Abstract
Spatial analysis is essential to understand the spreading of the COVID-19 pandemic. Due to numerous factors of multi-disciplines involved, the current pandemic is yet fully known. Hence, the current study aimed to expand the knowledge on the pandemic by exploring the roles of forests and CO2 emission in the COVID-19 case-fatality rate (CFR) at the global level. Data were captured on the forest coverage rate and CO2 emission per capita from 237 countries. Meanwhile, extra demographic and socioeconomic variables were also included to adjust for potential confounding. Associations between the forest coverage rate and CO2 emission per capita and the COVID-19 CFR were assessed using spatial regression analysis, and the results were further stratified by country income levels. Although no distinct association between the COVID-19 CFR and forest coverage rate or CO2 emission per capita was found worldwide, we found that a 10% increase in forest coverage rates was associated with a 2.37‰ (95%CI: 3.12, 1.62) decrease in COVID-19 CFRs in low-income countries; and a 10% increase in CO2 emission per capita was associated with a 0.94‰ (95%CI: 1.46, 0.42) decrease in COVID-19 CFRs in low-middle-income countries. Since a strong correlation was observed between the CO2 emission per capita and GDP per capita (r = 0.89), we replaced CO2 emission with GDP and obtained similar results. Our findings suggest a higher forest coverage may be a protective factor in low-income countries, which may be related to their low urbanization levels and high forest accessibilities. On the other hand, CO2 can be a surrogate of GDP, which may be a critical factor likely to decrease the COVID-19 CFR in lower-middle-income countries.
1. Introduction
At the end of 2019, a newly emerging virus, later known as SARS-CoV-2 or COVID-19, was spotted in China, which has unexpectedly started a global pandemic [1,2]. The novel virus is a sister clade to the previous SARS-CoV [3], less fatal [4] but more contagious [5]. As of February 2022, nearly 400 million confirmed cases and more than five million deaths were recorded globally [6], indicating the great impact of the pandemic on global public health.
In the past two years, numerous studies have been conducted on COVID-19, and those with spatial analysis may play an essential role in understanding the pandemic [7,8,9] because spatial spreading is a primary characteristic of all infectious diseases. Spatial methods have contributed to uncovering the relationships between the COVID-19 case-fatality rate (CFR) and sociodemographic or environmental factors, such as unemployment rate [10,11], commuting flows [12], and environmental pollution (e.g., NO2 and particulate matter) [13,14]. Although many factors have been identified, the COVID-19 pandemic is still full of unknowns because various factors were involved, and their joint influence may be complex [15]. Therefore, it is recommended to incorporate more variables of different kinds and disciplines to understand the COVID-19 phenomenon [16].
Forest is an ecological environment that provides mental and physical restoration resources during the COVID-19 pandemic [17], which may also help enhance the immune functions of visitors to fight against the disease [18]. Numerous studies have found negative associations between greenness and mortality rate [19,20,21]. Some recent studies have reported negative associations between green space coverage and COVID-19 CFRs, and air pollution reduction and immunoregulation are assumed to be potential reasons behind this [22,23,24]. However, most relevant studies did not focus on forests, and their data were only captured from one or several countries or regions. Therefore, the role of forests on the COVID-19 CFR requires further investigation.
CO2 emission is a common ecological variable that is associated with climate change. During the COVID-19 pandemic, numerous studies were conducted concerning the role of harmful gas in the pandemic. For example, ozone, nitrogen dioxide, carbon monoxide, formaldehyde, and PM 2.5 have been reported to associate with higher COVID-19 infection or fatality rates [25,26]. In contrast, fewer studies have focused on the relationship between CO2 emissions and COVID-19 CFRs, and the mechanisms are unclear [27,28]. CO2 emission may affect health expenditure and is also a reflection of the social lockdown/blockade [29,30], therefore worth more attention.
Ecological studies collect and analyze data at the population level, which are convenient and inexpensive, and help identify ecological or environmental factors that are associated with infectious diseases. The aims of ecological studies include monitoring population health so that public health strategies may be developed, making large-scale comparisons between countries and regions, studying the relationship between population-level exposure to risk factors and health outcomes, or looking at the contextual effect of risk factors on the population [31]. Although other study designs are generally considered more reliable, particularly in the inference of causation, the population contexts have been shown to be stronger determinants of disease at the population level than individual-level risk factors [31]. Therefore, we aimed to examine the associations between COVID-CFRs and forests and CO2 emissions worldwide while controlling socioeconomic factors’ potential confounding using country-level data. Our study may explore ecological factors that may help monitor, predict, and mitigate the pandemic.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
The data on the forest coverage rate by country were obtained from the World Bank [32]. The data providers include the Food Agriculture Organization, electronic files, and websites. Moreover, the data on the forest area per capita were also obtained from the Worldometer websites [33]. The data providers include the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, the United Nations Population Division, the United Nations Statistics Division, and the World Bank. The data on the CO2 emission by country were obtained from the Emission Database for Global Atmospheric Research, European Commission [34]. Following the latest update released in October 2021, CO2 emission data are now available for each country for the time period between 1970 and 2020.
The COVID-19 data included in this study were obtained from the Our World in Data website [35], a collection of the COVID-19 data maintained by the organization Our World in Data and updated daily. The dataset includes country-level daily data on confirmed cases, deaths, testing, and other variables of potential interest. There are 67 variables from 237 countries and territories in the dataset by 6 December 2021.
According to the ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 code for spatial modeling, the datasets were linked together using the global geospatial vector database. Variables with missing values in more than 70% of countries were excluded.
In total, 27 variables were included in the final analysis of the presented study. They are: country, country’s geographic variables/information (shape, location, longitude, and latitude of the centroid), forest coverage rate (in percentage of land area), forest area per capita, CO2 emission per capita, total reported COVID-19 cases, total confirmed COVID-19 deaths, population, population density, gross domestic product (GDP) per capita, cardiovascular diseases (CVD) death rate, diabetes prevalence, stringency index of government’s response to the COVID-19 pandemic (a composite measure based on 9 response indicators, including school closures, workplace closures, and travel bans, rescaled to a value from 0 to 100 with 100 = strictest response) [36], total tests for COVID-19, total vaccinations for COVID-19, life expectancy, median age of the population, percentage of population aged 65 years or older, percentage of population living in extreme poverty, percentage of female smokers, percentage of male smokers, hospital beds, percentage of population with basic handwashing facilities, and the human development index.
The study used data from publicly available worldwide databases, so it was not required and not possible to involve patients or the public in the design, conduct, reporting, or dissemination plans of our research. Hence, ethical approval is not applicable.
The study was conducted under the Guidelines for Accurate and Transparent Health Estimates Reporting (GATHER) statement [37].
2.2. Case-Fatality Rate (CFR)
The CFR of COVID-19 was defined as the number of total deaths due to COVID-19 divided by the number of confirmed COVID-19 cases by 6 December 2020 and multiplied by 1000. The CFR was selected for our study, as it may reflect disease severity and the efficiency of treatment and healthcare response, and strain [38]. Furthermore, the CFR is not constant, which can vary between populations and timeframes, and may depend on the interplay between the causative agent of the disease, the host, the environment, available treatments, and the quality of patient care. For instance, it can increase if the healthcare system collapses due to a sudden increase in cases [39]. The CFR in the current study is a crude rate without adjusting for age and sex due to no more detailed age/sex data available worldwide.
2.3. Statistical Analyses
Descriptive statistics (e.g., mean, standard deviation, median, minimum, maximum, and interquartile range (IQR)) were calculated for the variables.
Linear correlations between the variables were examined with Pearson’s correlation coefficient [40]. Spatial autocorrelation (or dependence) is the relationship between spatial proximity in observational units and similarity among their values. Positive spatial autocorrelation refers to situations in which the nearer the observational units mean more similar values (and vice versa for its negative counterpart) [41]. This feature violates the assumption of independence among observations to be included in regression analyses. Spatial autocorrelation among the COVID-19 CFRs of the investigated countries was tested using a multivariate linear regression model and the Moran’s I test [42]. The autocorrelation was visualized with the aid of the Matérn correlation coefficient [43].
Matérn correlation models were employed to check the relationship between the COVID-19 CFR and the ecological and socioeconomic variables. The latitude and longitude of the centroid of the countries were included as random effects in the Matérn correlation models [44].
Spearman’s correlation was employed to probe for general patterns of associations within the core variables (forest, CO2 emission, and COVID-19 CFR). Skewed variables were log-transformed before linear correlation or regression analysis. The multiple imputation method was employed to handle the missing values in the data (the missing values were assumed to be missing at random). A total of ten copies of the data were created, and each of the complete datasets was analyzed independently. Estimates of parameters of interest were then averaged across the ten copies to create a single estimate according to Rubin’s rule [45].
Given the associations might differ by economic level, we also stratified the analyses by income levels of the countries defined by the World Bank [46].
The associations of the investigated ecological and socioeconomic variables with the COVID-19 CFR were presented as changes in the COVID-19 CFR per 10% increase in the ecological and socioeconomic variables. The corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CI) were also provided. An association with a p-value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
All the analyses were performed in R V.4.1.2 (the R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria) using the package spaMM [47], and in Python V.3.7 (Python Software Foundation) using the packages geopandas and geoplot [48].
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Characteristics of the Variables
In total, 264,861,480 reported COVID-19 cases and 5,255,849 confirmed deaths related to COVID-19 between 1 January 2020 and 6 December 2021, from 194 countries were included in the study. The descriptive statistics of the variables are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Descriptive statistics of the variables.
Regarding the outcome and main factors of interests, we found a strong correlation between the COVID-19 CFR and CO2 emission per capita (spearman ρ = −0.37, p < 0.001). However, we did not observe a distinct linear correlation between the COVID-19 CFR and forest coverage rate (spearman ρ = 0.01, p = 0.859) or forest area per capita (spearman ρ = 0.07, p = 0.314) (Figure 1).

Figure 1.
The relationships between forest coverage rage, CO2 emission per capita, and COVID-19 CFR. Note: the solid line indicates significant linear correlation (p < 0.05); the dotted lines indicate non-significant linear correlation (p > 0.05).
In the linear correlation analysis for log-transformed variables (Supplemental Figure S1), high linear correlations were found between the forest coverage rate and forest area per capita (r = 0.70, p < 0.001); between CO2 emission per capita and GDP per capita (r = 0.89, p < 0.001), the median age of the population (r = 0.76, p < 0.001), percentage of the population living in extreme poverty (r = −0.83, p < 0.001), percentage of the population with basic handwriting facilities (r = 0.80, p > 0.001), and the human development index (r = 0.87, p < 0.001); and between life expectancy and the percentage of the population aged 65 years or older (r = 0.85, p < 0.001), therefore, forest area per capita, GDP per capita, median age of the population, percentage of population aged 65 years or older, percentage of the population living in extreme poverty, percentage of the population with basic handwriting facilities, and the human development index were excluded in later regression analysis.
3.2. Worldwide Distributions of Forest, CO2 Emission, and COVID-19 CFR
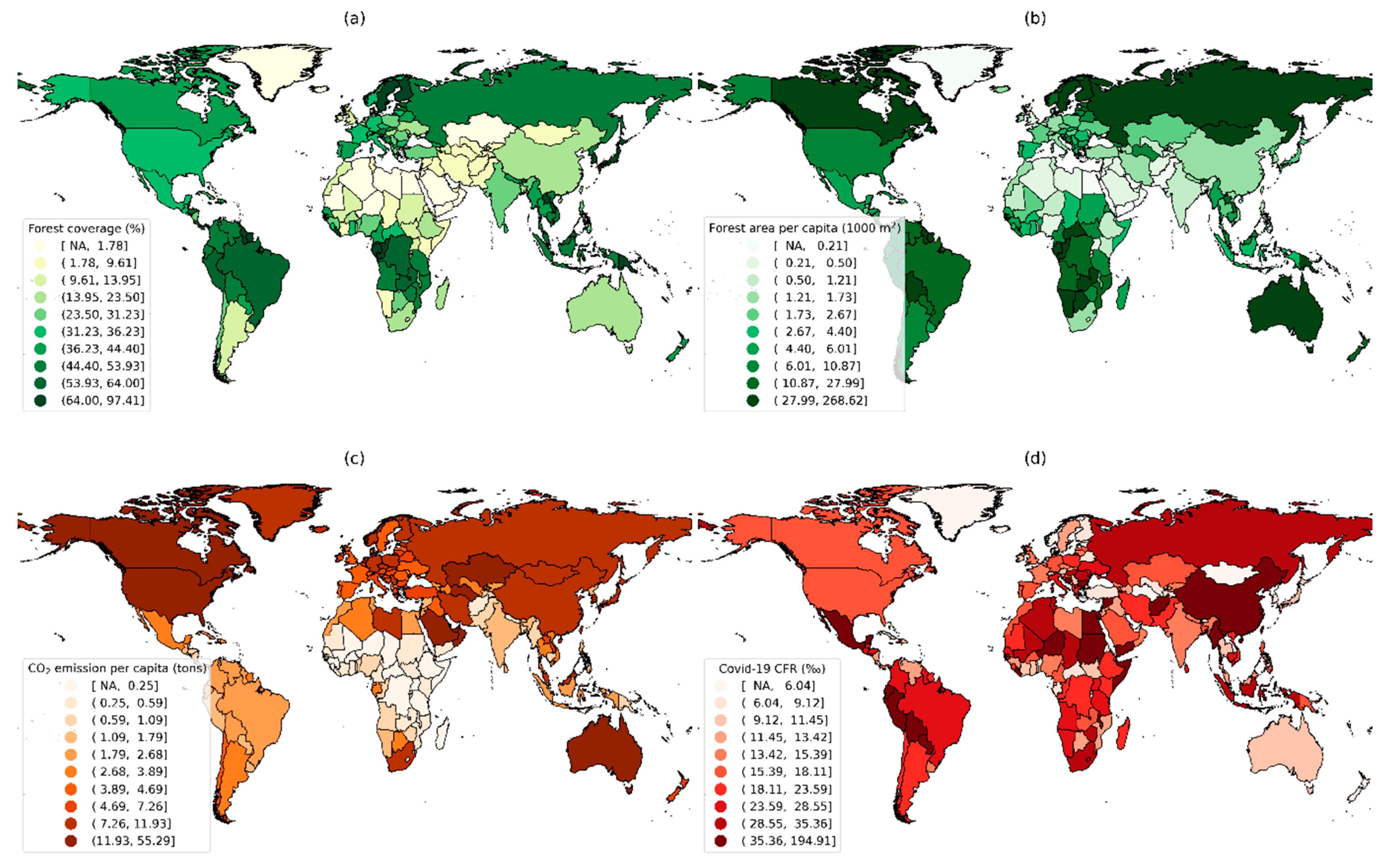
Distributions of forest coverage rate and area per capita, CO2 emission per capita, and COVID-19 CFRs of the countries with data available are shown in Figure 2. The highest values for the forest coverage rate and area per capita were found in North America, northern Europe, northern South America, and southern Africa; for CO2 emissions per capita, in North America, Western Europe, the Middle East, and Australia; for the COVID-19 CFR, in southern North America, western South America, northern Africa, and eastern Asia.
Figure 2.
Global distribution of (a) forest coverage rate, (b) forest area per capita, (c) CO2 emission per capita, and (d) COVID-19 CFR. CFR: case-fatality rate. NA: not available.
3.3. Spatial Autocorrelation of the COVID-19 CFR
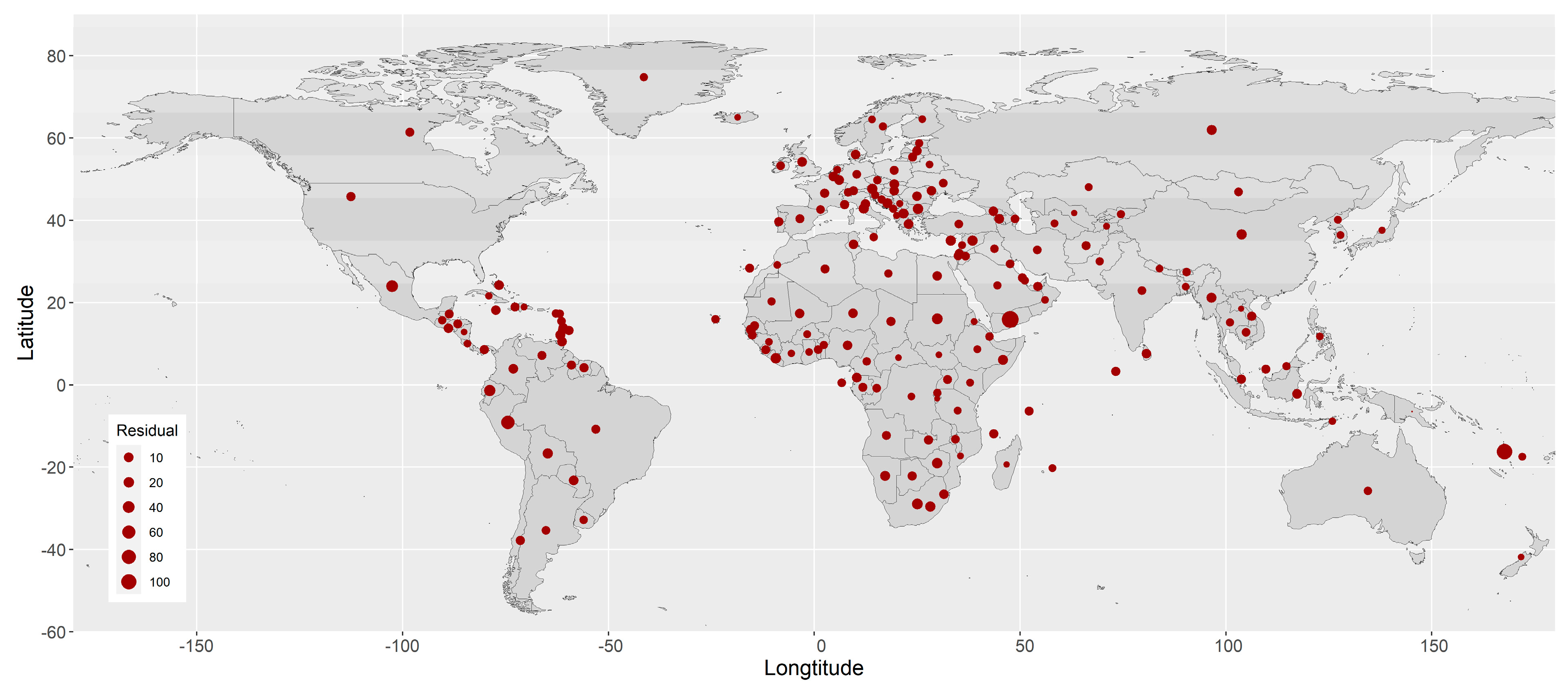
The residuals of the COVID-19 CFR from the common (non-spatial) multivariate linear regression model show apparent spatial dependence among the countries/territories (Figure 3). The p-value from Moran’s I test for the spatial autocorrelation of the residuals is 0.021.
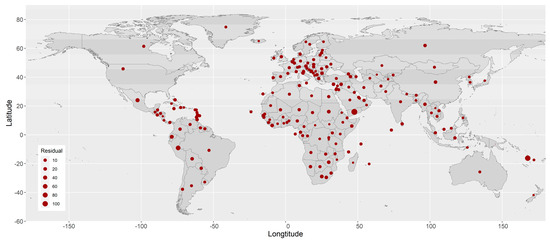
Figure 3.
Residuals from the common (non-spatial) multivariate linear regression model.
The estimated spatial autocorrelation coefficient of the COVID-19 CFR between two locations against their distance is shown in Supplemental Figure S2, with a strength parameter ν = 10.33 and a decay parameter ρ = 0.89. Basically, the autocorrelation coefficient is smaller than 0.5 if the distance between a pair of locations is larger than 6.2° in terms of the difference between their longitudes or latitudes. The ranges of longitude and latitude are (−177.1508°, 178.5574°) and (−54.4881°, 78.8286°), respectively. (Supplemental Figure S2).
3.4. Association of Ecological and Socioeconomic Variables with COVID-19 CFR
After controlling for the spatial dependence, the multivariable-adjusted associations of the investigated ecological variables (i.e., forest coverage rate and CO2 emission per capita) and socioeconomic variables are presented as changes in the COVID-19 CFR per 10% increase in the variables in Table 2.

Table 2.
Changes in COVID-19 CFR (‰) per 10% increase in the ecological and socioeconomic variables.
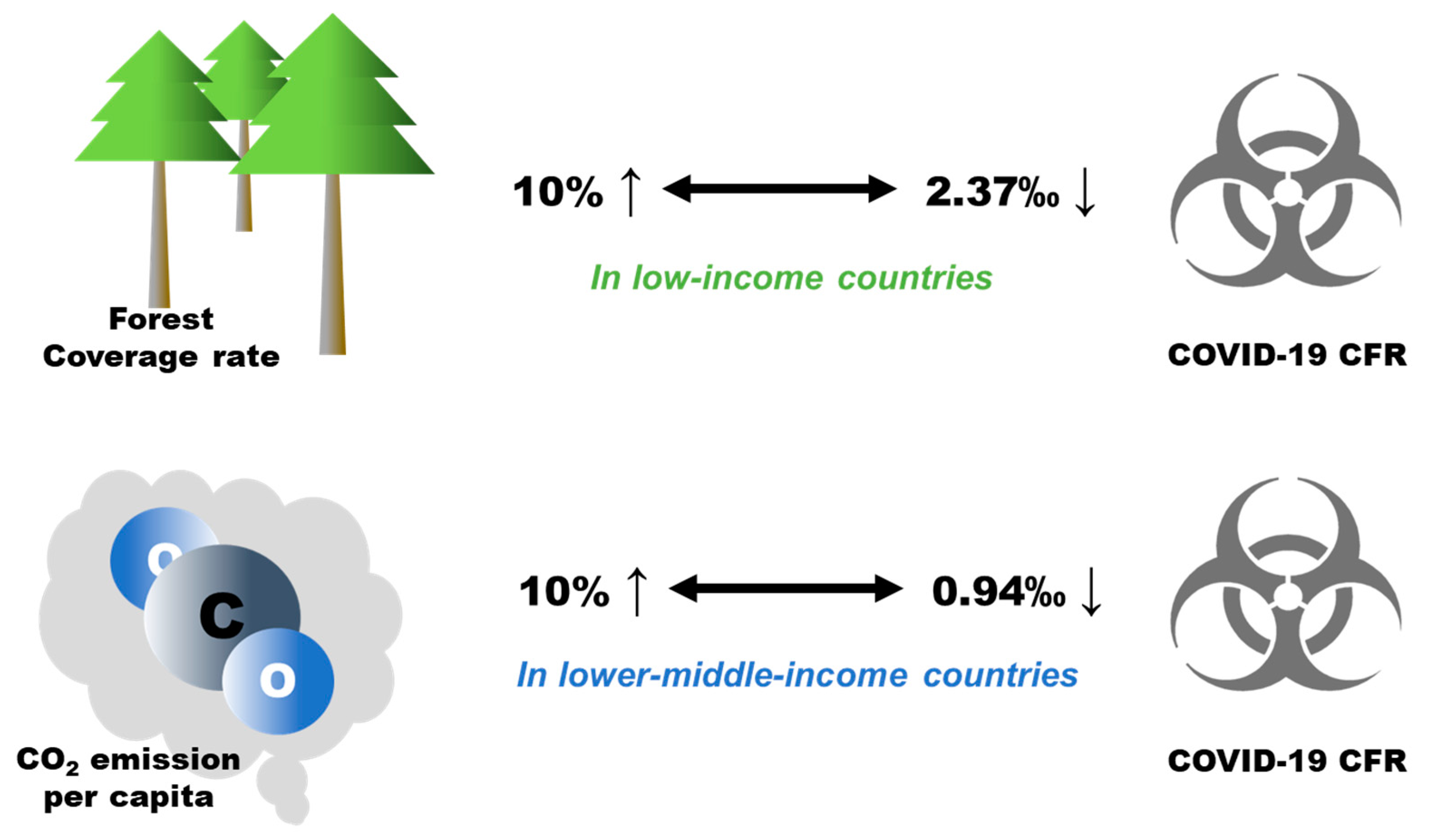
Worldwide, no statistically significant associations of forest coverage rate or CO2 emission per capita with COVID-19 CFRs were found. However, the stratified results by economic level of the countries indicate that per 10% increase in forest coverage rate was associated with a 2.37‰ (95%CI: 1.62–3.12‰) decrease in the COVID-19 CFR in low-income countries, and per 10% increase in CO2 emission per capita was associated with a 0.94‰ (95%CI: 0.42–1.46‰) decrease in the COVID-19 CFR in lower-middle-income countries (Figure 4).
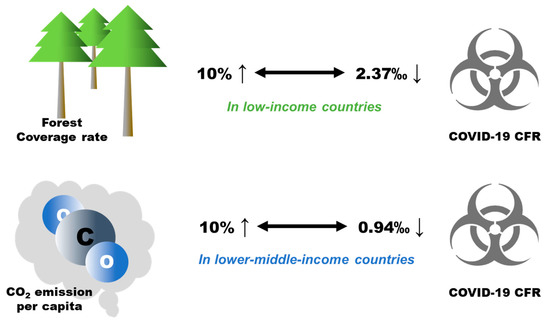
Figure 4.
The stratified analyses on associations between forest coverage rate, CO2 emission per capita, and COVID-19 CFR.
Regarding the socioeconomic variables, life expectancy and the CVD death rate were associated with 0.12‰ (95%CI: 0.04–0.20‰) and 1.05‰ (95%CI: 0.12–1.98‰) increases in the COVID-19 CFR, respectively, and the stringency index was associated with a 0.80‰ (95%CI: 0.51–1.09‰) decrease in the COVID-19 CFR worldwide (Table 2).
In low-income countries, besides the forest coverage rate, female smokers and COVID-19 vaccinations were associated with increased (2.14‰: 95%CI: 1.64–2.65‰) and decreased (−2.37‰; −3.12–−1.62‰) COVID-19 CFRs, respectively.
In lower-middle-income countries, total population and population density were associated with decreased (−0.94‰: 95%CI: −1.46–−0.42‰) and increased (0.33‰; 0.08–0.57‰) COVID-19 CFRs, respectively.
In upper-middle-income countries, only the stringency index was associated with a decreased (−0.95‰: 95%CI: −1.50–−0.41‰) COVID-19 CFR.
In high-income countries, female smokers and CVD death rates were associated with increased COVID-19 CFRs, with increments of 0.32‰ (95%CI: 0.12–0.51‰) and 1.01‰ (95%CI: 0.56–1.49‰), respectively; and the stringency index was associated with a decreased (−0.36‰ (95%CI: −0.49–0.23‰) COVID-19 CFR.
4. Discussion
This study examined the association between COVID-19 CFRs and forest or CO2. Although no general patterns were observed at the global level, some notable results were observed in specific countries. Our findings imply the indicative functions of forests and CO2 emission in the global pandemic. We could not provide solid mechanisms for explaining the observed phenomenon due to our study design. Nevertheless, we have tried to propose some potential clues or reasons to help understand the findings, which are presented in the following sections.
4.1. Forest Coverage and COVID-19 CFR
The current study included forest coverage rate and forest area per capita to indicate forest resources. The global analysis did not reveal a statistically significant association between the COVID-19 CFR and any of the forest variables. This result is inconsistent with a previous study where a dose-response association was spotted between green space and a reduced risk of COVID-19 mortality among counties in the USA from January to July 2020 [23]. However, another study reported that greenness was not associated with COVID-19 mortality in all counties in the USA [49]. These differences may come from different measures for the “natural environment” (leaf area index for the previous study), statistical methods, and spatiotemporal frameworks employed for analysis. The null effect we observed indicates that the role of and measures for “exposure to nature” should be considered cautiously. Currently, global urbanization has gathered most of the population into cities [50]. However, most forest areas are outside cities, especially in highly urbanized countries. Since distance strongly affects green space utilization [51,52], urban green spaces within or around cities may be the most popular and accessible type of natural environment for urban residents during the pandemic [53]. Thus, the forest variables calculated based on national forest area may not necessarily indicate the actual utilization or exposure to natural environments among residents in urbanized countries.
In the analysis stratified by income, we found that both the forest coverage rate and forest area per capita (Supplemental Table S1) were associated with decreased COVID-19 CFRs in low-income countries. Previous studies have speculated on some mechanisms to understand the decreased COVID-19 CFR, such as pollution reduction, physical activity promotion, and immunoregulation induced by microorganisms in natural environments [22,23,54]. However, these mechanisms did not consider low-income countries, and they cannot explain the discrepancies among countries with different income levels. As discussed above, the accessibility of forests may be a problem in urbanized countries. In contrast, those low-income countries are less urbanized due to being highly reliant on agriculture [55], and more residents are distributed in rural areas, such as living in small villages and small towns. Therefore, the residents in low-income countries may live closer to natural environments than residents in urbanized countries. According to Pichlerová, M., D. Önkal, A. Bartlett, J. Výbošťok, and V. Pichler [17], forest coverage rate and settlement size are both factors of forest accessibility. A higher forest coverage and a smaller settlement size both indicate more forest visits. Therefore, for residents scattered in rural areas, a higher forest coverage rate may imply a greater chance of forest visits. In addition to physically entering forests, forests around neighborhoods may also benefit them remotely. For example, a recent study in Italy found that the percentage of COVID-19 deaths was lower in greener areas when compared to the regions with low forest coverage [56]. The phenomenon, explained by the author, might partially result from non-deciduous Mediterranean plants, which emit volatile immunomodulatory and antiviral compounds. These volatile biogenic compounds are likely to benefit local residents and reduce COVID-19 CFRs [18]. According to the classification of the World Bank, most of the low-income countries are in tropical or subtropical Africa, where the climate is mild, and evergreen forests play a dominant role. Therefore, residents in low-income countries may have more chances to be affected by forests in their residential neighborhoods.
4.2. CO2 Emission and COVID-19 CFR
We did not observe a distinct association between CO2 emission per capita and COVID-19 CFRs worldwide, which is inconsistent with a recent study, where data from 119 countries or regions indicated a nonlinear relationship between the CFR and CO2 emission [27]. Some points may explain the inconsistency, such as the differences in countries or regions included, dates of data access, and the measures for CO2 emission (per capita vs. per country). Nevertheless, our results may, to a certain extent, challenge the view that CO2 emission is a critical factor likely to increase total coronavirus cases and death rates [27].
Aside from being a common environmental indicator [57], CO2 emission may somewhat reflect economic conditions, as economic growth mostly depends on the consumption of energy resources [58]. For example, many studies have suggested the potential relationship between CO2 emissions and GDP [59]. A recent study on COVID-19 has underlined the method of estimating the changes in CO2 emission with the aid of GDP when detailed energy activity data are unavailable [60]. In the current study, we also observed a strong positive correlation between the GDP per capita and CO2 emission (r = 0.89), implying that CO2 emission may be a surrogate of GDP. For this reason, we conducted a sensitivity analysis, which includes GDP (per capita) instead of CO2 emission in the model. We did not observe a distinct association between the GDP per capita and COVID-19 CFR in the global analysis either (Supplemental Table S2), suggesting that GDP might not be a critical factor associated with the COVID-19 CFR worldwide. This finding appears counter-intuitive, as GDP is associated with financial resources for health protection [29]. However, we should realize that pressures on medical and public health services due to COVID-19 varied among countries. For well-developed countries, such as Japan, healthcare services were affordable, and the medical system has remained functional throughout [61]. Therefore, other factors may play dominant roles in well-developed countries, such as age structure [62,63], which may mask the role of GDP in fighting the COVID-19 pandemic globally.
In the analysis stratified by income level, we found that CO2 emission was associated with a decreased COVID-19 CFR in lower-middle-income countries, and the association remained statistically significant in the sensitivity analysis when CO2 emission was replaced with GDP per capita (Supplemental Tables S2 and S3). This result is not surprising, given the reasons mentioned above. Compared to upper-middle and high-income countries, where medical and infrastructure resources are usually sufficient [64], lower-middle-income countries are more vulnerable to the pandemic [65], especially developing countries with poor economic conditions [66]. Therefore, a better economic condition may be more critical for lower-middle-income countries to fight against the pandemic.
In addition, the association between GDP and the COVID-19 CFR in low-income countries was ambiguous when the model was loaded with different forest variables (Supplemental Tables S2 and S3). We cannot conclude if GDP is an essential factor for low-income countries. Theoretically, they may face a similar crisis to lower-middle-income countries because resource shortage has also been reported as a common issue in low-income countries [64]. Further studies are warranted to check their differences.
4.3. Limitations
There are several notable limitations to the current study. First, to indicate the typical natural environment worldwide, we used forest coverage rate and forest area per capita in the analysis. As discussed above, these measures may not necessarily indicate a potential exposure to nature. There is not a satisfactory measure to indicate the actual exposure to natural environments at a worldwide level. Even if the results were limited to the residential areas, common measures such as the normalized difference vegetation index or enhanced vegetation index may not explore the properties of natural environments, as well as their qualities, accessibility, and availability [67]. Future studies may refer to the data of population mobility, such as location reports of smartphone applications, and incorporate it with green space indicators to quantify actual green space usage.
Second, there is no globally accepted definition of a COVID-19-related death. Thus, reporting bias cannot be ruled out. Moreover, given the fact that medical standards can vary with regions, it is not clear if some low-income countries can effectively report COVID-19-related deaths. Thus, their CFR values may be underestimated.
Third, though we tried to access the latest data worldwide, there are some discrepancies in their timeframes. Due to the impact of COVID-19, the patterns of CO2 emissions may be changed with time and region. Therefore, the identified relationships may need re-examination in further work.
5. Conclusions
This study aimed to examine the roles of forest and CO2 emission on COVID-19 CFRs while controlling known confounders. We conducted a spatial analysis that included worldwide-level data obtained from public access databases. Although we did not observe a distinct association between the COVID-19 CFR and forest coverage rate or forest area per capita worldwide, we found that the forest coverage rate and forest area per capita were associated with lower COVID-19 CFRs in low-income countries, which is preliminarily speculated to be related to their lower urbanized levels.
On the other hand, we did not find a distinct association between CO2 emissions per capita and COVID-19 CFRs at the worldwide level either. Nevertheless, we found that CO2 emissions per capita were associated with lower CFRs in lower-middle-income countries. Notably, we assumed that CO2 emission might be a surrogate of GDP as they showed a strong correlation. Similar results were obtained when we replaced the CO2 emission per capita with GDP per capita in the regression. These findings suggest that economic conditions may be a critical factor for lower-middle-income countries to fight against the current pandemic.
Generally, our findings suggest that forest and CO2 emissions are two potential ecological factors that may help to monitor and predict the global pandemic. Given the limitation of the public access data, further research is warranted to uncover the mechanisms behind the associations.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/f13050736/s1, Figure S1: Pairwise scatter plots and Pearson’s correlation coefficients of the independent variables; Figure S2: Strength and decay of the spatial autocorrelation between pair of locations: Table S1: Changes in COVID-19 CFR (‰) per 10% increase in the ecological and socioeconomic variables (including forest area per capita instead of forest cover); Table S2: Changes in COVID-19 CFR (‰) per 10% increase in the ecological and socioeconomic variables (including GDP per capita instead of CO2 emission per capita); Table S3: Changes in COVID-19 CFR (‰) per 10% increase in the ecological and socioeconomic variables (including GDP per capita instead of CO2 emission per capita; and forest area per capita instead of forest cover).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.C.; methodology, Y.C.; data curation, Y.C.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.C. and H.L.; writing—review and editing, Y.C. and H.L.; supervision, Y.C. and G.Z.; project administration, Y.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cucinotta, D.; Vanelli, M. WHO Declares COVID-19 a Pandemic. Acta Biomed. Atenei Parm. 2020, 91, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. COVID-19 Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC) Global Research and Innovation Forum. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/covid-19-public-health-emergency-of-international-concern-(pheic)-global-research-and-innovation-forum (accessed on 2 February 2022).
- Gorbalenya, A.E.; Baker, S.C.; Baric, R.S.; de Groot, R.J.; Drosten, C.; Gulyaeva, A.A.; Haagmans, B.L.; Lauber, C.; Leontovich, A.M.; Neuman, B.W.; et al. The species Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: Classifying 2019-nCoV and naming it SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Ji, F.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Hao, J.; Dai, M.; Liu, Y.; Pan, X.; Fu, J.; Li, L.; et al. Asymptomatic and Human-to-Human Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in a 2-Family Cluster, Xuzhou, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1626–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, Y.; Xia, E.; Fareed, Z.; Hashmi, S.H. Time–Frequency co-movement between COVID-19, crude oil prices, and atmospheric CO2 emissions: Fresh global insights from partial and multiple coherence approach. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 9397–9417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worldometer. COVID-19 CORONAVIRUS PANDEMIC. Available online: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/ (accessed on 2 February 2022).
- Wang, Q.; Dong, W.; Yang, K.; Ren, Z.; Huang, D.; Zhang, P.; Wang, J. Temporal and spatial analysis of COVID-19 transmission in China and its influencing factors. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 105, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, D.; Choi, H.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, J. Spatial epidemic dynamics of the COVID-19 outbreak in China. Int. J. Infect. Dis. IJID Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Infect. Dis. 2020, 94, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymundo, C.E.; Oliveira, M.C.; de Araujo Eleuterio, T.; André, S.R.; da Silva, M.G.; da Silva Queiroz, E.R.; de Andrade Medronho, R. Spatial analysis of COVID-19 incidence and the sociodemographic context in Brazil. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Hu, X.; Xie, J. Spatial inequalities of COVID-19 mortality rate in relation to socioeconomic and environmental factors across England. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 758, 143595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, R.; Adeyemi, O.; Ghosh, S.; Pokhrel, K.; Arif, A.A. Dynamics of COVID-19 mortality and social determinants of health: A spatiotemporal analysis of exceedance probabilities. Ann. Epidemiol. 2021, 62, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francetic, I.; Munford, L. Corona and coffee on your commute: A spatial analysis of COVID-19 mortality and commuting flows in England in 2020. Eur. J. Public Health 2021, 31, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinoudis, G.; Padellini, T.; Bennett, J.; Davies, B.; Ezzati, M.; Blangiardo, M. Long-term exposure to air-pollution and COVID-19 mortality in England: A hierarchical spatial analysis. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossak, B.H.; Andritsch, S. COVID-19 and Air Pollution: A Spatial Analysis of Particulate Matter Concentration and Pandemic-Associated Mortality in the US. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, H.; Hu, T. Geographical Detector-Based Spatial Modeling of the COVID-19 Mortality Rate in the Continental United States. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franch-Pardo, I.; Napoletano, B.M.; Rosete-Verges, F.; Billa, L. Spatial analysis and GIS in the study of COVID-19. A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 140033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichlerová, M.; Önkal, D.; Bartlett, A.; Výbošťok, J.; Pichler, V. Variability in Forest Visit Numbers in Different Regions and Population Segments before and during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roviello, V.; Gilhen-Baker, M.; Vicidomini, C.; Roviello, G.N. Forest-bathing and physical activity as weapons against COVID-19: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 20, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Ren, C.; Yuan, C.; Nichol, J.E.; Goggins, W.B. An Ecological Study of the Association between Area-Level Green Space and Adult Mortality in Hong Kong. Climate 2017, 5, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bauwelinck, M.; Casas, L.; Nawrot, T.S.; Nemery, B.; Trabelsi, S.; Thomas, I.; Aerts, R.; Lefebvre, W.; Vanpoucke, C.; Van Nieuwenhuyse, A.; et al. Residing in urban areas with higher green space is associated with lower mortality risk: A census-based cohort study with ten years of follow-up. Environ. Int. 2021, 148, 106365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villeneuve, P.J.; Jerrett, M.; Su, J.G.; Burnett, R.T.; Chen, H.; Wheeler, A.J.; Goldberg, M.S. A cohort study relating urban green space with mortality in Ontario, Canada. Environ. Res. 2012, 115, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meo, S.A.; Almutairi, F.J.; Abukhalaf, A.A.; Usmani, A.M. Effect of Green Space Environment on Air Pollutants PM2.5, PM10, CO, O(3), and Incidence and Mortality of SARS-CoV-2 in Highly Green and Less-Green Countries. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 13151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russette, H.; Graham, J.; Holden, Z.; Semmens, E.O.; Williams, E.; Landguth, E.L. Greenspace exposure and COVID-19 mortality in the United States: January-July 2020. Environ. Res. 2021, 198, 111195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adiba, A.; Jaelani, L.M. The Effect of Greenness Index on Case Fatality Rate of COVID-19 Analyzed by Using Landsat-8 Image (Case Study: DKI Jakarta). In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Surakarta, Indonesia, 27 July 2021; p. 012039. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Li, M. Ambient air pollutants and their effect on COVID-19 mortality in the United States of America. Pan Am. J. Public Health 2020, 44, e159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pansini, R.; Fornacca, D. COVID-19 Higher Mortality in Chinese Regions with Chronic Exposure to Lower Air Quality. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 597753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamsi, S.; Zaman, K.; Usman, B.; Nassani, A.A.; Haffar, M.; Abro, M.M.Q. Do environmental pollutants carrier to COVID-19 pandemic? A cross-sectional analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 29, 17530–17543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarfraz, M.; Mohsin, M.; Naseem, S.; Kumar, A. Modeling the relationship between carbon emissions and environmental sustainability during COVID-19: A new evidence from asymmetric ARDL cointegration approach. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 16208–16226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badulescu, D.; Simut, R.; Badulescu, A.; Badulescu, A.-V. The Relative Effects of Economic Growth, Environmental Pollution and Non-Communicable Diseases on Health Expenditures in European Union Countries. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Ciais, P.; Deng, Z.; Lei, R.; Davis, S.J.; Feng, S.; Zheng, B.; Cui, D.; Dou, X.; Zhu, B.; et al. Near-real-time monitoring of global CO2 emissions reveals the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, K.A. Study Design VI-Ecological Studies. Evid.-Based Dent. 2006, 7, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World-Bank. Forest Area (% of Land Area). 2020. Available online: https://databank.worldbank.org/reports.aspx?source=2&type=metadata&series=AG.LND.FRST3.ZS# (accessed on 11 February 2022).
- Worldometer. Forest Area by Country. 2017. Available online: https://www.worldometers.info/food-agriculture/forest-by-country/ (accessed on 6 December 2021).
- EDGAR. Emission Database for Global Atmospheric Research (EDGAR). 2022. Available online: https://data.jrc.ec.europa.eu/collection/edgar (accessed on 6 December 2021).
- Ourworldindata. Coronavirus Pandemic (COVID-19). 2022. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/coronavirus (accessed on 6 December 2021).
- Hale, T.; Webster, S.; Petherick, A.; Phillips, T.; Kira, B. Oxford COVID-19 government response tracker (OxCGRT). Last Updated 2020, 8, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Stevens, G.A.; Alkema, L.; Black, R.E.; Boerma, J.T.; Collins, G.S.; Ezzati, M.; Grove, J.T.; Hogan, D.R.; Hogan, M.C.; Horton, R.; et al. Guidelines for Accurate and Transparent Health Estimates Reporting: The GATHER statement. PLoS Med. 2016, 13, e1002056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajgor, D.D.; Lee, M.H.; Archuleta, S.; Bagdasarian, N.; Quek, S.C. The many estimates of the COVID-19 case fatality rate. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 776–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verity, R.; Okell, L.C.; Dorigatti, I.; Winskill, P.; Whittaker, C.; Imai, N.; Cuomo-Dannenburg, G.; Thompson, H.; Walker, P.G.T.; Fu, H.; et al. Estimates of the severity of coronavirus disease 2019: A model-based analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, C.H.; Perreault, W.D. Collinearity, Power, and Interpretation of Multiple Regression Analysis. J. Mark. Res. 1991, 28, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-I. Correlation and Spatial Autocorrelation. In Encyclopedia of GIS; Shekhar, S., Xiong, H., Zhou, X., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, T.; Long, Z.; Zhang, R.; Chen, Q. Moran’s I test of spatial panel data model—Based on bootstrap method. Econ. Model. 2014, 41, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matérn, B. Spatial Variation; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2013; Volume 36. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, M.D.; Gleditsch, K.S. Spatial Regression Models; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2018; Volume 155. [Google Scholar]
- Royston, P. Multiple imputation of missing values. Stata J. 2004, 4, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World-Bank. World Bank Country and Lending Groups. 2022. Available online: https://datahelpdesk.worldbank.org/knowledgebase/articles/906519 (accessed on 6 December 2021).
- Rousset, F.; Ferdy, J.B. Testing environmental and genetic effects in the presence of spatial autocorrelation. Ecography 2014, 37, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordahl, K.; Bossche, J.; Wasserman, J.; McBride, J.; Gerard, J.; Fleischmann, M.; Tratner, J. Geopandas/Geopandas, V0. 6.1; Zenodo: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Klompmaker, J.O.; Hart, J.E.; Holland, I.; Sabath, M.B.; Wu, X.; Laden, F.; Dominici, F.; James, P. County-level exposures to greenness and associations with COVID-19 incidence and mortality in the United States. Environ. Res. 2021, 199, 111331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlahov, D.; Galea, S. Urbanization, urbanicity, and health. J. Urban Health 2002, 79, S1–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ekkel, E.D.; de Vries, S. Nearby green space and human health: Evaluating accessibility metrics. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 157, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coombes, E.; Jones, A.P.; Hillsdon, M. The relationship of physical activity and overweight to objectively measured green space accessibility and use. Soc. Sci. Med. 2010, 70, 816–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ugolini, F.; Massetti, L.; Pearlmutter, D.; Sanesi, G. Usage of urban green space and related feelings of deprivation during the COVID-19 lockdown: Lessons learned from an Italian case study. Land Use Policy 2021, 105, 105437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Congdon, P. COVID-19 Mortality in English Neighborhoods: The Relative Role of Socioeconomic and Environmental Factors. J 2021, 4, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, X.; Hazell, P.; Thurlow, J. The role of agriculture in African development. World Dev. 2010, 38, 1375–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roviello, V.; Roviello, G.N. Less COVID-19 deaths in southern and insular Italy explained by forest bathing, Mediterranean environment, and antiviral plant volatile organic compounds. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 20, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanaoka, T.; Masui, T. Exploring effective short-lived climate pollutant mitigation scenarios by considering synergies and trade-offs of combinations of air pollutant measures and low carbon measures towards the level of the 2 C target in Asia. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 261, 113650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, M.; Zhang, M. Study on the changes of the decoupling indicator between energy-related CO2 emission and GDP in China. Energy 2017, 128, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebayo, T.S.; Awosusi, A.A.; Kirikkaleli, D.; Akinsola, G.D.; Mwamba, M.N. Can CO2 emissions and energy consumption determine the economic performance of South Korea? A time series analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 38969–38984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Cai, Q.; Oda, T.; Zeng, N.; Shan, Y.; Lin, X.; Liu, D. Assessing the recent impact of COVID-19 on carbon emissions from China using domestic economic data. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 750, 141688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashed, E.A.; Kodera, S.; Gomez-Tames, J.; Hirata, A. Influence of Absolute Humidity, Temperature and Population Density on COVID-19 Spread and Decay Durations: Multi-Prefecture Study in Japan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowd, J.B.; Andriano, L.; Brazel, D.M.; Rotondi, V.; Block, P.; Ding, X.; Liu, Y.; Mills, M.C. Demographic science aids in understanding the spread and fatality rates of COVID-19. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 9696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Onder, G.; Rezza, G.; Brusaferro, S. Case-Fatality Rate and Characteristics of Patients Dying in Relation to COVID-19 in Italy. JAMA 2020, 323, 1775–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, D.E.; Peters, G.A.; Ivers, L.C.; Freeman, E.E. Global resource shortages during COVID-19: Bad news for low-income countries. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, C.; Notter, J. COVID-19 1 year on: The challenge for low-middle income countries. Nurs. Crit. Care 2021, 26, 410–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asfahan, S.; Shahul, A.; Chawla, G.; Dutt, N.; Niwas, R.; Gupta, N. Early trends of socio-economic and health indicators influencing case fatality rate of COVID-19 pandemic. Monaldi Arch. Chest Dis. 2020, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trethewey, S.P.; Reynolds, E.K. Exposure to green spaces and all-cause mortality: Limitations in measurement and definitions of exposure. Lancet Planet. Health 2021, 5, e501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).