Abstract
The mountain pine beetle Dendroctonus ponderosae (Curculionidae: Scolytinae) (MPB) is one component of an intensively studied co-evolved insect–host system. We investigated the spatial genetic structure of the MPB within its historic and recent geographic range expansion as it relates to host use in western North America using 13 pre-selected microsatellite loci. Analysis of molecular variation (AMOVA) indicates that genetic structure is not correlated with the host tree species and therefore does not support the hypothesis of the formation of a host race within this species. STRUCTURE analysis delineates four main clusters in western North America: (1) northern: northern British Columbia/northern Alberta; (2) central: southern British Columbia/southern Alberta/Washington/Idaho/Montana; (3) southwestern: Oregon/California/Nevada; and (4) southeastern: Utah/Wyoming/Arizona/Colorado/South Dakota. Heterozygosity, allelic richness, and the number of private alleles are greatest in the Southwest cluster. This cluster correlates with one of the three refugia hypothesized from a recent analysis of neo-Y haplotypes and represents an important reservoir of MPBs’ genetic diversity.
1. Introduction
Insects have evolved to not only occupy virtually every terrestrial and aquatic ecosystem but also link other organisms in a multitude of symbiotic relationships. Interactions between organisms are a major determinant of the distribution and abundance of species [1], and co-evolved ecological relationships between insects and plants are ubiquitous, diverse, and highly consequential. In particular, bark beetles (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae) have a profound effect on conifer forest ecosystems, promoting forest succession and sustaining ecosystem services and functioning [2,3]. Scolytines appear predisposed to selection by their plant hosts and potential host specialization because they meet the criteria proposed by Thompson [4] for host use specialization, i.e., predictable co-occurrences of susceptible host tree species and abundant populations through space and time; complete their development in a single host tree, then mate and reproduce on another host tree; ability to circumvent host defenses; and utilization of host-tree volatiles to locate suitable material for colonization [5,6,7]. For example, species within Dendroctonus are generally restricted to Pinaceae as hosts and tend to specialize at the host tree genus level [8]. It is postulated that most speciation events of extant Dendroctonus could be correlated with the diversification of its primary genus of host tree from their glacial refugia during the Miocene [9]. The mountain pine beetle, D. ponderosae Hopkins (MPB), has remained conservative to the genus level of Pinus [10], with exceptions only occurring during extreme outbreak conditions [11]. Its predominant hosts are lodgepole (P. contorta Dougl.) and ponderosa (P. ponderosa Dougl. ex. Laws.) pine species, but the MPB is able to successfully reproduce within almost all pine species within its range [8,12]. The intimate association between the MPB, its symbiotic fungi, and host tree species is one of the most studied co-evolutionary relationships of bark beetles in North America.
The MPB is a facultative predatory bark beetle native to western North America with an extensive historical geographic and elevational range spanning from southern California (CA) to northern British Columbia (BC) and east to the western edge of the Great Plains in western South Dakota (SD). Cyclical MPB outbreaks have been recorded in BC since the early 1900s [13,14,15] and are part of a natural cycle facilitating the maintenance of biologically and functionally diverse forest ecosystems [16,17,18,19,20]. Its most recent geographic range expansion over the Rocky Mountains into northern Alberta (AB) during the extreme outbreak from 1999 to 2015 [21,22] was facilitated by wind and long-range beetle flights [23,24] and extended its host range into a naïve host, jack pine, Pinus banksiana Lambert [22]. Further climate-driven range expansion into sensitive higher elevation ecosystems in the western United States has negatively impacted naïve hosts such as whitebark (P. albicaulis Engelm.) and, more recently, Rocky Mountain bristlecone (P. aristata Engelm.) pine [25,26]. In western Nebraska, it is suspected that the MPB has been present for some time prior to its first recorded detection in 2011 due to the extent of ponderosa pine in western Nebraska, beetle occurrence in surrounding states, and rare encounters reported by forest entomologists [27]. The MPB is also considered rare or absent in Mexico but has recently been found in dead southwestern white pine (P. strobiformis Engelm.), south of Arizona (AZ) [28]. Concerns about further migration and establishment into vulnerable areas are substantiated by the cosmopolitan diet and potentially destructive nature of the MPB compounded by the environmental transition to increasingly favorable climate conditions. This has bolstered interest in the drivers of the genetic structure of this beetle in North America.
Influence of host species on the genetics of Dendroctonus has been investigated since the early work on the genus. Initial studies used allozymes to compare the genetic signatures of many species of bark beetles in North America. While variation was detected, many of these studies compared beetles sampled from multiple host tree species from different locations, thus conflating the effect of geography and host tree species (summarized in ref. [29]). A study that sampled declining MPB populations on sites containing two host species found that geographic location was likely a stronger influence than host tree [29]. In contrast, another study compared hosts in geographically proximal sites in Colorado and found that the effect of host was equal to that of location [30], concluding that host effects may increase genetic heterogeneity and lead to the development of pre-adapted sub-species, or host races, of MPBs. More recent studies using amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) markers of the MPB from eight sites in the United States and Canada expanded host species comparisons and added a landscape genetic structure component, finding a general pattern of isolation-by-distance with little host effect [21]. However, specimens from host tree species in divergent sites were combined, which may have obscured the influence of the host. Other studies assessed the landscape genetic structure of MPBs using microsatellites [31] and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) [32,33], finding two clusters of genetic similarity divided into north and south populations. However, the host tree was excluded from these analyses, and only Batista et al. [33] included sites from the United States.
The effect of MPB host use on genetic structure can be tested by comparing geographic variation found within the MPB from its most widespread host, lodgepole pine, to those found among the other host species with more limited geographic ranges. We use an analysis of molecular variation (AMOVA) approach to assess evidence of genetic structure associated with host use. This approach places the regional genetic differences among host sites in the context of the wider geographic variation. It explores the hypothesis that host tree species influence range-wide MPB genetic structure due to preferential host selection versus geography alone driving the observed differences among sites. In the analyses presented here, we expand upon previous research into the genetic structure of the MPB in the United States and Canada using an inclusive dataset of 82 sites and then use a subset of these sites for a detailed comparison of MPB host use.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Selection and Beetle Collection
Beetles were collected between 2003 and 2012 from 153 active sites in 105 locations in three provinces in western Canada and 11 states in the western United States (US) (Figure S1). The beetles were primarily collected from lodgepole pine but also included beetles infesting six other pine species (Table 1). Sample sites were selected based on current and historical mountain pine beetle outbreak activity. These include a subset of samples from 2005 to 2008 analyzed by Samarasekera et al. [31], insects collected by B. Bentz (USDA Forest Service Region 4, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Logan, UT, USA), and previously unreported samples collected from 2010 to 2012. The 2010–2012 sample collections were conducted in targeted areas and in host tree species that were not included in previous sampling efforts (Table 1). In prior studies [31], western Canada was sampled more intensively than the US. To minimize bias during analysis of genetic structure, 82 sites were selected for a representative geographical distribution throughout western North America. In locations where multiple sites were sampled, the site with the largest sample size was selected for analysis. Beetle specimens were collected prior to emergence from individual galleries in multiple trees at each location or after emergence using traps during dispersal windows. A Global Positioning System (GPS) location was determined for each tree sampled or trapping location, and beetles were sampled, then transported alive in bark discs, then flash-frozen in liquid nitrogen or preserved in 95% ethanol. Samples were stored at or below −20 °C for DNA extraction. Site locations were visualized using ArcGIS version 10.5.

Table 1.
Sampling locations (82) by country and province/state for the mountain pine beetle. Variables shown include GPS coordinates, elevation, beetle host species, flight year sampled, and number of beetles genotyped (N) (bracketed number indicates number of sites per location if multiple collections were conducted). Mean observed heterozygosity (HO), mean expected heterozygosity (HE), mean number of alleles (NA), allelic richness (AR), mean number of private alleles, and inbreeding coefficient (FIS); statistical significance: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.005.
2.2. DNA Extraction and Microsatellite Amplification
Genomic DNA was isolated from whole beetles using a standard phenol/chloroform procedure [34] or an UltraClean Tissue and Cells DNA isolation kit (Mo Bio Laboratories, Carlsbad, CA, USA) following the manufacturer’s protocol. Isolated DNA was resuspended in Tris-EDTA (pH 8.0) or eluted in the manufacturer’s buffer. A preliminary assessment of DNA quantity and quality was performed using a NanoDrop® ND-1000 UV-Vis Spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
A total of 3858 beetles were genotyped at 13 microsatellite loci used for previous analysis within western Canada [31], using four co-amplification procedures [35]. Amplified fragments were co-loaded into two injections on an AB 3730 DNA analyzer. Band sizes were determined relative to GeneScan-500 LIZ (Applied Biosystems, Waltham, MA, USA) and scored using GeneMapper 4.0 software.
2.3. Hardy–Weinberg Equilibrium and Linkage Disequilibrium
Genotypic data from each site were examined for Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium (HWE) across loci and sites using an expansion of Fisher’s exact test. To ensure that all loci were independently assorting at all sites, linkage disequilibrium (LD) was assessed using a likelihood ratio test [36]. Statistical significance was evaluated both before and after sequential Bonferroni correction for multiple tests [37,38]. All analyses were performed using ARLEQUIN 3.5.2.2 [39].
2.4. Genetic Variation
Gene diversity and allelic richness were used to describe patterns of genetic variation across the study area. Observed (HO) and expected (HE) heterozygosity were also calculated for each sample location using the PopGenKit package 1.0 for R 2.14.2 [40]. Allelic richness was corrected for variation in sample size through rarefaction [41] executed in FSTAT 2.9.3.2 [42]. Patterns of genetic diversity were assessed for the entire study area as well as within the main clusters identified by Bayesian analysis for population structure as described below.
2.5. Population Structure
Population genetic structure was determined using a Bayesian approach with STRUCTURE 2.3.4 [43], assuming an admixture model and correlated allele frequencies, without prior sampling information. Each run was performed with 100,000 burn-in and 50,000 MCMC steps with all other parameters maintained at default values. Population structure was tested at K ranging from 1 to 10 with 20 replicates. To assess membership proportions for clusters identified by STRUCTURE, the results of the 20 replicates at the best fit K were post-processed using Clumpp 1.1.2 [44] and Structure Harvester 0.6 [45]. To capture a hierarchical level of population structure, each cluster was subsequently analyzed for nested sub-structures and evaluated as previously described. Population structuring was visualized using ArcGIS version 10.5. To gain further insight into the underlying population genetic structure and provide additional support to the results generated using STRUCTURE, data were also explored within the framework of a discriminant analysis of principle components (DAPC) [46].
2.6. Genetic Differentiation
Genetic variance was partitioned among and within clusters, and AMOVA was performed in ARLEQUIN 3.5.2.2 [39] based on pairwise FST corrected for unequal sample size using the method of Weir and Cockerham [47]. Variance components were calculated among groups (FCT), among locations within groups (FSC), among locations (FST), and within sampling locations (FIS). Each AMOVA was run with 10,000 permutations at 0.05 significance levels.
To test portioning of variation associated with host use, subsets of data were created by pairing non-lodgepole pine sites with the closest lodgepole pine site(s) within a similar geographic range (<200 km), thus ameliorating the effects of geography on the AMOVA groups, resulting in 14 non-lodgepole sites paired with 11 lodgepole sites. Non-lodgepole sites in AZ and SD were not used due to the absence of sampling in lodgepole sites within 200 km (no sites within 400 km).
3. Results
Based on our samples from 82 sites, all 13 microsatellite loci typed displayed a high amount of polymorphism with between 10 and 36 alleles/loci reported (Table 1). Reflecting the large number of alleles, average HO was also high, ranging from 0.288 to 0.806. Similar to Samarasekara et al. [31], no evidence for linkage disequilibrium among loci was found. Further, no sites displayed a large number of loci out of the Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium (HWE), with each locus displaying a significant departure from HWE (p < 0.05) between 0 and 9 times out of the 82 sites tested. Significant positive FIS values (p < 0.05) were noted for 16 populations with an overall FIS value of 0.019 (p < 0.001).
Locus-specific FST values were all significant and ranged from 0.040 to 0.219 (Table 2). This evidence of range-wide genetic structure is also noted in the overall FST value of 0.0683 (p < 0.001) among all 82 sampling locations. Pairwise population FST values range from nonsignificant to a maximum of 0.431 between sites in AZ and northern AB (Figure 1). Specimens collected from sugar pine (Pinus lambertiana Dougl.) were also noted for their pairwise divergence (FST 0.404–0.168) from all other sites. Beetles from a successful brood noted in interior hybrid spruce (Picea glauca × engelmannii) were not significantly different from adjacent lodgepole pine sites in northern BC.

Table 2.
Loci typed. Total number of alleles (NA), mean expected heterozygosity (HE), mean observed heterozygosity (HO), number of loci deviated from HWE, and fixation indices FIS and FST, and significance values *** = p < 0.0001.
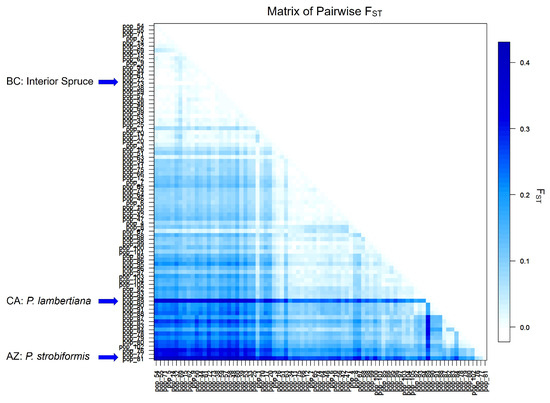
Figure 1.
Pairwise FST matrix of all sites sampled.
To test the effects of host use on the observed genetic structure, subsets of the data were divided into two groups: lodgepole and non-lodgepole hosts (Table 3), covering a similar geographic range (Figure 2). In the first test, 14 non-lodgepole sites were paired with 11 lodgepole sites. The overall FST and FSC were similar to each other and showed values consistent with the geographic range of sites examined. In contrast, FCT values, the percent variation due to host use, are not significantly different from zero. A second test paired proximal lodgepole pine sites with non-lodgepole host sites specifically grouped for (1) ponderosa pine (five pairs), (2) white bark pine (four pairs), and (3) all others (two western white pine, two limber pine, and one sugar pine). All showed similar results.

Table 3.
AMOVA of population structure due to host use. Four tests were performed, including ALL combined non-lodgepole, ponderosa pine, whitebark pine, and other pine test stands. Source of variation includes AG (FCT, among groups), APwG (FSC, among populations within groups), and WP (FST, within populations). Shown for each source of variation are degrees of freedom (d.f.), sums of squares (SS), variance component, percent of variation (% Var), and associated fixation index and p-value. The overall FST value is shown for comparison.
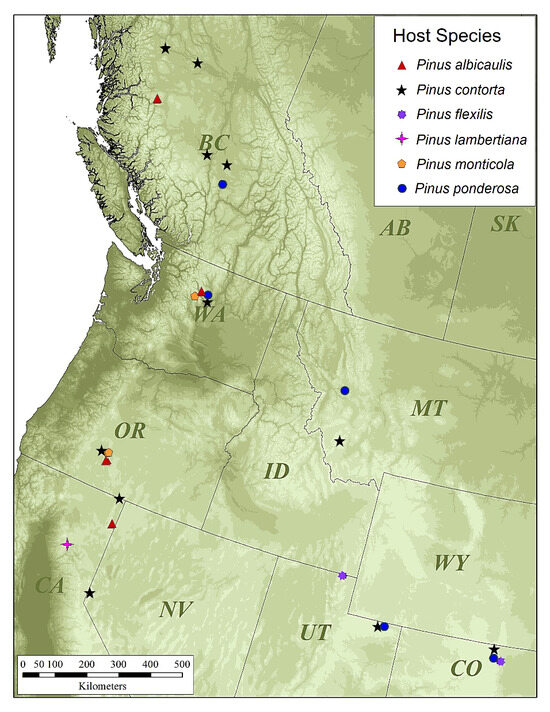
Figure 2.
Map of study area with collection sites separated by host tree species. Closely located site markers were displaced from their geographic location on the map to allow for better visibility.
All 82 sites were used to examine range-wide population structure. STRUCTURE analysis found two well-supported clusters at K = 2, dividing the samples into northern and southern groups (Figure 3). Among the southern cluster, additional sub-clustering was found at K = 3 and 4, supporting four clusters: (1) northern: northern BC/AB; (2) central: southern BC/AB/WA/ID/MT; (3) southwestern: OR/CA/NV; and (4) southeastern: UT/WY/AZ/CO/SD.
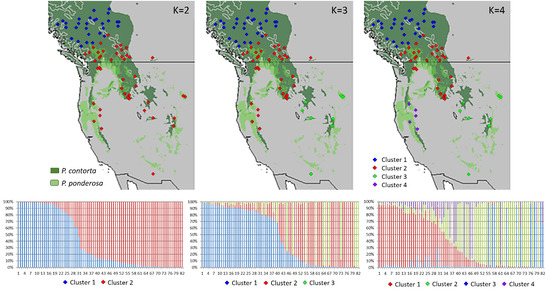
Figure 3.
STRUCTURE analysis of 82 sites in western North America. K = 2 is most strongly supported with weaker sub-clustering, K = 4, in the southern sampling locations. Distribution ranges for Pinus contorta and P. ponderosa are also shown. Note, to maximize contrast, different color coding in the cluster graphs was used for K = 4.
Patterns of genetic diversity varied among the four genetic clusters. Of the 82 sites typed, higher allelic richness and heterozygosity values were detected in sites grouped into the southwest cluster (Figure 4). Both heterozygosity and allelic richness decreased in locations further north and to the southeast. The maximum HO detected was 0.664 at Tahoe NF: Mount Rose Ski Resort, NV, and the minimum was 0.424 at Terrace, BC. The maximum allelic richness detected was 5.97 at Tahoe NF: Mount Rose Ski Resort, NV, and the minimum was 3.45 at Terrace, BC. The sites within the southwest cluster also showed the greatest number of private alleles (Table 1). The least amount of genetic variability was found in northern cluster populations compared to the remaining dataset (Figure 4).
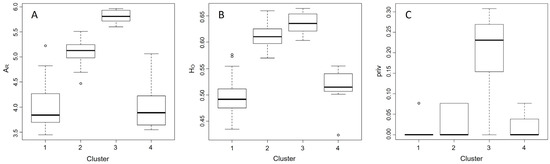
Figure 4.
(A) Allelic richness (AR), (B) observed heterozygosity (HO), and (C) private alleles (priv) grouped by STRUCTURE-generated cluster: (1) northern: northern: BC/Alberta; (2) central:southern: BC/Alberta/Washington/Idaho/Montana; (3) southwestern: Oregon/California/Nevada and; (4) southeastern: Utah/Wyoming/Arizona/Colorado/South Dakota. The boxplots incorporate Tukey’s 5-number summary as follows: the sample minimum, defined by the horizontal line at the bottom of each plot; the lower quartile, defined by the lower limit of the box in each figure; the sample median, represented by the heavy line inside each box; the upper quartile, defining the upper limit of each box; and the sample maximum, defining the horizontal line at the top of each plot. Open circles represent potential outliers falling outside the interquartile range.
4. Discussion
4.1. Host Use
Bark beetles exhibit behavioral plasticity in choosing host species, which allows adjustment for environmental variability, and such behaviors are likely modulated by genetic, environmental, and genetic-by-environmental drivers [48]. This study analyzes microsatellite data from a single MPB specimen per gallery from multiple host tree species and examines differences over the geographic range of MPBs. We found no evidence of genetic differentiation by host species and demonstrate the importance of geography to explain the genetic structure of MPBs, as indicated in previous studies using several different marker systems (e.g., refs. [21,31,33]). The emergence of host races requires host fidelity of beetle offspring [29], and a review by Barron [49] suggests growing evidence of Hopkins’ host-selection principle, initially proposed in 1916, which refers to the observation that many adult insects demonstrate a preference for the host species on which they themselves developed as larvae. During the most recent outbreak in BC, MPBs successfully infested non-traditional hosts, most notably Engelmann spruce. In a study comparing MPB mating and host acceptance behavior in hybrid spruce (Picea glauca (L.) H. Karst. × P. englemannii Parry ex Engelm.) and its traditional host, lodgepole pine, females reared in spruce more readily accepted spruce host material relative to pine and had higher rates of host acceptance of both pine and spruce host material than females that had developed in pine [50]. However, the opportunistic nature of MPB host use is shown by their utilization of spruce during extreme outbreak levels [50], in which the MPB was determined to be genetically identical to the surrounding lodgepole infections, and their expansion into boreal jack pine forests [22] during this recent outbreak. A preference for the host on which an insect developed could be the result of inheritance of a feeding or oviposition preference for the natal host. The basis of the heritable preference could be either genetic or an inherited environmental effect, for example, cues transmitted from the parental diet. While monoterpene composition and concentration vary with host, large variation within individual tree defensive capability is also found [51,52]. Monoterpene content of food sources of female MPBs has been shown to influence the feeding choice of offspring [53], and host selection behavior by MPBs differs between endemic and irruptive beetle populations [54], where irruptive populations select larger and better defended trees. Breeding lines derived from endemic and irruptive populations of Ips pini Say (Curculionidae: Scolytinae) exhibited differential responses to host phytochemical cues and have a heritable component, specifically in host acceptance and gallery development [55]. Furthermore, chemical similarities between historical and novel hosts can facilitate host range expansion [56,57].
Alternatively, the behavioral bias toward the rearing host could result strictly from experience within the insect’s lifetime. These mechanisms could act independently or synergistically; indeed, it is often difficult to disentangle genetic preferences from conditioned preferences. Natural successful infestation of alternate host species, including unrelated species, by irruptive MPBs may have aided in speciation of Dendroctonus [11,12]. This evidence for Hopkins’ host-selection principle in MPBs may be countered by host switching due to depleting ephemeral resources or availability of vulnerable hosts leading to no detectable effect of host use on the range-wide genetic structure. Cognato et al. [58] suggest that herbivores that utilize such hosts for only one or a few generations are less likely to become genetically isolated because any novel selection pressure imparted by a nonhost would be diminished through the use of other hosts in subsequent generations, thereby minimizing population structure caused by host selection. A possible exception to this trend was observed in beetles collected from a single site with sugar pine (P. lambertiana Douglas) in CA, which was noted as an outlier in pairwise FST comparisons (Figure 1). While the range of pairwise values falls within that observed among other sites, it becomes notable when compared with other sites in CA. Curiously, the sugar pine has a similar geographic range to Jeffrey pine (P. jeffreyi Balfour), which is infested by the Jeffrey pine beetle, Dendroctonus jeffreyi Hopkins, a host-specialist sister-species to the generalist MPB. Analysis of mitochondrial DNA variation, however, confirmed that the beetle mtDNA haplotypes collected from sugar pine were shared with or within the lineages found in MPBs [59]. However, because this result is limited to a single site, additional sites would be required to adequately investigate the possible effects of host use in this species.
4.2. Landscape-Level Genetic Structure
Knowledge of the genetic structure of populations is important for the understanding of their ecology and evolution [60]. The importance of geography to explain the genetic structure of the MPB is indicated in previous studies using several different marker systems (e.g., refs. [21,31,33]). Our expanded dataset presents strong evidence for grouping of MPB populations into two main clusters, southern and northern, consistent with previous studies [31,32,33,61]. The northern cluster is particularly genetically homogenous, showing comparative decreases in heterozygosity and allelic richness. This is consistent with the expectations of the founder effect during range expansion [62] and where mating practices are more random and traits are not exposed to the same level of environmental selection due to the number of new mutations and lineages within the expanded population [63]. While the MPB is not truly panmictic, even as an airborne insect, it is likely that environmental homogeneity of northern BC has facilitated more interbreeding than the southern populations that are separated by heterogeneous habitat and landscape barriers, such as mountains.
Our analyses also show sub-clustering in the southern cluster similar to that reported from mitochondrial [61] and SNP datasets [33,64]. Differences among the studies may be partially explained by the resolution of the different marker systems used and the distribution of sampling locations. Batista et al. [33] have a high number of sampling locations in Canada with relatively few in the US (n = 10), while Dowle et al. [63] have the majority of sampling locations in the US and few in Canada (n = 2). Our study attempted to balance the geographic distance among locations but still lacks important regions in the US sampled by Dowle et al. [64]. A general picture emerges of a central cluster extending from southern BC into the US states of ID and MT. Locations from the Cascade Mountains in WA more strongly cluster with this central cluster in our analysis, while SNP-based studies place MPBs collected in similar locations into a southwest cluster, which extends southward into OR and CA. Evidence for additional southeast clusters also exists. Our study shows a southeast cluster breaking from the central cluster at the Snake River Plain and including locations from UT/WY/CO/AZ/SD. Analysis of autosomal SNPs in this region, which includes a greater number of sampling locations in AZ and central NV, reveals the presence of an additional cluster(s)—locations from AZ, NV, and SD separate from those found in ID and CO [64]. Despite genetic evidence of gene flow among the clusters, mating studies have shown reproductive barriers among locations from the southwestern and central/southeastern clusters, which indicate possible incipient speciation [65,66]. However, MPBs are capable of extensive wind-borne transport rates above the forest canopy [23], and in the absence of reproductive barriers, should facilitate gene flow that would constrain evolution by preventing local genetic differentiation, whereas reduced dispersal is expected to lead to spatial genetic subdivisions [60,67].
4.3. Indications of Glacial Refugia
Observed heterozygosity (HO) and allelic richness are used as a proxy for expressing the genetic resilience and durability of populations [68,69]. High allelic richness is especially important as it provides a source for adaptive variation as populations face new pressures [70]. Of the four clusters generated by STRUCTURE in this study, the southwest cluster from OR/CA/NV had the highest values for HO, allelic richness, and private alleles, in agreement with previous research that also found high genetic variability within the same geographic region, with low diversity in the northern range [21,61]. This clinal reduction in variation in more northerly populations compared to southerly populations mirrors the glacial retreat from the last glacial period of the Quaternary [71,72]. It is likely that MPB populations followed the spread of pine northward during glacial retreat [73] but expanded more slowly than wind- and animal-assisted pine species, possibly due to a lack of confirmed presence of refugia in Canada and climate effects that limit population success [14]. Furthermore, invasion ecology dictates that for successful colonization to occur, the number of arriving individuals must arrive above an ‘invasion threshold’ [74], i.e., the minimum number of individuals required for colonization to occur. Increased propagule pressure has been shown to be positively related to colonization success for two bark beetle species with different host selection behaviors [75]; therefore, successful geographic and host range expansion may be constrained by lack of sustained sufficient propagule pressure exhibited during the endemic phase of the outbreak cycle.
It is important to note that, while the MPB is capable of flight, it requires external forces such as wind to assist its movement over large land barriers, such as mountain ranges [23,76]. This partitioning of habitat has led to the concept of refugia-within-refugia for the Pacific Northwest [77]. While the observed pattern of reduced diversity may be viewed as a pathway of post-glacial expansion (i.e., from the southwest glacial refugia to the central cluster, then north and southeast), an analysis of neo-Y haplotype diversity shows a more complicated pattern of post-glacial expansion. Dowle et al. [64] found three geographically separated neo-Y haplotype lineages: southwest (CA/OR/WA), southeast (AZ/NV/SD), and the Rocky Mountains (CO/UT/WY/ID/MT/BC/AB), indicating three core refugia. The Pacific Northwest of the United States has previously been identified as a glacial refugia for many different species (e.g., ref. [23]); however, the northern post-glacial expansion into Canada was primarily from a refugia associated with the rocky mountain neo-Y lineage but likely also carried an autosomal legacy from all three refugia.
4.4. Conclusions and Future Directions
Ecosystems experience considerable anthropogenic pressures, which can lead to regime shifts and changes in species distributions [78,79], and insects such as bark beetles are highly responsive to changes in environmental conditions and climate. Results from this study suggest that host tree species of MPBs have not contributed to the genetic structure of populations to a detectible level, an important finding contrary to the hypothesis of the development of cryptic host races of MPBs. However, our understanding of evolutionary processes that form the patterns of host plant use is not yet complete [80]. Different genetic and ecological conditions may result in different coevolutionary dynamics over broad geographic scales, essentially creating a coevolutionary mosaic across different spatial and temporal scales [81]. The genetic differentiation of MPBs will continue to evolve as cumulative pressures on forests from climate change, land-use change, and shifts in disturbance patterns, such as the frequency and intensity of bark beetle outbreaks, threaten forested landscape structure and function [3] and alter the distribution of hosts. If extreme epidemics become more commonplace, so may establishment into historically unfavorable landscapes and successful attacks on traditionally nonhost trees, which may be a mechanism by which host shifts and subsequent speciation events have occurred in Dendroctonus spp. [11]. Hence, detailed knowledge of host plant preferences and species-level phylogenies may provide a foundation for testing hypotheses related to the evolution of hosts and host preference [82]. The current lack of influence of host tree species provides insight into management strategies for forestry personnel, such as limiting decisions based not on species of attacked trees, but instead on stand structure and composition, ecological and environmental site conditions, and beetle population phase and brood success.
These studies can further be used to inform research on the genetic composition of the historic and current range expansion of the northern population because it also illustrates the complexity of interpreting spatial genetic patterns in terms of post-glacial expansion. Although the Pacific Northwest refugia likely represented a significant reservoir of genetic diversity, the role of this refugium in MPBs’ northern expansion into Canada remains unclear. Future studies that examine populations across the contact zone of the neo-Y haplotypes as identified by Dowle et al. [64] within WA and southern BC for both gene flow and mating success (i.e., ref. [66]) will improve understanding the genetic contribution of the refugia populations to the MPBs of WA, ID, MT, and southern BC. The wider genomic distribution of SNP datasets, including neo-Y coverage, makes these markers more suitable to address this question.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/f16040649/s1, Table S1: Cooperators for mountain pine beetle sample collections in western North America, 2011–2012; Figure S1: Map of sample sites for mountain pine beetle collections for population genetic studies, 2003–2012 inclusive.
Author Contributions
B.W.M. had oversight of the entire study and manuscript preparation. Analyses were conducted by C.K.B., K.M.T., B.W.M. and P.H. Manuscript preparation was performed by C.K.B., K.M.T. and B.W.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Funding for various aspects of this project was provided by a Genome Canada, Genome BC, Genome Alberta, and NSERC Strategic Network Grant to the TRIA Project.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article and Supplementary Materials. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The researchers wish to thank the many people who aided with sample collection and provided in-kind support (see Table S1). Thanks to Neil Thompson for his detailed GIS assistance. Special thanks to Sophie Dang for her excellent microsatellite typing work. We are grateful for the field and laboratory assistance of Rose Loerke, Shane Doddridge, Mike Prior, Rhiannon Montgomery, Cierra Hoerchl, Will Eisbrenner, Amanda Cookhouse and Marcelo Mora.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Jones, L.C.; Rafter, M.A.; Walter, G.H. Host interaction mechanisms in herbivorous insects–life cycles, host specialization and speciation. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2022, 137, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Lindgren, B.S.; Raffa, K.F. Evolution of tree killing in bark beetles (Coleoptera: Curculionidae): Trade-offs between the maddening crowds and a sticky situation. Can. Entomol. 2013, 145, 471–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, J.L.; Cottrell, S.; Fettig, C.J.; DeRose, R.J.; Mattor, K.M.; Carter, V.A.; Clear, J.; Clement, J.; Hansen, W.D.; Hicke, J.A.; et al. Bark beetles as agents of change in social–ecological systems. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2018, 16, S34–S43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.N. The Coevolutionary Process; The University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2021; 383p. [Google Scholar]
- Cognato, A.I.; Smith, S.M.; Jordal, B.H. Patterns of host tree use within a lineage of saproxlic snout-less weevils (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae: Scolytini). Mol. Phylogen. Evol. 2021, 159, 107107. [Google Scholar]
- Macías-Sámano, J.E.; Borden, J.H.; Gries, R.; Pierce, H.D., Jr.; Gries, G.; King, G.G.S. Lack of evidence for pheromone-mediated secondary attraction in the fir engraver, Scolytus ventralis, (Coleoptera: Scolytidae). J. Entomol. Soc. Br. Columbia 1998, 95, 117–125. [Google Scholar]
- Macías-Sámano, J.E.; Borden, J.H.; Gries, R.; Pierce, H.D., Jr.; Gries, G.; King, G.G.S. Primary attraction of fir engraver, Scolytus ventralis. J. Chem. Ecol. 1998, 24, 1049–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, C.S.L. The bark and ambrosia beetles of North and Central America (Coleoptera: Scolytidae), a taxonomic monograph. Great Basin Nat. Mem. 1982, 6, 1–1359. [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez-Reyes, T.; Armendáriz-Toledano, F.; Rodríguez, L.G.C. Rearranging and completing the puzzle: Phylogenomic analysis of bark beetles Dendroctonus reveals new hypotheses about genus diversification. Mol. Phylogen. Evol. 2023, 187, 107885. [Google Scholar]
- Six, D.; Bracewell, R. Dendroctonus. In Bark Beetles: Biology and Ecology of Native and Invasive Species; Vega, F.E., Hofstetter, R.W., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; Chapter 8; pp. 305–350. [Google Scholar]
- Huber, D.P.; Aukema, B.H.; Hodgkinson, R.S.; Lindgren, B.S. Successful colonization, reproduction, and new generation emergence in live interior hybrid spruce, Picea engelmannii × glauca by mountain pine beetle, Dendroctonus ponderosae. Agric. For. Entomol. 2009, 11, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furniss, M.M.; Schenk, J.A. Sustained natural infestation by the mountain pine beetle in seven new Pinus and Picea hosts. J. Econ. Entomol. 1969, 62, 518–519. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, C.S.; Unger, L. Mountain Pine Beetle—A History of Outbreaks in Pine Forests in British Columbia 1910 to 1995; Government of British Columbia: Victoria, BC, Canada, 1996; 61p.
- Safranyik, L.; Carroll, A.L. The biology and epidemiology of the mountain pine beetle in lodgepole pine forests. In The Mountain Pine Beetle: A Synthesis of Biology, Management, and Impacts on Lodgepole Pine; Safranyik, L., Wilson, W.R., Eds.; Natural Resources Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2006; pp. 3–66. [Google Scholar]
- Hrinkevich, K.; Lewis, K.J. Northern range limit mountain pine beetle outbreak dynamics in mixed sub-boreal pine forests of British Columbia. Ecosphere 2011, 2, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelson, J.; Alfaro, R.; Hawkes, B. Influence of fire and mountain pine beetle on the dynamics of lodgepole pine stands in British Columbia, Canada. For. Ecol. Manag. 2009, 257, 1874–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoroso, M.M.; Coates, K.D.; Astrup, R. Stand recovery and self-organization following large-scale mountain pine beetle induced canopy mortality in northern forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2013, 310, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro, R.I.; van Akker, L.; Hawkes, B. Characteristics of forest legacies following two mountain pine beetle outbreaks in British Columbia, Canada. Can. J. For. Res. 2015, 45, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, D.S.; Kulakowski, D. Long-term history and synchrony of mountain pine beetle outbreaks in lodgepole pine forests. J. Biogeogr. 2015, 42, 1029–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelson, J.N.; Hawkes, B.C.; van Akker, L.; Alfaro, R.I. Stand dynamics and the mountain pine beetle- 30 years of forest change in Waterton Lakes National Park, Alberta, Canada. Can. J. For. Res. 2018, 48, 1159–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mock, K.E.; Bentz, B.J.; O’Neill, E.M.; Chong, J.P.; Orwin, J.; Pfrender, M.E. Landscape-scale genetic variation in a forest outbreak species, the mountain pine beetle (Dendroctonus ponderosae). Mol. Ecol. 2007, 16, 553–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullingham, C.I.; Cooke, J.E.K.; Dang, S.; Davis, C.S.; Cooke, B.J.; Coltman, D.W. Mountain pine beetle host-range expansion threatens the boreal forest. Mol. Ecol. 2011, 20, 2157–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, P.; Straussfogel, D.; Lindgren, B.; Mitchell, S.; Murphy, B. Radar observation and aerial capture of mountain pine beetle, Dendroctonus ponderosae Hopk. (Coleoptera: Scolytidae) in flight above the forest canopy. Can. J. For. Res. 2008, 38, 2313–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Giroday, H.M.C.; Carroll, A.L.; Aukema, B.H. Breach of the northern Rocky Mountain geoclimatic barrier: Initiation of range expansion by the mountain pine beetle. J. Biogeogr. 2012, 39, 1112–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, J.A.; Powell, J.A. Ghost forests, global warming, and the mountain pine beetle (Coleoptera: Scolytidae). Am. Entomol. 2001, 47, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentz, B.J.E.; Hansen, E.M.; Vandygriff, J.C.; Stephens, S.S.; Soderberg, D. Rocky Mountain Bristlecone Pine (Pinus aristata) is a confirmed host to mountain pine beetle (Dendroctonus ponderosae), West. N. Am. Nat. 2021, 81, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Costello, S.L.; Schaupp, W.C., Jr. First Nebraska state collection record of the mountain pine beetle, Dendroctonus ponderosae Hopkins (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae). Coleopts. Bull. 2011, 65, 21–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armendáriz-Toledano, F.; Torres-Banda, V.; Zúñiga, G. The current status of Dendroctonus ponderosae Hopkins (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae) in Mexico. Coleopts. Bull. 2017, 3, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langor, D.; Spence, J. Host effects on allozyme and morphological variation of the mountain pine beetle, Dendroctonus ponderosae Hopkins (Coleoptera: Scolytidae). Can. Entomol. 1991, 123, 395–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturgeon, K.B.; Mitton, J.B. Allozyme and morphological-differentiation of mountain pine beetles Dendroctonus ponderosae Hopkins (Coleoptera: Scolytidae) associated with host tree. Evolution 1986, 40, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarasekera, G.D.N.G.; Bartell, N.V.; Lindgren, B.S.; Cooke, J.E.K.; Davis, C.S.; James, P.M.A.; Coltman, D.W.; Mock, K.E.; Murray, B.W. Spatial genetic structure of the mountain pine beetle (Dendroctonus ponderosae) outbreak in western Canada: Historical patterns and contemporary dispersal. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 2931–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janes, J.K.; Li, Y.; Keeling, C.I.; Yuen, M.M.S.; Boone, C.K.; Cooke, J.E.K.; Bohlmann, J.; Huber, D.P.W.; Murray, B.W.; Coltman, D.W.; et al. How the mountain pine beetle (Dendroctonus ponderosae) breached the Canadian Rocky Mountains. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 31, 1803–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, P.; Janes, J.K.; Boone, C.K.; Murray, B.W.; Sperling, F.A.H. Adaptive and neutral markers both show continent-wide population structure of mountain pine beetle (Dedroctonus ponderosae). Ecol. Evol. 2016, 6, 6292–6300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrook, J.; Russell, D.W. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 3rd ed.; Cold Spring Harbour Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, C.S.; Mock, K.E.; Bentz, B.J.; Bromilow, S.M.; Bartell, N.V.; Murray, B.W.; Roe, A.D.; Cooke, J.E.K. Isolation and characterization of sixteen microsatellite loci in the mountain pine beetle, Dendroctonus ponderosae Hopkins (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae). Mol. Ecol. Res. 2009, 9, 1071–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slatkin, M.; Excoffier, L. Testing for linkage disequilibrium in genotypic data using the Expectation-Maximization algorithm. Heredity 1996, 76, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holm, S. A simple sequential rejective multiple test procedure. Scand. J. Stat. 1979, 6, 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Rice, W.R. Analyzing tables of statistical tests. Evolution 1989, 43, 223–225. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Excoffier, L.; Lischer, H.E. Arlequin suite version 3.5: A new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol. Ecol Resour. 2010, 10, 564–567. [Google Scholar]
- Paquette, S.R. Useful Functions for (Batch) File Conversion and Data Resampling in Microsatellite Datasets, R Package Version 1.0; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2012.
- Petit, R.; Mousadik, A.; Pons, O. Identifying populations for conservation on the basis of genetic markers. Conserv. Biol. 1998, 12, 844–855. [Google Scholar]
- Goudet, J. FSTAT (Version 2.9.3.2): A Program to Estimate and Test Gene Diversities and Fixation Indices. 2002. Available online: https://www.scienceopen.com/document?vid=79097bb4-ec3c-47c3-94a1-47085d721e6b (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- Pritchard, J.K.; Stephens, M.; Donnelly, P. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 2000, 155, 945–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsson, M.; Rosenberg, N.A. CLUMPP: A cluster matching and permutation program for dealing with label switching and multimodality in analysis of population structure. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1801–1806. [Google Scholar]
- Earl, D.A.; VonHoldt, B.M. STRUCTURE HARVESTER: A website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv. Gen. Resour. 2012, 4, 359–361. [Google Scholar]
- Jombart, T. Adegenet: A R package for the multivariate analysis of genetic markers. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 1403–1405. [Google Scholar]
- Weir, B.S.; Cockerham, C.C. Estimating F-statistics for the analysis of population structure. Evolution 1984, 1, 1358–1370. [Google Scholar]
- Raffa, K.F.; Andersson, M.N.; Schlyter, F. Host selection by bark beetles: Playing the odds in a high-stakes game. In Advances in Insect Physiology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; Volume 50, pp. 1–74. [Google Scholar]
- Barron, A.B. The life and death of Hopkins’ host-selection principle. J. Insect Behav. 2001, 14, 725–737. [Google Scholar]
- McKee, F.R.; Huber, D.P.W.; Lindgren, B.S.; Hodgkinson, R.S.; Aukema, B.H. Effect of natal and colonised host species on female host acceptance and male joining behaviour of the mountain pine beetle (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) using pine and spruce. Can. Entomol. 2015, 147, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, J. Spatial and Temporal Dynamics of the Douglas-Fir Bark Beetle (Dendroctonus pseudotsugae, Hopk.) in the Detroit Ranger District, Oregon: A Landscape Ecology Perspective. Master’s Thesis, Forest Science, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Huber, D.P.W.; Ralph, S.; Bohlmann, J. Genomic hardwiring and phenotypic plasticity of terpenoid-based defenses in conifers. J. Chem. Ecol. 2004, 30, 2399–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, J.L.; Carroll, A.L. Breeding matters: Natal experience influences population state-dependent host acceptance by an eruptive insect herbivore. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172448. [Google Scholar]
- Boone, C.K.; Aukema, B.H.; Bohlmann, J.; Carroll, A.L.; Raffa, K.F. Efficacy of tree defense physiology varies with bark beetle population density: A basis for positive feedback in eruptive species. Can. J. For. Res. 2011, 41, 1174–1188. [Google Scholar]
- Wallin, K.F.; Rutledge, J.; Raffa, K.F. Heritability of host acceptance and gallery construction behaviors of the bark beetle Ips pini (Coleoptera: Scolytidae). Environ. Entomol. 2002, 31, 1276–1281. [Google Scholar]
- Erbilgin, N.; Ma, C.; Whitehouse, C.; Shan, B.; Najar, A.; Evenden, M. Chemical similarity between historical and novel host plants promotes range and host expansion of the mountain pine beetle in a naïve host ecosystem. New Phytol. 2014, 201, 940–950. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberger, D.W.; Venette, R.C.; Maddox, M.P.; Aukema, B.H. Colonization behaviors of mountain pine beetle on novel hosts: Implications for range expansion into northeastern North America. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176269. [Google Scholar]
- Cognato, A.I.; Harlin, A.D.; Fisher, M.L. Genetic structure among pinyon pine beetle populations (Scolytinae: Ips confusus). Environ. Entomol. 2003, 32, 1262–1270. [Google Scholar]
- Manhas, J. (University of Northern British Columbia, Prince George, BC, Canada); Murray, B.W. (University of Northern British Columbia, Prince George, BC, Canada). Undergraduate Research Award Report: Genetic Analysis of Mitochondrial DNA of Mountain Pine Beetle in California Sugar Pine. 2019; Unpublished work. [Google Scholar]
- Kerdelhué, C.; Magnoux, E.; Lieutier, F.; Roques, A.; Rousselet, J. Comparative population genetic study of two oligophagous insects associated with the same hosts. Heredity 2006, 97, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Cullingham, C.I.; Roe, A.D.; Sperling, F.A.H.; Coltman, D.W. Phylogeographic insights into an irruptive pest outbreak. Ecol. Evol. 2012, 2, 908–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allendorf, F.W.; Luikart, G.H.; Aitken, S.N. Conservation and the Genetics of Populations; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Klopfstein, S. The fate of mutations surfing on the wave of a range expansion. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005, 23, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowle, E.J.; Bracewell, R.R.; Pfrender, M.E.; Mock, K.E.; Bentz, B.J.; Ragland, G.J. Reproductive isolation and environmental adaptation shape the phylogeography of mountain pine beetle (Dendroctonus ponderosae). Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 6071–6084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bracewell, R.R.; Pfrender, M.E.; Mock, K.E.; Bentz, B.J. Cryptic postzygotic isolation in an eruptive species of bark beetle (Dendroctonus ponderosae). Evolution 2011, 65, 961–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracewell, R.R.; Bentz, B.J.; Sullivan, B.T.; Good, J.M. Rapid neo-sex chromosome evolution and incipient speciation in a major forest pest. Nat. Comm. 2017, 8, 1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slatkin, M. Gene flow and the geographic structure of natural populations. Science 1987, 236, 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromham, L. Reading the Story in DNA: A Beginner’s Guide to Molecular Evolution; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Caballero, A.; García-Dorado, A. Allelic diversity and its implications for the rate of adaptation. Genetics 2013, 195, 1373–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenbaum, G.; Templeton, A.R.; Zarmi, Y.; Bar-David, S. Allelic richness following population founding events—A stochastic modeling framework incorporating gene flow and genetic drift. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konnert, M.; Bergmann, F. The geographical distribution of genetic variation of silver fir (Abies alba, Pinaceae) in relation to its migration history. Plant Syst. Evol. 1995, 196, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaetzl, R.J.; Anderson, S. Soils: Genesis and Geomorphology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Burke, J.L.; Bohlmann, J.; Carroll, A.L. Consequences of distributional asymmetry in a warming environment: Invasion of novel forests by the mountain pine beetle. Ecosphere 2017, 8, e01778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, M.A.; Kareiva, P. Allee dynamics and the spread of invading organisms. Theor. Popul. Biol. 1993, 43, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chase, K.D.; Kelly, D.; Liebhold, A.M.; Brockerhoff, E.G. The role of propagule pressure in experimental bark beetle invasions. J. Appl. Ecol. 2023, 60, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evenden, M.L.; Whitehouse, C.M.; Sykes, J. Factors influencing flight capacity of the mountain pine beetle (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae). Environ. Entomol. 2014, 43, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafer, A.B.A.; Cullingham, C.I.; Côté, S.D.; Coltman, D.W. Of glaciers and refugia: A decade of study sheds new light on the phylogeography of northwestern North America. Mol. Ecol. 2010, 19, 4589–4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vucetich, J.A.; Waite, T.A. Spatial patterns of demography and genetic processes across the species’ range: Null hypotheses for landscape conservation genetics. Conserv. Genet. 2003, 4, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffa, K.F.; Aukema, B.H.; Bentz, B.J.; Carroll, A.L.; Hicke, J.A.; Turner, M.G.; Romme, W.H. Cross-scale drivers of natural disturbances prone to anthropogenic amplification: The dynamics of bark beetle eruptions. Bioscience 2008, 58, 501–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cognato, A.I.; Grimaldi, D. 100 million years of morphological conservation in bark beetles (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae). Syst. Entomol. 2009, 34, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.N. Specific hypotheses on the geographic mosaic of coevolution. Am. Nat. 1999, 153, S1–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, B.D.; Sequeira, A.; O’Meara, B.; Normark, B.B.; Chung, J.; Jordal, B.H. The evolution of agriculture in beetles (Curculionidae: Scolytinae and Platypodinae). Evolution 2001, 55, 2011–2027. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).