Abstract
The rapid economic growth of Saudi cities after the discovery of oil in 1960 had some disadvantages, the most significant of which was the rapid search for alternatives to urban development and the acceleration of urban growth in its major cities and villages. That contributed to the implementation of certain planning policies based on the heavy use of large-scale vehicles. These policies have been instrumental in increasing horizontal expansion, which has been linked to the increased need to rely on cars as a means of movement and not to adopt public transport such as metro and railways. In this research, one of the main cities in the Asir region, which is the administrative capital of Abha, which has been evaluated and analyzed. Space syntax is an informative theory that stands on the structure of urban graphs. Utilizing syntactic analysis, the impact of highways and arterial roads on the integration and connectivity orientation in the urban structure of the city is analyzed, and the constraints and opportunities for development in the building use map are identified. Resulting in isolated parts of districts with no pedestrian routes to connect them, this methodology allows us to determine the main points in the structure of the city where pedestrian accessibility can be added in order to provide the remedy to overcome the shortage in the city’s network system (i.e., crossovers, tunnels, etc.). In addition, the impact on the human dimension of the living community, the diversity of land use, and real estate financial classifications were discussed, while the principles of sustainable planning were used to enhance the integration of walkability in the built environment, which was the goal of this study.
1. Introduction
Urban movements of people, and those facilitated by cars, may play a vital role in the heritage planning of historic cities. Several issues relating to people’s movements in historic cities require a careful response that takes into account heritage, architecture, and urban planning and development. Such concerns must take into account the security of heritage resources, people’s vulnerability and the possibility of threats, the need for reappropriation, and the need to address or accommodate people in public spaces.
Traditionally, the spatial distribution of land use/land cover and socio-economic activity in an urban environment has been studied from various perspectives and scales. The spatial patterns of economic activity within the city’s spatial framework and its relative position highlight using classic city models, for example, concentric zones proposed by Burgess [1], sectors by Hoyt [2] and Alonzo’s model [3], as well as more recent models including those by Kropf [4] and Rotem-Mindali [5]. Moreover, if economic activity is analyzed at a higher level—at street level—the layout of the street network plays a vital role. From this perspective, in different cities, the association between economic activity and the configuration of the urban street network was addressed, including Berlin [6], Seoul [7], the Rijnland region, the Netherlands [8], Mexico City [9], Bologna [10], Shanghai [11], Baton Rouge, Louisiana [12], London [13], Bandung City, Indonesia [14], Barcelona [15], Chennai [16], Changchun, China [17], Buenos Aires [18] and China [19]. These studies, however, mainly explored urban areas where land-use patterns have been built through interaction with street networks, mostly in cities with a deformed grid-like street layout or a proposed perfect grid, such as in the cases of Mexico City [9] and Barcelona [15]. Although the complexity of cities is commonly accepted, many Middle Eastern cities seem to be more complicated than other cities due to their particular paths of emergence and growth.
If, as many have suggested, movement and its connections with space are necessary for cities in general, then these must be even more important for living historic and tourist cities. Although the densities of the movement of people and cars in these cities’ streets may be good indicators of liveliness and vitality, high-density movements that defy the traditional social logic of space can possibily harm the physical and social environments of these cities, thus forcing the traditional inhabitants of these cities to move elsewhere. Once they migrate out, the buildings they leave behind can be taken over by commercial activity, poor people or people with little knowledge of the traditional aspect of these cities.
In addition to the above, the environmental impacts of the excessive movements of cars and people may also harm cities. Among these, air quality is a big concern in developing countries, where less attention is given for the solutions that will reduce the risk of air pollution [20]. As a result, the health conditions of those who live in old cities are at serious risk [21]. Furthermore, excessive movement of cars and people in old cities may also increase moisture content, air temperature, acid rain, and air pollution. The effect of such environmental pollution, especially acid rain, is that it deteriorates buildings’ materials, affecting the historic structure as a result [22].
Space syntax theory and methods have long been used with a significant historical component in a wide variety of research. The theoretical framework for the techniques and measurements of space syntax were first given in The Social Logic of Space by Hillier and Hanson [23], and later expanded by Hillier [24] in Space is the Machine, as well as in several other papers that followed [25,26]. Among the various space syntax techniques, linear map analysis, visibility graph analysis and, convex map analysis are just a few. Such techniques have been applied to the configurations of city districts, neighborhoods, and even individual buildings to research how centrality and accessibility (visual, physical, or both) of spatial design affect measurable phenomena as diverse as pedestrian and vehicular movements, crime, wayfinding, urban liveliness, walkability and pollution. These were also used to define the organization of objects, people and functions that illustrate the social and cultural meaning of space. However, spatial syntax studies on urban areas and cities generally use linear map analysis techniques that include an axial map analysis and a more recent segment map analysis [25]. Both of these analyses include the representation of the urban configuration as a linear map, a network of the fewest number of lines required to cover each street and complete each layout circulation ring. In space syntax, therefore, a linear map is more commonly known as an axial map.
Space syntax is becoming a key method to study the relationship between space, spatial structures and human behaviour in the areas of urban geography, built environment and the stunning scenery of mountainous spots [24,27,28], specifically in the case of small areas. In the field of tourism, analysis of Abha city found that the distribution of natural habitat and unique socio-cultural aspect of Saudi Arabia was significantly correlated with the highways and arterial roads on urban growth and sustainable development. By interaction with local people and observing the spatial behaviour of the number of tourist spots (i.e., Al-Souda, Habalah, etc.), it was concluded that the decision to visit a location was significantly dependent on the spatial configuration of street networks. Furthermore, the spatial occupations of attractions affect human spatial behaviour, and various environmental elements have various effects on tourist behaviour [29].
Spatial configurations of street networks for the vehicle and pedestrian are often associated with crime, safety, and wayfinding. The lack of connectivity can describe it. Planners should pay more attention and reconsider issues such as walkability, sense of place and sustainability with the existing and new developments to achieve the desired outcomes of reducing crime and of enhancing walkability, livability and, eventually, the sustainability and well-being of isolated districts in particular to achieve the spatial logic of street networks [23]. Sustainability issues can be dealt with in different ways in urban developments. In general, research has shown a gap between economic and environmental goals in the early emphasis on sustainable development [30,31,32]. Societies should balance social, economic and environmental objectives in order to ease the transition to more sustainable development [33]. Sustainable development also involves the safety of physical environments [34]. In recent years, studies focused on steps to reduce crime opportunities and disadvantages which is expected to produce more immediate results. Bindajam [35] studied the use of spatial syntax theories and techniques to explore the effects of spatial and temporal factors on movement densities in the old and new parts of the historic cores of Riyadh (Old City) in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Street configuration and types and street-level building functions are the spatial factors included in the analysis, and the temporal factors are weekdays and weekends. The study reported that, in general, movement densities were lower in the older areas than in the newer areas of the Old City, and that street life was vibrant on both weekdays and weekends. People in the newer areas of the Old City walked less on major streets with more cars, but they did not wholly abandon these streets, and the movement densities of the Old City were associated with street configuration
2. Case Study
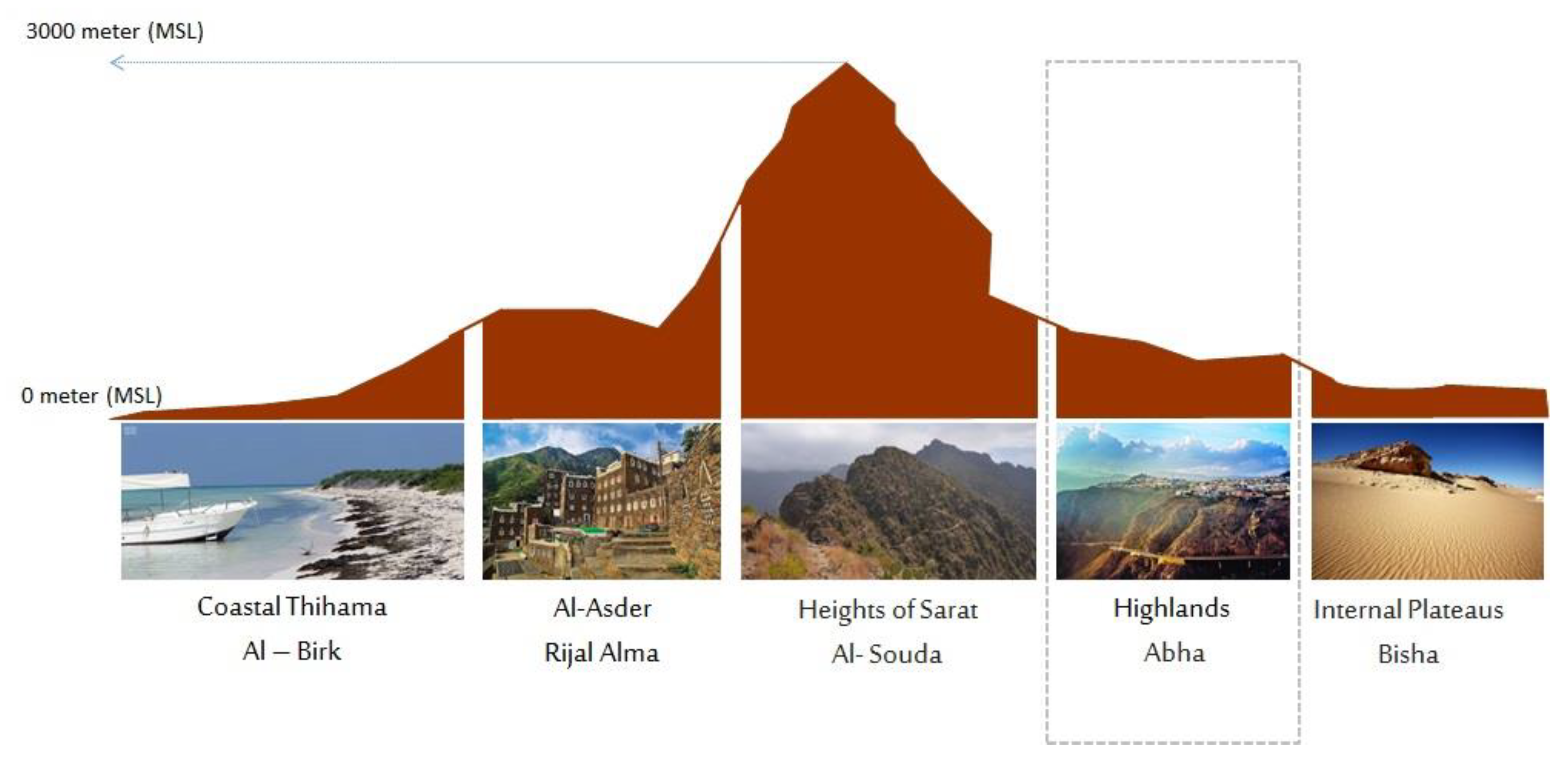
The city of Abha is located in the Asir region in the south-western part of Saudi Arabia. It is located within an important Afromontane region, where cold and semi-arid climatic conditions characterize the city climate. The average minimum and maximum temperatures are 19.3 °C and 29.70 °C, respectively. The elevation varies from 2000 to 2200 meters, with an average of 2107 meters. The Asir region section profile is shown in Figure 1.
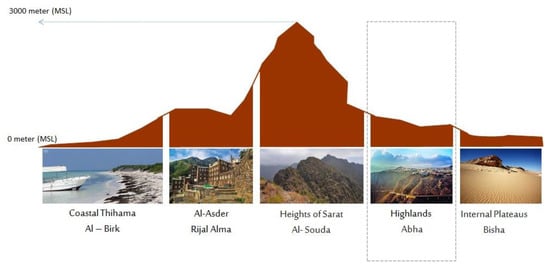
Figure 1.
Asir province section.
Historians have mentioned that Abha is 600 years old, called "Haifa" or "Eva", and it was one of the largest cities in the state of Saba. According to Mahmoud Shaker, in his book The Arabian Peninsula, Abha is a town not known in history but known as the valley of Abha, which was known later, and perhaps came from the name Baha, which means the qualities of beauty and prettiness. In the past, villages were scattered along the valley of Abha [36]. Currently, it is the administrative capital of the Asir region. According to the 2012 census carried out by the General Authority for Statistics, 289,975 people live there, 78% of whom are Saudis. It is stated in the history archives that it was not mentioned as an independent region from Hijaz, Yemen, and Bahrain until the beginning of the fourth century AH, as al-Hamdani mentioned in his book The Characteristics of the Arabian Peninsula [37].
The city of Abha was a single district called “manazer” and then other districts, such as moftahaeh, elqaree, al-rabou ’, al-khshe and qabal. At this point, there are more than fifty neighborhoods. The city center is the oldest area in the city and has historical elements with historical, political and economic importance.
In 1834, Abha was exposed to the greatest nineteenth-century invasion campaign entered by Muhammad Ali Pasha’s forces, and taken from the manazer district, the city’s largest neighborhood and perhaps the oldest meeting place and headquarters for its leadership and troops. In the moftahaeh district, which contained the Emirates palace designed by Ali bin Mgthel, Ayed bin Mari was ordered to burn the district before ordering the evacuation of his population’s town, as the prince chose to burn the palace as a hotbed of the invading forces. After the Ottoman withdrawal in 1918, the principal of Abha Mohieddin Pasha handed over the reins of power in Asir to the grandson Hassan bin Ali bin Ayed, who for several years had served as the ruler. Hassan’s rule lasted for less than a year. In 1919, Abha joined the Grand National Unity under the leadership of King Abdulaziz bin Abdul Rahman Al Saud [38].
A Background of the Urban Fabric Growth on the Case Study of the City of Abha
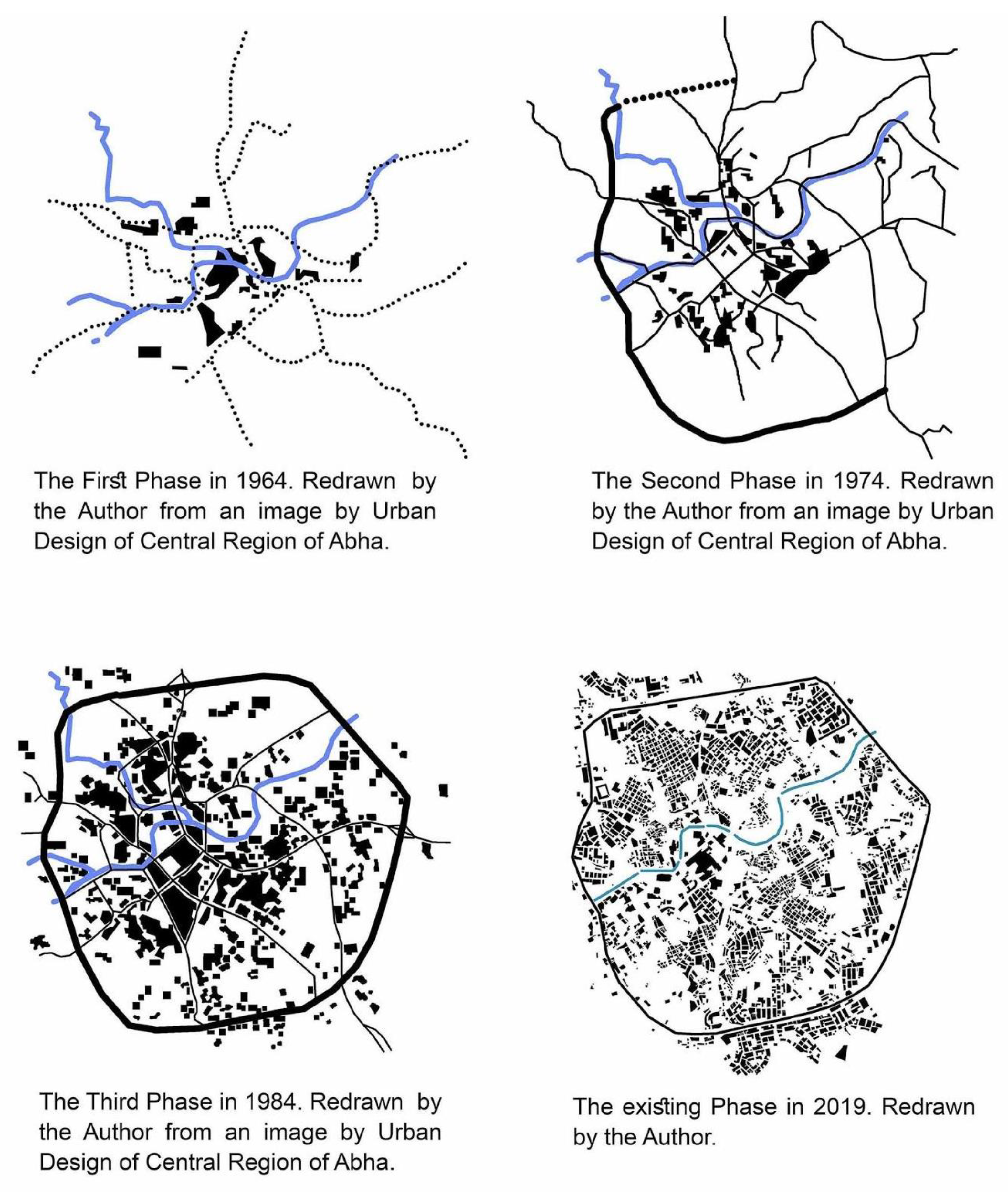
Since the early 1960s, the city of Abha has grown, and its main hubs have been defined and connected to several axes such as Abha-Al-Khamis road, Taif, Jizan through Aqaba dilae, and other roads connecting the city to the rest of the Asir villages such as Al-Souda and Rijal al Hajar villages. By the early 1970s, the beginning of the ring road or what is called the "belt" was half completed and serves as a barrier and a buffer zone for the urban development expansion out of the city, in addition to the geographical, topographic nature and privately owned properties.
At the beginning of the 1980s, the ring road began to enter the stage of maturity and completion of its full features and became wrapped around the entire city (Figure 2). It was linked to the main axes that connected it to the other the cities and provinces in the region. Since then, the city has grown outside the ring road and has formed a phase of near-saturation in its urban fabric. As mentioned earlier, the Valley of Abha, which is considered to be one of the most important axes in the formation of the city and worked as a delimiter, separates the north of the city from the south, and some axes have been linked by bridges to connect the two parts of the city. In addition, the nature of the city, which contains many topographical levels in all of its parts, eventually acted as a factor to guide the urban growth compass in the city. Therefore, some policies have been taken to redraw the urban growth, which was not accompanied by the redistribution and stimulation of the population in the most dense and connected places. Some of these policies include the redirection of some of the roads to be one-way, the expansion of some of the roads and increasing the number of pathways. Here, converting some roads and turning them into pedestrian paths will reduce the vehicles numbers.
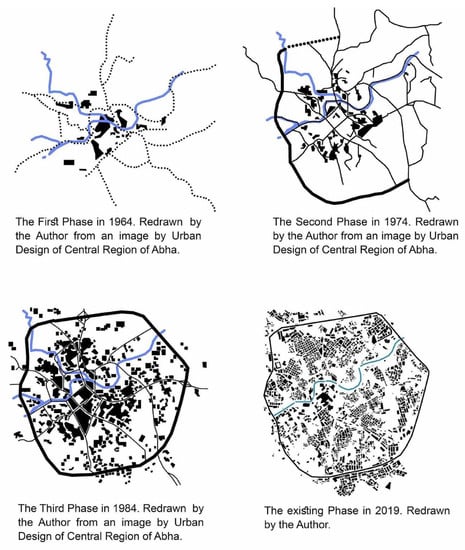
Figure 2.
Maps showing the urban growth of the City of Abha (Redrawn by the Author).
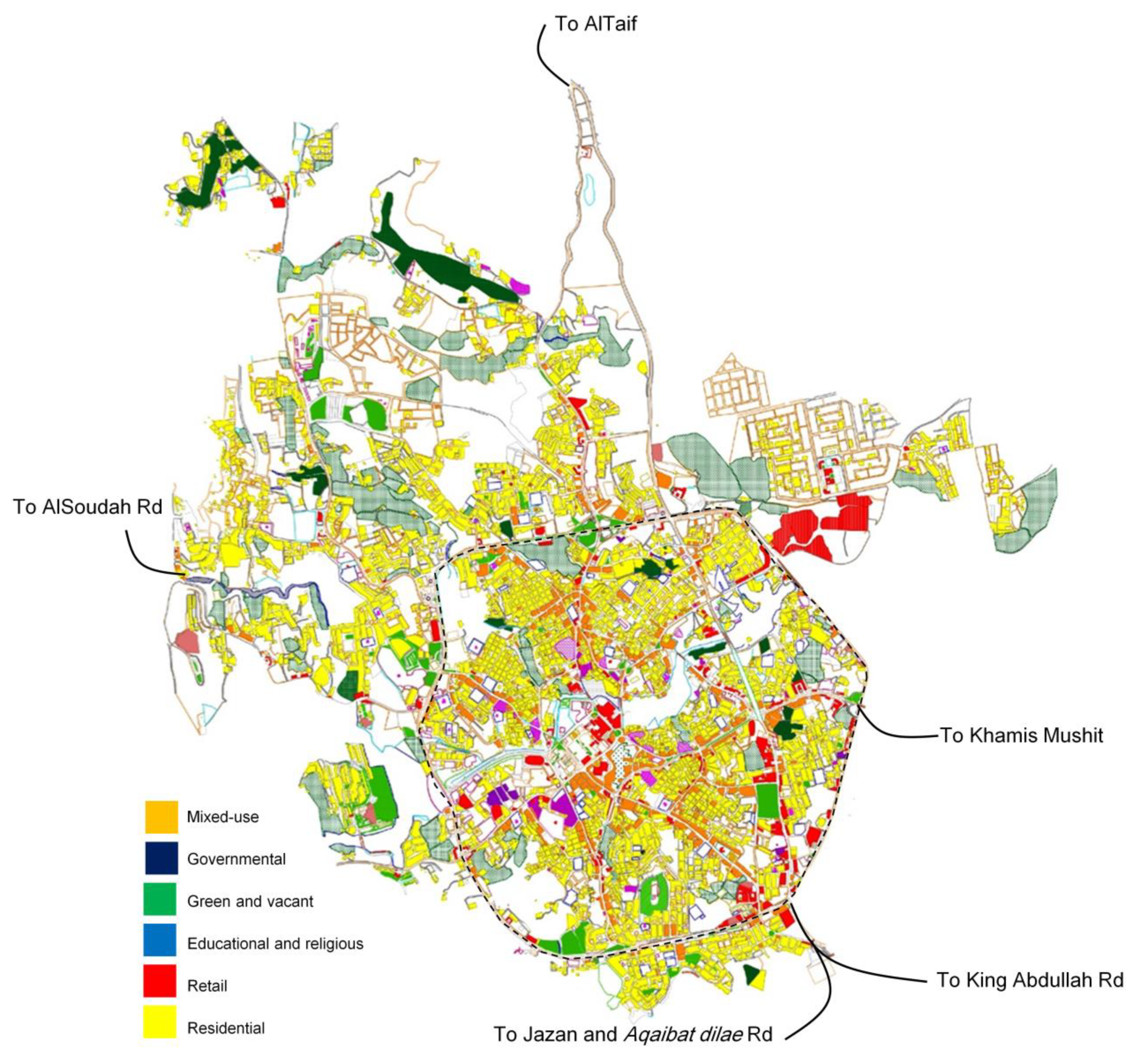
As stated earlier, the Valley of Abha, which is considered one of the most important axes in the development of the city and served as a delimiter, divides the north of the city from the south, and bridges connect the two parts of the city with certain axes. In addition, the nature of the city, which includes many topographical levels in all its parts (Figure 3), eventually led to urban growth in the city. Many initiatives have therefore been introduced to redefine urban growth, which has not been followed by population relocation and enhancement in the densest and most associated regions. Some of these policies, include the redirection of some of the roads to make them one-way, the expansion of some of the roads and increasing the number of pathways. Here, converting some roads and turning them into pedestrian paths will reduce vehicle numbers.
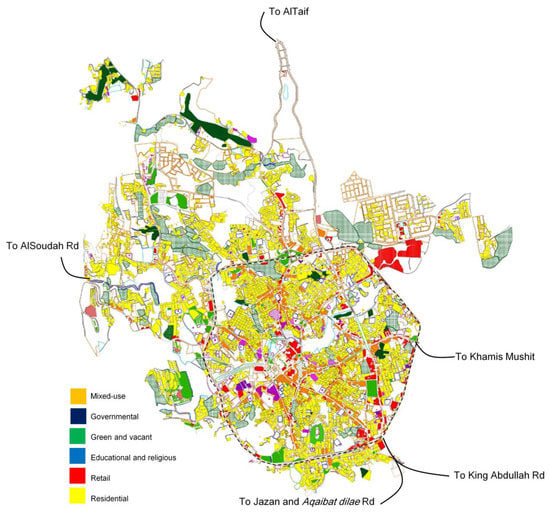
Figure 3.
A map showing building use in the City of Abha.
Mountain landscape attractions are the main attracting factors for tourists. The city of Abha expects a significant transformation development which is a mega project funded by the PIF (Public Investment Fund) in its downtown area and along Abha Valley. Moreover, the need for addressing a sustainable development understanding that will increase the quality of life for its residents and visitors is a must. The hypothesis is that the connectivity at the local scale will be higher over the whole city, while the lack of the connectivity will create segregated areas that will impact the quality of life in the small communities and will severely impact the mode of transportation for residents and visitors, which will lead to the use of more cars as the mode of commute between the downtown area and the rest of the city. This will increase the concern of raising the temperature and impact on the environment, causing an urban heat island in the city.
Hardly any research has examined the spatial patterns and tourist behaviour of scenic mountain areas and the effect of streets networks on the integration and connectivity orientation on urban growth and sustainable development. In this research, one of the main cities in the Asir region, which is the administrative capital of Abha, has been evaluated and analyzed for the impact of highways and arterial roads on the integration and connectivity orientation in the urban structure of the city, and the constraints and opportunities for development in the building use map are identified. This approach helps to evaluate the main points in the city layout where pedestrian mobility can be introduced so as to provide the solution for overcoming the shortage in the network system of the city (i.e., bridges, tunnels, etc.). The remainder of the paper is structured as follows. The following section offers a brief review of the syntax of space. The third section deals with the spatial analysis of Abha city. The fourth section presents results and discussion, and conclusions are presented to provide a better understanding of the impact on the human dimension of the living community, the diversity of land use and the principles of sustainable planning, pointing to enhancing the integration of walkability in the built environment, which was the goal of this study.
3. Methods
3.1. Space Syntax Theory
Space syntax theory is proposed as a computational methodology to describe the urban and spatial configuration. The theory relies on the assumption that urban structure or spatial configuration significantly affect human social interaction. Space syntax studies on urban areas and cities, however, generally use the techniques of linear map analyses that include the axial map analysis and the more recent segment map analysis [25]. Both these analyses involve representing the urban layout as a linear map, which is a network of the fewest number of lines needed to cover every street and complete every circulation ring of the layout. So defined, a linear map is more commonly known as an axial map in space syntax. In earlier times, the linear map of a layout was always drawn manually. Currently, software programs are available that automatically generate the linear map of a layout. When needed, breaking the lines of a linear map into segments at their intersections can generate a segment map. In the next stage of analysis, software programs use different centrality measures to describe the patterns of connections, differentiation, and centrality of the axial map and the axial lines, or of the segment maps and the segments. Finally, correlations between any observed phenomena along the axial lines or the segments and the centrality measures of the lines or their segments are studied to explain the effects of spatial patterns on these phenomena
The city typically has several interconnected components; physical components are "the physical city", indicating every material artefact that we create, use and signify in the city; and the city of human components, which is "the functional city" that defines how we communicate, for instrumental and symbolic purposes, with the surrounding physical city [24]. There is a dialectical relationship between the physical city and the interactive city. Then, from the practical actions and activities of people in it, the actual community emerges. Once it has appeared, it affects people’s behaviours and activities that have created it, creating the conditions for the physical city to change in circular connection, the dialectical process includes external representations that exist in physical cities, and internal representations in the form of intentions, ideas, recollections and thoughts that initiate and reside in individual human players and are a form of history, tradition and culture in institutions. The networks of spaces, forms and functionalities are multifaceted. The conclusion can be drawn from the physical city that its people and its institutional agents are also complex [39].
Although spatial syntax studies physical domain networks as described in urban environment plans, structural sociology studies social networks. Similarly, spatial networks research can be focused on their enclosures, partitions, overlapping, cross-sections, adjacencies and permeabilities in various spatial network configurations, which are typically included in spatial syntax studies [40].
3.1.1. Spatial Configuration
In space syntax theory, the spatial configuration is often used to imitate the fact that a network of spaces is a network which describes the relationship of the space components among each other, while it represents all possibilities of how spatial units are linked with each other. Likewise, a weighted relationship configuration can be made more exact by configuring the unwieldy relationships of the spatial components of a specific layout. The design created through the use of lines and segments can be useful because humans tend to move along straight lines and routes with few adjustments to minimize effort and time and to increase cost-effectiveness. Space syntax also assumes a different configuration for analytical purposes for the spatial network of an urban environment, but such configurations are present within social reality.
“All these ways of looking at space can be seen as layers of spatial structuring, co-existing within the same plan, each with its own contribution to intelligibility and function.” [24].
The scale of historical centers has been found in past research examining the growth of urban syntax centres in the Middle East. An analysis of the current literature found several studies addressing numerous issues such as socio-economic impacts, specialization, densities of travel and contemporary planning implications [41,42]. Space syntax examines these frameworks through methods and techniques which have been developed using modern math and powerful computers. The space syntax can be successfully identified, analyzed, and visualized in different scales by various configurations of the space networks of the physical city and how different configurations are related, as well as with individuals and society, by daily movement [43].
3.1.2. Axial and Segment Maps
Space syntax uses configurations of the first perception, which can be defined as simple 2D space units in an urban setting. These units comprise axial lines that are defined as straight lines of motion and visibility, segments representing parts of axial lines that have split at points of intersection with other axial lines, each of which is visible from other points globally.
Urban space refers to the space formed from the contour of the blocks, in which people can move freely and randomly. Three styles of street model, based on the literature review, describe urban spaces, namely axial rows, axial segments and natural streets. The network of the city is organized into three representative forms [44]. For better identification, each unit of the street is defined by a unique colour. It is composed of a series of naturally linked street patterns for original street design.
The axial lines are created by adding the most extended possible visibility lines on the natural roads, and the axial segment is formed by cutting the axial lines into segments at each intersection. The corresponding line is divided into sections, represented by various colours, a specific colour represents the axial line. The original approach of space syntax [23] is the axial line representation of urban spaces. The axial lines are the shortest lines of visibility in small urban areas. Jiang and Claramunt [45] argued that an axial line is as wide as it can be viewed from a single point of view from the viewpoint of how people perceive the urban space. The theory of axial lines reflects the great urban space; however, not that of infinite spaces [45]. Analysis of the connection and integration of these small unit areas can improve understanding of the urban structure and somehow predict human social behaviour amongst spaces [46].
The maps of the axial and segments also allow the comparison of urban cities or action areas with various figural patterns and unbuilt spaces. The structure of the areas defined by adjacent constructed designs commonly found in traditional cities in order to describe such difference is from the solid structure, where constructions are found as objects on a plane [47]
3.2. Spatial Analysis for Abha City
For the analysis of the urban structure of the city, this paper used spatial syntax theory and code depth map to generate the information required. It started by drawing the building plots all over the city and placing them in closed polygons. Additionally, this research aimed to identify the axial lines that represent roads and open spaces using better tools, so that they were automatically generated and reduced to the fewest possible numbers to represent the urban spaces instead of drawing the axial lines manually. Therefore, for better results, the generated map was converted into a segment map.
In order to determine the undisclosed possibilities and opportunities of the main plan, the research anticipated using the advantage of the syntactical analyzing. As discussed earlier, it is important to develop an axial map representing the street grid and the municipal grid as an essential step in the analysis of the spatial configuration needs [48]. All axial lines were of value in terms of their location and connection to the entire urban network [49]. In order to evaluate the map at the local and global context, the analysis was carried out on an analytical map. The study used a spectrum of radius from 1200 m to n. The weight of the segment longitude, as well as a broad spectrum of street lengths, were analyzed.
Abha City is a newly developed area, so the incremental hierarchy of roads was clearly addressed, reflecting connectivity for vehicles and pedestrians in the town. A radius of (n), which is the global analysis [50], was chosen in order to analyze the entire urban structure. The segments of the street strongly selected as the shortest route were selected. The map produced was for a critical angular path choice concerning the weight of the angular connection. This research took the angular segment analyses to achieve measurements of multiple radius (integration and choice). This was done to show inaccurate results on different design scales in various measurements [51].
4. Results and Discussion
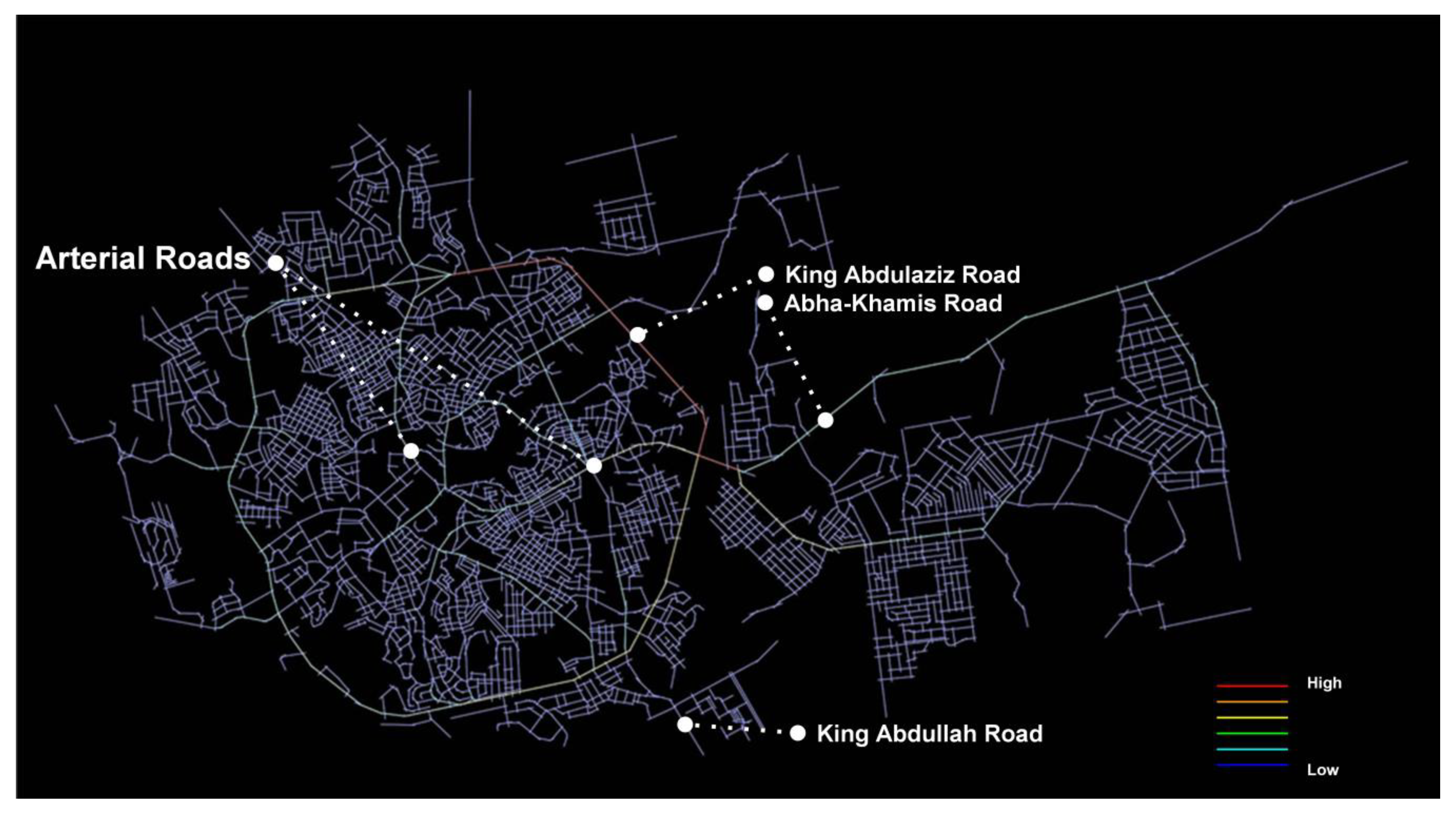
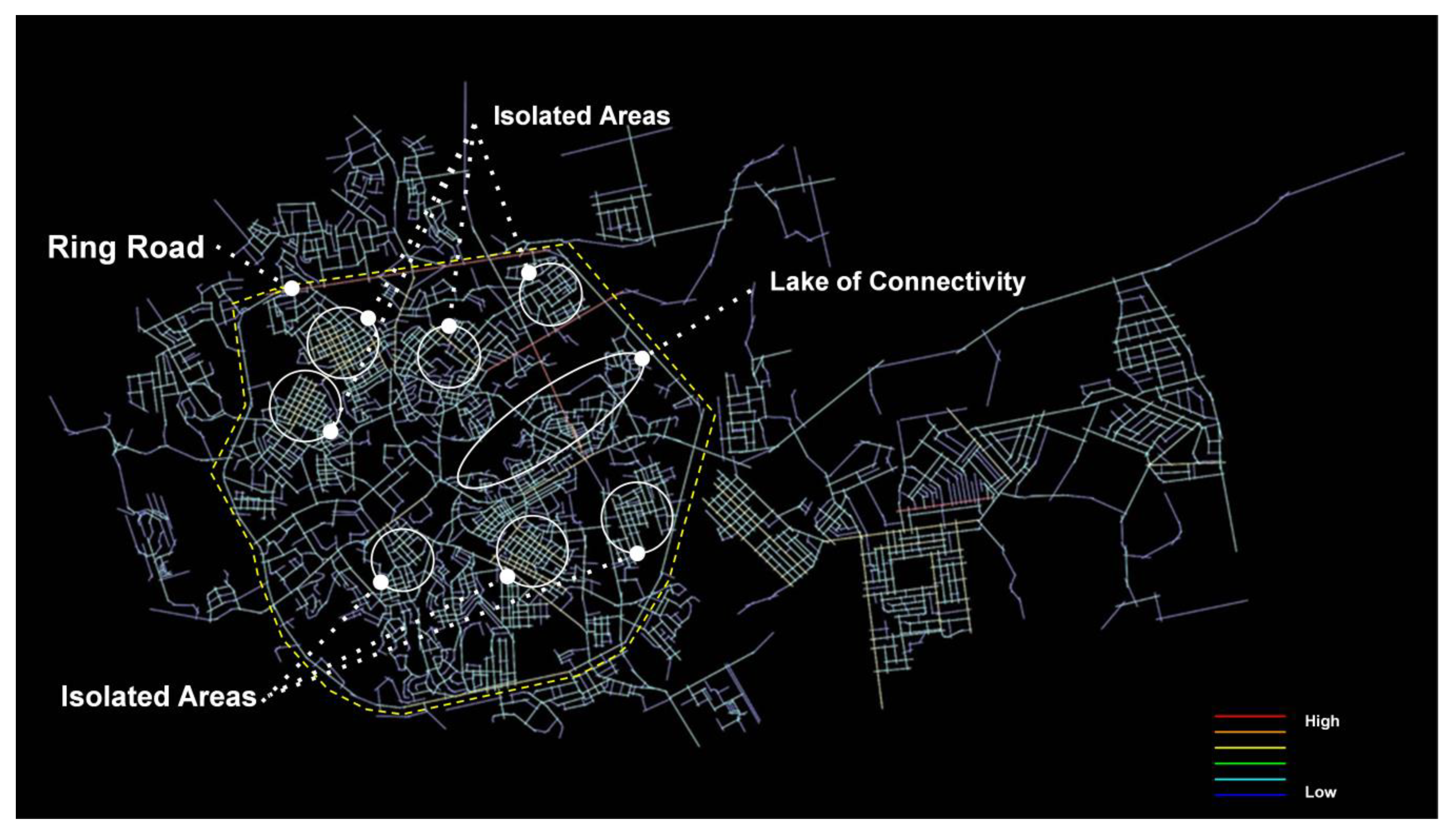
In Figure 4, the map shows that “King Abdulaziz Road” and “Abha-Khamis Road” are the highest choice values as main artery roads. Consequently, other artery roads represent the separation barrier between different residential districts and neighbourhoods (dividing the city into small segregated zones). This configuration articulates the hierarchical structure that shapes the city’s urban grid and shapes the movement patterns of the vehicle and pedestrian alike. The angular analysis clearly shows the network hierarchy system on a global scale. Furthermore, the main artery roads are the dominant choice for high movement potential in the city’s system; it could be concluded that those roads are the significant method of connectivity through the city and this represents an imbalance, as it is a minor road to hold the whole city connections. On the other hand, these roads are working as a barrier between different residential districts rather than connectors.
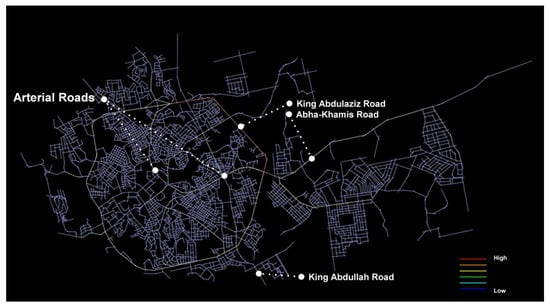
Figure 4.
Angular Segment Analysis_T1024 Choice_Rn (Global), (Generated using Depthmap).
On the other hand, Figure 5 shows that the total angular connectivity with a radius of 1200 m, which indicates to local-scale connectivity in districts and neighbourhoods. It is clear that there is significant connectivity on a local community scale, for example in the districts in the north and the districts in the south. It shows a good range of connectivity scale in the neighbourhoods and districts. However, it is hard to find that connection throughout the whole city, although the isolation of each district on its own is obvious. It also represents the hard connection between each district, especially the northern wing and the south. The same type of connectivity in the districts needs to be repeated in the whole city, and especially in the core city centre along Abha valley.
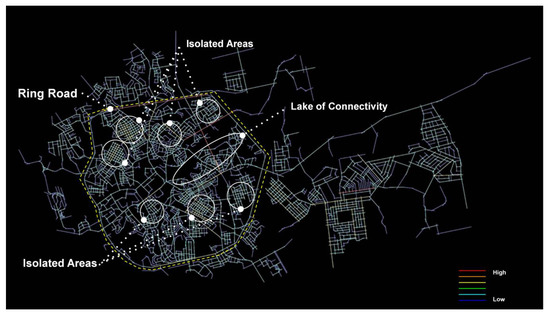
Figure 5.
Angular Segment Analysis_T1024 Choice_R1200, (Generated using Depthmap).
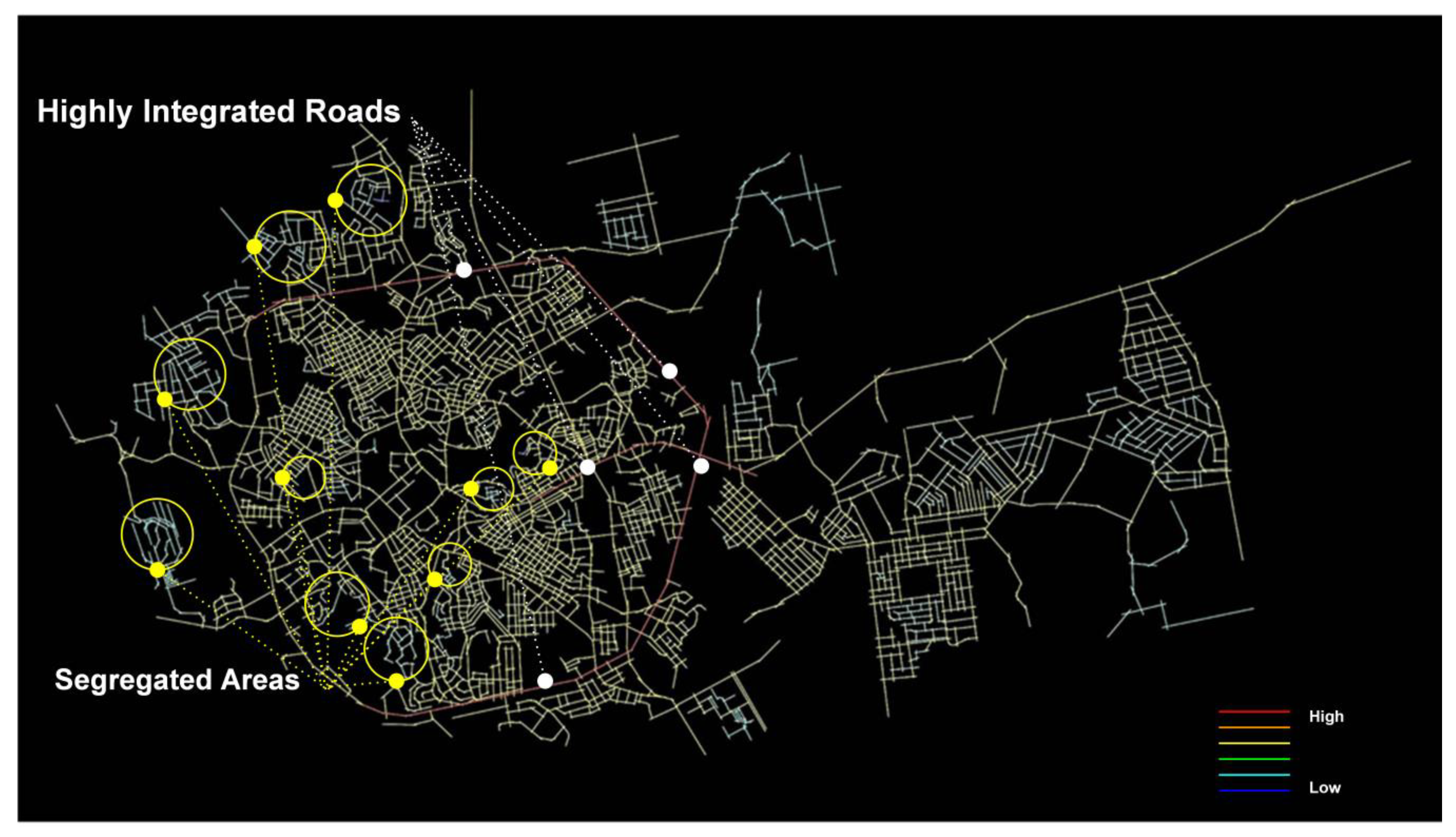
In Figure 6, an integration map is generated for the city on a global scale (n). The integration analysis is a measurement from any space of origin to the whole system. It shows that the city is committed to the gradual hierarchy of roads—artery roads have the highest values, while the local ones are segregated. It could be concluded that the highly integrated roads have been acting more like a destination than as through routes. The ring road (King Abdulaziz Rd) represents the main attractor in the whole city network system. Meanwhile, the local streets have less potential to be through routes. This makes the districts located away from the ring road in segregated areas, with a poor connection not only to the spine but also to another district on the opposite side in the north of the ring road and the southern districts of Abha Valley, more isolated.
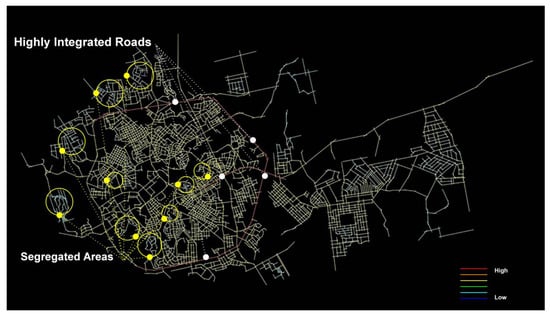
Figure 6.
Angular Segment Analysis_T1024_Integration_Rn (Global), (Generated using Depthmap).
The connectivity in the local scale is higher than in the core city centre along Abha valley as well as the whole city—the lack of the connectivity creates segregated areas that impact the quality of life in Abha’s communities and it has severely affected the mode of transportation for residents and visitors, resulting in more cars being used as a mode of transportation between the city center and the rest of the city. This effect demonstrates the difference between the street networks in the integration and connectivity orientation in the urban structure of the city and urban blocks or buildings [52]. That it may increase the concern about increasing the temperature and environmental impacts that cause an urban heat island in the city [53]. Moreover, the control value should receive more significant consideration in future research on mountain areas and streets networks, as visitors pay attention to tourist routes with consistency and numerous choices. Further research should take into account comparative analysis with other case studies involving urban thermal environments and also an analysis of the 3D space syntax or angular segment with a metric radius to take into consideration the deflection condition and distance factors [54]
5. Conclusions
Abha city is a decent example of a car-oriented city that respects the movement of vehicles over pedestrians. The analysis carried out showed through variant scales (global, local) that it is clear that connectivity on a local scale throughout the city is greatly interrupted by main artery roads that separate the city into isolated islands and make communication even more dangerous. Consequently, this study typically illustrates the adjustments and changes needed regarding these artery roads, particularly regardingincidents and connectivity over these severe barriers. Making wide roads does not lead to a beautiful cityscape or non-traffic problems. However, it causes more problems to fix and to adapt it into a human-scale city. The local planners need to consider the social, economical, sustainable and environmental (especially the urban heat island phenomenon) aspects while planning, in addition to using different urban tools and models that help to predict and articulate how things will be perceived in the future. This cannot be done by making streets wider or changing the direction of some major streets. New bridges and tunnels were added to “King Abdulaziz Road” as a way to overcome the significant negative effect of the lack of connectivity.
The results of this study also demonstrate the spatial pattern of human behaviour within a destination and provide operational advice for managers to reduce congestion and provide visual guidance to local communities and visitors to prepare their ideal route; these study implications enhance the existing literature and spatial configuration research in the urban tourism city structure.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.A.B.; methodology, A.A.B.; software, A.A.B.; formal analysis, A.A.B. and J.M.; writing—original draft preparation, A.A.B.; writing—review and editing, J.M.; project administration, A.A.B.; funding acquisition, A.A.B. and J.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Funding for this research was given under award numbers R.G.P2/92/41 by the Deanship of Scientific Research; King Khalid University, Ministry of Education, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
Acknowledgments
Authors thankfully acknowledge the Deanship of Scientific Research for proving administrative and financial supports.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Burgess, E.W. The growth of the city: An introduction to a research project. In The City; Park, R.E., Burgess, E.W., Mackenzie, R.D., Eds.; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1927; pp. 1–47. [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot, M.J.; Hoyt, H. The Structure and Growth of Residential Neighborhoods in American Cities; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1939.
- Alonso, W. Location and Land Use; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Kropf, K. Aspects of urban form. Urban Morphol. 2009, 13, 105. [Google Scholar]
- Rotem-Mindali, O. Retail fragmentation vs. urban livability: Applying ecological methods in urban geography research. Appl. Geogr. 2012, 35, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jake, D. The Relationship between Urban Street Configuration and Office Rent Patterns in Berlin. Ph.D. Thesis, University College London, London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.K.; Sohn, D.W. An analysis of the relationship between land use density of office buildings and urban street configuration: Case studies of two areas in Seoul by space syntax analysis. Cities 2002, 19, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nes, A. van Typology of shopping areas in Amsterdam. In Proceedings of the 5th International Space Syntax Symposium, Delft, The Netherlands, 13–17 June 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz-Chao, C.; Hillier, B. In search of patterns of land-use in Mexico City using logistic regression at the plot level. In Proceedings of the 6th International Space Syntax Symposium, Istanbul, Turkey, 12–15 June 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Porta, S.; Strano, E.; Iacoviello, V.; Messora, R.; Latora, V.; Cardillo, A.; Wang, F.; Scellato, S. Street centrality and densities of retail and services in Bologna, Italy. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 2009, 36, 450–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Jianhua, X.; Shen, Q.; Yang, Y. A research on urban spatial morphology and land use type based on space syntax: A case study on Lujiazui functional area Urban Geography 19 Downloaded by [University of California, San Diego] at 06:34 08 March 2016 of Shanghai. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Computer Engineering and Technology, Chengdu, China, 16–19 April 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Antipova, A.; Porta, S. Street centrality and land use intensity in Baton Rouge, Louisiana. J. Transp. Geogr. 2011, 19, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, L.; Jones, C.; Griffiths, S.; Haklay, M. The spatial signature of suburban town centres. J. Sp. Syntax 2010, 1, 77–91. [Google Scholar]
- Soesanti, S.; Nakai, N. Street network in Bandung city, Indonesia: Comparison between city center and new commercial area. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2010, 42, 1104–1114. [Google Scholar]
- Porta, S.; Latora, V.; Wang, F.; Rueda, S.; Strano, E.; Scellato, S.; Cardillo, A.; Belli, E.; Càrdenas, F.; Cormenzana, B.; et al. Street Centrality and the Location of Economic Activities in Barcelona. Urban Stud. 2012, 49, 1471–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srirangam, S.; Forsyth, W. Culture and Commerce of Chennai City—A spatial analysis of the relationship between temples and retail activity. In Proceedings of the 8th International Space Syntax Symposium, Santiago, Chile, 3–6 January 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Chen, C.; Xiu, C.; Zhang, P. Location analysis of retail stores in Changchun, China: A street centrality perspective. Cities 2014, 41, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scoppa, M.D.; Peponis, J. Distributed attraction: The effects of street network connectivity upon the distribution of retail frontage in the city of buenos aires. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 2015, 42, 354–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, J.; Wu, R.; Zhang, H. Spatial configuration and online attention: A space syntax perspective. Sustainability 2018, 10, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, V.; Parikh, K. The environmental consequences of urban growth: Crossnational perspectives on economic development, air pollution, and city size. Urban Geogr. 1992, 13, 422–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roorda-Knape, M.C.; Janssen, N.A.; De Hartog, J.J.; Van Vliet, P.H.; Harssema, H.; Brunekreef, B. Air pollution from traffic in city districts near major motorways. Atmos. Environ. 1998, 32, 1921–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanani, S.; Zandi, H. A study of the damages to historical monuments due to climatic factors and air pollution and offering solutions. WASET 2011, 56, 593–596. [Google Scholar]
- Hillier, B.; Hanson, J. The Social Logic of Space; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Hillier, B. Space Is the Machine; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Hillier, B. The art of place and the science of space. World Archit. 2005, 185, 96–102. [Google Scholar]
- Hillier, B. Space and spatiality: What the built environment needs from social theory. Build. Res. Inf. 2008, 36, 216–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bafna, S. Space Syntax A Brief Introduction to Its Logic and Analytical Techniques. Environ. Behav. 2003, 35, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Claramunt, C. Integration of Space Syntax into GIS: New Perspectives for Urban Morphology. Trans. Gis 2002, 6, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, A.; Wachowicz, M.; Va´zquez-Hoehne, A. Movement surface: A multilevel approach for predicting visitor movement in nature areas. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 2011, 38, 864–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozens, P.M. Sustainable urban development and crime prevention through environmental design for the British city, Towards an effective urban environmentalism for the 21st century. Cities 2002, 19, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Plessis, C. The Links between Crime Prevention and Sustainable Development. Open House Int. 1999, 24, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Holtz, S. Integrating Environmental, Social and Economic Policies. In The Cornerstone of Development; Schnurr, J., Holtz, S., Eds.; IDRC: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1998; pp. 283–293. [Google Scholar]
- Soberon, L. Concertación: Integrated Planning and Development in Peru. In Cornerstone of Development: Integrating Environmental, Social, and Economic Policies; IDRC: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Black, A.W. The Quest for Sustainable, Healthy Communities. Presented at the Effective Sustainability Education: What Works? Why? Where Next? Linking Research and Practice, Sydney, Australia, 19 February 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bindajam, A.A.A. Describing Movement Densities in the Historic Cities of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia USING SPACE SYNTAX: Lessons for Heritage Planning. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Kansas, Lawrence, KS, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Shaker, M. The Arabian Peninsula: The Peoples of Islamic Peoples in Asia 14-1; Islamic Office: Beirut, Lebanon, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Hamdani Abu Muhammad ibn Yusuf. Characteristics of the Arabian Peninsula; Brill Press: Leiden, The Netherlands, 1884. [Google Scholar]
- Brockelmann, C.; Perlmann, M.; Carmichael, J. History of the Islamic Peoples; Capricorn Books: New York, NY, USA, 1960; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Portugali, J. What makes cities complex? In Complexity, Cognition, Urban Planning and Design; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Al_Sayed, K.; Turner, A.; Hillier, B.; Iida, S.; Penn, A. Space Syntax Methodology; Bartlett School of Architecture, UCL: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Karimi, K. A configurational approach to analytical urban design: Space syntax methodology. Urban Des. Int. 2012, 17, 297–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, M.; Bindajam, A.A.A. Space, movement and heritage planning of the historic cities in Islamic societies: Learning from the Old City of Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Urban Des. Int. 2015, 20, 107–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, M.; Wineman, J.; Zimring, C. Space, behavior, and environmental perception in open-plan offices: A prospective study. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 2009, 36, 432–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peponis, J.; Ross, C.; Rashid, M. The Structure of Urban Space, Movement and Co-presence: The Case of Atlanta. Geoforum 1997, 28, 341–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Claramunt, C. Extending space syntax towards an alternative model of space within GIS. In Proceedings of the 3rd European Agile Conference on Geographic Information Science, Helsinki, Finland, 25–27 May 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher, T. Buildings and streets: Notes on configuration and use. In On Streets; Anderson, S., Ed.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1986; pp. 133–149. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, M. The Geometry of Urban Layouts; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hillier, B. Spatial Sustainability in Cities: Organic Patterns and Sustainable Forms. In Proceedings of the 7th International Space Syntax, Symposium, Stockholm, Sweden, 8–11 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hillier, B. A theory of the city as objects: Or, how spatial laws mediate the social construction of urban space. Urban Des. Int. 2002, 7, 153–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimzadeh, M.; Bjur, H. Transforming cities. The role of the configuration of the network of public spaces in urban life. In Proceedings of the 5th International Space Syntax Symposium, Delft, The Netherlands, 13–17 June 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hillier, B.; Yang, T.; Turner, A. Normalising least angle choice in Depthmap and it opens up new perspectives on the global and local analysis of city space. J. Sp. Syntax 2012, 3, 155–193. [Google Scholar]
- Ratti, C. Urban texture and space syntax: Some inconsistencies. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 2004, 31, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, J. Land characterization analysis of surface temperature of semi-arid mountainous city Abha, Saudi Arabia using remote sensing and GIS. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 2014, 6, 664–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A. From Axial to Road-Centre Lines: A New Representation for Space Syntax and a New Model of Route Choice for Transport Network Analysis. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 2016, 34, 539–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).