision-making process impossible to complete. Intelligent search engines can help users extract noise, and help consumers accurately find the target commodity. The above fully reflects that AI technology can bring accurate experiences to consumers. At present, leading online Chinese shopping platforms such as Taobao, Jingdong, Pinduoduo, and other search engines, have been able to realize the recognition of text, picture, and voice.
2.2.2. Insight Experience
Machine learning can customize the content of the company’s website to achieve consistency with user preferences and willingness to pay, and connect customers in all channels and devices in a seamless and personalized way. It can be said that machine learning is the best technology for understanding consumer preferences [30]. AI can realize accurate prediction of user needs and insight into users, and provide personalized solutions [31]. The marketing software system applying big data and AI technology is an interactive consultation and decision-making system [32]. Its most obvious feature is automatic knowledge discovery and intelligent decision-making [33]. From the perspective of users, the primary application of AI in the marketing field is to deliver precision marketing on demand for thousands of people [34], and the most common application is the personalized recommendation system [35], such as the intelligent push part of the “guess you like” feature of online shopping platforms. AI marketing technology makes full use of the large amount of data retained in the e-commerce platform to realize information insight into consumer behavior [36]. It uses the recommendation engine to recommend products that may be purchased in the future according to the past purchasing behavior of users, reduces the cognitive load of consumers, and is committed to providing optimal services for consumers through prediction. The accuracy and the effect of “intelligent” advertising carried out by AI technology are more significant than those of traditional retail [36]. The above reflects the insight function experience that AI marketing technology brings to consumers.
2.2.3. Interactive Experience
Natural language interaction and machine learning technology have led AI customer service to replace human customer service. AI customer service can understand consumer language and reply [32], provide users a human like communication mode [37], help enterprises carry out consumer marketing and sales services, and record customer behaviors and preferences. The virtual assistant of the online shopping platform has begun to play the role of intelligent customer service, and has been deeply applied in the communication between consumers and merchants, especially in the area of consulting on common questions related to products, inventory, invoice, logistics, return, and so on. Amazon, Jingdong, Alibaba, and other e-commerce platforms have developed smart speakers such as Echo, Dingdong, and Tmall genie. As the entrance, an AI virtual assistant can assist consumers in making complex purchase decisions and completing closed-loop consumption, and bring intelligent interactive experience to users through voice interaction with consumers. The above fully reflects the interactive experience that AI marketing technology brings to consumers.
2.3. Consumer Perceived Value
Consumer perceived value refers to the all evaluation of perceiving differences between consumers pay and obtain in the process of shopping [38]. In the process of explaining consumer behavior, a multi-dimensional perceived value survey can more specifically explain the impact of different consumption scenarios on consumers’ wishes than a one-dimensional structure, and some of the dimensions of perceived value research are embodied in the perception of commodity attributes [39], perception of cost [40], convenience perception [41], interactive relative preference experience perception [42], brand value perception [43], consumer lifetime value perception [44], and so on. Some scholars have also summarized consumer perceived value as perceived utility value, perceived hedonic value, perceived social value, and perceived cognitive value [45].
In the research on consumer perceived value in the use of technology systems, the technology acceptance model (TAM) proposed by Davis [46] in 1989 sets perceived ease of use and perceived usefulness as independent variables, and considers that perceived usefulness (the system helps improve work performance) and perceived ease of use (convenience of system use) will affect users’ attitudes towards technology use, and then affect their behavior. It is believed that a user’s use of technology is influenced by their purposes and intentions. Subsequently, Davis proposed that perceived usefulness has a greater impact on a user’s decision to use a system than perceived ease of use [47]. In a study of consumer behavior in the context of internet technology, Moon and Kim extended TAM, and proposed that the interest of websites (the sense of concentration, novelty seeking, and pleasure) is also an important factor affecting consumers’ perceived value [48]. Yang and Lin decomposed the perceived value dimension of online social platforms into hedonic value, social value, and cognitive value, and evaluated the mediating role of consumers in using social platforms [49]. Chu Tanming divides perceived value into three dimensions—perceived utilitarian value, perceived hedonic value, and perceived social value—as mediators, verifying that it has a significant impact on consumers’ online shopping channel choice intention [50]. Sang Jon Ahn divided consumer perception into perceived convenience value, perceived emotional value, and perceived use value to evaluate customer acceptance of online banking [51]. I Gusti N.M.W.A concluded that perceived utilitarianism and perceived hedonism play a promoting role in the influence of consumers’ online second purchase intention [52].
Perceived utilitarian value is usually defined as the utility-related value embodiment of a behavior or a product itself [47], including saving of shopping and time costs [40], and convenience of use [41,42]. Perceived hedonic value is defined as pleasure, relaxation [51], arousal, curiosity, and surprise [49,50], as well as mental concentration and interest in interactive process degree [49]. The reason why the marketing aspects of online shopping platforms can take the lead in the application of AI technology is mainly because e-commerce platforms have accumulated a large amount of consumer behavior data, including browsing records, consumer characteristics, and so on. AI technology can continuously self-study, use algorithm iteration, and directly bring consumers the practical value of analysis, recommendation, and rapid change of visual stimulation. Therefore, the perceived value of AI technology in online shopping can be measured by perceived utility value and perceived hedonic value.
3. Conceptual Model and Research Hypothesis
3.1. Model Framework
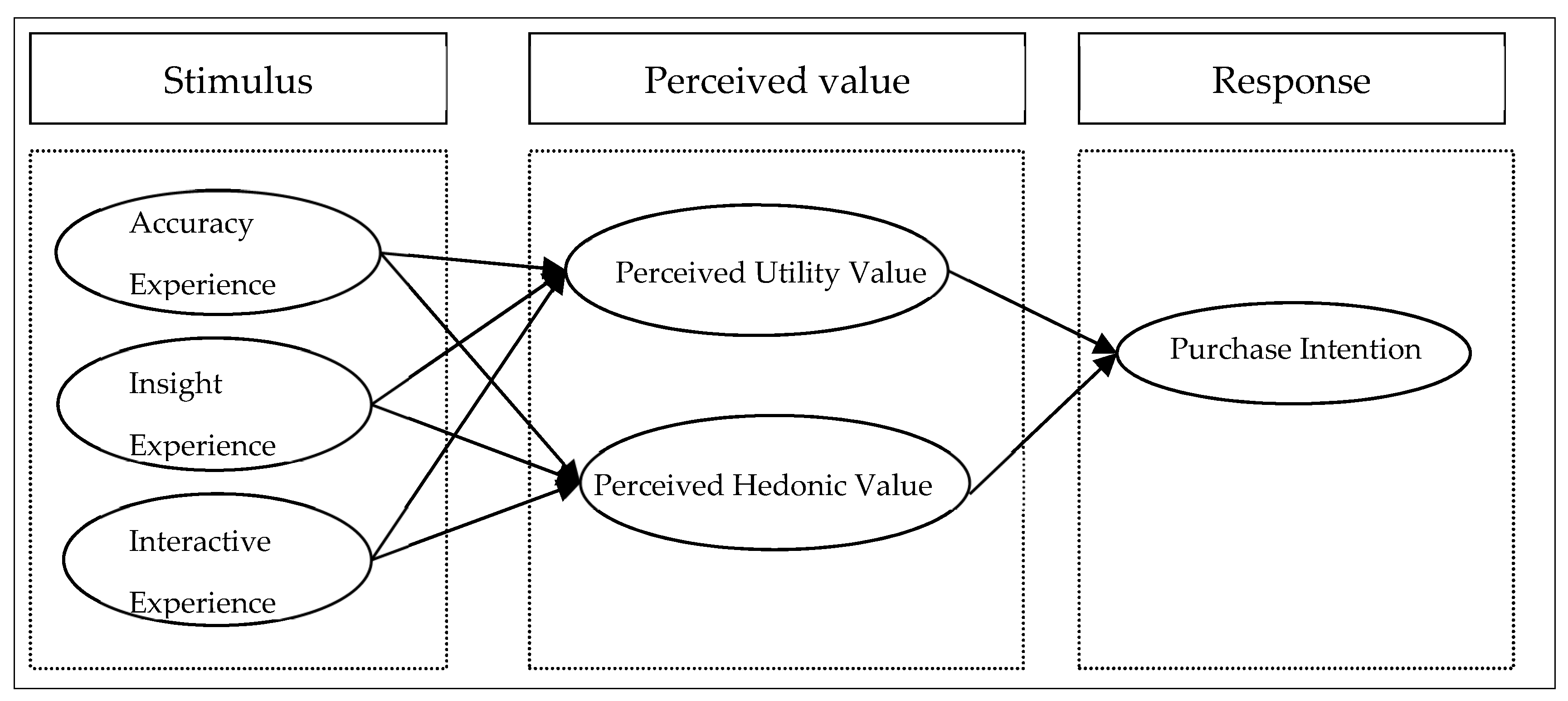
Based on the analysis of the above literature research results, this study draws on the SOR model research framework, and takes the online shopping platform AI marketing technology experience as the stimulus, the consumer perceived value as the emotional mechanism, and the consumer purchase intention as the response result. Based on the above views, the theoretical model shown in Figure 1 is obtained. As the antecedent variable, the online shopping platform AI marketing experience is divided into three dimensions: accuracy experience, insight experience, and interactive experience. As an intermediary variable, consumer perceived value can be divided into perceived utilitarian value and perceived hedonic value. Consumer purchase intention is taken as the result variable (Figure 2).
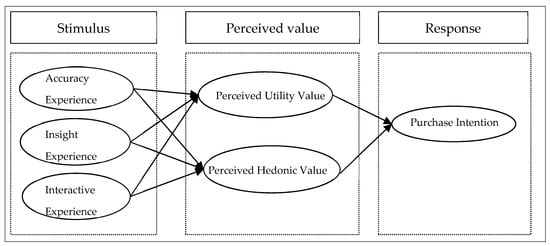
Figure 2.
Theoretical model framework.
3.2. Research Hypothesis
3.2.1. AI Marketing Technology Experience and Consumer Perceived Value of Online Shopping Platform
The stimulation of AI marketing technology is conducive to consumers making complex purchase decisions [37], which can save the time and cost of shopping for consumers [38], making shopping choices more accurate and more conducive to the improvement of consumers’ shopping efficiency [53]. The use of artificial intelligence technologies such as visual recognition, speech recognition, and machine vision can give better insight into consumer behavior in terms of five aspects—problem recognition, information collection, alternative evaluation, purchase decision-making, and post-purchase evaluation [54]—so as to provide consumers with a more efficient consumption reference and make the value perception form of the whole consumption process richer and smoother. In the process of interaction with an e-commerce platform, accurate and extended information stimulation can expand the boundary of consumers’ target selection. The visual impact of online shopping and surfing can meet consumers’ personalized customized information needs in terms of pleasure, respect, and attention. Through machine vision and deep learning technology, artificial intelligence can search for words, pictures, and voice, so that consumers can accurately identify product features, thus enriching the consumer search experience, saving consumers’ shopping time, reducing boredom in the shopping process, and increasing the interest of the consumption process [55]. Therefore, the following assumptions are put forward:
Hypothesis 1a (H1a).
The improvement of accuracy experience of AI marketing technology in online shopping platforms is conducive to promoting the formation of consumers’ perceived utility value.
Hypothesis 1b (H1b).
The improvement of accuracy experience of AI marketing technology in online shopping platforms is conducive to enhancing the formation of consumers’ perceived hedonic value.
Machine learning is an important branch of artificial intelligence. According to the algorithm of evolutionary behavior based on empirical data, it can accurately observe customers’ preferences and shopping needs, push personalized information for existing and potential customers, and provide more effective purchase suggestions for consumers [56]. However, the intelligent push of information needs to influence consumers’ purchasing behavior through some mechanism. The pushed information must make consumers perceive the utility and effectiveness of the information, or bring a certain degree of participation and enjoyment of physical and mental pleasure into the shopping process, otherwise the purpose and significance of shopping will be lost [57]. Therefore, the following assumptions are put forward:
Hypothesis 1c (H1c).
The improvement of insight experience of AI marketing technology in online shopping platforms is conducive to promoting the formation of consumers’ perceived utility value.
Hypothesis 1d (H1d).
The improvement of insight experience of AI marketing technology in online shopping platforms is conducive to promoting the formation of consumers’ perceived hedonic value.
People can have some positive or negative emotional connection with and influence from the power brought by artificial intelligence, even if they know that this power is not a real emotional interaction between people [58]. According to analysis of the application status of the Jingdong AI robot, some scholars believe that AI technology can help with the automation of consumer feedback management, and that emotional analysis driven by artificial intelligence can help marketers better respond to consumers, give robot customer service on e-commerce platforms better intelligence quotients, and bring better consumer value experience to consumers’ online shopping. Therefore, the following assumptions are put forward:
Hypothesis 1e (H1e).
The improvement of interactive experience of AI marketing technology in online shopping platforms is conducive to promoting the formation of consumers’ perceived utility value.
Hypothesis 1f (H1f).
The improvement of interactive experience of AI marketing technology in online shopping platforms is conducive to promoting the formation of consumers’ perceived hedonic value.
3.2.2. Perceived Value and Purchase Intention of Online Consumers
Empirical studies have confirmed that the perceived value of online store image in an online shopping environment can bring about purposeful and impulsive buying behavior [25]. A large number of studies have shown that purchase intention is based on the symbolic and functional attributes of the product, while the utilitarian value is reflected in the practicality, convenience, and cost-saving experienced by consumers in the shopping process [59,60,61]. Utilitarian value will play a role when consumers only focus on the visible benefits of the product itself, and will influence consumers to choose goods according to their own needs in the process of online shopping [62]. The utilitarian value brought by the convenience of technology and the improvement of shopping efficiency can improve consumer satisfaction, enhance consumption desire, and promote re-consumption [63]. Perceived hedonic value refers to the subjective experience of pleasure, interest, and relaxation obtained by consumers in the process of shopping. The pleasure of the consumption process can have a positive impact on impulse consumption intention. The perceived function value and perceived hedonic value of the consumption process are conducive to the occurrence of online repurchase behavior [20]. Artificial intelligence makes marketing more intelligent, more efficient, more conducive to consumer decision-making, and more able to obtain a better marketing effect. Therefore, the following assumptions are put forward:
Hypothesis 2a (H2a).
The perceived utility value brought by AI marketing technology experience of online shopping platforms can promote consumers’ purchase intention.
Hypothesis 2b (H2b).
The perceived hedonic value brought by AI marketing technology experience of online shopping platforms can promote consumers’ purchase intention.
4. Research Design
Recently, most of the existing studies have been based on questionnaire surveys and experimental methods. The normal data analysis and hypothesis-testing methods include regression analysis, structural equation model (SEM), analysis of variance, factor analysis, cluster analysis, chi square test, t-test, and so on [28]. In this study, we choose a questionnaire survey and SEM to test the hypothesis.
4.1. Scale Design
As for the measurement of AI marketing technology experience of online shopping platforms, there is no mature measurement scale belonging to the innovative research in this field. The measurement of AI marketing technology experience is mainly achieved through comprehensive research on the following: (1) literature review of current AI marketing technology experience research; (2) actual, functional scenarios of AI marketing from China’s top three e-commerce platforms; (3) industrial workers’ working judgment on the impact of AI marketing on consumer behavior; and (4) marketing experts’ opinions. From a summary of the above, this paper measures consumers’ AI marketing technology experience of online shopping platforms from the three dimensions of accuracy, insight, and interactivity. The measurement of accuracy experience comes from the online shopping websites of “Taobao”, “Jingdong”, and “Pinduoduo”, which are the top three e-commerce websites in China in 2020, to explore their AI marketing search engine for consumers and to measure the accuracy of the retrieval target by using the three methods of input: text, picture, and voice. The measurement of insight experience refers to the research viewpoints of V. Kumar et al. [29], Jordan et al. [30] and Qian M. [31], who have designed a scale combined the relevant functions of the above online shopping platforms’ AI marketing recommendation systems. The measurement of interactivity refers to the online interaction responsiveness measurement dimension of Jiang Shen [64], and fully combines the above e-commerce platforms’ artificial intelligence customer service functions to design the scale.
The perceived utility value which refers to the scale of Chu Tanming [50] modified according to the characteristics of AI technology experience. The scales of Moon et al. [48] and Yang et al. [49] are used to evaluate the perceived hedonic value. The consumers’ purchase intention refers to the scale of Carlota L.R. et al. [20].
According to the measurement items of the above scale, the questionnaire was compiled with a 5-point Likert scale, in which point 1 indicated strong disapproval and point 5 indicated strong approval. Three e-commerce industry experts and two e-commerce enterprise executives were invited to review and revise the questionnaire to form the draft of the questionnaire. In order to ensure the rationality and effectiveness of the questionnaire design, the survey was completed in two stages. The first was the pre-survey stage. We used the Questionnaire Star platform to make the questionnaire and forwarded it to 50 people through WeChat to fill it in. At the top of the questionnaire, we have explained the definition of AI and AI marketing technologies, including intelligent search, intelligent recommendation, and virtual customer service assistant, to make sure that respondents could understand the research terms and intentions. We eliminated any questionnaire that took less than 60 s to complete, to reduce the probability of random filling in. Finally, 43 valid questionnaires were confirmed, and the effective rate was 86%. Exploratory factor analysis was carried out for the questionnaire in the pre-survey stage. Through the test of 50 small-scale questionnaires, 6 latent variables and 23 questions were obtained. The α value of the related variables is 0.97, which is greater than 0.9, so the questionnaire has good reliability and can be used for formal research.
The main body of the questionnaire is divided into two parts: the first part is the measurement of statistics of basic personal information, and the second part is the measurement of six latent variables (Table 1).

Table 1.
Questionnaire scale.
4.2. Sample Data
The target e-commerce platforms for this study were selected as the top three online shopping platforms of China’s top 100 e-commerce platforms in 2020: Taobao, Jingdong, and Pinduoduo. The respondents were consumers with online shopping experience. In the process of conducting the research, the questionnaire was designed through the Questionnaire Star platform, and consumers filled in the questionnaire online.
In total, 688 questionnaires were collected in this study. Those with less than 60 s of answer time and those with repeated answers were considered invalid. Finally, 631 valid questionnaires were obtained, and the effective rate was 91.7%, which met the statistical requirement that the effective sample size was at least 5 times that of the measurement items.
Following is the demographic analysis of valid questionnaires. In terms of gender distribution, 38.99% were men and 61.01% were women. In terms of age distribution, 3.96% were under 20 years old, 38.51% were between 21 and 30 years old, 45.08% were between 31 and 40 years old, 8.40% were between 41 and 50 years old, and 3.33% were above 51 years old. In terms of educational background, 20.13% were under bachelor’s degree, 54.2% were bachelor’s degree, and 25.67% were master’s degree or above. In terms of family income, annual disposable income below 100,000 accounted for 26.47%, 100,000–200,000 accounted for 34.39%, 200,000–300,000 accounted for 21.24%, and more than 300,000 accounted for 17.9%. In terms of online shopping history, less than 3 years accounted for 6.81%, 3–6 years of shopping experience accounted for 35.5%, 7–9 years of shopping experience accounted for 28.05%, and more than 10 years accounted for 29.64%. In terms of online shopping frequency, 2–4 times a week accounted for 32.65%, and more than 5 times a day accounted for 5.71%.
4.3. Data Analysis Method
In this study, SPSS 23.0 and SPSS tests were used to analyze the data. Firstly, the reliability test, validity test, and exploratory factor analysis of the sample data of the scale were carried out. Secondly, confirmatory factor analysis was carried out on the structural equation model (SEM) to ensure that the data and the model could achieve good fitting. Finally, overall and multi-group path coefficient analysis were carried out on the theoretical model.
5. Analysis of Research Results
5.1. Reliability and Validity Analysis
We used Cronbach’s α coefficient to test the reliability of the latent variables. As shown in Table 2, the Cronbach’s α values of all latent variables in this study are between 0.743 and 0.836, and the combined reliability values are between 0.855 and 0.877, which are higher than 0.7. The Cronbach’s α values of the whole sample data reach 0.927, so it has good reliability for the measurement of variables. In the process of validity analysis, the KMO test and Bartlett spherical test were used first, and the final measurement data were calculated. The KMO value was 0.944, greater than 0.9, which was very suitable for factor analysis; the Bartlett spherical test level was significant (p < 0.001), which indicated that the above data were suitable for factor analysis. After analysis with SPSS25.0, the factor loads of all items on their latent variables were measured by factor analysis. All factor loads were more than 0.7, and the average variance extraction value (AVE) of each latent variable was more than 0.5, which indicated that the measurement of variables had good convergence.

Table 2.
Analysis of reliability and validity.
5.2. Common Method Deviation Test
In order to reduce the common method deviation, this study concealed the variable names in the questionnaire design process and adopted the Harman single-factor analysis method accepted by most studies. All items in the questionnaire were analyzed by factor analysis without rotation, and the highest explained factor variance contribution rate was 38.86%. It can be considered that the common method deviation in this study is not significant.
5.3. Hypothesis Test and Conclusion
In this study, Amos23.0 software was used to construct the structural equation for model fitting. From the fitting test results, the model fitting effect was relatively good: CMIN/DF = 3.769; AGFI, NFI, IFI, CFI values were 0.868, 0.867, 0.899, and 0.898, respectively; and RMESA value was 0.066. These met the recommended standard of model fitting, and were suitable for further path analysis.
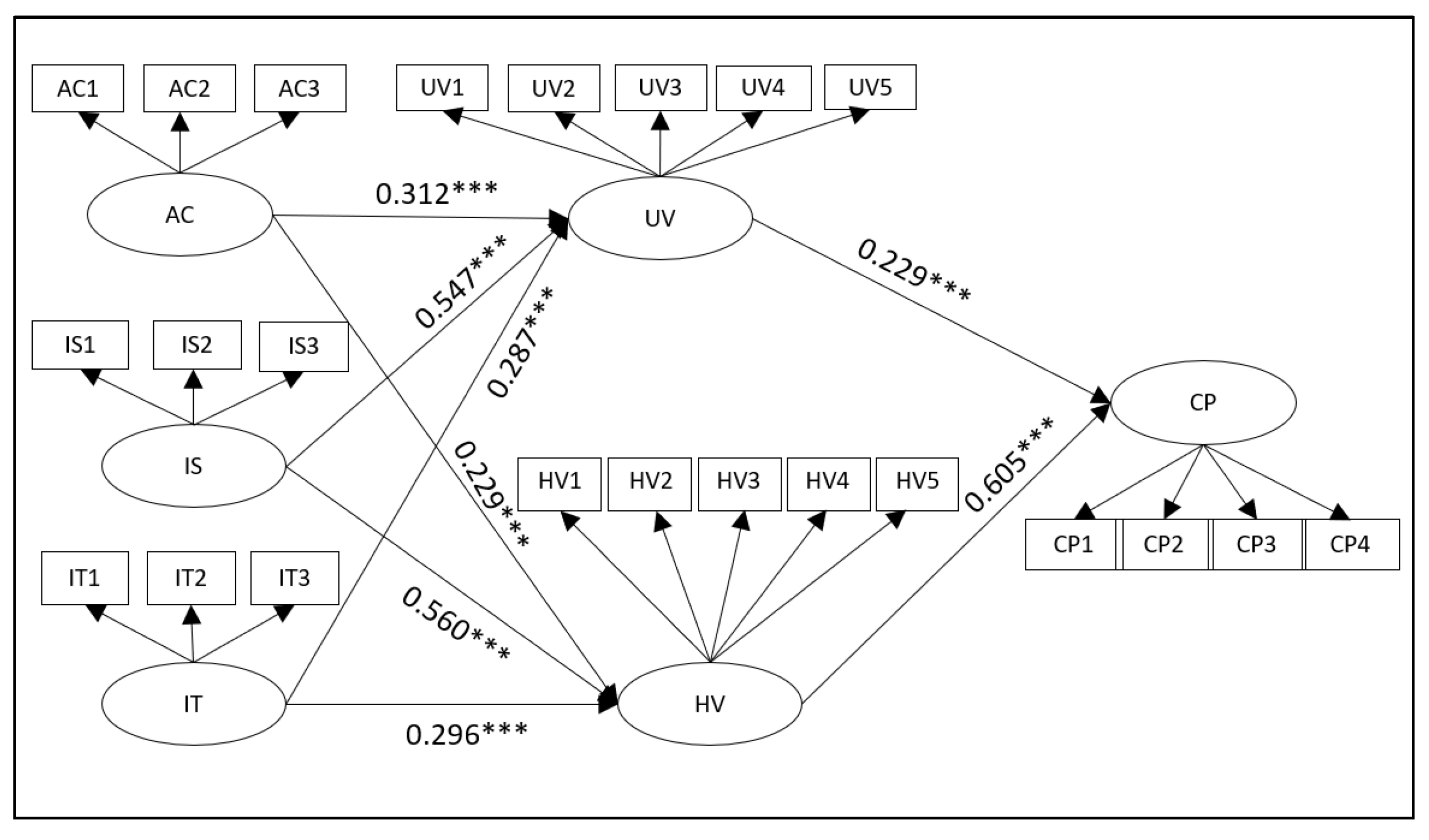
The hypothesis test results of the theoretical model are shown in Table 3. The results show that the p-values of all relationships are significant when they are less than 0.001, and the model and path coefficient are shown in Figure 3.

Table 3.
Results for hypotheses verification.
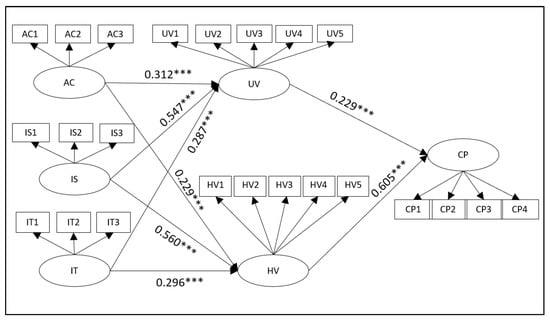
Figure 3.
Model and path coefficient (*** represents p < 0.001).
H1a and H1b have passed the significance test, which shows that the accuracy of AI marketing technology experience of online shopping platforms is conducive to improving consumers’ perceived utilitarian value and hedonic value. With the increase of the accuracy of AI marketing technology, consumers are more likely to perceive the utilitarian value and hedonic value in the process of shopping. H1c and H1d have passed the significance test, which shows that with the insight experience of AI marketing technology increasing, consumers’ perception of utilitarian value and hedonic value will increase significantly. In addition, h1e and H1f pass the significance test, which shows that the stronger the online interaction of AI marketing technology on an online shopping platform, the more conducive it is to increasing consumers’ perceptions of utilitarian value and hedonic value. (Table 3).
Both H2a and H2b have passed the significance test. This shows that the perceived utilitarian value and perceived hedonic value brought by AI marketing technology can promote the formation of consumers’ purchase intention. The path coefficient of perceived hedonic value (0.605) is higher than that of perceived utilitarian value (0.229), which indicates that perceived hedonic value can promote the formation of consumers’ purchase intention more than utilitarian value (Table 3).
This paper used the bootstrapping method. Consumer purchase intention was the dependent variable. The independent variables were accuracy experience, insight experience, and interactive experience. The mediating variables were perceived utilitarian value and perceived hedonic value. This was to further verify the mediating effect of perceived utilitarian value and perceived hedonic value in the whole influence path. The calculation results are shown in the table below. It can be seen from Table 4 that the bias-corrected and percentile confidence intervals of each influence path do not contain 0. Perceived utilitarian value and perceived hedonic value were indirect effects in the influence paths of AI technology experience (AC, IS, IT) and consumers’ purchase intention, and the p-value of each path was significant. (Table 4).

Table 4.
Intermediary test of perceived utilitarian value and perceived hedonic value.
6. Conclusions and Discussion
6.1. Research Conclusions
6.1.1. AI Marketing Technology Experience of Online Shopping Platform Is Conducive to Improving Consumers’ Perceived Value
The higher the accuracy of AI marketing technology, the more conducive it is to enhancing consumers’ perceived utilitarian value and perceived hedonic value. Combined with the survey results, consumers are most satisfied with the accuracy of text retrieval enabled by AI marketing technology, but less so with image recognition technology and voice recognition technology, as the accuracy brought by both will affect the retrieval experience of consumers. The perceived utilitarian value of AI marketing technology improved by accuracy is greater than the perceived hedonic value, which indicates that consumers think that AI marketing technology has higher utility in terms of shopping convenience, time, and cost-saving [47], while the perception of hedonic value brought by accuracy is not as strong as the degree of utilitarian value.
The greater the insight of AI marketing technology of an online shopping platform, the more conducive it is to enhancing consumers’ perceived utilitarian value and perceived hedonic value. Combined with the results of the questionnaire, consumers’ recognition of AI marketing technology insight is higher than its accuracy and interactivity. At the same time, AI marketing technology brings insight experience to online consumers [65], which is not only conducive to improving consumers’ perceived utilitarian value, but also can promote the pleasure of the shopping process through insight, increase the sense of curiosity in the consumption process, and stimulate shopping desire and interest. Consumers’ purchase intention through perceived hedonic value is stronger than perceived utilitarian value.
The higher the interaction of AI marketing technology on an online shopping platform, the more conducive to the formation of consumers’ perceived utility value and perceived enjoyment value. The consumers consider that the satisfaction of an AI virtual assistant is lower than the accuracy and insight satisfaction. At the same time, the interactive experience of AI marketing technology on online shopping platforms is weakest in promoting the formation of these two perceived values. This shows that for relatively complex semantic and human-computer interactions, the current AI technology is not enough to realize the needs of personalized and emotional communication of consumers. At present, AI customer service can only solve the conventional problems, such as product description, delivery time, and logistics information. The interaction of AI customer service has less perceived utility and hedonic value than insight and accuracy.
6.1.2. Perceived Utility Value and Hedonic Value of Online AI Marketing Technology Can Promote the Formation of Consumers’ Purchase Intention and the Influence of Perceived Hedonic Value Is Greater
Firstly, perceived utilitarian value and perceived hedonic value play a positive mediating role between AI marketing technology experience and consumers’ purchase intention, which indicates that AI marketing technology can promote the formation of purchase intention through the mediation of perceived value. Secondly, the promotion of perceived hedonic value on consumers’ purchase intention is greater than that of perceived utilitarian value. With AI technology widely used in online shopping platforms, functional requirements such as product selection, shopping efficiency, and convenience have become routine functions in mainstream e-commerce platforms, and consumers have no more value-added feeling, so perceived utilitarian value does not show more differences. Consumers prefer a more spiritual experience of stimulation, pleasure, and relaxation of shopping desire brought by AI technology in the process of online shopping. AI is good at flexibly changing its recommendation trajectory according to consumers’ behavior, continuously mining potential demand, and directly stimulating consumers’ shopping desire [66]. In the process of online shopping, hedonic value becomes the main factor to promote the formation of consumers’ purchase intention.
6.1.3. On the Online Shopping Platform, AI Marketing Technology Cannot Promote Consumer Purchase Intention Directly, and Perceived Utility Value and Hedonic Value Are Effective Mediators
AI as a kind of technology is widely used in online shopping platforms to help enterprises promote the volume of shopping, but it cannot work directly. In the process of online shopping, consumers must find a feeling that makes all kinds of services and help valuable to them, for example, cost and experience, which will lead to purchase intention and behavior [67]. In this paper, we found that both perceived utility value and hedonic value are effective mediators between AI technology experience and consumers’ purchase intention on the online shopping platform.
6.2. Academic Implications
The theoretical value and academic significance of this study are as follows. (1) In the field of AI marketing at home and abroad, the current analysis of the comprehensive application of AI technology in the field of online shopping is still a blank, and this study fills the gap. (2) This study expands the application field of SOR, takes the experience brought by AI technology as a stimulus variable, acts on consumers’ purchase intention through perceived value as a mediating mechanism, and verifies that perceived utilitarian value and perceived hedonic value have significant mediating effects. (3) This study verifies the accuracy, insight, and interactive experience of AI technology for the different paths of perceived utilitarian value and perceived hedonic value, and draws the conclusion that the utility of perceived hedonic value under the three kinds of experience is significantly greater than that of perceived utilitarian value. It provides a reference for AI technology to promote sustainable development in the application of online consumers’ purchase intentions.
6.3. Sustainable Management Inspiration
Online shopping platform enterprises should maintain the sustainability of AI technology development and investment in marketing; continuously optimize and upgrade the application of intelligent search, intelligent recommendation, and intelligent interaction technology; improve the accuracy of search engines for different forms of character fields, images, voice, and image retrieval; and strengthen the technical ability of big data retrieval services. The platform algorithm can be optimized sustainably, the AI insight ability of the platform can be strengthened, and the consumers’ desire for shopping can be stimulated by mining the consumer’s behavior rules, predicting the consumers’ intention, and optimizing the pleasure experience, such as relaxation and pleasure in shopping. Enterprises should increase the research and development ability of AI interaction technology, break through the existing technical bottleneck of natural language learning and understanding of AI customer service, and create a more accurate and satisfactory interaction environment for consumers.
Online shopping platform enterprises should pay attention to the technological influence of AI on consumers’ hedonic psychology, and expand the application boundary based on consumers’ online shopping behavior. At the same time, they should deepen the combination of machine vision, artificial neural networks, and other technologies with the online shopping field, while expanding the exploration of consumers’ eye movement, expression change, and reasoning psychological state change, and more accurately grasping the factors that stimulate consumers’ perception of hedonic value, to accelerate the formation of consumers’ purchase intention.
6.4. Limitations and Prospects
This study has certain limitations and needs to be further explored in the exploration of AI marketing in the future. First of all, in order to highlight the core influencing factors, this study only considers the core perceived value of the internal influencing mechanism of consumers as the intermediary influence, but does not consider other internal influencing factors such as perceived risk, flow experience, consumer attitude, and other mediating variables that affect consumer behavior. Second, this study only considers the influence differences under the differences of demographic characteristics, but does not consider other factors like the moderating effects of consumer self-construction, preference characteristics, experience, and cognitive style. Finally, in the empirical research, we only used the questionnaire survey method, which could be filled out online, but was unable to deeply analyze the thinking process of consumers and judge the errors caused by different motives. The above directions need further deep research.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.Y. and X.Q.; methodology, J.Y.; software, J.Y.; validation, J.Y.; formal analysis, J.Y.; investigation, J.Y.; data curation, J.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, J.Y.; writing—review and editing, J.Y.; supervision, X.Q. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by a grant from the National Social Science Fund of China (15AGL002).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not Applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not Applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to the raw data refer to consumers privacy.
Acknowledgments
Thanks to Qiu for his supervision and guidance. Thanks to my classmates and workmates for their suggestions on the questionnaire and their cooperation in filling in the questionnaire.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sterne, J. Artificial Intelligence for Marketing Practical Application, 1st ed.; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2019; pp. 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y. AI Marketing, 1st ed.; China Renmin University Press: Beijing, China, 2019; pp. 22–35. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Lei, S. Research on the influence of AI on consumption and shopping experience in the new retail environment—Based on the perspective of commercial retail reform and reconstruction of people-goods-yard system. J. Commer. Econ. 2018, 17, 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Overgoor, G.; Chica, M.; William, R. Letting the computers take over: Using AI to solve marketing problems. Calif. Manag. Rev. 2019, 8, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, N.; Kinghts, M. Amazon: How the World’s Most Relentless Retailer Will Continue to Revolutionize Commerce; CITIC Press Group: Beijing, China, 2019; pp. 167–175. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Effects of consumers’ perceived personalization on their click-through intention under AI personalized recommendations. J. Manag. Sci. 2020, 33, 44–57. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Yu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, X. Impact of Artificial Intelligence recommendation on consumers’ willingness to Adopt. J. Manag. Sci. 2020, 33, 29–43. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.; He, X. The effect of Artificial Intelligence pricing on consumers’ perceived price fairness. J. Manag. Sci. 2020, 33, 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Graeme, M.; Kofi, O.; Jennifer, B. Alexa, do voice assistants influence consumer brand engagement?—Examining the role of AI powered voice assistants in influencing consumer brand engagement. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 124, 312–328. [Google Scholar]
- Dogan, G.; Oscar, H.G. Consumers acceptance of artificially intelligent (AI) device use in service delivery. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2019, 49, 157–169. [Google Scholar]
- Jina, K.; Soyeon, S. Can AI be a content generator? Effects of content generators and information delivery methods on the psychology of content consumers. Telemat. Inform. 2020, 55, 101452. [Google Scholar]
- Lidija, L.; Christian, W. Consumers’ reasons and perceived value co-creation of using artificial intelligence-enabled travel service agents. J. Bus. Res. 2020, 129, 891–901. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, R.; Shams, R.; Rahman, M. Consumer trust and perceived risk for voice-controlled artificial intelligence: The case of Siri. J. Bus. Res. 2020, 131, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrabian, A.; Russell, J.A. An Approach to Environmental Psychology; MIT Press: Cambridge, UK, 1974; pp. 62–65. [Google Scholar]
- Donovan, R.J.; Rossiter, J.R. Store atmosphere: An environmental psychology approach. J. Retail. 1982, 58, 34–57. [Google Scholar]
- Eroglu, S.A.; Machleit, K.A.; Davis, L.M. Atmospheric qualities of online retailing—A conceptual model and implications. J. Bus. Res. 2001, 54, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroglu, S.A.; Machleit, K.A.; Davis, L.M. Empirical testing of a model of online store atmospherics and shopper responses. Psychol. Mark. 2003, 20, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L. Effects of Online Store Atmosphere on Consumer Purchase Intention; Chongqing University: Chongqing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Floh, A.; Madlberger, M. The role of atmospheric cues in online impulse-buying behavior. Electron. Commer. Res. Appl. 2013, 12, 425–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo-Romero, C.; Alarcón-del-Amo, M.D.; Gómez-Borja, M.Á. Analyzing the user behavior toward electronic commerce stimuli. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanjeev, P.T.S.V.; Chandan, P. Effects of online shopping values and website cues on purchase behavior: A study using S–O–R framework. J. Decis. Mak. 2017, 42, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P. Research on the influence mechanism of online return policy looseness on consumers’ purchase intention based on S-O-R theory. Consum. Econ. 2017, 1, 85–91. [Google Scholar]
- Fikri, A.; Nurmalina, R.; Najib, M. The determinants of online vegetables/fruits repurchase intention: Stimulus-organism-response model and theory of planned behaviour. Eur. Sci. J. 2019, 15, 147–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yun, Z.S.; Good, L.K. Developing customer loyalty from e-tail store image attributes. J. Serv. Theory Pract. 2007, 17, 4–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Zhao, H. B2C online store image, consumer perception and purchase behavior. Res. Financ. Econ. Issues 2013, 10, 116–122. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, X.; Lai, V.S. E-loyalty to Online Auction Websites: A Stimulus-Organism-Response Model. Ph.D. Thesis, Hong Kong Shue Yan University, Hong Kong, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gloria, E.; Ichalkaranje, N.; Lakhmi, C. Intelligent Decision Making: An AI-Based Approach, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Lv, W.; Zhang, J. Marketing research of AI: Prospect and challenges. J. Manag. Sci. 2019, 32, 75–86. [Google Scholar]
- Kunar, V.; Raian, B.; Aian, B.; Venkatesan, V.; Lecinski, J. Understanding the Role of Artificial Intelligence in Personalized Engagement Marketing. Calif. Manag. Rev. 2019, 8, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Jordan, M.I.; Ordan, M.I.; Mitchell, T.M. Machine learning: Trends, perspectives, and prospects. Science 2015, 349, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, M.; Xu, Z. A study of dynamic recognition of consumer brand decision-making preference based on machine learning method. Nankai Bus. Rev. 2019, 22, 66–76. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Z.; Xu, G. Artificial Intelligent and Application; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 1996; pp. 45–62. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Jia, J. Big data marketing: Review and prospect. Syst. Eng. Theory Pract. 2020, 40, 2150–2158. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.H.; Rust, R.T. A strategic framework for artificial intelligence in marketing. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2020, 8, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, T.S.; Wedel, M.; Rust, R.T. Adaptive personalization using social networks. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2016, 44, 66–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Feng, L. Consumers’ demand for dual values and retail marketing innovation from new economic sociology perspective. J. Beijing Technol. Bus. Univ. Soc. Sci. 2019, 34, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Tian, F.; Yi, D.U.; Liu, Z.; Dai, G. Thoughts on humancomputer interaction in the age of artificial intelligence. Sci. Sin. Inf. 2018, 48, 361–375. [Google Scholar]
- Zeithaml, V.A. Consumer perceptions of price, quality, and value: A means-end model and synthesis of evidence. Mark 1988, 52, 2–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodruff, R.B. Customer value: The next source for competitive advantage. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 1997, 25, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirdeshmukh, D.; Singh, J.; Sabol, B. Consumer trust, value and loyalty in relational exchanges. J. Mark. 2002, 66, 15–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overby, J.W.; Lee, E.J. The effects of utilitarian and hedonic online shopping value on consumer preference and intentions. J. Bus. Res. 2006, 59, 1150–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holbrook, M.B. Consumer Value: A Framework for Analysis and Research, 1st ed.; Psychology Press: London, UK, 1999; pp. 29–45. [Google Scholar]
- Fazal-e-hasan, S.M.; Ahmadi, H.; Mortimer, G.; Grimmer, M.; Kelly, L. Examining the role of consumer hope in explaining the impact of perceived brand value on customer-brand relationship outcomes in an online retailing environment. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2018, 41, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Q.; Dixit, A.; Friedmann, R.; Riedmann, R. Customer loyalty and lifetime value: An empirical investigation of consumer packaged goods. J. Mark. Theory Pract. 2010, 18, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, J.C.; Soutar, G.N. Consumer perceived value: The development of a multiple item scale. J. Retail. 2001, 77, 203–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, F.D.; Bagozzi, R.P.; Warshaw, P.R. User acceptance of computer technology: A comparison of two theoretical models. Manag. Sci. 1989, 35, 982–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, F.D. User acceptance of information technology: System characteristics, user perceptions and behavioral impacts. Int. J. Man Mach. Stud. 1993, 38, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.W.; Kim, Y.G. Extending the TAM for a world-wide-web context. Inf. Manag. 2001, 38, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.L.; Lin, C.L. Why do people stick to Facebook web site? A value theory-based view. Inf. Technol. People 2014, 27, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, T. A Study on Selection Intention of Consumers’ Online Shopping Channel Based on SOR Theory: Official Websites and Third Party Flagship Stores as Examples; Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, S.J.; Lee, S.H. The Effect of Consumers’ Perceived Value on Acceptance of an Internet-Only Bank Service. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astawa, I.G.N.M.W.; Sukawati, T.G.R.S. The role of perceived value mediate the effect of utilitarian and hedonic shopping value on intent to online repurchase. Int. J. Manag. Commer. Innov. 2019, 6, 1232–1242. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg, D. How marketers can start integrating AI in their work. Harv. Bus. Rev. Digit. Articals 2018, 5, 2–5. [Google Scholar]
- Jan, K.; Jeannette, P.; Emily, T. Artificial intelligence in advertising. J. Advert. Res. 2018, 9, 263–267. [Google Scholar]
- Aakash, S.; Panchal, N. Object detection using deep learning and artificial intelligence in E-Commerce. IRE J. 2019, 2, 37–40. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Sun, B. Machine learning and AI in marketing—Connecting computing power to human insights. Int. J. Res. Mark. 2020, 37, 481–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. The mediating effect of perceived value between product information push and consumer purchase behavior—Multiple intermediary analysis based on bootstrap method. Mod. Bus. 2019, 9, 41–43. [Google Scholar]
- Guerra, A. Millennial Consumption Values in Artificial Intelligence: An Exploratory Study of Millennial Consumer Values in Artificial Intelligence; Jönköping University: Jönköping, Sweden, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Batra, R.; Ahtola, O.T. Measuring the hedonic and utilitarian sources of consumer attitudes. Mark. Lett. 1990, 2, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.Y.; Wang, Q.; Yan, L.G. Are consumers what they consume? Linking lifestyle segmentation to product attributes: An exploratory study of the Chinese mobile phone market. J. Mark. Manag. 2009, 25, 295–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhang, X.G.; Wang, F. Impact of attributes inconsistency of online review on product sales. East China Econ. Manag. 2015, 29, 147–153. [Google Scholar]
- Fiore, A.M.; Kim, J. An intergrative framework capturing experiential and utilitarian shopping experience. Int. J. Retail Distrib. Manag. 2013, 35, 421–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Kui, W.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, C. Consumer shopping experience research based on artificial intelligence. Mod. Inf. Technol. 2019, 3, 153–155. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.; Zhao, H.; Meng, L. Research on online interaction and impulsive buying behavior of B2C online shopping. Inq. Econ. Issues 2014, 5, 64–73. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, C.; Song, C. User needs, algorithm recommendation and scene matching: Theoretical logic and practical thinking of intelligent advertising. Mod. Commun. 2020, 42, 119–128. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhang, X. People-oriented: Personalized Recommendations in the Era of Artificial Intelligence. J. Suibe 2020, 27, 90–99. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, N.; Wang, J. Research on consumer online purchase channel selection based on perceived value. Chin. J. Manag. 2019, 16, 1542–1551. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).