Abstract
The dominant Pvr4 gene in pepper (Capsicum annuum) confers resistance to members of six potyvirus species, all of which belong to the Potato virus Y (PVY) phylogenetic group. The corresponding avirulence factor in the PVY genome is the NIb cistron (i.e., RNA-dependent RNA polymerase). Here, we describe a new source of potyvirus resistance in the Guatemalan accession C. annuum cv. PM949. PM949 is resistant to members of at least three potyvirus species, a subset of those controlled by Pvr4. The F1 progeny between PM949 and the susceptible cultivar Yolo Wonder was susceptible to PVY, indicating that the resistance is recessive. The segregation ratio between resistant and susceptible plants observed in the F2 progeny matched preferably with resistance being determined by two unlinked recessive genes independently conferring resistance to PVY. Inoculations by grafting resulted in the selection of PVY mutants breaking PM949 resistance and, less efficiently, Pvr4–mediated resistance. The codon substitution E472K in the NIb cistron of PVY, which was shown previously to be sufficient to break Pvr4 resistance, was also sufficient to break PM949 resistance, a rare example of cross-pathogenicity effect. In contrast, the other selected NIb mutants showed specific infectivity in PM949 or Pvr4 plants. Comparison of Pvr4 and PM949 resistance, which share the same target in PVY, provides interesting insights into the determinants of resistance durability.
1. Introduction
Genetic resistance of plants to pathogens is an attractive means of controlling crop diseases because of its high efficacy, simplicity of implementation, relatively low cost, and lack of adverse effects on human health. In addition, resistance is usually highly specific, which avoids undesirable side effects on non-target organisms. The other side of this specificity is the narrow spectrum of action of most resistance systems in the face of the wide diversity of plant pathogens. The spectrum of action of a resistance can be considered at different taxonomic levels of the pathogen and is generally defined by the number of pathogen species and/or isolates within a species that are controlled by the resistance. Considered at the intraspecific level, the spectrum of action of resistance is related to the durability of resistance, i.e., the ability of the resistance to maintain its long-term efficacy despite widespread use under conditions favorable to pathogen development [1]. Poorly durable resistances generally have a narrow spectrum of action at the intraspecific level as the targeted pathogen populations can easily evolve into infectious forms in these plants, i.e., acquire “resistance-breaking” abilities [2,3]. Most resistances exploited by breeders have narrow spectra of resistance, usually restricted to members of a single or small number of pathogen species. Therefore, an important goal of plant breeding is to increase both the spectrum of action and durability of plant resistance to pathogens.
Potyviruses (members of genus Potyvirus, family Potyviridae) are a major constraint to pepper (Capsicum spp., family Solanaceae) production worldwide, affecting both yield and fruit quality [4]. Pepper potyviruses belong to three main clades [5,6]. The largest one is the Potato virus Y (PVY) clade, which includes 19 species, 10 of which infect solanaceous plants [7]. The other two clades, the Tobacco etch virus (TEV) and the Pepper veinal mottle virus (PVMV) clades comprise fewer species, all of which infect solanaceous plants. At least ten potyviruses frequently infect pepper crops. Several Capsicum spp. genes or gene combinations have been shown to confer resistance to potyviruses, but none of them cover all pepper potyviruses and their spectrum of action considered at the species level and their durability differ widely [3,8,9,10,11,12]. Here, we characterized the spectrum of resistance and durability potential of a new source of potyvirus resistance in C. annuum.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant and Viral Material
‘PM949’ is a Guatemalan accession of C. annuum that was previously characterized in pepper genetic resources as a novel source of PVY resistance [13]. The inbred line C. annuum cv. Yolo Wonder (YW) was used in all experiments as a potyvirus-susceptible control, and the doubled-haploid line ‘W4’, derived from the F1 hybrid (YW × ‘Criollo de Morelos 334’), was used as a reference for the dominant potyvirus resistance gene Pvr4 [14]. These pepper accessions are maintained by the INRAE GAFL CRB-Lég team [15]. For genetic analyses, PM949 was crossed with YW and an F2 population was derived from the F1 hybrid. Plants of Nicotiana tabacum cv. Xanthi were used to obtain virus inocula.
Twelve isolates representing the nine species of potyvirus PVMV, PVY, TEV, Pepper yellow mosaic virus (PepYMV), Pepper mottle virus (PepMoV), Chilli veinal mottle virus (ChiVMV) Pepper severe mosaic virus (PepSMV), Ecuadorian rocotto virus (EcRV), and Peru tomato mosaic virus (PTV) were used to characterize the resistance of PM949 and W4 [14] (Table 1). A variant of the PVY SON41p infectious cDNA clone carrying the K472E mutation in NIb cistron (Nuclear inclusion b), i.e., the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase cistron (RdRp), has been described previously [11].

Table 1.
Behavior of PM949 and W4 pepper lines after mechanical inoculation with potyviruses.
2.2. Virus Resistance Tests
Two types of virus inoculations on pepper plants were performed, direct mechanical inoculations and inoculations by grafting. Potyvirus isolates were propagated in N. tabacum cv. Xanthi. Inocula were prepared as described by Janzac et al. [14], and inoculations were performed on 3-week-old seedlings by manually rubbing the cotyledons and the first expanded leaf with the inoculum. For inoculations by grafting, PM949 scions were grafted onto 6-to-8-week-old YW rootstocks, and the rootstocks were mechanically inoculated with the virus two weeks after grafting. Inoculated plants were placed in an insect-proof greenhouse where the temperature varied between 18 and 25 °C and were tested for virus infection up to one or six months post inoculation (mpi) for mechanical and grafting inoculations, respectively.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) were performed on inoculated leaves or on uninoculated, apical leaves to test for the presence of virus infection at the local or systemic level, respectively. The presence of PepSMV, PepYMV, PTV, and EcRV was assessed using an antigen coated plate-ELISA (ACP-ELISA) with potyvirus-group antiserum (Agdia, Soisy sur Seine, France) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Other potyviruses (PVY, PepMoV, TEV, ChiVMV, and PVMV) were detected by double-antibody-sandwich-ELISA (DAS-ELISA) with previously described polyclonal antisera [14,16]. Samples were considered positive when the absorbance values at 405 nm (A405) were at least three times higher than the mean value of healthy controls.
2.3. Partial Sequencing of the PVY Genome
Total RNAs were purified from virus-infected leaves using the TRI Reagent kit (MRC, Cincinnati, OH, USA) following the manufacturer’s instructions. Direct sequencing of reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) fragments spanning the entire NIb cistron was performed for resistance-breaking PVY variants as described in Janzac et al. [11].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. PM949 Exhibits Narrow Spectrum Resistance to Potyviruses of the PVY Clade
Upon mechanical inoculation with PVY, two types of phenotypic responses were observed in PM949 (Table 1). Isolate PVY-Chile1 [17], synonymous with Crystal1 [14], was able to induce local necrotic lesions (NLs) in inoculated cotyledons 10 days post inoculation (dpi), whereas isolate PVY-LYE72 and a population derived from the PVY-SON41p infectious cDNA clone [16] (accession number AJ439544) did not induce any reaction. Thirty dpi, no symptoms were visible in apical leaves, and no virus was detectable by DAS-ELISA or RT-PCR, regardless of the PVY isolate. At that time, all three PVY isolates induced mosaic symptoms and high level of viral accumulation at the systemic level in the susceptible control line YW. PVY was also inoculated by grafting onto PM949. All three PVY isolates induced similar responses in inoculated plants. Ten to 14 dpi, leaves of YW rootstocks showed mosaic symptoms, and 14 to 20 dpi chlorotic and necrotic lesions appeared in leaves of PM949 scions and PVY could be detected in these leaves by DAS-ELISA. The necrotic reactions observed in scions of plants inoculated by grafting with the different PVY isolates and in cotyledons of plants mechanically inoculated with isolate PVY-Chile1 suggest that the resistance of PM949 is related to a hypersensitivity reaction (HR) and are reminiscent of the dominant resistance gene Pvr4 [14].
To get a broader view of the resistance spectrum of PM949, we inoculated it with isolates representing eight other potyvirus species and compared it to the reference line ‘W4’ carrying Pvr4 (Table 1 in Janzac et al. [11]). PM949 did not show resistance to PepYMV, PepMoV, PVMV, ChiVMV, and TEV, with mosaic symptoms and positive ELISA in apical leaves. In contrast, PM949 was resistant to PepSMV and EcRV, with phenotypic responses similar to those expressed following inoculation with PVY-Chile1, i.e., NLs in inoculated cotyledons, but no symptoms and no virus detected in apical leaves. A third type of reaction was observed with PTV isolates Quito and Cuzqueño, which induced NLs in both inoculated cotyledons and apical leaves, resulting in positive ACP-ELISA. All control YW plants showed infections at the systemic level from 14 to 20 dpi, depending on the potyvirus. Overall, as with Pvr4, resistance of PM949 was limited to viruses in the PVY clade and was not effective against viruses in the PVMV or TEV clades (Table 1). However, the spectrum of action of PM949 resistance was narrower than that of Pvr4 as it did not include PepYMV and PepMoV. The status of PTV is uncertain. It was able to infect PM949, but not W4 systemically, and induced HR-like necrotic reactions in both genotypes. It is possible that PTV triggers resistance in PM949 but that the level and/or timing of defense responses are insufficient to restrict cell-to-cell and systemic movement of the virus.
3.2. Genetic Inheritance of PM949 Resistance to PVY
The F1 hybrid between PM949 and the potyvirus-susceptible YW line was susceptible to PVY-SON41p, showing systemic infection in 20 of 20 inoculated plants, indicating that the resistance was recessive. In the F2 population, 159 of 278 plants (57%) were systemically infected, while the remaining plants were symptomless and DAS-ELISA negative. The simplest Mendelian inheritance model that fits this segregation pattern corresponds to two unlinked recessive genes, each sufficient to confer resistance (Khi2 test; p-value = 0.80). Resistance conferred by a single recessive gene or, alternatively, by the combination of two recessive genes does not fit the segregation data (Khi2 tests; p-value < 10−5). Although the resistance phenotypes expressed in PM949 and W4 are similar, their genetic determinants are different since W4 resistance is monogenic and dominant [18]. The major source of recessive resistance in pepper against potyviruses is the pvr2 gene, which encodes an eIF4E (eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E) and includes many resistance alleles corresponding to nonsynonymous substitutions [19]. The sequence of the eIF4E cDNA obtained from the pepper cultivar PM949 was determined as described in Ben Khalifa et al. [20] and revealed a nucleotide sequence identical to that of the susceptible genotype YW, indicating that the recessive resistance of PM949 to PVY cannot be attributed to the pvr2 gene.
3.3. Inoculations by Grafting Allowed Selection of PVY Variants Adapted to Pvr4 or PM949 Resistance
We analyzed the durability potential of PM949 resistance to potyviruses using experimental evolution in the laboratory and compared it to Pvr4. For Pvr4, no natural resistance-breaking (RB) PVY isolates were observed in the field, despite extensive cultivation of Pvr4-carrying cultivars worldwide for over 25 years. Furthermore, no RB potyvirus mutants could be selected by direct mechanical inoculation of the Pvr4-carrying W4 genotype [14]. In contrast, inoculations by grafting where the susceptible line YW was used as rootstock for W4 scions, and the rootstocks were inoculated with the virus 10 days after grafting resulted in the selection of PVY RB mutants for 3 of the 5 PVY isolates tested [14]. Using PVY-SON41p as inoculum, 6 out of 25 grafted plants resulted in the selection of an RB mutant around five mpi (Table 2). No RB mutants of the other potyviruses (PepYMV, PepSMV, PTV-Quito, PTV-Cuzqueño, PepMoV-Texas, or EcRV; 10 grafts with each virus) could be selected. In a previous study, four of the six RB PVY populations (SON41p-G1 to SON41p-G4) carried the codon substitution K472E in the NIb cistron (RdRp), which was found to be sufficient for Pvr4 breakdown by reverse genetics [11]. In the present study, NIb cistrons of the two PVY populations SON41p-G5 and SON41p-G6 were sequenced and found to carry three nonsynonymous substitutions (M365I + G471E + S478N and I94T + V416A + A504V, respectively).

Table 2.
Pathogenicity of PVY-SON41p towards pepper genotypes and mutations observed in the NIb cistron.
Graft-inoculations were also performed as described above for W4 to test whether PM949 could also select for RB potyvirus mutants, using PVY-SON41p, PepSMV, the Quito and Cuzqueño isolates of PTV and EcRV (10 grafted plants with each virus). While small necrotic and chlorotic lesions were observed on PM949 scions inoculated with PVY-SON41p, the other viruses induced large necrotic lesions on the scions (Figure 1), which led rapidly (50 dpi) to death of the grafted plants. At one mpi, no RB mutants could be observed with any of the viruses, as evidenced by the absence of infection on the back-inoculated PM949 seedlings. At six mpi, all ten plants inoculated by grafting with PVY-SON41p showed confluent chlorotic lesions or mosaic symptoms on parts of the scions, and the presence of RB mutants was demonstrated after back-inoculation to PM949 seedlings, with 100% infection (20 of 20 inoculated plants) at 21 dpi (Table 2 and Table 3). In contrast, no RB mutants of PepSMV, PTV, or EcRV could be obtained, probably because these viruses induced severe necrosis in scions and killed plants too early.

Figure 1.
Hypersensitive-like reactions in graft-inoculated PM949 (A,C) and W4 (B,D) plants. PM949 and W4 scions were grafted onto potyvirus susceptible Yolo Wonder rootstocks, and the latter was inoculated one week after grafting by PVY-SON41p (A,B) or PTV isolate Quito (C,D).

Table 3.
Pathogenicity of PVY-SON41p NIb mutants towards C. annuum W4 and PM949.
3.4. Substitution K472E in PVY NIb (RdRp) Determines Adaptation to PM949 Resistance
Due to the similarity of phenotypes observed in PM949 and W4 (carrying Pvr4) upon inoculation with potyviruses, we tested whether the RB mutants selected by W4 could also break PM949 resistance, and vice versa, by mechanical inoculation (Table 3). The four W4-selected SON41p-G1 to SON41p-G4 PVY populations carrying the K472E codon substitution in NIb cistron were able to infect PM949 (20 of 20 inoculated plants). In contrast, the SON41p-G5 and SON41p-G6 populations that did not carry the K472E substitution were unable to infect PM949 (no infected plants out of 20 inoculated). This result suggests that the K472E substitution in NIb may be involved in the breakdown of PM949 resistance in addition to Pvr4. This was verified using a mutagenized cDNA clone of PVY-SON41p containing the K472E substitution (Janzac et al. 2010 [11]). Virus derived from this mutant clone was inoculated into 40 PM949 plants and infected all plants at the systemic level, 15 dpi. No additional nucleotide substitutions were observed in the NIb cistron of viral progeny in the four PM949 plants analyzed.
These results reveal that the NIb cistron determines the breakdown of PM949 resistance and that the K472E substitution is sufficient for breakdown of both Pvr4 and PM949 resistance. Thus, the K472E substitution is one of the few examples of cross-infectivity effects, where a single mutation in the parasite results in the simultaneous breakdown of two or more resistances [12]. The fact that a single mutation in the PVY genome allows the simultaneous breakdown of a dominant and a recessive resistance may seem surprising given the contrasting modes of action usually considered for these two categories of resistance. Indeed, recessive resistance generally corresponds to a loss-of-function mode of action, where a host factor cannot be exploited by the pathogen, for example, due to of a lack of interaction with a pathogen protein [19]. In contrast, dominant resistance is usually based on the induction of defense responses following the recognition, whether direct or not, of a pathogen factor by a host resistance factor [21]. The dual effect of the PVY K472E mutation in resistance breakdown may be coincidental, with the same NIb domain being involved in physical interactions with two different plant ligands involved in either a recessive or in a dominant form of resistance. Alternatively, a resistance gene or different members of the same gene family may behave as dominant or recessive depending on their allelic forms or the alleles present on the other paralogue genes, as has been shown in the case of the eIF4E family [22,23]. A third hypothesis could be based on a gene-for-gene resistance mechanism as described by the guard model [24]. According to this model, a dominant monogenic resistance is expressed when triggered by the interaction (or alteration) of a host protein, the guardee, with (by) the pathogen’s avirulence factor, here NIb. Consistent with this model, resistance could be triggered in a dominant manner in some plant genotypes and could be determined by the absence or modification of a guardee protein in a recessive manner in other plant genotypes. In this framework, resistance breakdown could occur through a modification of NIb that would (i) allow its interaction with an alternative plant susceptibility factor in the context of the recessive resistance and simultaneously (ii) affect its interaction with the host guardee protein and thereby abolish the triggering of the resistance in the context of the dominant resistance.
3.5. Additional Amino Acid Substitutions in PVY NIb Are Associated with Adaptation to PM949 Resistance
The NIb cistron of all ten PM949-selected PVY populations from the graft-inoculation experiments was sequenced. In each PVY population, a single non-synonymous substitution was observed, with seven different substitutions in total (Table 2 and Table 3). These seven substitutions are distributed in three areas of the NIb cistron: At codon 47, from codon 94 to codon 108, and from codon 488 to codon 508. The latter area is close to codon position 472, that has been implicated in the breakdown of Pvr4 and PM949 resistance. Several arguments suggest the involvement of these substitutions in the breakdown of PM949 resistance: (i) the previous finding that the K472E substitution in NIb is sufficient for breakdown of PM949 resistance, (ii) the fact that all PM949 RB mutants carry a single nonsynonymous mutation in the NIb cistron, (iii) the fact that several of these mutations occurred repeatedly and independently in PM949, such as the E47K (2 times) and M502I (3 times) mutations, and (iv) the fact that several of the mutations are located in the same NIb region or even in the same codon (mutations at positions 472, 488, 502; mutations E508G and E508G). Of the 10 PVY-SON41p-derived populations breaking PM949 resistance, only 2, carrying either the R488G or E47K substitution, were able to infect only 1 of the 20 inoculated W4 plants (Table 3). The first PVY population could not be analyzed further because it lost its infectivity during storage. A sample of the second PVY population collected from the infected W4 plant was able to infect 25 of 25 back inoculated W4 plants, showing a gain of pathogenicity, and the additional Y271C substitution was observed in the NIb cistron (Table 3). Therefore, PM949 served as a springboard to PVY-SON41p to break the Pvr4 resistance, as has been shown for eIF4E-mediated recessive resistances in several solanaceous crops [12]. Indeed, upon mechanical inoculation with PVY-SON41p, no infection was observed in routine tests performed on >1500 W4 plants (Table 2). The frequency of infection of W4 by PVY populations from PM949 was significantly higher (0/1500 vs. 2/200 infections; p-value = 0.014; Khi2 test) (Table 3). Most of the RB-associated mutations (seven out of eight, with the exception of the M502I substitution) in PVY affect the local electrostatic potential or polarity of the NIb surface, and several of them (three of the five substitutions for which the NIb structure could be modelled) also affect the NIb structure (Table 3; Figure 2). Therefore, these mutations may be involved in RB by altering the interaction of PVY NIb with as yet unknown ligands, such as the plant proteins PABP, heat shock cognate 70-3, or the translation elongation factor eEF1A, which have been identified as interactors of potyvirus RdRp both in vitro and in vivo [25,26].They could also modulate NIb-RNA association, as RdRp is associated with the primer-template RNA duplex during replication.
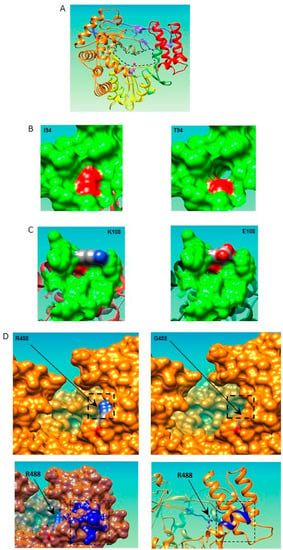
Figure 2.
Structural models of the NIb (Nuclear inclusion b protein), i.e., the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) of PVY-SON41p and its mutants based on the structure of the RdRp of Rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus (RHDV) (Protein Data Bank 1KHV). The NIb of the eight different single-amino-acid mutants of the SON41p isolate breaking Pvr4 and/or PM949 resistance (Table 2) was modeled using the Phyre2 protein modeling web portal [27] (http://www.sbg.bio.ic.ac.uk/~phyre2/html/page.cgi?id=index; accessed on 14 March 2015). For all these mutants, the highest scoring model was that of the RdRp of Rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus (RHDV; genus Lagovirus, family Caliciviridae) (Protein Data Bank 1KHV [28]), with at least 80% of the sequence modeled with 100% confidence. No satisfactory model could be obtained for the M502I, E508G, and E508K mutants of SON41p due to excessive coordinate uncertainties of the peptide backbone folding beyond residue 489. The other mutations associated with PM949 resistance breakdown that could be mapped were located in two distant regions of the protein, the finger and thumb domains (Table 3). (A) Global structural model of NIb from the PVY-SON41p isolate. The RHDV RdRp adopts the overall structure of a right hand with fingers, palm, and thumb domains, a folding shared by most other polynucleotide polymerases [29]. The finger, palm, and thumb domains are in orange, yellow, and red, respectively. The first 52 N-terminal amino acids were not modeled satisfactorily. The 63 N-terminal amino acids of the RHDV RdRp used as a model are shown in purple. In the crystal structure, this domain connects the finger and thumb domains. The GDD amino acid residues and the Mn2+ ion positioned in the catalytic site are shown in pink. The entrance of the RNA channel is delineated by a dashed black line. (B) Comparison of the local structure of PVY-SON41p and the SON41p-I94T mutant. In PVY-SON41p (left), the side chain of isoleucine 94 forms the bottom of a small crevice that becomes deeper upon substitution with the threonine residue (right), most likely due to the shorter side chain of threonine. Due to the hydroxyl moiety of threonine, the crevice also becomes more polar. (C) Comparison of the local structure of PVY-SON41p and the SON41p-K108E mutant. In PVY-SON41p (left), the lysine residue forms a straight, regular edge above a 15 Å-wide crevice. Upon substitution with glutamic acid (right), the shape of this edge is altered, with the two oxygen atoms (in red) of the side chain protruding to the outside. This substitution is accompanied by a net electrostatic change over the entire crevice from a slightly positive to a strongly negative state at physiological pH (not shown). (D) Comparison of the local structure of PVY-SON41p and the SON41p-R488G mutant. In PVY-SON41p (left), the nitrogen atom (blue sphere) of the arginine 488 side chain protrudes slightly 7 Å forward from the surface of the edge of the entrance of the RNA channel (enzyme thumb domain). At physiological pH, arginine 488 creates a strong positive surface potential. Upon substitution with glycine (right), a small depression 5 Å deep replaces the protruding lysine side chain, and the potential becomes neutral. This substitution could mitigate the likely strong electrostatic interaction between the negatively charged RNA backbone and arginine 488. This positive surface density is retained in the RHDV template. The glycine substitution also induces a more distant alteration of the first helix turn in the α-helix extending from amino acid 477 to 489. The structures of PVY-SON41p and its R488G mutant have been superimposed (lower panel; PVY-SON41p in orange and the R488G mutant in blue). Alterations are visible in both the backbone folding (lower right panel) and the surface topology (lower left panel).
3.6. Insights into the Durability Potential of Pvr4 and PM949 Resistance
Interestingly, Pvr4 appears to have both higher durability potential to PVY-SON41p and a broader spectrum of action than PM949. Indeed, a significantly higher frequency of graft-inoculated plants generated RB mutants with PM949 (10 out of 10 grafts) than with W4 (6 out of 25 grafts; p-value = 4.4 × 10−5; Khi2 test). In addition, Pvr4 confers resistance to two or three additional potyviruses compared with PM949 (Table 1). This reinforces the hypothesis that its spectrum of action may be a predictor of the potential durability of plant resistance, as observed for pvr2 alleles in C. annuum [3]. Indeed, a resistance with a broad spectrum of action, thus effective against pathogen species separated by large evolutionary time scales, is more likely to be durable against pathogen populations separated by shorter evolutionary time scales [3].
In practice, PM949 resistance appears to be less attractive than Pvr4 in terms of spectrum of action, durability potential and ease of introgression into elite cultivars. Worse, PM949 could act as an evolutionary springboard for PVY, facilitating the breakdown of Pvr4 in a second step (Table 3). Therefore, Pvr4 is a preferable source of resistance, and the use of PM949 resistance is not recommended, at least until Pvr4 is broken down. Based on our results, the only value of PM949 would be to counter-select Pvr4-breaking PVY isolates lacking the NIb K472E substitution, should such isolates emerge.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.M. and A.P.; methodology, B.M., T.M., V.S. and A.P.; software, not applicable; validation, B.M., T.M., V.S. and A.P.; formal analysis, B.M., T.M. and A.P.; investigation, B.M., T.M., V.S. and A.P.; resources, B.M. and A.P.; data curation, B.M. and A.P.; writing—original draft preparation, B.M.; writing—review and editing, B.M., T.M. and V.S.; visualization, B.M. and T.M.; supervision, B.M. and A.P.; project administration, not applicable; funding acquisition, no specific funding was obtained for this work. A.P. is deceased. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
All sequence data generated in this study are described in the present article.
Acknowledgments
We thank Bérenger Janzac and Marie-Françoise Fabre for their help with the experiments and Jean-Luc Gallois and Lucie Tamisier for their constructive comments on the manuscript. We thank the staff of the INRAE CRB-Lég (https://www6.paca.inrae.fr/gafl_eng/Vegetable-Germplasm-Centre; accessed on 24 April 2023) who maintained the pepper germplasm collection of the INRAE GAFL research unit and the experimental facility teams of the INRAE Pathologie Végétale (https://doi.org/10.15454/8DGF-QF70; accessed on 24 April 2023) and GAFL research units.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Johnson, R. Durable resistance–Definition of, genetic control, and attainment in plant breeding. Phytopathology 1981, 71, 567–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayme, V.; Souche, S.; Caranta, C.; Jacquemond, M.; Chadoeuf, J.; Palloix, A.; Moury, B. Different mutations in the genome-linked protein VPg of Potato virus Y confer virulence on the pvr23 resistance in pepper. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2006, 19, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moury, B.; Charron, C.; Janzac, B.; Simon, V.; Gallois, J.-L.; Palloix, A.; Caranta, C. Evolution of plant eukaryotic initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) and potyvirus genome-linked protein (VPg): A game of mirrors impacting resistance spectrum and durability. Inf. Genet. Evol. 2014, 27, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avilla, C.; Collar, J.L.; Duque, M.; Fereres, A. Yield of bell pepper (Capsicum annuum) inoculated with CMV and/or PVY at different time intervals. J. Plant Dis. Prot. 1997, 104, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, A.; Ohshima, K. Potyviruses and the digital revolution. Ann. Rev. Phytopath. 2010, 48, 205–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moury, B.; Verdin, E. Viruses of pepper crops in the Mediterranean basin: A remarkable stasis. Adv. Virus Res. 2012, 84, 127–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quenouille, J.; Vassilakos, N.; Moury, B. Potato virus Y: A major crop pathogen that has provided major insights into the evolution of viral pathogenicity. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2013, 14, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyle, M.M.; Palloix, A. Proposed revision of nomenclature for potyvirus resistance genes in Capsicum. Euphytica 1997, 97, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caranta, C.; Lefebvre, V.; Palloix, A. Polygenic resistance of pepper to potyviruses consists of a combination of isolate-specific and broad-spectrum quantitative trait loci. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 1997, 10, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grube, R.C.; Blauth, J.R.; Arnedo, M.S.; Caranta, C.; Jahn, M.K. Identification and comparative mapping of a dominant potyvirus resistance gene cluster in Capsicum. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2000, 101, 852–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janzac, B.; Montarry, J.; Palloix, A.; Navaud, O.; Moury, B. A point mutation in the polymerase of Potato virus Y confers virulence toward the Pvr4 resistance of pepper and a high competitiveness cost in susceptible cultivar. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2010, 23, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moury, B.; Janzac, B.; Ruellan, Y.; Simon, V.; Ben Khalifa, M.; Fakhfakh, H.; Fabre, F.; Palloix, A. Interaction pattern between Potato virus Y and eIF4E-mediated recessive resistance in the Solanaceae. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 9799–9807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sage-Palloix, A.M.; Jourdan, F.; Phaly, T.; Nemouchi, G.; Lefebvre, V.; Palloix, A. Analysis of diversity in pepper genetic resources: Distribution of horticultural and resistance traits in the INRA pepper germplasm. In Progress in Research on Capsicum & Eggplant; Niemirowicz-Szczytt, K., Ed.; Warsaw University of Life Sciences Press: Warsaw, Poland, 2007; pp. 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Janzac, B.; Fabre, M.-F.; Palloix, A.; Moury, B. Phenotype and spectrum of action of the Pvr4 resistance in pepper against potyviruses, and selection for virulent variants. Plant Pathol. 2009, 58, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinier, J.; Lefebvre, V.; Besombes, D.; Burck, H.; Causse, M.; Daunay, M.C.; Dogimont, C.; Goussopoulos, J.; Gros, C.; Maisonneuve, B.; et al. The INRAE Centre for Vegetable Germplasm: Geographically and Phenotypically Diverse Collections and Their Use in Genetics and Plant Breeding. Plants 2022, 11, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moury, B.; Morel, C.; Johansen, E.; Guilbaud, L.; Souche, S.; Ayme, V.; Caranta, C.; Palloix, A.; Jacquemond, M. Mutations in Potato virus Y genome-linked protein determine virulence toward recessive resistances in Capsicum annuum and Lycopersicon hirsutum. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2004, 17, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moury, B. A new lineage sheds light on the evolutionary history of Potato virus Y. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2010, 11, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogimont, C.; Palloix, A.; Daubèze, A.M.; Marchoux, G.; Gebre Selassie, K.; Pochard, E. Genetic analysis of broad spectrum resistance to potyviruses using doubled haploid lines of pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Euphytica 1996, 88, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charron, C.; Nicolai, M.; Gallois, J.L.; Robaglia, C.; Moury, B.; Palloix, A.; Caranta, C. Natural variation and functional analyses provide evidence for co-evolution between plant eIF4E and potyviral VPg. Plant J. 2008, 54, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Khalifa, M.; Simon, V.; Marrakchi, M.; Fakhfakh, H.; Moury, B. Contribution of host plant resistance and geographic distance to the structure of Potato virus Y (PVY) populations in pepper in northern Tunisia. Plant Pathol. 2009, 58, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacristán, S.; Garcia-Arenal, F. The evolution of virulence and pathogenicity in plant pathogen populations. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2008, 9, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Jahn, M.M.; Yeam, I. Allelic relationships at the pvr1 locus in Capsicum annuum. Euphytica 2013, 194, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauffier, C.; Lebaron, C.; Moretti, A.; Constant, C.; Moquet, F.; Bonnet, G.; Caranta, C.; Gallois, J.L. A TILLING approach to generate broad-spectrum resistance to potyviruses in tomato is hampered by eIF4E gene redundancy. Plant J. 2016, 85, 717–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Biezen, E.; Jones, J.D.G. Plant disease-resistance proteins and the gene-for-gene concept. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1998, 23, 454–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Ullah, Z.; Grumet, R. Interaction between zucchini yellow mosaic potyvirus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase and host poly-(A) binding protein. Virology 2000, 275, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufresne, P.J.; Thivierge, K.; Cotton, S.; Beauchemin, C.; Ide, C.; Ubalijoro, E.; Laliberté, J.F.; Fortin, M.G. Heat shock 70 protein interaction with Turnip mosaic virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase within virus-induced membrane vesicles. Virology 2008, 374, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, L.A.; Mezulis, S.; Yates, C.M.; Wass, M.N.; Sternberg, M.J.E. The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. Nature Protocols 2015, 10, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.K.; Cherney, M.M.; Vazquez, A.L.; Machin, A.; Alonso, J.M.; Parra, F.; James, M.N. Crystal structures of active and inactive conformations of a caliciviral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 1381–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steitz, T.A. DNA polymerases: Structural diversity and common mechanisms. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 17395–17398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).