Abstract
Accessibility is an important factor in measuring the recreational development potential of Wuhan lakeside areas where people like bike-sharing services for leisure. By using bike-sharing big data, this paper visualizes the spatiotemporal distribution characteristics and depicts the free flows of OD (Original Points and Destination Points) points of the bike-sharing activities taking place within 4 km of 21 lakes in the Wuhan Third Ring Road on an important holiday. Based on these distribution laws, statistics and spatial measurement are used to measure and compare the theoretical accessibility and actual accessibility of these lakeside areas at different grid scales in order to estimate the recreational development potential and explore the causes and possible suggestions behind the recreational potential. Results show that Ziyang Lake, Shai Lake, and South Lake have great recreational potential in improving their accessibility, whereas the Hankou lake dense area has a saturated recreational development potential due to its high accessibility characteristics. The differences in the water environment, surrounding road traffic conditions, and construction situations in these lakes influence their accessibility. Some differences are also observed between the actual and theoretical accessibility of most of these lakes, and there is a long way to go for real improvement of their recreational development potential. To better exploit the recreational development potential, improving the accessibility of these lakes remains an important issue that needs to be addressed as soon as possible.
1. Introduction
Urban lakes play important roles in conserving water, mitigating the heat island effect, and providing recreation to urban residents, as well as in urban modernization and sustainability [1,2,3,4]. The effective exploitation of the development potential of these lakes can be significantly improved along with their spatial quality [5]. However, present potential exploitations tend to focus on the land use, residential value or water environment based on insufficient data, such as questionnaires or surveys and pay less attention to the behavior of the users, especially from big data perspectives.
With the rapid development of location-based services and information and communication technologies in recent years, the amount of social media, point of interest, mobile phone signaling, and taxi trajectory data has increased. Using big data in studying urban spaces can highlight the behavioral characteristics of urban residents [6,7], thereby opening up a new space for examining behavioral problems [5,8,9,10,11]. Many studies have examined human behavioral activities by data mining and synthesis [8,9], analyzed and explored the relationship among human behavior characteristics, time and space [10,11,12,13], and public space potential [14], and proposed suggestions for improvement [15,16,17]. In studying people’s mobile space–time models, many researchers have focused on large cities, including Rome, Hong Kong, Shanghai, Wuhan, and Shenzhen [14,15,18,19,20,21,22]. As an emerging service, bike sharing uses GPS system (Global Positioning System) to conveniently collect a large amount of personal and location data that can clearly reflect the behavioral characteristics of people in the space–time mode [23]. The spatial–temporal bike-sharing data are full and perfect and have been widely used in examining human behavior. For example, these data have been used to determine the peak usage of bike-sharing services in a day [24] and travel duration [25]. The usage of these data has been extended to determining the relationship among the bike-sharing, weather, and private cycling behavior of users [26]. In terms of travel purpose, long-term users tend to use bike-sharing services for work, short-term users utilize these services for leisure and sightseeing, and convenience users utilize these services for their perceived benefits [25,27]. The cycling activities in the Netherlands, Germany, and the UK reveal that most cycling takes place around public transportation stations [28]. Research on the use of bike sharing around the Nanjing Metro Station reveals that this type of service produces different clusters according to time [29]. The shared bicycle partly takes the place of public transport and walking travel [30,31]. In areas with poor public transportation, bike sharing plays the role of a connector that solves the “first kilometer” and “last mile” problems [32]. These studies are mainly based on big data, which are less constrained by time and space and have strong representativeness. However, these data mainly reflect commute characteristics in daily traffic and cannot fully and intuitively reflect the random flow of people’s activities. Moreover, the leisure activities of people are supported by a limited amount of evidence.
The poor accessibility to opportunities and services presents a major obstacle to improving livelihoods and achieving overall development. The accessibility differences in urban public spaces will stratify the human economic, educational, and health conditions [33]. Therefore, the accessibility of a large number of urban public spaces needs to be further studied and improved [34], and the rapid development of time and space big data in recent years provides new research materials and methods for public space research [6]. Bike-sharing big data also provide a new foundation for examining public space accessibility [25,26,27,35,36] and can reflect the development potential of any public space [37,38,39]. As important public spaces in cities, lakeside areas are generally preferred by users of bike-sharing services [5]. An effective exploration of the development potential of these areas can positively influence urban growth, and some coupling effects may also be observed [18]. Some studies have combined time and space factors, explored the travel patterns of shared bicycles [36], and combined them with the surrounding influencing factors in analyzing the attractiveness of public spaces with potential for accommodating bike-sharing activities [26]. In fact, public space research based on bike-sharing big data is still in its infancy, related studies have mainly focused on the sustainability of bike sharing, and the destination area of shared bicycles lacks relevant analysis. Previous studies on urban public spaces are mainly empirical in nature and have generally focused on accessibility [40,41]. Most of these studies have examined the potential of public spaces by using economic survey data [42,43] and evaluated their accessibility by using simple methodologies, such as road network buffer analysis [44]. However, these studies have certain limitations. For instance, most of them are weak in analyzing the number of users, their actual choices, and their original points (O points) and destination points (D points). The conclusions of these studies also greatly differ from actual situations. Cycling has a strong randomness in time and space. Especially for recreational activities, bike sharing is popular recently, which can be highly representative of the behavioral characteristics, needs, and preferences of individuals.
The lakeside area in Wuhan City is among the most important public recreation spaces in the area and demonstrates great potential for development. In the Wuhan Urban Master Plan (2017–2035), the Wuhan Municipal Government proposed a full exploration of the development potential of the city’s lakeside area and to create benefits for the recreational activities of urban residents. The massive sharing of bike-sharing big data provides an opportunity for studying the development potential of this lakeside area. Supported by these data and accessibility analysis, the development potential of the Wuhan lakeside area can be explored. This research contributes to the future development and construction of this lakeside area by providing a basis for planning and decision making.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 presents the research materials and methods and discusses the overall urban impression and environment characteristics of the research area, the characteristics and acquisition of the Mobike data, and the Kernel density estimation, chord diagram method, and reachability probability measurement model used in this work. Section 3 presents the detailed procedure and results of the data processing, the overall space–time study, the OD (Origin and Destination) time series characteristics of the lake, the reachability measurement of the lakeside area, and the basic characteristics of various spatial–temporal distributions. Firstly, the Mobike data are statistically depicted to show the overall time series and spatial characteristics. Then the lakeside area is divided into some buffers to describe its OD flows by using chord diagrams. After that, the Kernel density estimation is used to estimate the maximum starting “nucleus” around each lake. Finally, these “nuclei” are fitted best to the buffers as the maximum starting areas to calculate the theoretical accessibility of lakeside areas. Section 4 analyzes the contradictions encountered in lake development and their possible reasons, examines the relationship between accessibility differences and the recreation development potential, proposes some suggestions for improving the development potential of lakeside areas, and highlights the shortcomings of this study. Section 5 concludes the paper and presents some directions for future research.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Wuhan (113°41′–115°05′ E, 29°58′–31°22′ N) is located in the eastern part of the Jianghan Plain (Figure 1a) and serves as the capital city of Hubei Province (Figure 1b). This city is considered the largest city in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River, with a land area of 8569.15 km2 and resident population of 10.89 million as of 2017 [45]. The rivers and lakes in the city are intertwined, and the water area accounts for one quarter of the city area. A total of 166 lakes can be found in Wuhan—of which, 40 can be found in the city center. Tangxun Lake is currently the largest urban lake in China, and Wuhan East Lake is well known throughout the country [45].
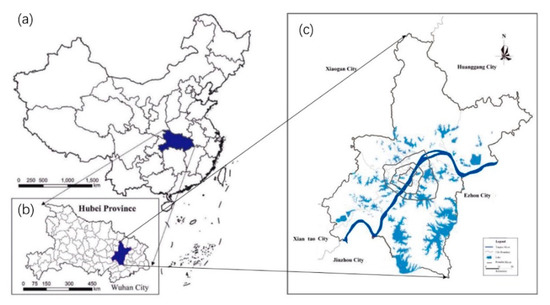
Figure 1.
Location of Wuhan City. (a) The location of Hubei Province in China (b) The location of Wuhan in Hubei Province (c) Wuhan City.
At the end of 2010, Wuhan completed its Third Ring Road plan, which involved its seven main districts (Figure 1c). The lakes in this plan are dotted, the water networks are dense, and the city is densely populated. Areas within the Wuhan Third Ring Road take up less than 15% of the whole city land but gather over 60% of the population and 50% of the economic output, and are the most concentrated areas of diverse activities [45]. Therefore, the scope of this paper is limited to the areas within the Wuhan Third Ring Road.
By referring to the “Wuhan Lake Protection Regulations” [46] issued by the Wuhan Municipal Water Affairs Bureau in 2015, a total of 21 lakes have been identified in the Wuhan Third Ring Road (Figure 2).
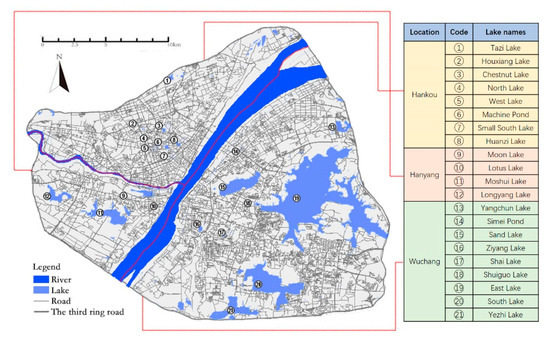
Figure 2.
Lakes in Wuhan within the Third Ring Road.
2.2. Data Source
2.2.1. Wuhan Lake Data
According to the row number 39 and strip number 123, the remote sensing images captured by the Landsat 8 satellite of the United States were downloaded from the website provided by the Chinese Academy of Sciences to extract data on urban lakes in Wuhan. The original data information (Table 1).

Table 1.
Original remote sensing picture dataset sample.
In ENVY 5.3, the standard false color image was synthesized by Band4, Band3 and Band2 of the image, and the lake data of Wuhan were extracted via an unsupervised classification. An improved normalized water body index (MNDWI) was formulated as follows [47]:
MNDWI = (Band 3 − Band 6)/(Band 3 − Band 6).
The contrast of the water in Band 6 was significantly improved, thereby greatly reducing the impact of buildings and plants on the water and improving the accuracy of water extraction. MNDWI was combined with visual interpretation methods to extract the lake data of Wuhan.
2.2.2. Mobike Data
The emergence of bike-sharing services in China is rapidly changing the face of Chinese cities and reshaping the pattern of urban leisure space in China [48]. The Beijing Mobike Technology Co. Ltd. is among the large companies that are operating bike-sharing services in China, accounting for 56.6% of the total market share in 2017. According to the report released by Mobike Bicycles, as of July 2017, Mobike is operating more than 200,000 bicycles in Wuhan, and the number of rides and travel distance during the first half of 2017 exceeded 120 million and 200 million km, respectively [49]. In sum, Mobike bicycles are preferred by the majority of the urban and travelers and residents in China.
Due to technical limitations, the data used in this study were only collected on 1 October 2018, which was the National Holiday of the People’s Republic of China. The day was cloudy with a temperature of 13 to 25 °C, which is suitable for cycling. A total of 227 data sheets were recorded, and more than 60 million records with a total size of 3.80 GB were collected. The original data sample Table 2 is presented below.

Table 2.
Original Mobike dataset sample.
As shown in the figure, when a journey starts or ends on bicycle, the time, longitude and latitude are recorded by bike_id, corresponding to the O points and D points in order.
However, some of the Mobike location data are incomplete or redundant and need to be cleaned and pre-processed to screen out the complete and effective location data within the Wuhan Third Ring Road. After cleaning and pre-treatment, 377,159 starting (point O) and 367,233 ending (point D) points were obtained.
It can be seen that the cleaned data are formatted (Table 3). The same bike_id may correspond to multiple points O and D. Combining time and point data, each OD combination forms a set of spatial OD flows.

Table 3.
Cleaned Mobike dataset sample.
The Mobike bicycle track data were classified into O, D, and O and D points and were visualized in ArcGIS 10.2. The distribution of OD points within the three rings in the lake area is presented in Figure 3.
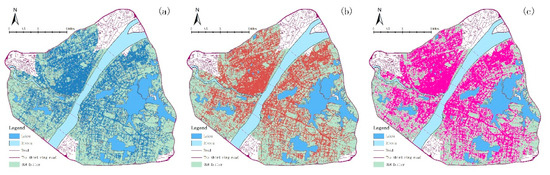
Figure 3.
Mobike spatial distribution. (a). Original points (O points); (b). Destination points (D points); (c). O points and D points.
As shown above, the distribution of O points is very dense on the south of Hankou, along Luoyu Road, and along the coasts of Sand Lake and Hanyang Moshui Lake. The distribution of D points in the three towns is densely distributed, especially in Hankou. The points in the Ministry, the western part of Wuchang, and the northern part of Hanyang are extremely concentrated. The O and D points overlap and cover almost the entire city.
2.3. Method
2.3.1. Chord Diagram
More than 90% of Mobike bicycles in Wuhan are concentrated within 4 km of lakes [49]. Therefore, the area within 4 km of these lakes was treated as the bicycle buffer zone, and the OD quantity was mapped to this area. The number of O or D points within the ring was used to measure the intensity value.
The one-day data for the O and D points of the same track record were further divided as
where i and j denote the spatial units after normalization.
The OD line is a streamline—motion trajectory of which is a vector from the spatial point O (, , ) to D (, , ). The directionality and temporality of this line are the same as those of the spatial position.
The rows and columns report the start and end of a journey, respectively, and form a 2D square matrix of i rows and i columns. Each matrix element records the statistical value of the OD points. This 2D matrix is converted into a chord diagram to visualize the direction and intensity of the OD flow [50,51].
By analyzing the starting and ending points of the shared bicycles on different buffers, the flow state of the users in space can be visualized, and more buffers at the starting point are areas where more people leave, and more buffers at the end point are more multi-person destinations. Thus, through analysis, the maximum starting buffer around the lake can be found.
2.3.2. Kernel Density Estimation
Kernel density estimation (KDE) is a density function used to estimate unknown values in probability theory [52,53,54]. A large gap is often observed between the basic assumption of the parametric model and that of the actual physical model. Given such a defect, Rosenblatt and Parzen proposed KDE as a non-parametric estimation method. The sample comprises n sample points with an independent and identical distribution F. The probability density function is denoted by f, and the kernel density is estimated as
where h > 0 is a smoothing parameter called bandwidth or window, and K(.) is a non-negative kernel function with a score of 1 (conforming to the probability density property) and a mean of zero.
This study uses the commonly used Gaussian kernel density function K(.), which is calculated as
Through estimation showed in ArcGIS, the central location of the spatial distribution of the O points in the lakeside areas can be observed, which includes the maximum starting points. Combine these maximum starting points and the maximum starting buffers from the chord diagram to obtain a more accurate maximum starting area.
2.3.3. Accessibility Possibility Model
The buffers within 4 km range of the lakes were divided into 200 m × 200 m, 400 m × 400 m, and 800 m × 800 m grids.
Theoretical reachability probability is a reachability probability model that is based on the spatial distance threshold [55,56]. Ingram proposed a reachability model and suggested that if the distance from a specific location to a service facility is the shortest, then the probability of reaching that location is the highest [57]. Distance attenuation is an important feature of this model [58].
Suppose B is the grid of a specific lake area, L is the departure area of all lake targets, B = {, ,…, } is a set of grids in B, L = {, ,…, }, is the arbitrary position grid in B, and is the maximum departure (O point) area of a specific lake in L, then starting from the position grid , the distance-based theoretical reachability probability D of the position grid of can be expressed as [55]
The reachability probability D satisfies the constraint
where represents the spatial distance of to , and represents the distance reachability of to .
When the coverage areas of different departure areas are superimposed upon one another, multiple assignments may occur for the same grid unit. At this time, the reachability probability of the grid unit can be expressed as the average value.
The data-based reachability probability model represents the actual reachability probability based on moving trajectory data. This model is defined by the number of shared bicycles arriving at the grid in the lake area. The actual reachability probability C can be expressed as
Analogous to D, both C and satisfy the constraints [56]
and
where represents the actual number of arrivals of to .
The comprehensive reachability probability (I) is expressed as a combination of D and C. An increase in D and C will result in an increase in I, and a combination of I and D exhibits a positive correlation with C. The linear combination of I, D, and C can reflect such relationship as [54]:
Given the easy operation of the formula, and .
To compare the accessibility of different lakes, their relative reachability must be calculated. The standardized probability (Z-score) of comprehensive reachability is calculated, and a larger relative reachability indicates a higher accessibility.
After obtaining the reachability probabilities D (based on spatial distance) and C, their average relative value (AAD) is computed, and the reachability threshold δ is set. The relative value of the recreational development potential of the lake area can then be estimated as
When the AAD is larger than a certain value, it can be considered that there is a big difference between theoretical and practical accessibility of lakes, reflecting the different recreational development potential of lakeside areas. According to the calculated results, by setting a certain threshold, δ, the accessibility analysis is promoted to the evaluation of the lakeside area’s recreational development potential.
Moreover, the value of the AAD is the comprehensive result of the chord diagram method, KDE and accessibility probability, which reflects the conclusion of a comprehensive measurement of lake development potential and is more accurate and reliable.
3. Results
3.1. Overall Spatial and Temporal Characteristics
3.1.1. Overall Timing Characteristics
According to the time series, the relationship between the OD number and Mobike time was plotted as follows (Figure 4), where the O point represents the car starting point and the D point represents the car ending point:
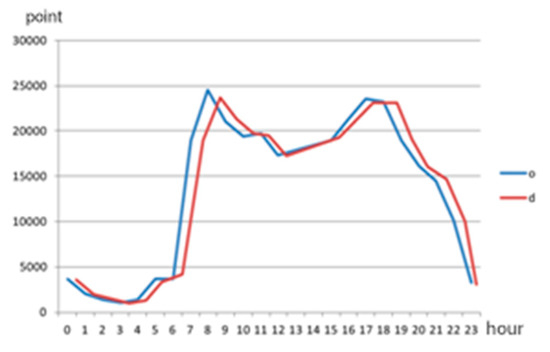
Figure 4.
Mobike time changes of O and D.
Obvious peaks were observed in the morning and evening of 1 October, while the peaks captured at night were extremely low. The Mobike time can be divided into four phases as follows (Figure 4):
(1) Early peak 07:30–08:30
In just an hour, the amount of used Mobike bicycles reached nearly 25,000, and the number of O points exceeds the D points. It is this holiday’s peak time of residents and tourists, and the trend of going out early is very obvious.
(2) Middle protrusion 11:30–12:30
At noon, a short-term rebound was observed between the morning and evening peaks. The short-term usage reached 18,000. Car O points and D points were approximately the same. Similar trends were recorded at lunchtime during which people used Mobike bicycles to search for their lunch.
(3) Late peak 17:30–18:30
During the evening peak hours, the number of Mobike users peaked at 110,000, and O significantly outnumbered D. These trends lasted until 19:30 at the end of the late peak. Due to the darkness, residents and tourists have chosen to give up sharing bicycles during this period, and shared bicycle recreation activities have gradually ended.
(4) Late night to 0:00–04:00 in the morning
The lowest Mobike usage level was observed in the early morning. O and D demonstrated simultaneity, but the total usage had reached 50,000, thereby indicating that the capacity of Mobike bicycles cannot be ignored even in relatively stagnant periods.
3.1.2. Spatial OD Relationship
The 4 km buffer zone was divided into 20, 10, and 5 buffer zones located 200 m (Figure 5c), 400 m (Figure 5b), and 800 m (Figure 5a) from the lake. A smaller buffer ring number near the lake corresponded to a larger position number far away from the lake. The following chord diagram was drawn by using the method presented in Section 2.3.
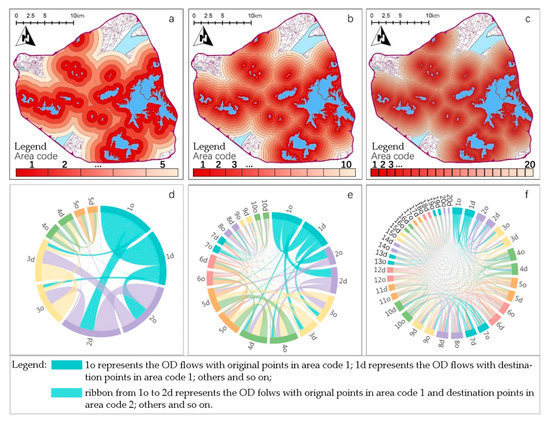
Figure 5.
Chord Diagrams of Mobike trajectory. (a) 800 m buffer; (b) 400 m buffer; (c) 200 m buffer; (d) 800 m chord diagram; (e) 400 m chord diagram; (f) 200 m chord diagram.
In Figure 5a–c, the red of the gradient indicates the different buffers of the lakeside areas, with area codes of 1, 2, 3, … corresponding to the code 1, 2, 3, … respectively in the Figure 5d–f, to distinguish different areas according to the distance from the lake. In Figure 5d–f, the colors represent different migration routes, o represents the departure area, d represents the arrival area, and o and d (the same color) represent the total arrival flow rate. For example, the ribbon from 1o to 2d represents all of the OD flows with an original area of code 1 one and destination area of code 2 one. The width of the migration zone represents the amount of migration.
At a bandwidth of 800 m (Figure 5d), regions 1 and 2 are significantly wider than the other regions—these two regions have the same number of ODs, and a large number of self-migrations is recorded within the region. The largest one-way migration is observed from region 1 to 2—farther distance from the lake corresponds to a lower migration flow. At the 400 m scale (Figure 5e), the OD quantities of regions 1 to 5 are highly quantitative, whereas those of regions 9 and 10 are significantly low. At a bandwidth of 200 m (Figure 5f), zones 1 to 10 account for approximately 2/3 of the total OD, whereas zones 1, 4, 6, and 8 show significant quantitative advantages.
The graph above reveals four key points. First, in the spatial distribution, the OD can form a circle structure centering on the lake. Second, the riding flow value decreases along with an increasing distance from the lake. Third, the riding flow value varies across different areas, and its distribution is not continuous. Fourth, a highly frequent migration is observed between one region and its adjacent region, and the migration in the nearest neighboring region and the sub-adjacent region of the lake reaches the maximum.
3.2. OD Time Series Characteristics of Lakes
According to the OD point of the lakeside area, the other point data in the 4 km buffer range of each lake were deleted, the same operation was repeated 21 times, and the differences among the O, D, and OD points within 4 km of each lake were computed (Table 4).

Table 4.
Number of O and D points around lakes.
The OD points within 4 km of lakes were grouped according to the time series characteristics to determine the changes in OD quantity around these lakes at different periods. The upper and lower areas of the horizontal axis indicate the number of OD points around each lake. A larger area corresponds to a larger number of OD points.
Table 4 shows that O points have obvious advantages in their distribution around East Lake, Shuiguo Lake, Sand Lake, and the Hankou lake dense area (including North Lake, Houxiang Lake, Huanzi Lake, Machine Pond, Chestnut Lake, Small South Lake, and West Lake), while, in Yezhi Lake and Tazi Lake, O points are relatively rare. D points are gathered around East Lake, Sand Lake, and the lake dense area in Hankou, showing obvious cluster distribution characteristics, but there are a few D points in Tazi Lake.
As shown in Figure 6, the peaks at North Lake, Chestnut Lake, and East Lake were recorded at 07:00–09:00 and 16:00–18:00, whereas those at Shuiguo Lake and Lotus Lake were observed at 11:00 and 06:00, respectively. The cycling intensity in the lake was generally consistent with the overall riding time distribution. The morning peak was observed at 08:00, whereas the evening peak was observed at 17:00 and was kept consistent at 06:00 and 22:00. The O and D points were then recorded.
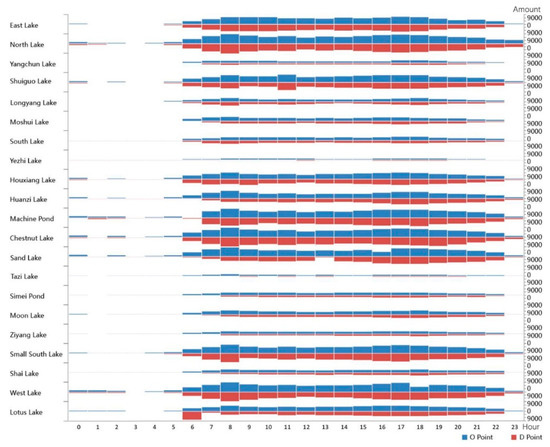
Figure 6.
Mobike time count divided by lakes.
3.3. Wuhan Lakeside Accessibility Measurement
3.3.1. Determining the Maximum Departure Area Based on KDE
The kernel density of all points was analyzed by using ArcGIS 10.2, and the overall kernel density in Figure 7 was estimated by using the method specified in Section 2.3.2. The kernel of the overall O point was observed on the south of Hankou.
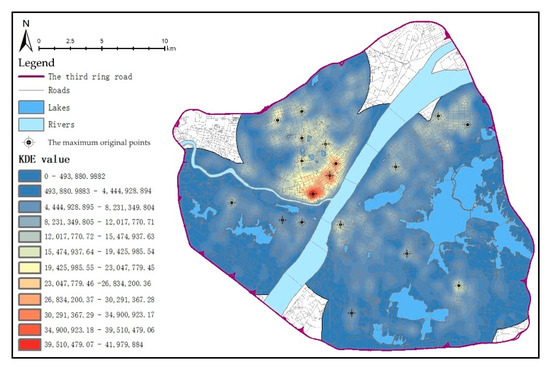
Figure 7.
Kernel density estimation (KDE) of Mobike O points.
The Mobike bicycles within 4 km of the lakes were screened to determine the maximum O point area around each lake. The maximum O point (group) L = {, ,…, } around each lake can be obtained according to the KDE results. Figure 7 presents the maximum departure point O around 21 lakes.
Although the kernel may have a wider range (maximum of 800 m × 800 m), the number of Ds that the kernel departs to reach other regions is extremely limited, and the difference in reachability cannot be delineated. Therefore, when measuring reachability probability, the results between the maximum starting buffers from the chord diagram and the maximum original points around the lake from the KDE (Kernel density estimation) are combined. In this case, the maximum O shown in Figure 7 falls within a certain distance of the buffer ring, and the series is the largest. The loop measures the theoretical reachability based on the distance from the center point of grid to the center line of the largest departure ring and measures the actual reachability based on the maximum starting ring to the OD number of a certain grid.
3.3.2. Comparison of Accessibility Differences in Different Lakeside Areas
The maximum starting buffer of the 800 m grid is area code 2 as specified in Section 3.3.1 (Figure 8a). The maximum starting buffer of the 400 m grid is approximated by area code 4 (Figure 8b), and the 200 m grid approximates area code 8 (Figure 8c), thereby increasing the accessibility of the surrounding areas of the lake, which facilitates the comparison of theoretical and actual accessibility.
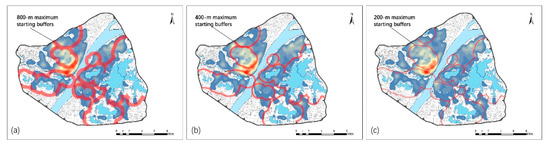
Figure 8.
Three max O rings within (a) 800 m grids; (b) 400 m grids; (c) 200 m grids.
For the actual arrival of shared bicycles, the distribution of actual reachable probability C is considered (Figure 9). In the vertical direction, with the refinement of the scale, the reach of Mobike bicycles from the largest starting ring gradually decreases, and the gap in accessibility narrows. Under the 800 m grid, the south bank of Hankou Lake shows good accessibility, whereas the Wuchang, Xudong, Simenkou, and Guanggu Square areas are identified as the most practically accessible blocks. Within the range of Hanyang, the actual accessibility probability is generally low. At the 400 m scale, the accessibility probability values of the Hankou lake compact area, Simei Pond, Dong Lake, Sand Lake, Moon Lake, and other areas significantly increase. At the 200 m scale, the Wangjiadun Commercial District, Jianghan Road Pedestrian Street, Tongji Hospital, and Zhongshan Park near the Hankou lake dense area have high accessibility, whereas the Zhang Zhidong Museum, Zhongjiacun Commercial District, Maying Road Subway Station in Hanyang, and Guiyuan Temple have good accessibility. In Wuchang area, the Ziyang Lake, Shouyi Cultural District, Wuhan University First Clinical College, Guanggu Square Commercial District, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan Engineering University, Xudong Commercial District, Garden Road Subway Station, and other areas have a significantly higher accessibility compared with other areas.
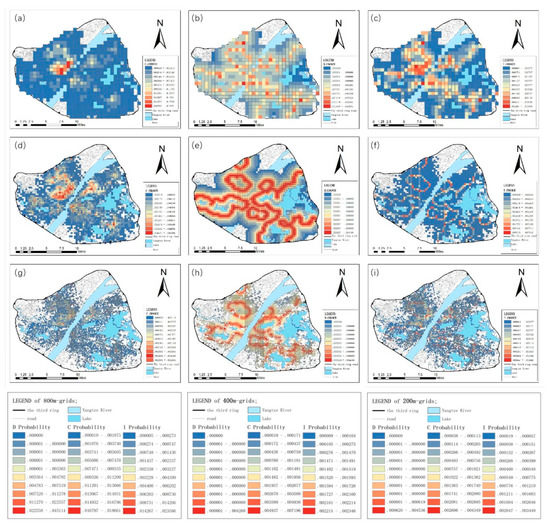
Figure 9.
Three kinds of accessibility of Mobike trajectory (a) D probability within 800 m grids (theoretical); (b) C probability within 800 m grids (actual); (c) I probability within 800 m grids (comprehensive); (d) D probability within 400 m grids; (e) C probability within 400 m grids; (f) I probability within 400 m grids; (g) D probability within 200 m grids; (h) C probability within 200 m grids; (i) I probability within 200 m grids.
When theoretical accessibility is considered, the reachability and maximum starting ring form a circular structure. The maximum accessibility grid in Figure 9b is roughly along that shown in Figure 8a and extends outwards per layer. The accessibility is very low in the region farthest from the lake is very low. Meanwhile, the Simenkou Commercial District in Wuchang, the Wangjiadun Commercial District in Hankou, and the Zhang Zhidong Museum in Hanyang showed the best theoretical accessibility. This feature is not obvious in Figure 9e,h and further improves the area of equal accessibility formed by the largest starting ring. Moreover, large areas of high reach are found in the Hankou lake dense area, Wuchang Sand Lake, East Lake, and Hanyang Moshui Lake, and similarly accessible grids are connected into a network to form a high-reaching area.
In the comprehensive probability model, the accessibility of the lakeside region is numerically similar to theoretical reachability. At the 800 m scale, the Hankou Lake dense area, Hanyang Zhang Zhidong Museum, Wuchang Xudong Business Circle, and Wuchang Luoyu Road form dense intensive areas, and the accessibility values of these locations significantly differ from those of other areas. At the 400 m scale, the comprehensive probability is obviously affected by the theoretical probability. The Wuchang East Lake, Sand Lake, Ziyang Lake, Shai Lake, Hankou lake dense area, Hanyang Moon Lake, and Moshui Lake form accessibility subsidence areas. Similar to the 200 m grid, the Wangjiadun Commercial Circle, Jianghan Road Pedestrian Street, Houxiang Lake Park, Qingchuan Bridge in Hankou, Zhongjiacun Commercial District in Hanyang, Wangjiawan Commercial District, Zhang Zhidong Museum, Xudong Commercial District in Wuchang, Hanjie Pedestrian Street, Zhongnan Road Commercial Area, and Guanggu Square Commercial Area have high accessibility and form a reachable central area.
3.3.3. Comparative Analysis of the Recreational Development Potential of Different Lakes
The average accessibility potential of the surrounding the lake is represented by the difference between the theoretical reachability probability D and actual mean probability C in the 200 m × 200 m grid unit within 4 km of each lake. The recreational development potential of the lakeside region is shown in Figure 10. In this figure, the vertical axis represents the AAD of lake recreational development potential, whereas the horizontal axis represents different lakeside regions. A larger AAD corresponds to a greater difference between theoretical and actual accessibility.
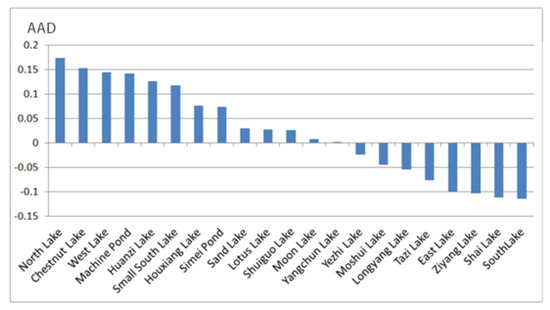
Figure 10.
The AAD (Average Relative Value) of different lakes.
The value of the AAD (Average Relative Value) is the comprehensive result of the chord diagram method, KDE and accessibility probability, which is more accurate and reliable.
Figure 10 shows that the 21 lakes in Wuhan can be divided into three categories. The first category includes lakes with good accessibility, such as North Lake, Chestnut Lake, West Lake, Machine Pond, Huanzi Lake, Small South Lake, Houxiang Lake, and Simei Pond. These lakes have a peripheral AAD greater than 0.05, have good accessibility, and are often visited by people. The second category includes reachable lakes, such as Sand Lake, Lotus Lake, Shuiguo Lake, Moon Lake, Yangchun Lake, Yezhi Lake, and Moshui Lake. These lakes have an AAD ranging from −0.05 to 0.05 and have numerically equivalent D and C. These lakes are located in areas where actual accessibility is close to theoretical accessibility. The third category include those lakes with poor accessibility, such as Longyang Lake, Tazi Lake, East Lake, Ziyang Lake, Shai Lake, and South Lake. These lakes have an AAD of less than −0.05, and their actual accessibility is significantly lower than their theoretical accessibility. The recreational development potential of these lakes still shows a large room for improvement, and their development should focus on environmental improvement.
4. Discussion
4.1. Theoretical Implications
We used a simple accessibility model to study the recreational development potential from shared bicycle big data. Different from other previous angles, such as taxi, green space, metro and so on, this paper provides a new perspective and supplements the theoretical accessibility in more complex areas—lakeside areas beside 21 lakes. Research on the theoretical significance of shared bicycle accessibility provides a higher reference for judging the development degree and gap of lakeside area.
4.2. Practical Implications
In order to explore the recreational development potential of the areas, the big data on bike tracks are used, with closer links between the OD points and the time distribution. In this paper, the combined methodology of chord diagrams, Kernel density estimation and accessibility possibility model is used to more accurately reflect the recreational behavior characteristics and evaluate the recreational potential based on accessibility, which is more practical and actionable.
4.3. Limitations and Future Research
Given the inherent limitations of the collected bike-sharing big data, the particularity of the acquisition time, the large mesh size, and insufficient information about the characteristics of bike-sharing service users, the findings of this work regarding the accessibility of lakes may not be accurate enough. In addition, a certain degree of subjectivity is observed in the acquisition of lake data from the visual interpretation of remote sensing images, which may lead to errors. Therefore, future research needs to improve these weaknesses and focus on more common topics rather than a standalone topic.
4.4. Key Conclusions
The difference in accessibility affects the use of lakeside areas, and the exploration of recreational potential is also different. Although the lakes are located in the densely populated main urban areas of Wuhan, they are considered main places where people can engage in recreation. However, as a result of the differences between the distances, surrounding traffic, facilities, and construction conditions, and the water environment of these lakes and those of the surrounding natural environment, some obvious differences can also be observed in their accessibility. Reasonable improvement of the accessibility is of great significance for the development of lakeside area recreation potential.
Generally, areas with good accessibility are considered along with great development potential. Large service stations are often found in lakes with good accessibility. The density of the transportation network in these lakes is large enough to accommodate bike-sharing services. The greater density of transportation networks also brings intensive commercial and residential space, entertainment facilities and public facilities, which improves their attractiveness. Seven lakes, namely, North Lake, Houxiang Lake, Huanzi Lake, Machine Pond, Chestnut Lake, Small South Lake, and West Lake, are located in the most densely populated area of Hankou, which has a dense surrounding road network, a strictly managed lake system, and a dense commercial space. The North Lake Park and another four city convenience parks have also been built around these lakes. These lakes are also adjacent to large public facilities, including the Jianghan District Government office, Wansongyuan Business Circle, Hankou Cultural and Sports Center, and Zhongshan Park. A total of 10 subway stations on the four lines of the Wuhan Metro have also been installed near these lakes. Given the short-distance traffic in these areas, bike-sharing services are crucial in solving the “last mile” problem. Given that the recreational development potential of these lakes has reached saturation, their accessibility needs to be strengthened to improve the quality of their services and their water environment.
In contrast, poor accessibility hinders the potential development of lakes. Although there are entertainment facilities, public facilities, residential areas, etc., around the lakes, the closed traffic still makes the four beautiful pools, Lotus lake, Moon Lake, Moshui lake, Sand Lake, Shuiguo lake, Yangchun lake, Yezhi lake and other lakes reach the upper limit. The surrounding area of simieichi is narrow; Lianhua Lake is the main road of the city, which is not suitable for cycling; Yuehu Lake is adjacent to viaduct; inkhu lake is surrounded by a large number of closed communities, resulting in fewer roads to the lake. Within the Wuchang area, the accessibility of lakes, including Sand Lake, Shuiguo Lake, Yangchun Lake, and Yezhi Lakeare located in the prosperous district of Wuchang. But only a few small urban parks have been built along the opening of the lake. Shuiguo Lake and East Lake are connected by only one bridge, with the two large institutes, the Hubei Provincial Committee and the Central South Hospital of Wuhan University, occupying a large amount of land but with high motor traffic density, thereby limiting their accessibility to non-motor vehicle traffic. Yangchun Lake is located adjacent to the Wuhan Railway Station, which has high traffic demand. However, this lake still has a large amount of land to be developed, and the constructed viaduct is not suitable for bike-sharing activities. A large amount of bare land can be found around Yezhi Lake. Although the surrounding residential areas are dense, they have poor accessibility and have limited land construction potential.
The actual accessibility of the remaining six lakes is lower than their respective theoretical accessibility, and these lakes show a great potential for recreational development. These lakes do not have poor basic conditions yet require highly stringent management and efficient development. The lake construction department should address the water pollution problem in these lakes, expand their waterfront space, improve their accessibility, balance the contradiction between land development and the service functions of these lakes, and address those problems that hinder their development. The Longyang Lake in Hanyang is located along the periphery of an urban built-up area. The surrounding industrial areas and farmland cause serious water pollution. Similarly, South Lake has a large amount of domestic sewage flowing in from residential areas and the expanding university town located nearby. The level of this domestic sewage far exceeds the bearing capacity of the lake, thereby significantly decreasing its water quality. The northern part of Tazi Lake is surrounded by a high-end villa district in Xianghu County. This lake has almost become a unique residential area and is difficult for the general public to reach. Ziyang Lake and Shai Lake have small areas and are located within the park, with a complex surrounding living environment and limited accessibility due to the surrounding roads. Many construction sites can be found around Shai Lake, and the lake itself is under strict governance. East Lake, which is the largest lake within the Wuhan Third Ring Road, also has poor accessibility. With an area of 88 sq. km, more than 100 km of greenery has been built around East Lake, and the surrounding universities, and the nearby large parks, such as the Wuhan Botanical Garden and Ma’an Mount Forest Park, and the nearby mountains, including the Lushan Mountain and Nanwang Mountain, have increased the people’s enthusiasm for using bike-sharing services around this lake. However, a significant gap can still be observed between the actual and theoretical accessibility of this lake. East Lake has a limited environment suitable for cycling, thereby affecting the enthusiasm of people to ride bicycles in the area.
The development of lakeside area recreational potential is constantly increasing, while the accessibility factor has been ignored for a long time. Urban construction has been pursuing the economic benefits brought about by large-scale expansion, the efficient use and effective development of urban land, and the fast and convenient traffic conditions, while considering the living conditions of people residing in cities. However, while an increasing number of closed, small systems are being built in cities, the motor vehicle traffic in these areas is becoming increasingly dense, thereby crowding out the space meant for non-motor vehicle traffic. The urban water environment represented by lakes has also been neglected and destroyed, thereby reducing the amount of space meant for free passage and the accessibility of waterfront environments. Moreover, as the number of motor vehicles in the city continues to increase, more motor vehicle lanes need to be built. Despite the flexibility in riding activities observed in these cities, these activities are obviously hindered by motorized traffic, the construction of a micro-enclosed system, and the poor density of road networks. Many areas that used to be easily accessible have become difficult to reach. Meanwhile, the construction of lakeside areas is not based on a “rider-friendly” principle. The construction of urban space in these areas does not consider the growing popularity of cycling recreational activities, and several obstacles, including the allocation of additional space for motor vehicles, have reduced the people’s enthusiasm to ride bicycles.
The improvement of accessibility is of great importance for real improvement of lakeside areas. Building a lakeside area that is more accessible and suitable for recreation, leisure, entertainment, and short-distance travel requires improvements in the water and surrounding environments of lakes and the effective construction of surrounding non-motorized traffic. By achieving these goals, a rational urban space layout and improved quality of life can also be realized.
5. Conclusions
Lakeside areas play an important role in urban sustainability and citizen’s well-being. To determine the lakeside area recreational development potential, this study uses Mobike big data to describe accessibility and recreational development potential with the chord diagram and the probability of reachability was used to visualize the OD points around 21 lakes within the Wuhan Third Ring Road. By using these points, the probability distribution of the accessibility of different lakes was measured and compared with the theoretical accessibility. The differences in the development potential of lakes within the area were then highlighted based on their actual and theoretical accessibility. Large differences can still be observed in the recreational development potential of lakes that are frequently visited by people, and cycling activities are conducive to discovering the potential of these lakes. According to the accessibility based potential, lakeside area development should focus on the improvement of accessibility, bike-friendly environments, and waterfront quality. Further, this study has shown that bike-sharing service accessibility is feasible and valid to determine the recreational potential, which may be valuable for urban governments. This work contributes to the discovery of the recreational development potential of lakeside waterfronts and to the creation of convenient lakeside spaces within cities. The methods proposed in this work are expected to play a role in the design and construction of urban public leisure spaces and provide references for studying public facilities and the development of urban green space parks.
Unfortunately, due to the limitations of the data analysis, this study focuses only on the development of recreational potential in the lakeside area. However, the effective development of the lakeside area is pretty complex. Holidays, weekends and workdays are likely to be different. These broader areas and deeper discoveries need further studies to verify the sustainability of the method proposed in the present paper.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.W.; methodology, J.W. and C.L.; software, X.L.; validation, J.W., C.L. and X.L.; formal analysis, X.L.; investigation, C.L.; resources, C.L.; data curation, X.L.; writing—original draft preparation, C.L.; writing—review and editing, J.W.; visualization, X.L.; supervision, J.W.; project administration, J.W.; funding acquisition, J.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China: 51808409; Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province: 2019CFB477; Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Interdisciplinary Project): 2042019kf0211.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Keyvanfar, A.; Shafaghat, A.; Mohamad, S.; Abdullahi, M.A.; Ahmad, H.; Mohd Derus, N.; Khorami, M. A Sustainable Historic Waterfront Revitalization Decision Support Tool for Attracting Tourists. Sustainability 2018, 10, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leporelli, E.; Santi, G. From psychology of sustainability to sustainability of urban spaces: Promoting a primary prevention approach for well-being in the healthy city designing. a waterfront case study in livorno. Sustainability 2019, 11, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostopoulou, S. On the revitalized waterfront: Creative milieu for creative tourism. Sustainability 2013, 5, 4578–4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anna, K.; Ryszard, G.; Renata, D.; Katarzyna, K.; Tomasz, H. Changes in Phytoplankton and water quality during sustainable restoration of an urban lake used for recreation and water supply. Water 2017, 9, 713. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Li, J.; Ma, Y. Exploring the relationship between potential and actual of urban waterfront spaces in Wuhan based on social networks. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Wang, F.; Xiao, Y.; Gao, S. Urban land uses and traffic ‘source-sink areas’: Evidence from GPS-enabled taxi data in Shanghai. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2012, 106, 73–87. [Google Scholar]
- Sui, T.; Jonathan, C.; Iderlina, M.; David, R. Exploring Bus Rapid Transit passenger travel behaviour using big data. Appl. Geogr. 2014, 53, 90–104. [Google Scholar]
- Widhalm, P.; Yang, Y.; Ulm, M.; Athavale, S.; González, M.C. Discovering urban activity patterns in cell phone data. Transportation 2015, 42, 597–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Liu, K.; Chen, J. Research on human mobility in big data era. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2014, 16, 665–672. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, L.; Liu, X.; Wu, L.; Liu, Y. Inferring trip purposes and uncovering travel patterns from taxi trajectory data. Cartogr. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2015, 43, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Huang, H.; Ni, X.; Zeng, W. Revealing spatial-temporal characteristics and patterns of urban travel: A large-scale analysis and visualization study with taxi GPS data. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2019, 8, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Ukkusuri, S.V. Spatial variation of the urban taxi ridership using GPS data. Appl. Geogr. 2015, 59, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Liu, F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H. Uncovering urban human mobility from large scale taxi GPS data. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2015, 438, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahas, R.; Aasa, A.; Silm, S. Daily rhythms of suburban commuters’ movements in the Tallinn metropolitan area: Case study with mobile positioning data. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2010, 18, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevtsuk, A.; Ratti, C. Does urban mobility have a daily routine? Learning from the aggregate data of mobile networks. J. Urban Technol. 2010, 17, 41–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Liu, F.; Janssens, D.; An, S.; Wets, G.; Cools, M. Detecting urban road network accessibility problems using taxi GPS data. J. Transp. Geogr. 2016, 51, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Clio, A.; Carlo, R. Uncovering cabdrivers’ behavior patterns from their digital traces. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2014, 53, 90–104. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Luo, J.; Tang, L. Coupling Relationship between Urban Expansion and Lake Change—A case study of Wuhan. Water 2019, 11, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Liu, C. Street—Based topological representations and analyses for predicting traffic flow in GIS. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2009, 23, 1119–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Kang, C.; Gao, S.; Xiao, Y.; Tian, Y. Understanding intra-urban trip patterns from taxi trajectory data. J. Geogr. Syst. 2012, 14, 463–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.; Qin, K. Understanding operation behaviors of taxicabs in cities by matrix factorization. Comput. Environ. Urban 2016, 60, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.B.; Yuan, J.; Wang, Y.; Si, H.B.; Shan, X.M. Exploring space–time structure of human mobility in urban space. Phys. A 2011, 390, 929–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Thapa, B.; Jang, S.; Yang, E. Seasonal spatial activity patterns of visitors with a mobile exercise application at Seoraksan National Park, South Korea. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfrommer, J.; Warrington, J.; Schildbach, G.; Morari, M. Dynamic vehicle redistribution and online price incentives in shared mobility systems. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2014, 15, 1567–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, E.; Washington, S.; Haworth, N. Bike share’s impact on car use: Evidence from the United States, Great Britain, and Australia. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2014, 31, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Jiao, S.H.; Zhang, S.; Liu, W.C.; Feng, L.; Wang, Y.S. TripImputor: Real-Time Imputing Taxi Trip Purpose Leveraging Multi-Sourced Urban Data. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. 2017, 19, 3292–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, D.; Buehler, R.; Happ, P.; Rawls, B.; Chung, P.; Borecki, N. Are bikeshare users different from regular cyclists? A first look at short-term users, annual members, and area cyclists in the Washington, D.C., Region. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2013, 2387, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, K. The bicycle as a feedering mode: Experiences from three European countries. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2004, 9, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Guo, X. Operating characteristics of dockless bike-sharing systems near metro stations: Case study in Nanjing City, China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, E.; Washington, S.; Haworth, N.; Watson, A. Factors influencing bike share membership: An analysis of Melbourne and Brisbane. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2014, 71, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Pang, Y. Travel behavior change after the introduction of public bicycle systems: Case study in Minhang District, Shanghai. In Proceedings of the Transportation Research Board 92nd Annual Meeting, Washington, DC, USA, 13–17 January 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Shaheen, S.; Martin, E. Unraveling the Modal Impacts of Bikesharing. Access Mag. 2015, 1, 8–15. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, D.J.; Nelson, A.; Gibson, H.S.; Temperley, W.; Peedell, S.; Lieber, A.; Hancher, M.; Poyart, E.; Belchior, S.; Fullman, N.; et al. A global map of travel time to cities to assess inequalities in accessibility in 2015. Nature 2018, 553, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, P.; Xu, L.; Yue, W.; Chen, J. Accessibility of public urban green space in an urban periphery: The case of Shanghai. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 165, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Rose, G.; Jacob, C. Impact of weather on commuter cyclist behavior and implications for climate change adaptation. In Proceedings of the ATRF2010: 33rd Australasian Transport Research Forum, Canberra, Australia, 29 September–1 October 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Froehlich, J.; Neumann, J.; Oliver, N. Sensing and Predicting the Pulse of the City through Shared Bicycling. In Proceedings of the 21st International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI-09), Pasadena, CA, USA, 11–17 July 2009; Volume 3, pp. 1420–1426. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Li, J.; Huang, Y. Operating characteristics of a public bicycle-sharing system based on the status of stations: Case study in Nanning City, China. In Proceedings of the Transportation Research Board 96th Annual Meeting, Washington, DC, USA, 8–12 January 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Zhang, S.; Chen, X.; Liu, F.; Zou, Y. Taxi trips distribution modeling based on Entropy-Maximizing theory: A case study in Harbin city—China. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2018, 493, 430–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Wang, S.; Hwang, M.; Padmanabhan, A.; Zhang, Z.; Soltani, K. A scalable framework for spatiotemporal analysis of location-based social media data. Comput. Environ. Urban 2015, 51, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkip, F. The distribution of urban public services: The case of parks and recreational services in Ankara. Cities 1997, 14, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Chen, Y.; Wu, J.; Xu, T.; Gao, L.; Zhao, X. Mapping spatial accessibility of public transportation network in an urban area—A case study of Shanghai Hongqiao Transportation Hub. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2018, 59, 478–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, I. Evaluating accessibility using house-level data: A spatial equity perspective. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2006, 30, 254–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.S.; Liao, C.H. Exploring an integrated method for measuring the relative spatial equity in public facilities in the context of urban parks. Cities 2011, 28, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, P.Y.; Samsudin, R. Effects of spatial scale on assessment of spatial equity of urban park provision. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 158, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuhan Municipal Bureau of Statistics. Wuhan Statistical Yearbook (2018); China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2018; p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- Standing Committee of the 13th People’s Congress of Wuhan. Wuhan Lake Protection Regulations; Wuhan Water Affairs Bureau: Wuhan, China, 2015; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ling, F.; Wang, Q.; Li, W.; Li, X. Water Bodies’ mapping from sentinel-2 imagery with modified normalized difference water index at 10-m spatial resolution produced by sharpening the SWIR band. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, J.; Dunford, M. Rethinking the utility of public bicycles: The development and challenges of station-less bike sharing in China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobai Bicycle Future Traffic Laboratory Wuhan Station. Wuhan Transportation Development Strategy Research Institute 2017 Wuhan Shared Bicycle Travel Report; Wuhan Transportation Development Strategy Research Institute: Wuhan, China, 2017; p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.T.; Liao, M.Z.; Liu, C.L. Acquiring and Geo-Visualizing Aviation Carbon Footprint among Urban Agglomerations in China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Abel, G.J.; Muttarak, R.; Liu, S.H. Circular visualization of China’s internal migration flows. Environ. Plan. A 2017, 49, 2432–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyla, D.; Mehdi, P.; Eftekhari, A.R.; Hasan, A. The identification and zoning of areas having rural deteriorated textures in the Tehran province by using KDE and GIS. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2019, 25, 475–504. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, X.J.; Wu, Z.F.; Cheng, J. Using kernel density estimation to assess the spatial pattern of road density and its impact on landscape fragmentation. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2013, 27, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.H.; Chen, C.; Xiu, C.L.; Zhang, P.Y. Location analysis of retail stores in Changchun, China: A street centrality perspective. Cities 2014, 41, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Kwan, M.P.; Yang, L.; Zhou, S.; Zuo, Z.; Wan, B. Evaluating the accessibility of healthcare facilities using an integrated catchment area approach. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Nakamura, A.; Mukuda, K.; Harada, M.; Kotani, K. Potential accessibility scores for hospital care in a province of Japan: GIS-based ecological study of the two-step floating catchment area method and the number of neighborhood hospitals. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2017, 26, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingram, D.R. The concept of accessibility: A search for an operational form. Reg. Stud. J. Reg. Stud. Assoc. 1971, 5, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Ai, T.H.; Yang, W.; Zhang, X.; Xin, R.; Chen, X.Y. Visual analysis of residents travel pattern based on Circos Graph. J. Cent. China Norm. Univ. 2016, 50, 471–480. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).