Isolation and Characterization of Cross-Reactive Human Monoclonal Antibodies That Potently Neutralize Australian Bat Lyssavirus Variants and Other Phylogroup 1 Lyssaviruses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Viruses
2.2. Phage Panning
2.3. Isolation and Characterization of hmAbs F11 and A6
2.4. Virus Neutralization Assays
2.5. Competitive ELISA
2.6. Lyssavirus Neutralizations
2.7. Statistics
3. Results
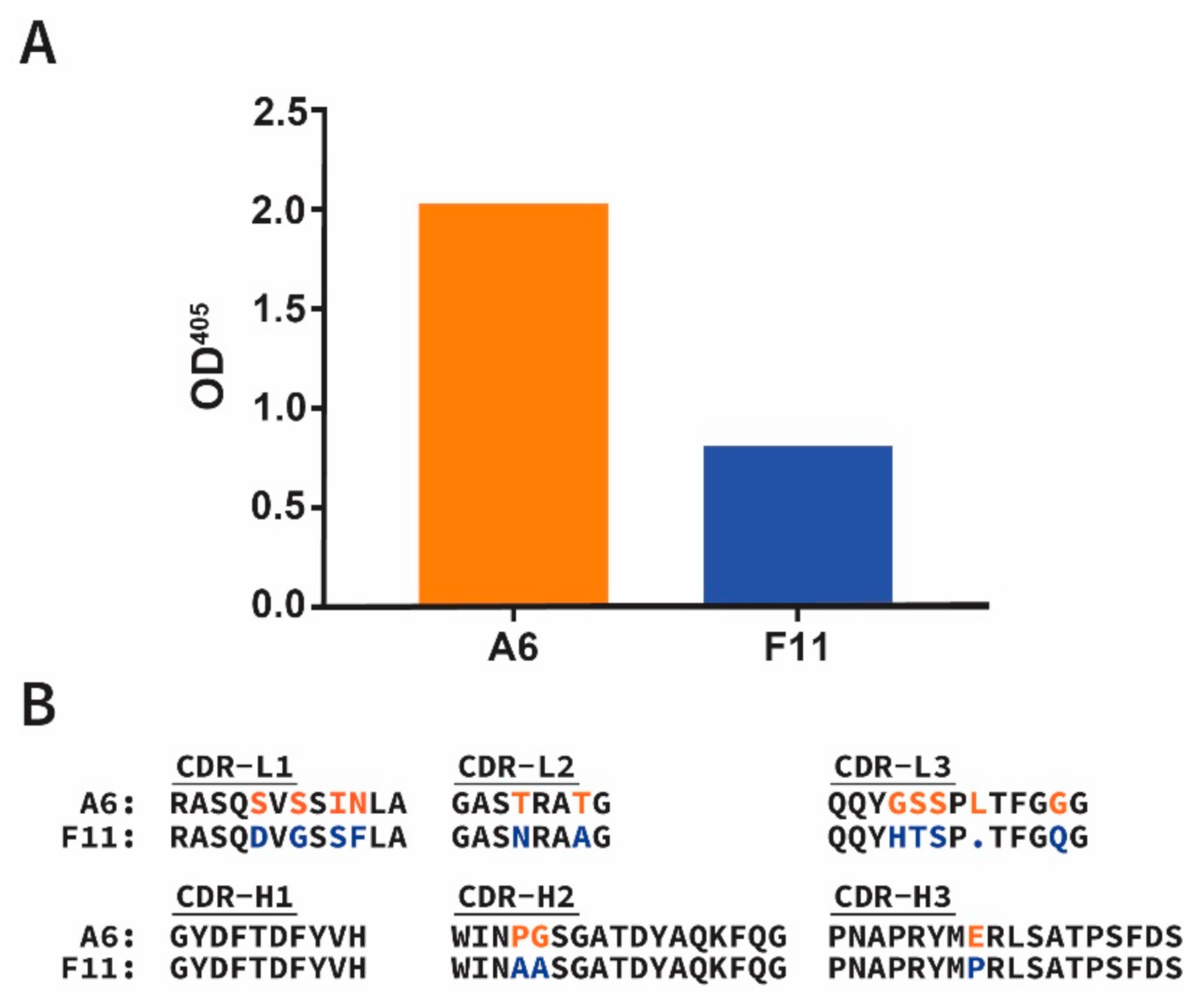
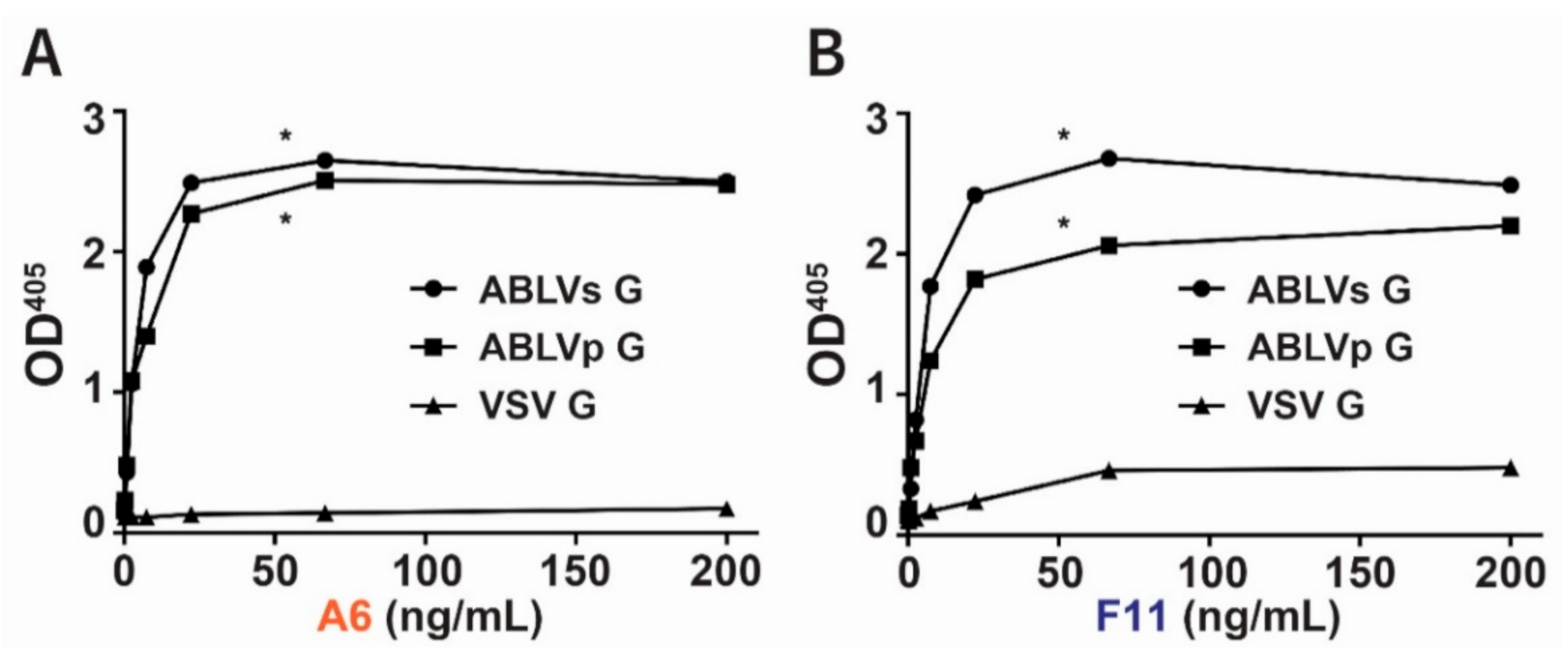
3.1. Identification of Phage-Displayed Fabs A6 and F11 That Are Specific for ABLVs Glycoprotein
3.2. Neutralization of Recombinant ABLV Variants and RABV by hmAbs A6 and F11
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fraser, G.C.; Hooper, P.T.; Lunt, R.A.; Gould, A.R.; Gleeson, L.J.; Hyatt, A.D.; Russell, G.M.; Kattenbelt, J.A. Encephalitis caused by a Lyssavirus in fruit bats in Australia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1996, 2, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, A.R.; Hyatt, A.D.; Lunt, R.; Kattenbelt, J.A.; Hengstberger, S.; Blacksell, S.D. Characterisation of a novel lyssavirus isolated from Pteropid bats in Australia. Virus Res. 1998, 54, 165–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, A.R.; Kattenbelt, J.A.; Gumley, S.G.; Lunt, R.A. Characterisation of an Australian bat lyssavirus variant isolated from an insectivorous bat. Virus Res. 2002, 89, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, H.E. Evidence of Australian bat lyssavirus infection in diverse Australian bat taxa. Zoonoses Public Health 2018, 65, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, J. Australian Bat Lyssavirus; The University of Queensland: St Lucia, Australia, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Barrett, J.; Hoger, A.; Agnihotri, K.; Oakey, J.; Skerratt, L.F.; Field, H.E.; Meers, J.; Smith, C. An unprecedented cluster of Australian bat lyssavirus in Pteropus conspicillatus indicates pre-flight flying fox pups are at risk of mass infection. Zoonoses Public Health 2020, 67, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allworth, A.; Murray, K.; Morgan, J. A human case of encephalitis due to a lyssavirus recently identified in fruit bats. J. Commun. Dis. Intellig. 1996, 20, 504. [Google Scholar]
- Samaratunga, H.; Searle, J.W.; Hudson, N. Non-rabies Lyssavirus human encephalitis from fruit bats: Australian bat Lyssavirus (pteropid Lyssavirus) infection. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 1998, 24, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, J.N.; Carney, I.K.; Smith, G.A.; Tannenberg, A.E.; Deverill, J.E.; Botha, J.A.; Serafin, I.L.; Harrower, B.J.; Fitzpatrick, P.F.; Searle, J.W. Australian bat lyssavirus infection: A second human case, with a long incubation period. Med. J. Aust. 2000, 172, 597–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, J.R.; Nourse, C.; Vaska, V.L.; Calvert, S.; Northill, J.A.; McCall, B.; Mattke, A.C. Australian Bat Lyssavirus in a child: The first reported case. Pediatrics 2014, 133, e1063–e1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, D.L.; Annand, E.J.; Reid, P.A.; Broder, C.C. Recent observations on Australian bat lyssavirus tropism and viral entry. Viruses 2014, 6, 909–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinwari, M.W.; Annand, E.J.; Driver, L.; Warrilow, D.; Harrower, B.; Allcock, R.J.; Pukallus, D.; Harper, J.; Bingham, J.; Kung, N.; et al. Australian bat lyssavirus infection in two horses. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 173, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badrane, H.; Bahloul, C.; Perrin, P.; Tordo, N. Evidence of two Lyssavirus phylogroups with distinct pathogenicity and immunogenicity. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 3268–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, P.J.; Siddell, S.G.; Lefkowitz, E.J.; Mushegian, A.R.; Adriaenssens, E.M.; Dempsey, D.M.; Dutilh, B.E.; Harrach, B.; Harrison, R.L.; Hendrickson, R.C.; et al. Changes to virus taxonomy and the Statutes ratified by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (2020). Arch. Virol. 2020, 165, 2737–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conzelmann, K.-K.; Cox, J.H.; Schneider, L.G.; Thiel, H.-J. Molecular cloning and complete nucleotide sequence of the attenuated rabies virus SAD B19. Virology 1990, 175, 485–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, D.L.; Laing, E.D.; Smith, I.L.; Wang, L.F.; Broder, C.C. Host cell virus entry mediated by Australian bat lyssavirus G envelope glycoprotein occurs through a clathrin-mediated endocytic pathway that requires actin and Rab5. Virol. J. 2014, 11, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Duan, M.; Wang, X.; Gao, J.; Guan, Z.; Zhang, M. Early events in rabies virus infection-Attachment, entry, and intracellular trafficking. Virus Res. 2019, 263, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belot, L.; Albertini, A.; Gaudin, Y. Structural and cellular biology of rhabdovirus entry. Adv. Virus Res. 2019, 104, 147–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flamand, A.; Raux, H.; Gaudin, Y.; Ruigrok, R.W. Mechanisms of rabies virus neutralization. Virology 1993, 194, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raux, H.; Coulon, P.; Lafay, F.; Flamand, A. Monoclonal antibodies which recognize the acidic configuration of the rabies glycoprotein at the surface of the virion can be neutralizing. Virology 1995, 210, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, T.; Dietzschold, B.; Ertl, H.; Fooks, A.R.; Freuling, C.; Fehlner-Gardiner, C.; Kliemt, J.; Meslin, F.X.; Franka, R.; Rupprecht, C.E.; et al. Development of a mouse monoclonal antibody cocktail for post-exposure rabies prophylaxis in humans. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2009, 3, e542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, D.L.; McElhinney, L.M.; Marston, D.A.; Wood, J.L.; Russell, C.A.; Lewis, N.; Kuzmin, I.V.; Fouchier, R.A.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Fooks, A.R.; et al. Quantifying antigenic relationships among the lyssaviruses. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 11841–11848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanlon, C.A.; Kuzmin, I.V.; Blanton, J.D.; Weldon, W.C.; Manangan, J.S.; Rupprecht, C.E. Efficacy of rabies biologics against new lyssaviruses from Eurasia. Virus Res. 2005, 111, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, J.R.; McCall, B.J.; Hutchinson, P.; Powell, J.; Vaska, V.L.; Nourse, C. Australian bat lyssavirus: Implications for public health. Med. J. Aust. 2014, 201, 647–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilde, H.; Chomchey, P.; Prakongsri, S.; Puyaratabandhu, P.; Chutivongse, S. Adverse effects of equine rabies immune globulin. Vaccine 1989, 7, 10–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilde, H.; Chomchey, P.; Punyaratabandhu, P.; Phanupak, P.; Chutivongse, S. Purified equine rabies immune globulin: A safe and affordable alternative to human rabies immune globulin. Bull. World Health Organ. 1989, 67, 731–736. [Google Scholar]
- Tawanwongsri, W.; Wattanakrai, P. Serum Sickness after Equine Rabies Immunoglobulin in Identical Male Twins: Two Case Reports. Case Rep. Dermatol. 2019, 11, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparrow, E.; Torvaldsen, S.; Newall, A.T.; Wood, J.G.; Sheikh, M.; Kieny, M.P.; Abela-Ridder, B. Recent advances in the development of monoclonal antibodies for rabies post exposure prophylaxis: A review of the current status of the clinical development pipeline. Vaccine 2019, 37 (Suppl. 1), A132–A139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilina, E.N.; Larina, M.V.; Aliev, T.K.; Dolgikh, D.A.; Kirpichnikov, M.P. Recombinant Monoclonal Antibodies for Rabies Post-exposure Prophylaxis. Biochemistry 2018, 83, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, D.L.; Smith, I.L.; Bossart, K.N.; Wang, L.F.; Broder, C.C. Host cell tropism mediated by Australian bat lyssavirus envelope glycoproteins. Virology 2013, 444, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laing, E.D.; Sterling, S.L.; Weir, D.L.; Beauregard, C.R.; Smith, I.L.; Larsen, S.E.; Wang, L.F.; Snow, A.L.; Schaefer, B.C.; Broder, C.C. Enhanced Autophagy Contributes to Reduced Viral Infection in Black Flying Fox Cells. Viruses 2019, 11, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Bossart, K.N.; Bishop, K.A.; Crameri, G.; Dimitrov, A.S.; McEachern, J.A.; Feng, Y.; Middleton, D.; Wang, L.F.; Broder, C.C.; et al. Exceptionally potent cross-reactive neutralization of Nipah and Hendra viruses by a human monoclonal antibody. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 197, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Dimitrov, A.S.; Bossart, K.N.; Crameri, G.; Bishop, K.A.; Choudhry, V.; Mungall, B.A.; Feng, Y.R.; Choudhary, A.; Zhang, M.Y.; et al. Potent neutralization of Hendra and Nipah viruses by human monoclonal antibodies. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastraccio, K.E.; Huaman, C.; Warrilow, D.; Smith, G.A.; Craig, S.B.; Weir, D.L.; Laing, E.D.; Smith, I.L.; Broder, C.C.; Schaefer, B.C. Establishment of a longitudinal pre-clinical model of lyssavirus infection. J. Virol. Methods 2020, 281, 113882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmin, I.V.; Niezgoda, M.; Franka, R.; Agwanda, B.; Markotter, W.; Beagley, J.C.; Urazova, O.Y.; Breiman, R.F.; Rupprecht, C.E. Lagos bat virus in Kenya. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 1451–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.G.; Gilbert, A.T. Comparison of a Micro-Neutralization Test with the Rapid Fluorescent Focus Inhibition Test for Measuring Rabies Virus Neutralizing Antibodies. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2017, 2, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO; Rupprecht, C.E.; Fooks, A.R.; Abela-Ridder, B. Laboratory Techniques in Rabies, 5th ed.; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Markotter, W.; Kuzmin, I.; Rupprecht, C.E.; Randles, J.; Sabeta, C.T.; Wandeler, A.I.; Nel, L.H. Isolation of Lagos bat virus from water mongoose. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 1913–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascal, K.E.; Dudgeon, D.; Trefry, J.C.; Anantpadma, M.; Sakurai, Y.; Murin, C.D.; Turner, H.L.; Fairhurst, J.; Torres, M.; Rafique, A.; et al. Development of Clinical-Stage Human Monoclonal Antibodies That Treat Advanced Ebola Virus Disease in Nonhuman Primates. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 218, S612–S626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulangu, S.; Dodd, L.E.; Davey, R.T., Jr.; Tshiani Mbaya, O.; Proschan, M.; Mukadi, D.; Lusakibanza Manzo, M.; Nzolo, D.; Tshomba Oloma, A.; Ibanda, A.; et al. A Randomized, Controlled Trial of Ebola Virus Disease Therapeutics. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2293–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markham, A. REGN-EB3: First Approval. Drugs 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franka, R.; Carson, W.C.; Ellison, J.A.; Taylor, S.T.; Smith, T.G.; Kuzmina, N.A.; Kuzmin, I.V.; Marissen, W.E.; Rupprecht, C.E. In Vivo Efficacy of a Cocktail of Human Monoclonal Antibodies (CL184) Against Diverse North American Bat Rabies Virus Variants. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2017, 2, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosniak, M.; Faber, M.; Hanlon, C.A.; Rupprecht, C.E.; Hooper, D.C.; Dietzschold, B. Development of a cocktail of recombinant-expressed human rabies virus-neutralizing monoclonal antibodies for postexposure prophylaxis of rabies. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 188, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kruif, J.; Bakker, A.B.; Marissen, W.E.; Kramer, R.A.; Throsby, M.; Rupprecht, C.E.; Goudsmit, J. A human monoclonal antibody cocktail as a novel component of rabies postexposure prophylaxis. Annu. Rev. Med. 2007, 58, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Chen, Z.; Yu, L.; Wei, J.; Li, C.; Jin, J.; Shen, X.; Lv, X.; Tang, Q.; Li, D.; et al. Generation and characterization of neutralizing human recombinant antibodies against antigenic site II of rabies virus glycoprotein. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 96, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, T.Y.; Ren, S.; Shen, E.; Moore, S.; Zhang, S.F.; Chen, L.; Rupprecht, C.E.; Tsao, E. SYN023, a novel humanized monoclonal antibody cocktail, for post-exposure prophylaxis of rabies. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0006133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Wu, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, X.; Hu, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Tsao, E.; Liu, M.; Li, C. Safety, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of SYN023 alone or in combination with a rabies vaccine: An open, parallel, single dose, phase 1 bridging study in healthy Chinese subjects. Antivir. Res. 2020, 184, 104956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kansagra, K.; Parmar, D.; Mendiratta, S.K.; Patel, J.; Joshi, S.; Sharma, N.; Parihar, A.; Bhoge, S.; Patel, H.; Kalita, P.; et al. A Phase 3, Randomised, Open-Label, Non-inferiority Trial Evaluating Anti-Rabies Monoclonal Antibody Cocktail (TwinrabTM) Against Human Rabies Immunoglobulin (HRIG). Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gogtay, N.J.; Munshi, R.; Ashwath Narayana, D.H.; Mahendra, B.J.; Kshirsagar, V.; Gunale, B.; Moore, S.; Cheslock, P.; Thaker, S.; Deshpande, S.; et al. Comparison of a Novel Human Rabies Monoclonal Antibody to Human Rabies Immunoglobulin for Postexposure Prophylaxis: A Phase 2/3, Randomized, Single-Blind, Noninferiority, Controlled Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 66, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banadyga, L.; Zhu, W.; Kailasan, S.; Howell, K.A.; Franaszek, K.; He, S.; Siragam, V.; Cheng, K.; Yan, F.; Moffat, E.; et al. Atypical Ebola Virus Disease in a Nonhuman Primate following Monoclonal Antibody Treatment Is Associated with Glycoprotein Mutations within the Fusion Loop. mBio 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosworth, A.; Rickett, N.Y.; Dong, X.; Ng, L.F.P.; Garcia-Dorival, I.; Matthews, D.A.; Fletcher, T.; Jacobs, M.; Thomson, E.C.; Carroll, M.W.; et al. Analysis of an Ebola virus disease survivor whose host and viral markers were predictive of death indicates the effectiveness of medical countermeasures and supportive care. Genome Med. 2021, 13, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| hmAbsα | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| μg/mL | A6 | F11 | m102.4 | |||||
| 10 | - | - | - | - | +++ | +++ | ||
| 5 | - | - | - | - | ND | ND | ||
| 2.5 | - | - | - | - | ND | ND | ||
| 1.25 | - | - | - | - | ND | ND | ||
| 0.62 | - | - | - | - | ND | ND | ||
| 0.31 | - | - | - | - | ND | ND | ||
| 0.16 | + | + | - | - | ND | ND | ||
| 0.08 | + | + | + | + | ND | ND | ||
| 0.04 | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ND | ND | ||
| 0.02 | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ND | ND | ||
| [hmAb]αμg/mL | ABLVs G | ABLVp G | RABV G | VSV G | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A6 | F11 | A6 | F11 | A6 | F11 | A6 | F11 | |||||||||||||||||
| 25 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ||||||||
| 12.5 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ND | ND | ND | ND | ||||||||
| 6.25 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ND | ND | ND | ND | ||||||||
| 3.12 | - | - | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ND | ND | ND | ND | ||||||||
| 1.56 | + | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ND | ND | ND | ND | ||||||||
| 0.78 | + | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ND | ND | ND | ND | ||||||||
| 0.39 | + | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ND | ND | ND | ND | ||||||||
| 0.19 | + | + | ++ | ++ | - | + | + | + | - | - | + | + | ND | ND | ND | ND | ||||||||
| 0.10 | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ND | ND | ND | ND | ||||||||
| 0.05 | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | + | + | ++ | ++ | + | + | + | + | ND | ND | ND | ND | ||||||||
| 0.02 | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | ND | ND | ND | ND | ||||||||
| hmAbs δ | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Virusα | Accession Numberβ | Phylogroupγ | A6 | F11 |
| ABLV/P. alecto/AUS/1998/RV634 | AY062067 | I | 1:781250 | 1:781250 |
| RABV/T. brasiliensis/USA/2003/FL385 | JQ685905 | I | 1:781250 | 1:781250 |
| RABV/D. rotundus/BRA/1998 | AF070449 | I | 1:781250 | 1:781250 |
| RABV/U. cinereoargeteus/USA/2009/2401 | JQ685934 | I | 1:781250 | 1:781250 |
| EBLV-1/E. serotinus/DNK/1986/RV20 | KF155003 | I | 1:781250 | 1:781250 |
| EBLV-2 /M. daubentonii/GBR/1996/RV628 | KY688136 | I | 1:781250 | 1:781250 |
| ARAV/M. blythi/KGZ/1991 | EF614259 | I | 1:781250 | 1:781250 |
| DUVV/M. musculus/RSA/2008/SA06 | EU623444 | I | 1:781250 | 1:781250 |
| IRKV/M. leucogaster/RUS/2003 | EF614260 | I | 1:781250 | 1:781250 |
| KHUV/M. mystacinus/TJK/1992 | EF614261 | I | 1:781250 | 1:781250 |
| MOKV/F. catus/RSA/2014/14/024 | KP899612 | II | - | - |
| SHIBV/H. commersoni/KEN/2009 | GU170201 | II | - | - |
| LBV/R. aegypticus/EGY/1999/LBVAfr1999 | EF547432 | II | - | - |
| LBV/E. wahlbergi/RSA/2016/UP6414 | MH643893 | II | - | - |
| LBV/R. aegypticus/KEN/2010/KE576 | GU170202 | II | - | - |
| IKOV/C. civetta/TZA/2009/RV2508 | JX193798 | U | - | - |
| WCBV/M. schreibersi/2003/RUS | EF614258 | U | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weir, D.L.; Coggins, S.A.; Vu, B.K.; Coertse, J.; Yan, L.; Smith, I.L.; Laing, E.D.; Markotter, W.; Broder, C.C.; Schaefer, B.C. Isolation and Characterization of Cross-Reactive Human Monoclonal Antibodies That Potently Neutralize Australian Bat Lyssavirus Variants and Other Phylogroup 1 Lyssaviruses. Viruses 2021, 13, 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13030391
Weir DL, Coggins SA, Vu BK, Coertse J, Yan L, Smith IL, Laing ED, Markotter W, Broder CC, Schaefer BC. Isolation and Characterization of Cross-Reactive Human Monoclonal Antibodies That Potently Neutralize Australian Bat Lyssavirus Variants and Other Phylogroup 1 Lyssaviruses. Viruses. 2021; 13(3):391. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13030391
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeir, Dawn L., Si’Ana A. Coggins, Bang K. Vu, Jessica Coertse, Lianying Yan, Ina L. Smith, Eric D. Laing, Wanda Markotter, Christopher C. Broder, and Brian C. Schaefer. 2021. "Isolation and Characterization of Cross-Reactive Human Monoclonal Antibodies That Potently Neutralize Australian Bat Lyssavirus Variants and Other Phylogroup 1 Lyssaviruses" Viruses 13, no. 3: 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13030391
APA StyleWeir, D. L., Coggins, S. A., Vu, B. K., Coertse, J., Yan, L., Smith, I. L., Laing, E. D., Markotter, W., Broder, C. C., & Schaefer, B. C. (2021). Isolation and Characterization of Cross-Reactive Human Monoclonal Antibodies That Potently Neutralize Australian Bat Lyssavirus Variants and Other Phylogroup 1 Lyssaviruses. Viruses, 13(3), 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13030391







