Bioavailability of the Common Cold Medicines in Jellies for Oral Administration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Oral Jelly
2.3. Preparation of IR Tablets
2.4. Determination of Drug Content in the Formulations
2.5. Dissolution Test
2.6. Pharmacokinetic Study in Beagle Dogs
2.7. LC/MS/MS Analysis of Drugs in Plasma
2.8. Pharmacokinetic Data and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Drug Contents in the Formulations
3.2. In Vitro Dissolution in Various pH Media
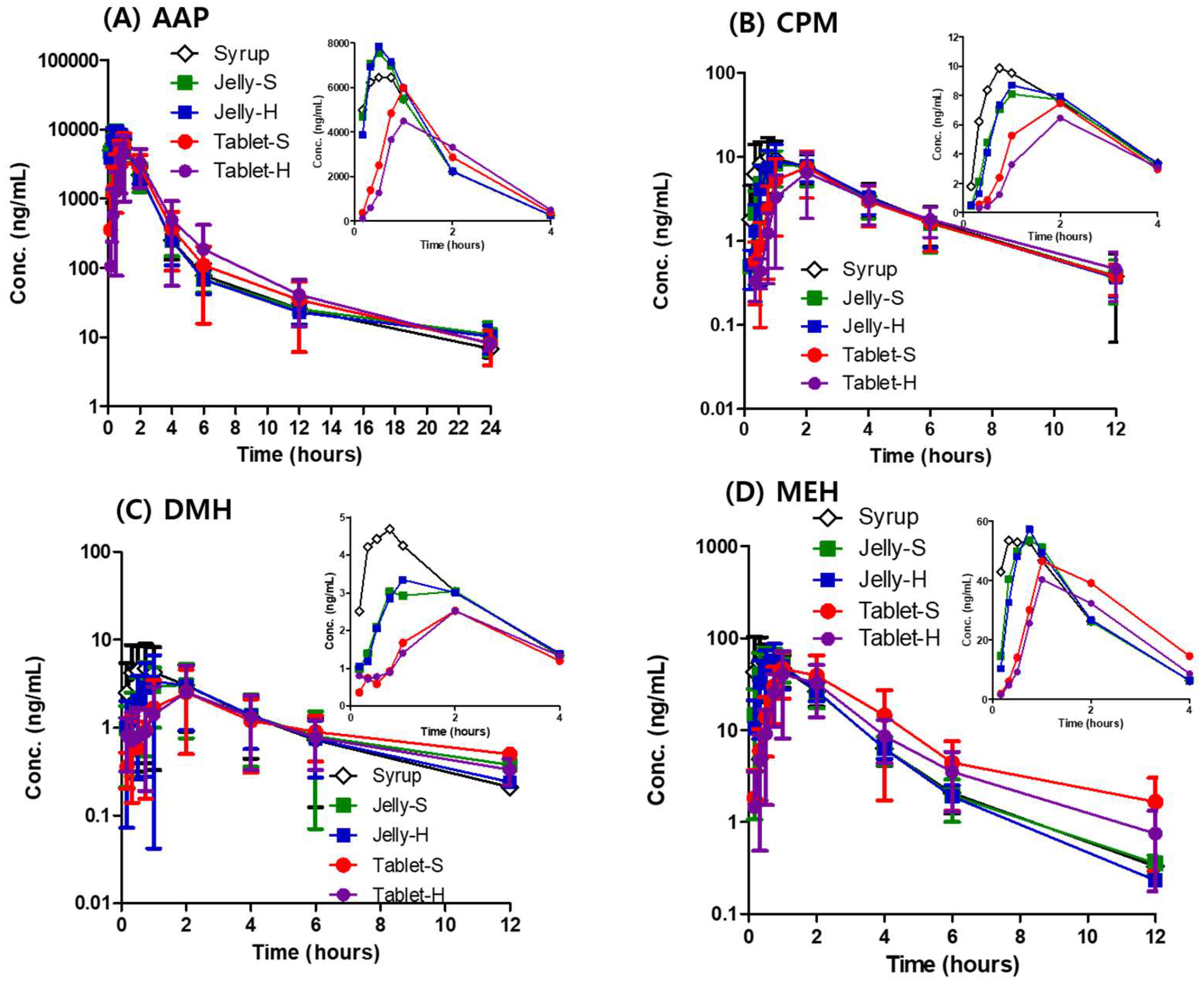
3.3. In Vivo Pharmacokinetics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allan, G.M.; Arroll, B. Prevention and Treatment of the Common Cold: Making Sense of the Evidence. CMAJ 2014, 186, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, B. Viral Upper Respiratory Infection. Integr. Med. 2018, 170–179.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grattan, T.; Hickman, R.; Darby-Dowman, A.; Hayward, M.; Boyce, M.; Warrington, S. A Five Way Crossover Human Volunteer Study to Compare the Pharmacokinetics of Paracetamol Following Oral Administration of Two Commercially Available Paracetamol Tablets and Three Development Tablets Containing Paracetamol in Combination with Sodium Bicarbonate Or Calcium Carbonate. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2000, 49, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bertolini, A.; Ferrari, A.; Ottani, A.; Guerzoni, S.; Tacchi, R.; Leone, S. Paracetamol: New Vistas of an Old Drug. CNS Drug Rev. 2006, 12, 250–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarode, A.; Wang, P.; Cote, C.; Worthen, D.R. Low-Viscosity Hydroxypropylcellulose (HPC) Grades SL and SSL: Versatile Pharmaceutical Polymers for Dissolution Enhancement, Controlled Release, and Pharmaceutical Processing. AAPS PharmSciTech 2013, 14, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Yu, L.; Clark, S.; Trehy, M.; Moore, T.; Westenberger, B.; Buhse, L.; Kauffman, J.; Bishop, B.; Velazquez, L.; et al. Dissolution Testing for Bioavailability of Over-the-Counter (OTC) Drugs—A Technical Note. AAPS PharmSciTech 2015, 16, 1227–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical Preparations, 40th ed.; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006; p. 395. [Google Scholar]
- Kalantzi, L.; Reppas, C.; Dressman, J.B.; Amidon, G.L.; Junginger, H.E.; Midha, K.K.; Shah, V.P.; Stavchansky, S.A.; Barends, D.M. Biowaiver Monographs for Immediate Release Solid Oral Dosage Forms: Acetaminophen (Paracetamol). J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 95, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amidon, G.L.; Lennernäs, H.; Shah, V.P.; Crison, J.R. A Theoretical Basis for a Biopharmaceutic Drug Classification: The Correlation of in Vitro Drug Product Dissolution and in Vivo Bioavailability. Pharm. Res. 1995, 12, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffa, R.B.; Pergolizzi, J.V., Jr.; Taylor, R., Jr.; Decker, J.F.; Patrick, J.T. Acetaminophen (Paracetamol) Oral Absorption and Clinical Influences. Pain Pr. 2014, 14, 668–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumore, M.M. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Chlorpheniramine. Drug Intell. Clin. Pharm. 1984, 18, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasim, N.A.; Whitehouse, M.; Ramachandran, C.; Bermejo, M.; Lennernäs, H.; Hussain, A.S.; Junginger, H.E.; Stavchansky, S.A.; Midha, K.K.; Shah, V.P. Molecular Properties of WHO Essential Drugs and Provisional Biopharmaceutical Classification. Mol. Pharm. 2004, 1, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallner, J.; Kotzan, J.; Stewart, J.; Brown, W.; Honigberg, I.; Needham, T.; Dighe, S. Blood Levels Following Multiple Oral Dosing of Chlorpheniramine Conventional and Controlled Release Preparations. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 1982, 3, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yacobi, A.; Stoll, R.G.; Chao, G.C.; Carter, J.E.; Baaske, D.M.; Kamath, B.L.; Amann, A.H.; Lai, C. Evaluation of Sustained-Action Chlorpheniramine-Pseudoephedrine Dosage Form in Humans. J. Pharm. Sci. 1980, 69, 1077–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotzan, J.; Vallner, J.; Stewart, J.; Brown, W.; Viswanathan, C.; Needham, T.; Dighe, S.; Malinowski, R. Bioavailability of Regular and Controlled-Release Chlorpheniramine Products. J. Pharm. Sci. 1982, 71, 919–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, S.; Tang, A. GLC Determination of Chlorpheniramine in Human Plasma. J. Pharm. Sci. 1974, 63, 1954–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimiuk, M.; Wasilewska, K.; Winnicka, K. How to Modify Drug Release in Paediatric Dosage Forms? Novel Technologies and Modern Approaches with Regard to Children’s Population. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Maghraby, G.M.; Elzayat, E.M.; Alanazi, F.K. Development of Modified in Situ Gelling Oral Liquid Sustained Release Formulation of Dextromethorphan. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2012, 38, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sai Sathavahana, C.; Allena, R.T.; Getyala, A.; Gangadharappa, H. Formulation and Evaluation of Dextromethorphan Hydrobromide Controlled Release Hollow Microspheres using Natural Polymer. Indones. J. Pharm. 2014, 25, 181–188. [Google Scholar]
- DRUGBANK. Available online: https://www.drugbank.ca/ (accessed on 14 August 2020).
- Kunsman, G.W.; Jones, R.; Levine, B.; Smith, M.L. Methylephedrine Concentrations in Blood and Urine Specimens. J. Anal. Toxicol. 1998, 22, 310–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Slavkova, M.; Breitkreutz, J. Orodispersible Drug Formulations for Children and Elderly. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 75, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksovski, A.; Dreu, R.; Gašperlin, M.; Planinšek, O. Mini-Tablets: A Contemporary System for Oral Drug Delivery in Targeted Patient Groups. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2015, 12, 65–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almukainzi, M.; Araujo, G.L.B.; Löbenberg, R. Orally Disintegrating Dosage Forms. J. Pharm. Investig. 2019, 49, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranmal, S.R.; Cram, A.; Tuleu, C. Age-Appropriate and Acceptable Paediatric Dosage Forms: Insights into End-User Perceptions, Preferences and Practices from the Children’s Acceptability of Oral Formulations (CALF) Study. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 514, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitkreutz, J.; Boos, J. Paediatric and Geriatric Drug Delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2007, 4, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, K. Alendronate Sodium Hydrate (Oral Jelly) for the Treatment of Osteoporosis: Review of a Novel, Easy to Swallow Formulation. Clin. Interv. Aging 2013, 8, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MFDS of Republic of Korea. The Korean Pharmacopoeia, 11th ed.; Kp 11; MFDS: Cheongju, Korea, 2014.
- Harada, T.; Yasuoka, K.; Sakurai, M.; Murase, T.; Owaki, T. Development of a Novel Oral Jelly Formulation for Elderly Patients. Yakugaku Zasshi 2015, 135, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MFDS of Republic of Korea. Chapter 8 General Test Methods. In Food Code; 1.5 Physical Test of Jelly; MFDS: Cheongju, Korea, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Helmy, S.A.; El Bedaiwy, H.M. In Vitro Dissolution Similarity as a Surrogate for in Vivo Bioavailability and Therapeutic Equivalence. Dissolution Technol. 2016, 8, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Ye, A.; Liu, W.; Liu, C.; Han, J.; Singh, H. Behaviour of Liposomes Loaded with Bovine Serum Albumin during in Vitro Digestion. Food Chem. 2015, 175, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawe, R.C.; Sheskey, P.J.; Cook, W.G.; Fenton, M.E. (Eds.) Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients, 6th ed.; Pharmaceutical Press: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2012; pp. 130–134. [Google Scholar]
- Bolger, M.B.; Macwan, J.S.; Sarfraz, M.; Almukainzi, M.; Löbenberg, R. The Irrelevance of in Vitro Dissolution in Setting Product Specifications for Drugs Like Dextromethorphan that are Subject to Lysosomal Trapping. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanagan, T. Potential for Pharmaceutical Excipients to Impact Absorption: A Mechanistic Review for BCS Class 1 and 3 Drugs. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 141, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Straughn, A.; Sadrieh, N.; Meyer, M.; Faustino, P.; Ciavarella, A.; Meibohm, B.; Yates, C.; Hussain, A. A Modern View of Excipient Effects on Bioequivalence: Case Study of Sorbitol. Pharm. Res. 2007, 24, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Arieta, A. Interactions between Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients and Excipients Affecting Bioavailability: Impact on Bioequivalence. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 65, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Os, S.; Relleke, M.; Piniella, P.M. Lack of Bioequivalence between Generic Risperidone Oral Solution and Originator Risperidone Tablets. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2007, 45, 293–299. [Google Scholar]
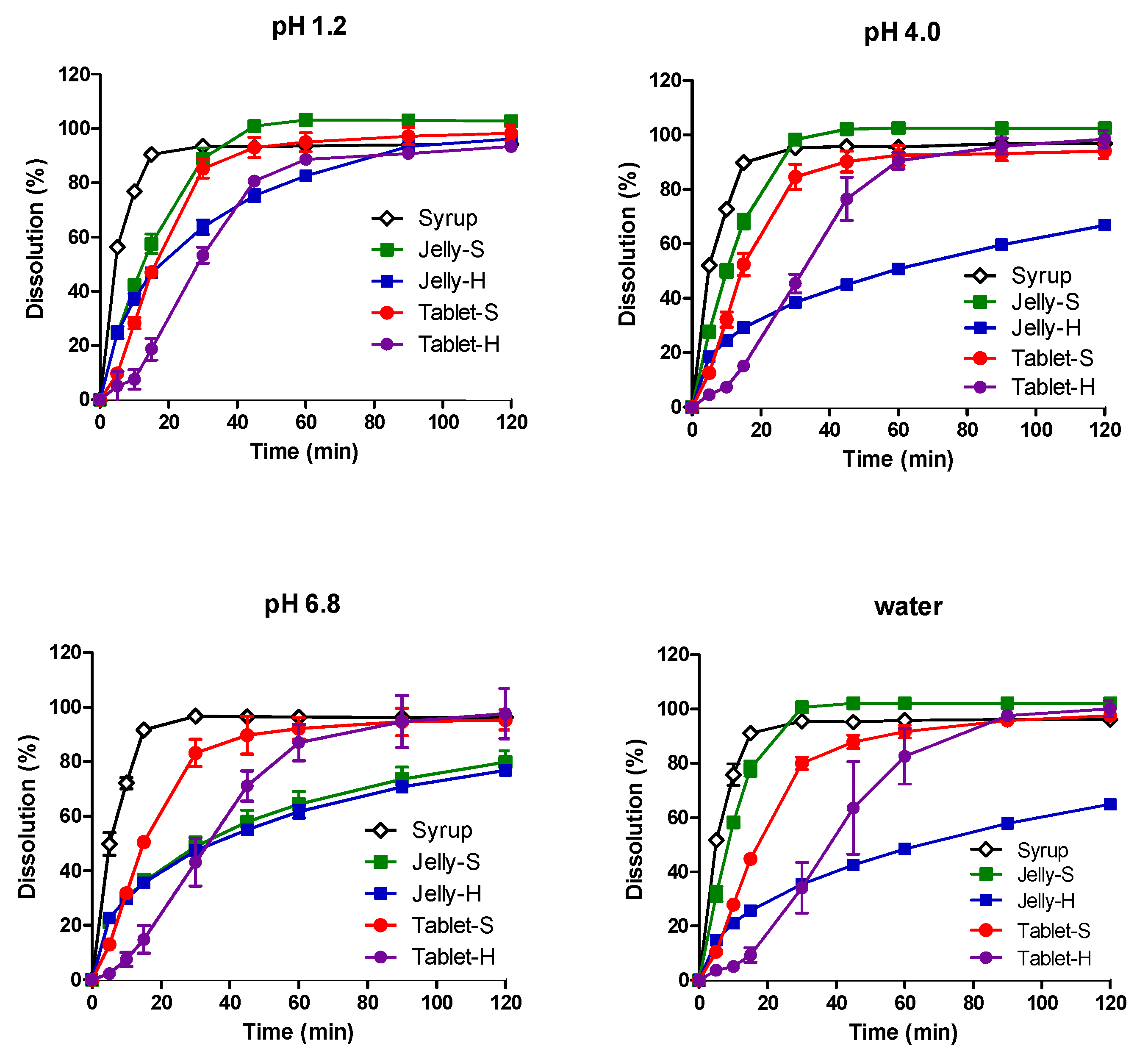
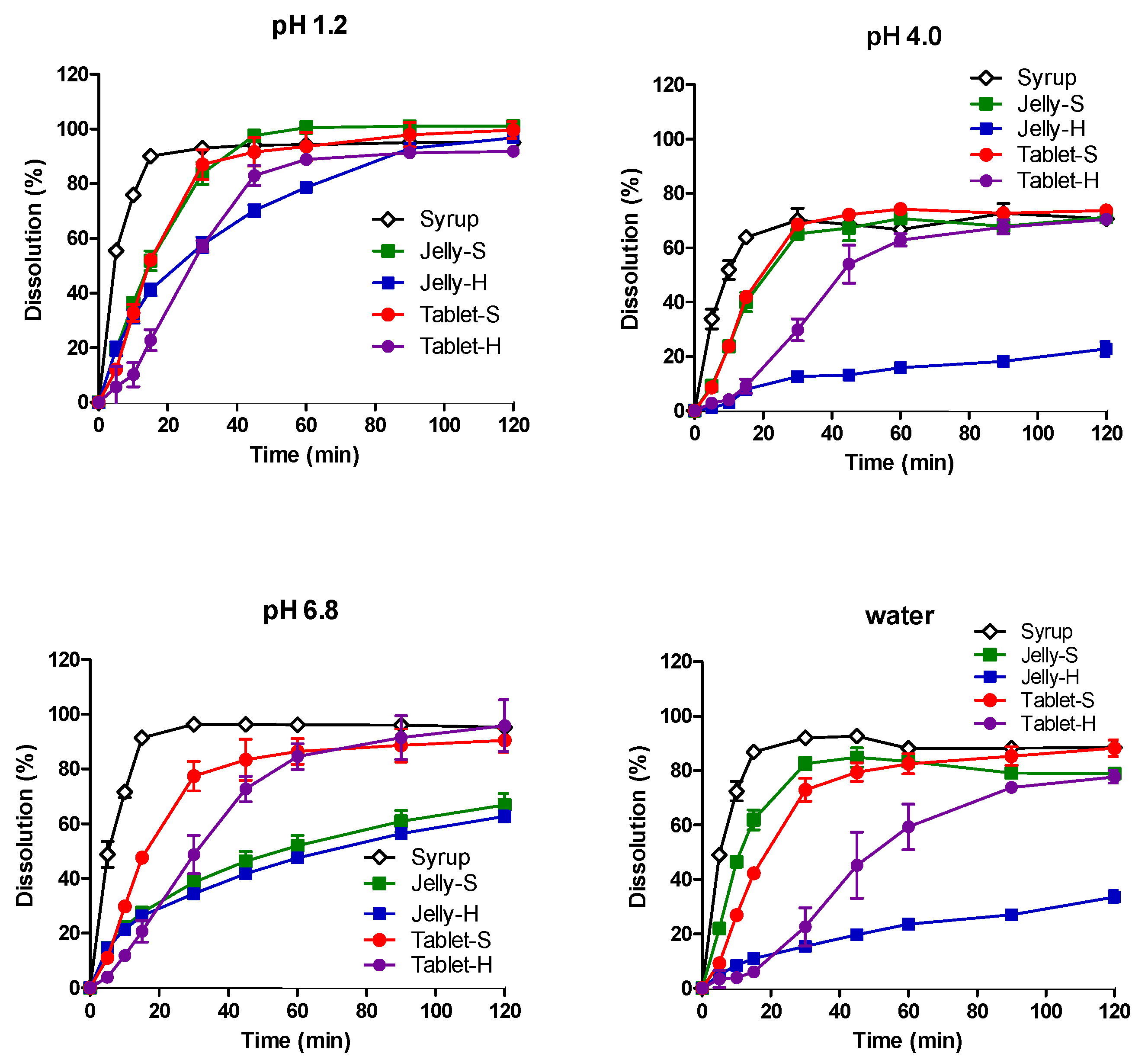
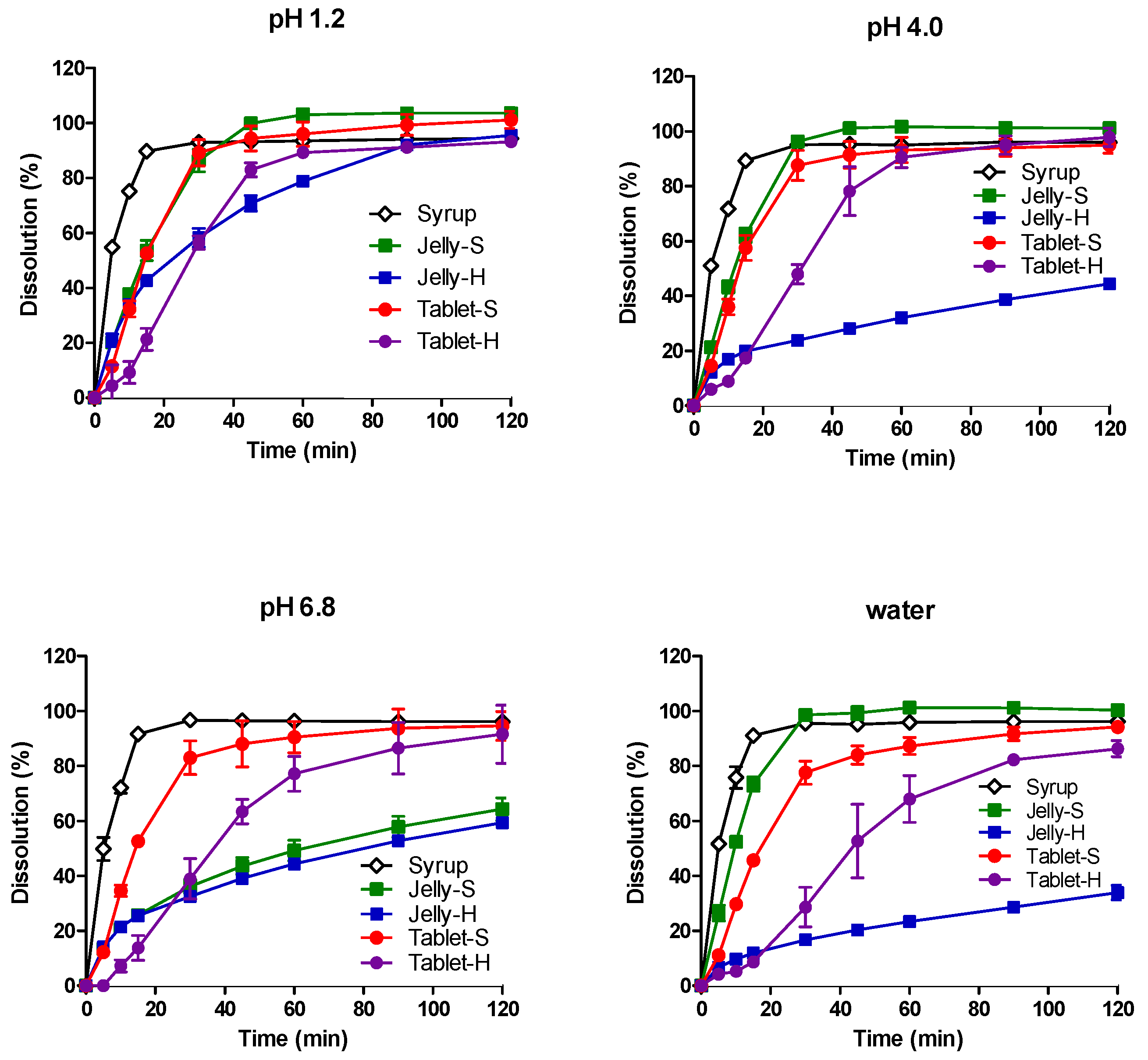
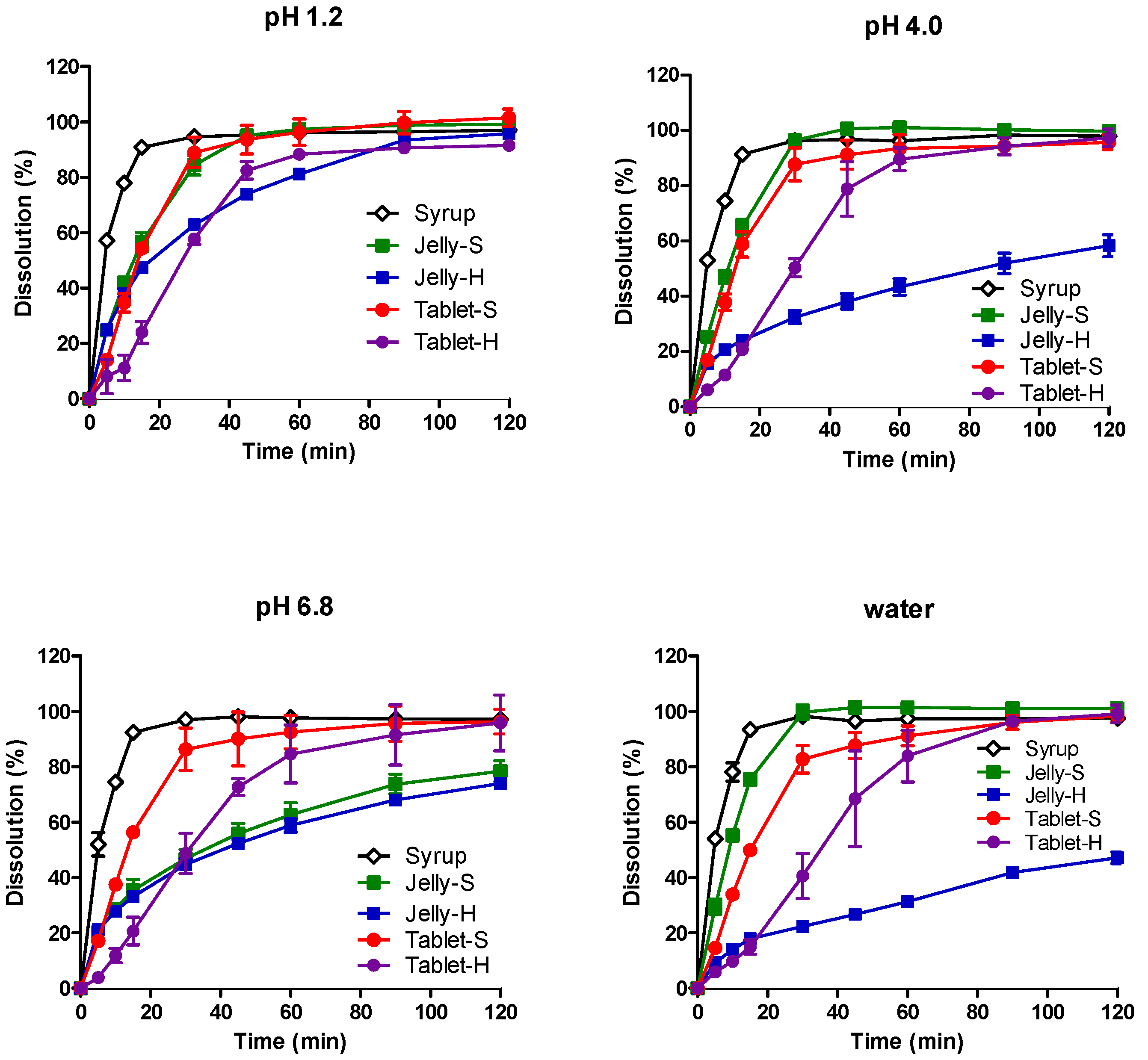
| Composition | Jelly-S (gel Strength: 3–4 N) | Jelly-H (gel Strength: 8–9 N) |
|---|---|---|
| 15 g contains mg of | ||
| Acetaminophen (AAP) | 150 | 150 |
| Chlorpheniramine maleate (CPM) | 1.875 | 1.875 |
| Dextromethorphan hydrobromide (DMH) | 11.25 | 11.25 |
| dl-Methylephedrine hydrochloride (MEH) | 18.75 | 18.75 |
| Carageenan(kappa) | 45 | 45 |
| Carageenan(iota) | 60 | 60 |
| Locust bean gum | 60 | 60 |
| Xanthan gum | - | 45 |
| KCl | 15 | - |
| Sucralose | 15 | 15 |
| Stevia glucoside | 10 | 10 |
| D-sorbitol | 3000 | 3000 |
| Sodium citrate hydrate | 45 | 45 |
| Citric acid hydrate | 18 | 18 |
| Methyl paraben | 1.14 | 1.14 |
| Propyl paraben | 0.285 | 0.285 |
| Orange flavor | 270 | 270 |
| Purified water | q.s. | q.s. |
| Composition | Tablet-S (Hardness: 15 kPa) | Tablet-H (Hardness: 20 kPa) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 tablet contains mg of | ||
| AAP | 150 | 150 |
| CPM | 1.875 | 1.875 |
| DMH | 11.25 | 11.25 |
| MEH | 18.75 | 18.75 |
| Microcrystalline cellulose (PH-101) | 223.125 | 223.125 |
| Microcrystalline cellulose (PH-102) | 37 | 37 |
| Lactose hydrate | 50 | 50 |
| Low substituted HPC | 200 | 200 |
| HPC | 50 | 50 |
| Colloidal silicon dioxide | 50 | 50 |
| Glyceryl behenate | 42 | 42 |
| Magnesium stearate | 8 | 24 |
| Opadry® (03B28796, White) | 26 | 26 |
| Drugs | Syrup | Jelly-S | Jelly-H | Tablet-S | Tablet-H |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AAP | 99.5 ± 0.9 | 101.5 ± 0.2 | 98.9 ± 0.4 | 100.2 ± 0.8 | 100.8 ± 0.5 |
| CPM | 100.3 ± 1.2 | 100.1 ± 0.9 | 98.7 ± 0.7 | 99.8 ± 0.1 | 99.2 ± 0.5 |
| DMH | 99.8 ± 0.3 | 98.7 ± 0.4 | 98.7 ± 0.6 | 99.7 ± 0.4 | 99.9 ± 0.8 |
| MEH | 99.4 ± 0.8 | 98.2 ± 0.1 | 99.5 ± 0.6 | 100.3 ± 1.2 | 99.5 ± 0.8 |
| Drugs | Parameters | Syrup | Jelly-S | Jelly-H | Tablet-S | Tablet-H |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AAP | AUC 0-t (µg·h/mL) | 12.52 ± 3.01 | 13.03 ± 4.52 | 13.22 ± 3.64 | 11.42 ± 4.27 | 11.03 ± 4.43 |
| AUC 0-∞ (µg·h/mL) | 12.59 ± 3.00 | 13.11 ± 4.57 | 13.29 ± 3.65 | 11.55 ± 4.20 | 11.16 ± 4.34 | |
| Cmax (µg/mL) * | 7.66 ± 2.85 | 8.48 ± 3.24 | 8.75 ± 2.90 | 6.22 ± 2.68 | 5.38 ± 3.29 | |
| Tmax (h) *** | 0.7 ± 0.5 | 0.5 ± 0.2 | 0.5 ± 0.2 | 1.0 ± 0.3 | 1.1 ± 0.5 | |
| T1/2 (h) | 3.1 ± 1.6 | 3.7 ± 2.6 | 3.9 ± 3.0 | 3.5 ± 2.2 | 3.3 ± 1.6 | |
| MRT (h) | 1.6 ± 0.3 | 1.6 ± 0.4 | 1.6 ± 0.4 | 2.2 ± 0.6 | 2.8 ± 1.5 | |
| CPM | AUC 0-t (ng·h/mL) | 35.2 ± 18.4 | 32.1 ± 15.3 | 32.6 ± 15.6 | 27.6 ± 15.4 | 25.0 ± 13.9 |
| AUC 0-∞ (ng·h/mL) | 36.4 ± 18.4 | 33.8 ± 15.4 | 34.5 ± 15.5 | 29.5 ± 14.8 | 29.9 ± 13.4 | |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 11.3 ± 6.3 | 9.4 ± 3.9 | 9.5 ± 4.9 | 7.9 ± 4.7 | 6.9 ± 4.3 | |
| Tmax (h) ** | 1.0 ± 0.6 | 1.4 ± 0.5 | 1.3 ± 0.5 | 1.8 ± 0.4 | 2.5 ± 1.2 | |
| T1/2 (h) | 2.0 ± 0.3 | 2.1 ± 0.5 | 2.0 ± 0.4 | 2.7 ± 1.9 | 2.2 ± 0.4 | |
| MRT (h) | 3.2 ± 0.5 | 3.3 ± 0.6 | 3.3 ± 0.4 | 4.6 ± 2.5 | 4.1 ± 0.6 | |
| DMH | AUC 0-t (ng·h/mL) | 14.6 ± 12.6 | 12.5 ± 10.2 | 12.0 ± 9.7 | 8.5 ± 6.2 | 9.2 ± 7.1 |
| AUC 0-∞ (ng·h/mL) | 16.0 ± 12.5 | 13.9 ± 10.8 | 13.8 ± 9.7 | 13.3 ± 8.1 | 12.0 ± 7.9 | |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 5.6 ± 4.4 | 3.8 ± 2.5 | 3.7 ± 3.3 | 2.6 ± 2.0 | 2.6 ± 2.5 | |
| Tmax (h) *** | 0.8 ± 0.5 | 1.2 ± 0.6 | 1.0 ± 0.4 | 2.1 ± 1.2 | 2.3 ± 1.2 | |
| T1/2 (h) | 2.0 ± 0.4 | 1.9 ± 0.3 | 2.0 ± 0.4 | 2.6 ± 1.6 | 2.5 ± 1.0 | |
| MRT (h) | 3.0 ± 0.6 | 3.2 ± 0.6 | 3.4 ± 0.5 | 4.6 ± 2.2 | 4.6 ± 1.4 | |
| MEH | AUC 0-t (ng·h/mL) | 127.1 ± 46.2 | 122.2 ± 37.6 | 118.6 ± 38.4 | 116.0 ± 36.8 | 111.1 ± 47.4 |
| AUC 0-∞ (ng·h/mL) | 129.0 ± 46.0 | 124.1 ± 37.5 | 120.9 ± 38.1 | 118.9 ± 35.9 | 115.0 ± 45.5 | |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 73.7 ± 46.6 | 62.5 ± 22.2 | 63.0 ± 27.3 | 55.0 ± 27.1 | 45.5 ± 30.9 | |
| Tmax (h) * | 0.7 ± 0.5 | 0.8 ± 0.4 | 0.8 ± 0.4 | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 1.2 ± 0.5 | |
| T1/2 (h) | 1.4 ± 0.4 | 1.3 ± 0.4 | 1.2 ± 0.3 | 1.6 ± 0.9 | 1.7 ± 1.3 | |
| MRT (h) | 1.8 ± 0.4 | 1.9 ± 0.3 | 1.8 ± 0.2 | 2.5 ± 1.1 | 3.0 ± 1.6 |
| Test | Parameters | Reference | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Syrup | Jelly-S | Jelly-H | Tablet-S | Tablet-H | ||
| Syrup | AUC0-t | - | 0.99 (0.86–1.13) a | 0.96 (0.83–1.09) a | 1.14 (0.99–1.31) | 1.19 (1.04–1.37) |
| Cmax | - | 0.91 (0.68–1.21) | 0.85 (0.65–1.15) | 1.28 (0.96–1.71) | 1.63 (1.22–2.17) | |
| Jelly-S | AUC0-t | 1.01 (0.88–1.16) a | - | 0.97 (0.84–1.11) a | 1.16 (1.00–1.33) | 1.21 (1.05–1.39) |
| Cmax | 1.10 (0.83–1.47) | - | 0.95 (0.71–1.26) | 1.41 (1.06–1.88) | 1.80 (1.35–2.39) | |
| Jelly-H | AUC0-t | 1.05 (0.91–1.20) a | 1.03 (0.90–1.18) a | - | 1.19 (1.04–1.37) | 1.25 (1.09–1.43) |
| Cmax | 1.16 (0.87–1.55) | 1.05 (0.79–1.40) | - | 1.49 (1.12–1.98) | 1.89 (1.42–2.52) | |
| Tablet-S | AUC0-t | 0.88 (0.76–1.00) | 0.86 (0.75–0.99) | 0.84 (0.73–0.96) | - | 1.04 (0.91–1.20) a |
| Cmax | 0.78 (0.59–1.04) | 0.71 (0.53–0.94) | 0.67 (0.50–0.89) | - | 1.27 (0.95–1.69) | |
| Tablet-H | AUC0-t | 0.84 (0.73–0.96) | 0.83 (0.72–0.95) | 0.80 (0.70–0.92) | 0.96 (0.84–1.10) a | - |
| Cmax | 0.61 (0.46–0.82) | 0.56 (0.42–0.74) | 0.53 (0.40–0.70) | 0.79 (0.59–1.05) | - | |
| Test | Parameters | Reference | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Syrup | Jelly-S | Jelly-H | Tablet-S | Tablet-H | ||
| Syrup | AUC0-t | - | 1.10 (0.92–1.31) | 1.06 (0.89–1.26) | 1.36 (1.14–1.6) | 1.43 (1.20–1.70) |
| Cmax | - | 1.13 (0.85–1.51) | 1.13 (0.85–1.50) | 1.54 (1.16–2.06) | 1.74 (1.31–2.32) | |
| Jelly-S | AUC0-t | 0.91 (0.76–1.08) | - | 0.96 (0.81–1.15) a | 1.23 (1.04–1.47) | 1.30 (1.09–1.54) |
| Cmax | 0.88 (0.66–1.17) | - | 1.00 (0.75–1.33) | 1.37 (1.03–1.82) | 1.54 (1.16–2.05) | |
| Jelly-H | AUC0-t | 0.94 (0.79–1.12) | 1.04 (0.87–1.24) a | - | 1.28 (1.07–1.52) | 1.35 (1.13–1.60) |
| Cmax | 0.88 (0.66–1.18) | 1.00 (0.75–1.33) | - | 1.37 (1.03–1.82) | 1.54 (1.16–2.05) | |
| Tablet-S | AUC0-t | 0.74 (0.62–0.88) | 0.81 (0.68–0.97) | 0.78 (0.66–0.93) | - | 1.05 (0.88–1.25) a |
| Cmax | 0.65 (0.48–0.86) | 0.73 (0.55–0.97) | 0.73 (0.55–0.97) | - | 1.13 (0.85–1.50) | |
| Tablet-H | AUC0-t | 0.70 (0.59–0.83) | 0.77 (0.65–0.92) | 0.74 (0.62–0.88) | 0.95 (0.80–1.13) a | - |
| Cmax | 0.57 (0.43–0.76) | 0.65 (0.49–0.87) | 0.65 (0.49–0.86) | 0.89 (0.67–1.18) | - | |
| Test | Parameters | Reference | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Syrup | Jelly-S | Jelly-H | Tablet-S | Tablet-H | ||
| Syrup | AUC0-t | - | 1.20 (0.94–1.53) | 1.17 (0.92–1.49) | 1.81 (1.42–2.31) | 1.64 (1.29–2.08) |
| Cmax | - | 1.34 (1.01–1.80) | 1.42 (1.06–1.89) | 2.22 (1.66–3.00) | 2.40 (1.80–3.21) | |
| Jelly-S | AUC0-t | 0.82 (0.66–1.06) | - | 0.97 (0.77–1.24) | 1.51 (1.19–1.92) | 1.36 (1.07–1.74) |
| Cmax | 0.74 (0.56–0.99) | - | 1.05 (0.79–1.41) | 1.65 (1.24–2.21) | 1.79 (1.34–2.38) | |
| Jelly-H | AUC0-t | 0.86 (0.67–1.09) | 1.03 (0.81–1.30) a | - | 1.55 (1.22–1.97) | 1.40 (1.10–1.78) |
| Cmax | 0.71 (0.53–0.94) | 0.95 (0.71–1.27) | - | 1.57 (1.17–2.09) | 1.69 (1.27–2.26) | |
| Tablet-S | AUC0-t | 0.55 (0.43–0.70) | 0.66 (0.52–0.84) | 0.65 (0.51–0.82) | - | 0.90 (0.71–1.15) |
| Cmax | 0.45 (0.34–0.60) | 0.61 (0.45–0.81) | 0.64 (0.48–0.85) | - | 1.08 (0.81–1.44) | |
| Tablet-H | AUC0-t | 0.61 (0.48–0.78) | 0.73 (0.58–0.93) | 0.71 (0.56–0.91) | 1.11 (0.87–1.41) | - |
| Cmax | 0.42 (0.31–0.56) | 0.56 (0.42–0.75) | 0.59 (0.44–0.79) | 0.93 (0.69–1.24) | - | |
| Test | Parameters | Reference | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Syrup | Jelly-S | Jelly-H | Tablet-S | Tablet-H | ||
| Syrup | AUC0-t | - | 1.03 (0.90–1.17) a | 1.05 (0.93–1.20) a | 1.08 (0.95–1.23) a | 1.16 (1.02–1.32) |
| Cmax | - | 1.08 (0.83–1.41) | 1.09 (0.84–1.43) | 0.31 (1.00–1.71) | 1.70 (1.30–2.22) | |
| Jelly-S | AUC0-t | 0.97 (0.86–1.11) a | - | 1.03 (0.90–1.17) a | 1.06 (0.93–1.20) a | 1.13 (0.99–1.29) |
| Cmax | 0.93 (0.71–1.21) | - | 1.01 (0.77–1.32) | 1.21 (0.93–1.58) | 1.57 (1.20–2.05) | |
| Jelly-H | AUC0-t | 0.95 (0.83–1.08) a | 0.97 (0.85–1.11) a | - | 1.03 (0.90–1.17) a | 1.10 (0.97–1.25) a |
| Cmax | 0.91 (0.70–1.19) | 0.99 (0.76–1.29) | - | 1.20 (0.92–1.56) | 1.55 (1.19–2.03) | |
| Tablet-S | AUC0-t | 0.92 (0.81–1.05) a | 0.95 (0.83–1.08) a | 0.97 (0.86–1.11) a | - | 1.07 (0.94–1.22) a |
| Cmax | 0.76 (0.59–1.00) | 0.83 (0.63–1.08) | 0.84 (0.64–1.09) | - | 1.30 (0.99–1.70) | |
| Tablet-H | AUC0-t | 0.86 (0.81–1.05) a | 0.88 (0.78–1.00) | 0.91 (0.80–1.04) a | 0.94 (0.82–1.06) a | - |
| Cmax | 0.59 (0.45–0.77) | 0.64 (0.49–0.83) | 0.64 (0.49–0.84) | 0.77 (0.59–1.00) | - | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, K.H.; Jun, M.; Lee, M.-K. Bioavailability of the Common Cold Medicines in Jellies for Oral Administration. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12111073
Kim KH, Jun M, Lee M-K. Bioavailability of the Common Cold Medicines in Jellies for Oral Administration. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(11):1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12111073
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Ki Hyun, Minju Jun, and Mi-Kyung Lee. 2020. "Bioavailability of the Common Cold Medicines in Jellies for Oral Administration" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 11: 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12111073
APA StyleKim, K. H., Jun, M., & Lee, M.-K. (2020). Bioavailability of the Common Cold Medicines in Jellies for Oral Administration. Pharmaceutics, 12(11), 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12111073




