Early Phase of Specific Cellular Immune Status Associates with HCV Infection Outcomes in Marmosets
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Marmosets and Virus Inoculation
2.3. RT-qPCR for Viremia Detection
2.4. Biochemical Test
2.5. Histopathological Examination
2.6. ELISpot Assay
2.7. Flow Cytometry
2.8. Measurement of Cytokines
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
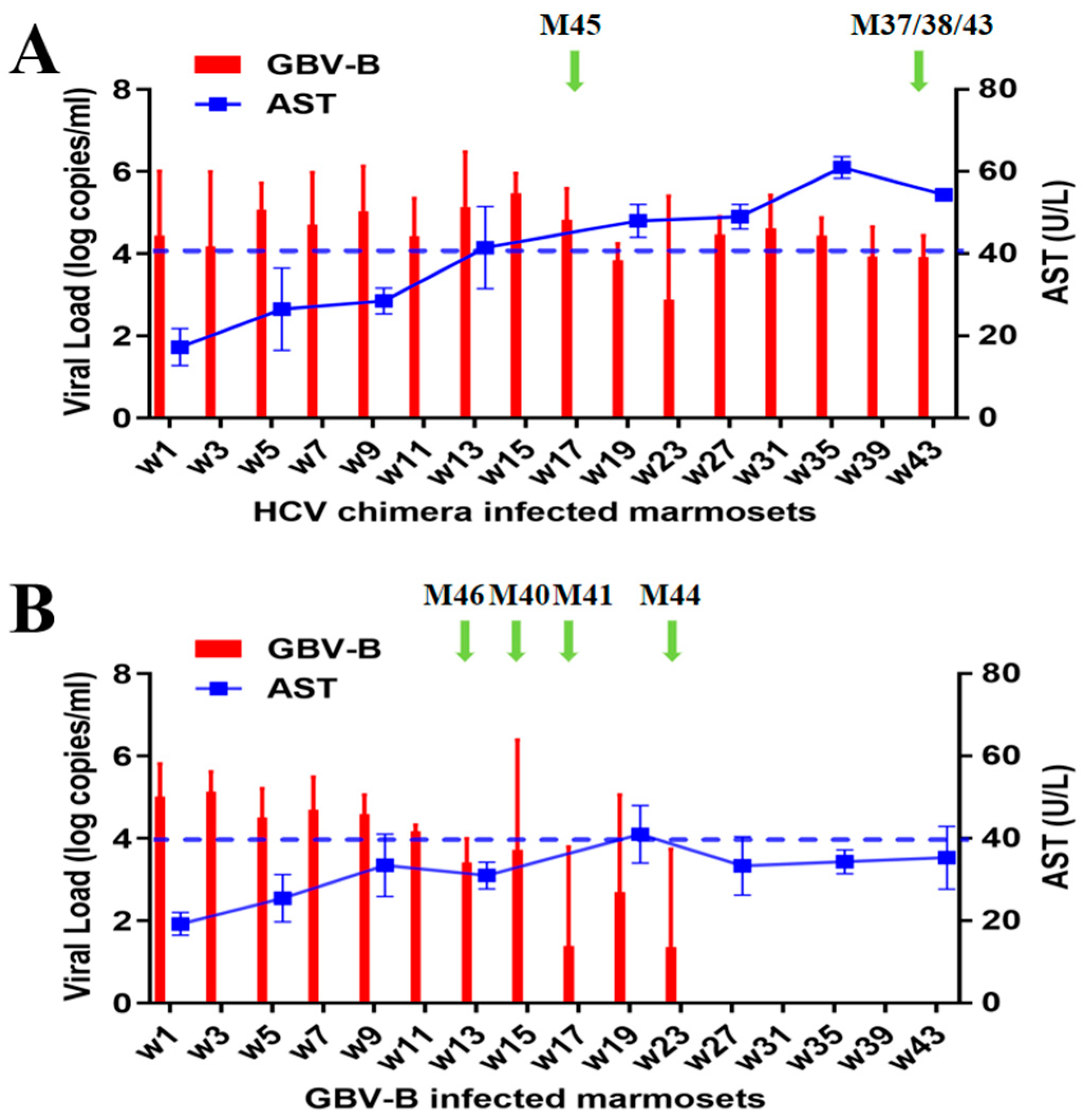
3.1. Different Outcome of Viral Persistence from HCV Chimera or Clearance from GBV-B-Infected Marmosets
3.2. HCV Chimera Was More Pathogenic to Marmosets Than GBV-B
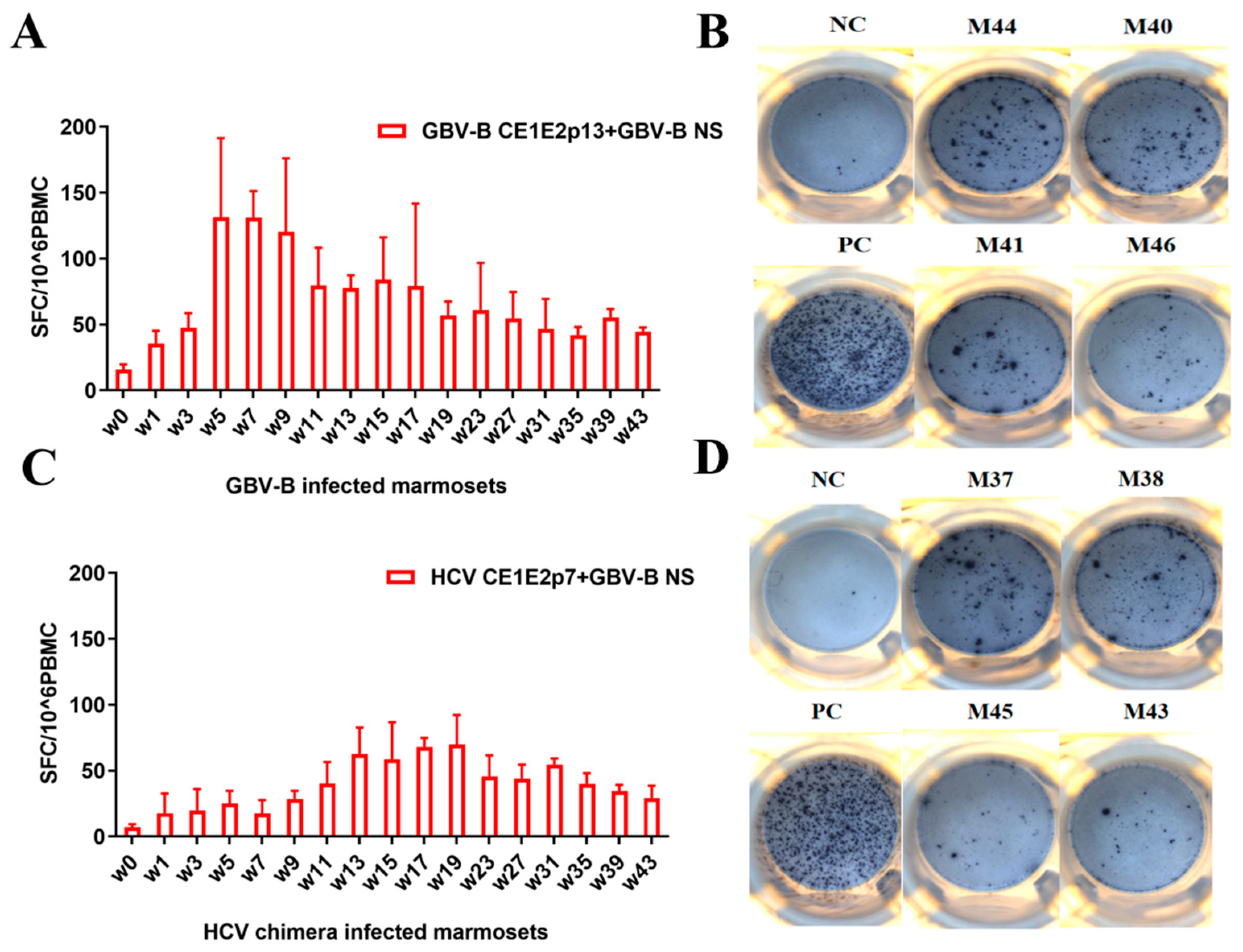
3.3. GBV-B Infection Induced Significantly Higher IFN-γ-Secretion T Cell Response Than HCV Chimera Infection in Marmosets
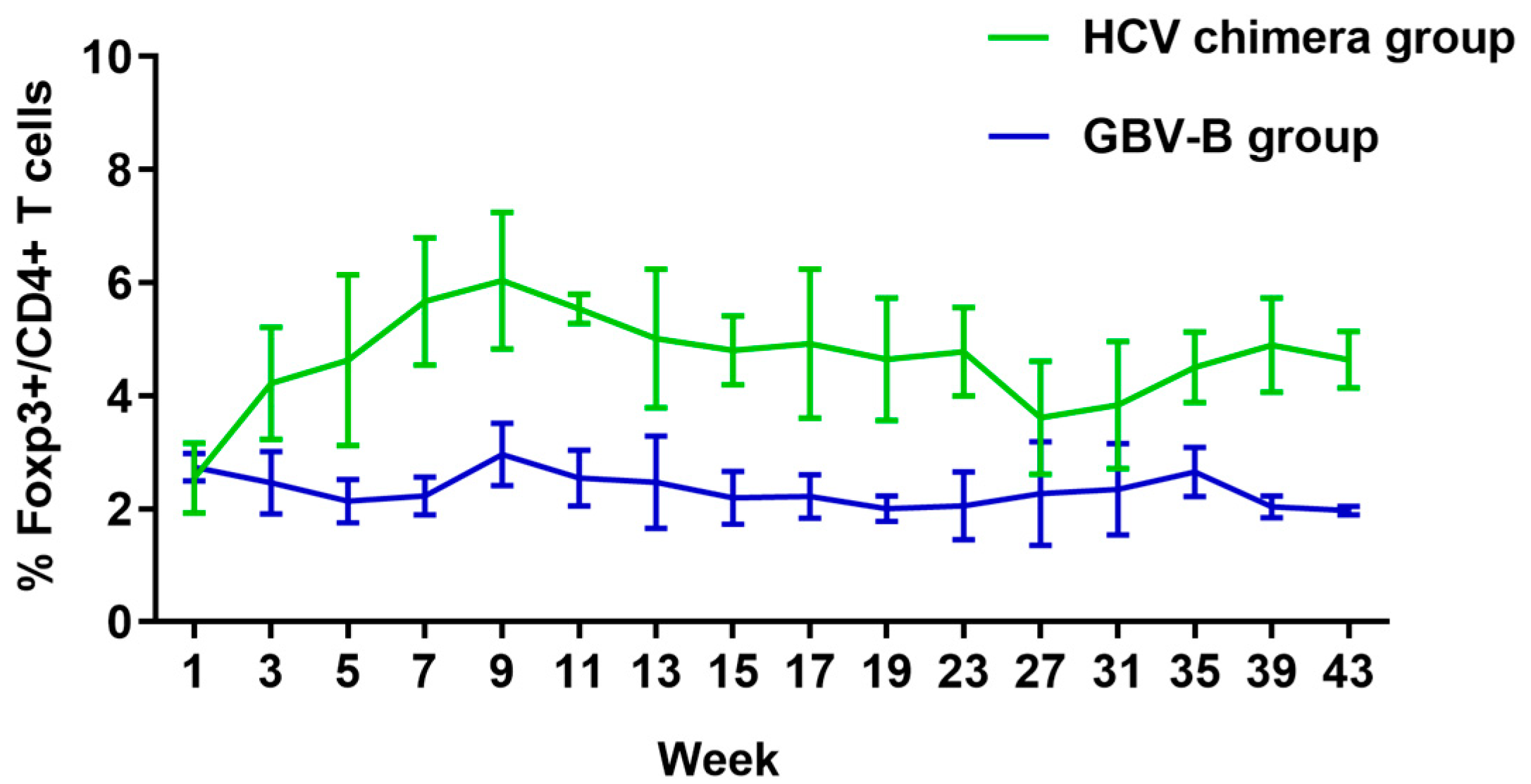
3.4. HCV Chimera Infection Induced Significantly Higher Treg Cell Response Than GBV-B Infection in Marmosets
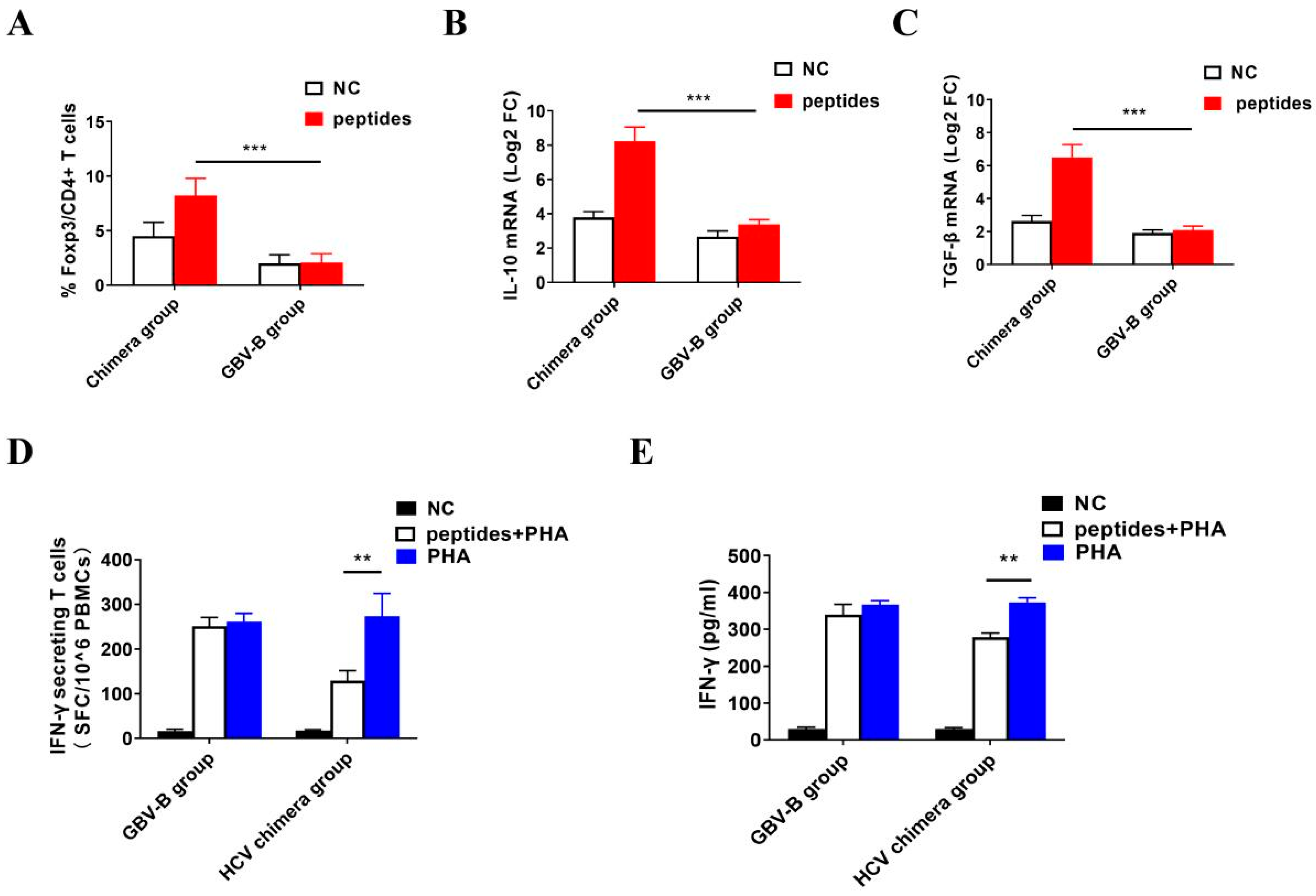
3.5. Activation of Treg Cell Response by HCV Structural Proteins
3.6. Inhibition of IFN-γ-Secretion T Cell Response by Activated Treg Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- The Polaris Observatory HCV Collaborators. Global prevalence and genotype distribution of hepatitis C virus infection in 2015: A modelling study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandiera, S.; Bian, C.B.; Hoshida, Y.; Baumert, T.F.; Zeisel, M.B. Chronic hepatitis C virus infection and pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2016, 20, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alter, H.J.; Seeff, L.B. Recovery, persistence, and sequelae in hepatitis C virus infection: A perspective on long-term outcome. Semin. Liver Dis. 2000, 20, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Major, M.E.; Mihalik, K.; Fernandez, J.; Seidman, J.; Kleiner, D.; Kolykhalov, A.A.; Rice, C.M.; Feinstone, S.M. Long-Term Follow-Up of Chimpanzees Inoculated with the First Infectious Clone for Hepatitis C Virus. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 3317–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popescu, C.-I.; Riva, L.; Vlaicu, O.; Farhat, R.; Rouillé, Y.; Dubuisson, J. Hepatitis C Virus Life Cycle and Lipid Metabolism. Biology 2014, 3, 892–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santangelo, L.; Bordoni, V.; Montaldo, C.; Cimini, E.; Zingoni, A.; Battistelli, C.; D’Offizi, G.; Capobianchi, M.R.; Santoni, A.; Tripodi, M.; et al. Hepatitis C virus direct-acting antivirals therapy impacts on extracellular vesicles microRNAs content and on their immunomodulating properties. Liver Int. 2018, 38, 1741–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Ossorio, M.J.; Sarmento, E.C.R.; Granados, R.; Macías, J.; Morano-Amado, L.E.; Ríos, M.J.; Merino, D.; Álvarez, E.N.; Collado, A.; Pérez-Pérez, M.; et al. Impact of interferon-free regimens on the glomerular filtration rate during treatment of chronic hepatitis C in a real-life cohort. J. Viral Hepat. 2018, 25, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolucci, S.; Fiorina, L.; Mariani, B.; Gulminetti, R.; Novati, S.; Barbarini, G.; Bruno, R.; Baldanti, F. Naturally occurring resistance mutations to inhibitors of HCV NS5A region and NS5B polymerase in DAA treatment-naïve patients. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukh, J.; Apgar, C.L.; Yanagi, M. Toward a Surrogate Model for Hepatitis C Virus: An Infectious Molecular Clone of the GB Virus-B Hepatitis Agent. Virology 1999, 262, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bright, H.; Carroll, A.R.; Watts, P.A.; Fenton, R.J. Development of a GB Virus B Marmoset Model and Its Validation with a Novel Series of Hepatitis C Virus NS3 Protease Inhibitors. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 2062–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, J.R.; Lin, K.-C.; Tennant, B.C.; Mansfield, K.G. GB virus B infection of the common marmoset (Callithrix jacchus) and associated liver pathology. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 2525–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanford, R.E.; Chavez, D.; Notvall, L.; Brasky, K.M. Comparison of tamarins and marmosets as hosts for GBV-B infections and the effect of immunosuppression on duration of viremia. Virology 2003, 311, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Zhu, S.; Shuai, L.; Xu, Y.; Yin, S.; Bian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zuo, B.; Wang, W.; Zhao, S.; et al. Infection of common marmosets with hepatitis C virus/GB virus-B chimeras. Hepatology 2014, 59, 789–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knodell, R.G.; Ishak, K.G.; Black, W.C.; Chen, T.S.; Craig, R.; Kaplowitz, N.; Kiernan, T.W.; Wollman, J. Formulation and application of a numerical scoring system for assessing histological activity in asymptomatic chronic active hepatitis. Hepatology 1981, 1, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepard, C.W.; Finelli, L.; Alter, M.J. Global epidemiology of hepatitis C virus infection. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2005, 5, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, S.J.; Cole, S.R.; Westreich, D.; Edmonds, A.; Hurt, C.B.; Albrecht, S.; Anastos, K.; Augenbraun, M.; Fischl, M.; French, A.L.; et al. Chronic hepatitis C virus infection and subsequent HIV viral load among women with HIV initiating antiretroviral therapy. Aids 2018, 32, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, H.; Shiratori, Y.; Moriyama, M.; Arakawa, Y.; Ide, T.; Sata, M.; Inoue, O.; Yano, M.; Tanaka, M.; Fujiyama, S.; et al. Interferon Therapy Reduces the Risk for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: National Surveillance Program of Cirrhotic and Noncirrhotic Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C in Japan. Ann. Intern. Med. 1999, 131, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woollard, D.J.; Haqshenas, G.; Dong, X.; Pratt, B.F.; Kent, S.J.; Gowans, E.J. Virus-Specific T-Cell Immunity Correlates with Control of GB Virus B Infection in Marmosets. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 3054–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaki, A.; Wiese, M.; Maertens, G.; Depla, E.; Seifert, U.; Liebetrau, A.; Miller, J.L.; Manns, M.P.; Rehermann, B. Cellular immune responses persist and humoral responses decrease two decades after recovery from a single-source outbreak of hepatitis C. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 578–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smyk-Pearson, S.; Tester, I.A.; Klarquist, J.; Palmer, B.E.; Pawlotsky, J.-M.; Golden-Mason, L.; Rosen, H.R. Spontaneous Recovery in Acute Human Hepatitis C Virus Infection: Functional T-Cell Thresholds and Relative Importance of CD4 Help. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 1827–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-H.; Veerapu, N.S.; Shin, E.-C.; Biancotto, A.; McCoy, J.P.; Capone, S.; Folgori, A.; Rehermann, B. Subinfectious hepatitis C virus exposures suppress T cell responses against subsequent acute infection. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1638–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chigbu, D.I.; Loonawat, R.; Sehgal, M.; Patel, D.; Jain, P. Hepatitis C Virus Infection: Host–Virus Interaction and Mechanisms of Viral Persistence. Cells 2019, 8, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thimme, R. T cell immunity to hepatitis C virus: Lessons for a prophylactic vaccine. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiringhelli, F.; Ménard, C.; Martin, F.; Zitvogel, L. The role of regulatory T cells in the control of natural killer cells: Relevance during tumor progression. Immunol. Rev. 2006, 214, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvas, S.; Azkur, A.K.; Kim, B.S.; Kumaraguru, U.; Rouse, B.T. CD4+CD25+ Regulatory T Cells Control the Severity of Viral Immunoinflammatory Lesions. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 4123–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvas, S.; Kumaraguru, U.; Pack, C.D.; Lee, S.; Rouse, B.T. CD4+CD25+ T Cells Regulate Virus-specific Primary and Memory CD8+ T Cell Responses. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasenkrug, K.J.; Chougnet, C.A.; Dittmer, U. Regulatory T cells in retroviral infections. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1006776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyk-Pearson, S.; Golden-Mason, L.; Klarquist, J.; Burton, J.J.R.; Tester, I.A.; Wang, C.C.; Culbertson, N.; Vandenbark, A.A.; Rosen, H.R. Functional Suppression by FoxP3+CD4+CD25(high) regulatory T Cells during Acute Hepatitis C Virus Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 197, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, N.; Chi, X.; Li, T.; Song, H.; Li, H.; Jin, X.; Crispe, I.N.; Su, L.; Niu, J.; Tu, Z. Hepatitis C virus core protein triggers expansion and activation of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in chronic hepatitis C patients. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 12, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Ma, X.; Wang, Q.; Luo, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W.; Fu, Y.; Allain, J.-P.; Li, C.; Li, T. Marmoset Viral Hepatic Inflammation Induced by Hepatitis C Virus Core Protein via IL-32. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, B.; Zhang, E.; Ma, X.; Luo, S.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W.; Fu, Y.; Allain, J.-P.; Li, C.; et al. Early Phase of Specific Cellular Immune Status Associates with HCV Infection Outcomes in Marmosets. Viruses 2023, 15, 1082. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15051082
Liu B, Zhang E, Ma X, Luo S, Wang C, Zhang L, Wang W, Fu Y, Allain J-P, Li C, et al. Early Phase of Specific Cellular Immune Status Associates with HCV Infection Outcomes in Marmosets. Viruses. 2023; 15(5):1082. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15051082
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Bochao, Enhui Zhang, Xiaorui Ma, Shengxue Luo, Chong Wang, Ling Zhang, Wenjing Wang, Yongshui Fu, Jean-Pierre Allain, Chengyao Li, and et al. 2023. "Early Phase of Specific Cellular Immune Status Associates with HCV Infection Outcomes in Marmosets" Viruses 15, no. 5: 1082. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15051082
APA StyleLiu, B., Zhang, E., Ma, X., Luo, S., Wang, C., Zhang, L., Wang, W., Fu, Y., Allain, J.-P., Li, C., & Li, T. (2023). Early Phase of Specific Cellular Immune Status Associates with HCV Infection Outcomes in Marmosets. Viruses, 15(5), 1082. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15051082





