Abstract
Pine wilt disease (PWD), a destructive pine forest disease caused by pine wood nematode (PWN), Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, has led to huge economic losses and ecological environment damage. Thaumatin-like proteins (TLPs) are the products of a complex gene family involved in host defense and a wide range of developmental processes in fungi, plants, and animals. In this study, a tlp gene of B. xylophilus (Bxtlp) (GenBank: OQ863020.1) was amplified via PCR and cloned into the expression vector pET-15b to construct the recombinant vector PET-15b-Bxtlp, which was then transformed into Escherichia coli BL-21(DE3). The recombinant protein was successfully purified using Ni-NTA affinity chromatography. The effect of the Bxtlp gene on the vitality and pathogenicity of PWNs was elucidated through RNA interference (RNAi) and overexpression. Bxtlp dsRNA significantly reduced the feeding, motility, spawning, and reproduction abilities of PWN; shortened its lifespan; and increased the female–male ratio. In contrast, the recombinant BxTLP markedly enhanced the reproductive ability of PWN. In addition, Bxtlp dsRNA increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) content in nematodes, while the recombinant BxTLP was confirmed to have antioxidant capacity in vitro. Furthermore, the bioassays on Pinus thunbergii saplings demonstrated that Bxtlp could significantly influence PWN pathogenicity. Overall, we speculate that Bxtlp affects the pathogenicity of PWNs mainly via regulating ROS levels, the motility, and hatching of PWN.
1. Introduction
Pine wilt disease (PWD), mainly caused by pine wood nematode (PWN), has been considered as one of the most serious pine forest diseases in the world. The life cycle of PWNs includes two stages: reproductive and dispersal [1,2]. Because of the huge economic and ecological losses caused by PWD, the prevention and control of the disease has become urgent [3]. Up to now, one of the most effective and sustainable methods for the control of PWD is injecting insecticides into the trunk, which can avoid spray drift of chemical pesticides and reduce environmental pollution [4,5]. However, prolonged use of the same insecticide may cause biological resistance resulting from a single drug target; hence, it is important to find new drug targets for developing novel nematicides to control PWN [6,7].
Thaumatin-like proteins (TLPs), a complex gene family product with amino acid sequence highly homologous to that of the sweet protein thaumatin from the West African plant Thaumatococcus danielli, widely exist in plants and are involved in plant defense and an extensive development process [8,9,10]. TLPs from watermelon, emperor bananas, chestnut, and wheat have anti-fungal function and could be used as botanical fungicide or as a potential gene in the engineering of disease-resistant plants [9,11,12,13,14]. In addition, Fierens et al. found that a TLP from wheat (Triticum aestivum) has a unique inhibition specificity on xylanase [15]. Bormann et al. and Osmond et al. suggested that TLP may have β-1, 3-glucanase activity and be able to interact with β-1, 3-glucan to disrupt the synthesis of fungal cell walls [16,17]. Plant TLPs play important roles in response to abiotic stresses including cold [18], drought [19], and salinity [20]. Animal TLPs were first reported in Caenorhabditis elegans (Maupas) Kitajima and Sato (1999) [21]. Brandazza et al. reported that a TLP in the desert locust Schistocerca gregaria with glucanase activity played a defense role against pathogens [22].
RNA interference (RNAi) technology is an effective method to explore gene function, which can down-regulate the expression of specific genes by degrading homologous mRNA induced by double-stranded RNA [23,24,25,26]. Cheng et al. found that PWN cellulase has an important influence on its parasitism and penetration in host plants, feeding, development, and propagation by the knockdown of a cellulase gene (Bx-eng-1) of B. xylophilus using RNAi [27]. Zhao et al. assessed the function of the BxSapB2 gene in PWN by RNAi and confirmed that BxSapB2 silencing affects the virulence of PWN [28].
At present, there are few reports on the function of tlp in PWN. The data from this study will support the understanding of the action mode of Bxtlp on PWN, which may be an important pathogenic factor of B. xylophilus and can be used as a new target for developing potential nematocides to control PWD.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
PWNs were extracted from forest samples collected in Yantai, Shandong Province, using the Baermann funnel method. They were subsequently cultured on Botrytis cinerea in Potato Dextrose Agar (PDA) medium in the dark at 25 °C [29,30]. Mixed-stage PWNs were placed in Petri dishes at 25 °C and cultured in the dark for 2 h to collect the eggs. The PWN eggs developed into J2 larvae after 24 h, and J4 larvae were obtained from J2 ones cultured for 48 h [31,32,33,34,35].
2.2. Cloning of Bxtlp and Construction of Expression Vector
RNA extraction was performed on mixed stages of PWNs employing TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, United States) [36], followed by cDNA synthesis using a commercial reverse transcription kit (Takara, Dalian, China).
The Bxtlp without a putative signal sequence was amplified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using a pair of primers designed according to the sequence of Bxtlp (Forward: 5′-AAACATATGAAGACCCTCATTC-3′; Reverse: 5′-AAAGGATCCTTAAGGACAGTAG). The target DNA fragments obtained by PCR amplification were inserted into the pET-15b expression vector using T4 DNA ligase (Sangon Biotech, Shanghai, CN), successfully generating the recombinant plasmid pET-15b-Bxtlp (Takara, Dalian, China) [35].
2.3. Bioinformatics Analysis of Bxtlp and BxTLP
The amino sequences of BxTLP were deduced according to the nucleotide sequences by using the Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi, accessed on 6 March 2023). Using the ORF (open reading frame) Finder tool (NCBI, Bethesda, MD, USA; http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gorf/gorf.html, accessed on 6 March 2023), the ORF of PWN-derived BxTLP was identified, and its structural organization was analyzed via the WormBase ParaSite database (http://parasite.wormbase.org/index.html, accessed on 6 March 2023). Multiple comparisons were conducted using DNAMAN software (Lynnon Biosoft, 2020, DNAMAN, Version 8, ON, Canada), and the phylogenetic tree was constructed using MEGA-X software (Kumar Lab, 2020, MEGA-X, Version 10.2, PA, USA). SignalP 5.0 (https://services.healthtech.dtu.dk/services/SignalP-5.0/, accessed on 6 March 2023) was employed to predict signal peptides of BxTLP, with transmembrane helices analyzed using TMHMM (CBS, 2020, TMHMM, Version 2.0, N/A, DK) (https://services.healthtech.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM-2.0/, accessed on 6 March 2023). SWISS-MODEL (https://swissmodel.expasy.org/, accessed on 6 March 2023) was used to predict the structures of BxTLP and further analyzed using PyMOL 2.3.2 software.
2.4. Expression and Purification of Recombinant BxTLP
Plasmid pET-15b-Bxtlp was introduced into Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) (Takara, Dalian, China) via transformation. One positive colony was inoculated into LB broth with 100 µg/mL ampicillin for cultivation at 37 °C overnight. The culture was further incubated for 4 h under the same conditions; then a final concentration of 0.5 mM isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) (Sangon Biotech, Shanghai, China) was added to induce the expression of recombinant BxTLP for 4 h at 28 °C [37]. After centrifugation at 10,000 rpm for 25 min, the engineered bacterial cells were resuspended in 25 mL of binding buffer (20 mM Tris-HCl, 0.5 M NaCl, 5 mM imidazole, pH 8.0) and disrupted via ultrasonication (400 W, 4 s, 12 s, 120 cycles). The lysate was then centrifuged at 10,000 g for 30 min to remove debris. The purification of recombinant BxTLP was achieved through Ni-NTA (GE Healthcare, Chicago, IL, USA) affinity chromatography [38].
2.5. Synthesis of Bxtlp dsRNA
A T7 promotor was added to the RNA interference fragment (441bp), including the full-length ORF of Bxtlp through PCR with T7-labeled gene-specific primers (Forward: 5′-GATCACTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGCATATGAAGACCCTCAT TC-3′; Reverse: 5′-GATCACTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGGGATCCTTAAGGA CAGTAG-3′).
The 323 bp GFP gene fragment was amplified using pET-15b-gfp as template and T7-labeled primers (Forward: 5′-GATCACTAATAC GACTCACTATAGGGAACGGCCACAAGTTCAGC-3′; Reverse: 5′-GATCACTAAT ACGACTCACTATAGGGAAGTCGATGCCCTTCAGC-3′) The amplified products were used as templates for dsRNA synthesis with the MEGAscript RNAi Kit (Invitrogen, Vilnius, Lithuania) per the manufacturer’s protocol. The soak method was employed for RNAi, with 3000 PWNs incubated in 50 µL Bxtlp dsRNA (1.0 µg/µL; 20 °C, 72 h). Controls included sterilized water and gfp dsRNA (1.0 µg/µL) under the same conditions [38].
2.6. Effects of Bxtlp dsRNA on the Vitality of PWNs
For RNAi treatment, 3000 mixed-stage PWNs were maintained in 50 µL Bxtlp dsRNA (1.0 µg/µL) at 20 °C under dark conditions for 72 h. The vitality indexes, including motility, feeding, reproduction, oviposition, and hatching, were investigated according to the methods reported previously [39,40].
A total of 100 PWNs were observed under a microscope (Motic, ECO-SZ-745, Xiamen, China) to evaluate the motility ability of PWN by counting head oscillation times in 30 s [33].
Approximately 100 double-stranded RNA-treated PWNs were placed on B. cinerea (PDA, 25 °C, dark) to evaluate RNAi effects on their feeding behavior.
Fifty PWN couples were cultured on B. cinerea plates (PDA, 25 °C, dark) for 9 days; then the PWNs were collected and quantified to assess their reproductive impact [39].
Fifteen PWN pairs in sterile water (96-well plate, 25 °C, dark, 48 h) were assessed for control, and gfp dsRNA-treated nematodes were used as negative controls.
PWNs soaked in buffer solution containing sterilized water and gfp dsRNA were used as controls.
2.7. Effects of Bxtlp dsRNA on ROS Levels, Lifespan, and Female–Male Ratio in PWNs
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels in Bxtlp dsRNA-treated PWNs were measured using a reactive oxygen assay kit (Nanjing Jiancheng, Nanjing, China), with fluorescence detection (excitation/emission: 485/528 nm; Olympus IX73 (OLYMPUS, Tokyo, Japan)).
In order to investigate the effect of Bxtlp dsRNA on the lifespan of PWN, 100 PWNs were cultured in 48-well plates to observe the survival of PWNs using a microscope (Motic, ECO-SZ-745, Xiamen, China). The PWNs were considered dead if the nematodes were stiff and did not move even by physical stimuli with a dissection needle.
Approximately 100 PWNs were cultured in a Petri dish covered with Botrytis cinerea at 25 °C in the dark for 24 h to investigate the effect of Bxtlp dsRNA on the female–male ratio of PWN. The male and female individuals of PWN were counted under a microscope (Motic, ECO-SZ-745, Xiamen, China), and the female–male ratio was calculated.
2.8. Effect of Recombinant BxTLP on PWN
PWNs were soaked in the recombinant BxTLP solution (40 µg/mL) for 24 h, and their motility, feeding, reproduction, oviposition, and hatching capabilities were determined according to the methods described in Section 2.6.
2.9. Determination of Antioxidant Activity of Recombinant BxTLP
A 2 mL solution A (1.25 × 10−4 M recombinant BxTLP in 20 mM Tris-HCl buffer, pH 8.0) was mixed with 2 mL of DPPH (Sangon Biotech, Shanghai, CN) ethanolic solution (1 × 10−4 M) to react for 30 min in the dark, and then the absorbance of the mixture was determined at 517 nm using a microplate reader (Tecan, Spark, Shanghai, China) to be marked as ABxTLP [41,42]. A0 was the absorbance of the reaction mixture without BxTLP.
The DPPH clearance rate (R%) was calculated according to the following formula (1):
R(%) = (1 − ABxTLP/A0) × 100%
At the same time, the DPPH clearance rate of Vc solution (1.25 × 10−5 M) was used as a positive control.
2.10. The Effect of dsRNA and Recombinant BxTLP on the Pathogenicity of PWN
Approximately 2000 mixed-stage PWNs were immersed in a 50 µL buffer (1.0 µg/µL) containing Bxtlp dsRNA and incubated at 20 °C in the dark for 72 h [39]. Then, the nematodes were inoculated into 1-year-old Pinus thunbergii saplings. PWNs in sterilized water or gfp dsRNA were selected as controls [43]. The inoculated P. thunbergii saplings were cultured in a greenhouse at 25 °C with 16 h of light and 8 h of darkness. The wilting symptoms of the saplings were monitored and photographed.
The effect of recombinant BxTLP on the pathogenicity of PWN was determined using the same method described above. PWNs in either Tris-HCl buffer or BSA (Sangon Biotech, Shanghai, China) solution were designed for controls.
2.11. Data Analysis
For all biological tests, each experiment was performed twice with three replications for each treatment. All values of repeated experiments were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (S.D.), and SPSS 25.0 software (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA) was used for statistical analysis. The independent samples t-test and one-way analysis of variance were used among different groups. A p-value < 0.05 indicated statistical significance.
3. Results
3.1. Cloning and Sequence Analysis of Bxtlp in PWN
Sequence analysis of the Bxtlp showed that the Bxtlp (BXY_0431000.1) gene with 1090 bp was composed of 3 exons and 2 introns (Figure 1A), and the Bxtlp ORF with 441 bp encoded a protein with 146 amino acid residues, including 49 metal ion-chelating residues, which were 9 lysine residues, 9 aspartate residues, 8 asparagine residues, 6 cysteine residues, 5 arginine residues, 5 glutamine residues, 4 glutamic acid residues, and 3 histidine residues (Figure 1B). The amino acid sequence similarity of BxTLP to that of Bursaphelenchus okinawaensis, Hypsibius exemplaris, Pinus monticola, Apophysomyces ossiformis, and Pinus massoniana was 64%, 28%, 32%, 23%, and 31%, respectively (Figure 1C). Further bioinformatic analysis revealed the presence of a signal peptide containing 16 amino acids in the amino acid sequence of BxTLP, suggesting that BxTLP may be a secreted protein (Figure 1D,E). The phylogenetic tree of the primary structure of this protein showed that the protein had high homology with that of B. okinawaensis and H. exemplaris, as well as P. monticola and P. massoniana (Figure 2). The advanced structure prediction of BxTLP showed that a β-pleated sheet accounted for 56% of the secondary structure, and random curling accounted for 26% (Figure 3A). The GMQE value of the modeling result was 0.88, and the similarity was 99.32%, which proved that the tertiary structure prediction was highly reliable. BxTLP consisted of 12 β-folded structures contributing to its stability and had strong hydrophilicity (www.novopro.cn/tools/protein-hydrophilicity-plot.html, accessed on 6 March 2023). Molecular surface modeling revealed mainly the presence of white patches; the electrostatic potential surface prediction results showed that the surface of the molecule was mainly neutral and a part of charged regions (Figure 3B,C).
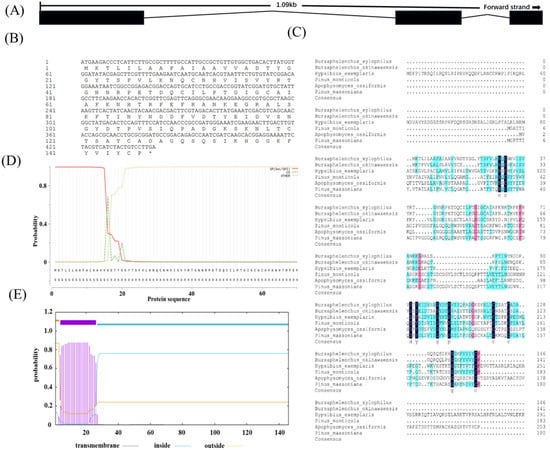
Figure 1.
Bioinformatic analysis of Bxtlp. (A) Genomic DNA structure of Bxtlp. The lines represent introns, and the black parts represent exons. (B) Genomic sequence of Bxtlp and its translated amino acid sequence. “*” represents the termination codon. (C) Amino acid sequence alignment of BxTLP across Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, Bursaphelenchus okinawaensis, Hypsibius exemplaris, Pinus monticola, Apophysomyces ossiformis, and Pinus massoniana. Colors indicate conserved amino acid residues. (D) Predicted BxTLP signal peptide. (E) Predicted BxTLP transmembrane structure.
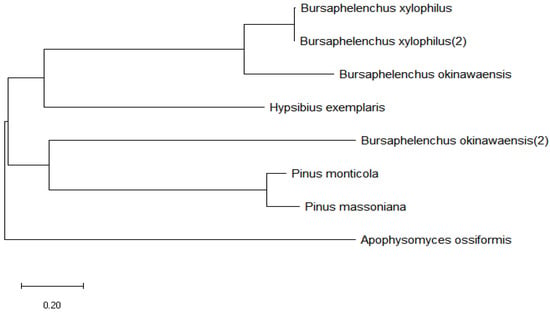
Figure 2.
Unrooted phylogeny of BxTLP. Scale bar: 0.2 substitutions/site.
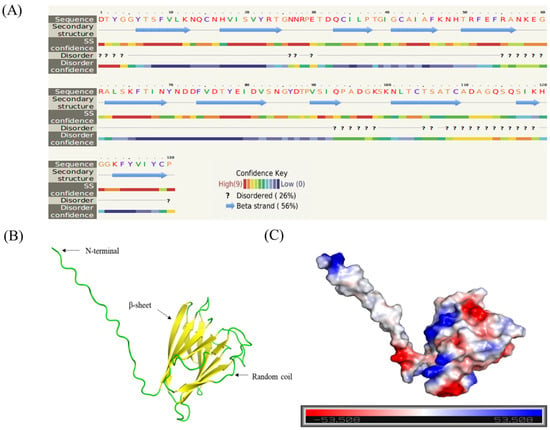
Figure 3.
Predicted structure of BxTLP. (A) Secondary structure prediction of BxTLP. (B) Three-dimensional structure of BxTLP. (C) Electrostatic map of BxTLP displaying negative (red, −5KBT/e), positive (blue, +5KBT/e), and neutral (white) regions.
3.2. Expression and Purification of Recombinant BxTLP Protein
According to the sequence of Bxtlp, a pair of primers were designed to amplify the Bxtlp gene from the cDNA of PWN by PCR. pET-15b-Bxtlp was constructed by inserting the PCR product into pET-15b and was then introduced into E. coli BL21(DE3). The recombinant BxTLP was overexpressed in the engineering bacteria induced by IPTG (Figure 4A) and mainly existed in soluble form (Figure 4B). The recombinant protein was purified by Ni2+ affinity chromatography to homogeneity with a relative molecular weight of 16 kDa based on SDS-PAGE analysis (Figure 4B), which was consistent with that of BxTLP without the putative signal peptide.
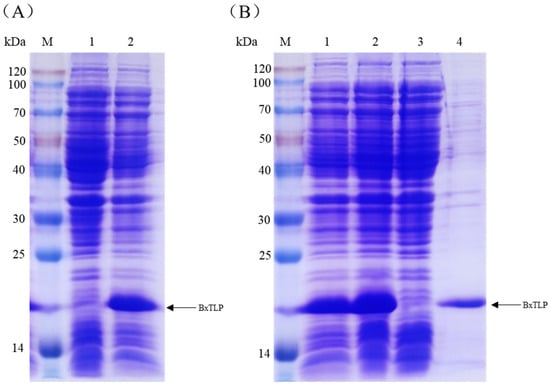
Figure 4.
Analyses of recombinant protein expression and purification by SDS-PAGE. (A) Recombinant BxTLP expression. Lane 1: E. coli BL21(DE3) total proteins; lane 2: pET-15b-Bxtlp-transformed BL21(DE3) total proteins. (B) Purified recombinant BxTLP analyzed by SDS-PAGE. Lane 1: total proteins of E. coli BL21 (DE3) harboring pET-15b-Bxtlp; lane 2: supernatant; lane 3: cell lysate precipitation; lane 4: purified recombinant protein.
3.3. Determination of Antioxidant Activity of Recombinant BxTLP
The DPPH clearance rate of the recombinant BxTLP was 67.9%, similar to that of 12.5 μM Vc (61.71%) (Figure 5), which indicated that the recombinant protein had strong antioxidant activity and could effectively remove free radicals [44].
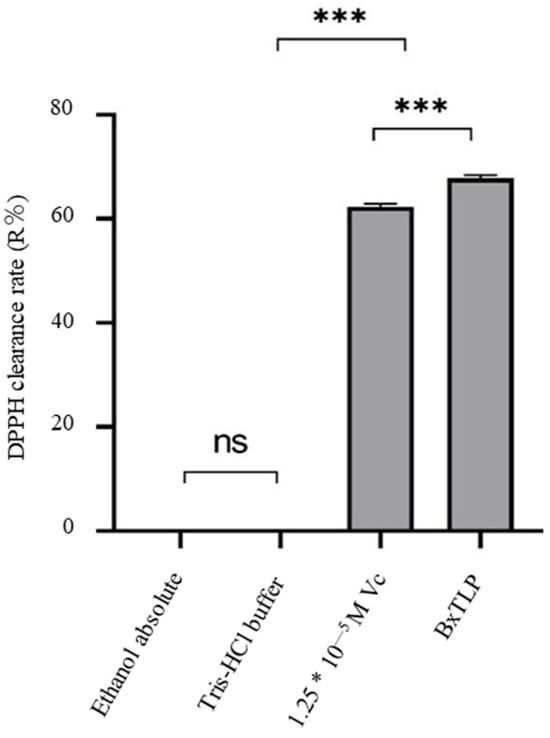
Figure 5.
Antioxidant activity of recombinant BxTLP. *** p < 0.001, ns = not significant.
3.4. Bxtlp dsRNA Can Effect PWN Vitality
The head oscillation times of PWNs treated by Bxtlp dsRNA solution was 10.87 ± 3.45 per 30 s, while the ones treated by sterilized water and gfp dsRNA solution were 25.41 ± 3.58 and 25.63 ± 4.13 per 30 s, respectively (Figure 6A). The results showed that Bxtlp dsRNA could significantly reduce the motility ability of PWN.
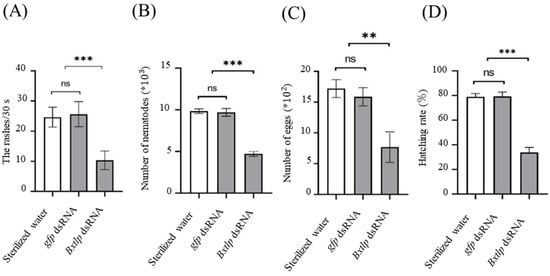
Figure 6.
Effects of Bxtlp dsRNA on PWN motility (A), reproduction (B), oviposition (C), and egg hatchability (D) of PWNs. gfp dsRNA and sterile water as the control treatments. ** p < 0.005, *** p < 0.001, ns = not significant.
After 9 d, the collected nematodes in the Bxtlp dsRNA, sterilized water, and gfp dsRNA groups were 4713 ± 270, 9839 ± 249, and 9696 ± 412, respectively (Figure 6B), which indicated that Bxtlp played an import role in the PWN reproduction.
After 48 h, the eggs laid by the PWNs treated with Bxtlp dsRNA, sterilized water, and gfp dsRNA were 7.69 ± 2.16, 17.21 ± 1.25, and 15.86 ± 1.29, respectively (Figure 6C). In addition, the hatching rates of the PWNs soaked in Bxtlp dsRNA, sterilized water, and gfp dsRNA were 33.81%, 78.98% ± 2.66%, and 79.29% ± 3.61%, respectively (Figure 6D). The results showed that Bxtlp dsRNA markedly decreased the oviposition and hatching ability of PWN.
PWNs treated with Bxtlp dsRNA, gfp dsRNA, and sterilized water for 72 h were cultured on a PDA plate covered with B. cinerea. The feeding ability of the Bxtlp dsRNA group was significantly lower than those of the control groups. On the 9th day, almost all of B. cinerea in the sterilized water and gfp dsRNA groups had been consumed, while only a little of B. cinerea in the Bxtlp dsRNA group had been consumed (Figure 7).
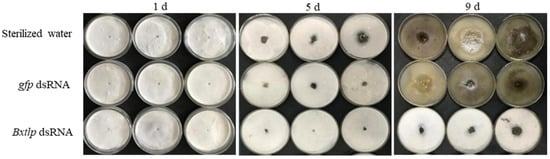
Figure 7.
RNAi effect of Bxtlp on PWN feeding B. cinerea. PWNs treated with gfp dsRNA or sterile water were used as control groups.
3.5. Effects of Bxtlp dsRNA on ROS Content, Lifespan, and Female–Male Ratio of PWN
The fluorescence intensity of ROS in PWNs after Bxtlp dsRNA immersion was higher than those in the control groups (Figure 8A). The female–male ratio of PWNs in the Bxtlp dsRNA treatment group was 5, while the ratios of gfp dsRNA and sterilized water in the control group were 1.3 and 1.5, respectively (Figure 8B). Furthermore, the lifespan of PWN was investigated, and the results showed that it took 15 days for the PWNs soaked in Bxtlp dsRNA solution to reach the mortality of 80%, while it took 19 days for the ones soaked in sterilized water to reach the same mortality, which demonstrated that the lifespan of PWN was shortened after Bxtlp interference (Figure 8C).
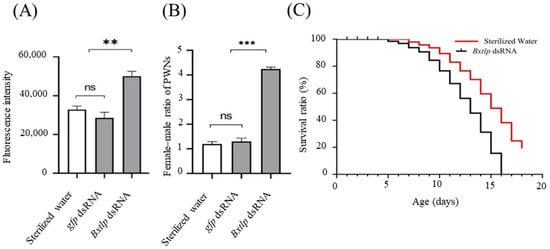
Figure 8.
Effects of Bxtlp dsRNA on ROS levels (A), lifespan (B), and female–male ratio (C) of PWNs. PWNs treated with gfp dsRNA or sterile water were used as control groups. Level of significance: ** p < 0.005, *** p < 0.001, ns = not significant.
3.6. Effect of Recombinant BxTLP on PWN
The recombinant BxTLP had no significant effect on the motility of PWN (Figure 9A). After 9 days, the collected PWNs from the Bxtlp dsRNA, sterilized water, and gfp dsRNA groups were 38,400; 21,540; and 21,600, respectively (Figure 9B), indicating that recombinant BxTLP could significantly enhance the reproductive capacity of PWN. The eggs collected from the Tris-HCl buffer group, BSA group, and recombinant BxTLP group were 10, 11, and 19, respectively (Figure 9C), and the corresponding hatching rates were 70.14%, 70.28%, and 83.74%, respectively (Figure 9D). The feeding assays demonstrated that recombinant BxTLP could enhance the feeding capacity of PWN (Figure 10).
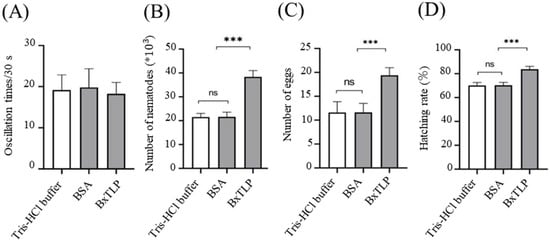
Figure 9.
Effect of recombinant BxTLP on motility (A), reproduction (B), oviposition (C), and egg hatching (D). Control treatments: Tris-HCl buffer, BSA. Data analyzed by Student’s t-test; error bars indicate SE; *** p < 0.001, ns = not significant.
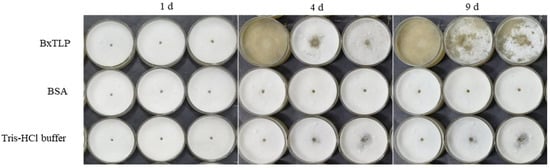
Figure 10.
PWN feeding activity on B. cinerea following BxTLP treatment, with PWN soaked in BSA and Tris-HCl as control groups.
3.7. Bxtlp Affects the Pathogenicity of PWN
PWNs treated with Bxtlp dsRNA, gfp dsRNA, or sterile water (72 h) were inoculated into 1-year-old saplings for pathogenicity assessment. Bxtlp dsRNA-treated PWNs exhibited significantly reduced virulence compared with controls (sterilized water and gfp dsRNA). Specifically, the control saplings started wilting after 10 days of coculture; the ones treated with Bxtlp dsRNA had no wilt symptom (Figure 11). Control saplings exhibited severe wilting after 20 days of coculture, whereas Bxtlp dsRNA treatment saplings began to show a slight wilt symptom.

Figure 11.
Pathogenicity of Bxtlp dsRNA-treated PWNs in Pinus thunbergii saplings at (A) 1, (B) 10, and (C) 20 dpi. Controls: sterile water and gfp dsRNA.
PWNs treated with recombinant BxTLP solution, Tris-HCl buffer, and BSA solution for 24 h were inoculated into 1-year-old saplings. On 5 dpi, the saplings inoculated with recombinant BxTLP-treated PWNs began to wilt. At the same time, the Tris-HCl buffer- and BSA-treated groups had no wilt symptoms. On 11 dpi, the Tris-HCl buffer- and BSA-treated groups began to show slight wilt symptoms. Most of the saplings in the recombinant BxTLP-treated group had completely withered at 14 days, while the ones in the Tris-HCl buffer and BSA treatment groups were still alive (Figure 12).

Figure 12.
Impact of recombinant BxTLP on PWN pathogenicity in Pinus thunbergii at (A) 1, (B) 5, and (C) 14 dpi. Controls: Tris-HCl buffer and BSA.
The aforementioned results indicated that Bxtlp could significantly affect the pathogenicity of PWNs.
4. Discussion
PWD management has been increasingly urgent because of its rapid spread and difficult control, and nematicide treatment is considered as one of the most effective methods to prevent PWD [43]. Finding a novel target gene for the development of high-efficiency nematicides against PWN has become a prospective research focus due to the occurrence of drug resistance. Wang et al. reported that three cytochrome P450 genes played a critical role in the low-temperature resistance mechanism of PWN [45]. In our previous study, sft-4 was found to affect the pathogenicity of PWN by influencing the motility, reproduction, and development of PWN [46].
TLP widely exists in plants and has various biological activities, including antifungal activity, glucanase activity, and anti-abiotic stresses [8,47]. In this study, amino acid sequence prediction showed that the recombinant BxTLP contained 6 cysteine residues with reducing ability and 50 metal ion-chelating residues, accounting for 4.62% and 38.46% of the total amino acid residues, respectively. We speculated that maybe the metal ion-chelating amino acid residues decrease free Fe2+ ions to inhibit the Haber–Weiss reaction and reduce hydroxyl radical content [48,49]. Coincidentally, ROS content in Bxtlp dsRNA-treated PWNs was higher than in controls, and the recombinant BxTLP had antioxidant activity in vitro by DPPH assay. Furthermore, the results of Bxtlp RNAi and BxTLP overexpression in PWNs showed that BxTLP could significantly enhance the reproductive capacity, lifespan, feeding ability, and pathogenicity of PWN. Here, we speculated that BxTLP could strengthen PWN vitality and pathogenicity by scavenging free radical to improve the anti-stress of PWN.
Overall, Bxtlp was a key pathogenic gene and could be used as a potential drug target to develop new nematicides for PWN control.
5. Conclusions
This study demonstrated the critical roles of the Bxtlp gene in the vitality and pathogenicity of PWN. RNAi-mediated suppression of Bxtlp expression not only impaired PWN feeding, motility, oviposition, and reproductive capacity, but also shortened its lifespan, altered the male-to-female ratio, and increased intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels. In contrast, the recombinant BxTLP protein exhibited in vitro antioxidant activity and enhanced PWN reproduction, feeding efficiency, and virulence. Inoculation assays confirmed that Bxtlp dsRNA-treated PWNs showed significantly attenuated pathogenicity in P. thunbergii seedlings, whereas BxTLP protein-treated PWNs accelerated pine wilting. These findings suggest that BxTLP modulates PWN pathogenicity via ROS regulation, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic target for pine wilt disease management.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.L., R.L. and G.D.; methodology, S.L., R.L., G.D. and Q.G.; software, S.L.; validation, R.L., G.D. and Q.G.; formal analysis, S.L.; investigation, S.L., Z.H., Y.Z. and W.F.; resources, R.L., G.D. and Q.G.; data curation, S.L., R.L., G.D. and Q.G.; writing—original draft preparation, S.L.; writing—review and editing, R.L., G.D. and Q.G.; visualization, S.L. and W.Z.; supervision, R.L., G.D. and Q.G.; project administration, R.L., G.D. and Q.G.; funding acquisition, R.L. and Q.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Qingdao Natural Science Foundation (24-4-4-zrjj-183-jch) and the Qingdao Science and Technology Benefiting the People Demonstration Project, China (23-2-8-cspz-7-nsh).
Data Availability Statement
This study did not generate new datasets.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Rodrigues, J.M. Pine Wilt Disease: A Worldwide Threat to Forest Ecosystems; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.S.; Zhang, T.T.; Pan, Z.S.; Lin, L.L.; Dong, G.Q.; Wang, M.; Li, R.G. The alcohol dehydrogenase with a broad range of substrate specificity regulates vitality and reproduction of the plant-parasitic nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Parasitology 2019, 146, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Futai, K. Pine wood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2013, 51, 61–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takai, K.; Suzuki, T.; Kawazu, K. Development and preventative effect against pine wilt disease of a novel liquid formulation of emamectin benzoate. Pest Manag. Sci. 2003, 59, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.C.; Lee, H.R.; Kim, D.S.; Kwon, J.H.; Huh, M.J.; Park, I.K. Emamectin benzoate 9.7% SL as a new formulation for a trunk-injections against pine wood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. J. For. Res. 2020, 31, 1399–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanendra, S.; Sun, L.; Junhyun, J. Identification of Potential Nematicidal Compounds Against the Pine Wood Nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus Through an In Silico Approach. Molecules 2018, 23, 1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.I.; Hwang, B.O.; Jin, C.H.; Li, W.U.; Park, D.I.; Seo, S.A.; Kim, C.I. Screening, isolation and evaluation of a nematicidal compound from actinomycetes against the pine wood nematode. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 1585–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.J.; Sturrock, R.; Ekramoddoullah, A.K.M. The superfamily of thaumatin-like proteins: Its origin, evolution, and expression towards biological function. Plant Cell Rep. 2010, 29, 419–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, V.S.M.; Wong, J.H.; Ng, T.B. A thaumatin-like antifungal protein from the emperor banana. Peptides 2007, 28, 760–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wel, H.; Loeve, K. Isolation and characterization of thaumatin I and II, the sweet-tasting proteins from Thaumatococcus daniellii Benth. Eur. J. Biochem. 2010, 31, 221–225. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Xu, J.H.; Liu, G.; Yang, X.P. Antifungal properties of a thaumatin-like protein from watermelon. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2018, 40, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Casado, C.; Collada, C.; Allona, I.; Soto, A.; Casado, R.; Rodriguez-Cerezo, E.; Gomez, L.; Aragoncillo, C. Characterization of an apoplastic basic thaumatin-like protein from recalcitrant chestnut seeds. Physiol. Plant. 2000, 110, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, K.T.; Ng, T.B. Isolation of a large thaumatin-like antifungal protein from seeds of the Kweilin chestnut Castanopsis chinensis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 301, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayasankar, S.; Li, Z.J.; Gray, D.J. Constitutive expression of Vitis vinifera thaumatin-like protein after in vitro selection and its role in anthracnose resistance. Funct. Plant Biol. 2003, 30, 1105–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierens, E.; Rombouts, S.; Gebruers, K.; Goesaert, H.; Brijs, K.; Beaugrand, J.; Volckaert, G.; Van Campenhout, S.; Proost, P.; Courtin, C.M.; et al. TLXI, a novel type of xylanase inhibitor from wheat (Triticum aestivum) belonging to the thaumatin family. Biochem. J. 2007, 403, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bormann, C.; Baier, D.; Hörr, I.; Raps, C.; Berger, J.; Jung, G.; Schwarz, H. Characterization of a novel, antifungal, chitin-binding protein from Streptomyces tendae Tu901 that interferes with growth polarity. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 7421–7429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmond, R.I.W.; Hrmova, M.; Fontaine, F.; Imberty, A.; Fincher, G.B. Binding interactions between barley thaumatin-like proteins and (1,3)-β-D-glucans: Kinetics, specificity, structural analysis and biological implications. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 4190–4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.M.; Griffith, M. Antifreeze proteins in winter rye leaves form oligomeric complexes. Plant Physiol. 1999, 119, 1361–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkhi, V.; Kumar, V.; Sunilkumar, G.; Campbell, L.M.; Singh, N.K.; Rathore, K.S. Expression of apoplastically secreted tobacco osmotin in cotton confers drought tolerance. Mol. Breed. 2009, 23, 625–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husaini, A.M.; Abdin, M.Z. Development of transgenic strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa Duch.) plants tolerant to salt stress. Plant Sci. 2008, 174, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitajima, S.; Sato, F. Plant pathogenesis-related proteins: Molecular mechanisms of gene expression and protein function. J. Biochem. 1999, 125, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandazza, A.; Angeli, S.; Tegoni, M.; Cambillau, C.; Pelosi, P. Plant stress proteins of the thaumatin-like family discovered in animals. Febs Lett. 2004, 572, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fire, A.; Xu, S.Q.; Montgomery, M.K.; Kostas, S.A.; Driver, S.E.; Mello, C.C. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 1998, 391, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi-Ham, C.L.; Clark, K.L.; Bennett, A.B. The intellectual property landscape for gene suppression technologies in plants. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, J.H.; Jian, H.; Xu, J.M.; Guo, Y.D.; Liu, Q.A. RNAi technology extends its reach: Engineering plant resistance against harmful eukaryotes. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 7573–7582. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Wang, D.D.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, W.C.; Hou, X.M.; Huang, X.Y.; Xie, B.Y.; Cheng, X.Y. Double-stranded RNA-mediated interference of dumpy genes in Bursaphelenchus xylophilus by feeding on filamentous fungal transformants. Int. J. Parasitol. 2016, 46, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.Y.; Dai, S.M.; Xiao, L.; Xie, B.Y. Influence of cellulase gene knockdown by dsRNA interference on the development and reproduction of the pine wood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Nematology 2010, 12, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Hu, L.J.; Wu, X.Q.; Wang, Y.C. A key effector, BxSapB2, plays a role in the pathogenicity of the pine wood nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. For. Pathol. 2020, 50, e12600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viglierchio, D.R.; Schmitt, R.V. On the methodology of nematode extraction from field samples: Baermann funnel modifications. J. Nematol. 1983, 15, 438–444. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Q.Q.; Du, G.C.; Qi, H.T.; Zhang, Y.A.; Yue, T.Q.; Wang, J.C.; Li, R.G. A nematicidal tannin from Punica granatum L. rind and its physiological effect on pine wood nematode (Bursaphelenchus xylophilus). Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2017, 135, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.-J.; Hu, J.-F.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Xu, L.; Lu, Q.; Li, Y.-X.; Zhang, X.-Y. Behavioural features of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus in the matingprocess. Nematology 2014, 16, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.J.; Bai, L.Q.; Schütz, S.; Liu, B.J.; Liu, Z.Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Yu, H.S.; Hu, J.F. Observation and Quantification of Mating Behavior in the Pinewood Nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. JoVE-J. Vis. Exp. 2016, 118, e54842. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Ma, R.Q.; Zhu, N.J.; Guo, K.; Guo, Y.Q.; Bai, L.Q.; Yu, H.S.; Hu, J.F.; Zhang, X.Y. Bxy-fuca encoding α-L-fucosidase plays crucial roles in development and reproduction of the pathogenic pinewood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinya, R.; Takeuchi, Y.; Miura, N.; Kuroda, K.; Ueda, M.; Futai, K. Surface coat proteins of the pine wood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus: Profiles of stage- and isolate-specific characters. Nematology 2009, 11, 429–438. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Du, G.C.; Fang, J.N.; Wang, L.S.; Guo, Q.Q.; Zhang, T.T.; Li, R.G. UGT440A1 Is Associated With Motility, Reproduction, and Pathogenicity of the Plant-Parasitic Nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 862594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Huang, X.L.; Li, J.; Mei, M.; Zeng, W.Q.; Lu, X.J. Evaluation of the RNA extraction methods in different Ginkgo biloba L. tissues. Biologia 2021, 76, 2393–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, S.N.; Lu, F.; Guo, K.; Huang, L.L.; Su, X.; Chen, Y. Nematotoxicity of a Cyt-like protein toxin from Conidiobolus obscurus (Entomophthoromycotina) on the pine wood nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.L.; Wu, X.Q.; Ye, J.R.; Huang, L. Molecular Characterization and Functional Analysis of Three Pathogenesis-Related Cytochrome P450 Genes from Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Tylenchida: Aphelenchoidoidea). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 5216–5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wang, P.; Tian, M.Q.; Zhu, L.H.; Ye, J.R. Major sperm protein BxMSP10 is required for reproduction and egg hatching in Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Exp. Parasitol. 2019, 197, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.E.; Lee, K.Y.; Lee, S.J.; Oh, W.S.; Jeong, P.Y.; Woo, T.; Kim, C.B.; Paik, Y.K.; Koo, H.S. The efficiency of RNA interference in Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Mol. Cells 2008, 26, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.C.; Gao, Y.X.; Li, F.; Liang, A.F.; Xu, Z.M.; Bai, Y.; Mai, W.Q.; Han, L.; Chen, D.F. Maclurin protects against hydroxyl radical-induced damages to mesenchymal stem cells: Antioxidant evaluation and mechanistic insight. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2014, 219, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.J.; Cui, S.Y. DPPH Radical Scavenging Mechanism of Ascorbic Acid. Food Sci. 2011, 32, 86–90. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, X.W.; Wu, X.Q.; Huang, L.; Ye, J.R. Influence of Bxpel1 Gene Silencing by dsRNA Interference on the Development and Pathogenicity of the Pine Wood Nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.C. Comparative Study of 1,1-Diphenyl-2-picryl-hydrazyl Radical (DPPH•) Scavenging Capacity of the Antioxidant Xanthones Family. Chemistryselect 2018, 3, 13081–13086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.W.; Hao, X.; Xu, J.Y.; Wang, B.Y.; Ma, W.; Liu, X.F.; Ma, L. Cytochrome P450 metabolism mediates low-temperature resistance in pinewood nematode. FEBS Open Bio 2020, 10, 1171–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.S.; Wang, L.S.; Li, R.G.; Chen, M.Y.; Deng, W.J.; Wang, C.; Du, G.C.; Guo, Q.Q. Cloning of sft-4 and its influence on vitality and virulence of pine wood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. J. For. Res. 2024, 35, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwabara, C.; Takezawa, D.; Shimada, T.; Hamada, T.; Fujikawa, S.; Arakawa, K. Abscisic acid- and cold-induced thaumatin-like protein in winter wheat has an antifungal activity against snow mould, Microdochium nivale. Physiol. Plant. 2002, 115, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehrer, J.P. The Haber-Weiss reaction and mechanisms of toxicity. Toxicology 2000, 149, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liochev, S.I.; Fridovich, I. The Haber-Weiss cycle—70 years later: An alternative view. Redox Rep. 2002, 7, 55–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).