In the original publication [1], there was a mistake in Figure 2B. The corrected Figure 2B appears below. The authors state that the scientific conclusions are unaffected. This correction was approved by the Academic Editor. The original publication has also been updated.
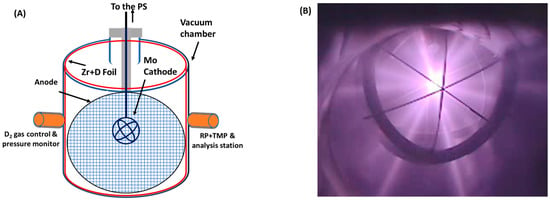
Figure 2.
(A) A schematic representation of the MSF chamber, featuring a Mo cathode, Zr mesh (anode), and cylindrical Zr foil (depicted by the red line). (B) The plasma during the system operation at 30 mA current and 30 kV voltage.
Reference
- Bakr, M.; Wallace-Smith, T.; Mukai, K.; Martin, E.; Thomas, O.L.; Liu, H.-Y.; Lemon-Morgan, D.; Holland, E.; Firestone, T.; Scott, T.B. The Effect of Electrode Materials on the Fusion Rate in Multi-State Fusion Reactors. Materials 2025, 18, 3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.