Synthesis of Phosphorus-Modified Magnetic Chitosan and Its Application for Cr(VI) Removal from Aqueous Solution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Phosphorus-Modified Magnetic Chitosan (PCC/Fe3O4) Preparation
2.2. Batch Experiments for Cr (VI) Removal
2.3. Characterization of the PCC/Fe3O4
2.4. Stability and Regeneration Test of PCC/Fe3O4
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization
3.2. Cr(VI) Removal of PCC/Fe3O4 and the Influencing Factors
3.3. Adsorption Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, M.F. Review on Heavy Metal Remediation Technology of Soil and Groundwater at Industrially Contaminated Site in China. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2014, 29, 327–335. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, H.; Yuan, E.J.; Shi, L.Q.; Peng, H.M.; Cha, C.L.; Chong, D.G.; Xu, J.D. Characterization, Health Risks and Source Analysis of Heavy Metal Pollution in Soil Surrounding an Iron and Steel Plant. Chin. J. Inorg. Anal. Chem. 2025, 15, 1135–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhal, B.; Thatoi, H.N.; Das, N.N.; Pandey, B.D. Chemical and Microbial Remediation of Hexavalent Chromium from Contaminated Soil and Mining/Metallurgical Solid Waste: A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 250–251, 272–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markiewicz, B.; Komorowicz, I.; Sajnóg, A.; Belter, M.; Barałkiewicz, D. Chromium and Its Speciation in Water Samples by HPLC/ICP-MS—Technique Establishing Metrological Traceability: A Review since 2000. Talanta 2015, 132, 814–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; An, Y.; Jin, D.; Jin, T.; Wang, X. Effects of Chromium Pollution on Soil Bacterial Community Structure and Assembly Processes. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 1197–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.T.; Lan, G.H.; Liu, Y.Q.; Zhang, T.L.; Qiu, H.Y.; Li, F.; Yan, J.H.; Lu, Y.C. Enhanced Adsorption of Cr(VI) from Aqueous Solution by Zirconium Impregnated Chitosan Microspheres: Mechanism and Equilibrium. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 2532–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Song, C.Y.; Jiang, X.Y.; Li, T.L.; Wang, H.T. Mechanochemical Synthesis of Redox-Active Fe-Based Nanocomposites for Efficient Cr(VI) Remediation in Water and Soil. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 377, 134212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.X.; Xu, N.; Sun, W.; Du, F. Construction of Clay-Mediated nZVI Composites to Alleviate the Decline in Cr(VI) Removal during Co-Transport with Humic Acid and Phosphate. Environ. Sci. Nano 2025, 12, 3317–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koetsem, F.V.; Havere, L.V.; Laing, G.D. Impact of Carboxymethyl Cellulose Coating on Iron Sulphide Nanoparticles Stability, Transport, and Mobilization Potential of Trace Metals Present in Soils and Sediment. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 168, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, S.A.; Asgharnejad, L.; Najafi, H.; Asasian-Kolur, N.; Sharifian, S. Investigation of Adsorptive and Catalytic Performance of a Aovel Nano-Sized Amine-Modified Metal Organic Framework toward Levofloxacin. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Lyu, H.H.; Du, Y.Q.; Cheng, Q.L.; Liu, Y.X.; Ma, J.W.; Yang, S.M.; Lin, H. Unraveling How Fe-Mn Modified Biochar Mitigates Sulfamonomethoxine in Soil Water: The Activated Biodegradation and Hydroxyl Radicals Formation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, H.H.; Tang, J.C.; Cui, M.K.; Gao, B.; Shen, B.X. Biochar/Iron (BC/Fe) Composites for Soil and Groundwater Remediation: Synthesis, Applications, and Mechanisms. Chemosphere 2020, 246, 125609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.B.; Tang, Y.Y.; Ding, Y.R.; Lyu, Y.P.; Su, W.H.; Nadeem, M.; Zhang, P.; Rui, Y.K. Carboxymethyl Cellulose Surface Modification Alleviates the Toxicity of Fe-13 MOFs to Rice and Improves Iron Absorption. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Q.M.; Xu, D.S.; Wang, X.J.; Lou, T. Regenerable Fe3O4-decorated Chitosan/Carboxymethyl Cellulose Hollow Spheres for Adsorption and Catalytic Degradation of Dyes. Cellulose 2022, 29, 7251–7262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudzielwana, R.; Gitari, W.M.; Ndungu, P. Removal of As(III) from Synthetic Groundwater Using Fe-Mn Bimetal Modified Kaolin Clay: Adsorption Kinetics, Isotherm and Thermodynamics Studies. Environ. Process. 2019, 6, 1005–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.F.; Chen, J.Y.; Sun, H.; Qian, P.H.; Wang, D.F.; Zhuang, W.C.; Dong, L.M. Enhancing Adsorption Performance of Ce(III) by Amine-Thiourea and Aniline-Modified Magnetic Chitosan Nanocomposites. Langmuir 2024, 40, 23398–23405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Nie, Y.X.; Sun, D.L.; Wu, D.Y.; Ban, L.; Zhang, H.; Yang, S.; Chen, J.S.; Du, H.S.; et al. Recent Advances and Perspectives in Functional Chitosan-based Composites for Environmental Remediation, Energy, and Biomedical Applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2025, 52, 101460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-qarhami, F.; Abdallah, A.B.; Khalifa, M.E.; Awad, F.S. Glutaraldehyde-crosslinked Magnetic Chitosan Nanocomposite for Efficient Cr(VI) Removal: A Sustainable Approach to Aquatic Remediation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 310, 43459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Arputharaj, E.; Dahms, H.U.; Patel, A.K.; Huang, Y.L. Chitosan-based Nanocomposites for Removal of Cr(VI) and Synthetic Food Colorants from Wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 351, 127018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, S.K.; Bolan, N.S.; Lombi, E.; Skinner, W.; Guibal, E. Sulfur-Containing Chitin and Chitosan Derivatives as Trace Metal Adsorbents: A Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 43, 1741–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Zhang, A.L.; Zhou, J.T.; Sun, X.Y. Characterization and Thermodynamic Properties of Cu(II) Imprinted Chitosan Crosslinked Membrane. Environ. Sci. 2012, 33, 2403–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilela, P.B.; Dalalibera, A.; Duminelli, E.C.; Becegato, V.A.; Paulino, A.T. Adsorption and Removal of Chromium (VI) Contained in Aqueous Solutions Using a Chitosan-Based Hydrogel. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 28481–28489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragan, E.S.; Platon, I.V.; Nicolescu, A.; Dinu, M.V. Structural, Mechanical, Antioxidant and Antibacterial Properties of Double Cross-Linked Chitosan Cryogels as Hosts for Thymol. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 304, 140968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.M.; An, Q.D.; Xiao, Z.Y.; Zhai, S.R.; Yang, D.J. Efficient Removal of Pb(II), Cr(VI) and Organic Dyes by Polydopamine Modified Chitosan Aerogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 202, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahgui, F.; Delgado Cano, B.; Avalos Ramirez, A.; Heitz, M.; Hadjar, H.; Kaddour, S. Development of New Biosorbent Based on Crosslinked Chitosan Beads with High Brilliant Blue FCF Removal Efficiency. Molecules 2025, 30, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.K.; Guo, X.T.; Zhao, L.Y.; Duan, W.Q.; Huang, Y.Q.; Wang, X.J. Synergistic Removal Mechanism of Tetracycline by Ethylenediamine Modified Magnetic Chitosan Based Fenton-like Catalyst. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 36507–36516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragan, E.S.; Dinu, M.V.; Ghiorghita, C.A.; Lazar, M.M.; Doroftei, F. Preparation and Characterization of Semi-IPN Cryogels Based on Polyacrylamide and Poly(N,N-Dimethylaminoethyl Methacrylate); Functionalization of Carrier with Monochlorotriazinyl-β-Cyclodextrin and Release Kinetics of Curcumin. Molecules 2021, 26, 6975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sessarego, S.; Rodrigues, S.C.G.; Xiao, Y.; Lu, Q.Y.; Hill, J.M. Phosphonium-Enhanced Chitosan for Cr(VI) Adsorption in Wastewater Treatment. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 211, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Zheng, H.L.; Zhong, Z.; Zhao, C.; Sun, Y.J.; Huang, Y.Y.; Zheng, X.Y. Efficient Removal of Diclofenac from Surface Water by the Functionalized Multilayer Magnetic Adsorbent: Kinetics and Mechanism. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 760, 144307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.R.; Su, J.J.; Yang, Q.; Yang, Z.L. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Zr-Doped Chitosan Carbon-Shell Protected Magnetic Composites (Zr–Fe3O4@C) for Stable Removal of Cr(VI) from Water: Enhanced Adsorption and pH Adaptability. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2023, 306, 128057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, D.G.; Jin, P.; Guo, W.H.; Liu, J.; Wang, W.; Li, P.; Cao, Y.J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. Recyclable Magnetic Iron Immobilized onto Chitosan with Bridging Cu Ion for the Enhanced Adsorption of Methyl Orange. Molecules 2023, 28, 2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, H.A.; Eddine, L.S.; Hasan, G.G.; Meneceur, S.; Salmi, C.; Abdullah, J.A.A.; Abdullah, M.M.S.; Menaa, F. Efficient Removal of Heavy Metals, Dyes, and Contaminants from Industrial Wastewater Using Chitosan-Coated Fe3O4 Nanocomposites: Biosynthesis, Characterizations, and Performance Evaluation. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2024, 14, 30719–30734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, F.B.; da Silva Bruckmann, F.; da Rosa Salles, T.; Rhoden, C.R.B. Study of Phenobarbital Removal from the Aqueous Solutions Employing Magnetite-Functionalized Chitosan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 12658–12671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.L.; Li, T.; Yang, D.D.; Li, Y.J.; He, J.Y.; Zhou, L.D.; Zhang, Q.H.; Wang, C.Z.; Yuan, C.S. Constructing a Dummy-Template Adsorbent Using Magnetic Molecular-Imprinted Chitosan for Rapid Enrichment of Flavonoids Compounds from Penthorum Chinense Pursh. Microchem. J. 2023, 191, 108833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Garg, U.; Khan, K.U.; Azim, Y. Removal of Organic and Inorganic Pollutants Using CSFe3O4@CeO2 Nanocatalyst via Adsorption–Reduction Catalysis: A Focused Analysis on Methylene Blue. J. Polym. Environ. 2022, 30, 4435–4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafaati, M.; Miralinaghi, M.; Shirazi, R.H.S.M.; Moniri, E. The Use of Chitosan/Fe3O4 Grafted Graphene Oxide for Effective Adsorption of Rifampicin from Water Samples. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2020, 46, 5231–5254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.X.; Ma, M.M.; Yan, X.H.; Wan, D.M.; Zeng, Z.L.; Yu, P.; Gong, D.M. Immobilization of Lipase on β-Cyclodextrin Grafted and Aminopropyl-Functionalized Chitosan/Fe3O4 Magnetic Nanocomposites: An Innovative Approach to Fruity Flavor Esters Esterification. Food Chem. 2022, 366, 130616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogolitsyn, K.G.; Parshina, A.E.; Ivanchenko, N.L.; Bogdanovich, N.I.; Arkhilin, M.A. The Capillary and Porous Structure of the Protein-Cellulose Complexes of Arctic Brown Algae Laminaria digitata and Saccharina latissima. Cellulose 2022, 29, 7037–7048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.C.; Tan, X.; Qiu, T.T.; Zhou, L.S.; Li, R.N.; Deng, Z.L. A Novel and Biocompatible Fe3O4 Loaded Chitosan Polyelectrolyte Nanoparticles for the Removal of Cd2+ Ion. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 141, 1165–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altun, T. Chitosan-coated Sour Cherry Kernel Shell Beads: An Adsorbent for Removal of Cr(VI) from Acidic Solutions. J. Anal. Sci. Technol. 2019, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ma, K.; Peng, H.; Gong, Y.; Huang, Y. Imidazolium Functionalized Polysulfone/DTPA-chitosan Composite Beads for Simultaneous Removal of Cr(VI) and Cu(II) from Aqueous Solutions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 310, 123145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subedi, N.; Lähde, A.; Abu-Danso, E.; Iqbal, J.; Bhatnagar, A. A Comparative Study of Magnetic Chitosan (Chi@Fe3O4) and Graphene Oxide Modified Magnetic Chitosan (Chi@Fe3O4GO) Nanocomposites for Efficient Removal of Cr(VI) from Water. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 137, 948–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, S.; Peng, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, S.; Tao, E. Chitosan-based Composite Featuring Dual Cross-linking Networks for the Removal of Aqueous Cr(VI). Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 348, 122859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, M.; Mas Haris, M.R.H. Chromium (VI) Removal from Neutral Aqueous Media using Banana Trunk Fibers (BTF)-reinforced Chitosan-based Film, in Comparison with BTF, Chitosan, Chitin and Activated Carbon. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, B.; Wu, J.Z.; Zhao, K.L.; Ye, Z.Q.; Yuan, F. Novel Insight into the Adsorption Mechanism of Fe-Mn Oxide-Microbe Combined Biochar for Cd(II) and As(III). Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 1584–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.J.; Liu, F.; Liu, X.; Li, M. Removal of Cr(VI) by Glutaraldehyde-Crosslinked Chitosan Encapsulating Microscale Zero-Valent Iron: Synthesis, Mechanism, and Longevity. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 142, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, F.N. Hexavalent Chromium in the Ground Water in Paradise Valley, Arizona. Groundwater 1975, 13, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.Q.; Zhang, X.F.; He, X.; Xiao, M.J.; Zhang, W.; Lu, C.H. A Super Biosorbent from Dendrimer Poly(Amidoamine)-Grafted Cellulose Nanofibril Aerogels for Effective Removal of Cr(VI). J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 14703–14711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ningtyas, R.D.; Yanti, D.D.; Amin, A.K.; Aji, A. Fabrication of a Fe3O4/CS/AgNPs Composite from Indigenous Iron Sand for Enhanced Methylene Blue Adsorption. J. Clust. Sci. 2024, 35, 1463–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şentürk, İ. Effective Adsorption of Congo Red by Eco-Friendly Granite-Modified Magnetic Chitosan Nanocomposite (G@Fe3O4@CS). Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2024, 14, 30641–30658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.K.; Pei, M.S.; He, Y.J.; Yu, F.Q.; Guo, W.J.; Wang, L.Y. Preparation, Characterization and Application of Magnetic Fe3O4-CS for the Adsorption of Orange I from Aqueous Solutions. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Hu, Z.Y.; Cui, J.J.; Yang, N.N.; Bao, R.; Dai, Y.Z.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Cui, P. Tailoring of a Chitosan-Based Adsorbent with Target-Specific Sites for Efficient Adsorption-Reduction of Chromium Ion Pollutant. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 360, 131055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anfar, Z.; Amedlous, A.; El Fakir, A.A.; Zbair, M.; Ait Ahsaine, H.; Jada, A.; El Alem, N. High Extent Mass Recovery of Alginate Hydrogel Beads Network Based on Immobilized Bio-Sourced Porous carbon@Fe3O4-NPs for Organic Pollutants Uptake. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, K.; Joseph, R.G.; Patole, S.P.; Al-Qawasmeh, R.A. Development of Magnetic Fe3O4-Chitosan Immobilized Cu(II) Schiff Base Catalyst: An Efficient and Reusable Catalyst for Microwave Assisted One-Pot Synthesis of Propargylamines via A3 Coupling. Catal. Commun. 2023, 174, 106588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, S.Y.; Wang, M.T.; Wang, K.X.; Hou, Y.Q.; Yu, J.; Shi, Q.Q.; Pei, X.J.; Chu, W. Preparation of CS-Fe@Fe3O4 Nanocomposite as an Efficient and Recyclable Adsorbent for Azo Dyes Removal. Desalination Water Treat. 2017, 95, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.J.; Li, X.M.; Gao, W.G.; Zhang, H.Q.; Luo, M. An MOF-Derived C@NiO@Ni Electrocatalyst for N2 Conversion to NH3 in Alkaline Electrolytes. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2020, 4, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.J.; Ma, X.D.; Du, X.Y.; Song, P.; Xia, L.X. Silver-Nanoparticle-Coated Fe3O4/Chitosan Core–Shell Microspheres for Rapid and Ultrasensitive Detection of Thiram Using Surface Magnetic Solid-Phase Extraction–Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SMSPE-SERS). Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 914, 170027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, J.; Cai, T.M.; Dai, J.B.; Yao, L.H.; Liu, F.F.; Liu, Y.; Shu, J.C.; Fan, J.P.; Peng, H.L. High Strength Chitin/Chitosan-Based Aerogel with 3D Hierarchically Macro-Meso-Microporous Structure for High-Efficiency Adsorption of Cu(II) Ions and Congo Red. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 230, 123238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.S.; Liu, Y.B.; Zhu, Y.Q.; Jiang, W.L.; Shi, F.S.; Hu, J.P.; Jiang, S.H.; Jian, S.J. Epichlorohydrin and Triethylenetetramine Functionalized Electrosprayed Fe3O4/Chitosan Magnetic Microspheres for Removal and Separation of Congo Red. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 476, 146907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.J.; Wang, Y.X.; Chen, Y.Q.; Zhang, T.T.; Zhang, Z.B.; Li, H.F.; Shan, F.J.; Ma, T.G. Anti-Stacking, Recyclable and Electron-Rich Fe3O4 Modified L-Glutamic Acid Functionalized Graphene Oxide towards Cr(VI) Removal by Adsorption-Reduction Behavior. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 363, 132090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, S.R.; Yuan, Z.D.; Yang, S.B.; Li, T.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, F.L.; Dong, W.F. pH Responsive THPS Crosslinked Injectable Hydrogel with Cu-Metformin Sustained-Release for Accelerating Wound Healing. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 492, 152373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flury, B.; Eggenberger, U.; Mäder, U. First Results of Operating and Monitoring an Innovative Design of a Permeable Reactive Barrier for the Remediation of Chromate Contaminated Groundwater. Appl. Geochem. 2009, 24, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
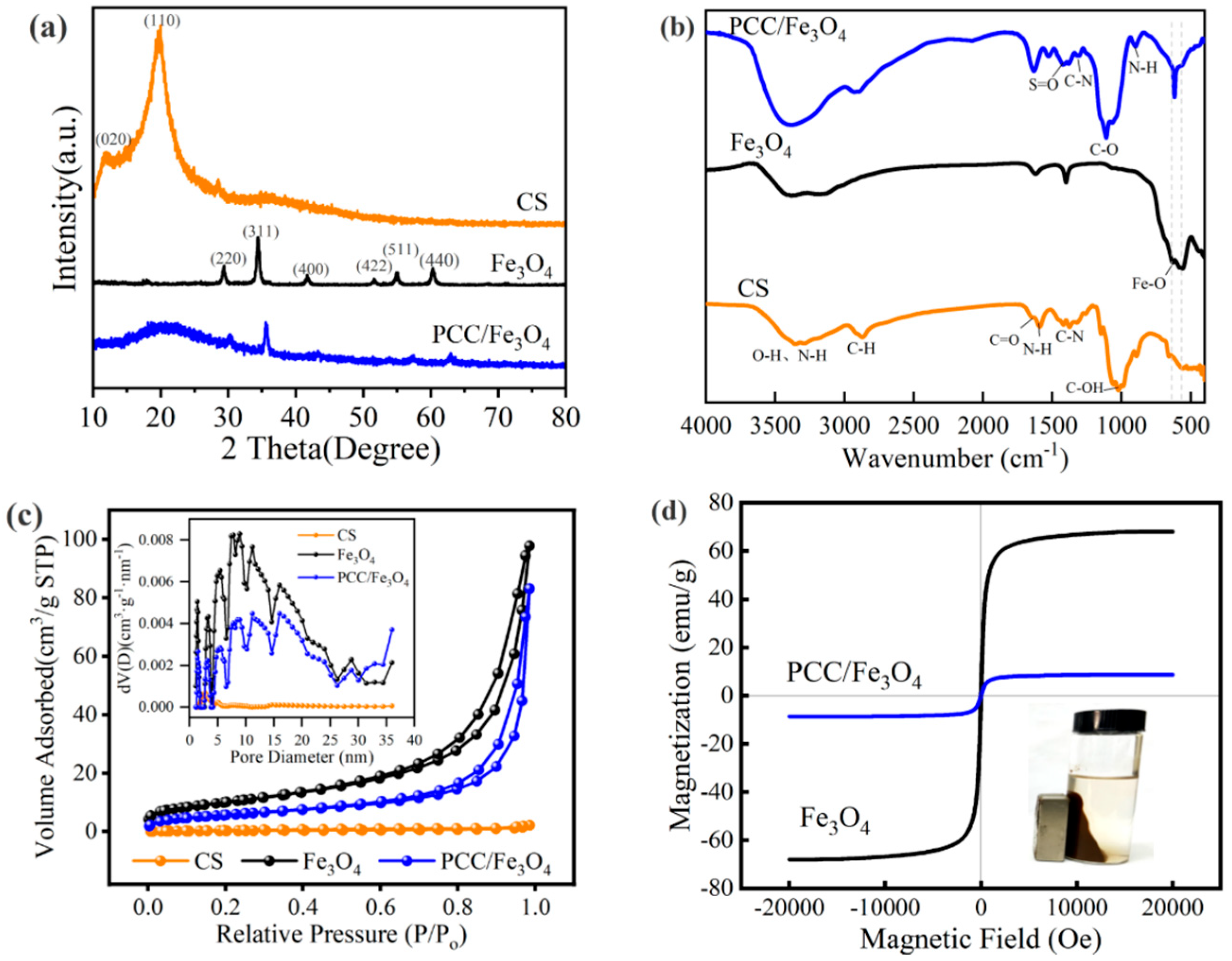

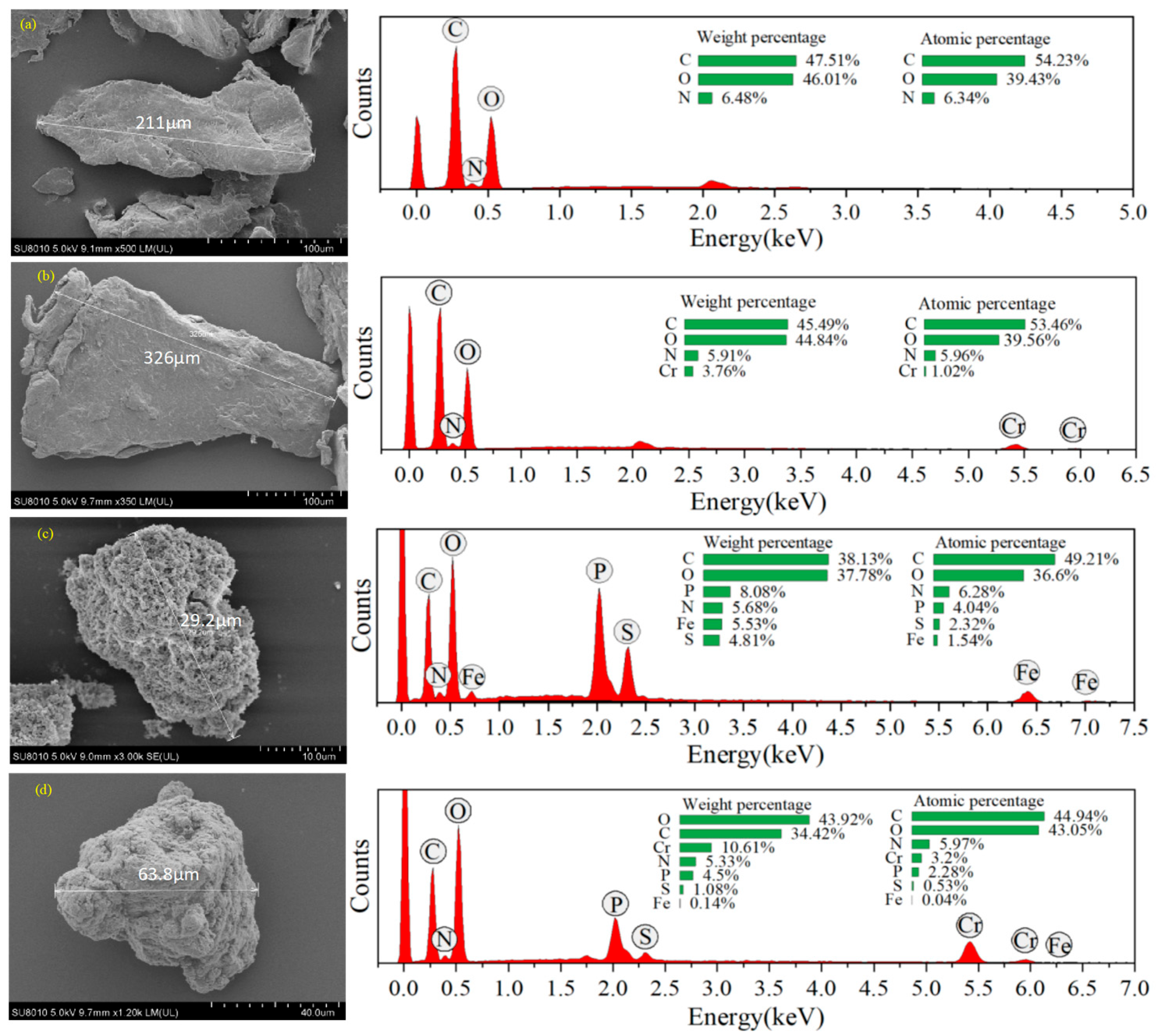
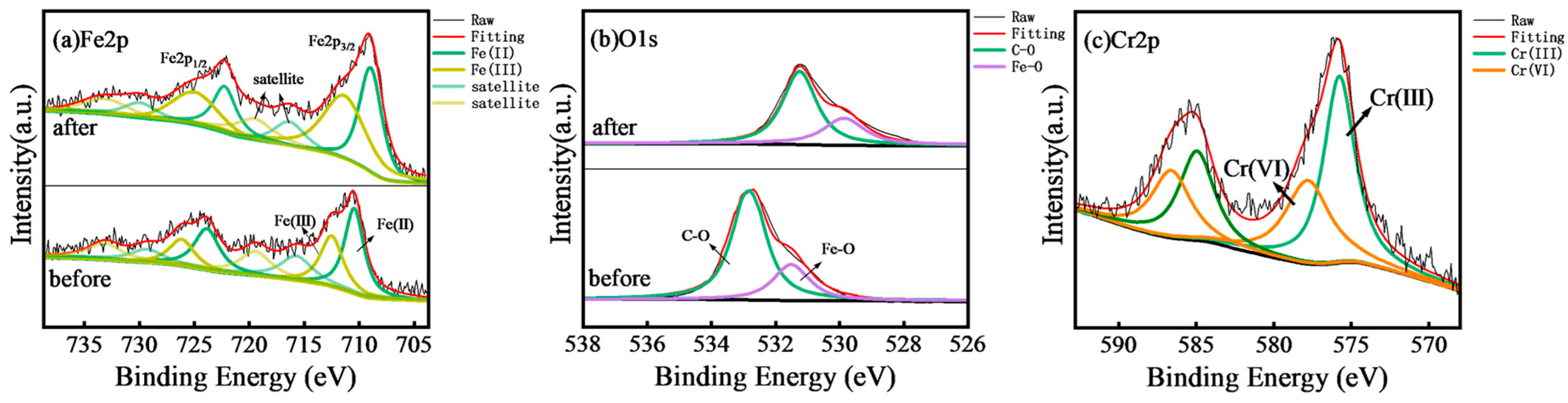

| Adsorbent Material | Specific Surface Area (m2/g) | Average Pore Size (nm) | Total Adsorption Pore Volume (cm3/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CS | 1.058 | 12.30 | 0.0033 |
| Fe3O4 | 36.502 | 16.58 | 0.1513 |
| PCC/Fe3O4 | 20.671 | 24.88 | 0.1286 |
| Adsorbent Material | Adsorption Conditions | Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | Ref. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Conc (mg/L) | Temp. (°C) | Time (min) | pH | |||
| Chitosan-coated sour cherry kernel shell beads | 10.0 | 25 | 45 | 2 | 24.5 | [40] |
| Poly-sulfone/diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid-chitosan composite beads | 120 | 28 | 1440 | 5 | 56.72 | [41] |
| Magnetic chitosan graphene oxide composite | 40 | 25 | 180 | 2 | 100.51 | [42] |
| Sodium alginate-polyvinyl alcohol-chitosan composite | 10.0 | 35 | 60 | 2 | 37.7 | [43] |
| Banana trunk fiber-reinforced chitosan | 50.0 | 27 | 120 | 7 | 12.7 | [44] |
| PCC/Fe3O4 | 1.00 | 25 | 60 | 6 | 23.6 | This study |
| Adsorbents | Quasi-First-Order Dynamic Model | Pseudo-Second Order Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1/min−1 | R2 | qe/mg·g−1 | k2/min−1 | R2 | qe/mg·g−1 | |
| Fe3O4 | 0.096 | 0.950 | 2.759 | 0.037 | 0.985 | 3.187 |
| CS | 0.076 | 0.993 | 5.398 | 0.017 | 0.976 | 6.066 |
| PCC/Fe3O4 | 0.441 | 0.995 | 22.931 | 0.055 | 0.999 | 23.576 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Luo, Y.; Hu, Q.; Cao, A.; Ding, L.; Xu, S. Synthesis of Phosphorus-Modified Magnetic Chitosan and Its Application for Cr(VI) Removal from Aqueous Solution. Materials 2025, 18, 5019. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18215019
Wang H, Luo Y, Hu Q, Cao A, Ding L, Xu S. Synthesis of Phosphorus-Modified Magnetic Chitosan and Its Application for Cr(VI) Removal from Aqueous Solution. Materials. 2025; 18(21):5019. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18215019
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Hong, Yiran Luo, Qing Hu, Anyuan Cao, Longzhen Ding, and Shengbin Xu. 2025. "Synthesis of Phosphorus-Modified Magnetic Chitosan and Its Application for Cr(VI) Removal from Aqueous Solution" Materials 18, no. 21: 5019. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18215019
APA StyleWang, H., Luo, Y., Hu, Q., Cao, A., Ding, L., & Xu, S. (2025). Synthesis of Phosphorus-Modified Magnetic Chitosan and Its Application for Cr(VI) Removal from Aqueous Solution. Materials, 18(21), 5019. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18215019






