Abstract
More than two thirds of emerging viruses are of zoonotic origin, and among them RNA viruses represent the majority. Ceratopogonidae (genus Culicoides) are well-known vectors of several viruses responsible for epizooties (bluetongue, epizootic haemorrhagic disease, etc.). They are also vectors of the only known virus infecting humans: the Oropouche virus. Female midges usually feed on a variety of hosts, leading to possible transmission of emerging viruses from animals to humans. In this context, we report here the analysis of RNA viral communities of Senegalese biting midges using next-generation sequencing techniques as a preliminary step toward the identification of potential viral biohazards. Sequencing of the RNA virome of three pools of Culicoides revealed the presence of a significant diversity of viruses infecting plants, insects and mammals. Several novel viruses were detected, including a novel Thogotovirus species, related but genetically distant from previously described tick-borne thogotoviruses. Novel rhabdoviruses were also detected, possibly constituting a novel Rhabdoviridae genus, and putatively restricted to insects. Sequences related to the major viruses transmitted by Culicoides, i.e., African horse sickness, bluetongue and epizootic haemorrhagic disease viruses were also detected. This study highlights the interest in monitoring the emergence and circulation of zoonoses and epizooties using their arthropod vectors.
1. Introduction
There are more than 200 viral species that are known to be able to infect humans. Since the discovery of the yellow fever virus in 1901, three to four new species have been discovered every year [1]. There is, however, a substantial pool of unknown human viral species which are yet to be discovered, and the development and democratisation of Next-Generation Sequencing techniques (NGS) has enabled the identification of many new viruses, for which the potential risk to humans remains mostly unknown. More than two-thirds of viral species infecting humans are of zoonotic origin, and RNA viruses represent more than 70% of these [1,2], resulting in the recent increase in studies of viral communities of wild and domestic animals [3]. However, and despite the fact that haematophagous arthropods usually act as vectors of transmission between animals and humans, few studies have analysed viral communities of arthropods [3]. The studies that have been previously conducted have focused on mosquito viromes [4,5,6,7,8] and have reported the discovery of novel viruses, including bunyaviruses, rhabdoviruses, reoviruses, and flaviviruses. More recently, two studies described the composition of viral communities of hard ticks [9,10] and reported the identification of novel viruses belonging to the Nairovirus, Phlebovirus, and Flavivirus genera, highlighting, as for mosquitoes, potential new zoonotic risks to humans.
Ceratopogonidae, and particularly the genus Culicoides, are small (1–3 mm) and highly diverse midges, with more than 1300 species around the world [11,12]. Of these, 96% are haematophagous and only the females require blood meal for egg fertilisation. Biting midges are well-known vectors of several parasites (such as Mansonella sp.) [13,14] and viruses infecting animals (i.e., bluetongue virus, African horse sickness virus, epizootic haemorrhagic disease virus, Schmallenberg virus, etc.) [15]. The Oropouche virus is the only human virus known to be transmitted by biting midges in Latin and South America [16].
We report here the first comprehensive analysis of viral communities from Senegalese Culicoides biting midges and the identification of several novel viruses, including a novel thogotovirus and a novel rhabdovirus.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
Biting midges were collected using a modified Centers for Disease Control (CDC) light trap in the villages of Dielmo and Ndiop in the Sine-Saloum region of Senegal, in November 2013. Traps were placed near places where cattle rested and were left overnight. Morphological identification of the arthropods was conducted the following morning. Three types of pools of arthropods were created: STE0043 (more than 200 adult Culicoides sp., with no distinction between male and female, or engorged status); STE0044 (N = 15 engorged female Culicoides imicola) and STE0045 (N = 100 non-engorged male and female Culicoides imicola).
2.2. Virome Preparation
The three pools of arthropods were crushed with two 3 mm tungsten beads and a TissueLyser at 25 Hz for two minutes (Qiagen, Courtaboeuf, France). The clarified supernatant was subsequently used as a template for virome preparation, as previously described [17]. Briefly, the clarified supernatant was filtered through a 0.45 µm filter (Millipore, Molsheim, France), and free nucleic acids were digested with a cocktail of nucleases. Finally, the digested supernatant was purified onto a discontinuous 66%–30% sucrose gradient and ultracentrifuged at 130,000 g for two hours at + 4 °C on a MLS-50 rotor (Beckman-Coulter, Villepinte, France). The viral fraction was harvested at the interphase between the 66% and 30% sucrose layers. Total RNAs were extracted from the purified viral fraction with Trizol LS® reagent (Life Technologies, Saint Aubin, France), according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Random amplification was performed using the Froussard [18] random RT-PCR. and amplification products were purified with Agencourt AMPure Beads (Beckman-Coulter, Villepinte, France) according to the manufacturer’s protocol, eluted to a final volume of 15 µL and sequenced using MiSeq Technology using paired-end and barcode strategies according to a Nextera XT library kit in a 2 × 300 bp format (Illumina Inc., San Diego, CA, USA).
2.3. Bioinformatic Analyses of Viromes
Raw reads were imported in pairs into the CLC Genomics Workbench 6.0.1 programme (CLC Bio, Aarhus, Denmark) and trimmed according to their quality score, the presence of ambiguities, and their length (reads which were shorter than 50 nt were discarded). The pre-processed viral metagenomes are publicly available on the Metavir server [19] under the “Arthrovirome” project and on the MG-RAST server [20,21] with the identifiers 4604249.3, 4604250.3, and 4604251.3 for the STE0043, STE0044 and STE0045 RNA viromes, respectively.
Cleaned paired reads were assembled into contigs using the CLC Genomics programme and the following parameters: word size of 20 nt, minimum contig length of 200 nt, mismatch cost of 2, insertion/deletion cost of 3, length fraction of 0.5 and similarity fraction of 0.8. Contigs and non-assembled reads were compared to the NCBI nucleotide database using the BlastN algorithm, with a minimum coverage of 50%, minimum identity of 50% and E-value < 10−5. Sequences having no significant hits according to the criteria described above were classified as “unknown”. Contigs were then compared to the NCBI viral database using the BlastX program with a minimum coverage of 50%, minimum identity of 50% and E-value < 10−5. Finally, to confirm the specificity of the BlastX result, contigs were compared to the NCBI non-redundant nucleotide database using the same criteria. The taxonomic assignation of contigs was conducted by selecting the best BlastX score result between the two Blast run for each contig. Figure S1 presents the pipeline for bioinformatic analyses.
Principal Component Analysis (PCA) was used to compare data in the MG-RAST server [21] with a maximum E-value of 10−5, a minimum identity of 60%, and a minimum alignment length of 15 amino-acids for protein and 15 bp for RNA databases. Data were normalised to values between 0 and 1, and distances were measured using the Bray-Curtis distance matrix.
2.4. Phylogenetic Analyses
Contigs with a significant hit for viruses were translated, and predicted open reading frames (ORFs) were aligned with other amino-acid sequences retrieved from the GenBank database using MUSCLE aligner [22] implemented through MEGA6 [23]. The amino-acid substitutions models that best fitted the data were performed on MEGA6 and were considered for all phylogenetic analyses. The best substitution model was selected using the corrected Akaike information criterion. Phylogenetic trees were constructed using Maximum Likelihood (ML) implemented through the MEGA6 package software, according to the selected substitution model. Nodal support was evaluated using 1000 bootstrap replicates. Bayesian phylogenetic inference (BI) was carried out using MrBayes [24] with two independent runs of four incrementally-heated, Metropolis-coupled Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) starting from a random tree. The MCMC were run for 106 iterations and associated model parameters were sampled every 500 generations. The initial 2000 trees in each run were discarded as burning samples and the harmonic mean of the likelihood was calculated by combining the two independent runs.
Molecular evolutionary distances between sequences were calculated using MEGA6 [23]. For analysis of evolutionary distances between thogotoviruses, individual sequences available in GenBank and the p-distances algorithm were used. For analysis of molecular evolutionary distances between rhabdoviruses, sequences available in GenBank were grouped according to their recognised or putative genus (defined by phylogenetic analyses) and distances were calculated (i) within genera using the p-distance algorithm (ii) between genera using net distance calculations (i.e., MEGA6 takes into account the mean distance within genera) and the p-distance algorithm.
2.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
Approximately 50 mg of STE0043 arthropod samples were washed in 70% ethanol and crushed in 2 mL of sterile EMEM medium (Life Technologies). The supernatant was harvested after low speed clarification and subsequently filtered through a 0.8-µm filter (Millipore) followed by ultracentrifugation onto a discontinuous 66%–30% sucrose gradient at 130,000 g for two hours at + 4 °C. The viral fraction was harvested at the interphase between the 66% and 30% sucrose layers and fixed for one hour at + 4 °C with 2% final glutaraldehyde. The fixed viral fraction was then diluted to a final volume of 4 mL in PBS and directly adsorbed onto formvar carbon films on 400 mesh nickel grids (FCF400-Ni, EMS) by ultracentrifugation at 130,000 g for one hour at + 4 °C, as previously described [25]. Grids were stained for 10 seconds with 1% molybdate solution in filtered water at room temperature. Electron micrographs were obtained on a Tecnai G2 transmission electron microscope (FEI) operated at 200 keV equipped with a 4096 × 4096 pixel resolution Eagle camera (FEI).
3. Results
3.1. Diversity of Viral Communities in Haematophagous Biting Midges
RNA viromes of samples STE0043, STE0044 and STE0045 were sequenced using Illumina MiSeq technology. Sequencing statistics are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Virome dataset statistics.
The taxonomic assignment of reads identified only 5%–25% of sequences which had similarities with known sequences (Figure 1A). Of these, eukaryotes represented the majority of sequences, with 72.52%, 62.10% and 83.95% of total known reads of the STE0043, STE0044 and STE0045 RNA viromes, respectively (Figure 1A). Most eukaryotic reads were assigned to arthropods (>60% of total eukaryotic reads), and they mainly consisted of arthropod ribosomal RNAs. Bacteria-related sequences ranged from 9% to 37% depending on the sample (Figure 1A).

Figure 1.
Taxonomic assignment of reads (A) BlastN search against the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) nucleotide database (dashes correspond to the arthropod-borne proportion of eukaryotic reads) (B) Relative abundance of viral families in biting midge metagenomes according to their target hosts (Green: plant viruses, Brown: insect viruses, Grey: bacteriophages, Red: arboviruses, Yellow: mammalian viruses, Blue: amoeba-infecting giant viruses).
Virus-related sequences represented 0.73%–18.48% of total known reads. Of them, plant viruses (i.e., Partitiviridae, Tymoviridae) composed 15.48%, 10.10% and 0.00% of total viral reads for STE0043, STE0044 and STE0045 RNA viromes, respectively (Figure 1B). Insect viruses (i.e., Iflaviridae, Mesoniviridae, Dicistroviridae, and non-classified insect viruses) represented the majority of viral reads, with 55.51%, 76.23% and 33.66% of total viral reads for STE0043, STE0044 and STE0045 RNA viromes, respectively. Several mammalian viruses were detected, such as Picobirnaviridae-related viruses, but only in the STE0045 C. imicola male and non-engorged female virome, with a global abundance of 33.73% of total viral reads. Animal-infecting arboviruses belonging to the Reoviridae family were identified and represented 26.34%, 0.04% and 17.79% of total viral reads for STE0043, STE0044 and STE0045 RNA viromes, respectively (Figure 1B). Finally, several reads were assigned to Orthomyxoviridae (1.69% and 1.84% of total viral reads for STE0043 and STE0045 viromes, respectively) and Rhabdoviridae (0.96% and 1.86% of total viral reads for STE0043 and STE0044 viromes, respectively) but they presented a relatively low identity of 57%–62% in the RNA polymerase after BlastX analysis (Figure 1B). Few DNA viruses were also identified in the RNA viromes (bacteriophages and amoeba-infecting giant viruses, representing 0.02%, 5.24% and 12.97% of total viral reads for STE0043, STE0044 and STE0045 RNA viromes, respectively), possibly due to residual contamination of the RNA fraction by viral DNA (Figure 1B).
Electron microscopy images of the STE0043 Culicoides sp. purified viral fraction showed the presence of virus-like particles (VLPs) with various diameters, morphologies, and contrasts (Figure 2). Some VLPs presented a round structure with a distinct envelope, while others appeared with more contrast. The diameters of the particles ranged from 100 nm to 600 nm (Figure 2).
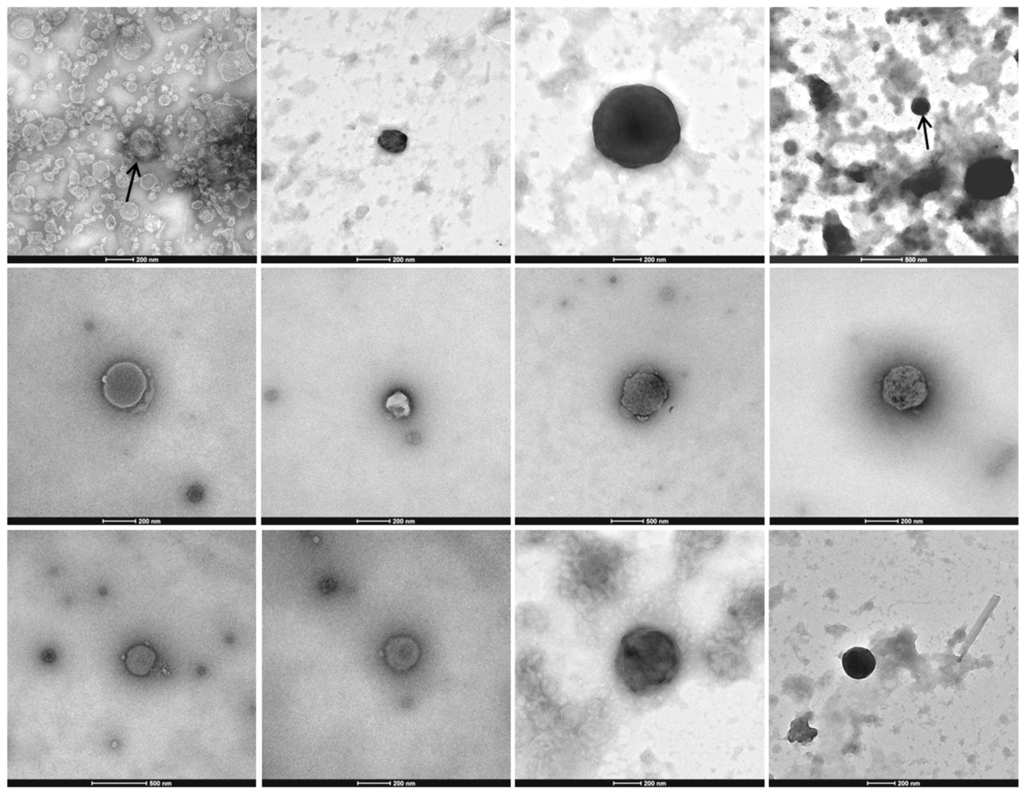
Figure 2.
Repertory of transmission electron microscopy images of Culicoides sp. viral communities.
Principal component analysis (PCA) was used to compare viral communities of biting midges with other haematophagous and non-haematophagous arthropod RNA viromes available in public databases (Figure 3, Table S1). RNA viromes of biting midges clustered together, but the STE0043 Culicoides sp. virome was more distant than the STE0044 C. imicola engorged female and STE0045 C. imicola male and non-engorged female viromes. In addition, biting midge viromes were closer to field and artificially-infected mosquito metagenomes than to whitefly and butterfly viromes (Figure 3).
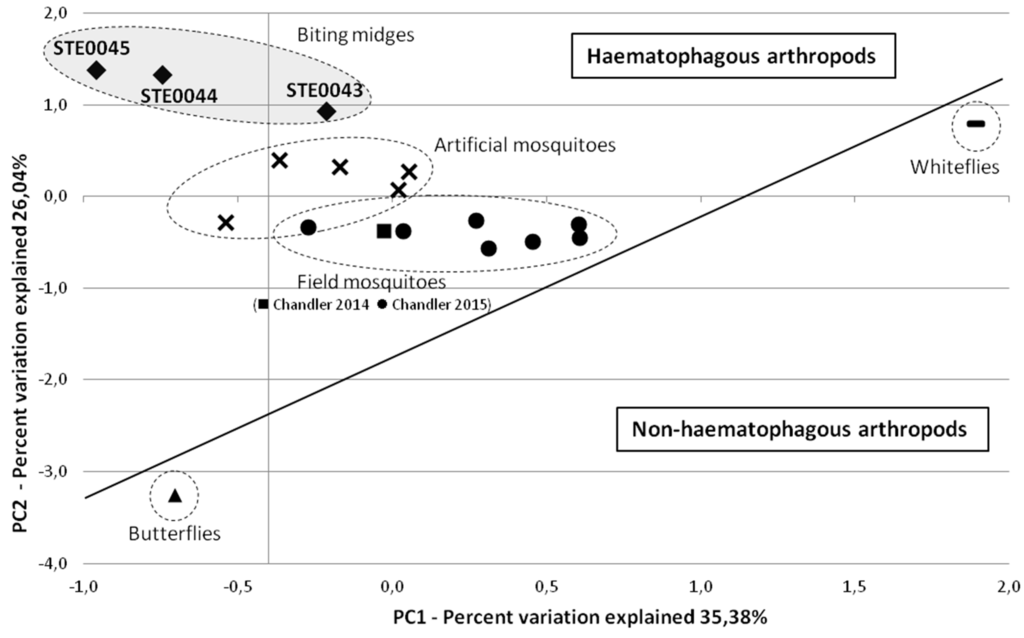
Figure 3.
Comparison between viromes of biting midges with available arthropod RNA metagenomes based on a taxonomic classification of reads. Principal component analysis (PCA) was used to compare data in MG-RAST server [21] with a maximum E-value of 10−5, a minimum identity of 60%, and a minimum alignment length of 15 amino-acids for protein and 15 bp for RNA databases. Data were normalised to values between 0 and 1 and distances were measured using the Bray-Curtis distance matrix.
3.2. Orbiviruses Were Abundant in Senegalese Biting Midges
Within the viral reads, Reoviridae-related sequences represented 26.34%, 0.04% and 17.79% in STE0043, STE0044 and STE0045 RNA viromes, respectively; with the presence of bluetongue-related sequences in STE0043 (N = 3656 reads) and STE0045 (N = 678 reads) viromes while epizootic haemorrhagic disease virus (EHDV) was detected in STE0043 (N = 5454 reads) and STE0044 (N = 5 reads) viromes. African horse sickness virus (AHSV) was only detected in the STE0043 Culicoides sp. RNA virome (N = 1647 reads).
Various segments of these 10-segmented double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) orbiviruses were detected in the metagenomes. For example EHDV-related sequences matched with VP4 protein of segment 4 in the STE0044 C. imicola engorged female virome. In the STE0045 sample, all reads matched with segment 8 (NS2 protein) of the bluetongue virus (BTV). Within the STE0043 Culicoides sp. virome, sequences related to segments 1-2-3-4-6-7-8 and 9 of AHSV were present, while NS1 (segment 5) and NS3 (segment 10) were not detected. Segments 1-2-3-4-8 and 9 of BTV and segments 1-3-4-6 and 8 of EHDV were detected, with a global coverage of the genome estimated after mapping at 37.27%, 34.58% and 33.16% for AHSV, BTV and EHDV, respectively, in the STE0043 metagenome (data not shown).
3.3. Novel Thogotovirus Species
Within the virome of the STE0043 Culicoides sp. and STE0045 C. imicola male and non-engorged female samples, large contigs of 1903 nt and 1217 nt, respectively, matched with the viral RNA polymerase PB1 segment of viruses belonging to the genus Thogotovirus (family Orthomyxoviridae), with a nucleotide identity of 61.26% and 57.61%, respectively. Phylogenetic analyses enabled the identification of a clade formed by the identified thogotovirus-like orthomyxovirus, tentatively named “Dielmo orthomyxovirus” (DOV), with a high bootstrap value of 99.2 and a high posterior probability of 1 (Figure 4A). The clade formed by DOV, placed at the root of the group formed by viruses belonging to the Thogotovirus genus, is supported by high bootstrap value and posterior probability, suggesting that DOV could constitute either a novel species within the Thogotovirus genus or a novel genus within the Orthomyxoviridae family (Figure 4A). However, analyses of genetic distances between DOV and other orthomyxoviruses supported the classification of DOV among the Thogotovirus genus rather than a new genus since it presented similar distances with other thogotoviruses and distances in the same range as those observed between other thogotoviruses and Influenzavirus genus (Figure 4B).
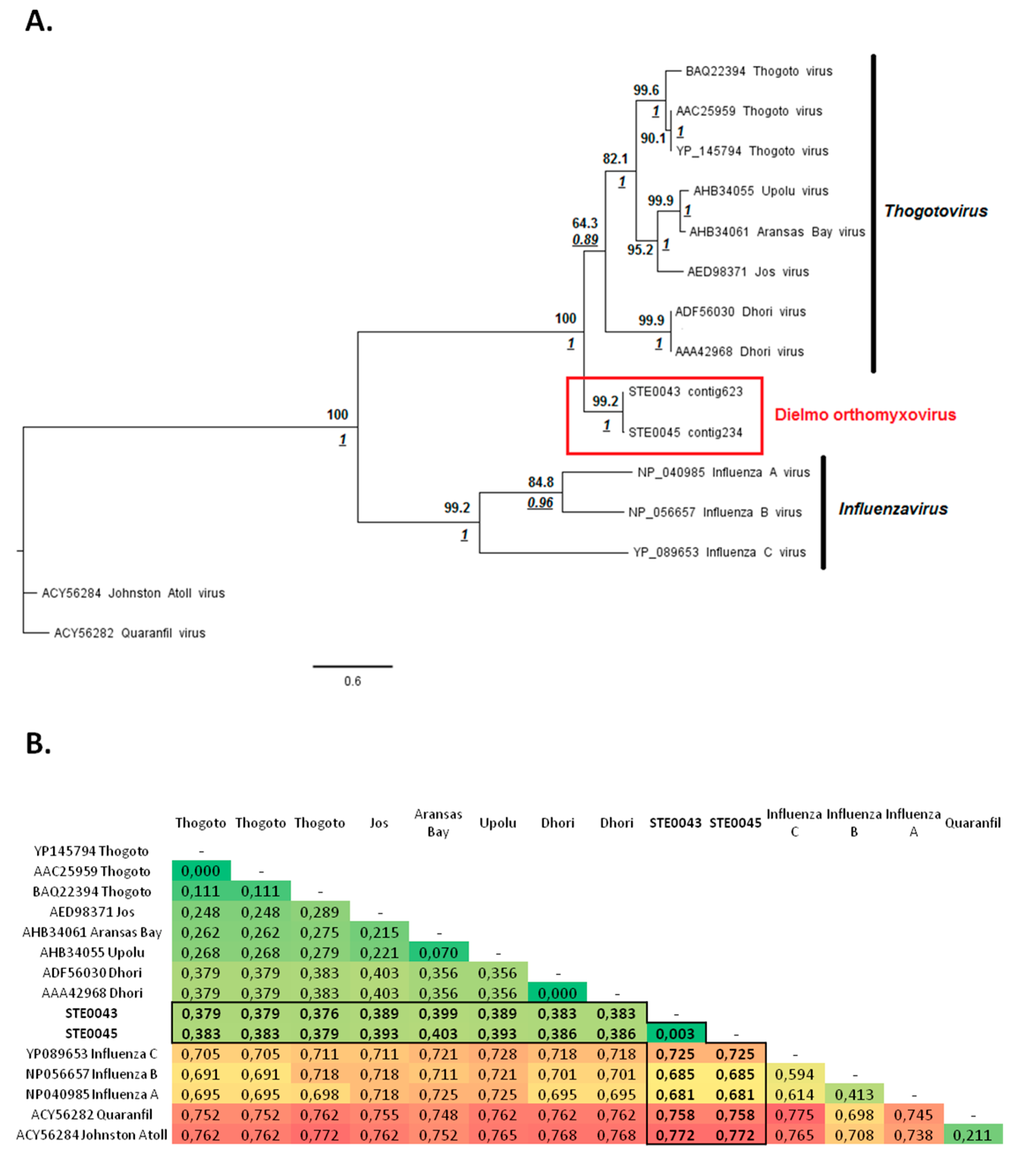
Figure 4.
Phylogenetic analyses of Dielmo orthomyxovirus compared to other Thogotovirus viruses. (A) Phylogenetic analysis of a fragment of 358 amino-acids of PB1. ML analysis was used to fix tree topology. ML analysis was performed on 1000 iterations and bootstrap values are represented in bold. Bayesian posterior probabilities are underlined and represented in italics where nodes coincided with ML. Substitutions models for ML and Bayesian analyses were determined as LG+I+G and rtREV+I+G, respectively. Scale bar indicates the number of amino-acid substitutions per site; (B) Matrix of genetic distances observed between PB1 amino-acid sequences of Dielmo orthomyxovirus and other representative thogotoviruses. Diversity was calculated by the pairwise-distance algorithm implemented through MEGA [23].
3.4. Novel Rhabdoviridae Genus
Within the virome of the STE0043 Culicoides sp. and STE0044 C. imicola engorged female samples, large contigs of 1397 nt and 1572 nt, respectively, matched with the viral RNA polymerase of North Creek virus (NCV), a novel rhabdovirus detected in Australian mosquito metagenomes [26]. The new Senegalese rhabdovirus, tentatively named “Dielmo rhabdovirus” (DRV), was distant from North Creek virus, with only 62.61% and 61.06% of nucleotide homologies, respectively. Nucleotide and amino-acid sequences of STE0043 and STE0044 Dielmo rhabdovirus were 100% identical, while they presented a genetic distance from Australian mosquito North Creek virus of 0.352 and 0.377 in nucleotide and amino-acid sequences, respectively.
In order to identify whether DRV could either constitute a novel species or a novel genus within the Rhabdoviridae family, we selected GenBank sequences according to the Walker et al. dataset [27] in order to clearly identify recognised or putative Rhabdoviridae genera (Figure 5). Phylogenetic analysis identified a clade (sub-clade I) formed by biting midge DRV and Australian mosquito NCV, with a high bootstrap value of 99 and a high posterior probability of 1. Beaumont virus, another rhabdovirus identified in Australian mosquito metagenomes [26] and Culex tritaeniorhynchus rhabdovirus (CTRV), identified in Japanese mosquitoes [28] formed a sub-clade II at the root of sub-clade I (Figure 5, Figure S2). This group, consisting of the two sub-clades, could constitute a novel genus within the Rhabdoviridae family (Figure 5, Figure S2). This putative genus was tentatively named Dielmovirus genus. Dielmoviruses belong to the Dimarhabdovirus supergroup (dipteran-mammal rhabdoviruses) (Figure S2).

Figure 5.
Phylogenetic analysis of Dielmovirus genus compared to other Rhabdoviridae. Phylogenetic analysis of a fragment of 463 amino-acids of the RNA-dependant RNA polymerase. Bayesian inference (BI) analysis was used to fix tree topology. BI analysis was performed on 1,000,000 iterations and nodes with a posterior probability above 0.80 are represented. ML analysis was performed on 1000 iterations and nodes above 65 are represented, when nodes coincided with BI. Recognised or a putative genera are defined as described in [27]. Substitutions models for ML and Bayesian analyses were determined as LG+I+G and rtREV+I+G, respectively. Scale bar indicates the number of amino-acid substitutions per site. Cytorhabdoviruses, Novirhabdoviruses and Nucleorhabdoviruses were excluded from the analysis because sequences were too divergent.
The genetic distances of Dielmovirus genus compared to other Rhabdoviridae genera, as defined by Walker et al. [27], are presented in Figure 6. The mean genetic distance between viruses within the Dielmovirus genus is higher than that observed within each recognised or putative genus (Figure 6A), with the exception of Sigmaviruses, supporting the distinction of two sub-clades within the Dielmovirus genus: one formed by NCV and DRV, and the other composed of Beaumont and CTR viruses. In addition, the putative Dielmovirus genus presented a distribution of distances with other genera in the same range than the global distribution of distances observed between other genera (Figure 6B). Viruses belonging to the Dielmovirus genus diverge by approximately 15%–26% in the amino-acid sequence of the RNA-dependant RNA polymerase from other Rhabdoviridae genera, which is globally observed for all other genera with the exception of the Lyssavirus, Almendravirus, Bahiavirus and Sawgravirus genera, which seemed to present a greater genetic distance (Figure 6B). Interestingly, these four recognised and putative genera did not belong to the Dimarhabdovirus supergroup (Figure 6B, Figure S2). The Sigmavirus genus presented the least distance with Dielmovirus, and Bahiavirus presented the greatest distance, which is consistent with phylogenetic observations.
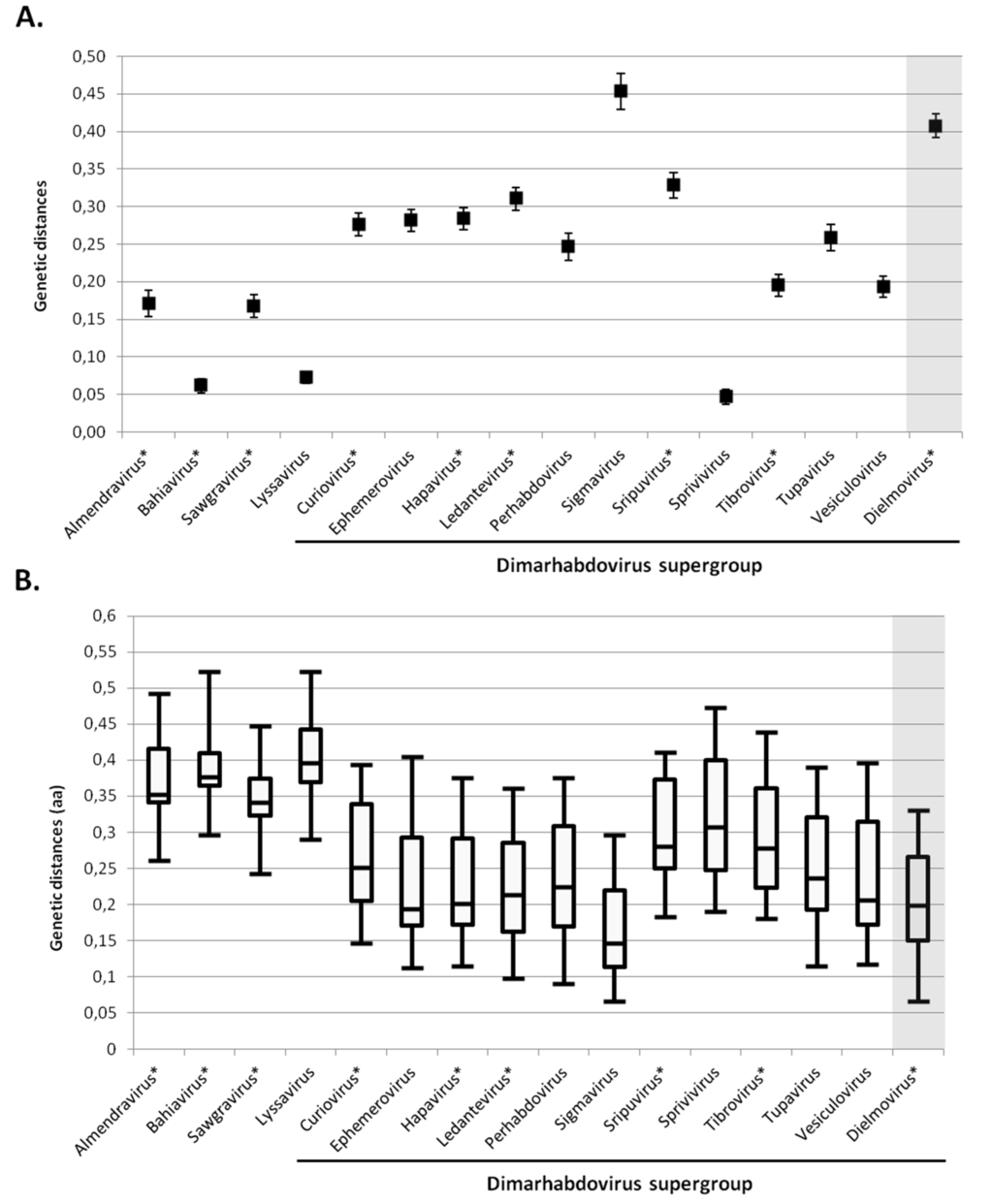
Figure 6.
Genetic distances of Dielmovirus genus compared to other Rhabdoviridae. (A) Mean distances within recognised and putative Rhabdoviridae genera (putative genera, as reported in [27], are indicated by a *). Diversity was calculated by the pairwise-distance algorithm implemented through MEGA6 [23], and 1000 bootstrap replications; (B) Distribution of distances between recognised and putative Rhabdoviridae genera (putative genera are indicated by a *). Diversity was calculated by the pairwise-distance algorithm implemented through MEGA6 [23]
3.5. Detection of Jingmen Tick Virus-Related Sequences
Within the virome of the STE0043 Culicoides sp. sample, one contig of 609 nt matched with the NS5 segment of Jingmen Tick virus (JTV), a novel chimerical virus isolated in Chinese ticks and composed of four segments: two originating from a flavivirus (NS3 and NS5-like segments) and two with high similarities with Toxocara canis nematode cDNA library [29]. The Senegalese biting midge Jingmen Tick-like virus (JTV-like virus) presented a low nucleotide identity of 57.95% with the JTV NS5 segment. Phylogenetic analysis of several representative flaviviruses, JTV and Mogiana tick virus (MTV, another virus isolated in ticks which has similarities with flaviviruses [30]) performed in the NS5 gene revealed that the Senegalese JTV-like virus was located at the root of a clade formed by these new flavi-like viruses with a high bootstrap value of 97 and a high posterior probability of 1. This clade does not belong to the Flavivirus genus (posterior probability of 1 for the node defining this clade apart from the Flavivirus genus clade), but belongs to the Flaviviridae family (Figure 7).
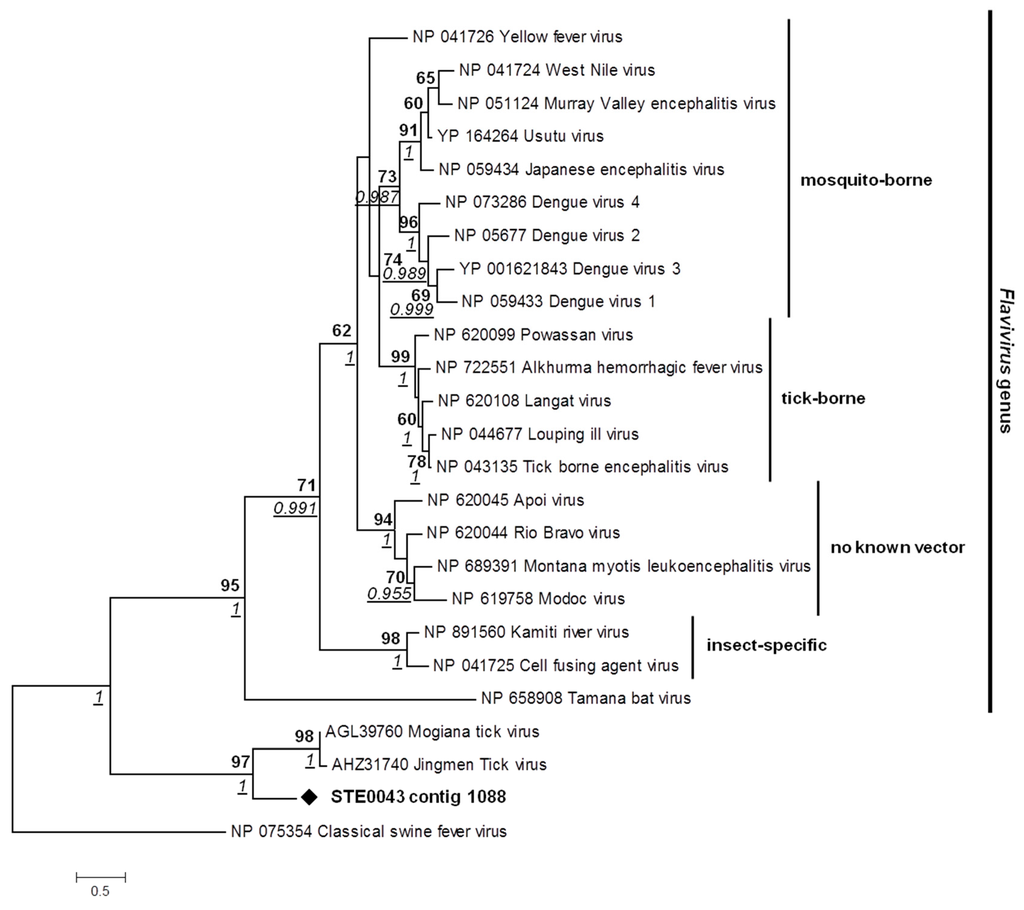
Figure 7.
Phylogenetic analysis of Jingmen Tick-like virus. Phylogenetic analysis of a fragment of 319 amino-acids of the NS5 segment. ML analysis was used to fix tree topology. ML analysis was performed on 1000 iterations. Bootstrap values above 60 and posterior probabilities above 0.5 are indicated. Bayesian posterior probabilities are underlined and represented in italics where nodes coincided with ML. Substitution models for ML and Bayesian analyses were determined as LG+G and rtREV+ G, respectively. Scale bar indicates the number of amino-acid substitutions per site.
In addition, by re-analysing contigs with low identities and coverage that were previously discarded, we detected one contig which matched the JTV NS3 segment with a homology percentage of 41.3% in nucleotide and an E-value of 10−9, and a contig which matched Toxocara canis ANT-5 with an E-value of 10−59 and homology of 34.18%.
3.6. Presence of Endogenous Viral Elements?
To verify the presence of endogenous viral elements (EVE) within the major detected arboviruses, we screened for the presence of possible integration sites within the viral contigs. Among the 3′ portion of the JTV-like viral contig, only 23 nt did not match with a viral sequence but matched with Ovis canadensis chromosome 25. We were not able to detect similar sequences in other viral contigs.
In addition, and due to reports of a rhabdoviral EVE in mosquitoes [31], we performed a Bayesian inference phylogenetic analysis of the Dielmovirus rhabdovirus genus compared to other rhabdoviruses and Rhabdoviridae-related EVEs, which confirmed that Dielmoviruses did not correspond to the previously identified A. aegyti RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRP)-related EVE (Figure S3).
Finally, the presence of EVEs in the glycoprotein gene of Orthomyxoviridae in the genome of Ixodes scapularis ticks had previously been reported [32], but not among the PB1 segment of the RdRP detected in our biting midge orthomyxovirus.
3.7. Other Viruses Present in Biting Midges
Sequencing the viral communities of Senegalese biting midges revealed the presence of viruses infecting a wide variety of hosts, including mammals, insects, plants and bacteria.
Mammalian-infecting viruses were only detected in STE0045 C. imicola male and non-engorged female RNA viromes and consisted of 33.73% of total viral reads (Figure 1B). The viral family which was most represented was Picobirnaviridae (57.59% of all mammalian viral reads). Interestingly, the Picobirnaviridae-related contig matched with a feline picobirnavirus with a nucleotide identity of 53.91%, suggesting the presence of a possible new picobirnavirus either originating from Culicoides or from animals on which arthropods feed.
Insect-specific viruses were also highly abundant in the viromes, representing 55.51%, 76.23% and 33.66% of total viral reads in the STE0043, STE0044 and STE0045 RNA viromes, respectively (Figure 1B). Iflaviridae were abundant, but most insect-specific viral reads matched with novel viruses, currently not recognised by the International Committee for Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV). Indeed, sequences matching the Loreto virus, Negev virus and Negev-like virus 174, Piura virus and Nora virus were retrieved, with low nucleotide identities comprised between 50% and 56%, 50% and 60%, 63% and 74%, 51% and 63% and 67% and 69%, respectively.
Plant-infecting viruses belonging to the Partitiviridae and Tymoviridae families were detected in the STE0043 and STE0044 viromes. Partitiviridae-related sequences from Alphapartitivirus, Betapartitivirus, Gammapartitivirus genera and unclassified partitiviruses were detected in the STE0043 virome whereas only unclassified partitiviruses were identified in the STE0044 virome. All sequences displayed low nucleotide identities (53%–75%) suggesting the detection of potentially new viruses. Tymoviridae-related sequences, again with low nucleotide identities (51%–64%), were also detected in the STE0043 virome and were assigned to the Maculavirus and Marafivirus genera.
Several reads related to bacteriophages were also detected in the STE0044 and STE0045 samples, and amoeba-infecting giant viral sequences were identified in the STE0045 virome, probably reflecting a residual contamination of DNA in the RNA preparations (Figure 1B) or the carriage of mRNAs within viral particles.
4. Discussion
We report in this study an extensive characterisation of the RNA viral communities of Senegalese biting midges. Analysis of the taxonomic assignment of reads revealed a high proportion of unknown sequences. This result, in the same range as those observed in tick [10] and mosquito [8] metagenomes, again reflects the lack of data about RNA viruses in the databases, and highlights the potential pool of unknown viruses yet to be discovered and which could represent future emerging viruses.
The pattern of composition of RNA viral communities was highly divergent in terms of relative abundance and of the composition of viruses within the three metagenomes, although arthropods were collected at the same place during the same night in the same trap. This suggests that these differences may result from intrinsic characteristics of the insects rather than the environment. However, the three biting midge viromes clustered together in the principal component analysis when compared to other haematophagous and non-haematophagous arthropods, suggesting the presence of a “core” viral community shared by all biting midges, and “accessory” viral communities specific to a species, gender or haematophagous status. Indeed, STE0043 Culicoides sp. was more distant than the STE0045 pool of C. imicola males and non-engorged females and the STE0044 pool of C. imicola engorged females, despite the fact that they differ only by arthropod species composition. In addition, biting midge viromes were closer to other haematophagous arthropods than to non-haematophagous arthropods, potentially highlighting the influence of blood meal in the composition of viromes.
Orbivirus-related sequences were the most represented in the viromes. These Reoviridae are livestock-restricted viruses which cause significant economic losses: AHSV causes malfunctions of the circulatory and respiratory systems leading to the death of equines, while BTV and EHDV cause significant decreases in milk production and death in ruminants [15,33,34,35]. In Europe and Africa, the main vector of AHSV and BTV is C. imicola, while EHDV is transmitted by the C. schultzei group in Africa [15]. In Senegal, several Culicoides species are present: the C. imicola, C. schultzei, C. milnei, C. magnus and C. fulvithorax groups [36], which can represent a potential epizootic risk to livestock. In 2007, Senegal reported a significant AHSV epidemic among equines and, since then, animals have been vaccinated [37]. BTV also highly circulates among ruminants, as shown in sero-epidemiological studies [38], although no recent epidemics have been reported. In addition, to our knowledge, no EHD epidemic or study has been reported in Senegal, but the symptoms of BTV or EHDV infections are very similar, resulting in a possible wrong diagnosis of an etiology as a bluetongue-like pathology [15]. In this study we reported the detection of sequences related to AHSV, BTV and EHDV Reoviridae viruses. The STE0043 pool of Culicoides sp. presented the majority of Reoviridae reads, and within them, AHSV, BTV and EHDV represented 15.3%, 34.0% and 50.7% of total Reoviridae-related sequences, respectively. Interestingly, only a few BTV reads were detected in the STE0044 C. imicola engorged female and STE0045 C. imicola males and non-engorged females despite the fact that C. imicola is known to be the main vector of this virus in Africa. Despite the fact that this study constitutes a snapshot of the composition of viral communities present in biting midges sampled at a given time and location and may not reflect the composition of the viral communities of Senegalese Culicoides through one year, this result may suggest that other midge species could be vectors of BTV in Senegal, as demonstrated by the high prevalence of BTV in the STE0043 Culicoides sp. pool. Diarra et al. completed in 2014 a one-year survey of Culicoides midge populations in Senegal [39]. They showed that Culicoides oxystoma, followed by C. kingi and C. imicola, were the most prevalent species of biting midges, and they could constitute alternative vectors of BTV. In addition, the authors showed that C. imicola presented a globally constant abundance throughout the year lower than the ones observed for C. oxystoma and C. kingi, while C. oxystoma peaked during August to November and C. kingi during May to October, suggesting that possible other midges species may play the role of vectors of BTV in Senegal, depending on the season. Further follow-up of circulating viruses in different midge populations throughout the year would help clarify vector(s) and seasonality of BTV in Senegal. Finally, the detection of EHDV-related reads matching nearly all of the viral segments suggests that the virus is probably circulating among the vector populations and may precede the onset of an outbreak. Thus, it highlights the importance of monitoring the emergence of epizooties by studying viral communities of haematophagous arthropods [3].
In 2009, Peter Daszak noted that only 0.2% of the total estimated viral diversity possibly infecting humans is currently known [40]. By allowing the identification of potential new viruses, next-generation sequencing techniques allow reducing this gap. Indeed, in this study we reported the description of new viruses in biting midge RNA viromes, including a novel thogotovirus. Dielmo Orthomyxovirus (DOV) was detected in the pool of Culicoides sp. and the pool of C. imicola males and non-engorged females. Phylogenetic analyses and calculation of genetic distance resulted in the identification of a new thogotovirus species, distinct from other known thogotoviruses. Thogotoviruses are single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) negative-strand segmented viruses belonging to the Orthomyxoviridae family. All isolated from hard ticks [41] (with the exception of the Batken virus, which was also isolated from mosquitoes [42]), thogotoviruses are able to infect a wide variety of vertebrate hosts, including birds, rodents, livestock and humans [43,44,45,46,47,48,49]. In humans, these viruses cause fever and, in some cases, neurological symptoms such as meningitis or encephalitis [50,51]. Recently, a novel thogotovirus, tentatively named “Bourbon virus” was responsible for the death of an individual who had previously been bitten by a tick, due to a decrease in blood platelets and white cells but with no neurological symptoms [52]. The status of the newly described Dielmo Orthomyxovirus is currently unknown, but the successful isolation of DOV should permit to (i) determine its phylogenetic relationships with other thogotoviruses by sequencing its genome; (ii) review experiences of the vector competence of Culicoides midges to transmit the virus and allow its possible classification as an “arbovirus”; and (iii) develop an animal model of infection to determine its pathogenicity.
Novel Rhabdoviridae-related viral sequences were also detected. These sequences clustered together in a monophyletic group with North Creek virus, a virus recently discovered in Culex sitiens mosquitoes in Australia [26]. We propose that this sub-clade, in addition to another sub-clade formed by the Beaumont virus [26] and Culex tritaeniorhynchus rhabdovirus [28], form a new genus within the Rhabdoviridae family, tentatively named Dielmovirus. Dielmoviruses cluster with the Sigmavirus genus, within which viruses were only isolated from Drosophila flies. Many rhabdoviruses were previously isolated from biting midges [27]: for example, Fukuoka virus (a cattle virus), vesicular stomatitis New Jersey virus (a cattle virus), Wongabel virus (a seabird virus), Ngaingan virus (a cattle virus), Curionopolis virus (a primate virus) and Tibrogargan virus (a cattle virus). Nearly all of them belong to the “arbovirus” group, with the exception of the Itacaiunas virus, which is restricted to midges and which form a distinct clade. Dielmoviruses, such as the Sigmaviruses, appear to be restricted to haematophagous (mosquitoes, biting midges) and non-haematophagous (flies) Diptera, and phylogenetic analyses revealed that insect-specific rhabdoviruses form distinct monophyletic groups, suggesting that stringent host specificity occurs for these viruses (Figure 5, [27]). In contrast, arbo-rhabdoviruses, possibly due to significant host switching between vertebrate hosts and arthropod vectors, appear to be more diverse. Indeed, higher genetic distances among recognised or putative genera were observed for Sigmavirus and Dielmovirus, reinforcing the observation that strong host specificity occurs among insect-specific rhabdoviruses. Vasilakis and Tesh recently noted that insect-specific rhabdoviruses, as well as bunyaviruses and flaviviruses, are ancient and probably evolved and diversified in parallel with their insect hosts [53], via vertical transmission or integration within the host genome.
It is well-known that arthropod genomes, as well as vertebrate animals, contain integrated fragments or entire genomes of viral RNA [31,32,54,55,56,57,58]. These regions, called EVE [32], can be functional in the genomes of several hosts [58,59,60] and often derive from ancient viral infections for which the integration was vertically transmitted and evolve in parallel with their eukaryotic host. In our study, we demonstrated that the newly described Thogotovirus species and Rhabdoviridae genera did not correspond to previously reported related EVEs [31,32], suggesting that these viruses could constitute novel viral species and genus.
To conclude, this study reports the first description of viral communities of haematophagous arthropods which have an impact on human and veterinary medicine: the Culicoides. We detected the presence of several novel viruses, including a novel Thogotovirus species and a novel Rhabdoviridae genus, which may constitute potential risks for human and animal health. This study thus highlights the importance of characterising the viral communities of haematophagous arthropods as a first step in the evaluation of the emergence of epizooties and/or zoonoses using next-generation sequencing techniques.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at www.mdpi.com/1999-4915/8/3/77/s1, Figure S1: Pipeline for bioinformatic analyses, Figure S2: Phylogenetic analysis of Dielmovirus genus compared to other Rhabdoviridae. Figure S3. Phylogenetic analysis of Dielmovirus genus compared to other Rhabdoviridae and the endogenous viral element A. aegypti. Table S1. Characteristics of metagenomes used for PCA analysis.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Hervé Pascalis for his critical comments on phylogenetic analysis, Catherine Cêtre-Sossah for her expertise on orbiviruses, and Ti Thien Nguyen for her help in preparing the libraries. This work was partly supported through a SANOFI-PASTEUR international prize awarded to Christelle Desnues.
Author Contributions
S.T., O.M. and C.D. conceived and designed the experiments; S.T., S.M.B., C.R., J.P.B., and N.L. performed the experiments; S.T., M.S. and M.A.L. collected the samples on the field, S.T. analyzed the data; S.T. wrote the paper; D.R., O.M. and C.D. reviewed the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Woolhouse, M.; Scott, F.; Hudson, Z.; Howey, R.; Chase-Topping, M. Human viruses: discovery and emergence. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2012, 367, 2864–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutler, S.J.; Fooks, A.R.; van der Poel, W.H. Public health threat of new, reemerging, and neglected zoonoses in the industrialized world. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temmam, S.; Davoust, B.; Berenger, J.M.; Raoult, D.; Desnues, C. Viral metagenomics on animals as a tool for the detection of zoonoses prior to human infection? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 10377–10397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop-Lilly, K.A.; Turell, M.J.; Willner, K.M.; Butani, A.; Nolan, N.M.; Lentz, S.M.; Akmal, A.; Mateczun, A.; Brahmbhatt, T.N.; Sozhammannan, S.; et al. Arbovirus detection in insect vectors by rapid, high-throughput pyrosequencing. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2010, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinsdale, E.A.; Edwards, R.A.; Hall, D.; Angly, F.; Breitbart, M.; Brulc, J.M.; Furlan, M.; Desnues, C.; Haynes, M.; Li, L.; et al. Functional metagenomic profiling of nine biomes. Nature 2008, 452, 629–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandler, J.A.; Thongsripong, P.; Green, A.; Kittayapong, P.; Wilcox, B.A.; Schroth, G.P.; Kapan, D.D.; Bennett, S.N. Metagenomic shotgun sequencing of a Bunyavirus in wild-caught Aedes aegypti from Thailand informs the evolutionary and genomic history of the Phleboviruses. Virology 2014, 464–465, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandler, J.A.; Liu, R.M.; Bennett, S.N. RNA shotgun llinoisics sequencing of northern California (USA) mosquitoes uncovers viruses, bacteria, and fungi. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, T.F.; Willner, D.L.; Lim, Y.W.; Schmieder, R.; Chau, B.; Nilsson, C.; Anthony, S.; Ruan, Y.; Rohwer, F.; Breitbart, M. Broad surveys of DNA viral diversity obtained through viral metagenomics of mosquitoes. PLoS ONE 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokarz, R.; Williams, S.H.; Sameroff, S.; Sanchez Leon, M.; Jain, K.; Lipkin, W.I. Virome analysis of Amblyomma americanum, Dermacentor variabilis, and Ixodes scapularis ticks reveals novel highly divergent vertebrate and invertebrate viruses. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 11480–11492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, H.; Hu, C.; Zhang, D.; Tang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Kou, Z.; Fan, Z.; Bente, D.; Zeng, C.; Li, T. Metagenomic profile of the viral communities in Rhipicephalus spp. Ticks from Yunnan, China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borkent, A. World Species of Biting Midges (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae). 2014. Available online: http://wwx.inhs.illinois.edu/files/9913/9144/3328/CeratopogonidaeCatalog.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2015).
- Borkent, A. The Subgeneric Classification of Species of Culicoides-Thoughts and a Warning. 2014. Available online: http://wwx.inhs.illinois.edu/files/9613/9136/7590/CulicoidesSubgenera.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2015).
- Bassene, H.; Sambou, M.; Fenollar, F.; Clarke, S.; Djiba, S.; Mourembou, G.; L Y, A.B.; Raoult, D.; Mediannikov, O. High prevalence of Mansonella perstans filariasis in rural Senegal. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 93, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agbolade, O.M.; Akinboye, D.O.; Olateju, T.M.; Ayanbiyi, O.A.; Kuloyo, O.O.; Fenuga, O.O. Biting of anthropophilic Culicoides fulvithorax (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae), a vector of Mansonella perstans in Nigeria. Korean J. Parasitol 2006, 44, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellor, P.S.; Boorman, J.; Baylis, M. Culicoides biting midges: Their role as arbovirus vectors. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2000, 45, 307–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesh, R.B. The emerging epidemiology of Venezuelan hemorrhagic fever and Oropouche fever in tropical South America. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1994, 740, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temmam, S.; Monteil-Bouchard, S.; Robert, C.; Pascalis, H.; Michelle, C.; Jardot, P.; Charrel, R.; Raoult, D.; Desnues, C. Host-Associated Metagenomics: A Guide to Generating Infectious RNA Viromes. PLoS ONE 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froussard, P. A random-PCR method (rPCR) to construct whole cDNA library from low amounts of RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992, 20, 2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metavir server. Available online: http://metavir-meb.univ-bpclermont.fr (accessed on 20 October 2015).
- MG-RAST server. Available online: http://metagenomics.anl.gov/ (accessed on 20 October 2015).
- Meyer, F.; Paarmann, D.; D’Souza, M.; Olson, R.; Glass, E.M.; Kubal, M.; Paczian, T.; Rodriguez, A.; Stevens, R.; Wilke, A.; et al. The metagenomics RAST server-a public resource for the automatic phylogenetic and functional analysis of metagenomes. BMC Bioinformatics 2008, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: a multiple sequence alignment method with reduced time and space complexity. BMC Bioinform. 2004, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1572–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sime-Ngando, T.; Mignot, J.P.; Amblard, C.; Bourdier, G.; Desvilettes, C.; Quiblier-Lloberas, C. Characterization of planktonic virus-like particles in a French mountain lake: methodological aspects and preliminary results. Annal. Limnol. 1996, 32, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffey, L.L.; Page, B.L.; Greninger, A.L.; Herring, B.L.; Russell, R.C.; Doggett, S.L.; Haniotis, J.; Wang, C.; Deng, X.; Delwart, E.L. Enhanced arbovirus surveillance with deep sequencing: Identification of novel rhabdoviruses and bunyaviruses in Australian mosquitoes. Virology 2014, 448, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, P.J.; Firth, C.; Widen, S.G.; Blasdell, K.R.; Guzman, H.; Wood, T.G.; Paradkar, P.N.; Holmes, E.C.; Tesh, R.B.; Vasilakis, N. Evolution of genome size and complexity in the Rhabdoviridae. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuwata, R.; Isawa, H.; Hoshino, K.; Tsuda, Y.; Yanase, T.; Sasaki, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Sawabe, K. RNA splicing in a new rhabdovirus from Culex mosquitoes. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 6185–6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.C.; Shi, M.; Tian, J.H.; Lin, X.D.; Gao, D.Y.; He, J.R.; Wang, J.B.; Li, C.X.; Kang, Y.J.; Yu, B.; et al. A tick-borne segmented RNA virus contains genome segments derived from unsegmented viral ancestors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 6744–6749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruyama, S.R.; Castro-Jorge, L.A.; Ribeiro, J.M.; Gardinassi, L.G.; Garcia, G.R.; Brandão, L.G.; Rodrigues, A.R.; Okada, M.I.; Abrão, E.P.; Ferreira, B.R.; et al. Characterisation of divergent flavivirus NS3 and NS5 protein sequences detected in Rhipicephalus microplus ticks from Brazil. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2014, 109, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fort, P.; Albertini, A.; Van-Hua, A.; Berthomieu, A.; Roche, S.; Delsuc, F.; Pasteur, N.; Capy, P.; Gaudin, Y.; Weill, M. Fossil rhabdoviral sequences integrated into arthropod genomes: ontogeny, evolution, and potential functionality. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katzourakis, A.; Gifford, R.J. Endogenous viral elements in animal genomes. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, S.; Groschup, M.H.; Garros, C.; Felippe-Bauer, M.L.; Purse, B.V. Culicoides biting midges, arboviruses and public health in Europe. Antiviral Res. 2013, 100, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kedmi, M.; Van Straten, M.; Ezra, E.; Galon, N.; Klement, E. Assessment of the productivity effects associated with epizootic hemorrhagic disease in dairy herds. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 2486–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nusinovici, S.; Souty, C.; Seegers, H.; Beaudeau, F.; Fourichon, C. Decrease in milk yield associated with exposure to bluetongue virus serotype 8 in cattle herds. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sambou, M.; Aubadie-Ladrix, M.; Fenollar, F.; Fall, B.; Bassene, H.; Almeras, L.; Sambe-Ba, B.; Perrot, N.; Chatellier, S.; Faye, N.; et al. Comparison of matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry and molecular biology techniques for identification of Culicoides (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) biting midges in Senegal. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diouf, N.D.; Etter, E.; Lo, M.M.; Akakpo, A.J. Outbreaks of African horse sickness in Senegal, and methods of control of the 2007 epidemic. Vet. Rec. 2013, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefèvre, P.C.; Calvez, D. La fièvre catarrhale du mouton (bluetongue) en Afrique Intertropicale: influence des facteurs écologiques sur la prévalence de l’infection. Rev. Elev. Med. Vét. Pays Trop. 1986, 39, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Diarra, M.; Fall, M.; Fall, A.G.; Diop, A.; Seck, M.T.; Garros, C.; Balenghien, T.; Allène, X. Seasonal dynamics of Culicoides (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) biting midges, potential vectors of African horse sickness and bluetongue viruses in the Niayes area of Senegal. Parasit. Vectors. 2014, 7, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daszak, P. Can we predict future trends in disease emergence? Chapter 5: Infectious disease emergence: Past, present and Future. In Microbial Evolution and Co-Adaptation, A Tribute to the Life and Scientific Legacies of Joshua Lederberg: Workshop Summary; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Karabatsos, N. International Catalogue of Arboviruses, Including Certain Other Viruses of Vertebrates, 3rd ed.; American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene for The Subcommittee on Information Exchange of the American Committee on Arthropod-borne Viruses: San Antonio, TX, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Frese, M.; Weeber, M.; Weber, F.; Speth, V.; Haller, O. Mx1 sensitivity: Batken virus is an orthomyxovirus closely related to Dhori virus. J. Gen. Virol. 1997, 78, 2453–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubálek, Z.; Rudolf, I.; Nowotny, N. Arboviruses pathogenic for domestic and wild animals. Adv. Virus Res. 2014, 89, 201–275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hubálek, Z.; Rudolf, I. Tick-borne viruses in Europe. Parasitol. Res. 2012, 111, 9–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filipe, A.R.; Calischer, C.H.; Lazuick, J. Antibodies to Congo-Crimean haemorrhagic fever, Dhori, Thogoto and Bhanja viruses in southern Portugal. Acta Virol. 1985, 29, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ogen-Odoi, A.; Miller, B.R.; Happ, C.M.; Maupin, G.O.; Burkot, T.R. Isolation of thogoto virus (Orthomyxoviridae) from the banded mongoose, Mongos mungo (Herpestidae), in Uganda. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1999, 60, 439–440. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, E.V.; Da Rosa, A.P.; Nunes, M.R.; Diniz, J.A.; Tesh, R.B.; Cruz, A.C.; Tesh, C.M.; Vasconcelos, P.F. Araguari virus, a new member of the family Orthomyxoviridae: serologic, ultrastructural, and molecular characterization. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2005, 73, 1050–1058. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lutomiah, J.; Musila, L.; Makio, A.; Ochieng, C.; Koka, H.; Chepkorir, E.; Mutisya, J.; Mulwar, F.; Khamadi, S.; Miller, B.R.; et al. Ticks and tick-borne viruses from livestock hosts in arid and semiarid regions of the eastern and northeastern parts of Kenya. J. Med. Entomol. 2014, 51, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briese, T.; Chowdhary, R.; Travassos da Rosa, A.; Hutchison, S.K.; Popov, V.; Street, C.; Tesh, R.B.; Lipkin, W.I. Upolu virus and Aransas Bay virus, two presumptive bunyaviruses, are novel members of the family Orthomyxoviridae. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 5298–5309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, D.L.; Causey, O.R.; Carey, D.E.; Reddy, S.; Cooke, A.R.; Akinkugbe, F.M.; David-West, T.S.; Kemp, G.E. Arthropod-borne viral infections of man in Nigeria, 1964–1970. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1975, 69, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Butenko, A.M.; Leshchinskaia, E.V.; Semashko, I.V.; Donets, M.A.; Mart’ianova, L.I. Dhori virus—A causative agent of human disease. 5 cases of laboratory infection. Vopr. Virusol. 1987, 32, 724–729. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kosoy, O.I.; Lambert, A.J.; Hawkinson, D.J.; Pastula, D.M.; Goldsmith, C.S.; Hunt, D.C.; Staples, J.E. Novel thogotovirus associated with febrile illness and death, United States, 2014. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 760–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasilakis, N.; Tesh, R.B. Insect-specific viruses and their potential impact on arbovirus transmission. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2014, 15, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.X.; Shi, M.; Tian, J.H.; Lin, X.D.; Kang, Y.J.; Chen, L.J.; Qin, X.C.; Xu, J.; Holmes, E.C.; Zhang, Y.Z. Unprecedented genomic diversity of RNA viruses in arthropods reveals the ancestry of negative-sense RNA viruses. Elife 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Holmes, E.C. Endogenous RNA viruses of plants in insect genomes. Virology 2012, 427, 77–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballinger, M.J.; Bruenn, J.A.; Hay, J.; Czechowski, D.; Taylor, D.J. Discovery and evolution of bunyavirids in arctic phantom midges and ancient bunyavirid-like sequences in insect genomes. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 8783–8794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feschotte, C.; Gilbert, C. Endogenous viruses: insights into viral evolution and impact on host biology. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Fu, Y.; Xie, J.; Cheng, J.; Ghabrial, S.A.; Li, G.; Peng, Y.; Yi, X.; Jiang, D. Widespread endogenization of densoviruses and parvoviruses in animal and human genomes. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 9863–9876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boller, K.; Schönfeld, K.; Lischer, S.; Fisher, N.; Hoffmann, A.; Kurth, R.; Tönjes, R.R. Human endogenous retrovirus HERV-K113 is capable of producing intact viral particles. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bézier, A.; Louis, F.; Jancek, S.; Periquet, G.; Thézé, J.; Gyapay, G.; Musset, K.; Lesobre, J.; Lenoble, P.; Dupuy, C.; et al. Functional endogenous viral elements in the genome of the parasitoid wasp Cotesia congregata: insights into the evolutionary dynamics of bracoviruses. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosario, K.; Capobianco, H.; Ng, T.F.; Breitbart, M.; Polston, J.E. RNA viral metagenome of whiteflies leads to the discovery and characterization of a whitefly-transmitted carlavirus in North America. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparks, M.E.; Gundersen-Rindal, R.E. The Lymantria dispar IPLB-Ld652Y cell line transcriptome comprises diverse virus-associated transcripts. Viruses 2011, 3, 2339–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).