Abstract
With the deepening of multi-energy coupling and the integration of high proportions of renewable energy, the Park Integrated Energy System (PIES) 1demonstrates enhanced energy utilization flexibility. However, the random fluctuations in photovoltaic (PV) output also pose new challenges for system dispatch. Existing distributed robust scheduling approaches largely rely on offline predictive models and therefore lack dynamic correction mechanisms that incorporate real-time operational data. Moreover, the initial probability distribution of PV output is often difficult to obtain accurately, which further degrades scheduling performance. To address these limitations, this paper develops a PV digital twin model capable of providing more accurate and continuously updated initial probability distributions of PV output for distributed robust scheduling in PIESs. Building upon this foundation, this paper proposes a distributed robust scheduling method for the PIES based on digital twins. This approach aims to maximize the flexibility of energy utilization in PIESs and overcome the challenges posed by random fluctuations in PV output to PIES operational scheduling. First, a PIES model is established after investigating a park-level practical integrated energy system. To describe the uncertainty of PV output, a PV digital twin model that incorporates historical data and temporal features is developed. The long short-term memory (LSTM) neural network is employed for output prediction, and real-time data are integrated for dynamic correction. On this basis, error perturbations are introduced, and PV scenario generation and reduction are carried out using Latin hypercube sampling and k-means clustering. To achieve multi-energy cascade utilization, the objective of optimization is defined as the minimization of the sum of system operating cost and curtailment cost. To this end, a two-stage distributed robust optimization model is constructed. The optimal scheduling scheme was obtained by solving the problem using the column-and-constraint generation (CCG) algorithm. The proposed method was finally validated through a case study involving an actual industrial park. The findings indicate that the constructed digital twin model achieves a significant improvement in prediction accuracy compared to traditional models, with the root mean square error and mean absolute error reduced by 13.3% and 10.81%, respectively. Furthermore, the proposed distributed robust scheduling strategy significantly enhances the operational economics of PIESs while maintaining system robustness, compared to conventional methods, thereby demonstrating its practical application value in PIES scheduling.
1. Introduction
In the context of global environmental degradation and the pressing need for a transition to low-carbon energy solutions, Park Integrated Energy Systems (PIESs) emerge as a pivotal solution. PIESs are characterized by multi-energy complementarity, cascading energy utilization, enhanced energy efficiency, and increased integration of renewable sources such as photovoltaics and wind power. These features position PIESs as a critical component in achieving carbon peaking and carbon neutrality goals [1,2]. PV generation exhibits significant environmental sensitivity, resulting in inherent fluctuations and randomness. These characteristics pose challenges to the safe and stable operation of power systems. Therefore, incorporating the uncertainty of photovoltaic output into the optimization and scheduling of PIESs is crucial for ensuring the secure and stable operation of the system.
In describing PV output uncertainty, commonly employed methods primarily encompass several major categories including probabilistic, stochastic process-based, and scenario-based approaches. Probabilistic methods, grounded in the statistical characteristics of historical data, fit PV output to specific probability distributions (such as Beta, log-normal, or hybrid distributions), proving suitable for scenarios with ample data and relatively stable distribution characteristics. Stochastic process methods (such as ARIMA, GARCH, Markov chains, Gaussian processes, etc.) can characterize the correlations within time series, but they often prove inadequate for capturing the non-stationarity and extreme volatility inherent in PV output. Scenario-based approaches, generating extensive samples via Monte Carlo simulations, LHS or Copula methods, then extracting a small number of representative scenarios through clustering, currently represent the most widely applied pathway in integrated energy system scheduling. Furthermore, while deep generative models (GANs, VAE) and machine learning methods such as random forests can fit complex distributions, they suffer from high training costs, strong parameter sensitivity, and insufficient interpretability. Consequently, their application in engineering scheduling remains limited.
Compared to traditional Monte Carlo sampling, Latin Hypercube Sampling (LHS) achieves more uniform coverage of values with the same sample size. By partitioning the input variable range into non-overlapping subintervals and sampling within each interval, it ensures balanced distribution of samples, thereby enhancing estimation accuracy and sample utilization efficiency. During the scenario reduction phase, K-means clustering generates a smaller number of well-defined representative scenarios while preserving distributional representativeness. This approach offers good interpretability and significantly reduces the computational scale of the subsequent DRO scheduling model. Compared to complex distribution generation methods such as Copula, GAN, and VAE, K-means offers straightforward computation, intuitive results, and effectively controls the computational scale of the DRO scheduling model, thereby enhancing the convergence efficiency of the CCG algorithm.
In summary, this paper employs LHS for sample generation and combines it with K-means clustering to construct typical photovoltaic scenarios. This approach balances accuracy, interpretability, and algorithmic convergence, rendering it more suitable for the integrated energy system dispatch scenarios described herein.
In PIES optimization scheduling, two main strategies mitigate PV output variability: improving forecasting accuracy and applying advanced optimization techniques. With respect to forecasting, methods can be classified into two categories: physical forecasting and statistical forecasting, based on the differing prediction models [3]. The physical prediction method is an engineering-based approach that utilizes a comprehensive simulation model encompassing the entire process, from solar irradiation to photovoltaic power generation. While it does not require extensive data, it necessitates accurate photovoltaic parameter information and complex photovoltaic mechanism modeling.
Conversely, the statistical prediction method utilizes big data models to ascertain the correlation between photovoltaic power generation inputs and outputs for forecasting. This data-driven approach exhibits a reduced reliance on physics-based modeling. Reference [4] examines the spatiotemporal characteristics of PV output and designs a discriminator structure that integrates CNN and LSTM networks. In this structure, the earth mover’s distance is employed as the loss function of the discriminator to generate PV output scenarios. Reference [5] addresses alterations in weather patterns caused by significant meteorological fluctuations by proposing a weather classification algorithm based on multi-scale volatility features. A multi-channel structured LSTM modeling approach is employed for comprehensive PV forecasting. While the aforementioned PV forecasting models take into account a variety of parameters, they are fundamentally reliant on pre-trained models for prediction. Reference [6] employs multiple data-driven models to forecast PV output, including Elastic Net regression, linear regression, random forests, k-nearest neighbors, gradient boosting regressors, lightweight gradient boosting regressors, extreme gradient boosting regressors, and decision tree regressors. This study systematically compares the performance of different machine learning methods in PV forecasting, providing guidance for selecting data-driven predictive models. Reference [7] proposes a novel fractional-order whale optimization algorithm enhanced support vector regression framework. By incorporating fractional calculus into the whale optimization algorithm, it effectively improves the balance between exploration and exploitation during hyperparameter optimization, yielding significantly enhanced prediction accuracy compared to traditional benchmark models.
The aforementioned PV forecasting studies have thoroughly explored aspects such as feature construction, model selection, and parameter optimization, achieving satisfactory prediction outcomes. However, such methods generally rely on static models trained offline, whose predictive performance becomes fixed after model training. When external conditions change—such as abrupt weather shifts, PV module aging, or increased dust contamination—the original model’s input-output relationship may become inaccurate. Consequently, prediction accuracy degrades over time, rendering the model incapable of continuously adapting to the dynamic variations inherent in real-world operational scenarios [8].
Therefore, it is necessary to compare the established models with their physical entities in real time, continuously track their accuracy, and perform online corrections when the accuracy requirement is not met. This can be achieved by constructing a digital twin (DT) model of PV, which enables real-time tracking of the physical PV system and iterative correction of the virtual model.
DT principally utilizes historical and real-time data to construct a virtual twin of physical entities, thereby enabling the reflection of their real-time status [9]. Reference [10] provides a comprehensive review of the current application status and key advancements of DT technology within the power generation sector, establishing a novel DT classification framework based on temporal scales and application scenarios. As one of the core enabling technologies for DT, machine learning has demonstrated formidable modeling capabilities across multiple energy contexts. In related research, Reference [11] proposed a novel hybrid quantum genetic algorithm–proximal policy optimization framework. This method combines the efficient global search capability of the quantum genetic algorithm with the adaptive policy update mechanism of proximal policy optimization, thereby achieving automatic parameter tuning and efficient feature space refinement. Reference [12] constructed a high-precision artificial intelligence diagnostic system successfully applied to wind turbine fault detection, demonstrating outstanding intelligent recognition performance. Reference [13] employed advanced deep learning image classification models for screening and evaluation, achieving exceptional results in image processing. These studies have yielded significant outcomes in machine learning algorithm design and model construction. Reference [14] employs advanced analytical modules such as CNN-LSTM and optimization algorithms to construct a proactive cognitive DT system. This system enables forward-looking power grid anomaly identification by predicting future health states and comparing them against real-time monitoring data.
The aforementioned research has achieved significant results in both DT architecture design and intelligent model construction. However, it has primarily focused on application scenarios such as condition monitoring, anomaly detection, or fault identification, without yet integrating DTs with distributed robust scheduling. In other words, how to leverage the real-time calibration capabilities of digital twins to construct uncertainty-driven probabilistic scenarios and serve the distributed robust scheduling of PIESs remains an unaddressed gap in current research.
The PV DT model constructed herein possesses not only self-learning capabilities but also dynamically calibrates itself based on real-time data, thereby ensuring its predictive accuracy remains consistently stable over time. This characteristic provides enhanced adaptability and reliability for PV forecasting. Furthermore, the DT model delivers more precise initial probability information for distributed robust scheduling, thereby improving the economic efficiency and robustness of the scheduling model when confronting PV output uncertainty.
With respect to the optimization techniques employed, the scheduling methods of PIES can be classified according to their uncertainty modeling approaches. These approaches include fuzzy optimization [15], stochastic optimization [16], robust optimization [17], and distributionally robust optimization (DRO) [18]. Fuzzy optimization and stochastic optimization are relatively dependent on subjective factors in the selection of related functions. While these systems offer notable economic advantages, their inherent fragility poses significant challenges to the reliable and secure operation of the system. Conversely, robust optimization addresses the worst-case scenarios, ensuring system resilience but often resulting in overly conservative outcomes and significant economic expenditures. DRO integrates the advantages of both stochastic optimization and robust optimization. The primary focus of this study is the uncertainty surrounding parameters in probability distribution functions. The objective is to ascertain the probability distribution of PV output under the most unfavorable conditions. Reference [19] established a DRO scheduling model for PIESs based on historical wind and solar data. In comparison with alternative optimization methodologies, DRO strikes a balance between economic efficiency and robustness. However, the initial scenarios required for its implementation are often challenging to obtain. Consequently, this paper employs a photovoltaic digital twin model, incorporates error, and utilizes Latin hypercube sampling and k-means clustering to provide typical PV output scenarios and corresponding scenario probabilities for DRO scheduling.
To overcome such problems and challenges, this paper proposes a DRO scheduling approach for PIESs based on DT. First, a DT model of PV is established, and on this basis, initial PV output scenarios are generated to characterize output uncertainty using Latin hypercube sampling and k-means clustering. Then, with the minimization of the total system operating cost and curtailment cost as the optimization objective, a two-stage distributionally robust optimization model is constructed considering the constraints of various equipment in PIES. To demonstrate the effectiveness and engineering applicability of the proposed methodology, a PV DT model and the corresponding DRO scheduling framework were implemented and validated at a representative site within an industrial park in Shanxi Province.
2. Integrated Energy Structure of the Industrial Park
Given that the actual campus energy system underpinning this research does not incorporate combined heat and power (CHP) equipment, this paper builds upon the PIES architecture proposed in reference [20]. It removes CHP-related equipment and their coupling relationships, thereby constructing a system model more suited to the research scenario. The adjusted structure of the PIES is illustrated in Figure 1.
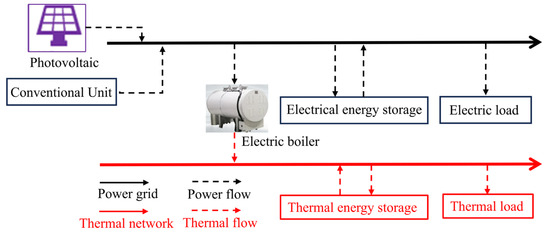
Figure 1.
PIES Architecture.
The source side encompasses PV output, conventional power units. The electric boiler functions as a thermoelectric conversion device, thereby facilitating complementary multi-energy flows. Concurrently, thermal and electrical storage devices facilitate the absorption of surplus photovoltaic output, thereby mitigating the fluctuations in photovoltaic power generation.
2.1. Digital Twin Framework of Photovoltaic System
The concept of DTs can be traced back to a proposal by Professor Grieves of the University of Michigan in 2002 regarding product lifecycle management [21,22]. Photovoltaic systems are characterized by their high susceptibility to environmental influences and the presence of complex operational mechanisms. Consequently, it is necessary to extract intrinsic characteristics from the data available in order to establish a data-driven model. A DT primarily achieves this by mining and analyzing vast amounts of real-time and historical data to reflect the real-time status of physical models.
The physical object constructed in this paper is the photovoltaic system within PIES, with the primary focus of this study being the establishment of a digital twin model for its forecasting capabilities. The Digital Twin Framework for PV in PIES is illustrated in Figure 2.
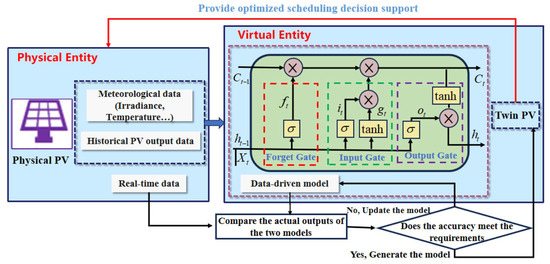
Figure 2.
Digital Twin Framework for PV in PIES.
As shown in Figure 2, the DT model constructed herein employs a bidirectional data interaction mechanism: operational data collected in real time at the physical layer drives updates and corrections to the virtual model, whilst predictive outcomes generated at the virtual layer exert a reciprocal influence upon the physical system, guiding its underlying operational strategies. This establishes a closed-loop, collaborative system architecture.
The primary process for constructing a PV DT model is as follows:
First, collect meteorological and historical output data from physical photovoltaic systems, then input this data into the data-driven model shown in Figure 2. This model is based on an LSTM neural network. The advantages of this model are detailed in the next section. After inputting the data, the initial model is trained using the LSTM.
Employ the following formula for error assessment and error classification.
where denotes the actual PV output, represents the predicted PV output, denotes the error threshold.
An error assessment is conducted every five minutes. If the error meets the required level of precision, the final DT model is generated. Otherwise, the data-driven model is updated by adjusting its hyperparameters through Bayesian optimization and retraining. If the error consistently fails to meet the requirements, comprehensive retraining is performed at hourly intervals. It is important to note that this data-driven model is not static but rather undergoes real-time updates.
To evaluate the performance of the DT model constructed in this paper for PV output forecasting, the root mean square error (RMSE) and mean absolute error (MAE) were employed as evaluation metrics to quantitatively assess its predictive accuracy, specifically, as shown in the following equation:
2.2. Photovoltaic Power Forecasting Based on LSTM
The photovoltaic power output demonstrates significant diurnal periodicity and seasonal variations and is also influenced by short-term meteorological changes. In order to circumvent issues such as gradient vanishing and gradient explosion that commonly occur during the training process of traditional neural networks, a memory unit and gating mechanism were introduced, leading to the development of LSTM. LSTM has been shown to enhance stability and applicability when processing time series data by forgetting unnecessary information while retaining key features. The LSTM architecture is illustrated in Figure 3.
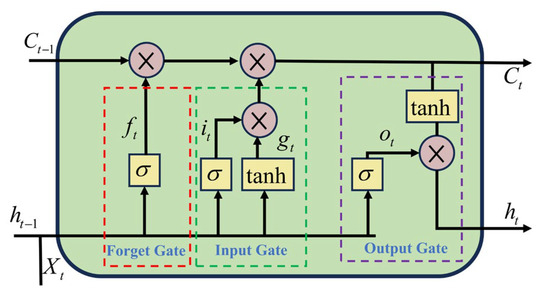
Figure 3.
LSTM architecture.
In Figure 3, , , and represent the cell state, output, and input at time . , , , and denote the computational formulas for each gate unit. The specific formulas are provided in References [23,24].
2.3. Scenario Generation Based on Latin Hypercube Sampling and Scenario Reduction with K-Means Clustering
In order to account for subsequent scheduling robustness requirements, it is necessary to superimpose error margins on the PV forecast. However, PV forecast results incorporating uncertainty errors are calculated during the scheduling process. Consequently, multi-scenario techniques can be utilized to transform PV forecasts with uncertainty errors into a set of deterministic scenarios [25,26]. The prediction error of PV output can be modeled as a population following a normal distribution with zero mean. Consequently, the actual PV power can be expressed as in Equation (5).
where represents the actual PV output, represents the predicted PV output, is the random disturbance at time and is the standard deviation in the normal distribution.
The Latin hypercube sampling (LHS) method can be utilized to generate PV output scenarios that align with the distribution of PV forecasting errors. In comparison with Monte Carlo simulation sampling, LHS attains a more uniform distribution of values while maintaining an equivalent sample size. The range of each input variable is divided into multiple non-overlapping subintervals, and a single sample is randomly selected from each subinterval. This stratified sampling technique ensures that all sampling regions are covered by the sampling points, thereby improving estimation accuracy and sample utilization.
The scenarios generated by LHS are frequently characterized by their expansive scale. The utilization of raw scenarios invariably leads to a marked reduction in the efficiency and speed of solutions. Therefore, it is necessary to reduce the large number of original scenarios by selecting a few representative scenarios and assigning corresponding probability values to each. In this paper, the k-means clustering algorithm is employed for scenario reduction. The k-means clustering algorithm first determines the initial cluster centers using the elbow method then computes the Euclidean distance between the remaining scenarios and the cluster centers, assigning each scenario to the nearest cluster center. The specific implementation of this method is described in reference [27].
The contour coefficient serves to describe the clarity of each cluster’s outline following clustering, constituting a vital metric for evaluating clustering efficacy. Its core function lies in simultaneously measuring intra-cluster compactness and inter-cluster separation, thereby determining the validity of the clustering. The contour coefficient comprises two components: the intraclass average distance and the interclass minimum distance . The specific expression is as follows:
where denotes the distance from to , while represents the cluster to which sample belongs. A smaller value of a indicates more compact cluster. denotes the average distance between sample and all samples in other clusters, taking the minimum value. A larger value of indicates more pronounced separation from other clusters. The larger the value defined by combining these two parameters, the more reasonable the clustering result for that sample and the better the overall clustering performance.
3. Distributed Robust Scheduling Model for Integrated Energy Systems in Industrial Parks
The overall logic of the distributed robust scheduling model for PIES is demonstrated in Figure 4. Firstly, a digital twin model for photovoltaic generation is established, along with a basic PIES scheduling model that aims to minimize system operational costs without considering the uncertainty in photovoltaic output. As a consequence of photovoltaic power forecasting, errors are introduced, and multiple scenarios are generated to match the error distribution. These scenarios are then reduced to a small number of representative ones, each assigned a corresponding probability. The inherent variability in photovoltaic output is then integrated into the fundamental PIES scheduling model, thereby transforming it into a distributed, robust scheduling model for PIES. Ultimately, the CCG algorithm is employed to solve and obtain the final distributed robust scheduling solution for PIES.
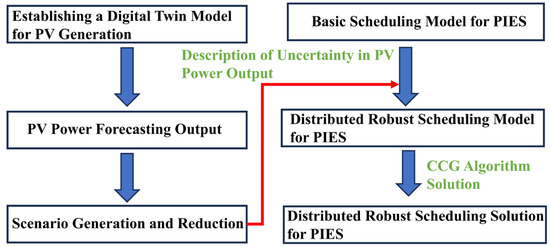
Figure 4.
Overall Logic of PIES’ Distributed Robust Scheduling.
3.1. Dispatch Model for Integrated Energy Systems in Industrial Parks
(1) Objective function
This section first constructs the basic scheduling model for PIES without considering the uncertainty in PV power output, which serves as the foundation for the subsequent distributed scheduling. The objective function of this model is to minimize system operational costs and curtailment costs, as shown in the following equation.
where represents the system operating cost, and represents the curtailment cost. The system operating cost comprises the start-up and shutdown costs of conventional generating units, and the power generation cost, denoted by and, respectively.
The generation cost can be represented by the corresponding fuel coefficient.
The generation costs for conventional units are expressed as follows:
where and represent the equivalent nonlinear and linear power generation cost functions for the j-th conventional unit, respectively. denote fixed costs for the j-th unit generators such as maintenance expenses. denotes the total number of time periods. denote the total number of units for conventional. denote the power output of the j-th unit for conventional units at time .
In order to address potential fluctuations, conventional units incur corresponding startup and shutdown costs.
The startup and shutdown costs are given as
where and represent the startup and shutdown costs for conventional units, while and denote the startup/shutdown status flags of the j-th unit for conventional units at time . When equals 1 and equals 0, it indicates startup; when equals 1 and equals 0, it indicates shutdown.
In order to achieve greater decarbonization, it is essential to prioritize the maximization of PV power accommodation. Consequently, the financial implications of PV curtailment are integrated into the objective function.
where denotes the number of PV units, represents the linear coefficient of curtailment costs, and denote the actual output and predicted output of the j-th PV unit at time , respectively.
(2) Constraints
To ensure the safe and stable operation of the system and to account for the inherent characteristics of various devices, the PIES scheduling must satisfy a set of constraint conditions. The power balance constraints include both electrical power balance and thermal power balance.
The electrical power balance constraint is given as
where and represent the number of electrical energy storage units and electric boilers, respectively. denotes the j-th energy storage charge/discharge indicator at time, where −1 indicates charging and +1 indicates discharging. is the output value of the j-th electrical energy storage unit at time . is the electrical power consumed by the j-th electric boiler at time . is the electrical load at time .
The thermal power balance constraint is given as
where denotes the thermal output of the j-th thermal energy storage unit at time ; is the thermal output of the j-th electric boiler at time ; and represents the thermal load at time .
Conventional units must satisfy corresponding electrical power constraints and ramping constraints.
Electrical power constraints are defined as:
where and represent the upper and lower limits of the output of the j-th unit, respectively.
Ramp rate constraints:
where denotes the climbing rate of a conventional unit, and denotes the sliding rate.
The start-up and shutdown status of conventional units is represented by a single state variable, namely:
The output of the electric boiler must also meet the upper and lower limit requirements and coupling requirements, with its coupling efficiency also being a fixed value:
where
and
represent the upper and lower limits of the output for the j-th electric boiler unit, respectively, and
denotes the electrical-to-thermal conversion efficiency of the electric boiler.
Photovoltaic output must meet its upper and lower limit requirements:
where and represent the upper and lower limits of the j-th photovoltaic output, respectively.
The operation of energy storage systems must satisfy the mutually exclusive charging and discharging requirement, as well as the upper and lower limits of charging/discharging power and storage capacity. In addition, the initial and final states of the storage system must be consistent. Since the operational principles of electrical and thermal energy storage are similar, this paper takes electrical energy storage as an example, and the thermal energy storage model is therefore not presented in detail.
The electrical energy storage constraints as follows:
where / are the energy storage charge/discharge status bits. A value of 1 indicates charging/discharging, while a value of 0 indicates no charging/discharging. and denote the charging/discharging power of the j-th energy storage unit at time . , , , and represent the upper and lower limits of charging/discharging for the j-th unit. and are the charging/discharging conversion coefficients. indicates the capacity of the j-th unit at time . and denote the initial and final storage capacities of the j-th unit.
To simplify the analysis, the basic scheduling model underlying the above construction can be expressed by the following equation:
where represents deterministic variables that are not affected by PV forecast errors, including the start-up and shutdown status of conventional units as well as the charging and discharging states of electrical and thermal energy storage systems. represents real-time adjustable variables that vary with PV output, including the power outputs of various units. denotes the equivalent start-up and shutdown costs coefficient, while represents the generation cost and the cost associated with PV curtailment. is the PV forecast vector. , , , , , and are coefficient matrices.
Equation (22) represents the objective function, while Equations (23)–(26) correspond to the constraint conditions. Equation (23) describes the start-up/shutdown and charging/discharging state constraints, corresponding to Equations (18) and (21). Equation (24) represents the upper limit constraint of PV output, corresponding to Equation (20). Equations (25) and (26) encompass all the remaining equality and inequality constraints that must be satisfied, including power balance constraints.
3.2. Distributed Robust Dispatch Model for Integrated Energy Systems in Industrial Parks
Even after prediction using DT, PV output still contains uncertainties. Therefore, a distributionally robust approach is adopted to account for this portion of uncertainty. In the previous section, a basic scheduling model was established; based on this model, a distributionally robust model will be constructed.
Distributed robust models combine robust optimization methods with stochastic optimization methods, deriving scheduling schemes by seeking the most unfavorable probability distribution of PV output.
To facilitate analysis and solution, this paper constructs a two-stage DRO scheduling framework: in the first stage, decision variable remains constant regardless of actual scenario variations; in the second stage, decision variable is adjusted according to different scenarios to describe feasible scheduling strategies under the worst-case probability distribution. This model identifies optimal scheduling solutions that balance economic efficiency and robustness by searching for the probability distribution of the worst-case scenario within the uncertainty set.
Building upon this foundation, Equation (22) can be further modified as follows:
where and denote the feasible domains of and formed by their respective constraints; represents the probability of the scenario occurring; denotes the set of feasible domains for the scenario’s probability distribution.
Equation (27) represents the two-stage distributed robust model constructed in this paper. In the first stage, remains constant regardless of actual scenario changes, while represents the quantity subject to change in the second stage. This primarily involves probabilistically modeling the worst-case scenario to identify an optimized value that meets economic objectives.
To identify the worst-case probability distribution of the scenarios, the most straightforward method is to enumerate the probability values of each scenario and iterate. However, to ensure the reasonableness of the probability distribution, two additional constraints—the norm and norm—are imposed on based on its initial value. The initial value is obtained from the PV output predicted by the digital twin in Section 2, after clustering and reduction.
To avoid the occurrence of extreme conditions, both the norm and the norm must be considered simultaneously. Their constraints can be expressed as
where and represent the probability-allowed deviation values under the norm and norm conditions, respectively.
According to Reference [28], the confidence constraints of and satisfy
where is the opportunity constraint function.
The right-hand side of Equations (29) and (30) can also be expressed in terms of the confidence levels and of the uncertainties.
Consequently, and can be determined as
It is worth noting that Equations (29) and (30) also contain absolute value variables, which complicate the solution process. Therefore, two auxiliary variables and are introduced into these constraints. This allows the absolute values to be transformed into
where and denote the positive and negative offsets of the initial values.
Similarly, it can be obtained that:
where and are also auxiliary variables.
3.3. Model Solution
Equation (27) can be considered as a min-max-min problem. For this problem structure, the column-and-constraint generation (CCG) algorithm is highly suitable. This is due to the fact that it facilitates the decomposition of the original problem into a primary problem and a series of subsidiary problems. The approach entails the alternating resolution of the primary and secondary problems, thereby circumventing the computational explosion that would otherwise ensue from the direct solution of a large-scale model. This, in turn, enhances solution efficiency. The solution process to this problem is outlined below:
(1) Main Problem (MP)
MP lies in obtaining variables that satisfy optimal economic conditions under the most adverse probability distributions. It provides a lower bound (LB) for model Equation (27), as shown in Equation (34).
where is the number of iterations.
(2) Subproblem (SP)
The subproblem essentially involves identifying the most unfavorable probability distribution while fixing the variable , thereby providing an upper bound (UB) for Equation (27) to facilitate further iterative computation in the main problem. Specifically, as demonstrated in Equation (35):
First set and . Then fix to solve the main problem Equation (27) to obtain . Update the value of such that . At this point, fix the obtained and solve the subproblem Equation (28) to obtain a new value. Update the value of such that .
(3) After obtaining the new value, solve Equation (35) to obtain the new value, and update the values of and . Repeat this process until .
It is posited that, by means of this iterative, alternating solution process, an optimal scheduling scheme that satisfies economic efficiency can ultimately be obtained.
4. Case Study
4.1. Scenario Description
This case study selects an industrial park in Shanxi as the research object. The system includes photovoltaic units, electric boilers, and electrical and thermal energy storage systems.

Table 1.
Parameters of Conventional Units.

Table 2.
Energy Storage Parameters.

Table 3.
Electric Boiler Operating Parameters.
The load curve for the example is shown below Figure 5:
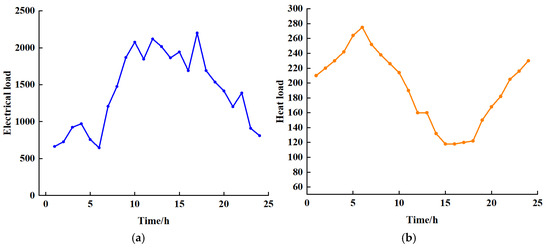
Figure 5.
(a) Electricity load curve; (b) Heat load curve.
4.2. Results of PV Output Scenario Construction
Using solar irradiance, temperature, and humidity as input variables and PV output power as the output variable, an LSTM model is constructed. The data resolution is 5 min, with 70% of the data used as the training set and the remaining 30% as the test set. The time window is set to three steps (equivalent to 15 min) using a single-step forecasting approach. To prevent overfitting, an early stopping mechanism is incorporated into the training of the model. This mechanism monitors the loss in the validation set after each epoch; if the loss in the validation set fails to improve over five consecutive epochs (patience = 5), training is terminated prematurely. All input features undergo standardization via the maximum–minimum normalization method, expressed in Equation (36).
During model training, Adam was used as the optimizer and MAE was used as the loss function. Both MAE and RMSE were used as evaluation metrics. To validate the advantages of the proposed DT model’s predictive performance over traditional LSTMs, comparative experiments were conducted using a baseline LSTM model and the prediction model within the digital twin framework. Both models were configured with 200 hidden units and a maximum iteration count of 64. The comparison chart of DT and traditional LSTM predictions is presented in Figure 6.
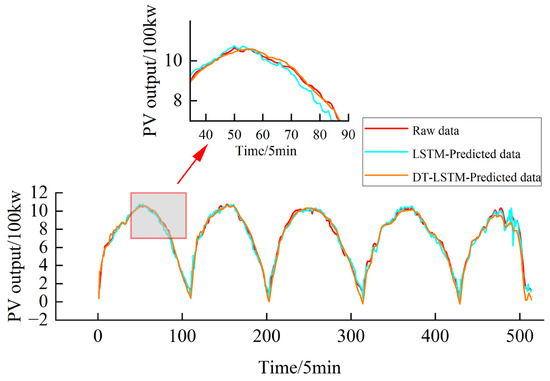
Figure 6.
The comparison chart of DT and traditional LSTM predictions.
The comparisons of prediction error results are listed in Table 4. This enables a straightforward comparison of the predictive accuracy differences between various models.

Table 4.
Comparison of Prediction Error Results.
As shown in Table 4, the DT model demonstrates a marked improvement in prediction error compared to the baseline LSTM, with RMSE and MAE reduced by 13.3% and 10.81%, respectively. This outcome indicates that the DT framework enhances both the robustness and predictive accuracy of the model.
Based on the PV output forecast results, LHS was employed to generate 1000 PV output scenarios conforming to the PV forecast output error distribution. With K values set to equal intervals from 2 to 7, elbow diagrams based on the sum of squared errors and contour coefficient diagrams were plotted, as shown in Figure 7 and Figure 8.
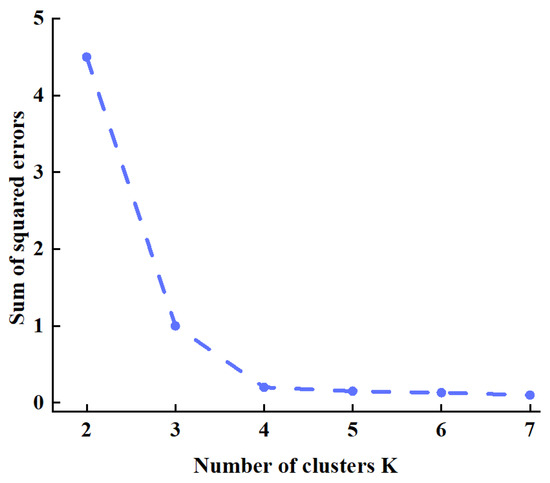
Figure 7.
Elbow diagrams based on the sum of squared errors.
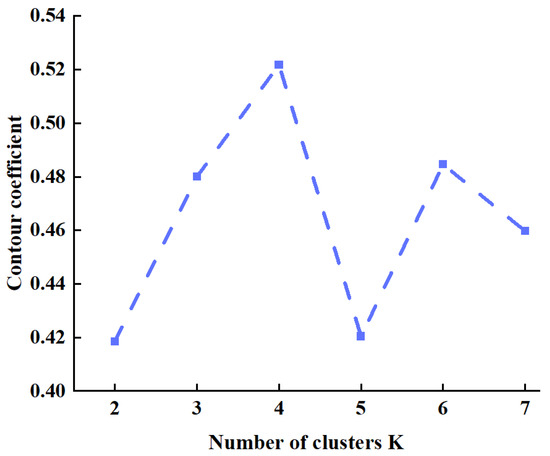
Figure 8.
Contour coefficient diagram.
The results of the elbow method shown in Figure 6 reveal that the sum of squared errors exhibits the most pronounced inflection point at K = 4, indicating that the marginal benefit of further increasing the number of clusters for improving clustering performance has markedly diminished. Concurrently, the contour coefficient evaluation in Figure 7 reveals that the average contour coefficient attains its maximum value when K = 4, indicating this clustering number achieves optimal intra-cluster compactness and inter-cluster separation. Combining these two metrics, K = 4 is ultimately selected as the optimal scenario count. Following determination of the cluster number, the k-means method is applied to cluster the PV output data, yielding the initial PV scenarios depicted in Figure 9.
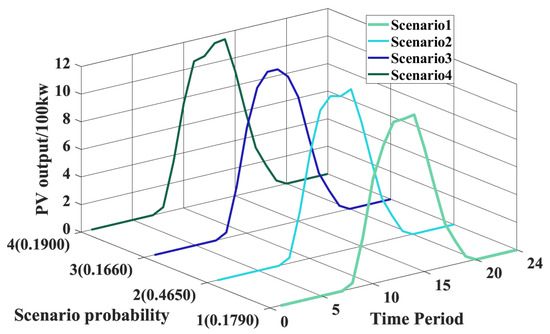
Figure 9.
Initial Scenario of PV Output.
The employment of scenario reduction techniques facilitates the acquisition of the initial PV output scenarios and their probability distributions. This provides the initial probability values and distribution scenarios for distributed robust PV scheduling, facilitating the subsequent derivation of a distributed robust scheduling solution.
4.3. Analysis of Distributed Robust Scheduling Performance
Following the acquisition of the initial photovoltaic output scenario and initial probabilities in the preceding section, distributed robust scheduling was performed on the integrated energy system.
The integrated energy power optimization results are demonstrated in Figure 10:
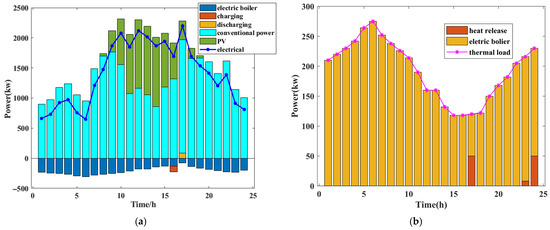
Figure 10.
(a) Electrical power optimization results; (b) Thermal power optimization results.
From the electrical power distribution results in Figure 10, it can be observed that the system consistently adheres to an operational strategy of ‘prioritizing the consumption of renewable energy’ on the power supply side. Due to the existence of curtailment costs, when PV output is high, the PV electricity first satisfies the system’s load demand, reflecting the priority of renewable energy in dispatch. For portions of PV output exceeding real-time demand, the dispatch strategy proactively activates the electrical energy storage system for charging, absorbing and storing surplus electricity. This approach not only prevents curtailment but also enhances local consumption capacity for new energy sources. During periods of low or fluctuating PV output, conventional generating units assume primary responsibility for power supply, effectively compensating for shortfalls caused by renewable energy fluctuations. This ensures the stability of power system operation and maintains supply reliability.
In terms of thermal power scheduling, Figure 10 illustrates that thermal loads are primarily supplied by electric boilers. These boilers convert electrical power into thermal energy, serving as the key equipment for electricity-heat coupling. When thermal load levels within the system are high and electrical supply cannot fully meet thermal demand, thermal storage units release previously stored heat to bridge the thermal gap, thereby maintaining thermal equilibrium. During periods of high PV output, low electricity prices, or energy storage charging, electric boilers can utilize inexpensive or surplus electricity for heating and store it in thermal storage units, thereby achieving time-shifted energy utilization.
The synergy between electricity and heat enhances the flexibility of energy systems. The coordinated operation of electrical energy storage and thermal storage devices not only smooths out the random fluctuations in photovoltaic output but also deepens the coupling between electrical and thermal systems. This improves the efficiency of cascading energy utilization and significantly reduces energy wastage such as curtailed solar power and unused thermal energy. Overall, the dispatch strategy achieves an effective trade-off between renewable energy integration, electricity-heat balance, and operational economics, demonstrating the advantages of coordinated optimization within integrated energy systems.
4.4. Comparative Analysis with Other Methods
To validate the effectiveness of the proposed method, it is compared with both fuzzy optimization and robust optimization approaches. The comparison results are shown in Table 5:

Table 5.
Optimization Costs of Different Optimization Methods.
Table 5 demonstrates that the three methods exhibit distinct differences in scheduling costs: fuzzy optimization incurs the lowest cost, robust optimization the highest, while distributed robust optimization’s cost lies between the two. This outcome is closely linked to the distinct approaches each method employs in handling PV output uncertainty.
Firstly, fuzzy optimization empirically compresses PV output uncertainty into a single fuzzy value or membership interval, inherently disregarding extreme or worst-case output scenarios. Consequently, the optimization process adopts relatively aggressive scheduling strategies, minimizing costs associated with unit output and energy storage regulation. However, fuzzy optimization offers limited coverage of uncertainty. Should actual PV output deviate from projections, the system becomes more susceptible to power shortfalls or insufficient reserves, exhibiting weaker robustness and heightened operational risks.
Traditional robust optimization usually uses box-shaped uncertainty sets, considering all potential PV errors to be worst-case scenarios. This ‘global worst-case’ assumption significantly increases reserve requirements and often results in unit dispatch based on extreme conditions. Although it offers high safety margins, the drawbacks are equally pronounced: dispatch plans become excessively conservative, substantially increasing economic costs—a phenomenon that is particularly evident in systems with high PV penetration.
In contrast, DRO improves robustness by introducing scenario probability distributions and their uncertainty sets. It focuses solely on ‘worst-case scenarios with a certain probability’. This approach avoids the excessive conservatism of traditional robust optimization and outperforms the lack of robustness of fuzzy optimization. Within DRO, modifying robust boundaries allows models to reduce unnecessary standby costs while maintaining reliability, thus striking a balance between economic efficiency and robustness.
In summary, DRO effectively mitigates the risk of excessive conservatism in scheduling schemes while ensuring system safety. Of the three approaches, it is the optimal strategy, balancing economic efficiency, flexibility and robustness. Clearly, the DRO method successfully reconciles economic considerations with robustness.
4.5. Analysis of Solution Algorithms
An analysis of the CCG algorithm reveals that the specific results of the iterative cases described herein are presented in Table 6.

Table 6.
CCG Algorithm Iteration Results.
As shown in Table 6, after three iterations, the difference between the upper and lower bounds falls below the convergence criterion. The termination of iterations indicates that the CCG algorithm achieves rapid solution speeds for the DRO problem addressed in this paper.
5. Conclusions
This paper develops a digital twin model for PV systems, which, in contrast to traditional models, allows for adjustments over time. Based on forecasting, the Latin Hypercube Sampling and k-means clustering methods are employed to generate initial scenarios and probabilities for PV output.
A comprehensive energy system for the park has been established, and the uncertainty of PV output has been addressed using a distributed robust optimization method with norm-based constraints. This has resulted in a distributed, robust scheduling solution that has been solved using the CCG algorithm.
Through comparative analysis, it is concluded that the distributed robust approach, compared to traditional methods, better balances both the economic efficiency and robustness of the system.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.L.; Methodology, X.C. and Q.W.; Investigation, L.J.; Writing—review and editing, B.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is supported by State Grid Shanxi Electric Power Company Science and Technology Project Research (52053024000V).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by State Grid Shanxi Electric Power Company Science and Technology Project Research (52053024000V). We would like to thank the State Grid Shanxi Electric Power Company Electric Power Research Institute and Shanghai University of Electric Power for their assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Xiao Chang, Shengwen Li and Qiang Wang were employed by the State Grid Shanxi Electric Power Company. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| PIES | Park Integrated Energy Systems |
| PV | Photovoltaic |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| DT | Digital Twin |
| DRO | Distributionally Robust Optimization |
| LHS | Latin Hypercube Sampling |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error |
| CCG | Column-And-Constraint Generation |
| UB | Upper Bound |
| LB | Lower Bound |
References
- Yue, Y.; Miao, A.; Wu, H.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Z.; Qian, K. Review of the Research Framework and Key Issues for Low-carbon Integrated Energy System. High Volt. Eng. 2024, 50, 4019–4036. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, D.; Cheng, H.; Song, Y.; Yuan, K.; Du, W. Key Technologies and Challenges of Low-carbon Integrated Energy System Planning for Carbon Emission Peak and Carbon Neutrality. Autom. Electr. Power Syst. 2022, 46, 189–207. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dong, C.; Wang, Z.; Bai, J.; Jiang, J.; Wang, B.; Liu, G. Review of Ultra-short-term Forecasting Methods for Photovoltaic Power Generation. High Volt. Eng. 2023, 49, 2938–2951. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qin, W.; Tang, H.; Ren, M.; Liang, X.; Wang, T.; Chen, T. Improved CGAN Photovoltaic Short-Term Output Scenario Generation Method Based on CNN-LSTM. J. Sol. Energy 2025, 46, 263–272. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, F.; Li, L.; Bian, D.; Bian, W.; Wang, Q.; Wang, S. Photovoltaic power prediction based on multi-scale photovoltaic power fluctuation characteristics and multi-channel LSTM prediction models. Renew. Energy 2025, 246, 122866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.; Shaf, A.; Ali, T.; Zafar, M.; AlThobiani, F.; Almas, M.A.; Attar, H.M.; Alqhatani, A.; Rahman, S.; Almawgani, A.H.M. Global horizontal irradiance prediction for renewable energy system in Najran and Riyadh. AIP Adv. 2024, 14, 035137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadood, A.; Albalawi, H.; Alatwi, A.M.; Anwar, H.; Ali, T. Design of a Novel Fractional Whale Optimization-Enhanced Support Vector Regression (FWOA-SVR) Model for Accurate Solar Energy Forecasting. Fractal Fract. 2025, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Zhang, D.; Han, X.; Xie, Z. Digital Twin Model of Photovoltaic Power Generation Prediction Based on LSTM and Transfer Learning. Power Syst. Technol. 2022, 46, 1363–1372. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lai, B.; Hao, J.; Yang, T.; Du, X.; Wang, S.; Lyu, H.; Chen, J. Development and Challenges of Intelligent Operation and Maintenance of Integrated Energy Systems Based on Digital Twin. Proc. CSEE 2025, 1–17. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahmoradi, S.; Imani, M.H.; Mazza, A.; Pons, E. Applications of the Digital Twin and the Related Technologies Within the Power Generation Sector: A Systematic Literature Review. Energies 2025, 18, 5627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindi, A.T.; Irfan, M.; Yasin, S.; Draz, U.; Ali, T.; Yasin, I.; Rahman, S. Hybrid quantum-inspired proximal policy optimization for fault detection in wind turbine on supervisory control and data acquisition system. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part I J. Syst. Control Eng. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.; Yasin, S.; Draz, U.; Ali, T.; Yasin, I.; Kareri, T.; Rahman, S. Revolutionizing wind turbine fault diagnosis on supervisory control and data acquisition system with transparent artificial intelligence. Int. J. Green Energy 2025, 22, 2029–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alatwi, A.M.; Albalawi, H.; Wadood, A.; Anwar, H.; El-Hageen, H.M. Deep Learning-Based Dust Detection on Solar Panels: A Low-Cost Sustainable Solution for Increased Solar Power Generation. Sustainability 2024, 16, 8664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, H.; Luo, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, D.; Dang, P.; Gao, J.; Lin, L.; Wang, H. Forecasting to Foresight: Building an Autonomous O&M Brain for the New Power System Based on a Cognitive Digital Twin. Electronics 2025, 22, 4537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiming, C.; Qian, X.; Yong, L. Optimal Dispatch of Electricity-Natural Gas Interconnection System Considering Source-Load Uncertainty and Virtual Power Plant with Carbon Capture. J. Sol. Energy 2023, 44, 9–18. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.; Wang, C.; Niu, Y.; Wang, K.; Yao, W.; Liu, C. Two-stage Stochastic Optimization Decision of Integrated Energy System Considering the Uncertainty of Integrated Demand Response. Power Syst. Technol. 2025, 45, 2232–2242. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, H.; Sun, S. Stackelberg Game-Robust Optimal Scheduling of Integrated Energy System in Parks Accounting for Multi-Scenario Collaborative Carbon Reduction. J. Sol. Energy 2025, 1–15. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, D.; Dongmei, Z.; Xin, L. Research Review on Optimal Scheduling Considering Wind Power Uncertainty. Proc. CSEE 2023, 43, 2608–2626. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, S.; Lu, Y.; Wang, C. Distributed robust optimal scheduling for a regional integrated energy system considering coordinated operation of P2G-CCS-HFC. Power Syst. Prot. Control 2025, 53, 87–101. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shui, Y.; Liu, J.; Gao, H.; Huang, S.; Jiang, Z. A Distributionally Robust Coordinated Dispatch Model for Integrated Electricity and Heating Systems Considering Uncertainty of Wind Power. Proc. CSEE 2018, 38, 7235–7248. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Grieves, M. Product Lifecycle Management: Driving the Next Generation of Lean Thinking by Michael Grieves; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Ai, Q.; Zhu, T.; Qiu, C.; Zhang, D. Opportunities and Challenges of the Digital Twin in Power System Application. Power Syst. Technol. 2020, 44, 2009–2019. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Xiong, G.; Fang, H.; Luo, Y. Short-term photovoltaic power interval prediction model based on MODWT-CEEMDAN-LSTM. J. Sol. Energy 2025, 46, 416–424. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Li, C.; Liu, J.; Li, C. Short term photovoltaic power prediction based on GRO-SSA-LSTM. J. Sol. Energy 2025, 46, 401–409. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Nan, B.; Jiang, C.; Dong, S.; Xu, C. Day-ahead and Intra-day Coordinated Optimal Scheduling of Integrated Energy System Considering Uncertainties in Source and Load. Power Syst. Technol. 2023, 47, 3669–36683. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.; Xu, H.; Lang, J.; Xia, H. Multi-scenario distributed robust optimal scheduling of multi-area integrated energy systems considering photovoltaic uncertainty. J. Sol. Energy 2024, 45, 460–469. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wen, X.; He, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, K.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, F. Research on ultra-short-term power forecasting of photovoltaic clusters based on K-means clustering. Power Syst. Prot. Control 2025, 53, 165–172. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ju, Y.; Kang, X.; Liu, W.; Zhang, J. Distributed Coordinated Day-ahead Scheduling Method for Distribution Network and Microgrid Based on Distributionally Robust Optimization. Power Syst. Autom. 2024, 48, 48–58. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).