Abstract
New strategies to rapidly develop broad-spectrum antiviral therapies are urgently required for emerging and re-emerging viruses. Host-targeting antivirals (HTAs) that target the universal host factors necessary for viral replication are the most promising approach, with broad-spectrum, foresighted function, and low resistance. We and others recently identified that host dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH) is one of the universal host factors essential for the replication of many acute-infectious viruses. DHODH is a rate-limiting enzyme catalyzing the fourth step in de novo pyrimidine synthesis. Therefore, it has also been developed as a therapeutic target for many diseases relying on cellular pyrimidine resources, such as cancers, autoimmune diseases, and viral or bacterial infections. Significantly, the successful use of DHODH inhibitors (DHODHi) against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection further supports the application prospects. This review focuses on the advantages of HTAs and the antiviral effects of DHODHi with clinical applications. The multiple functions of DHODHi in inhibiting viral replication, stimulating ISGs expression, and suppressing cytokine storms make DHODHi a potent strategy against viral infection.
1. Introduction
In recent years, emerging or re-emerging viruses have appeared with increasing frequency, severely threatening global public health security and causing enormous economic losses [1]. At present, the World Health Organization has announced six international public health emergencies, the H1N1 influenza pandemic in 2009 [2], the polio epidemic in 2014 [3], the Ebola epidemic in West Africa in 2014 [4], the Zika epidemic in 2015–2016 [5], the Ebola epidemic in the Democratic Republic of Congo that began in 2018 (announced in July 2019) [6,7], and the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) pneumonia pandemic that broke out at the end of 2019 [8]. In addition, Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV), SARS-CoV, dengue virus (DENV), Chikungunya virus, and other viruses cause epidemic infections worldwide [9,10,11,12]. These virus epidemics and pandemics remind us that a broad-spectrum antiviral must be prepared to combat the continual outbreaks of various viruses.
At present, most approved antivirals target viral proteins to inhibit specific steps in the viral infection cycle and are called direct-acting antivirals (DAAs). Taking SARS-CoV-2 as an example, in the rush of anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug development competition, remdesivir is highly expected. It targets viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) to terminate viral RNA chain elongation by competing with the natural substrate of RdRp, adenosine triphosphate [13,14]. Unfortunately, although remdesivir showed fair anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity in vitro, clinical results showed no significant benefit compared with placebo [15,16], probably because of three reasons. (1) Remdesivir needs to be converted into remdesivir-TP in vivo to function [17,18]. (2) Remdesivir is originally developed by targeting the Ebola virus (EBOV) RdRp [19], making it unlikely to have an equivalent impact on the SARS-CoV-2 RdRp because of the plasticity of the virus. (3) The proofreading function of SARS-CoV-2 nsp14 exonuclease limits the potential of remdesivir [20]. Similar to remdesivir, many DAAs have been proven to be clinically successful only against a certain kind of virus but not others. Overall, DAAs have some inherent disadvantages. (1) They have narrow-spectrum antiviral properties. Viral proteins usually share few structural similarities among different species or classes. (2) Drug resistance develops against DAAs. DAAs act directly on viral proteins, promoting mutagenesis during viral replication. (3) DAAs are expensive and inefficient. DAAs apply the “one bug, one drug” strategy so that the development of individual DAA to each virus is an expensive and inefficient process in the context of continually emerging viruses [21].
Viruses are obligate parasites that rely entirely on the internal host environment to produce progeny viral particles. Therefore, viruses usually need to hijack the host machinery to replicate. For this reason, host-targeting antivirals (HTAs), which target the host factors required for viral infection, represent a broad-spectrum antiviral strategy. Moreover, the treatment of acute viral infections requires only a few days, greatly facilitating tolerance of the relative toxicity from the targeted host pathway. Compared with DAAs, HTAs have advantages. (1) HTAs show broad-spectrum antiviral activities because viruses use many of the same host proteins to replicate. (2) HTAs may also be effective against future emerging viruses. HTAs inhibit the host proteins essential for viral replication, which may also be effective against emerging viruses. (3) HTAs poorly induce the development of drug resistance. The host genetic material is double-stranded DNA with a lower mutation rate than RNA. Table 1 summarizes the host targets for antiviral treatment, such as dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH), chemokine receptor type 5, inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase, cyclophilins, eukaryotic initiation factor 2α, dihydrofolate reductase, and et al.

Table 1.
Host targets and antiviral activities of host-targeting antivirals (HTAs).
2. The Pyrimidine Synthesis Pathway Is a Reliable HTA Target
Pyrimidine is a heterocyclic compound and a vital component of cells [22]. Therefore, antivirals targeting the pyrimidine synthesis pathway may be effective and have a broad spectrum of activity. Pyrimidine participates in synthesizing not only nucleotides but also polysaccharides and phospholipids, which play an essential role in human metabolism. When cells become cancerous [23] or infected by pathogenic microorganisms [24,25], the overall metabolic activity and the demand for pyrimidines are increased compared with those in quiescent cells. Munger et al. researched human cytomegalovirus (HCMV)-infected human fibroblasts using liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry and identified 167 differentially abundant metabolites. Among these metabolites, those related to de novo pyrimidine biosynthetic pathways, such as carbamoyl-aspartic acid, cytidine triphosphate, uridine triphosphate, and thymidine triphosphate, were significantly enriched compared to those in the uninfected group [26]. Another study by Consigli et al. found a similar phenomenon. The activity of aspartate transcarbamylase, which is essential for pyrimidine synthesis, was significantly increased in adenovirus type 5-infected HeLa cells [27]. These reports suggested that viruses would hijack the host pyrimidine synthesis pathway to benefit their replication.
There are two ways to synthesize pyrimidines in the human body, namely, the de novo biosynthesis and salvage pathways [25], as shown in Figure 1. The salvage pathway utilizes extracellular uridine or cytidine to resynthesize pyrimidine nucleotides through simple enzymatic reactions (green arrow in Figure 1). The salvage pathway is the primary source of quiescent or differentiated cells, but it is insufficient to provide the pyrimidine pool for highly proliferating and virus-infected cells [28,29]. Therefore, the de novo synthesis pathway is required for these cells. The de novo synthesis pathway provides a large pool of pyrimidine nucleotides by using simple precursor molecules (such as amino acids, CO2, and pentose phosphate) as substrates through a series of complex enzymatic reactions (blue arrow in Figure 1) [30]. Step 4 is the rate-limiting step in the de novo synthesis pathway, and dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH) is the only enzyme that oxidizes dihydroorotate (DHO) acid to orotate (ORO) [31].
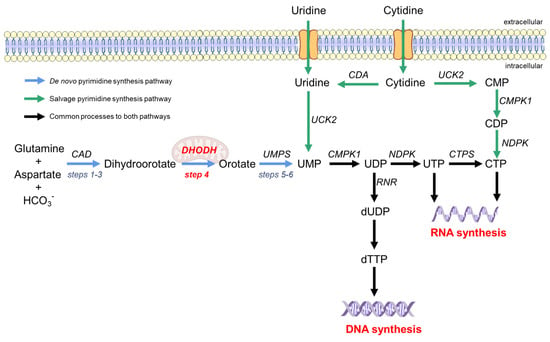
Figure 1.
Pyrimidine synthesis pathway in humans. The de novo synthesis pathway of pyrimidine is represented by blue arrows, and the salvage pathway is represented by green arrows. The de novo synthesis pathway begins with dihydroorotate from glutamine and aspartate under the action of CAD multifunctional enzymes (steps 1–3). The mitochondrial inner membrane protein DHODH oxidizes DHO to produce orotate (step 4). Orotate is subsequently phosphorylated and produces UMP from the bifunctional enzyme UMPS (steps 5–6). In the salvage pathway, exogenous uridine and cytidine can be transformed into UMP and CTP, respectively. UDP is the raw material for DNA synthesis. CTP and UTP are the raw materials for RNA synthesis. CAD, carbamoyl phosphate synthetase, aspartate transcarbamoylase, and dihydroorotase; UMP, uridine monophosphate; DHODH, dihydroorotate dehydrogenase; UDP, uridine diphosphate; UTP, uridine triphosphate; CMP, cytidine monophosphate; CDP, cytidine diphosphate; CTP, cytidine triphosphate; CTPS, CTP synthase; dUDP, deoxy-UDP; dTTP, deoxythymidine triphosphate; UMPS, uridine monophosphate synthetase; CMPK, cytidine monophosphate kinase; NDPK, nucleoside-diphosphate kinase; CDA, cytidine deaminase; UCK, uridine or cytidine kinase; RR, ribonucleotide reductase.
3. The Essential Role of DHODH in the De Novo Pyrimidine Synthesis Pathway
The de novo pyrimidine synthesis pathway is divided into six steps (Figure 1) [30]. The first three steps proceed via the multifunctional CAD (carbamyl phosphate synthase, aspartate transcarbamylase, and dihydroorotate) enzymes catalyzing the conversion of L-glutamine, aspartic acid, and bicarbonate to dihydroorotate (DHO) (steps 1–3). Then, the mitochondrial membrane protein dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH) oxidizes DHO to ORO (step 4), which is the rate-limiting step of the de novo pyrimidine synthesis pathway [32]. ORO undergoes the action of orotate phosphoribosyltransferase and orotate 5′-monophosphate decarboxylase to generate uridine monophosphate (steps 5 and 6). In step 4, DHODH, as an oxidoreductase, removes two electrons from DHO and transfers them to flavin mononucleotide (FMN). FMN regeneration is necessary for sustained DHODH catalysis. For this reason, ubiquinone, the electron acceptor in the mitochondrial electron transport chain, is required to receive electrons from FMN to complete the catalytic cycle [30]. This specific role of DHODH, which is involved in the de novo pyrimidine synthesis and links this pathway to the electron transport chain of aerobic respiration, makes DHODH the most attractive drug target in the pyrimidine synthesis pathway.
DHODH inhibitors (DHODHi) have been used to treat malignant tumors, autoimmune diseases, viral or bacterial infections, parasitic diseases, and other diseases [23,31,33,34,35]. DHODHi inhibit viral infection by three mechanisms: (1) inhibiting viral replication (pathway 1 in Figure 2), (2) promoting interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs) expression (pathway 2 in Figure 2), and (3) regulating inflammation (pathway 3 in Figure 2). This article reviews the critical role of DHODH in the de novo pyrimidine synthesis pathway during viral infections, with examples of several DHODHi and their clinical applications.
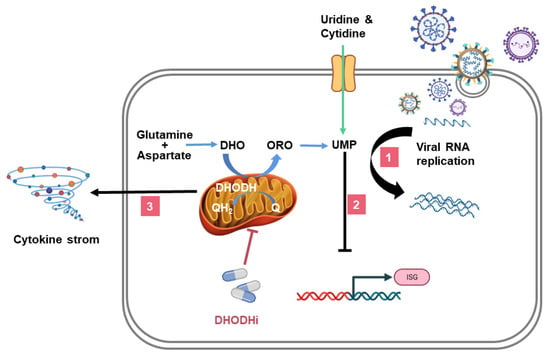
Figure 2.
The role of DHODHi in viral infection. The triple mechanism of DHODHi is as follows: (1) DHODHi reduce the pyrimidine pool required for viral replication; (2) DHODHi activate ISGs expression; and (3) DHODHi suppress the inflammatory factor storm caused by the virus. The mechanisms by which human cells obtain pyrimidines: the de novo biosynthesis (blue arrow) and the salvage pathway (green arrow). UMP, uridine monophosphate; DHO, dihydroorotate; ORO, orotate; Q, ubiquinone; QH2, ubiquinol; ISG, interferon-stimulated gene.
4. DHODHi Inhibit the Virus Replication Cycle
Cytosine, thymine, and uridine are essential components of DNA and RNA. Therefore, viral genome replication requires the synthesis of large amounts of pyrimidines, which enables the broad-spectrum antiviral activity of DHODHi. Compared with DNA viruses, RNA viruses require the unique uridine monophosphate (particular nucleotide produced by DHODH) in their genomes instead of thymidine monophosphate, which suggests that RNA viruses are more sensitive to DHODH activity [36]. At present, increasing studies have found that DHODHi inhibit the replication of RNA viruses, especially from the early stage of the virus replication cycle. In IBRS-2 cells infected with 100 TCID50 of FMDV (O/MY98/BY/2010), administration of 300 μM teriflunomide at the early stage of infection (0–4 h after infection) significantly inhibited 99% of the 2B mRNA level and VP1 viral protein expression [32]. Similarly, in a Junin virus-infected Vero cell model (MOI = 0.1), 50 μM teriflunomide mainly inhibited viral replication in the early and middle stages (0–6 h after infection) [37]. Intriguingly, in Vero or A549 cell models infected with DENV serotype 2 (MOI = 2), brequinar inhibited not only the early and middle phases, but also the later phases (RNA synthesis, virion assembly, or release) of the viral replication cycle [38]. Therefore, DHODHi may have potent antiviral effects at all steps of RNA virus replication.
Although not as powerful as they are against RNA viruses, DHODHi are also reported to inhibit the replication of DNA viruses. For example, in HCMV (Towne strain)-infected human primary embryonic lung fibroblasts (HEL 299), FK778, an oral DHODHi, exhibited a potential antiviral effect with an EC50 of 1.97 μM [39]. In the A549 cell model infected with human adenovirus 5 (MOI = 5), the virus titers were reduced by 6 logs by compound A3. Vaccinia virus was also sensitive to compound A3 [35].
5. DHODHi Stimulate the Expression of ISGs
Lucas-Hourani et al. screened stimulators of the innate antiviral response and established a link between pyrimidine biosynthesis and ISGs expression [40]. They identified a DHODHi, DD264, which possessed ideal antiviral effects by enhancing ISGs expression. Moreover, supplementation with uridine abolished the amplification of ISGs expression by DD264. However, whether DHODHi induction of the expression of ISGs depends on the classic JAK-STAT pathway is not yet clear. Jin et al. used the JAK inhibitor CP-690550 to block the JAK-STAT pathway in Peste des petits ruminants virus (PPRV)-infected HEK293T cells. Surprisingly, the transcription of ISGs could still be upregulated by brequinar. This result indicated that the induction of ISGs by brequinar was independent of the JAK-STAT pathway [41]. In addition, an anti-influenza virus study suggested that leflunomide could still play an antiviral role after inhibiting the tyrosine phosphorylation of JAK1 and JAK3 [42]. In contrast, the antiviral activity of FA-613 relied on interferon-dependent ISGs stimulation [43]. It seems that different DHODHi activate ISGs expression by triggering different pathways.
6. DHODHi Inhibit the Production of Inflammatory Cytokines
For a long time, cytokines and chemokines have been considered to play essential roles in immunopathology during viral infection, because excessive virus-induced inflammation contributes to severe disease and death [44,45,46,47,48,49]. The DHODHi, such as leflunomide and teriflunomide, have been clinically used to treat autoimmune diseases and suppress cytokine production [50,51,52,53,54], they may also regulate excessive inflammation induced by viruses. We previously proved that the combination of S312 and oseltamivir vastly reduced the pathogenic inflammatory cytokine levels of IL6, MCP-1, IL5, KC/GRO (CXCL1), IL2, IFN-γ, IP-10, IL9, TNF-α, GM-CSF, EPO, IL12p70, MIP3α, and IL17A/F in influenza A virus-infected mice [36]. Similarly, it was reported that elevated inflammatory factor levels are positively correlated with the severity of COVID-19, such as those of IL-2, IL-6, IL-7, IL-10, G-CSF, MCP, MIP1α, IFN-γ, IP-10, and TNF-α [55,56,57,58,59,60]. Our unpublished data indicated that DHODHi could also regulate hyperinflammation reactions in severe SARS-CoV-2-infected animals by reducing pathogenic inflammatory cytokines levels. Although more research and clinical studies are expected to illustrate the immune-regulation role of DHODHi against SARS-CoV-2 infection, our clinical observation already showed that leflunomide could reduce lung inflammation and the serum C-reactive protein level in COVID-19 patients [61].
Moreover, DHODHi would offer dual effects in minimizing immune overreaction induced by viral infection. It is believed that SARS-CoV-2 induces lung damage in two stages [46,62]. The virus replicates in the lungs directly, causing lung tissue damage in the first stage. The second stage is characterized by the massive expression of cytokines and chemokines and the migration of immune cells to the lungs, resulting in an excessive inflammatory response [55,56,57,58,59,60,63]. The severity of tissue damage in the first stage determines the degree of inflammation in the second stage. Thus, DHODHi could act in both stages to reduce lung damage by limiting viral replication in the first stage [64] and further inhibit the overexpression of cytokines and chemokines from the residue tissue damage in the second stage [65].
8. Conclusions and Prospects
DHODHi were initially used to treat cancers or autoimmune disorders and have gradually been applied to antiviral therapies. When viruses infect host cells, nucleotide biosynthesis flux increases, and the cytokine storm is also triggered [55,94]. The triple antiviral effects of DHODHi, including inhibiting viral replication, suppressing inflammation, and activating ISGs expression, make DHODHi excellent antivirals. The large-scale screening has also resulted in DHODHi becoming leading antiviral compounds [35,75,85,95]. Of note, leflunomide and brequinar have been associated with clinical side effects, such as gastrointestinal symptoms, thrombocytopenia, reversible alopecia areata, and elevated liver enzyme levels [96,97,98,99,100]. The off-target effects, not pyrimidine synthesis blockade, may be responsible for the side effects [31]. Fortunately, these side effects were reversed after stopping treatment [101].
Although most DHODHi exhibit broad-spectrum antiviral activity in vitro, several small-molecule DHODHi have failed to show significant therapeutic effects in animal models or clinically. The failure might be due to the narrow window of these molecules or the recovery of exogenous uridine from the host. Therefore, developing a more efficient DHODHi is a priority. Our previous research indicated the high target occupancy rate and low toxicity of S416, making S416 the most potent anti-SARS-CoV-2 candidate compound in vitro reported to date [36]. The potent antiviral activity of S416 (CC50 = 178.6 μM, EC50 = 0.017 μM, SI = 10,505.88) fully illustrates the great potential of DHODHi in the treatment of viral infections.
Moreover, the combination of an HTA and a DAA showed superior antiviral effects compared to that of a single drug, such as teriflunomide in combination with ribavirin [37], brequinar in combination with molnupiravir (a DAA that inhibits viral RdRp) [78], and S312 in combination with oseltamivir [36]. As the drug targets are distinct between an HTA and a DAA, a synergistic treatment by combining these drugs could block multiple steps and factors in the virus life cycle. Especially, DHODHi have several significant advantages when combined with DAAs. (1) Due to the rapid replication cycle of viruses, DAAs usually need to be applied shortly after infection because the targeted viral components will amplify exponentially during the illness duration. However, DHODHi target the host DHODH, which keeps a relatively stable level during infection. A combination of DHODHi and DAA would have a superimposing inhibitory effect throughout the disease course compared to a single drug alone. (2) DAAs directly target viruses but have no effects on the host’s inflammatory responses. DHODHi harbor dual functions of inhibiting both viral replication and excessive inflammation cytokine expressions by reducing the cellular pyrimidine pool. (3) The uptake or incorporation of the nucleoside analogs may be increased when pyrimidines are limiting [78]. Therefore, when DHODHi are used in combined with DAAs of nucleoside analogs, the incorporation efficiency of nucleoside analogs would be further increased. (4) DHODHi are effective to various viruses and viral variants regardless of mutagenesis, so combining with DAA could expand the targeted viral spectrum.
Targeting universal host factors necessary for viruses can finally achieve broad-spectrum antiviral effects. As a promising example, DHODHi, which can effectively reduce the pyrimidine pool for viral replication, stimulate the ISGs expression, and suppress the virus-induced cytokine storm, could serve as a broad antiviral strategy against emerging and re-emerging viruses.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization of the manuscript, K.X. and Y.Z. (Yucheng Zheng); design and production of illustrations, K.X. and Y.Z. (Yucheng Zheng); writing—original draft preparation, Y.Z. (Yucheng Zheng), S.L. (Shiliang Li), K.S., J.Y., W.L., Y.Z. (Yifan Zhong), Z.F. and S.L. (Simeng Liang); writing—review and editing, K.X., Y.Z. (Yucheng Zheng) and Z.C.; funding acquisition, K.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grants 31922004 and 81772202), the Innovation Team Research Program of Hubei Province (2020CFA015), the Application & Frontier Research Program of the Wuhan Government (2019020701011463).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the Taikang Insurance Group Co., Ltd.; Beijing Taikang Yicai Foundation, Special Fund for COVID-19 Research of Wuhan University.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gao, G.F. From “A”IV to “Z”IKV: Attacks from Emerging and Re-emerging Pathogens. Cell 2018, 172, 1157–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- WHO. H1N1 IHR Emergency Committee. Available online: https://www.who.int/groups/h1n1-ihr-emergency-committee (accessed on 15 March 2022).
- WHO. Poliovirus IHR Emergency Committee. Available online: https://www.who.int/groups/poliovirus-ihr-emergency-committee (accessed on 15 March 2022).
- WHO. Ebola Virus Disease in West Africa (2014–2015) IHR Emergency Committee. Available online: https://www.who.int/groups/ebola-virus-disease-in-west-africa-(2014-2015)-ihr-emergency-committee (accessed on 15 March 2022).
- WHO. Zika Virus IHR Emergency Committee. Available online: https://www.who.int/groups/zika-virus-ihr-emergency-committee (accessed on 15 March 2022).
- WHO. Ebola Virus Disease in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (Equateur) IHR Emergency Committee. Available online: https://www.who.int/groups/ebola-virus-disease-in-the-democratic-republic-of-the-congo-equateur-ihr-emergency-committee (accessed on 15 March 2022).
- WHO. Ebola Virus Disease in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (Kivu and Ituri) IHR Emergency Committee. Available online: https://www.who.int/groups/ebola-virus-disease-in-the-democratic-republic-of-the-congo-kivu-and-ituri-ihr-emergency-committee (accessed on 15 March 2022).
- WHO. COVID-19 IHR Emergency Committee. Available online: https://www.who.int/groups/covid-19-ihr-emergency-committee (accessed on 15 March 2022).
- WHO. Summary of probable SARS cases with onset of illness from 1 November 2002 to 31 July 2003. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/summary-of-probable-sars-cases-with-onset-of-illness-from-1-november-2002-to-31-july-2003 (accessed on 15 March 2022).
- WHO. MERS-CoV IHR Emergency Committee. Available online: https://www.who.int/groups/mers-cov-ihr-emergency-committee (accessed on 15 March 2022).
- Guzman, M.G.; Harris, E. Dengue. Lancet 2015, 385, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, F.J.; Chen, W.; Miner, J.J.; Lenschow, D.J.; Merits, A.; Schnettler, E.; Kohl, A.; Rudd, P.A.; Taylor, A.; Herrero, L.J.; et al. Chikungunya virus: An update on the biology and pathogenesis of this emerging pathogen. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, e107–e117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Yan, L.; Huang, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhao, Y.; Cao, L.; Wang, T.; Sun, Q.; Ming, Z.; Zhang, L.; et al. Structure of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from COVID-19 virus. Science 2020, 368, 779–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Cao, R.; Zhang, L.; Yang, X.; Liu, J.; Xu, M.; Shi, Z.; Hu, Z.; Zhong, W.; Xiao, G. Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, B.; Tan, T.T.; Leo, Y.S. The place for remdesivir in COVID-19 treatment. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 20–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grein, J.; Ohmagari, N.; Shin, D.; Diaz, G.; Asperges, E.; Castagna, A.; Feldt, T.; Green, G.; Green, M.L.; Lescure, F.X.; et al. Compassionate Use of Remdesivir for Patients with Severe Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2327–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirian, E.S.; Levy, J.K. Current knowledge about the antivirals remdesivir (GS-5734) and GS-441524 as therapeutic options for coronaviruses. One Health 2020, 9, 100128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, C.J.; Tchesnokov, E.P.; Feng, J.Y.; Porter, D.P.; Götte, M. The antiviral compound remdesivir potently inhibits RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 4773–4779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warren, T.K.; Jordan, R.; Lo, M.K.; Ray, A.S.; Mackman, R.L.; Soloveva, V.; Siegel, D.; Perron, M.; Bannister, R.; Hui, H.C.; et al. Therapeutic efficacy of the small molecule GS-5734 against Ebola virus in rhesus monkeys. Nature 2016, 531, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogando, N.S.; Zevenhoven-Dobbe, J.C.; van der Meer, Y.; Bredenbeek, P.J.; Posthuma, C.C.; Snijder, E.J. The Enzymatic Activity of the nsp14 Exoribonuclease Is Critical for Replication of MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e01246-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adalja, A.; Inglesby, T. Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Agents: A Crucial Pandemic Tool. Expert Rev. Anti. Infect. Ther. 2019, 17, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Löffler, M.; Fairbanks, L.D.; Zameitat, E.; Marinaki, A.M.; Simmonds, H.A. Pyrimidine pathways in health and disease. Trends Mol. Med. 2005, 11, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Tao, L.; Zhou, X.; Zuo, Z.; Gong, J.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, C.; Sang, N.; Liu, H.; et al. DHODH and cancer: Promising prospects to be explored. Cancer Metab. 2021, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.; Chitranshi, N.; Agarwal, A.K. Significance and biological importance of pyrimidine in the microbial world. Int. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 2014, 202784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Evans, D.R.; Guy, H.I. Mammalian pyrimidine biosynthesis: Fresh insights into an ancient pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 33035–33038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Munger, J.; Bajad, S.U.; Coller, H.A.; Shenk, T.; Rabinowitz, J.D. Dynamics of the cellular metabolome during human cytomegalovirus infection. PLoS Pathog. 2006, 2, e132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Consigli, R.A.; Ginsberg, H.S. Control of aspartate transcarbamylase activity in type 5 adenovirus-infected HeLa cells. J. Bacteriol. 1964, 87, 1027–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Traut, T.W. Physiological concentrations of purines and pyrimidines. Mol. Cell Biochem. 1994, 140, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okesli, A.; Khosla, C.; Bassik, M.C. Human pyrimidine nucleotide biosynthesis as a target for antiviral chemotherapy. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2017, 48, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, R.A.G.; Calil, F.A.; Feliciano, P.R.; Pinheiro, M.P.; Nonato, M.C. The dihydroorotate dehydrogenases: Past and present. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2017, 632, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munier-Lehmann, H.; Vidalain, P.-O.; Tangy, F.; Janin, Y.L. On Dihydroorotate Dehydrogenases and Their Inhibitors and Uses. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 3148–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei-Jiao, G.; Shi-Fang, L.; Yan-Yan, C.; Jun-Jun, S.; Yue-Feng, S.; Ting-Ting, R.; Yong-Guang, Z.; Hui-Yun, C. Antiviral effects of selected IMPDH and DHODH inhibitors against foot and mouth disease virus. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 118, 109305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alamri, R.D.; Elmeligy, M.A.; Albalawi, G.A.; Alquayr, S.M.; Alsubhi, S.S.; El-Ghaiesh, S.H. Leflunomide an immunomodulator with antineoplastic and antiviral potentials but drug-induced liver injury: A comprehensive review. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 93, 107398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Maqbool, M.; Mobashir, M.; Hoda, N. Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase: A drug target for the development of antimalarials. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 125, 640–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, H.H.; Kunz, A.; Simon, V.A.; Palese, P.; Shaw, M.L. Broad-spectrum antiviral that interferes with de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 5777–5782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, R.; Zhang, L.; Li, S.; Sun, Y.; Ding, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Shang, W.; Jiang, X.; et al. Novel and potent inhibitors targeting DHODH are broad-spectrum antivirals against RNA viruses including newly-emerged coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. Protein Cell 2020, 11, 723–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepúlveda, C.S.; García, C.C.; Damonte, E.B. Antiviral activity of A771726, the active metabolite of leflunomide, against Junín virus. J. Med. Virol. 2018, 90, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, M.; Zou, G.; Wang, Q.-Y.; Xu, H.Y.; Dong, H.; Yuan, Z.; Shi, P.-Y. Characterization of dengue virus resistance to brequinar in cell culture. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 3686–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evers, D.L.; Wang, X.; Huong, S.M.; Andreoni, K.A.; Huang, E.S. Inhibition of human cytomegalovirus signaling and replication by the immunosuppressant FK778. Antivir. Res. 2005, 65, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas-Hourani, M.; Dauzonne, D.; Jorda, P.; Cousin, G.; Lupan, A.; Helynck, O.; Caignard, G.; Janvier, G.; André-Leroux, G.; Khiar, S.; et al. Inhibition of pyrimidine biosynthesis pathway suppresses viral growth through innate immunity. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, L.; Li, Y.; Pu, F.; Wang, H.; Zhang, D.; Bai, J.; Shang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Ma, X.X. Inhibiting pyrimidine biosynthesis impairs Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus replication through depletion of nucleoside pools and activation of cellular immunity. Vet. Microbiol. 2021, 260, 109186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Hu, J.; Wang, C.; Prinz, R.A.; Peng, D.; Liu, X.; Xu, X. A77 1726, the active metabolite of the anti-rheumatoid arthritis drug leflunomide, inhibits influenza A virus replication in vitro and in vivo by inhibiting the activity of Janus kinases. Faseb. J. 2020, 34, 10132–10145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, N.N.; Lai, K.K.; Dai, J.; Kok, K.H.; Chen, H.; Chan, K.H.; Yuen, K.Y.; Kao, R.Y.T. Broad-spectrum inhibition of common respiratory RNA viruses by a pyrimidine synthesis inhibitor with involvement of the host antiviral response. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 946–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, S.L.; de Lang, A.; van den Brand, J.M.; Leijten, L.M.; van IJcken, W.F.; Eijkemans, M.J.; van Amerongen, G.; Kuiken, T.; Andeweg, A.C.; Osterhaus, A.D.; et al. Exacerbated innate host response to SARS-CoV in aged non-human primates. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaw, A.C.; Goldstein, D.R.; Montgomery, R.R. Age-dependent dysregulation of innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 875–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Channappanavar, R.; Fehr, A.R.; Vijay, R.; Mack, M.; Zhao, J.; Meyerholz, D.K.; Perlman, S. Dysregulated Type I Interferon and Inflammatory Monocyte-Macrophage Responses Cause Lethal Pneumonia in SARS-CoV-Infected Mice. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davidson, S.; Maini, M.K.; Wack, A. Disease-promoting effects of type I interferons in viral, bacterial, and coinfections. J. Interferon. Cytokine. Res. 2015, 35, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockx, B.; Baas, T.; Zornetzer, G.A.; Haagmans, B.; Sheahan, T.; Frieman, M.; Dyer, M.D.; Teal, T.H.; Proll, S.; van den Brand, J.; et al. Early upregulation of acute respiratory distress syndrome-associated cytokines promotes lethal disease in an aged-mouse model of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 7062–7074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhou, C.; Wu, Z.; Zhong, S.; Liu, J.; Luo, W.; Chen, T.; Qin, Q.; Deng, P. Characterization of cytokine/chemokine profiles of severe acute respiratory syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 171, 850–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, M.L.; Schleyerbach, R.; Kirschbaum, B.J. Leflunomide: An immunomodulatory drug for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune diseases. Immunopharmacology 2000, 47, 273–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breedveld, F.C.; Dayer, J.M. Leflunomide: Mode of action in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2000, 59, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutolo, M.; Sulli, A.; Ghiorzo, P.; Pizzorni, C.; Craviotto, C.; Villaggio, B. Anti-inflammatory effects of leflunomide on cultured synovial macrophages from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2003, 62, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vergne-Salle, P.; Léger, D.Y.; Bertin, P.; Trèves, R.; Beneytout, J.L.; Liagre, B. Effects of the active metabolite of leflunomide, A77 1726, on cytokine release and the MAPK signalling pathway in human rheumatoid arthritis synoviocytes. Cytokine 2005, 31, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, D.; Begué-Pastor, N.; Benavent, S.; Gruaz, L.; Kaufmann, M.T.; Chicheportiche, R.; Dayer, J.M. The active metabolite of leflunomide, A77 1726, inhibits the production of prostaglandin E(2), matrix metalloproteinase 1 and interleukin 6 in human fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Rheumatology 2003, 42, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ryabkova, V.A.; Churilov, L.P.; Shoenfeld, Y. Influenza infection, SARS, MERS and COVID-19: Cytokine storm—The common denominator and the lessons to be learned. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 223, 108652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Jiang, M.; Chen, X.; Montaner, L.J. Cytokine storm and leukocyte changes in mild versus severe SARS-CoV-2 infection: Review of 3939 COVID-19 patients in China and emerging pathogenesis and therapy concepts. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2020, 108, 17–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Yang, J.W.; Lee, K.H.; Effenberger, M.; Szpirt, W.; Kronbichler, A.; Shin, J.I. Immunopathogenesis and treatment of cytokine storm in COVID-19. Theranostics 2021, 11, 316–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustine, J.N.; Jones, D. Immunopathology of Hyperinflammation in COVID-19. Am. J. Pathol. 2021, 191, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afrin, L.B.; Weinstock, L.B.; Molderings, G.J. Covid-19 hyperinflammation and post-Covid-19 illness may be rooted in mast cell activation syndrome. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 100, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluge, S.; Janssens, U.; Welte, T.; Weber-Carstens, S.; Schälte, G.; Salzberger, B.; Gastmeier, P.; Langer, F.; Welper, M.; Westhoff, M.; et al. Recommendations for treatment of critically ill patients with COVID-19: Version 3 S1 guideline. Anaesthesist 2021, 70, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, K.; Wang, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; Zheng, Z.; Li, X.; Zeng, S.; Zhao, D.; Li, H.; et al. A Small-Scale Medication of Leflunomide as a Treatment of COVID-19 in an Open-Label Blank-Controlled Clinical Trial. Virol. Sin. 2020, 35, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merad, M.; Blish, C.A.; Sallusto, F.; Iwasaki, A. The immunology and immunopathology of COVID-19. Science 2022, 375, 1122–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merad, M.; Martin, J.C. Pathological inflammation in patients with COVID-19: A key role for monocytes and macrophages. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Jiang, H. Potential treatment of COVID-19 by inhibitors of human dihydroorotate dehydrogenase. Protein Cell 2020, 11, 699–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luban, J.; Sattler, R.A.; Mühlberger, E.; Graci, J.D.; Cao, L.; Weetall, M.; Trotta, C.; Colacino, J.M.; Bavari, S.; Strambio-De-Castillia, C.; et al. The DHODH inhibitor PTC299 arrests SARS-CoV-2 replication and suppresses induction of inflammatory cytokines. Virus Res. 2021, 292, 198246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, J.E.; Neidhardt, E.A.; Grossman, T.H.; Hedstrom, L. Multiple inhibitor analysis of the brequinar and leflunomide binding sites on human dihydroorotate dehydrogenase. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragoso, Y.D.; Brooks, J.B. Leflunomide and teriflunomide: Altering the metabolism of pyrimidines for the treatment of autoimmune diseases. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 8, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, I.C.; Lazarowski, E.R.; Chen, F.P.; Hickman-Davis, J.M.; Sullender, W.M.; Matalon, S. Post-infection A77-1726 blocks pathophysiologic sequelae of respiratory syncytial virus infection. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2007, 37, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilger, A.; Plowshay, J.; Ma, S.; Nawandar, D.; Barlow, E.A.; Romero-Masters, J.C.; Bristol, J.A.; Li, Z.; Tsai, M.H.; Delecluse, H.J.; et al. Leflunomide/teriflunomide inhibit Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV)-induced lymphoproliferative disease and lytic viral replication. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 44266–44280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davis, I.C.; Lazarowski, E.R.; Hickman-Davis, J.M.; Fortenberry, J.A.; Chen, F.P.; Zhao, X.; Sorscher, E.; Graves, L.M.; Sullender, W.M.; Matalon, S. Leflunomide prevents alveolar fluid clearance inhibition by respiratory syncytial virus. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 173, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bernhoff, E.; Tylden, G.D.; Kjerpeseth, L.J.; Gutteberg, T.J.; Hirsch, H.H.; Rinaldo, C.H. Leflunomide inhibition of BK virus replication in renal tubular epithelial cells. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 2150–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chacko, B.; John, G.T. Leflunomide for cytomegalovirus: Bench to bedside. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2012, 14, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knecht, W.; Löffler, M. Species-related inhibition of human and rat dihydroorotate dehydrogenase by immunosuppressive isoxazol and cinchoninic acid derivatives. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1998, 56, 1259–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, P.I.; Krpina, K.; Ianevski, A.; Shtaida, N.; Jo, E.; Yang, J.; Koit, S.; Tenson, T.; Hukkanen, V.; Anthonsen, M.W.; et al. Novel Antiviral Activities of Obatoclax, Emetine, Niclosamide, Brequinar, and Homoharringtonine. Viruses 2019, 11, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luthra, P.; Naidoo, J.; Pietzsch, C.A.; De, S.; Khadka, S.; Anantpadma, M.; Williams, C.G.; Edwards, M.R.; Davey, R.A.; Bukreyev, A.; et al. Inhibiting pyrimidine biosynthesis impairs Ebola virus replication through depletion of nucleoside pools and activation of innate immune responses. Antiviral. Res. 2018, 158, 288–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales Vasquez, D.; Park, J.-G.; Ávila-Pérez, G.; Nogales, A.; de la Torre, J.C.; Almazan, F.; Martinez-Sobrido, L. Identification of Inhibitors of ZIKV Replication. Viruses 2020, 12, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-f.; Gong, M.-j.; Sun, Y.-f.; Shao, J.-j.; Zhang, Y.-g.; Chang, H.-y. Antiviral activity of brequinar against foot-and-mouth disease virus infection in vitro and in vivo. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 116, 108982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, D.C.; Johnson, R.M.; Ayyanathan, K.; Miller, J.; Whig, K.; Kamalia, B.; Dittmar, M.; Weston, S.; Hammond, H.L.; Dillen, C.; et al. Pyrimidine inhibitors synergize with nucleoside analogues to block SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2022, 604, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Han, L.; Diao, Y.; Ren, X.; Xu, M.; Xu, L.; Li, S.; Li, Q.; Dong, D.; Huang, J.; et al. Design, synthesis, X-ray crystallographic analysis, and biological evaluation of thiazole derivatives as potent and selective inhibitors of human dihydroorotate dehydrogenase. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 1123–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Luan, G.; Ren, X.; Song, W.; Xu, L.; Xu, M.; Zhu, J.; Dong, D.; Diao, Y.; Liu, X.; et al. Rational Design of Benzylidenehydrazinyl-Substituted Thiazole Derivatives as Potent Inhibitors of Human Dihydroorotate Dehydrogenase with in Vivo Anti-arthritic Activity. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cao, L.; Weetall, M.; Trotta, C.; Cintron, K.; Ma, J.; Kim, M.J.; Furia, B.; Romfo, C.; Graci, J.D.; Li, W.; et al. Targeting of Hematologic Malignancies with PTC299, A Novel Potent Inhibitor of Dihydroorotate Dehydrogenase with Favorable Pharmaceutical Properties. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Şimşek-Yavuz, S.; Komsuoğlu Çelikyurt, F.I. An update of anti-viral treatment of COVID-19. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 51, 3372–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muehler, A.; Peelen, E.; Kohlhof, H.; Gröppel, M.; Vitt, D. Vidofludimus calcium, a next generation DHODH inhibitor for the Treatment of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2020, 43, 102129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, F.; Wangen, C.; Häge, S.; Peter, A.S.; Dobler, G.; Hurst, B.; Julander, J.; Fuchs, J.; Ruzsics, Z.; Überla, K.; et al. IMU-838, a Developmental DHODH Inhibitor in Phase II for Autoimmune Disease, Shows Anti-SARS-CoV-2 and Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Efficacy In Vitro. Viruses 2020, 12, 1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Riaño, E.; Ngo, N.; Devito, S.; Eggink, D.; Munger, J.; Shaw, M.L.; de la Torre, J.C.; Martínez-Sobrido, L. Inhibition of arenavirus by A3, a pyrimidine biosynthesis inhibitor. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 878–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Christian, S.; Merz, C.; Evans, L.; Gradl, S.; Seidel, H.; Friberg, A.; Eheim, A.; Lejeune, P.; Brzezinka, K.; Zimmermann, K.; et al. The novel dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH) inhibitor BAY 2402234 triggers differentiation and is effective in the treatment of myeloid malignancies. Leukemia 2019, 33, 2403–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mathieu, C.; Touret, F.; Jacquemin, C.; Janin, Y.L.; Nougairède, A.; Brailly, M.; Mazelier, M.; Décimo, D.; Vasseur, V.; Hans, A.; et al. A Bioluminescent 3CL(Pro) Activity Assay to Monitor SARS-CoV-2 Replication and Identify Inhibitors. Viruses 2021, 13, 1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegmann, K.M.; Dickmanns, A.; Heinen, N.; Groß, U.; Görlich, D.; Pfaender, S.; Dobbelstein, M. N4-hydroxycytidine and inhibitors of dihydroorotate dehydrogenase synergistically suppress SARS-CoV-2 replication. bioRxiv 2021. preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainas, S.; Pippione, A.C.; Lupino, E.; Giorgis, M.; Circosta, P.; Gaidano, V.; Goyal, P.; Bonanni, D.; Rolando, B.; Cignetti, A.; et al. Targeting Myeloid Differentiation Using Potent 2-Hydroxypyrazolo [1,5-a]pyridine Scaffold-Based Human Dihydroorotate Dehydrogenase Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 6034–6055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calistri, A.; Luganini, A.; Mognetti, B.; Elder, E.; Sibille, G.; Conciatori, V.; Del Vecchio, C.; Sainas, S.; Boschi, D.; Montserrat, N.; et al. The New Generation hDHODH Inhibitor MEDS433 Hinders the In Vitro Replication of SARS-CoV-2 and Other Human Coronaviruses. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luganini, A.; Sibille, G.; Mognetti, B.; Sainas, S.; Pippione, A.C.; Giorgis, M.; Boschi, D.; Lolli, M.L.; Gribaudo, G. Effective deploying of a novel DHODH inhibitor against herpes simplex type 1 and type 2 replication. Antiviral. Res. 2021, 189, 105057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Cao, L.; Gao, H.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fang, F.; Lan, T.; Lou, Z.; Rao, Y. Discovery, Optimization, and Target Identification of Novel Potent Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 4056–4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, M.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Gan, T.; Wu, Y.; Gao, H.; Li, Q.; Nie, J.; Huang, W.; Wang, Y.; et al. Novel quinolone derivatives targeting human dihydroorotate dehydrogenase suppress Ebola virus infection in vitro. Antiviral. Res. 2021, 194, 105161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Li, W.; Xie, J.; Hou, Y.; You, C. Cytokine storm induced by SARS-CoV-2. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 509, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rane, J.S.; Pandey, P.; Chatterjee, A.; Khan, R.; Kumar, A.; Prakash, A.; Ray, S. Targeting virus-host interaction by novel pyrimidine derivative: An in silico approach towards discovery of potential drug against COVID-19. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 39, 5768–5778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaltwasser, J.P.; Nash, P.; Gladman, D.; Rosen, C.F.; Behrens, F.; Jones, P.; Wollenhaupt, J.; Falk, F.G.; Mease, P. Efficacy and safety of leflunomide in the treatment of psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis: A multinational, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 1939–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koller, G.; Cusnir, I.; Hall, J.; Ye, C. Reversible alopecia areata: A little known side effect of leflunomide. Clin. Rheumatol. 2019, 38, 2015–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro-Lara, R.; Espinosa-Ortega, H.F.; Arce-Salinas, C.A. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of leflunomide and methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Reumatol. Clin. 2019, 15, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pally, C.; Smith, D.; Jaffee, B.; Magolda, R.; Zehender, H.; Dorobek, B.; Donatsch, P.; Papageorgiou, C.; Schuurman, H.J. Side effects of brequinar and brequinar analogues, in combination with cyclosporine, in the rat. Toxicology 1998, 127, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makowka, L.; Sher, L.S.; Cramer, D.V. The development of Brequinar as an immunosuppressive drug for transplantation. Immunol. Rev. 1993, 136, 51–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiff, M.H.; Strand, V.; Oed, C.; Loew-Friedrich, I. Leflunomide: Efficacy and safety in clinical trials for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Drugs Today 2000, 36, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).