Abstract
Tongzhou District is designated as a city sub-center with 33.3% forest cover, representing significant ecological value for Beijing. However, this extensive forest area has lacked detailed conservation measures, leading to inefficient resource utilization over the years. Therefore, determining the various maintenance measures for the different areas is very important. This study focused on exploring the relationship between the soil nutrient structure and vegetation indices in the area to develop a more precise plan for forest maintenance. This study collected 163 sample points in the four zones of Tongzhou district, including electrical conductivity, acidity and alkalinity, bulk density, soil organic matter, total nitrogen, available nitrogen, total phosphorus, total potassium, available potassium, available phosphorus, as well as vegetation characteristics such as richness, coverage, and height. The normalized difference vegetation index, difference vegetation index, ratio vegetation index, green light vegetation index, and soil-adjusted vegetation index were calculated by remote sensing images. To test the spatial distribution of soil nutrient construction and the relationship between soil and vegetation indices using the spatial interpolation method and Pearson correlation analysis, the results showed that: (1) The soil organic matter and total nitrogen were extremely low (1.282 and 0.461 g/kg). In contrast, the available and total potassium was extremely high (227.994 mg/kg and 16.866 g/kg); (2) High-value areas of available and total potassium are in the northern area, the available and total phosphorus in the central area, and the pH in the northeast area, with overall neutral-to-alkaline conditions; (3) The mean of coverage is 72.120, with high-value areas concentrated in northern parts of the central areas. While the overall coverage is extensive, height varies significantly (3.300–479.867), and high-density vegetation is limited to the northern part of the central area; (4) Vegetation height shows a significant negative correlation with total potassium and a significant positive correlation with pH values. We suggest that it is necessary to properly retain fallen leaves and dead grass in the forest to increase the organic matter content of the soil, apply more organic fertilizers, and supplement nitrogen fertilizers. In Tongzhou District, potassium fertilizer application should be reduced, particularly in the northeast and northern areas, to prevent excess fertility. In the central area, phosphorus fertilizer application should also be controlled, while in alkaline areas, fertilizer use should be optimized, and lime should be added to improve pH. Compost or humic acid can improve the soil’s ability to absorb and release phosphorus, thereby enhancing plant phosphorus uptake and increasing vegetation height and coverage. This study only analyzed spatial changes without further examining soil layer differences at varying depths and the effects of soil microorganisms. In the future, soil fertility in various depths and the functionality and diversity of soil microorganisms are worth further exploring.
1. Introduction
Soil is an essential component of the ecological environment and serves as the foundation for plant growth and development [1]. The structural characteristics of soil nutrients, such as spatial distribution, physicochemical properties, availability, and forms are closely associated with plant growth [2]. The strength of the soil is upheld through specific combinations of its physicochemical properties [3], with physical properties enhancing water retention and drainage to directly impact water availability to the root system [4,5] and chemical properties intrinsically linked to soil vigor dictate nutrient availability and facilitate nutrient uptake by roots. Healthy soils are resilient to pests, diseases, drought, and climate change, increasing vegetation survival and growth potential [6]. Therefore, deficiencies in soil physical and chemical properties often lead to various adverse conditions: when the soil lacks nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, soil aggregates decrease, negatively affecting aeration and water permeability [7]; when the soil color darkens and organic matter accumulation decreases, the decline in microbial activity results in stunted plant growth [8], underdeveloped root systems, slower growth rates, and reduced stress resistance [9]. The size of sandy soil particles significantly affects water retention, nutrient availability, aeration, and permeability. Soil pH indicates acidity or alkalinity and can be influenced by substances in the plant’s apoplast [10]. Acidic soil generally results in short, thick root systems with reduced root hair development, inhibiting growth, while alkaline soils promote slender roots. Moderate pH levels enhance plant growth and are vital to soil self-protection [11]. Additionally, soil organic matter (SOM) is reflected in vegetation, as decomposing apoplastic materials contribute to humus formation, increasing SOM content [12]. SOM formed from vegetation apoplasts is essential for improving soil structure and porosity [12]. Spatial distribution highlights the variability and correlation between soil properties and vegetation [13]. Remote sensing technology can effectively identify these characteristics and the unique ecological processes in different regions, which can help target soil fertilization and vegetation maintenance. Therefore, it is essential to understand the spatial distribution relationships between soil physicochemical properties and vegetation growth.
The forest coverage rate in Tongzhou District of Beijing has reached 33.3%. Of this area, arbor encompasses approximately 30,051.26 hectares (about 450,800 acres), accounting for 96.725% of the total forest. The maintenance of these extensive woodlands requires not only attention to the growth conditions of the vegetation but also the careful management of soil nutrients. It is reported that Beijing allocates around CNY 300,000 (primarily for vegetation restoration) per hectare annually for forestland protection and green space maintenance [14]. The total funding needed to keep its 30,000 hectares of woodland is about CNY 1.5 billion annually for Tongzhou District [15]. Previous studies indicate that unilateral uniform fertilization wastes significant financial and material resources and damages soil nutrient structures [16], harming vegetation growth. The Tongzhou District is characterized by a variety of soil types, including tidal, brown, and salt soils, highlighting its spatial heterogeneity. Thus, it is crucial to accurately characterize soil properties, assess soil fertility, and understand the relationships between soil physicochemical properties and vegetation. A key component in developing effective management and conservation strategies for forest soils and vegetation is evaluating how soil fertility influences vegetation growth, as this provides a scientific basis for targeted practices in these areas.
This study aims to investigate the spatial distribution of soil physical and chemical properties and vegetation growth in the forested areas of Tongzhou District. The relationship between soil properties and vegetation health will also be explored to provide scientific recommendations for the targeted management of forestlands in the district. The specific objectives of the study are as follows: (1) Evaluation of soil nutrients in the forestland of Tongzhou District, (2) Spatial distribution characteristics of soil physical and chemical indicators in the forestland of Tongzhou District, (3) Spatial distribution characteristics of forest vegetation growth in Tongzhou District, (4) Effects of soil physical and chemical indicators on vegetation growth in Tongzhou District.
2. Study Area
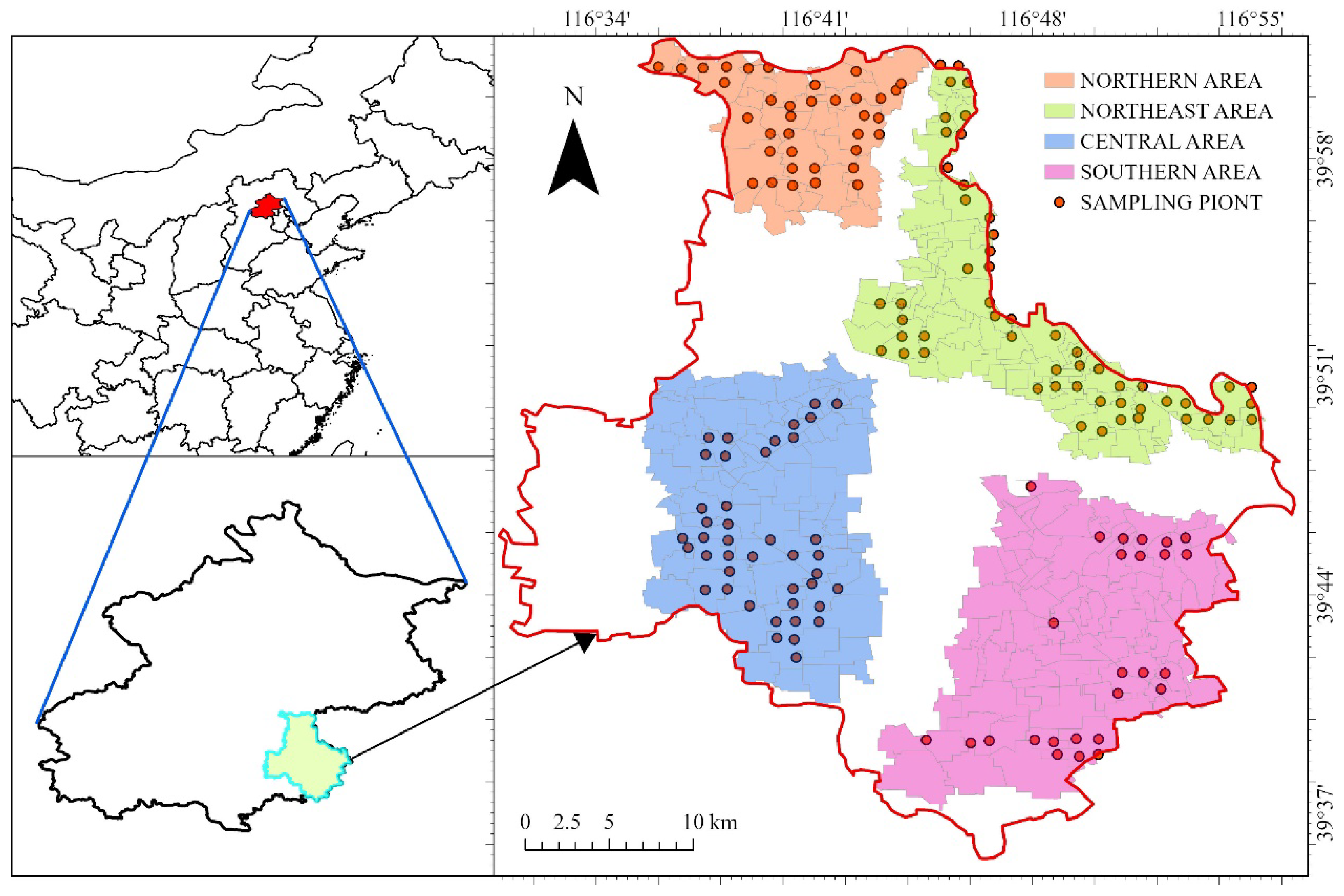
The study area is located in the Tongzhou District of southeastern Beijing (39°36′–40°02′ N latitude and 116°32′–116°56′ E longitude), which covers 906 square kilometers and is characterized by a temperate–tropical continental monsoon climate. The average annual temperature is 11.3 °C, with a frost-free period of 190 days, annual precipitation of 620.9 mm, and 2435.3 h of sunshine [17]. The district has an annual evapotranspiration rate of 1895 mm, encompassing approximately 30,051.26 hectares of forestland (about 74,231 acres). Elevations range from 8.2 to 27.6 m, and predominant soil types include sandy and loamy soils, classified as tidal, brown, swampy, and, less commonly, windy sandy soils [17]; the soil in this area has varying levels of total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP), total potassium (TK), available nitrogen (AN), available phosphorus (AP), available potassium (AK), and pH [18], which contribute to its permeability and water retention, benefiting crop growth. In the Tongzhou District, particularly near the river, sandy soils are more prevalent, though they tend to have lower fertility. The climate in this study area is characterized by dry, hot, and rainy summers, while winter temperatures drop significantly, leading to dryness [19]. The surface layer (0–20 cm) in Tongzhou District is dark brown to dark gray, with a sandy loam texture, good aeration, water permeability, and a pH of 7.5 to 8.0. The subsurface and deeper layers (20–60 cm) transition to clayey textures, with reduced water permeability and root penetration, resulting in a more compact soil structure [20]. Bulk density (BD) can vary across different types of land, being higher in constructed areas and major transportation routes [21] while lower in untouched soils, resulting in some adverse environmental conditions. According to the afforestation project plan for Tongzhou District, the study area can be divided into northern, northeastern, southern, and central areas. Forestland use in Tongzhou District, Beijing, is not spatially continuous, with afforestation efforts concentrated around villages. Consequently, a spatial distribution study is conducted across four areas (Figure 1).
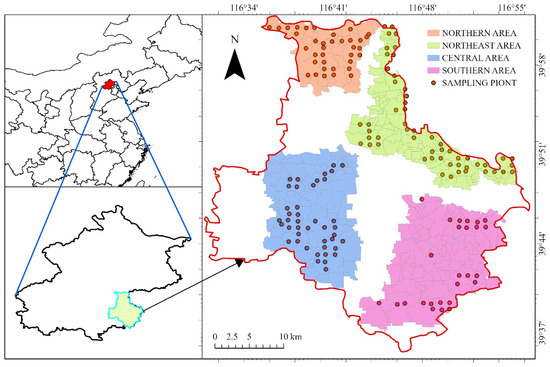
Figure 1.
Regional overview map of Tongzhou District, showing the northern area (orange), northeast area (green), central area (blue), and southern area (pink), with sampling points marked as red dots.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sample Points Setting
A 30 m resolution Landsat 8 remote sensing image was downloaded from the USGS website (https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/, accessed on 23 October 2024) and corrected for geometric and atmospheric factors using ENVI 5.3 software. The fishnet tool in ArcGIS Pro 3.1.5 was used to create a 1-kilometer grid, with intersection points designated as sampling points. A total of 193 sample points within forested regions were identified after excluding points in non-forested areas, such as roads and water bodies. During field sampling, GPS navigation adjusted the sampling points according to field conditions, resulting in a 0 to 30 m deviation and yielding 163 valid sample points.
3.2. Sampling Method
In the field sampling process, we identified the plants within the designated sample area and measured their heights at high, middle, and low positions using a tape measure. Subsequently, we calculated plant coverage utilizing the grid method (10 cm × 10 cm). Additionally, we measured the temperature, humidity, and pH levels using the ESM101-01T soil-integrated sensor (TERASAK, Osaka, Japan), recording all relevant data. Afterwards, we removed any weeds and stones from the surface layer of the sampling area. A ring knife was employed to extract a 100 cm3 soil sample to determine BD [22]. We used the five-point method to collect soil from the surface layer at 0–20 cm depth, ensuring thorough mixing of the sample. More than 1000 g of the mixed soil was placed into a polyethene sample bag, labeled, and recorded for reference before being returned to the laboratory. In the laboratory, the samples were stored in a refrigerator at a temperature of 2–5 °C to ensure preservation for subsequent experimental analysis.
3.3. Experiments Testing
In the laboratory, the empty ring knife was first weighed before sampling. The wet weight of the soil sample in the ring knife was measured using a balance with appropriate accuracy. The soil was subsequently placed into a cleaned aluminum box and baked for 2 h at 105 °C. It was then dried in a dryer for 24 h at the same temperature. Subsequently, the dry weight of the soil was measured. Finally, the BD of the soil was calculated using the volume of the ring knife, along with the wet and dry weight measurements. A 1000 g soil sample was laid flat on the test bench, away from direct sunlight, and dried for 24 h in the shade. The sample was manually ground, sieved through a soil sieve with a 2 mm (18 mesh) mesh and a 1 mm (20 mesh) mesh, and stored in soil sample bottles for chemical analysis. The content of SOM was determined by potassium dichromate oxidative titration, and the TN content in the soil was measured using the NaOH reagent photometric method [4]. The TP content in the soil was determined using the NaOH-melting flame photometric method [23]. The TK content in the soil was determined using the NaOH-melting flame photometric method, AN was measured using the alkaline dissolution–diffusion method [24], and AP was determined by the sodium bicarbonate leaching–molybdenum antimony colorimetric method [25]. The AK content was also measured using the sodium acetate leaching–flame photometry method [26].
3.4. Statistical and Analysis
3.4.1. Vegetation Indices Calculation
Vegetation index calculations were performed in ArcGIS Pro using remote sensing image data (Table 1). The normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) reflects vegetation growth using the near-infrared (NIR) and red bands, indicating the nitrogen demand of crops across different seasons, with values ranging from −1 to 1. A range of −1 to 0 indicates cloudy, watery, or snowy ground, while zero corresponds to rocks or bare land. Values between 0 and 1 indicate vegetation cover, with higher values representing denser vegetation [27]. The difference vegetation index (DVI) is sensitive to soil background and reflects vegetation trends through the difference between NIR and red bands. It is also commonly used in ecological monitoring [28]. The soil-adjusted vegetation index (SAVI) introduces a soil adjustment coefficient (L). It enhances the accuracy of vegetation detection, with values close to 0 indicate minimal vegetation cover, such as bare soil or sandy areas, and positive values indicating areas with high vegetation cover. The coefficient L is typically 0.5 [29]. The green vegetation index (GVI) assesses vegetation greenness using the green and red bands, with the degree of greenness indicating chlorophyll content and plant health. Negative values suggest a decrease in vegetation cover, while positive values indicate an increase [30]. The ratio vegetation index (RVI), based on the ratio of NIR to red bands, is used for vegetation classification and ecological monitoring. Theoretically, RVI values range from 0 to infinity, with values closer to 0 indicating non-vegetated areas and higher values indicating more excellent vegetation coverage and vigorous plant growth [31]. The remote sensing image data for Tongzhou District were processed using a raster calculator to compute the vegetation index and to mask the resulting raster map within the boundaries of the district. The vegetation index for each sample point was extracted and corrected. An analysis of the vegetation cover index for Tongzhou District was conducted to obtain vegetation coverage based on remote sensing [32,33].

Table 1.
Calculation formulas of various vegetation indices.
3.4.2. Data Organization and Statistical Methods
All soil physicochemical indices obtained from field measurements and laboratory analyses were organized into an M × N data matrix (M = 163, number of sample points; N = 10, soil physicochemical property variables) and richness (R), height (H), CVG, NDVI, GVI, DVI, SAVI, RVI were statistically organized into an (M × Q) data matrix, (M = 163, number of sample points; Q = 8, vegetation variables) in Excel 2019. Ordinary Kriging spatial interpolation [34] was performed for each soil physicochemical and vegetation indicator separately using the interpolation tools in ArcGIS Pro. Pearson correlation analysis [35] was performed on the log-transformed soil and vegetation data, which were adjusted to better align with a normal distribution using Origin 2021 software. The correlation analysis was used to examine the relationship between nutrient supply and vegetation growth, assess vegetation cover and biomass in the region, and identify key soil factors influencing vegetation health.
4. Results
4.1. Overall Assessment of the Soil Nutrients
According to the soil nutrient content standards and the coefficient of variation (CV) analysis of organic matter from the second soil census in China, Table 2 shows the CVs for the northern area in descending order: TN > AK > SOM > AN > AP > TP > electrical conductivity (EC) > TK > BD > pH. The mean of AK is 283.135 mg/kg, ranging from 41.920 mg/kg to 757.152 mg/kg, indicating medium variability. AN and AP means are 71.272 mg/kg and 41.535 mg/kg, respectively, with AK > AN > AP ranked in descending order. AK and AP belong to level 1, while AN belongs to level 4, which is considered not very high. The variation range of EC is relatively small, with values ranging from 1.340 µs/m to 3.087 µs/m and a mean of 2.232 µs/m. The SOM content ranges from 0.569% to 3.363%, exhibiting weak variability and spanning two grades. In descending order, the means for TN, TP, and TK are TK > TP > TN. The TN is classified as Class 5 with very low content, while TP and TK are categorized into Class 2 and Class 3, respectively, with relatively higher content. The range of TP and TK spanned two levels with a small range. The standard deviations for the three variables were 0.284 g/kg, 0.849 g/kg, and 3.251 g/kg, respectively, with TN exhibiting more significant variation. In contrast, TK showed only slight variation and remained relatively stable. The pH coefficient of variation is 0.040, indicating low variability, with a mean pH value of 7.618, ranging from 6.700 to 8.367, reflecting a neutral to alkaline pH. The mean BD in the northern area is 1.488 g/cm3, indicating loose soil, and the coefficient of variation is 0.084, reflecting low variability.

Table 2.
Statistical characteristics of soil physical and chemical indicators in the Northern area.
The top three indicators with the highest coefficients of variation in the northeast area (Table 3) are AK, SOM, and TN. The AK content ranges from 42.382 mg/kg to 645.580 mg/kg, showing medium variability; the mean AP content is 38.342 mg/kg, falling under the second-level standard, with a standard deviation of 14.765 mg/kg, indicating significant variation; the AN content spans from 16.100 mg/kg to 172.130 mg/kg, with a standard deviation of 32.704 mg/kg, suggesting notable variability. The means of AK, AN, and AP, except for AK, show significant differences in soil content. The range of EC variation is broad, from 1.840 µs/m to 4.040 µs/m, indicating substantial differences in soil moisture. The coefficient of variation for SOM is medium, with a mean of 1.282 and a very low overall content, classified at level six. The standard deviation of TN is 0.220 g/kg, reflecting slight variation and relatively stable data, while the range of variation for TN, TP, and TK is from 0.081 g/kg to 0.861 g/kg, showing significant variation in content. The mean pH value is 8.173, indicating alkaline soil, with a standard deviation of 0.319, reflecting relatively stable soil with slight fluctuation. The variation in BD is similarly low, ranging from 1.261 g/cm3 to 1.753 g/cm3, with a low coefficient of variation.

Table 3.
Statistical characteristics of soil physical and chemical indicators in the northeast area.
In the southern area (Table 4), the coefficients of variation rank as TN, AK, and AN. The mean AK value is 227.994 mg/kg, lower than in other areas, while AP ranges from 20.810 mg/kg to 78.681 mg/kg, exhibiting significant fluctuations, and AN has a mean of 83.58 mg/kg, placing it at the lower level of grade 4. The SOM is 1.277 (grade 6, very low content). The mean TK value is 20.406 g/kg, indicating medium levels, with a range from 13.271g/kg to 25.655 g/kg, while the mean TP content is 0.815 g/kg, classified as level 2 with high content, and its range spans from 0 g/kg to 1.589 g/kg. The TP content in the southern area showed heterogeneity. The coefficient of variation for pH was 0.033, indicating weak variability. Overall, the soil pH was weakly alkaline.

Table 4.
Statistical characteristics of soil physical and chemical indicators in the Southern area.
In descending order, the top three coefficients of variation in the central area (Table 5) were TN > AK > SOM, all classified as medium variability. The range of AK was from 34.974 mg/kg to 631.056 mg/kg, spanning grades 2 to 6, with significant variation and a standard deviation of 148.702 mg/kg, indicating uneven distribution. In comparison, the means of AN and AP were 97.759 mg/kg and 49.481 mg/kg, respectively, classified under levels 3 and 1, with high overall content and medium variability. The SOM content was very low. The mean TK content was 16.866 g/kg (level 3), with a standard deviation of 0.217 g/kg, while TP had a mean of 0.837 g/kg and exhibited minimal variation. TN ranged from 0.026 g/kg to 0.808 g/kg, with a standard deviation of 0.226 g/kg, indicating considerable fluctuation. The pH was weakly alkaline in the central area.

Table 5.
Statistical characteristics of soil physical and chemical indicators in the Central area.
Overall, the mean BD values are similar across the four areas, with slightly higher values in the northeast and southern areas compared to the northern and central areas. The pH in the northeast area was higher compared to the other three areas. The northeast area had the highest AK content (255.288 mg/kg) and the lowest AP content (49.481 mg/kg). In contrast, the central area had the highest AN (87.759 mg/kg), while the northern area had the highest SOM (1.678), and the lowest SOM was observed in the central area (1.195).
4.2. Spatial Distribution of the Soil Physicochemical Properties
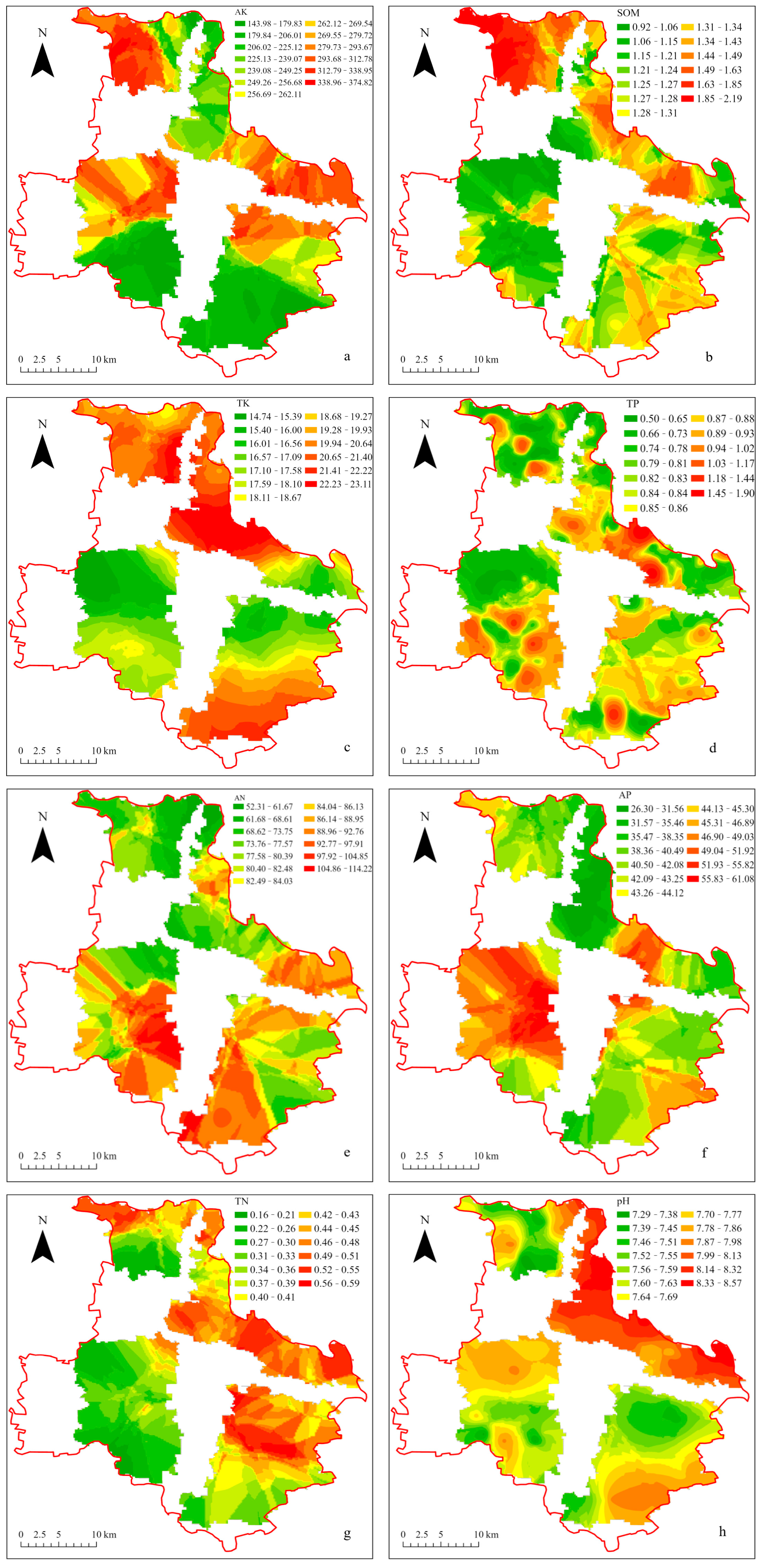
The results are shown in Figure 2. The four areas display distinct patterns for AK distribution (Figure 2a), with the northern area showing a decrease in AK content from west to east, marked by a clear division in the middle. In contrast, the northeast area shows a gradual decrease from southeast to northwest, with high-value areas located along the northeastern edge of the river and the western part of the region. The southern and central areas generally exhibit higher AK content in the northern parts. In the southern area, AK content is distributed in blocks. In contrast, in the northern area, high-value regions follow a striped distribution pattern, with most high-value areas situated in the lateral central region of Tongzhou District. Figure 2e shows that high AN content is primarily found in the central and southern areas, where values gradually increase from the periphery inward, with localized high concentrations in the northern and northeastern parts of the southern area. For AP content (Figure 2f), elevated values are mainly located in the central area and exhibit a scattered distribution. Unlike AK, the northern and northeast areas have relatively low AP content, while high-value zones in the southern area are concentrated in the northwest corner As shown in Figure 2, the distribution of AP and AN content follows a similar pattern, which is inversely related to that of AK content. Overall, the distribution of AN and AP follows a typical bar-shaped pattern. For SOM (Figure 2b), the northern area is identified as a high-value region. In the northeast area, higher SOM content is mainly distributed along the boundary of Tongzhou District, decreasing toward the southwest. The content of SOM ranges from low to very low, with an irregular distribution in the southern area. In contrast, most low-value areas in the central region are located near villages and active human settlements. This spatial distribution, combined with the AK and SOM patterns in the northern area, suggests a potential interactive relationship between the two indicators.
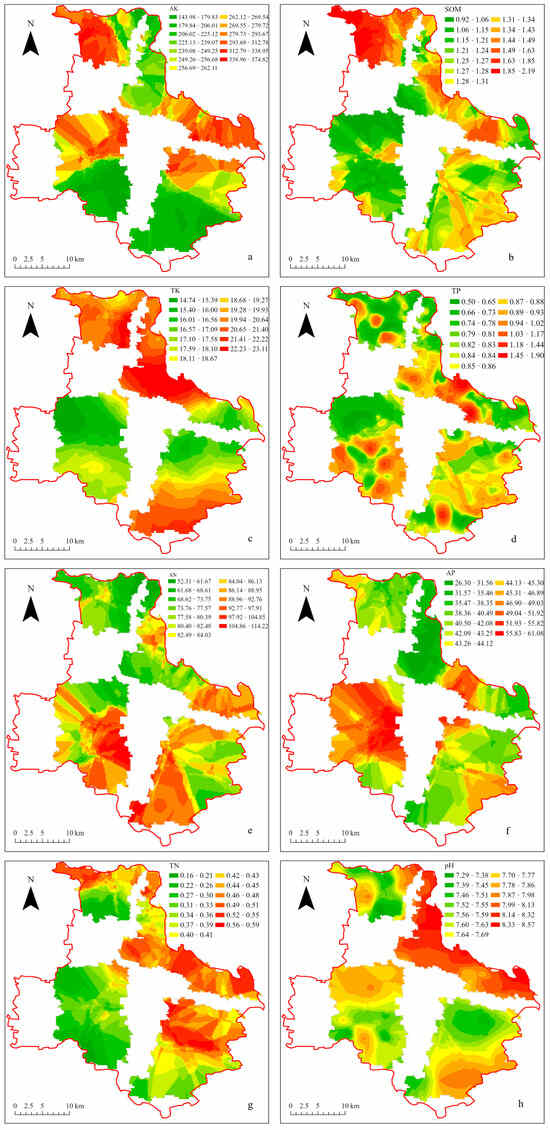
Figure 2.
Spatial distribution results of soil chemical indicators in the afforestation area of the Tongzhou District plain. (a) Available potassium (AK), (b) Soil organic matter (SOM), (c) Total potassium (TK), (d) Total phosphorus (TP), (e) Available nitrogen (AN), (f) Available phosphorus (AP), (g) Total nitrogen (TN), (h) pH.
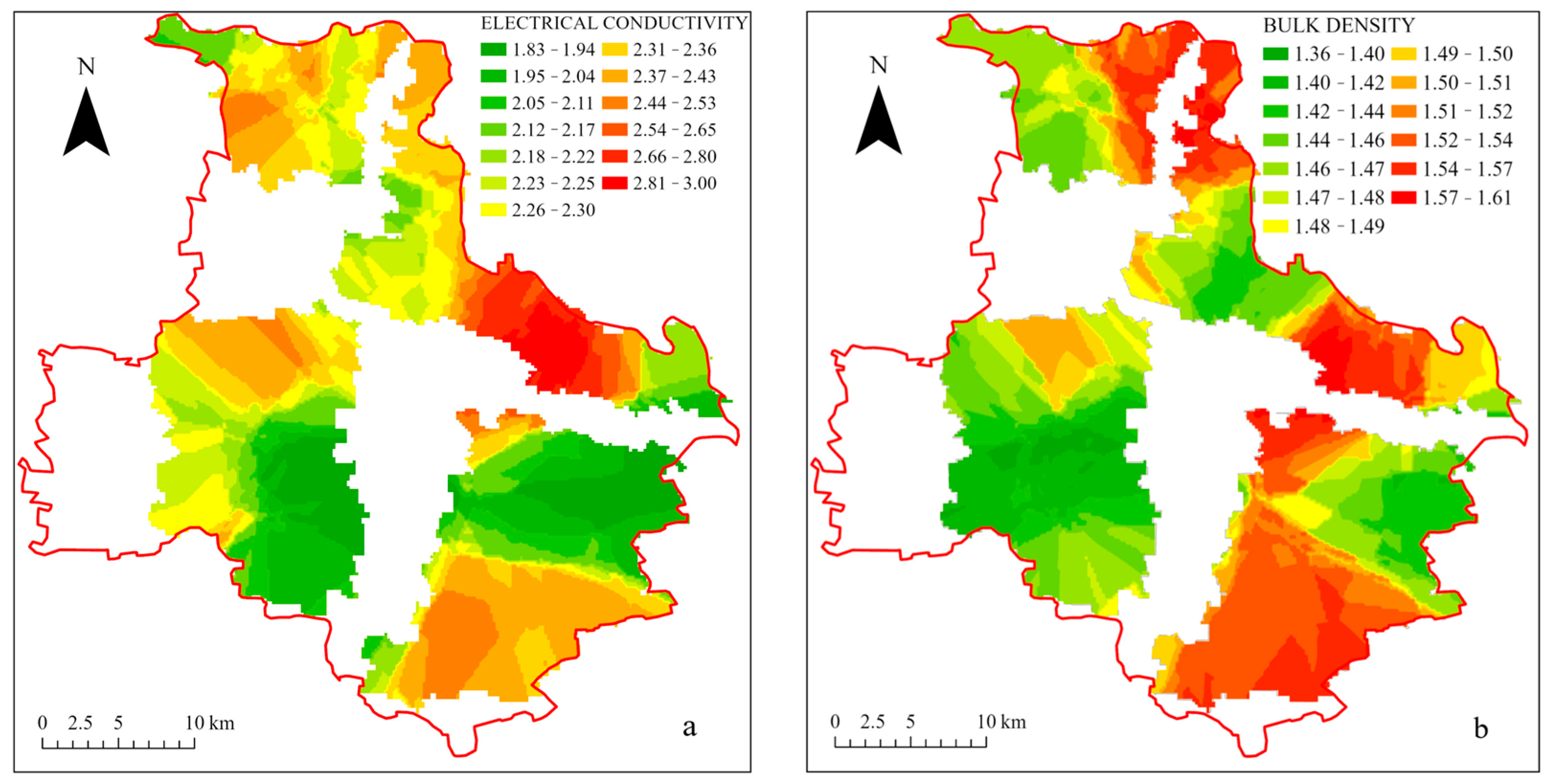
Figure 2c illustrates the trapezoidal distribution of TK content, with high-value areas concentrated in the northern and northeast areas, gradually decreasing toward the center of Tongzhou District, potentially influenced by factors such as SOM. In contrast, the AK only in the northern area exhibits high values in both. The distribution of TP content is more dispersed, as shown in Figure 2d, with high-value areas exhibiting a patchy pattern concentrated primarily in the central and southern areas, as well as the central parts of the northeast area, while the distribution of AP indicates a significant interaction between the two in this region. TN (Figure 2g) exhibits a linear distribution, primarily concentrated along the borders of the northern and northeast areas. The content in the central area is generally lower, with high-value areas skewed toward the northeast and lower values in the southwest. Overall, TN content is very low. As shown in Figure 3a, the EC exhibits high-value areas in the central area, gradually decreasing toward the northern area and the northern part of the central area, with no higher values observed in either the northern or central areas. The southern area shows higher values in the south, with lower values in the north. In Figure 2h, the pH is highest along the northeastern district boundary, following a linear distribution. The entire region tends toward neutral to alkaline conditions. A small portion of the northern area exhibits a gradual decrease in pH from east to west. The figure indicates a correlation between the high-value EC areas in the northwest corner of the southern and northeastern areas, suggesting that low EC areas in Tongzhou District may be linked to SOM and salinity.
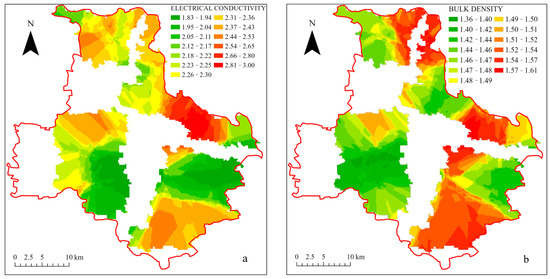
Figure 3.
Spatial distribution of soil physical indicators in Tongzhou District. (a) Electrical conductivity (EC), (b) Bulk density (BD).
Based on the analysis of Figure 3b, the spatial distribution of BD generally follows a block pattern, with high-value areas primarily concentrated in regions with relatively high SOM levels. It is suggested that SOM and other related factors may influence BD. Additionally, BD values in the southern area gradually decrease from the northwest and south to the east, exhibiting a clear hierarchical pattern. Low-value regions are concentrated in the northeastern part of the southern area, which aligns with the SOM heatmap.
4.3. Spatial Distribution of the Herb Diversity and Vegetation Growth Index
The coefficients of variation for vegetation indicators in Tongzhou District, summarized in Table 6, are ranked from highest to lowest as H > R > CVG > NDVI > SAVI > GVI > RVI > DVI. The range of R varies from 0 to 8, with some sample points showing no vegetation. Compared with the mean value, the standard deviation of 1.364 indicates an inevitable fluctuation, with data points dispersed at a mean value of 2.654. However, most data points are relatively concentrated near the mean value. The coefficient of variation for R is 0.514, suggesting a relatively stable distribution. The mean value of CVG is 72.120, with a coefficient of variation of 0.374, indicating weak variability and a higher proportion of sample points showing vegetation cover. The range of H is 3.300 cm–479.867 cm, exhibiting a wide variation with high coefficients of variation, although the mean is relatively low, suggesting high dispersion and significant fluctuations. The fluctuation is slight for NDVI, with a standard deviation of 0.115 and a mean of 0.561, indicating weak variability. The RVI range is from 1.356 to 2801, showing a smaller range of variation and a standard deviation of 0.286, indicating that the data are relatively centralized and stable, with a small coefficient of variation. GVI shows medium variability with a slight overall range. SAVI ranges from 0.227 to 0.711, exhibiting limited variation, with a standard deviation of 0.104 and minimal data fluctuation. The mean of 0.489 indicates that changes in the data are not significant. DVI ranges from 7511.500 to 20,015, showing a wide variation with a standard deviation of 1916.895, indicating considerable dispersion and fluctuation.

Table 6.
Statistical characteristics of herbaceous plant indicators.
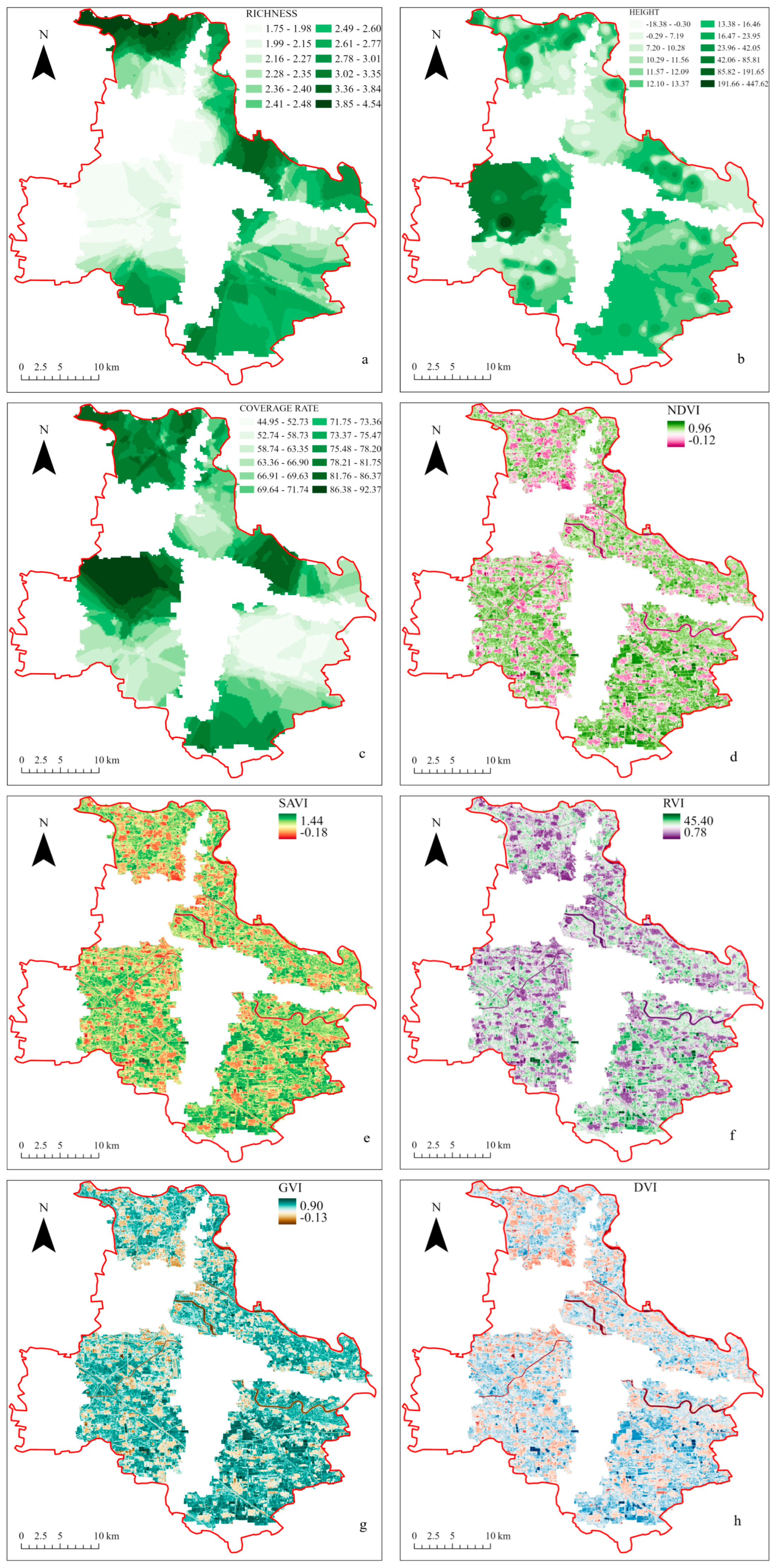
The vegetation indicators in Tongzhou District were analyzed using Kriging spatial interpolation. The spatial distribution of R (Figure 4a) revealed numerous high-value areas in the north, especially in the northwest, with values gradually decreasing from north to south. The eastern part of the central area had relatively high R values, while most southern areas exhibited low values. The middle of the northeast area also displayed high values, gradually decreasing towards the edges. The southern area exhibited a block-like distribution, with lower R values concentrated in densely populated regions. Figure 4b illustrates the spatial distribution of H, with high values generally absent in the southern area. The northern part of the central area exhibits higher H values, likely influenced by human activities. The distribution of H follows a concentric pattern, with values gradually decreasing from the center. The CVG reflects land use and growing environmental conditions. As shown in Figure 4c, the northern area has more vegetation and extensive woodland cover, representing a typical block distribution, primarily high-value regions with only a tiny portion of low-value areas. In contrast, the southern area shows a gradient distribution.
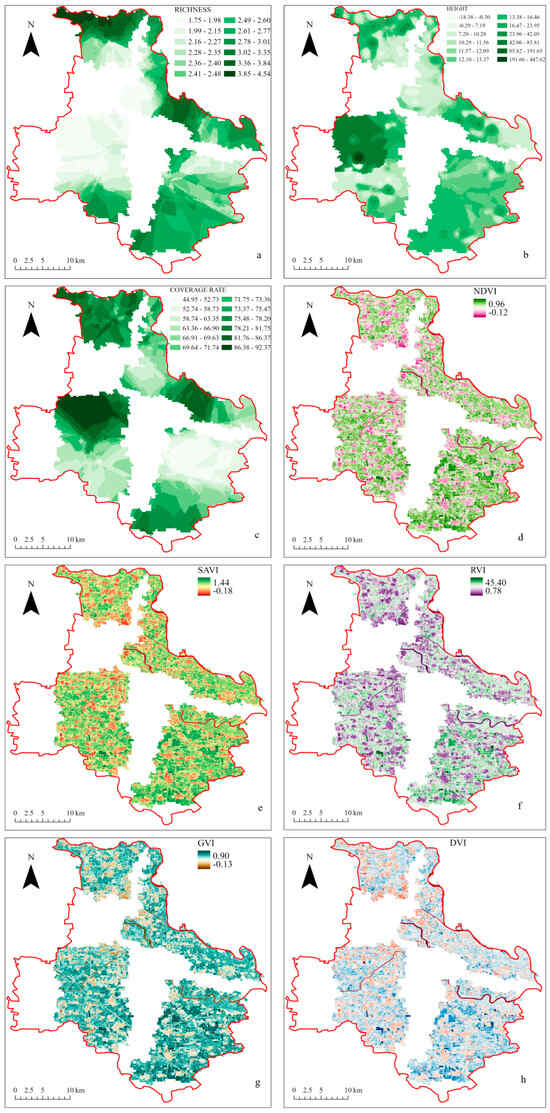
Figure 4.
Spatial distribution of vegetation indicators in the plain afforestation area of Tongzhou District. (a) Richness (R), (b) Height (H), (c) Coverage (CVG), (d) Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), (e) Soil Adjusted Vegetation Index (SAVI), (f) Ratio Vegetation Index (RVI), (g) Green Vegetation Index (GVI), (h) Difference Vegetation Index (DVI).
As shown in Figure 4d, the overall NDVI range of Tongzhou District is −0.12 to 0.96. The central area in the middle district to the left side is green, indicating high vegetation coverage and dense vegetation. The rivers in the study area show the lowest values, suggesting that they are water areas. The southern district exhibits good vegetation coverage, with peak NDVI values concentrated in this region, while the northeast area shows relatively scattered vegetation distribution. Other vegetation indices also reflect the overall vegetation health in Tongzhou District compared to NDVI. The four vegetation maps consistently show high vitality in the southern and central areas. Among them, SAVI (Figure 4e) is less influenced by soil than other indices, and urban vegetation coverage is more prominent in the southern part of the northern area and the western part of the central area. RVI (Figure 4f) predominantly indicates healthy vegetation, though vegetation in densely populated areas tends to have lower health levels. Vegetation around rivers, marked by the lowest values, shows moderate health. In contrast, GVI (Figure 4g) exhibits a more distinct green light reflection, with high vegetation coverage in the southern area. DVI (Figure 4h) reveals fewer areas with extremely healthy vegetation, mainly around woodlands and rivers.
4.4. Relationships Between Soil Nutrients and Vegetation Growth
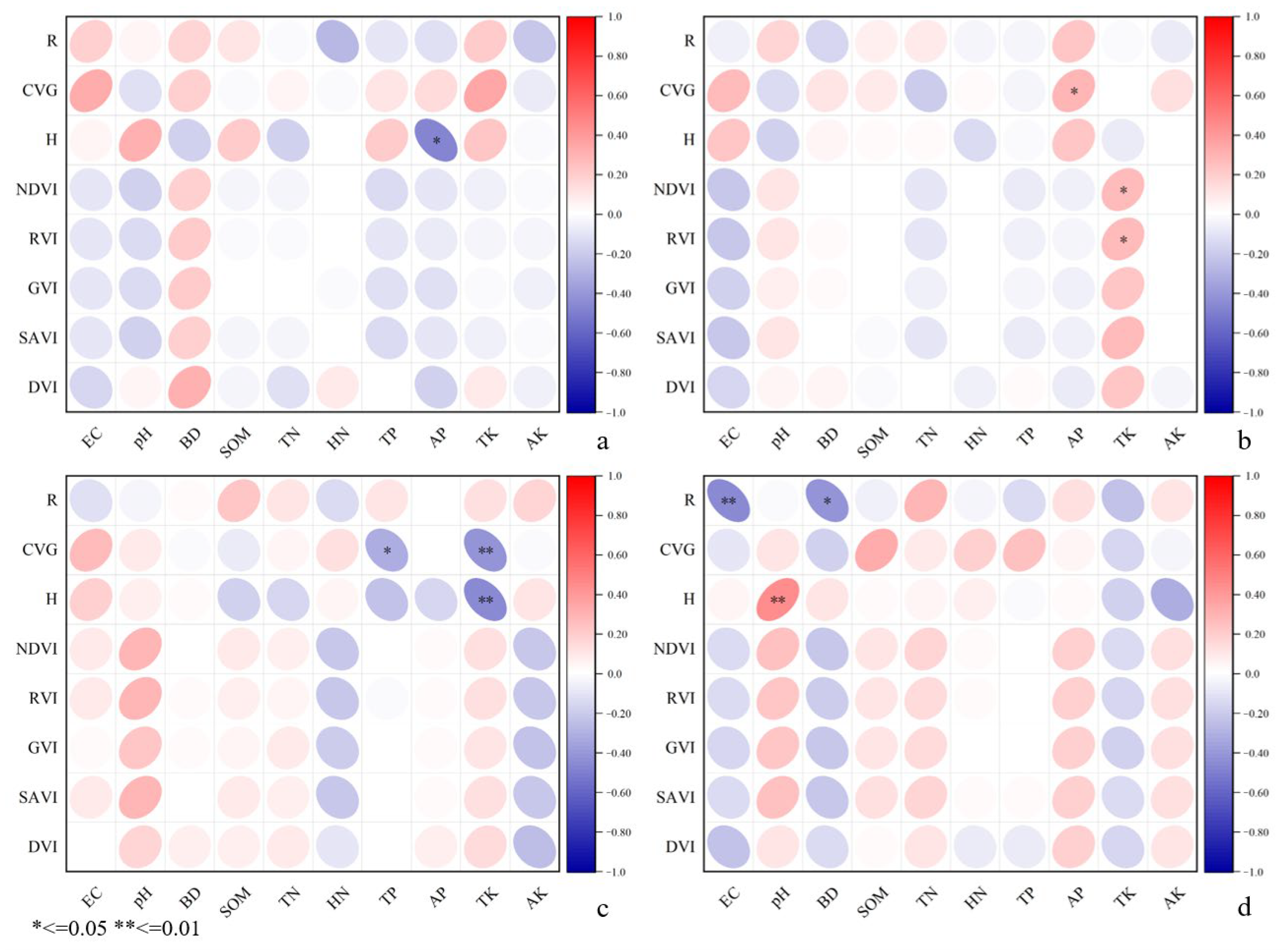
A significant negative correlation is observed between H and AP in the southern area (Figure 5a), indicating that as AP content increases, H decreases. BD exhibits a positive correlation with the vegetation index in the southern and northeast areas (Figure 5b), while the correlation weakens in the central area (Figure 5c). This relationship suggests that increased BD contributes to soil compaction, facilitating enhanced vegetation growth, while a negative correlation is observed in the northern area (Figure 5d). Additionally, higher EC levels are associated with reductions in vegetation indices. TK and CVG exhibit a significant positive correlation, where increased TK content contributes to higher CVG values.
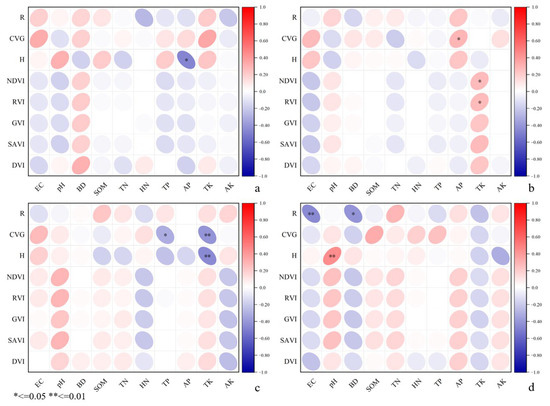
Figure 5.
Pearson product–moment correlation analysis between soil physical and chemical properties and vegetation indicators: (a) southern area, (b) northeast area, (c) central area, (d) northern area.
CVG in the northeast area (Figure 5b) shows a significant positive correlation with AP (0.6 to 0.8), indicating that reduced AP may restrict vegetation growth. At the same time, AP also exhibits a weak positive correlation with R and H. In contrast, a negative correlation exists between AP and the vegetation index in the southern and northeast areas, where increased AP content affects vegetation performance. TK shows a significant positive correlation with NDVI and RVI, with a weak linear correlation (−0.2 to 0.2). A higher TK content enhances NDVI and RVI performance. CVG shows a significant negative correlation with TP in the central area (Figure 5c), where higher CVG results in lower TP content. TK shows a highly significant negative correlation with both H and CVG, with a significant correlation coefficient. A decrease in TK content in the soil is associated with an increase in vegetation R and H, which shows a positive correlation with CVG. The AN shows a negative correlation with the vegetation index. Figure 5d shows a highly significant negative correlation between R and EC in the northern area, indicating that EC greatly influences R. R also shows a highly significant negative correlation with BD, although the correlation is weak. Finally, H and pH show a highly significant positive correlation.
5. Discussion
5.1. Causes of Differences in Soil Nutrients Composition
The content of AN, AK, and AP in the central area is relatively high, combined with soil physical and chemical indicators and spatial distribution. Based on the relevant information from the reports published by the Beijing Land and Resources Bureau and the Third National Land Survey, the central area has more cultivated land, with extensive use of artificial fertilizers, and the crops are mainly grain crops. These crops have a significant demand for nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. However, excessive or insufficient fertilizers pose certain risks and may lead to environmental pollution [36]. Another possible reason is the significant climate variation in Tongzhou District, where suitable temperature and humidity accelerate organic matter decomposition [37].
EC levels influence pH, and the spatial distribution of both is relatively consistent across the district, except in the northeast area, possibly due to increased ion concentration leading to more dissolved salts and raising pH levels [38]. Another is that soluble salts impact the high-value area near the river in the northeast area. Salts accumulate in plant roots and leach out [39]. Therefore, periodic leaching irrigation and drip irrigation are recommended to manage high EC areas. The SOM content in Tongzhou District is extremely low. It is mainly due to the frequent harvesting of forestland, which requires clearing the ground cover before it dries to prevent fires. As a result, fallen leaves and dead grass do not decompose back into the soil, reducing SOM levels [40]. Additionally, the monoculture forests significantly affect SOM content, disrupting soil microbial activity and limiting the decomposition and accumulation of SOM [41]. It was found that TP and TK levels were relatively high, while TN content was extremely low when comparing the contents and grades of TN, TP, and TK. This may be due to the abundance of these elements in groundwater and surface water, which are transported to the soil through groundwater flow. The northern area may have low-lying regions [42] with poor drainage, resulting in high alkali content. Studies [43] have shown that long-term nitrogen fertilizer deficiency can cause reverse vegetation growth and reduce crop yields. Moreover, the close relationship between TN content and SOM, as most TN is stored in organic form, may explain the poor TN content in the soil of Tongzhou, which reduces fertilizer retention capacity and impacts soil buffering performance [44]. The uneven spatial distribution of TP content may be attributed to the significant effects of pH and SOM on phosphorus availability. This spatial distribution aligns with the findings of Fabian Alt et al. When the pH is approximately 6.5, applying lime-containing fertilizers enhances phosphorus availability in the soil [45]. Additionally, areas with higher TP content tend to be near forests and rivers. In certain areas, particularly forests with low-lying terrain and steep slopes, soil erosion and water loss can lead to the accumulation of surface phosphorus [46].
The overall pH ranges from neutral to weakly alkaline, while it is distinctly alkaline in the northeast area. This may be attributed to Tongzhou District’s location in a semi-arid region, where salt is difficult to leach [47], and it is also due to the use of highly alkaline groundwater and saltwater for irrigation [48]. The southern area has the most extensive BD range. The reason may be that the forest plant species are single, and large-scale afforestation and ecological afforestation are located here. Human activities, including intensive land use, contribute to soil compaction [49]. It may also be due to the densely cultivated area in the southern area and the long-term use of heavy agricultural tools, which repeatedly compact the soil, thereby increasing the BD and affecting the soil’s air and water permeability [50].
5.2. Effects of the Soil Nutrients on the Vegetation
The correlation analysis between vegetation and soil shows that the overall R is low, with R showing a significant negative correlation with EC and BD. This may be because salt leaching due to the soil’s pore structure leads to a decrease in the R, and salts are easily leached out [51], resulting in relatively low EC. The low R may result from single vegetation species that cause soil compaction and hinder microbial activity [52], but deep plowing and regular irrigation could help alleviate this issue. The overall variation in H is relatively significant, typically ranging from moderate to low values. H and pH in the soil show a highly significant positive correlation, consistent with the findings of S.D. Veresoglou that higher pH does not necessarily support better vegetation growth [53]. It also may be that the overall pH in Tongzhou District is neutral to alkaline, directly affecting nutrient availability in the soil. The concentrations of other soil components are higher compared to pH and influence nutrient absorption by vegetation, which is ultimately reflected in H [54]. H shows a significant negative correlation with AP. This may occur because excessive AP content impairs the absorption of other nutrients (e.g., iron), forming insoluble compounds that inhibit plant cell division and elongation, decreasing the H [55]. Another possible explanation is the low SOM content in Tongzhou District, which alters the physical properties of the soil, reduces porosity and increases BD. As a result, AP efficiency decreases, and AP content becomes relatively higher in areas with low SOM, eventually leading to an excess that adversely affects plant roots and inhibits growth [56]. Since plants require moderate pH conditions for optimal growth, pH adjustments may be necessary across different areas [53].
The higher CVG level in Tongzhou District indicates that ecological protection and forestland restoration efforts have been more effectively implemented. AP and CVG in the northeast area have a significant positive correlation. In contrast, the other three regions show a weak positive correlation, suggesting that other soil components may hinder CVG. For example, soil texture in these regions is relatively sticky, which can reduce the effectiveness of AP and impair vegetation absorption [57]. Another possibility is that extremely low SOM levels in these areas may affect phosphorus transformation, limiting plant phosphorus absorption and growth [58]. Both RVI and NDVI show a significant positive correlation with TK. This is likely because potassium promotes cell elongation and division, accelerating vegetation growth [59]. The higher TK content in Tongzhou District enhances CVG, increasing the vegetation index [60]. Overall, the soil in Tongzhou District plays a positive role in regulating CVG, improving soil fertility, and promoting vegetation growth. BD is negatively correlated with the vegetation index in the northern area, which differs from the other three areas. This is likely because the regions have more vegetation and denser farmland. Additionally, forest and cultivated land have been repeatedly irrigated and fertilized, leading to soil compaction and increased BD. In semi-arid areas, this increases water retention capacity and, in turn, the vegetation index [61]. However, BD should ideally be moderate, so the positive correlation between the two needs further adjustment. Another possibility is that the sandy soil in Tongzhou District increases BD without negatively impacting plant growth. Instead, it enhances the vegetation index [62]. TK shows a highly significant negative correlation with CVG and H. The spatial distribution indicates that higher vegetation correlates with lower TK content (northern part of the central area), which also applies to CVG. This may result from ion imbalance caused by excessive potassium, disrupting plant cell ion balance [63]. Excess potassium can also hinder nutrient absorption, affecting plant growth and reducing CVG. The negative correlation between AN and the vegetation index is likely due to the low TN content in Tongzhou District. A higher AN content is found only in the northeast and northern parts of the southern areas, indicating lower nitrogen fertilizer levels. However, low TN content slows vegetation growth, impacting CVG and growth status [64]. So, nitrogen fertilization should be adjusted based on spatial distribution.
6. Conclusions
Based on the above analysis, the soil physicochemical characteristics and vegetation indicators for Tongzhou District are summarized as follows: (1) According to soil nutrient classification standards, SOM and TN contents are extremely low. In contrast, AK and TK contents are high, with other indicators at an upper-middle level. (2) H and AP, CVG and TP, and R and BD show a significant negative correlation, while H and TK, CVG and TK, and R and EC show a highly significant negative correlation. This indicates decreasing AP and TK levels, limiting vegetation growth, causing soil nutrient imbalance, and affecting soil fertility. (3) TK and TP consumption can be reflected in CVG, suggesting the need for further ecological restoration and fertilization in Tongzhou District. Increases in soil EC may inhibit plant growth and density. (4) TK has a significant positive correlation with NDVI and RVI. The high TK content in Tongzhou District promotes plant growth and increases vegetation coverage. H has a highly significant positive correlation with pH, but the correlation coefficient is small, so the pH should remain neutral to alkaline for proper soil hydration. (5) CVG has a significant positive correlation with AP. The high AP content promotes root absorption and phosphorus transformation, and soil microorganisms can convert unavailable phosphorus into AP. However, this study has some limitations, such as the lack of consideration for the impact of human activities after field sampling. This cross-sectional study mainly analyzes soil and vegetation characteristics in one season, limiting the results’ comprehensiveness. The data collection method was not systematic enough, leading to potential deviations. These issues will be addressed in future studies to improve the scientific rigor and reliability of the research. In conclusion, the improvements to soil and vegetation in Tongzhou District are as follows: (1) The plain afforestation areas located at the southeast end of Tongzhou District, with alkaline soil ranging from pH 7.5 to 8.5, can be improved by applying organic fertilizers and alkaline soil conditioners and mixing in coniferous or pine needle soil. (2) Areas with low SOM and TN content directly impact plant growth and productivity, especially in the southern and central areas. Organic soil conditioners can improve soil texture by being applied, spread on the soil surface, deeply plowed, or mixed into the soil. More organic fertilizers should be used, nitrogen fertilizers should be added, and the number and variety of shrubs and ground covers should be increased. (3) At the same time, attention should be paid to the depth of fertilization, the amount of fertilizer applied should be reasonably controlled, the soil testing and fertilization formula should be strengthened, tree species should be reasonably allocated, suitable vegetation should be planted, the loss of water and soil nutrients should be reduced, and the content of adequate nutrients in the soil should be increased. (4) Choose to plant mixed forests. The organic carbon content of coniferous species is generally lower than that of broad-leaved species. However, the study area has many coniferous trees, such as Chinese pine and white pine. They have little litter and are rich in non-degradable lignin, vitamins, and other substances. The amount of biological return is minimal. Choosing mixed forests is more conducive to increasing the soil’s nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium content than pure forests. (5) When maintaining forestland, retain an appropriate amount of surface litter to reduce the death of trees and soil erosion caused by inadequate maintenance and management in plain afforestation areas. (6) The BD in the southern and northeast areas of Tongzhou District is relatively large, which may be due to the compaction caused by frequent cultivation in cultivated land and human activities during the ecological restoration of forestland. Therefore, it is necessary to limit excessive reclamation and reduce forest development to avoid deterioration of soil structure. (7) Overall optimization of fertilizer use. Increasing the effectiveness of phosphorus in alkaline areas can adjust pH and improve the absorption efficiency of phosphorus fertilizers. (8) The TK content in the central area and northern area, the northeast area, and the southern part of the southern area is relatively high. The use of potassium fertilizers should be reduced to avoid excessive accumulation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, data curation, formal analysis, statistical analysis, visualization, writing—original draft, and editing, Y.Z.; formal analysis, investigation, data curation, statistical analysis, and visualization, S.L.; conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, investigation, data curation, reviewing and editing, project administration, supervision, and funding acquisition, X.L.; data curation, formal analysis, and statistical analysis, H.S.; reviewing and data curation, S.H.; investigation and data curation, X.Q., J.C., N.Z. and H.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Central Government Guides Local Funds for Science and Technology Development, grant number 236Z3304G, Biodiversity Survey and Assessment Project in Tongzhou District, Beijing (06TI02) and the Central University Basic Research Fund, grant number 3142023028.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author due to confidentiality and the need to protect sensitive research information.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Wen Chuanhui, Gao Wenwen, Liu Zhixuan, Su Yang, Yin Tenglei, Li Huan, and Yu Shiqi for their support in data organization and field investigation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Saha, J.K.; Selladurai, R.; Coumar, M.V.; Dotaniya, M.L.; Kundu, S.; Patra, A.K. Soil and its role in the ecosystem. In Soil pollution—An emerging threat to agriculture, Environmental Chemistry for a Sustainable World; Springer: Singapore, 2017; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Binkley, D.; Vitousek, P. Soil nutrient availability. In Plant Physiological Ecology: Field Methods and Instrumentation; Pearcy, R.W., Ehleringer, J.R., Mooney, H.A., Rundel, P.W., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1989; pp. 75–96. [Google Scholar]
- Schoenholtz, S.H.; Miegroet, H.V.; Burger, J.A. A review of chemical and physical properties as indicators of forest soil quality: Challenges and opportunities. For. Ecol. Manag. 2000, 138, 335–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, S.H.; Pollard, A.G. Determination of nitrogen in agricultural materials by the nessler reagent. II.—Micro-determinations in Plant Tissue and in Soil Extracts. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1954, 5, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawls, W.J.; Gish, T.J.; Brakensiek, D.L. Estimating Soil Water Retention from Soil Physical Properties and Characteristics. In Advances in Soil Science; Stewart, B.A., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1991; Volume 16, pp. 213–234. [Google Scholar]
- Delgado, A.; Gómez, J.A. The Soil, Physical, Chemical and Biological Properties. In Principles of Agronomy for Sustainable Agriculture; Villalobos, F.J., Fereres, E., Villalobos, F.J., Fereres, E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- Song, M.; Tang, Q.; Han, C.; Yuan, C.; Yang, Q.; Wei, J.; He, X.; Lv, X.; Collins, A.L. Divergent behaviour of soil nutrients imprinted by different land management practices in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2024, 12, 896–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Li, C.; Sokolwski, E.; Magen, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Zhou, J. Crop yield and soil available potassium changes as affected by potassium rate in rice-wheat systems. Field Crops Res. 2017, 214, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aye, H.N.; Masih, S. Role of Nutrients in Plants, Its Deficiency and Management. Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 2023, 35, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengel, Z. Soil pH, Soil Health and Climate Change. In Soil Health and Climate Change; Singh, B.P., Cowie, A.L., Chan, K.Y., Singh, B.P., Cowie, A.L., Chan, K.Y., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 69–85. [Google Scholar]
- Kavitha, S.; Kotadi, C. Soil nutrient prediction for paddy cultivation via soil fertility and pH trained hybrid architecture: Recommendations based on nutrient deficiency. Intell. Decis. Technol. 2024, 18, 685–703. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Gao, M.; Zexin, X.U.; Wang, J.; Xie, X. Hyper-spectral estimation of soil organic matter in apple orchard based on CWT. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; p. 734. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, W.; Li, Y.; Fu, W.; Jiang, P.; Zhao, K.; Li, Y.; Penttinen, P. Spatial variability of soil nutrients in forest areas: A case study from subtropical China. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2018, 181, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beijing Municipal Bureau of Landscaping and Landscaping. Notice of the Beijing Municipal Bureau of Landscaping and Landscaping on the Implementation Standard of the Expenses Required for “Restoration of Vegetation and Forestry Production Conditions”. 2020. Available online: https://yllhj.beijing.gov.cn/zwgk/fgwj/qtwj/202101/t20210121_2228701.shtml (accessed on 21 January 2021).
- Beijing Tongzhou District Forestry Work Station. Beijing Tongzhou District Forestry Work Station 2023 Budget Statement. 2023. Available online: https://www.bjtzh.gov.cn/bjtz/xxfb/202302/1639327.shtml (accessed on 6 November 2024).
- Margenot, A.J.; Singh, B.R.; Rao, I.M.; Sommer, R. Phosphorus fertilization and management in soils of Sub-Saharan Africa. In Soil Phosphorus; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 151–208. [Google Scholar]
- Guichao, Z.; Sun, X.; Li, S.; Yu, L.; Yue, Z.; Wang, C.; Wei, N.; Xu, X. Characteristics of soil organic carbon and its components in different green space types in Tongzhou District of Beijing, China. Acta Agric. Zhejiangensis 2023, 35, 1699–1708. [Google Scholar]
- Quanhe, Y.; Yonglong, A. Comprehensive Evaluation of Soil Fertility in Yujiawu Town of Tongzhou District Using Geostatistics and GIS. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 32, 882–891. [Google Scholar]
- Yonglong, A.; Zha, G.; Sun, X.; Li, S.; Yu, L.; Yue, Z.; Wang, C.; Wei, N.; Xu, X. Analysis of the Sources and Risk Assessment of PAHs in the Soil of a Reconstruction Area in Tongzhou, Beijing. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2017, 44, 112–120. [Google Scholar]
- Beijing Municipal Bureau of Agriculture and Rural Affairs. Beijing Tongzhou District Third National Soil Survey Pilot Achievement Rated as “Excellent”. 2023. Available online: https://nyncj.beijing.gov.cn/nyj/snxx/gzdt/436312830/index.html (accessed on 3 December 2024).
- Rui, Z. Spatial Variability of Soil Properties and Comprehensive Evaluation of Fertility of Cultivated Land in the Suburbs of Beijing; Beijing Forestry University: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Forster, J.C. Soil sampling, handling, storage and analysis. In Methods in Applied Soil Microbiology and Biochemistry; Alef, K., Nannipieri, P., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1995; pp. 49–121. [Google Scholar]
- Kara, D.; Özsavaşçi, C.; Alkan, M. Investigation of suitable digestion methods for the determination of total phosphorus in soils. Talanta 1997, 44, 2027–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Fu, M.J.; Liang, Y.J.; Guan, Z.Y.; Li, J.D. Soil Nitrogen Forms and Availability in Paddy Soil under Different Fertilization Methods. Adv. Mater. Res. 2015, 1073, 643–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, S.R.; Sommers, L.E. Estimation of Available Phosphorus in Soils by Extraction with Sodium Bicarbonate; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Surleva, A.; Angelova, L. Plant available potassium and phosphorus in arable soil: A comparative study on testing methods. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 1251, 012008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, T.N.; Ripley, D.A. On the relation between NDVI, fractional vegetation cover, and leaf area index. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 62, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viña, A.; Gitelson, A.A.; Nguy-Robertson, A.L.; Peng, Y. Comparison of different vegetation indices for the remote assessment of green leaf area index of crops. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 3468–3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.R. A soil-adjusted vegetation index (SAVI). Remote Sens. Environ. 1988, 25, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, J.; Huisman, J. The GDL Vulnerability Index (GVI). Soc. Indic. Res. 2024, 174, 721–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonenc, A.; Ozerdem, M.S.; Emrullah, A.C.A.R. Comparison of NDVI and RVI Vegetation Indices Using Satellite Images. In Proceedings of the 2019 8th International Conference on Agro-Geoinformatics (Agro-Geoinformatics), Istanbul, Turkey, 16–19 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanasundaram, S.; Baghel, T.; Thakur, V.; Udmale, P.; Shrestha, S. Reconstructing NDVI and land surface temperature for cloud cover pixels of Landsat-8 images for assessing vegetation health index in the Northeast region of Thailand. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 195, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Zhao, D.; Wu, S.; Dai, E.; Gao, J. Using the NDVI to analyze trends and stability of grassland vegetation cover in Inner Mongolia. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2019, 135, 1629–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostan, P. Basic kriging methods in geostatistics. Yuz. Yıl Univ. J. Agric. Sci. 2017, 27, 10–20. [Google Scholar]
- Asuero, A.G.; Sayago, A.; González, A.G. The Correlation Coefficient: An Overview. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2006, 36, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, R.; Xia, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, C.; Zhang, R.; Fan, Z.; Chen, F.; Liu, Y. Interactions between N, P and K fertilizers affect the environment and the yield and quality of satsumas. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2019, 19, e00663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; He, N.; Wang, Q.; Lü, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, J. Effects of Temperature and Moisture on Soil Organic Matter Decomposition Along Elevation Gradients on the Changbai Mountains, Northeast China. Pedosphere 2016, 26, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, T.; Liu, K.; Wang, L.; Wang, K.; Zhou, Y. Effects of different amendments for the reclamation of coastal saline soil on soil nutrient dynamics and electrical conductivity responses. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 159, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismayilov, A.I.; Mamedov, A.I.; Fujimaki, H.; Tsunekawa, A.; Levy, G.J. Soil Salinity Type Effects on the Relationship between the Electrical Conductivity and Salt Content for 1:5 Soil-to-Water Extract. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, G.S. Soil Organic Matter: A Link Between Forest Management and Productivity; American Society of Agronomy, Crop Science Society of America, and Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1995; pp. 419–435. [Google Scholar]
- Pankhurst, C.E.; Ophel-Keller, K.; Doube, B.M.; Gupta, V.V.S.R. Biodiversity of soil microbial communities in agricultural systems. Biodivers. Conserv. 1996, 5, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, T.B.; Gonçalves, M.C.; Branco, M.A.; Brito, D.; Rodrigues, S.; Sánchez-Pérez, J.M.; Sauvage, S.; Prazeres, Â.; Martins, J.C.; Fernandes, M.L.; et al. Sediment and nutrient dynamics during storm events in the Enxoé temporary river, southern Portugal. Catena 2015, 127, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.; Stewart, B.; Yong, W.; Junjie, L.; Guangye, Z. Long-term fertilization effects on grain yield, water-use efficiency and soil fertility in the dryland of Loess Plateau in China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 106, 313–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Sun, W.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, J.; Yang, R.; Zou, Z.; Ding, F.; Su, J. Temporal and spatial variability of soil organic matter and total nitrogen in an agricultural ecosystem as affected by farming practices. Geoderma 2007, 139, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alt, F.; Oelmann, Y.; Herold, N.; Schrumpf, M.; Wilcke, W. Phosphorus partitioning in grassland and forest soils of Germany as related to land-use type, management intensity, and land use–related pH. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2011, 174, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gu, Z.; Shao, H.; Zhou, F.; Peng, S. N–P stoichiometry in soil and leaves of Pinus massoniana forest at different stand ages in the subtropical soil erosion area of China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordán, M.M.; Navarro-Pedreno, J.; García-Sánchez, E.; Mateu, J.; Juan, P. Spatial dynamics of soil salinity under arid and semi-arid conditions: Geological and environmental implications. Environ. Geol. 2004, 45, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Sabagh, A.; Hossain, A.; Barutçular, C.; Iqbal, M.A.; Islam, M.S.; Fahad, S.; Sytar, O.; Çiğ, F.; Meena, R.S.; Erman, M. Consequences of Salinity Stress on the Quality of Crops and Its Mitigation Strategies for Sustainable Crop Production: An Outlook of Arid and Semi-arid Regions. In Environment, Climate, Plant and Vegetation Growth; Fahad, S., Sytar, O., Çiğ, F., Meena, R.S., Erman, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 503–533. [Google Scholar]
- Gent, J.A.; Ballard, R. Impact of Intensive Forest Management Practices on the Bulk Density of Lower Coastal Plain and Piedmont Soils. South. J. Appl. For. 1985, 9, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathirana, S.; Lambot, S.; Krishnapillai, M.; Cheema, M.; Smeaton, C.; Galagedara, L. Integrated ground-penetrating radar and electromagnetic induction offer a non-destructive approach to predict soil bulk density in boreal podzolic soil. Geoderma 2024, 450, 117028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.; Yuan, S.; Chen, D.; Kang, Y.; Shaghaleh, H.; Okla, M.K.; AbdElgawad, H.; Hamoud, Y.A. Changes in salinity and vegetation growth under different land use types during the reclamation in coastal saline soil. Chemospher 2024, 366, 143427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, M.; Eisenhauer, N.; Sierra, C.A.; Bessler, H.; Engels, C.; Griffiths, R.I.; Mellado-Vázquez, P.G.; Malik, A.A.; Roy, J.; Scheu, S.; et al. Plant diversity increases soil microbial activity and soil carbon storage. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veresoglou, S.D.; Voulgari, O.K.; Sen, R.; Mamolos, A.P.; Veresoglou, D.S. Effects of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Fertilization on Soil pH-Plant Productivity Relationships in Upland Grasslands of Northern Greece. Pedosphere 2011, 21, 750–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rorison, I.H. The Effects of Soil Acidity on Nutrient Availability and Plant Response. In Effects of Acid Precipitation on Terrestrial Ecosystems; Hutchinson, T.C., Havas, M., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1980; pp. 283–304. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Liu, C.; Liang, C.; Wang, T.; Tian, J. The Phosphorus-Iron Nexus: Decoding the Nutrients Interaction in Soil and Plant. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, A.E. Prospects for using soil microorganisms to improve the acquisition of phosphorus by plants. Funct. Plant Biol. 2001, 28, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Parent, L.E.; MacLeod, J.A. Influence of soil texture on fertilizer and soil phosphorus transformations in Gleysolic soils. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2003, 83, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magid, J.; Tiessen, H.; Condron, L.M. Chapter 11—Dynamics of Organic Phosphorus in Soils under Natural and Agricultural Ecosystems. In Humic Substances in Terrestrial Ecosystems; Piccolo, A., Ed.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. 429–466. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, T. Effects of potassium on cell elongation and division in plants. J. Plant Physiol. 2007, 294, 294–298. [Google Scholar]
- Mazur, P.; Gozdowski, D.; Wnuk, A. Relationships between Soil Electrical Conductivity and Sentinel-2-Derived NDVI with pH and Content of Selected Nutrients. Agronomy 2022, 12, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naher, N.; Zannat, J.S.; Sharna, J.J. Detection of vegetation cover change in the Southern region of Bangladesh using the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) and Climate Smart Agriculture (CSA) practices. J. Appl. Nat. Sci. 2024, 16, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dam, R.; Mehdi, B.; Burgess, M.; Madramootoo, C.; Mehuys, G.; Callum, I. Soil bulk density and crop yield under eleven consecutive years of corn with different tillage and residue practices in a sandy loam soil in central Canada. Soil Tillage Res. 2005, 84, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanuzzaman, M.; Bhuyan, M.H.M.B.; Nahar, K.; Hossain, M.S.; Mahmud, J.A.; Hossen, M.S.; Masud, A.A.C.; Moumita Fujita, M. Potassium: A vital regulator of plant responses and tolerance to abiotic stresses. Agronomy 2018, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaitán, J.J.; Bran, D.; Oliva, G.; Ciari, G.; Nakamatsu, V.; Salomone, J.; Ferrante, D.; Buono, G.; Massara, V.; Humano, G.; et al. Evaluating the performance of multiple remote sensing indices to predict the spatial variability of ecosystem structure and functioning in Patagonian steppes. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 34, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).