Abstract
Electrochemical mechanisms of molten salt electrolysis from TiO2 to titanium were investigated by Potentiostatic electrolysis, cyclic voltammetry, and square wave voltammetry in NaCl-CaCl2 at 800 °C. The composition and morphology of the product obtained at different electrolysis times were characterized by XRD and SEM. CaTiO3 phase was found in the TiO2 electrochemical reduction process. Electrochemical reduction of TiO2 to titanium is a four-step reduction process, which can be summarized as TiO2→Ti4O7→Ti2O3→TiO→Ti. Spontaneous and electrochemical reactions take place simultaneously in the reduction process. The electrochemical reduction of TiO2→Ti4O7→Ti2O3→TiO affected by diffusion was irreversible.
1. Introduction
Titanium is considered a rare metal because it is dispersed in nature and difficult to extract. However, it is relatively abundant, ranking tenth among all elements. Titanium ore mainly ilmenite and rutile, widely distributed in the earth’s crust and lithosphere. Titanium and its alloys have been widely used in aerospace, national defense, ocean, energy, transportation, medical, and other fields due to its advantages of low density, high specific strength, good heat resistance, and corrosion resistance [1,2,3]. Therefore, titanium has a “21st century metal”, “all-round metal”, and “modern metal” reputation [4].
Due to titanium and oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, hydrogen, and other elements have a strong affinity, making the titanium production process complex, a long process with high energy consumption and high cost, limiting the application of titanium in many industries. In order to reduce the production cost of titanium, researchers continue to improve the traditional process and develop new extraction methods. At present, Kroll process is the most important industrial process for titanium production. However, the complex process, long process, high energy consumption, and high cost limit the application of titanium in many industries [5,6]. In order to reduce the production cost of titanium, researchers have developed many new processes, among which the molten salt electrolysis method has attracted a lot of attention worldwide because of its characteristics of short process, low energy consumption, and simple process [7,8,9,10,11,12]. Using alkaline metal or alkaline earth metal salt as electrolyte, TiO2 as cathode, and graphite as anode, titanium was prepared by direct electrodeoxidation of TiO2 in the molten salt electrolysis method. Titanium can be obtained in one-step reduction process [13,14]. At present, the electrochemical method has already been intensely studied in preparation of alloys [15,16,17,18,19] and carbides [20].
In order to clarify the deoxidation process of TiO2 in molten salt electrolysis, the preparation of titanium by direct electro-deoxidation of TiO2 in NaCl-CaCl2 binary molten salt system was carried out in this work. The reduction process and electrochemical mechanism of the molten salt electrolysis from TiO2 to titanium were studied by potentiostatic electrolysis and electrochemistry analysis in detail.
2. Experimental Procedures
2.1. Raw Materials and Cathode Precursor Preparation
TiO2 (96 wt.%) and carbon (4 wt.%) powders of 2 g were used as raw materials and mixed homogeneously. The mixed powders were die-pressed at 20 MPa in a cylindrical mold (30 mm in diameter). The die-pressed bodies were sintered at 353 K for 8 h; then, the sintered disc was tied in the titanium electrode rod with a nickel wire as a cathode.
2.2. Electro-Deoxidation Process
Anhydrous NaCl and CaCl2 salt (500 g in molar ratio 0.48:0.52) were placed in graphite crucible and dried in the steel reactor at 473 K for 8 h to remove moisture in the salt. When the molar ratio was NaCl:CaCl2 = 0.48:0.52, the lowest eutectic temperature point of the binary salt was 762 K [21]. In order to ensure that the molten salt system has low viscosity and high conductivity, the temperature conducted for this experiment is 1073 K. Then the temperature of the binary salt was programmatically raised in the reactor to 1073 K, while argon was continuously pumped into the reactor. The anode was graphite crucible, which was connected by a titanium electrode rod. The electro-deoxidization experiment was conducted at a constant potential of 3 V for 6 h. The schematic diagram of the experimental device was shown in Figure 1. The obtained cathodic products were washed by deionized water in the ultrasonic cleaners and vacuum dried at 333 k.
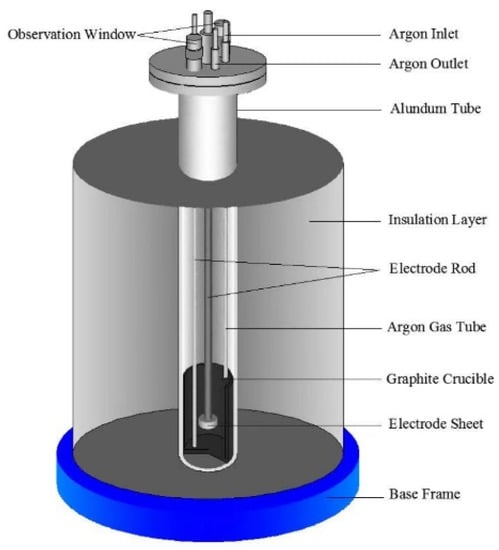
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the electrolysis experimental device.
2.3. Electrochemical Test
The electrochemical deoxidation process from TiO2 to titanium was evaluated in a three-terminal electrochemical cell by PARSTAT 2273 electrochemical workstation. Pt wire (99.99%, φ = 0.5 mm), Mo wire (99.99%, φ = 0.5 mm), and graphite crucible were used as the reference, work, and counter electrodes, respectively. Cyclic voltammetry (CV) and square wave voltammetry were used to analyze the reduction of TiO2 to titanium in NaCl-CaCl2 at 800 °C. The schematic diagram of the experimental platform is shown in Figure 2.
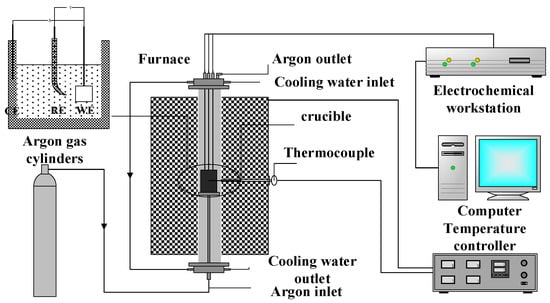
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of the electrochemical experimental platform.
2.4. Characterization
The electrolytic voltage was supplied by DC power supply (DP310, MESTEK, China). The phase composition of the solid precursors and cathodic products were determined by X-ray diffraction (XRD) (Noran7, Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA, USA). Each scan was 5°–90° and step size is 0.02°. The morphology and chemical composition of the solid precursors and cathodic products were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) (S-4800, Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan) and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX). The acceleration voltage of SEM is 20 kV and the working distance (WD) is 10 mm.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Calculation of the Theoretical Decomposition Potentials
Alkaline metal molten salts with low melting point, wide electrochemical window, and good electrical conductivity are commonly used as electrolytes for electrochemical preparation of metals. The Gibbs free energy of the possible reactions can be calculated by HSC thermodynamics software. The theoretical decomposition potentials (E) of the metal molten salts and TiO2 were calculated by the following equation [22,23]:
where ΔGΘ (kJ/mol) is the standard Gibbs free energy change; n and F represent the electron transfer number and Faraday’s constant (96,485 C/mol), respectively. The theoretical decomposition potentials and reactions that occurred in the electro-deoxidation cell from 773 K to 1273 K are listed in Figure 3. The results show that the theoretical decomposition potentials of TiO2 and the binary salt are positively correlated with temperature. The theoretical decomposition potentials of NaCl and CaCl2 is −3.29 V and −3.23 V, respectively, which is much higher than that of TiO2. It indicates that the experiment voltage of 3 V, conducted in a two-electrode system, is sufficient to electro-deoxidize TiO2 to titanium without the electrolyte decomposition.
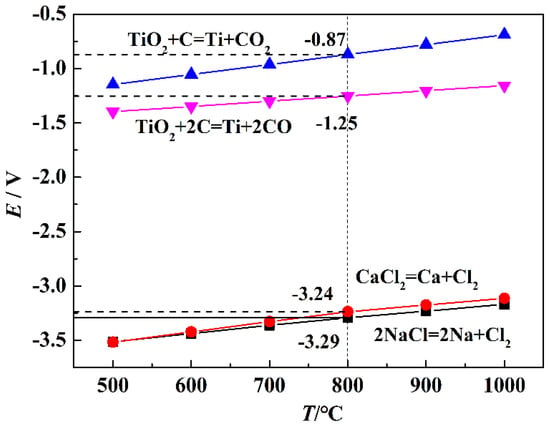
Figure 3.
Theoretical decomposition potentials and reactions occurred in the electro-deoxidation cell from 773 K to 1273 K.
3.2. Electro-Deoxidization of the Cathode Precursor
Figure 4 presents the XRD patterns of the products at different electro-deoxidation time. It can be seen from the product electrolyzed for 0 h that TiO2 is the main component of the cathode precursor, which indicates that the little carbon did not react with TiO2 in the sintering process. The product electrolyzed for 8 h shows the intermediate valence titanium oxides (Ti4O7, Ti2O3, TiO) and CaTiO3 are the main phases of the product after 8 h electrolysis. CaTiO3 is generated by the reaction between TiO2 and calcium ions in molten salt and oxygen ions extracted from TiO2. Table 1 lists the possible reaction ΔGΘ in the electrolysis process at 1073 K. Reaction (1) has an extremely negative ΔGΘ(−1045.43 kJ/mol) at 1073 K, indicating that the formation of CaO betweent Ca2+ and O2− extracted from TiO2 is easy to proceed. The ΔGθ of CaTiO3 generated by the reaction of CaO and TiO2 was −86.94 kJ/mol, demonstrating that the reaction could occur spontaneously. Literatures show that there is a high concentration of oxygen in the material at this stage; that is, CaTiO3 will be spontaneously formed when calcium ions and oxygen ions existed in the molten salt [24]. The diffraction peak of titanium detected in the product electrolyzed for 8 h indicates that titanium metal can be reduced after 8 h of electrolysis. Compared with the product of electrolysis for 8 h, the diffraction peak of titanium in the product of electrolysis for 24 h is significantly increased (shown in the XRD pattern of the product electrolyzed for 24 h), indicating that the reduction of titanium metal is further carried out with the extension of the electrolysis time. Figure 5 presents SEM images and EDX analysis of the products electrolysis for 8 h and 24 h. Combined with XRD data analysis in Figure 4, they show that CaTiO3 was formed in the products electrolysis for 8 h during the electrolysis process, shown in reaction (2). The main phase is the intermediate valence titanium oxides, and the CaTiO3 phase almost disappears in the products electrolysis for 24 h, which is due to the spontaneous decomposition between CaTiO3 and titanium, shown in reaction (3). The deposited carbon can react with the metal on the cathode, resulting in high carbon content in the cathode product. It can be explained by the following two reactions.
In anode:
In cathode:
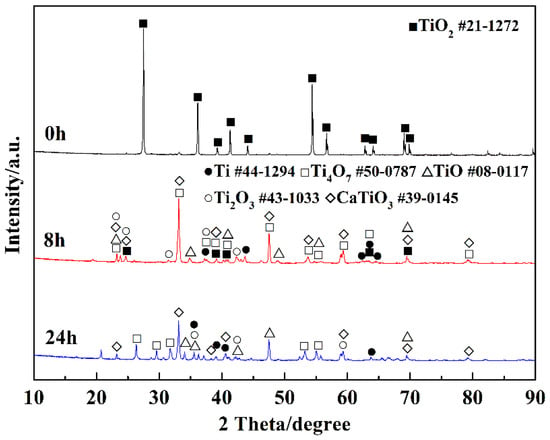
Figure 4.
XRD patterns of the products at different electro-deoxidation times.
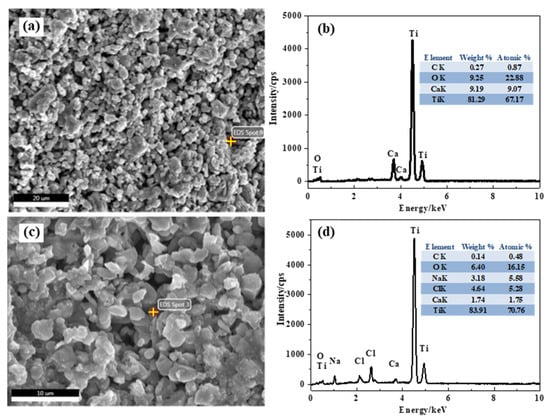
Figure 5.
SEM images and EDX analysis of the products electrolysis for (a,b) 8 h and (c,d) 24 h.

Table 1.
ΔGθ of possible reaction in the electrolysis process at 1073 K.
Table 1.
ΔGθ of possible reaction in the electrolysis process at 1073 K.
| Possible Reactions | ΔGθ1073 K (kJ/mol) | No. |
|---|---|---|
| Ca2+ + O2− = CaO | −1045.43 | (1) |
| CaO + TiO2 = CaO·TiO2 | −86.94 | (2) |
| Ti + CaTiO3 = 2TiO + CaO | −21.29 | (3) |
3.3. Electro-Deoxidation Thermodynamics of Titanium Oxides in Molten Salt Systems
The main phases in TiO2 electro-deoxidation products include Ti4O7, Ti2O3, TiO, and Ti. When graphite was used as the anode material, the main anode product in molten salt electrolysis was CO2 [25]. In order to simplify the calculation, CO2 was considered as the only gas component in the anode product. Table 2 listed ΔGθ and E of TiO2 electro-deoxidation reactions at 1073 K. The theoretical decomposition potentials of TiO2 deoxidized to Ti4O7 is 0.34 V, which is lower than TiO2 deoxidized to Ti2O3, TiO, and Ti. Therefore, the reaction (4) is preferentially carried out under the voltage driving force, and the first step reaction controlled by electrochemistry produces Ti4O7 [26].

Table 2.
ΔGθ and E of TiO2 electro-deoxidation reactions at 1073 K.
Table 3 listed ΔGθ and E of Ti4O7, Ti2O3, and TiO electro-deoxidation reactions at 1073 K. The results show that E of Ti4O7 deoxidized to Ti2O3 is 0.48 V, which is lower than Ti4O7 deoxidized to TiO and Ti. Therefore, the second step reaction controlled by electrochemistry was Ti4O7 deoxidized to Ti2O3. In the same way, the third step reaction was Ti2O3 deoxidized to TiO. Finally, TiO deoxidized to Ti. According to the products obtained at different electrolysis times and electro-deoxidation thermodynamics analysis, the molten salt electrolysis from TiO2 to titanium is a multi-step electrochemical reaction process, which can be summarized as: TiO2→Ti4O7→Ti2O3→TiO→Ti.

Table 3.
ΔGθ and E of Ti4O7, Ti2O3, and TiO electro-deoxidation reactions at 1073 K.
3.4. Analysis of Electrochemical Deoxidation of TiO2 in NaCl-CaCl2 System
Then, 3 wt.% TiO2 was added to NaCl-CaCl2 binary molten salt system, and then the samples from the upper, middle, and lower crucibles were taken for XRD analysis after being heated to 1073 K for 4 h. The XRD patterns (Figure 6) show that no other substances were found in the samples taken from the upper and middle crucibles and TiO2 was deposited in the bottom of the crucible. It indicates that there is no chemical dissolution of TiO2 in the molten salt system. CaTiO3 cannot be formed spontaneously, because there is no electro-deoxidation reaction conducted to produce oxygen ions in the binary molten salt system.
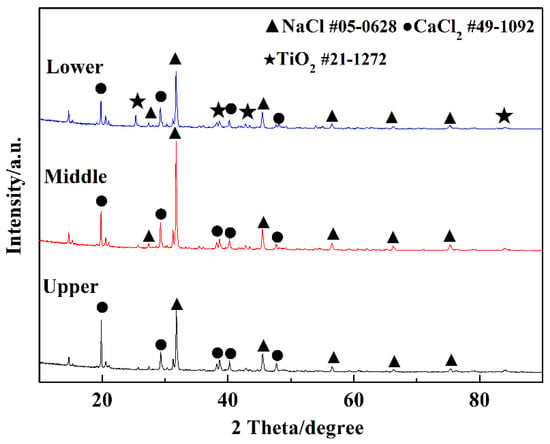
Figure 6.
XRD patterns of the binary salt samples taken from upper, middle, and lower crucibles.
Figure 7 displays the CV curves of NaCl-CaCl2 system before and after TiO2 addition. There is no redox peak found in the CV curve of NaCl-CaCl2 system without 3 wt.% TiO2; it demonstrates that the electrochemical properties of the binary molten salt electrolyte are stable, and the trace impurities in the salt have no influence on the experiment. CV curve of NaCl-CaCl2 system with 3 wt.% TiO2 shows that there are four reduction peaks, a, b, c, and d, which appear in the reduction process, and one oxidation peak d’ appears in the oxidation process. The asymmetric CV curve of NaCl-CaCl2 system without 3 wt.% TiO2 and |ipa/ipc|≠1 prove that the existence of reduction was an irreversible process. According to the four reduction peaks on the CV curve, the reduction of TiO2 to titanium metal may be divided into four steps, which was consistent with the above thermodynamic calculation results.
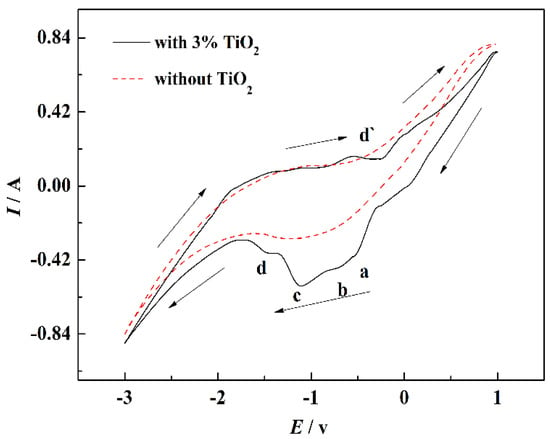
Figure 7.
CV curves of NaCl-CaCl2 system before and after 3 wt.% TiO2 addition with 0.7 V/s vs. Pt scan rate.
Figure 8 displays the CV curves of NaCl-CaCl2-TiO2 system with different scan rates. With the increase of the scan rate, the peak currents of the four reduction peaks gradually increased. The reduction potential corresponding to peaks a, b, and c shifted negatively with the increase of the scan rate, indicating that the reduction process was irreversible or quasi-reversible. Figure 9 displays the relationship between the scan rates of peaks a, b, and c and the peak current in NaCl-CaCl2-TiO2 system. It can be seen that the square root of the scan rate of reduction peaks a, b, and c has a linear relationship with the peak current, demonstrating that the reduction processes of a, b, and c are completely irreversible processes controlled by diffusion. The potential of peak d has no obvious deviation, so the reduction process corresponding to peak d is a reversible reaction. In consequence, both reversible and irreversible processes exist in the electrochemical reduction of TiO2 to titanium metal in the NaCl-CaCl2 binary system.
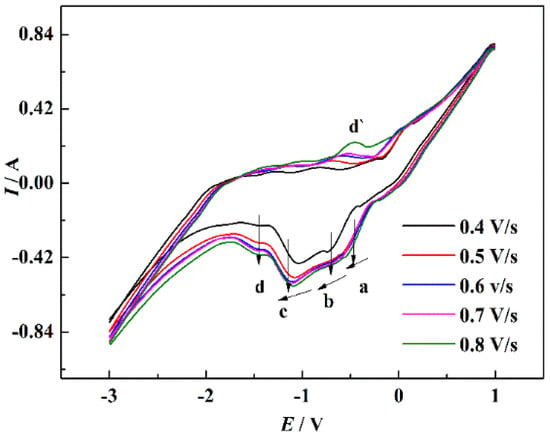
Figure 8.
CV curves of the NaCl-CaCl2-TiO2 system with different scan rate.
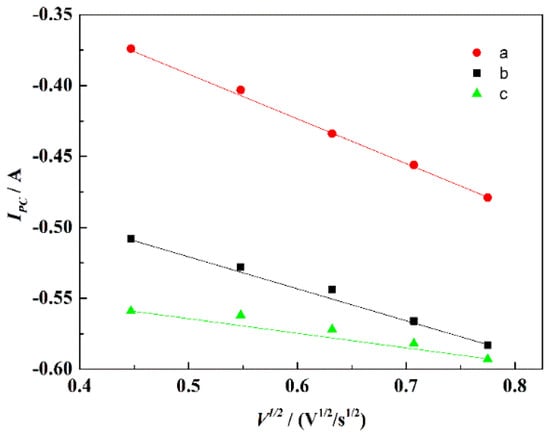
Figure 9.
Relationship between V1/2 of peaks a, b, and c and Ipc in the NaCl-CaCl2-TiO2 system.
For the irreversible process of the potentiodynamic scanning, the peak potential and logarithm of scan rate has the following relation, as shown in Equation (2). When Epc and lnv are in a linear function, the electron transfer number (n) in the process can be calculated according to the slope (k) of the fitting curve, shown in Equation (3).
where E is the peak potential (V); R, T, n, v, α, and F represent the ideal gas constant (8.314 J/(mol·K)), absolute temperature (K), the electron transfer number, the scan rate (V/s), the charge transfer coefficient, and Faraday’s constant (96,485 C/mol), respectively.
According to the CV curve, the reduction potential difference of peak a and b is 0.15 V, which is consistent with the theoretical decomposition potentials difference 0.14 V of the reactions (4) and (8). Figure 10 shows the fitting curves of the peak potential (Epc) and the logarithm scan rate (lnv). According to the slope of the fitting line, the electron transfer number in the combined process of peaks a and b was calculated to be 1.303, approximately 1, but there were also non-stoichiometric Ti4O7 in the reduction process of TiO2 to Ti2O3. Due to the small theoretical decomposition potential difference, the two independent peaks a and b could be approximately regarded as one peak. Peaks a and b represent the reduction process from TiO2 to Ti2O3 by direct reduction or a step-by-step process with an electron transfer number of 1, and Ti4O7 reduced to Ti2O3 was also controlled by diffusion [25]. The electron transfer number of peak c was calculated to be 1.298, approximately 1. According to the electron transfer number, the diffusion coefficients of diffusion-controlled processes A, B, and C are 0.349 × 10−5 cm/s and 0.2352 × 10−4 cm/s, respectively. The formula is shown in Equation (4) [27]:
where iP is peak current density (A/cm2); Co, A, and Do represent the concentration of the reactants (mol/cm3), work electrode area (1.95465 cm2), and diffusion coefficient (cm2/s), respectively.
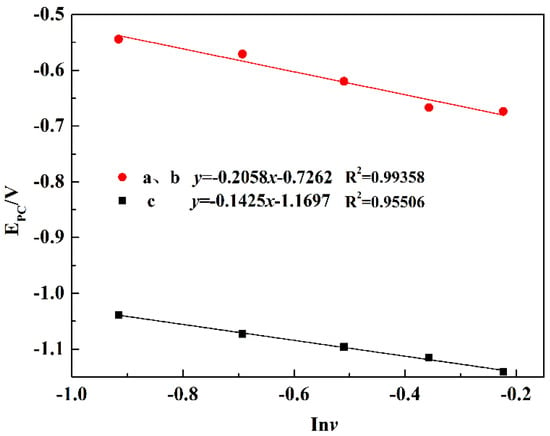
Figure 10.
Fitting curves of the peak potential (Epc) and the logarithm scan rate (lnv).
Figure 11 shows the square wave voltammetry curve of the NaCl-CaCl2-TiO2 system. Three obvious reduction peaks between −1.5 V and 0 V can be seen from the curve. The first peak of process a and b is near −0.5 V, the second peak of process c is near −1.0 V, and the third peak of process d is near −1.4 V, which is roughly the same as the reduction peak potential of the CV curve. The irreversible process in the reduction process is the main reason for a little shift of the reduction peak. Process d is a reversible process, so the relationship between the half-peak width and the electron transfer number can be expressed in Equation (5) [28]. The electron transfer number in process d calculated by Equation (5) is 2.324, approximately 2, which corresponds to reaction (13). The reduction process of TiO2 to titanium was further confirmed as TiO2→Ti4O7→Ti2O3→TiO→Ti.
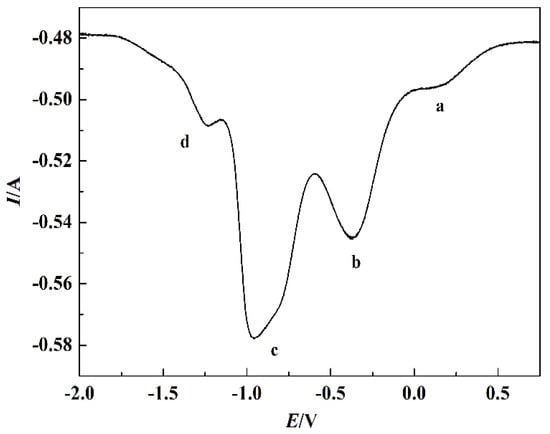
Figure 11.
Square wave voltammetry curves of the NaCl-CaCl2-TiO2 system with 4 V/s scan rate.
4. Conclusions
Titanium metal was prepared by the electrochemical reduction in NaCl-CaCl2 binary molten salt at 1073 K, and the reduction process of TiO2 to titanium can be summarized as TiO2→Ti4O7→Ti2O3→TiO→Ti. As an intermediate product in the deoxidation process of TiO2, CaTiO3 can be spontaneously generated among Ca2+, O2−, and TiO2 in the NaCl-CaCl2 system. The dissolution behavior of TiO2 showed that there is no chemical dissolution of TiO2 in the NaCl-CaCl2 molten salt system at 1073 K. Electro-deoxidation thermodynamics and electrochemical studies further confirmed that the reduction of TiO2 to titanium in four steps, and the processes were controlled by diffusion.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.M., H.Z. and S.B.; methodology, Z.J., X.M., Z.Y. and Y.Y.; validation, Z.Y., J.L. and H.L.; investigation, H.L., Z.J. and S.B.; resources, J.L., Y.Y. and H.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 52074125, and Tangshan Science and Technology Innovation Team Training Program Project under Grant No. 21130207D.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sibum, H.; Güther, V.; Roidl, O.; Habashi, F.; Wolf, H.U.; Siemers, C. Titanium, Titanium Alloys, and Titanium Compounds. In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istrate, B.; Munteanu, C.; Luca, D.; Earar, K.; Antoniac, I. Tribological tests and SEM analysis for titanium oxide layers. Key Eng. Mater. 2014, 614, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istrate, B.; Munteanu, C.; Strugaru, S.I.; Barca, A.; Biniuc, C.; Iulia, C.C. Influence of time on thermal oxidation of CP-Ti grade Ⅱ at 850 °C. Key Eng. Mater. 2014, 614, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Wang, D.H. The electrochemical reduction processes of solid compounds in high temperature molten salts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 3215–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanyam, R.B. Some recent innovations in the Kroll process of titanium sponge production. Bull. Mater. Sci. 1993, 16, 433–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagesh, C.R.V.S.; Rao, C.S.; Ballal, N.B. Mechanism of titanium sponge formation in the Kroll reduction reactor. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2004, 35, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, K.; Suzuki, R.O. A new concept for producing Ti sponge: Calciothermic reduction. JOM 2002, 54, 59–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, R.O.; Ono, K.; Teranuma, K. Calciothermic reduction of titanium oxide and in-situ electrolysis in molten CaCl2. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2003, 34, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.Z.; Fray, D.; Farthing, T. Direct electrochemical reduction of titanium dioxide to titanium in molten calcium chloride. Nature 2000, 407, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkader, A.M.; Kilby, K.T.; Cox, A.; Fray, D.J. DC voltammetry of electro-deoxidation of solid oxides. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 2863–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Wang, D.H.; Wang, W.G.; Hu, X.H.; Jin, X.B.; Chen, G.Z. Extraction of titanium from different titania precursors by the FFC Cambridge process. J. Alloy. Compd. 2006, 420, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.X.; Luo, X.Y.; Yang, Y.; Hu, M.L.; Wen, L.Y.; Zhang, S.F.; Hu, L.W. Reducing Carbon Contamination by Controlling CO32− Formation During Electrochemical Reduction of TiO2. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2021, 52, 1061–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.Z.; Gordo, E.; Fray, D.J. Direct electrolytic preparation of chromium powder. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2004, 35, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Wang, D.H. Rare metals preparation by electro-reduction of solid compounds in high-temperature molten salts. Rare Met. 2016, 35, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Jia, L.; Liang, J.L.; Yan, H.Y.; Cai, Z.Y.; Reddy, R.G. Study on the direct electrochemical reduction of Fe2O3 in NaCl-CaCl2 melt. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2019, 14, 11267–11278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Luo, X.Y.; Ma, T.X.; Wen, L.Y.; Hu, L.W.; Hu, M.L. Effect of Al on characterization and properties of AlxCoCrFeNi high entropy alloy prepared via electro-deoxidization of the metal oxides and vacuum hot pressing sintering process. J. Alloy. Compd. 2021, 864, 158717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Luo, X.Y.; Ma, T.X.; Hu, L.W.; Wen, L.Y.; Hu, M.L. Formation process of CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy via electro-deoxidization of metal oxides in molten salt. Rare Metal Mat. Eng. 2021, 50, 3116–3124. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, H.; Wang, M.; Tu, J.; Jiao, S. Production of AlCrNbTaTi high entropy alloy via electro-deoxidation of metal oxides. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, D574–D579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sure, J.; Vishnu, D.S.M.; Schwandt, C. Electrochemical conversion of oxide spinels into high-entropy alloy. J. Alloy. Compd. 2019, 776, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sure, J.; Vishnu, D.S.M.; Kim, H.K.; Schwandt, C. Facile electrochemical synthesis of nanoscale (TiNbTaZrHf)C high-entropy carbide powder. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 132, 11928–11933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freidina, E.B.; Fray, D.J. Study of the ternary system CaCl2–NaCl–CaO by DSC. Thermochim. Acta 2000, 356, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lair, D.C.V.; Cassir, M. CO2 electrochemical reduction into CO or C in molten carbonates: A thermodynamic point of view. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 160, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, W.; Wang, M.Y.; Gong, X.Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Guo, Z.C. Electrochemical reduction behavior of soluble CaTiO3 in Na3AlF6-AlF3 melt for the preparation of metal titanium. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, D551–D557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwandt, C.; Alexander, D.; Fray, D.J. The electro-deoxidation of porous titanium dioxide precursors in molten calcium chloride under cathodic potential control. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 3819–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, R.O. Calciothermic reduction of TiO2 and in situ electrolysis of CaO in the molten CaCl2. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2005, 66, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, W.; Wang, M.; Gong, X.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Z. Thermodynamic analysis on the direct preparation of metallic vanadium from NaVO3 by molten salt electrolysis. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 24, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.J.; Wang, X.; Xiao, J.S.; Hou, J.G.; Jiao, S.Q.; Zhu, H.M. Electrochemical behavior of silicon (IV) ion in BaF2-CaF2-SiO2 melts at 1573 K. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2013, 160, D81–D84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, R.S.; Shain, I. Theory of stationary electrode polarography. single scan and cyclic methods applied to reversible, irreversible, and kinetic systems. Anal. Chem. 1964, 36, 706–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).