Abstract
Background: Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) is a chronic and aggressive liver disease that rapidly evolves into cirrhosis and end-stage liver disease if not timely diagnosed and treated with immunosuppressive therapy. AIH is classified into type 1 and type 2 according to the autoantibody pattern, with smooth muscle antibodies and/or antinuclear antibodies as serological markers of AIH-1, while antiliver cytosol antibody type 1 and/or antiliver/kidney microsomal antibody type 1 characterize type 2 AIH, which mainly affects children, including infants, and adolescents. Case Summary: We describe a case of type 2 AIH, clinically onset in a 34-year-old woman with decompensated cirrhosis. Only a thorough analysis of the autoantibody profile allowed for a diagnosis of an AIH-2 evolved into cirrhosis. The patient received a moderate corticosteroid therapy without achieving optimal disease control. We discuss the controversial decision of whether or not to treat the patient with immunosuppressive therapy, which should be balanced with the potential risk of infectious and other complications. A review of the literature on the management of patients with autoimmune cirrhosis is also presented. Conclusions: AIH-2 can be clinically onset in adult patients with cirrhosis and its complications, without being preceded by major clinical signs. Due to the difficult management of cirrhosis with immunosuppressive treatments, a patient-tailored strategy with a case-by-case approach is needed to prevent major complications such as infections, potentially precluding liver transplantation the only curative therapy.
1. Introduction
Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) is a chronic and severe liver disease of unknown etiology, which mainly affects young women and can quickly develop into cirrhosis and end-stage liver disease if not timely diagnosed and treated with immunosuppressive therapy [1,2,3].
AIH is historically classified into type 1 and type 2 based on the autoantibody profile, with antinuclear antibodies (ANA) and/or smooth muscle antibodies (SMA) as serological markers of AIH type 1, while liver/kidney microsomal type 1 (LKM1) autoantibody and/or liver cytosol antibody type 1 (LC1) autoantibody characterize AIH type 2. The detection of a further autoantibody named anti-soluble liver antigen (anti-SLA/LP) in ANA, SMA and LKM1 seronegative patients has resulted in the proposal of a third type of AIH [4]. Therefore, in the 1990s, on the basis of the autoantibody profile, AIH was classified into three main types: type 1 characterized by ANA and/or SMA positivity, type 2 marked by anti-LKM1 anti-LC1, and finally type 3 exhibiting anti-SLA antibodies.
The identification of occasional patients with all the clinical, biochemical and histological features of AIH, including an overt response to an immunosuppressive treatment, but lacking one of the recognized autoantibody markers, has suggested the hypothesis of a fourth type of AIH, called ‘autoantibody-negative’ AIH. [5,6]. The subclassification of AIH into two forms, type 1 and type 2, seems to have a certain relevance in pediatric settings: anti-LKM1 positive forms are characteristic of children with higher levels of bilirubin and transaminases at onset who more frequently present fulminant liver failure, while the presence of cirrhosis in the baseline biopsy and a severely compromised liver function is more frequent in AIH-1 [7,8].
The clinical course of AIH is characterized by fluctuated periods of decreased or increased activity, and therefore its clinical presentation is variable, ranging from no symptoms to severe acute hepatitis and even fulminant hepatic failure. Most common clinical phenotypes (almost two-thirds of patients) are characterized by one or more nonspecific symptoms like fatigue, mild pain in the right upper quadrant, lethargy, malaise, anorexia, nausea, pruritus, jaundice and arthralgia.
The “acute” presentation of AIH includes two distinct clinical forms: the acute exacerbation of chronic AIH and ‘true’ acute AIH without histological features of chronic disease. One-third of patients at diagnosis have progressed to cirrhosis regardless of the presence or absence of symptoms, suggesting a diagnostic delay owing to unfamiliar physicians and laboratories [1,2].
However, while the patterns of clinical presentation of type 1 AIH are widely described, for type 2 AIH the available data are more limited [9,10,11].
Immunosuppressive therapy with corticosteroids and other immunosuppressive agents is the standard treatment of AIH, while liver transplantation (LT) is the only available treatment for patients with advanced/end-stage liver disease [10].
While treatment of AIH in noncirrhotic patients is well established with adequate proof that response to immunosuppressive therapy ensures a good prognosis, very little data are available on the optimal management of patients presenting with cirrhosis. Here, we report a very rare and poorly described LKM1/LC1-positive AIH-2 in an adult patient who presented with decompensated cirrhosis and discuss the difficulty of managing autoimmune cirrhosis and the need for a personalized approach in the choice of therapy and patient management.
2. Case Presentation
We report the case of a 34-year-old woman admitted to the local hospital for an incidental finding of thrombocytopenia (34,000/mm3), INR elevation (1.6), moderate hypertransaminasemia (AST/ALT: 81/122 U/L, limit of normal: 40 U/L), hyperbilirubinemia (2.9 mg/dL), hypoalbuminemia (26 g/L) and serum IgG elevation (3213/1600 mg/dL).
From a clinical point of view, she had abdominal distension that appeared progressively over the last four weeks. The clinical-laboratory profile was therefore suggestive of cirrhosis with ascitic decompensation, Child–Pugh B10 and MELD 15. Her past medical history was negative, while her family history only documented autoimmune thyroiditis in her mother. Laboratory tests excluded HBV-, HCV-, CMV- and EBV-related hepatitis. The serum levels of ceruloplasmin, alpha1-antitrypsin and ferritin were normal. She also exhibited a selective IgA deficiency (7 mg/dL) and autoimmune hypothyroidism. The abdominal ultrasound showed signs of cirrhosis with portal hypertension, splenomegaly and moderate–severe ascites. The upper gastrointestinal endoscopy showed esophageal varices F1 without red signs. Diuretic therapy was set with furosemide, potassium canrenoate and albumin infusion. After obtaining a clinical improvement, the patient was sent to our Center for suspected autoimmune liver disease in light of the marked increase in serum IgG. We performed an accurate diagnostic work-up and the search for non-organ-specific autoantibodies (NOSA) by standard indirect immunofluorescence (IIF) technique showed anti-LKM1 autoantibody positivity at a titre of 1:1260 (Figure 1A,B).
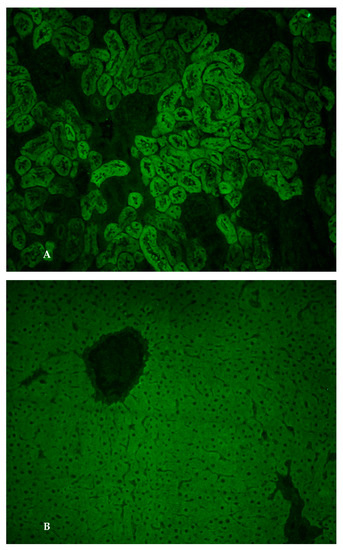
Figure 1.
(A). Anti-liver kidney microsomal type 1 antibodies. Immunofluorescence pattern of anti-liver kidney microsomal type 1 antibodies (anti-LKM-1) on a rodent kidney section: they stain the third portion of the larger proximal tubules (magnification 20×); (B). Anti-liver kidney microsomal type 1 antibodies. Immunofluorescence pattern of anti-liver kidney microsomal type 1 antibodies (anti-LKM-1) on a rodent liver section: homogenous staining of the hepatocyte cytoplasm throughout the liver lobule (magnification 20×).
To confirm the finding of LKM1 positivity in the absence of HCV infection, a more accurate second level technique was performed with immunoblot (Liver Profile, Euroimmune, Lübeck, Germany), which showed a strong positivity for LKM1 and LC1, thus confirming an autoantibody profile typical for AIH-2.
Liver biopsy was performed and showed cirrhosis with moderate inflammatory activity (stage 5, grading 8 according to the Ishak scoring system), with the presence of plasma cell clusters, interface hepatitis and rosettes (Figure 2A–C).
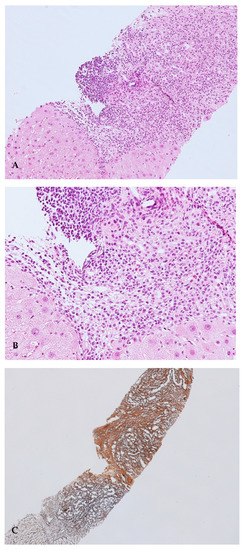
Figure 2.
(A). Portal tracts show a moderate-to-severe inflammatory infiltrate, with interface hepatitis. Haematoxylin–Eosin (HE) stain, 10× magnification; (B). At a high magnification, portal tract inflammatory infiltrate is mainly composed of lymphocytes, plasma cells and rare eosinophils granulocytes. Haematoxylin–Eosin (HE) stain, 20× magnification; (C). Areas of dense fibrosis are present (upper right), as well as areas of collapse of the lobular architecture (lower left). Reticulin silver stain, 4× magnification.
The revised score of the International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group (IAHG) was 23, while the simplified score was 8, both scores being indicative of defined AIH [1,4,12]. Table 1 shows the clinical-laboratory picture at diagnosis.

Table 1.
Patient laboratory parameters at diagnosis.
After the resolution of ascites, in view of the hypertransaminasemia (2–3× UNL), histological grading and high IgG values indicative of active disease, after a collegial discussion, we considered it appropriate to start a steroid therapy with prednisone at 15 mg/day with the aim of suppressing the residual inflammatory activity, minimizing the risk of infectious complications and given the recent episode of ascitic decompensation.
In light of the severe liver function impairment and the risks associated with immune suppressive therapy, the patient was evaluated and listed for LT.
Two months later, there was a reduction in the AST-ALT serum levels (1.5–2× UNL), hyperbilirubinemia (1.5 mg/dL) and a normalization of the serum IgG (1500 mg/dL), and in view of acceptable platelet (120.000/mmc), hemoglobin (13 g/dL) and white blood cell (5.500/mmc) values, azathioprine (50 mg/day) was added with steroid tapering up to a maintenance daily dose of 7.5 mg, given the failure to normalize transaminases and the persistent γGT elevation.
Due to the persistent AST/ALT and γGT elevation and IgA deficiency, in June 2019 she underwent a magnetic resonance (MR) cholangiography that did not show bile duct stones or biliary obstruction, and an IgG antitissue transglutaminase assay that turned out negative. The histological and radiological (MR) aspects, as well as AMA, PBC-specific ANAs (anti-sp100 and anti-gp210) and pANCA negativity, ruled out the hypothesis that the persistent γGT elevation could be a possible sign of an AIH-PBC or AIH-primary sclerosing cholangitis overlap syndrome [13,14,15].
During the follow-up, the patient presented two episodes of Streptococcus Pneumoniae sepsis respectively in December 2019 and June 2020, with a concomitant worsening of the liver function (Child–Pugh and MELD scores up to B9 and 18, respectively) and a need to discontinue the immunosuppressive treatment.
In September 2020, she showed mild hypertransaminasemia (AST-ALT: 1.5–1.6× UNL), a persistent γGT elevation (6.8× UNL) in the absence of ascites, with Child–Pugh B8 and MELD 14. Table 2 summarizes the clinical history of the patient with the trend of her laboratory parameters.

Table 2.
Patient history in a timeline format.
Currently, the patient is clinically stable, liver disease appears to be compensated, but transaminases are fluctuating (1.5–2× UNL), and the disease activity does not seem to be affected by immunosuppressive therapy, which cannot be further increased due to the risk of infectious complications. Unfortunately, depending on waiting list capabilities, the MELD score has never been so deteriorated to allow LT.
3. Discussion
In our opinion, this case report features at least three aspects of clinical relevance. First, the patient presented a clinical onset of AIH-2 in adulthood with decompensated cirrhosis. The patient is therefore likely to have previously presented a clinical course of “insidious” AIH with the development of cirrhosis and its complications over time without any previous signs. This clinical presentation has been described for type 1 AIH but, to our knowledge, has never been previously reported in AIH-2, classically characterized by a clinical onset in childhood [9,10,11,12].
Second, this case emphasizes that the detection of autoantibodies plays a pivotal role in the differential diagnosis of cirrhosis of unknown origin. Both the laboratory personnel and the clinician need to become more familiar with the interpretation of the liver autoimmune serology to derive a maximum benefit for the patient, as recommended by a pivotal paper of the International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group [16].
According to the IAHG recommendations, anti-LC1 can be detected by IIF using the standard tissue panel, and it stains the cytoplasm of liver cells with relative sparing of the centrilobular area. However, it is usually obscured by the concurrent presence of anti-LKM-1, which stains hepatocyte cytoplasm throughout the lobule [16,17].
Due to the concomitant presence of LKM1 autoantibodies, in our patient LC1 autoantibodies could be only revealed by immunoblot. Therefore, the search for LC1 should also be carried out using second-level, more sensitive diagnostic tools such as immunoblot, which is not affected by the simultaneous positivity of LKM1 that would instead reduce the sensitivity of the IIF.
Since LKM1 and LC1 autoantibodies are classically associated with the pediatric autoimmune hepatitis (AIH-2), the search for these autoantibodies might not be taken into account in adult patients. Our case emphasizes the need to search for autoantibodies of AIH-2 diagnostic relevance, such as LKM1and LC1, in cirrhosis of undetermined etiology in adult patients also, since, even if AIH starts in childhood, the disease could run a chronic course over years, leading into adulthood [18].
A further feature of this case, which is clinically relevant and therefore deserves to be emphasized, is the presence of IgA deficiency, a common finding in patients with AIH-2, as previously reported [19].
The only study addressing the management of decompensated autoimmune cirrhosis was, however, only focused on type 1 AIH patients and compared 64 patients treated with corticosteroids with 18 patients not receiving any corticosteroids; the study showed that survival was greater in the corticosteroid-treated group, with the benefit being greatest in patients with the greatest decrease in total bilirubin at day 7 after starting corticosteroid therapy [20].
Third, this case effectively demonstrates that the decision to establish immunosuppressive therapy is not unequivocal in a cirrhotic patient with a modest histological inflammatory activity. The literature data are heterogeneous and describe both experiences in which the response to immunosuppressive therapy of cirrhotic patients was optimal, with survival similar to that of patients without cirrhosis, and also experiences in which cirrhosis represented a negative prognostic factor both in terms of the response to therapy and in terms of the prognosis "quoad vitam" [12,20,21,22,23,24,25].
The treatment of patients with AIH that has progressed to cirrhosis remains critical unless contraindicated by associated comorbidities. Cirrhosis at diagnosis has been reported to be a predictor of shorter survival and is associated with the need for LT [26]. The finding of inflammatory activity upon biopsy in patients with cirrhosis would require treatment, as a failure to normalize histological inflammation is associated with a lower chance of fibrosis regression and worse overall survival [20,27].
In fact, the improvement of inflammatory activity and fibrosis may explain previous findings of similar survival rates between patients with and without cirrhosis at diagnosis [28].
However, the impact of immunosuppressive therapy on the overall outcome could be minimal at best and may even increase the risk of drug-related side effects [23,29].
On the other hand, current international guidelines would suggest treating all patients with cirrhosis and a degree of histological activity [30].
Our case would thus suggest the need to individualize the therapeutic decision for each patient with AIH and a mild histological activity, evaluating the potential risks resulting from immunosuppressive therapy, such as infections.
Of course, these patients need to be listed primarily for LT, which remains the only viable option for AIH-related cirrhosis [12,25,26].
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, this case clearly shows that AIH-2 can have a clinical onset in adult patients with cirrhosis and its complications without being preceded by major clinical signs.
Due to the difficult management of cirrhosis with immunosuppressive treatments, a multidisciplinary approach may lead to an appropriate diagnosis and management of such difficult cases.
A patient-tailored strategy with a case-by-case approach is needed to prevent major complications such as infections potentially precluding LT, the only curative therapy.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.M, A.G.; Methodology, A.G., M.L., L.M., F.V., P.M.; Investigation, A.G., S.P., C.R., M.F., L.M., M.L., T.F., P.M.; Data Curation, A.G., P.M.; Writing—original draft preparation, A.G., P.M.; Writing—review and editing, A.G., P.M., L.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by Ethics Committee of “Comitato Etico di Aerea Vasta Emilia Centro” (protocol code 405/2018/Oss/AOUBo 18/07/2018).
Informed Consent Statement
The patient provided informed consent.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Zachou, K.; Muratori, P.; Koukoulis, G.K.; Granito, A.; Gatselis, N.; Fabbri, A.; Dalekos, G.N. Review article: Autoimmune hepatitis—current management and challenges. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 38, 887–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muratori, P.; Granito, A.; Quarneti, C.; Ferri, S.; Menichella, R.; Cassani, F.; Pappas, G.; Bianchi, F.B.; Lenzi, M.; Muratori, L. Autoimmune hepatitis in Italy: The Bologna experience. J. Hepatol. 2009, 50, 1210–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czaja, A.J. Review article: The management of autoimmune hepatitis beyond consensus guidelines. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 38, 343–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muratori, L.; Muratori, P.; Granito, A.; Pappas, G.; Cassani, F.; Lenzi, M. Current topics in autoimmune hepatitis. Dig Liver Dis. 2010, 42, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarlane, I.G. The relationship between autoimmune markers and different clinical syndromes in autoimmune hepatitis. Gut 1998, 42, 599–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czaja, A.J. Autoantibody-negative autoimmune hepatitis. Dig. Dis Sci. 2012, 57, 610–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggiore, G.; Bernard, O.; Homberg, J.-C.; Hadchouel, M.; Alvarez, F.; Hadchouel, P.; Odièvre, M.; Alagille, D. Liver disease associated with anti-liver-kidney microsome antibody in children. J. Pediatr. 1986, 108, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muratori, P.; Granito, A.; Pappas, G.; Muratori, L.; Lenzi, M.; Bianchi, FB. Autoimmune liver disease 2007. Mol Aspects Med. 2008, 29, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanos, D.P.; Mieli-Vergani, G.; Vergani, D. Liver-kidney microsomal antibody-positive autoimmune hepatitis in the United States. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2001, 96, 3447–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homberg, J.C.; Abuaf, N.; Bernard, O.; Islam, S.; Alvarez, F.; Khalil, S.H.; Poupon, R.; Darnis, F.; Lévy, V.G.; Grippon, P.; et al. Chronic active hepatitis associated with antiliver/kidney microsome antibody type 1: A second type of "autoimmune" hepatitis. Hepatology 1987, 7, 1333–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchini, A.; McHutchison, J.G.; Pockros, P.J. LKM-positive autoimmune hepatitis in the western United States: A case series. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 95, 3238–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, C.L.; Adams, D.; Assis, D.N.; Kerkar, N.; Manns, M.P.; Mayo, M.J.; Vierling, J.M.; Alsawas, M.; Murad, M.H.; Czaja, A.J. Diagnosis and Management of Autoimmune Hepatitis in Adults and Children: 2019 Practice Guidance and Guidelines from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2020, 72, 671–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granito, A.; Muratori, P.; Quarneti, C.; Pappas, G.; Cicola, R.; Muratori, L. Antinuclear antibodies as ancillary markers in primary biliary cirrhosis. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2012, 12, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granito, A.; Muratori, P.; Ferri, S.; Pappas, G.; Quarneti, C.; Lenzi, M.; Bianchi, F.B.; Muratori, L. Diagnosis and therapy of autoimmune hepatitis. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 847–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muratori, L.; Cassani, F.; Pappas, G.; Guidi, M.; Mele, L.; Lorenza, V.; Lenzi, M.; Bianchi, F.B.; Muratori, P. The hepatitic/cholestatic "overlap" syndrome: An Italian experience. Autoimmunity 2002, 35, 565–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergani, D.; Alvarez, F.; Bianchi, F.B.; Cançado, E.L.; Mackay, I.R.; Manns, M.P.; Nishioka, M.; Penner, E. International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group. Liver autoimmune serology: A consensus statement from the committee for autoimmune serology of the International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group. J. Hepatol. 2004, 41, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terziroli Beretta-Piccoli, B.; Mieli-Vergani, G.; Vergani, D. The clinical usage and definition of autoantibodies in immune-mediated liver disease: A comprehensive overview. J. Autoimmun. 2018, 95, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mieli-Vergani, G.; Vergani, D.; Czaja, A.J.; Manns, M.P.; Krawitt, E.L.; Vierling, J.M.; Lohse, A.W.; Montano-Loza, A.J. Autoimmune hepatitis. Nat. Rev. Dis Primers 2018, 4, 18017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorio, G.V.; Portmann, B.; Reid, F.; Donaldson, P.T.; Doherty, D.G.; McCartney, M.; Mowat, A.P.; Vergani, D.; Mieli-Vergani, G. Autoimmune hepatitis in childhood: A 20-year experience. Hepatology 1997, 25, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Sheng, L.; Yang, Y.; Yang, F.; Xiao, X.; Hua, J.; Guo, C.; Wei, Y.; Tang, R.; Miao, Q.; et al. The Management of Autoimmune Hepatitis Patients with Decompensated Cirrhosis: Real-World Experience and a Comprehensive Review. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2017, 52, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, H.A.; Czaja, A.J. The role of histologic evaluation in the diagnosis and management of autoimmune hepatitis and its variants. Clin. Liver Dis. 2002, 6, 685–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiniakos, D.G.; Brain, J.G.; Bury, Y.A. Role of Histopathology in Autoimmune Hepatitis. Dig. Dis. 2015, 33 (Suppl. 2), 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feld, J.J.; Dinh, H.; Arenovich, T.; Marcus, V.A.; Wanless, I.R.; Heathcote, E.J. Autoimmune hepatitis: Effect of symptoms and cirrhosis on natural history and outcome. Hepatology 2005, 42, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czaja, A.J. Difficult treatment decisions in autoimmune hepatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 934–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manns, M.P.; Czaja, A.J.; Gorham, J.D.; Krawitt, E.L.; Mieli-Vergani, G.; Vergani, D.; Vierling, J.M.; American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Diagnosis and management of autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatology 2010, 51, 2193–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirstein, M.M.; Metzler, F.; Geiger, E.; Heinrich, E.; Hallensleben, M.; Manns, M.P.; Vogel, A. Prediction of short- and long-term outcome in patients with autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatology 2015, 62, 1524–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaliwal, H.K.; Hoeroldt, B.S.; Dube, A.K.; McFarlane, E.; Underwood, J.C.; Karajeh, M.A.; Gleeson, D. Long-Term Prognostic Significance of Persisting Histological Activity Despite Biochemical Remission in Autoimmune Hepatitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 110, 993–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, S.K.; Therneau, T.M.; Czaja, A.J. Prognosis of histological cirrhosis in type 1 autoimmune hepatitis. Gastroenterology 1996, 110, 848–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe, M.; Go, V.L.; Kluge, D. Prednisone for chronic active hepatitis: Pharmacokinetics and serum binding in patients with chronic active hepatitis and steroid major side effects. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 1984, 6, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Autoimmune hepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 971–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).