Abstract
To address the continuous growth in high-speed ubiquitous access required by residential users and enterprises, Telecommunication operators must upgrade their networks to higher data rates. For optical fiber access networks that directly connect end users to metro/regional network, capacity upgrade must be done in a cost- and energy-efficient manner. 40 Gb/s is the possible lane rate for the next generation passive optical networks (NG-PONs). Ideally, existing 10 G PON components could be reused to support 40 Gb/s lane-rate NG-PON transceiver, which requires efficient modulation format and digital signal processing (DSP) to alleviate the bandwidth limitation and fiber dispersion. The major contribution of this work is to offer insight performance comparisons of 40 Gb/s lane rate electrical three level Duobinary, optical Duobinary, and four-level pulse amplitude modulation (PAM-4) for incorporating low complex DSPs, including linear and nonlinear Volterra equalization, as well as maximum likelihood sequence estimation. Detailed analysis and comparison of the complexity of various DSP algorithms are performed. Transceiver bandwidth optimization is also undertaken. The results show that the choices of proper modulation format and DSP configuration depend on the transmission distances of interest.
1. Introduction
The continuous growth of bandwidth demand from residential users and enterprises urgently pushes telecommunication operators to upgrade the capacity of access networks to higher data rates. Among various access technologies that connect end users to metropolitan or regional networks, the passive optical network (PON) is the most efficient one, as it does not require any active components such as switches in the optical distribution network (ODN), instead, a passive power splitter or a wavelength router is usually deployed in the remote node. Figure 1 shows the standardization roadmap of PONs released by FSAN in November 2016. The roadmap not only shows the evolving history of PONs, but also predicts the future PONs beyond today’s standardized NG-PON2 which adopts time/wavelength division multiplexing (TWDM) technology capable of delivering 40 Gb/s transmission over four wavelengths [1]. The future access networks have to offer more features, such as system reconfigurability, flexibility, and a high availability of network equipment. Among these features, high capacity and long reach are of great importance, because of the significant bandwidth demand from emerging high-speed mobile services such as 5G Infrastructure Public Private Partnership (5G PPP) which anticipates to cope with a 1000-fold increase in data traffic, as well as the Internet of things (IoT). Low-cost mobile front-haul will become one of the major drivers for optical access networks. To meet the emerging service requirements, the roadmap also indicates that alternative ODNs such as wavelength-routed ODN (namely WDM-PONs) may also be considered, especially for green field deployments.
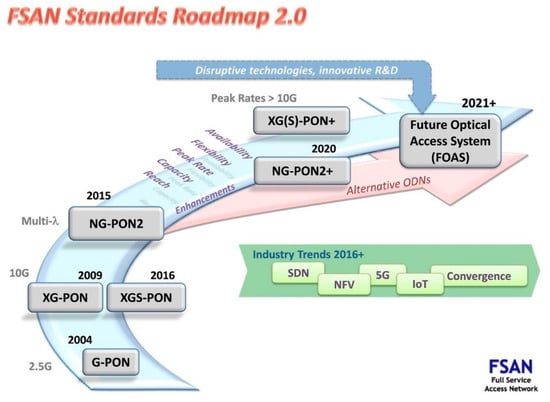
Figure 1.
FSAN standard roadmap released in 2016.
Intensive research has been performed on upgrading today’s TWDM-PON from its 10 Gb/s lane data rate into 25 Gb/s or 40 Gb/s. Much effort has been made to delivering beyond 10 Gb/s data by using existing 10-G, optics in order to upgrade the capacity of PONs in a cost and energy-efficient manner. Example demonstrations include 25 Gb/s, 40 Gb/s, or 50 Gb/s electrical Duobinary [2,3,4,5,6], optical Duobinary [3,5,6,7], and four-level pulse amplitude modulation (PAM-4) [2,4,5,6,8]. More complex multi-band or multi-carrier modulation schemes [9,10] have also been demonstrated. These schemes have shown the feasibility of supporting 25 Gb/s or 40 Gb/s data rates using 10-G transmitters [2,3,7,8] and/or 10-G receivers [2,3], and thus they can offer low-cost solutions. The measurements use either optical domain dispersion compensation [2,3], or simple digital signal processing (DSP) for dispersion compensation [4,5,6,7,8]. DSP is vital for enabling a practical low-cost realization of high-speed next-generation (NG) PON, without changing the optical infrastructure. In addition, DSP-based schemes have relatively simple transceiver structure, and thus they are potentially cost- and energy-efficient solutions.
Despite various NG-PONs beyond the 10 Gb/s lane rate having been demonstrated, a fair complete comparison between different modulation schemes under a wide range of DSP configurations has been lacking. Electrical/optical Duobinary and PAM-4 represent relatively simple and efficient schemes for practical implementations. By examining and comparing the achievable performance and DSP complexity between 40 Gb/s lane rate electrical/optical Duobinary and PAM-4 NG-PONs, the choice of the optimum modulation scheme and DSP configuration would be identified for different application scenarios. This includes different cases with different fiber distances, and whether advanced or low-complex DSPs should be considered. The more complex multi-band or multi-carrier schemes may find superior advantages in long-reach PONs [9]; however, here we focus on the maximum achievable performance for simple single carrier schemes. This work extends our previous work in [11,12] via contributing a fair performance comparison between all three schemes by considering symbol-spaced equalization, including both linear and nonlinear equalizers. A low complex maximum likelihood estimation equalization has also been considered for the first time. This work distinguishes from previous work [4,5,6] where comparison between different modulation formats is made by using DSP with similar complexities, and with the same feedforward equalizer (FFE)/decision feedback equalizer (DFE) tap count and maximum likelihood sequence estimation (MLSE) state count, although Duobinary schemes can use a smaller number of MLSE states. An analysis and comparison of the complexity of all equalization strategies are also undertaken in the present contribution. Results show that the choice of proper modulation format and the DSP configuration depends on the transmission distances of interest.
2. System Architecture and Simulation Parameters
The WDM-PON architecture with downstream transceivers is depicted in Figure 2a, based on electrical Duobinary modulation. Figure 2b,c is for optical Duobinary and PAM-4, respectively, which adopts the same WDM-PON architecture that is shown in Figure 2a. For the electrical Duobinary case, the optical line terminal (OLT) transmitter simply consists of a digital pre-coder conventional and an external electro-absorption modulator (EAM). The transmitter is like a non-return-to-zero (NRZ) transmitter. The pre-coder helps to overcome the error propagation in decoding. The EAM output signal passes through a fiber link, which is comprised of a WDM multiplexer (MUX), a standard single-mode fiber (SMF), and a WDM de-multiplexer (De-MUX), which is in the remote node, to select the signal of a specific wavelength to a targeted optical network unit (ONU). At the ONU receiver, the transmitted signal is detected by an avalanche photo-detector (APD), and then recovered by DSP. The DSP includes a nonlinear equalizer, a low complex MLSE, and a Duobinary-to-NRZ convertor that which is based on two-threshold slicers, followed by an exclusive-or (XOR) gate [3]. The equalizer performs as a duobinary filter targeting a three-level Duobinary signal.
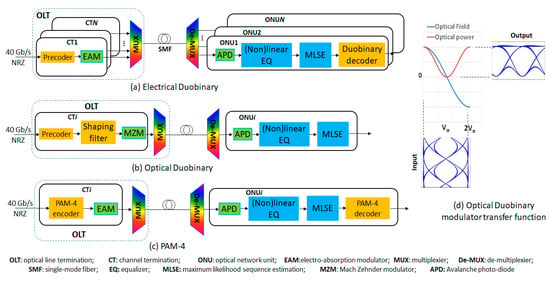
Figure 2.
Schematic architectures of 40 Gb/s lane rate NG-PON downstream links with (a) electrical Duobinary; (b) optical Duobinary; and (c) PAM-4 formats; (d) the optical Duobinary modulator transfer function where the Mach-Zehnder modulator (MZM) is biased at the null point, and the eye-diagrams correspond to the electrical driving signal, and the output optical intensity signal.
For optical Duobinary, the transmitter consists of a pre-coder, a shaping filter and a Mach-Zehnder modulator (MZM). The shaping filter is designed to generate a three-level electrical Duobinary waveform, as indicated in Figure 2d. A fully driven MZM with a push–pull configuration is used for both amplitude and phase modulations for optical Duobinary signals. The MZM is biased at the null point; thus the output signal has only two intensity levels, as indicated in Figure 2d. The receiver is a simple NRZ receiver. The receiver DSP also consists of a nonlinear equalizer and a MLSE.
For PAM-4, the transmitter has a bits-to-symbol encoder and an EAM. The receiver also incorporates an APD, a nonlinear equalizer followed by a MLSE, and a symbol-to-bits decoder.
It should be noted that MLSE is also considered for nonlinear equalization operation. MLSE is especially efficient for compensating channel memory-caused inter-symbol interference (ISI). The MLSE process involves Trellis, as defined by states and branches, which analyze the KL+1 branches per each symbol, where K is the alphabet size of the modulation scheme, and L is the memory length. The MLSE processor chooses the path with the smallest metric, and produces the most likely sequence by tracing back [13]. The complexity of MLSE is exponentially proportional to memory length. Therefore, we limit the memory length to 2 for electrical/optical Duobinary and 1 for PAM-4, so that all three schemes have four states of MLSE. Electrical/optical Duobinary can also incorporate 2-state MLSE with a memory length of 1.
The MZM used for optical Duobinary is configured in a push-pull mode, and it has zero chirp. Comparatively, both electrical Duobinary and PAM-4 uses an EAM, which considers the chirp model based on experimental measurements [14] and behaves a negative chirp. The detailed modeling of EAM can be found in [11]. The model reveals an important relationship relating the carrier frequency deviations with the power variations through the time-dependent chirp-parameter for electro-absorption modulated lasers (EMLs). It is essentially similar to, but slightly different from the frequency chirp model that is used for the directly modulated laser [15]. The receiver equalizer for each scheme is similar. The equalizer is based on an FFE) and DFE structure, and includes both linear and nonlinear terms. The nonlinear part includes only the second-order Volterra kernels, and higher order kernels are discarded due to complexity reasons. The considered equalizer can be further simplified for considerations of practical implementation, since ONU receivers are very cost-sensitive. The FFE/DFE filter is expressed by [12]:
where M(N) is the FFE(DFE) filter order. y(y′) denotes the filter input(output) sample. The first term on the right-hand-side of Equation (1) is the linear part, and the remainder is the nonlinear part.
For our simulations, MatLab is used, and all models are self-developed. A Gaussian response lowpass filter (LPF) is used to model the joint frequency response of a driver and an EAM. The Gaussian LPF may cover the effect of an analogue digital-to-analogue convertor (DAC), where it is needed in practical systems. In addition, the optical Duobinary transmitter requires a shaping filter that adopts a fifth-order Bessel filter model. The shaping filter bandwidth is optimized, and the identified optimum value is approximately 17 GHz [11]. The APD-trans-impedance amplifier (TIA) receiver is used for all systems [11], and a LPF model covers the joint frequency response of the ADP-TIA, and an analogue-to-digital convertor (ADC). The APD-TIA thermal noise and shot noise model is based on that presented in [16], and the key parameters include an average APD gain of 4, an amplifier noise figure of 2, an ionization constant of 0.5, and a dark current of 25 nA. The Volterra filter consists of 7-tap symbol-spaced FFE and 5-tap DFE (M = 7, N = 5) which correspond to 12 linear taps and 38 second-order nonlinear taps. Note that in practical implementations, there significant parts of the second-order Volterra kernel terms, having very small weights; thus, the complexity can be reduced significantly by disabling these negligible terms, but without degrading their performance [17]. A feedforward error correction (FEC) RS(255,223) with a threshold bit error rate (BER) of 1.0 × 10−3 is assumed, which has been adopted in 10G Ethernet PON standard. The transmitter output optical power is set to be 10 dBm, and the signal carrier wavelength is 1550 nm. A split-length SMF model is adopted with a fiber loss of 0.2 dB/km, a chromatic dispersion of 17 ps/km/nm, and a nonlinear coefficient γ = 1.3 W−1/km. A second-order optical band-pass Gaussian filter is considered to model the MUX/De-MUX with a 40 GHz 3 dB bandwidth, which corresponds to a 50G WDM grid. A responsivity of 3.2 A/W is used for the optical receiver. Note that the optimization of the thresholds is performed in the receiver decoders for all cases.
3. Simulation Results
3.1. Optimization of Transceiver Bandwidth
Figure 3 shows the optimization of 40 Gb/s PAM-4 transceiver bandwidths, and the dependence of PAM-4 receiver sensitivity at a BER of 1 × 10−3 on chromatic dispersion subject to different transceiver bandwidths is shown in the figure. It clearly indicates that there exists an optimum transmitter/receiver bandwidth, corresponding to which PAM-4 has the best dispersion tolerance, and/or the maximum receiver optical power sensitivity. The optimum transmitter bandwidth is identified to be 20 GHz, which gives rise to the best trade-off between dispersion tolerance and receiver sensitivity. This is attributed to the fact that a larger transmitter bandwidth allows less ISI but experiences a stronger impact of chromatic dispersion. The optimum receiver bandwidth is 12.5 GHz, which is mainly determined by two factors: the receiver noise and the receiver-caused ISI. The optimization of transceiver bandwidths for 40-Gb/s electrical Duobinary and optical Duobinary is similar, which has been detailed in [18] and [11], respectively. The optimum transmitter/receiver bandwidth for electrical Duobinary (optical Duobinary) is 25 GHz/12.5 GHz (17 GHz/17.5 GHz) [11,18]. Note that the 50 G-ITU grid is adopted for all cases. It is worth mentioning that the system performance not only depends on transceiver 3-dB bandwidth, but can also be affected by the spectral profile beyond the 3 dB bandwidth frequency [5].
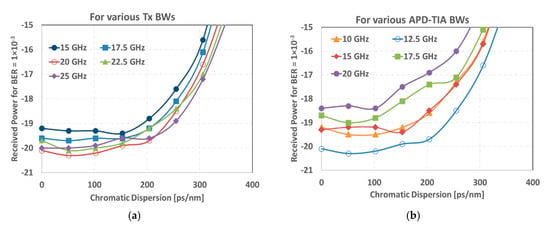
Figure 3.
Receiver sensitivity versus fiber dispersion for PAM-4, subject to various (a) transmitter bandwidths and (b) avalanche photo-detector trans-impedance amplifier (APD-TIA) receiver bandwidths. An Rx bandwidth of 12.5 GHz is used in (a), and a Tx bandwidth of 20 GHz is used in (b). (De-)MUX filters as shown in Figure 2 are included. Only seven tap feedforward equalizer (FFE) and five tap decision feedback equalizer (DFE) with first-order terms are considered.
3.2. Transmission Performance
By adopting the identified optimum transceiver bandwidth, the receiver optical power sensitivity for each modulation scheme is shown in Figure 4 at different fiber distances. The optical power sensitivity is obtained at a FEC threshold BER of 1 × 10−3. The performance comparison considers four receiver signal processing cases: without equalization, which adopts only simple threshold devices in the receiver side [11], linear equalization only, linear and nonlinear equalizations, and MLSE together with (non-)linear equalizations. Figure 2a shows the optical Duobinary system where the optical sensitivity shows little variation with different SMF lengths within 10 km, beyond which the power penalty increases with increasing fiber length. Without equalization, the system shows the worst power sensitivity at all considered fiber lengths. Linear equalization brings about a slightly improvement in power sensitivity, compared to the no equalization case, which agrees with published results in [19]. The optical Duobinary performance is dominated by the nonlinear interaction of MZM modulation response with fiber dispersion. Such a nonlinear effect is further enhanced by the three-level signal to two-level signal transformation upon the square-law direct detection [11]. Not surprisingly, nonlinear equalization enables an approximately 1dB improvement in sensitivity at different fiber lengths compared to the case without equalization. The MLSE can further improve the power sensitivities for fiber lengths beyond 10 km. Significant improvement is achievable when the number of MLSE states increases from 2 to 4. Only nonlinear equalization and MLSE enable an SMF transmission distance of 20 km, and a 4-state MLSE can further achieve 25 km of SMF transmission.
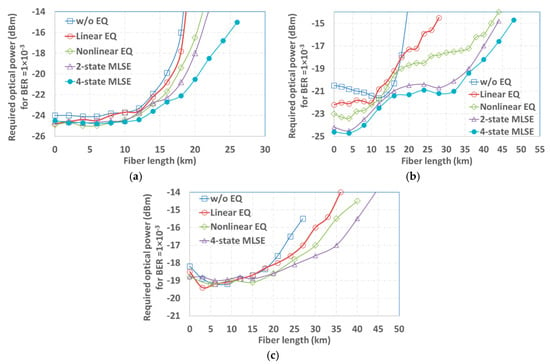
Figure 4.
Optical power sensitivity at a bit error rate (BER) of 10-3 versus fiber lengths for (a) optical Duobinary; (b) electrical Duobinary; and (c) PAM-4 subject to different post-equalization and detection conditions. For receiver digital signal processing (DSP), the following configurations are considered: without equalization (w/o EQ) where no DSP considered; linear EQ, which uses only 7-tap/5-tap linear FFE/DFE; nonlinear EQ includes both linear FFE/DFE terms and second-order nonlinear FFE/DFE terms; maximum likelihood sequence estimation (MLSE) contains linear and nonlinear EQ, as well as 2- or 4-state MLSE. Unless indicated explicitly, the four DSP configurations apply throughout this work.
Figure 4b presents the results for the electrical Duobinary system. Unlike optical Duobinary, the benchmark performance of electrical Duobinary without equalization shows that the optical power sensitivity improves with increasing fiber length until approximately 12 km, beyond which the penalty occurs and increases with fiber length. This is attributed to the EAM negative chirp, which can offset certain amounts of fiber chromatic dispersion. By using linear or nonlinear equalization, optical sensitivity can improve the optical power sensitivity below 10 km and beyond 18 km of SMFs as it further alleviates the negative chirp in the short fiber length case, and equalization is efficient to mitigate the fiber dispersion. Nonlinear equalization outperforms linear equalization, simply because the former is efficient in combating the EAM nonlinearity [11]. Note that a better performance when not using the equalizer as compared to using a linear and/or a nonlinear equalizer in the 10–15 km range is obtained because the transmitter bandwidth was chosen, subject to an optimum dispersion tolerance and cost trade-off, rather than only an optimum power sensitivity criterion [18]. The use of MLSE brings about an enormous enhancement in optical power sensitivity, compared to cases without MLSE at different fiber lengths. This verifies the strong capability of MLSE in alleviating both the linear and nonlinear effects of a channel with memory. It is noticeable that the increase of the number of MLSE states from two to four enables only a slightly improvement in power sensitivity until the fiber lengths exceeds 40 km.
The performance for the PAM-4 system is shown in Figure 4c. Compared to optical/electrical Duobinary, PAM-4 has the best benchmark dispersion tolerance: it is the only scheme that can support 20 km of SMF transmission without using equalizations. For SMF lengths below 20 km, the use of linear or nonlinear equalization does not bring about a significant improvement in optical power sensitivity. This is because of the relatively small fiber dispersion that PAM-4 experiences, since it has half the symbol rate compared to other two schemes. Considerable optical power sensitivity improvement occurs only beyond 20 km SMF lengths where fiber dispersion becomes more and more strong with increasing fiber length. Similar to other systems, nonlinear equalization outperforms linear equalization regarding fiber dispersion tolerance, although the improvement enabled by linear or nonlinear equalization is far less compared to that of the electrical Duobinary case. The reason might be because PAM-4 is more vulnerable to a strong eye skew at a long fiber distance [11] because PAM-4 has more amplitude levels compared to the other two systems. By introducing a 4-state MLSE, PAM-4 shows moderate enhancement in power sensitivity for fiber lengths beyond 20 km.
3.3. Link Power Budget
Figure 5 summarizes the achievable link power budgets of various 40 Gb/s PONs using different DSPs at typical fiber lengths ranging from 10 km to 40 km. The link power budget is calculated by considering the corresponding receiver power sensitivity at a BER of 1 × 10−3, obtained in Figure 4 and for a 10 dBm of optical launch power. The vertical length of each bar in Figure 5 represents the corresponding link power budget, and it is explicitly marked with a value in dB. Comparatively, for fiber lengths beyond 10 km, there are some blank area with bars missing, which means that the link under such a receiver signal processing configuration fails, because the receiver BER cannot achieve 1 × 10−3.
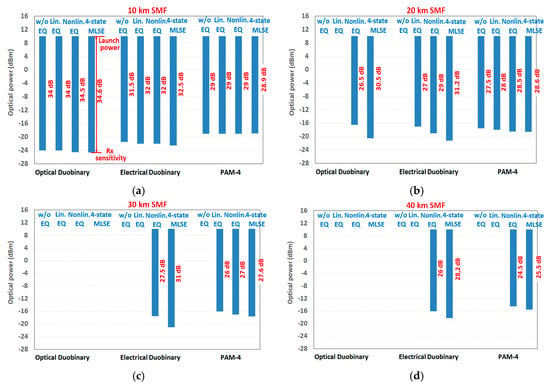
Figure 5.
Link power budget for each modulation format under various DSP configurations for transmission distances of (a) 10 km, (b) 20 km, (c) 30 km, and (d) 40 km. The optical power sensitivity shown in Figure 4 is considered to calculate the link power budget.
At a 10 km SMF distance, optical Duobinary with 4-state MLSE offers the largest link power budget of 34.6 dB, which outperforms electrical Duobinary and PAM-4 by 2.1 dB and 5.7 dB, respectively even if a 4-state MLSE is used for the latter schemes. In addition, for each modulation scheme, the receiver power sensitivity shows very little variation among different receiver signal processing configurations, ranging from the case without equalization, to the case of MLSE, as indicated. This is because the chirp and fiber chromatic dispersions almost offset each other at such a distance. For the 20 km case, however, electrical Duobinary using 4-state MLSE achieves the best link power budget of 31.2 dB. Optical Duobinary with a 4-state MLSE gives rise to a similar link power budget of 30.5 dB. Optical Duobinary without equalization or by using only a linear equalization fails. PAM-4 is the only scheme that succeeds for all four DSP configurations, and the link power budget varies little among different DSP configurations. For 30 km and 40 km SMF cases, optical Duobinary fails even if a 4-state MLSE is considered. Electrical Duobinary with a 4-state MLSE brings about 31 dB and 28.2 dB link power budgets, which are the best for 30 km and 40 km cases, respectively. PAM-4 shows approximately a 3 dB worse link power budget in either case, compared to optical Duobinary. Both the electrical Duobinary and PAM-4 must incorporate equalizations, otherwise links fail.
3.4. DSP Complexity
Similar to other short- and medium-reach applications [20,21], it is important to assess the various DSP algorithms from the complexity point of view for access networks. Here, the complexity is measured as the required number of real-valued multiplications and summations per symbol. Considering the first term of the right-hand side (RHS) of Equation (1), the required multiplication (summation) count per symbol is M + N (M + N − 1) for FFE/DFE with linear taps. For the second-order FFE terms, as indicated in the second term of RHS of Equation (1), two types of multiplications are performed: the first type is , representing the product between two symbols, which can be expressed by a M × M lower triangular matrix. M such multiplications are required for each symbol, since the (M − 1) × (M − 1) lower triangular matrix terms from the previous symbol period are reserved, and only M new product terms are updated. The second type is which is the multiplication with tap coefficient that requires multiplications. In total, there are multiplications per symbol for nonlinear FFE. Similarly, for the second-order nonlinear DFE terms as shown by the last term of the RHS of Equation (1), the required multiplication count is , with the difference that the symbols’ square terms are not considered. The total number of sums for the second-order FFE&DFE is .
For Viterbi MLSE, the key parameters include the constellation alphabet size K, the memory length L, and the trellis length R which also determines the backtrack length. The trellis has states and analyzes branches per each symbol. The multiplication takes place when calculating branch metrics by using typical Euclidian distance [22,23]:
where c is the channel impulse response coefficient, and is transmitted symbol sequence. Simplifying MLSE using the absolute value of the distance instead of the square of the distance in branch metric can save complexity without performance degradation [22], and thus it is used in this work. The required number of multiplications is , where multiplications are for the convolution operation of . The number of sums is also . After R symbols, it backtracks the trellis to determine the MLSE solution, which involves if-statements, which can be equivalently viewed as a sum operation.
Table 1 summarizes the complexity of various DSP configurations for all of the modulation schemes. Note that the complexity of FFE/DFE is the same for all three schemes, since the tap count is the same, but the MLSE complexity depends on the modulation constellation size K and memory length L. It clearly indicates that the majority of complexity is from the FFE/DFE whose second-order nonlinear equalizations account for approximately 50% of overall multiplication or sums. Linear FFE/DFE has the least complexity. MLSE with a small memory length shows moderate complexity regarding both the required multiplication and sum operations.

Table 1.
Complexity (number of multiplications and sums per symbol) of various DSP algorithms.
The complexity of the second-order FFE/DFE can be significantly reduced by neglecting the terms whose corresponding tap coefficients are much less weighted [17,24]. Recent experimental demonstrations show that a 75% complexity reduction is possible [24]. For MLSE, first, for the optical or electrical Duobinary scheme, the memory length can be further reduced to 1, leading to halved multiplication and sum operations at the cost of the degradation of the power budget performance to some extent for >10 km SMF cases. The MLSE complexity for all modulation schemes can further be reduced by calculating the metrics using histogram and averaging, whose result can replace the term in Equation (2). Since the histogram and averaging can be performed at the beginning of the communication, and it rarely needs further calculations, as the optical channel is relatively stable, it can be assumed that such an operation does not contribute to MLSE complexity. As a result, it gives almost no multiplications, and also reduces the sum operation count for MLSE. This indicates the superior complexity performance of MLSE and its feasibility for access networks.
4. Discussion
The choice of modulation format and DSP configuration depends on the fiber distance. For short-reach SMFs of up to 10 km, optical Duobinary without any DSP offers the best trade-off between the link power budget. For the typical standardized transmission distance of 20 km SMF, DSP-free PAM-4 can be considered if the minimization of the receiver complexity is the priority, while electrical Duobinary with 4-state MLSE is preferred if a link with link budget as large as possible is preferred. For 30 km and 40 km, electrical Duobinary is preferred from both the link power budget and the DSP complexity points of view. Note that electrical Duobinary has the best performance with MLSE, but it requires a larger transmitter bandwidth, as indicated in Section 3.1, which may require simple pre-equalization if a lower bandwidth transmitter is used in practice. As indicated in [25], pre-equalization, together with receiver FFE/DFE, do reduce the transceiver bandwidth requirement. In addition, PAM-4 halves the baud rate compared to electrical/optical Duobinary, which must be considered as a higher priority when the system DAC/ADC sampling rate and signal processing speed are limited. The complexity of both nonlinear FFE/DFE and MLSE can be reduced by optimizing implementation, indicating that the proposed DSP is feasible for access networks.
The IEEE and ITU-T standardization ends up with 25 Gb/s and 50 Gb/s per wavelength of next generation high-speed PON systems. For the 50 Gb/s case, the general performance trend, as well as the performance difference between each modulation format would be similar with the 40 Gb/s case. The difference would be the transceiver bandwidth requirement and the achievable power budget.
5. Conclusions
Comprehensive numerical investigations and comparisons have been made between 40 Gb/s lane rate electrical Duobinary, optical Duobinary, and PAM-4 systems, using practical linear and nonlinear equalizations and low complex MLSE for NG-PONs. The results are useful for choosing the optimum modulation scheme and the DSP configuration for upgrading the capacity in optical access networks. The trade-off between link power budget performance and transceiver complexity determines the choice of modulation format and DSP configuration. DSP-free optical Duobinary is always preferred for short-reach SMF links of up to 10 km. For 20 km SMF, DSP-free PAM-4 is the only option with the least complexity, otherwise electrical Duobinary is preferred if a high-link power budget is critical. Electrical Duobinary outperforms PAM-4 for cases of SMF beyond 20 km.
Author Contributions
J.L.W. conceived, designed and performed the simulations; J.L.W., J.Z., E.G., P.A.H., and J.M.T. analyzed the data and wrote the paper.
Funding
This research was funded by the European Union under CEEOALAN project with grant number No. 623,515.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Christoph Wagner, Klaus Grobe, and Helmut Griesser from ADVA Optical Networking SE, Germany for useful discussions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
References
- ITU-T G.989 Series of Recommendations. Available online: https://www.itu.int/rec/T-REC-G.989/en (accessed on 18 September 2018).
- Houtsma, V.; Veen, D.V. Demonstration of symmetrical 25 Gbps TDM-PON with 31.5 dB optical power budget using only 10 Gbps optical components. In Proceedings of the 2015 European Conference on Optical Communication (ECOC), Valencia, Spain, 27 September–1 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Houtsma, V.; Veen, D.V.; Gnauck, A.; Iannone, P. APD-Based Duobinary Direct Detection Receiver for 40 Gb/s TDM-PON. In Proceedings of the Optical Fiber Communication Conference, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 22–26 March 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, S.; Houtsma, V.; Veen, D.V.; Vetter, P. Optical Amplified 40-Gbps Symmetrical TDM-PON Using 10-Gbps Optics and DSP. J. Lightwave Technol. 2017, 35, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Ferrera, P.; Ferrero, V.; Valvo, M.; Gaudino, R. Impact of the Overall Electrical Filter Shaping in Next-Generation 25 and 50 Gb/s PONs. J. Opt. Commun. Netw. 2018, 10, 493–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houtsma, V.; Veen, D.V. A Study of Options for High-Speed TDM-PON Beyond 10G. J. Lightwave Technol. 2017, 4, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Li, S.; Cheng, N.; Liu, X. Demonstration of high-performance cost-effective 100-Gb/s TWDM-PON using 4 × 25-Gb/s optical Duobinary channels with 16-GHz APD and receiver-side post-equalization. In Proceedings of the 2015 European Conference on Optical Communication (ECOC), Valencia, Spain, 27 September–1 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.L.; Eiselt, N.; Griesser, H.; Grobe, K.; Eiselt, M.; Vegas-Olmos, J.J.; Monroy, I.T.; Elbers, J.-P. First Demonstration of Real-Time End-to-End 40 Gb/s PAM-4 System using 10-G Transmitter for Next Generation Access Applications. In Proceedings of the 2015 European Conference on Optical Communication (ECOC), Valencia, Spain, 27 September–1 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.L.; Giacoumidis, E. Multi-band CAP for next generation optical access networks using 10-G optics. J. Lightwave Technol. 2018, 36, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.M.; Cao, B.; Deng, M.L.; Giddings, R.; Duan, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, M. RSOA intensity modulator frequency chirp-enabled 40 Gb/s over 25 km IMDD PON systems. In Proceedings of the Optical Fiber Communication Conference, Los Angeles, LA, USA, 22–26 March 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.L.; Grobe, K.; Sánches, C.; Giacoumidis, E.; Griesser, H. Comparison of Cost- and Energy-Efficient Signal Modulations for Next Generation Passive Optical Networks. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 28271–28281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.L.; Grobe, K.; Wagner, C.; Giacoumidis, E.; Griesser, H. 40 Gb/s Lane Rate NG-PON using Electrical/Optical Duobinary, PAM-4 and Low Complex Equalizations. In Proceedings of the Optical Fiber Communication Conference, Anaheim, CA, USA, 20–22 March 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Proakis, J.G. Digital Communications, 4th ed.; McGraw-Hill Book Co.: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, W.-J.; Bond, A.E.; Kim, J.; Zhang, J.; Jambunathan, R.; Foulk, H.; O’Brien, S.; Norman, J.V.; Vandegrift, D.; Wanamaker, C.; et al. Lower insertion loss and low dispersion penalty InGaAsP quantum-well high-speed electroabsorption modulator for 40-Gb/s very-short-reach, long-reach, and long-haul applications. J. Lightwave Technol. 2002, 20, 2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.; Kim, H.; Chung, Y. Transmission of 51.56-Gb/s OOK signal using 1.55-μm directly modulated laser and duobinary electrical equalizer. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 22555–22562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, G.P. Fiber Optic Communication Systems, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.L.; Giacoumidis, E. 40 Gb/s/λ optical amplified PAM-4 PON with transmission over 30 km SMF using 10-G Optics and simple DSP. In Proceedings of the 2017 Optical Fiber Communications Conference and Exhibition (OFC), Los Angeles, CA, USA, 19–23 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.L.; Tang, J.M.; Cheng, Q.; Penty, R.V.; White, I.H.; Griesser, H. Optimization of Transceiver Bandwidths of 40 Gb/s NG-PONs using Electrical Three-Level Duobinary. In Proceedings of the Asia Communications and Photonics Conference, Hongkong, China, 19–23 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenkranz, W.; Xia, C. Electrical Equalization for Advanced Optical Communication Systems. AEÜ Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2006, 51, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.L.; Cheng, Q.; Penty, R.V.; White, I.H.; Cunningham, D.G. 400 Gigabit Ethernet Using Advanced Modulation Formats: Performance, Complexity, and Power Dissipation. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2015, 53, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.L.; Sanchez, C.; Giacoumidis, E. Fair comparison of complexity between a multi-band CAP and DMT for data center interconnects. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 3860–3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Li, Z.; Peng, J.; Tan, A.; Song, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, M. Decoding of 10-G Optics-Based 50-Gb/s PAM-4 Signal Using Simplified MLSE. Photonics J. 2018, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myburgh, H.C.; Olivier, J.C. Low Complexity MLSE Equalization in Highly Dispersive Rayleigh Fading Channels. Eur. J. Adv. Signal. Process. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.L.; Lam, C.F.; Giacoumidis, E.; Cheng, Q.; Penty, R.V.; White, I.H. Towards Ultra-Low Cost and Power Next Generation Optical Access Networking. Nat. Commun. 2018. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Stark, A.; Detwiler, T. Equalization Strategies for 25G PON. In Proceedings of the Optical Fiber Communication Conference on OSA Technical Digest (Online) (Optical Society of America, 2017), Los Angeles, VA, USA, 19–23 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).