Urban Wind as a Pathway to Positive Energy Districts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
- Titles and abstracts were first reviewed to evaluate their relevance to the research topic.
- Full-text articles were then examined to identify scientific and technical contributions, methodologies, and key findings pertinent to the study.
- The extracted findings were categorized into thematic areas and incorporated into the corresponding sections of the review.
- peer-reviewed journal articles and conference proceedings were preferred—120 (98.4% of all references);
- articles published in the last 10 years were primarily considered—110 (91.7%), including 79 articles published in the period 2020–2025 and 31 articles published in the period 2015–2019;
- articles from well-established editorial sources were mainly cited, including Elsevier, MDPI, Wiley, Springer Nature, Frontiers, EDP Sciences, IOPscience, and IntechOpen.
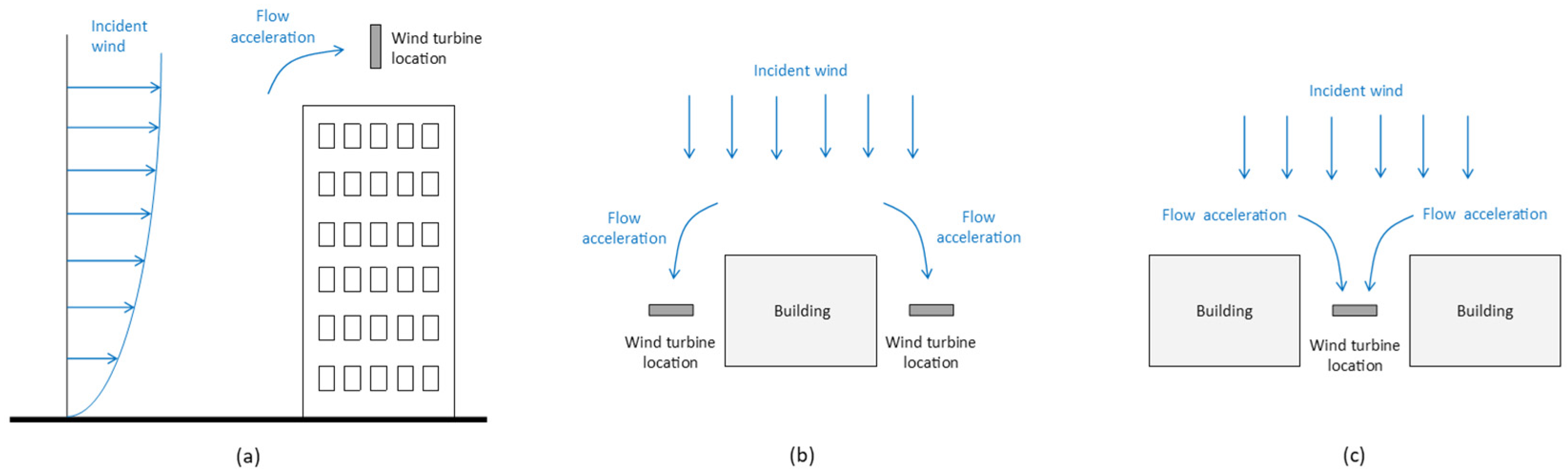
3. Overview of Urban Wind Energy Assessment
3.1. GIS-Based Mapping
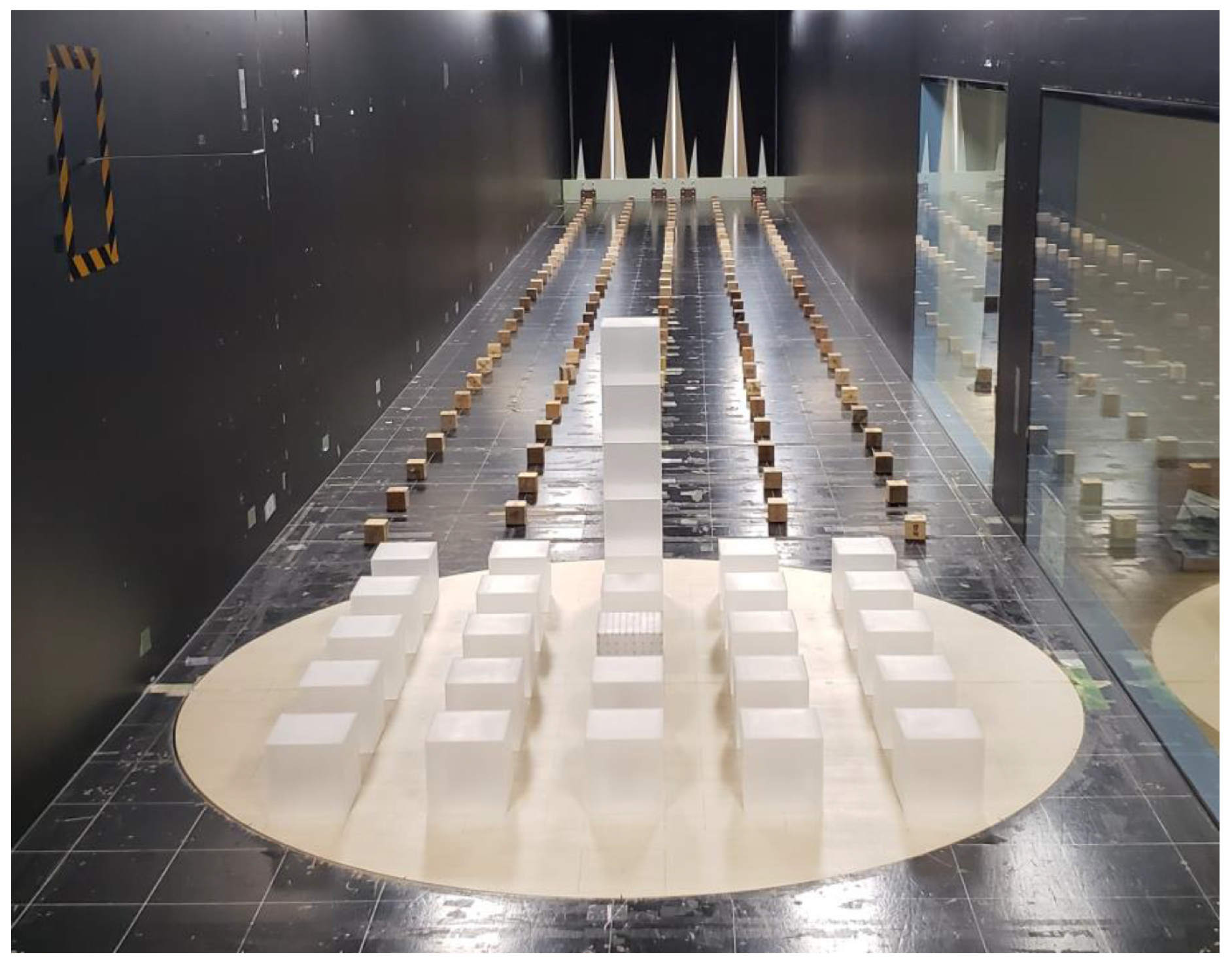
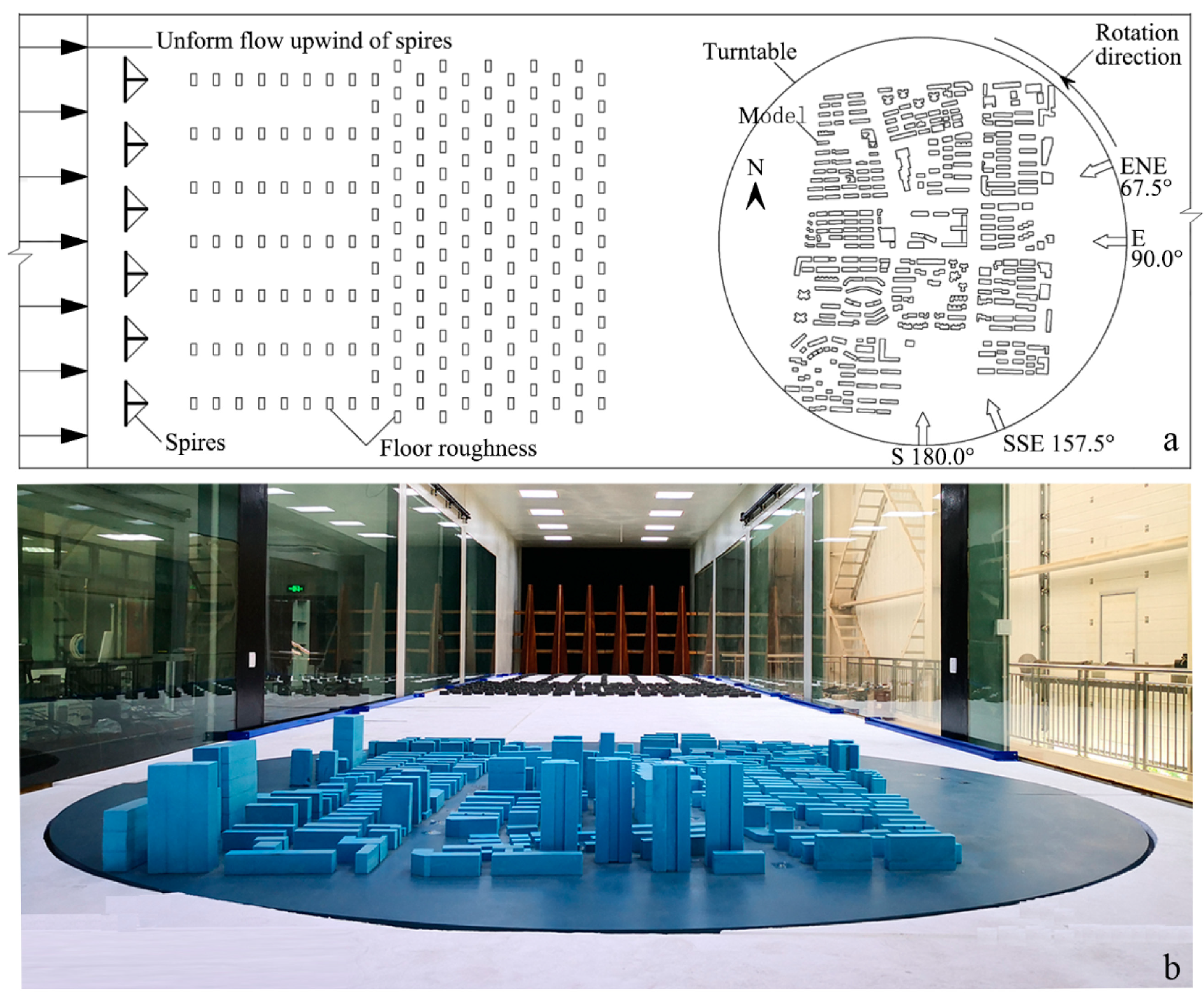
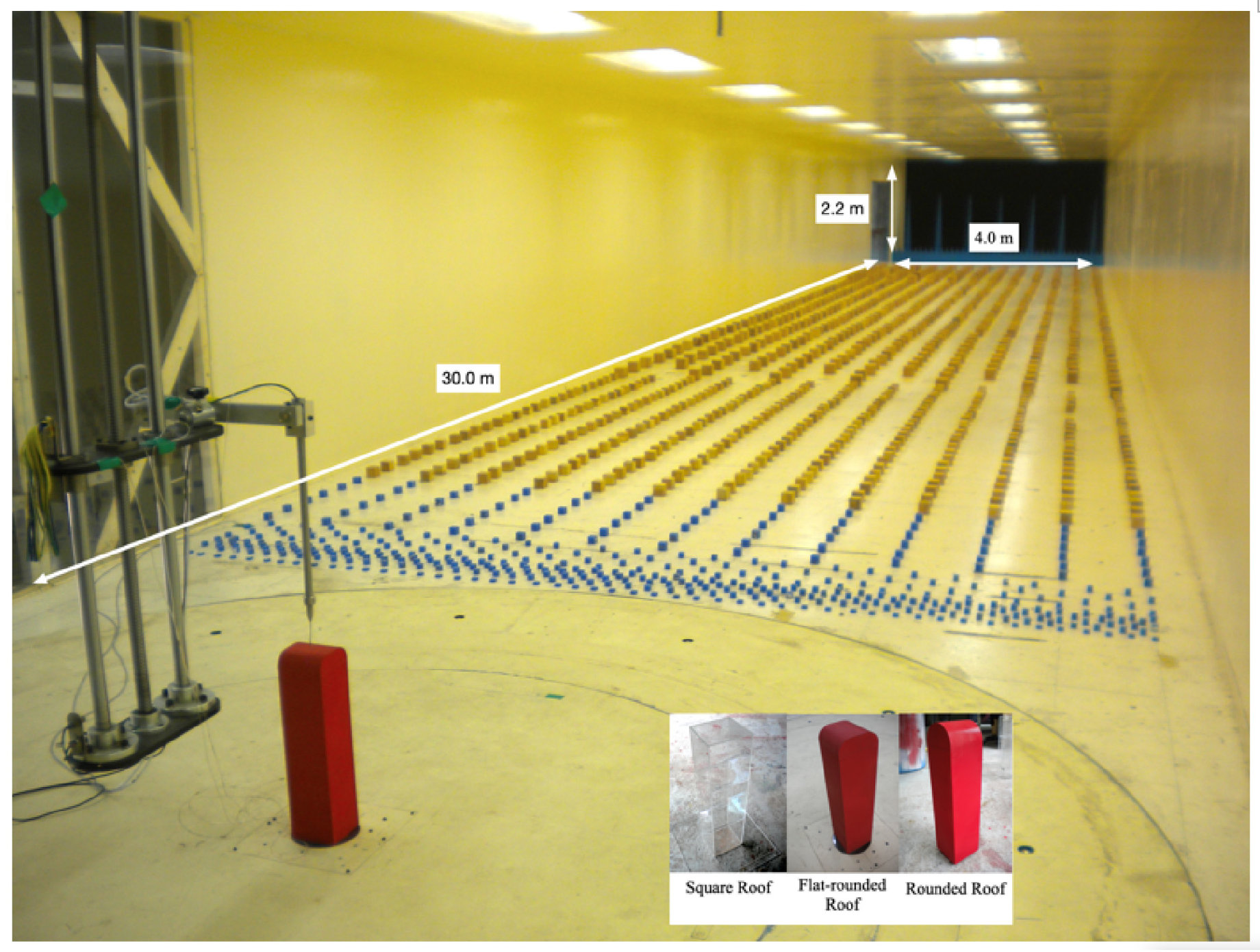
3.2. Wind Tunnel Experiments
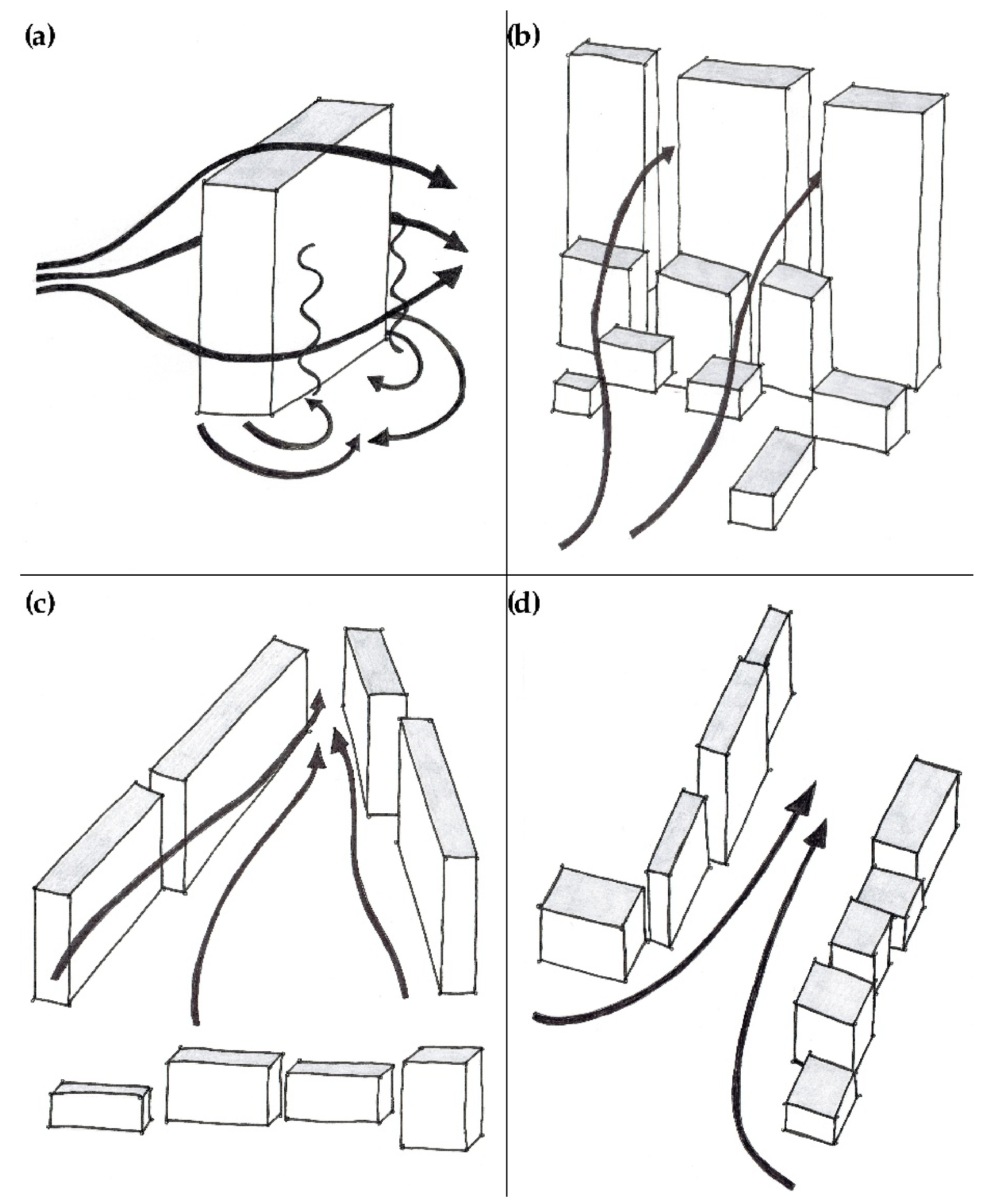
3.3. CFD in Urban Wind Resource Assessments
- -
- RANS (Reynolds-Averaged Navier–Stokes). This is the most widely used approach for urban wind simulations due to its computational efficiency. This method relies on the Reynolds decomposition to separate the flow into mean and fluctuating components, introducing unknown Reynolds stresses that are resolved using turbulence closure models, such as the k-ε, k-ω, and SST k-ω models. RANS is considered an industry standard for urban wind flow and pollution dispersion studies due to its computational efficiency. However, it has limitations, particularly in accurately representing vertical wind speed gradients and turbulence in the ABL [58,59].
- -
- LES (Large Eddy Simulation). This offers higher fidelity by resolving large-scale turbulent structures. LES is increasingly applied in detailed studies at the pedestrian level and for siting urban wind turbines, though it demands significant computational resources. LES models use low-pass filters to solve the Navier–Stokes equations by focusing on small-scale turbulent motions. LES offers a balance between accuracy and computational efficiency, producing results with higher accuracy than RANS [60,61].
- -
- -
3.4. Comparison of the Methods Discussed for Urban Wind Resource Assessment
4. Overview of Urban Wind Energy Technologies
4.1. Horizontal and Vertical-Axis Turbines
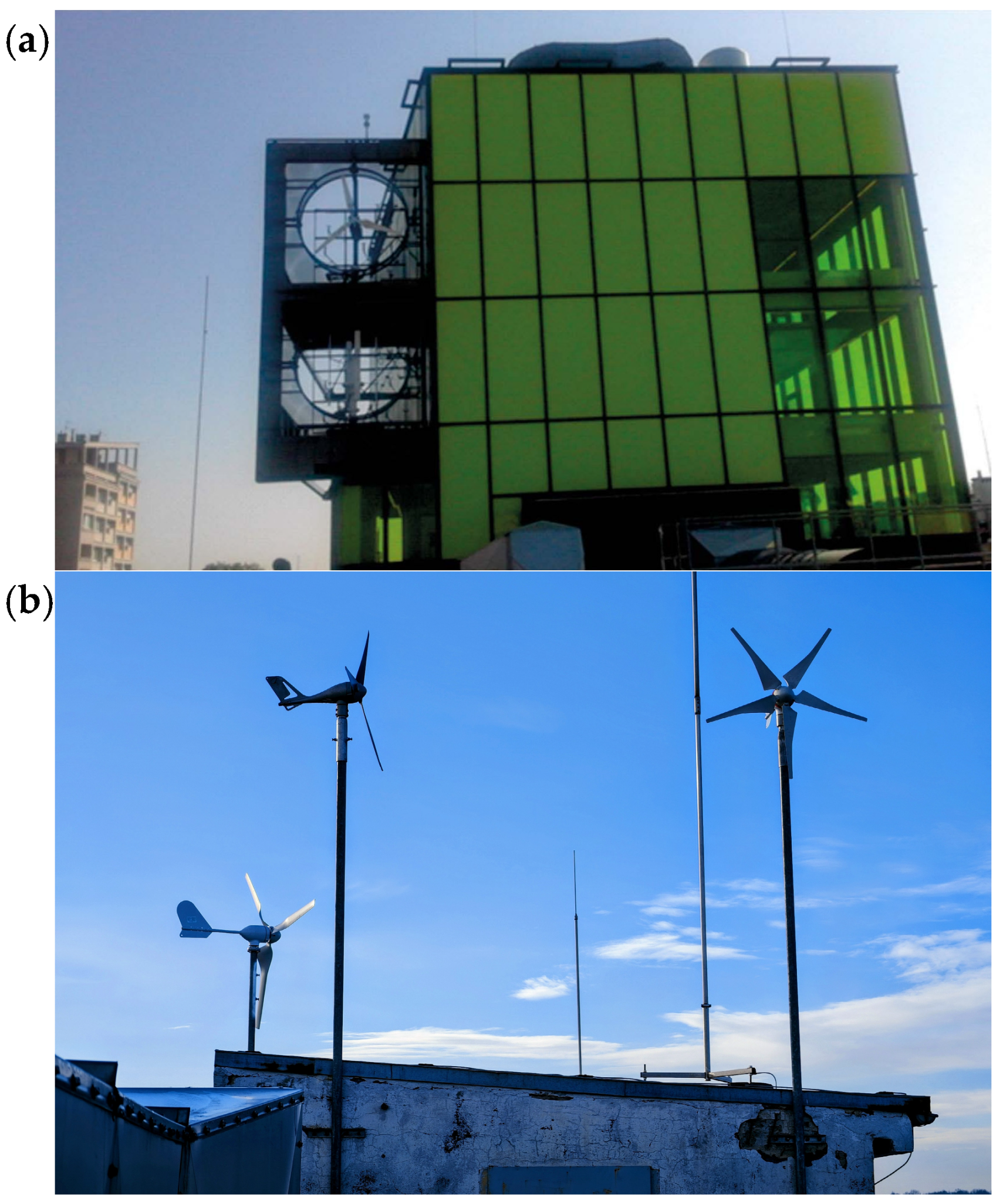
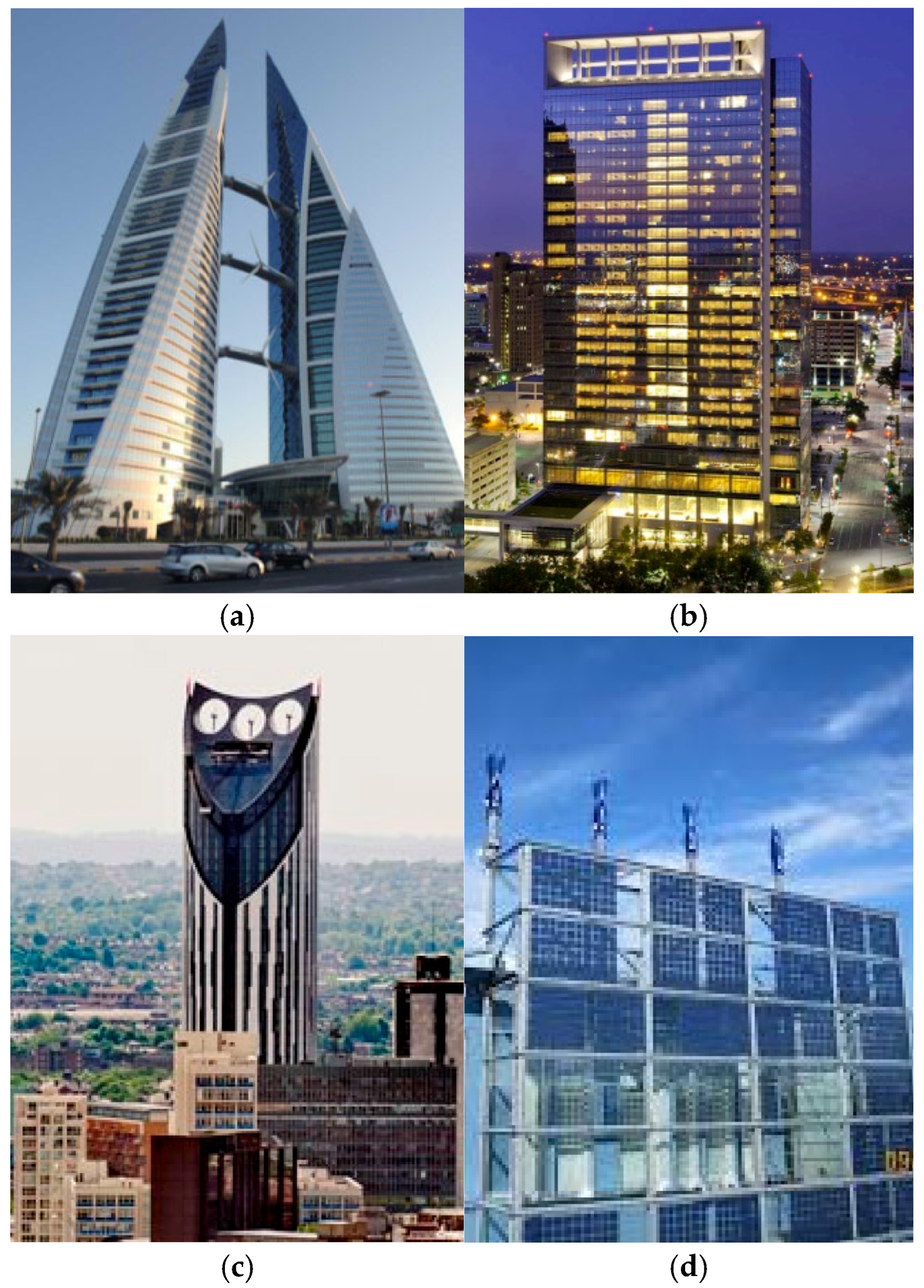
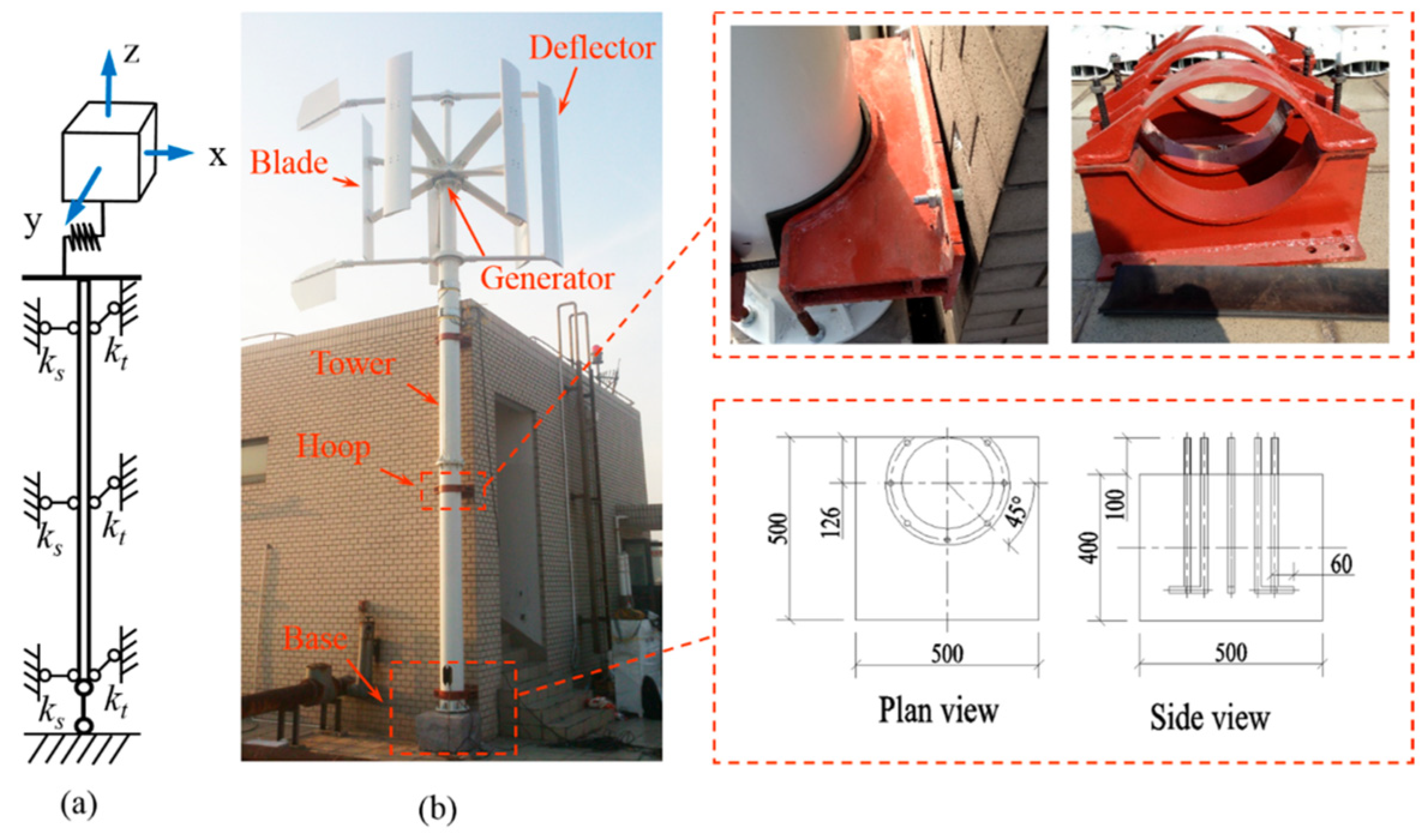
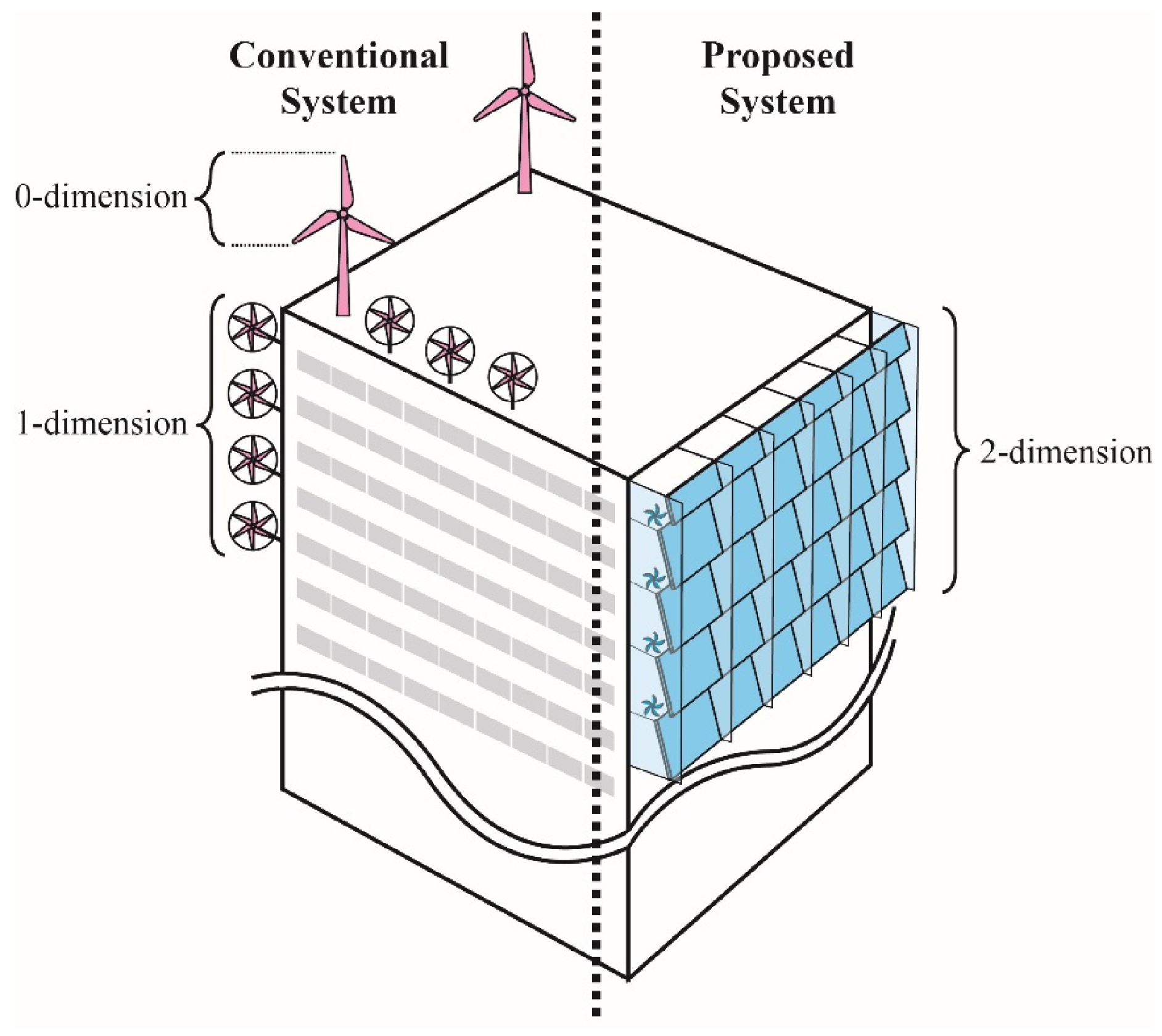
4.2. Building-Integrated Wind Turbines
- -
- Micro systems designated for use in residential buildings or smaller commercial premises with low energy requirements (power rating 0.01 to 0.4 kW).
- -
- Small systems suitable for residential buildings, schools, or smaller commercial facilities (power rating from 0.4 to 2.5 kW).
- -
- Medium systems used in taller buildings or industrial facilities with good wind orientation (power rating from 2.5 to 50 kW).
- -
- Commercial turbines suitable in megastructures with optimized aerodynamic design (from 50 kW) [88].
4.3. Integrating Urban Wind into PED Energy Systems
5. Case Studies of Urban Wind Projects
6. Future of Urban Wind in PEDs: Challenges and Opportunities
- Technical barriers and challenges
- Economic viability
- Social acceptance and safety
- Regulatory and institutional barriers
- Further optimization of urban wind turbine technology
- Implementation of IoT, Digital Twins, and AI
- Hybrid installations utilizing renewable energy resources
7. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Regan, A.C.; Nyhan, M.M. Towards Sustainable and Net-Zero Cities: A Review of Environmental Modelling and Monitoring Tools for Optimizing Emissions Reduction Strategies for Improved Air Quality in Urban Areas. Environ. Res. 2023, 231, 116242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomelli, M.; Görgün, E.K.; Salata, S.; Ronchi, S.; Bernardini, C.; Costa, M.M.; Arcidiacono, A.; Concilio, G. Climate Neutrality and Urban Planning: A State of the Art from Literature and the European Cities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2025, 130, 106570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkenbaeva, E.; Halleck Vega, S.; Hofstede, G.J.; van Leeuwen, E. Positive Energy Districts: Mainstreaming Energy Transition in Urban Areas. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 153, 111782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sessa, E.; Brunetti, A.; Ciulla, G.; Guarino, F.; Longo, S.; Cellura, M.; Dragomir, A.; Papina, C. Towards Positive Energy District Assessment: The Case Study of Bucharest. Energy 2025, 325, 136208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clerici Maestosi, P.; Salvia, M.; Pietrapertosa, F.; Romagnoli, F.; Pirro, M. Implementation of Positive Energy Districts in European Cities: A Systematic Literature Review to Identify the Effective Integration of the Concept into the Existing Energy Systems. Energies 2024, 17, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada Granja, C.; Yang, X.; Siakas, D.; Siakas, K.; Lampropoulos, G. Positive Energy District Success Factors: Learning from Global Challenges and Success Stories. Designs 2025, 9, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlowska, A.; Guarino, F.; Volpe, R.; Bisello, A.; Gabaldòn, A.; Rezaei, A.; Albert-Seifried, V.; Alpagut, B.; Vandevyvere, H.; Reda, F.; et al. Positive Energy Districts: Fundamentals, Assessment Methodologies, Modeling and Research Gaps. Energies 2024, 17, 4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terés-Zubiaga, J.; Bolliger, R.; Almeida, M.G.; Barbosa, R.; Rose, J.; Thomsen, K.E.; Montero, E.; Briones-Llorente, R. Cost-Effective Building Renovation at District Level Combining Energy Efficiency & Renewables—Methodology Assessment Proposed in IEA EBC Annex 75 and a Demonstration Case Study. Energy Build. 2020, 224, 110280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salite, D.; Miao, Y.; Turner, E. A Comparative Analysis of Policies and Strategies Supporting District Heating Expansion and Decarbonisation in Denmark, Sweden, the Netherlands and the United Kingdom—Lessons for Slow Adopters of District Heating. Environ. Sci. Policy 2024, 161, 103897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sornek, K.; Homa, M.; Frigura-Iliasa, F.M.; Frigura-Iliasa, M.; Jankowski, M.; Papis-Frączek, K.; Katerla, J.; Janus, J. Power-to-Heat and Seasonal Thermal Energy Storage: Pathways Toward a Low-Carbon Future for District Heating. Energies 2025, 18, 5577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, S.; Pallonetto, F.; De Donatis, L.; De Rosa, M. District Energy Modelling for Decarbonisation Strategies Development—The Case of a University Campus. Energy Rep. 2024, 11, 1256–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghamolaei, R.; Shamsi, M.H.; Tahsildoost, M.; O’Donnell, J. Review of District-Scale Energy Performance Analysis: Outlooks towards Holistic Urban Frameworks. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 41, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeuerle, Y.I.; Arpagaus, C.; Haller, M.Y. A Review of Seasonal Energy Storage for Net-Zero Industrial Heat: Thermal and Power-to-X Storage Including the Novel Concept of Renewable Metal Energy Carriers. Energies 2025, 18, 2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, J.; Leal, V.; Azevedo, I.; Silva, M.C. Designing Carbon Neutral, Net-Zero, Nearly-Zero and Positive Energy Districts or Neighbourhoods: Current Approaches and Solutions. Adv. Build. Energy Res. 2024, 18, 602–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaeiha, A.; Montazeri, H.; Blocken, B. A Framework for Preliminary Large-Scale Urban Wind Energy Potential Assessment: Roof-Mounted Wind Turbines. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 214, 112770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Ge, M.; Tan, W.; Li, Q. Impacts of Coexisting Buildings and Trees on the Performance of Rooftop Wind Turbines: An Idealized Numerical Study. Renew. Energy 2021, 177, 164–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Jung, H.J.; Lee, S.W.; Park, J. A New Building-Integrated Wind Turbine System Utilizing the Building. Energies 2015, 8, 11846–11870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palusci, O.; Cecere, C. Urban Ventilation in the Compact City: A Critical Review and a Multidisciplinary Methodology for Improving Sustainability and Resilience in Urban Areas. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Jeong, S.; Park, H.; Kim, J.; Park, C.R. Urbanization Has Stronger Impacts than Regional Climate Change on Wind Stilling: A Lesson from South Korea. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 054016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palusci, O.; Monti, P.; Cecere, C.; Montazeri, H.; Blocken, B. Impact of Morphological Parameters on Urban Ventilation in Compact Cities: The Case of the Tuscolano-Don Bosco District in Rome. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsichritzis, L.; Nikolopoulou, M. The Effect of Building Height and Façade Area Ratio on Pedestrian Wind Comfort of London. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2019, 191, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnfield, A.J. Two Decades of Urban Climate Research: A Review of Turbulence, Exchanges of Energy and Water, and the Urban Heat Island. Int. J. Climatol. 2003, 23, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, E.; Yuan, C.; Chen, L.; Ren, C.; Fung, J.C.H. Improving the Wind Environment in High-Density Cities by Understanding Urban Morphology and Surface Roughness: A Study in Hong Kong. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 101, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadatjoo, P.; Moradi, H.; Hamdan, N.; Farouq, M.M.; Mirzaei, P.A. On the oversimplification of neighborhood impact in urban microclimate and building energy models. Building and Environment 2025, 283, 113301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toja-Silva, F.; Lopez-Garcia, O.; Peralta, C.; Navarro, J.; Cruz, I. An Empirical–Heuristic Optimization of the Building-Roof Geometry for Urban Wind Energy Exploitation on High-Rise Buildings. Appl. Energy 2016, 164, 769–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagubień, A.; Wolniewicz, K. Energy Efficiency of Small Wind Turbines in an Urbanized Area—Case Studies. Energies 2022, 15, 5287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sornek, K.; Filipowicz, M.; Goryl, W.; Mokrzycki, E.; Mirowski, T.; Duraczyński, M. The Analysis of the Wind Potential in Selected Locations in the Southeastern Poland. E3S Web Conf. 2017, 14, 01014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prudden, S.; Fisher, A.; Marino, M.; Mohamed, A.; Watkins, S.; Wild, G. Measuring Wind with Small Unmanned Aircraft Systems. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2018, 176, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stathopoulos, T.; Alrawashdeh, H.; Al-Quraan, A.; Blocken, B.; Dilimulati, A.; Paraschivoiu, M.; Pilay, P. Urban Wind Energy: Some Views on Potential and Challenges. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2018, 179, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vranešević, K.K.; Vita, G.; Bordas, S.P.A.; Glumac, A.Š. Furthering Knowledge on the Flow Pattern around High-Rise Buildings: LES Investigation of the Wind Energy Potential. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2022, 226, 105029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boikos, C.; Ioannidis, G.; Rapkos, N.; Tsegas, G.; Katsis, P.; Ntziachristos, L. Estimating Daily Road Traffic Pollution in Hong Kong Using CFD Modelling: Validation and Application. Build. Environ. 2025, 267, 112168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadhyar, A.; Sridhar, S.; Reshma, T.; Radhakrishnan, J. A Critical Assessment of the Factors Associated with the Implementation of Rooftop VAWTs: A Review. Energy Convers. Manag. X 2024, 22, 100563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.S.; Yigitcanlar, T.; Guaralda, M.; Degirmenci, K.; Liu, A. Spatial Modelling of Urban Wind Characteristics: Review of Contributions to Sustainable Urban Development. Buildings 2024, 14, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reja, R.K.; Amin, R.; Tasneem, Z.; Ali, M.F.; Islam, M.R.; Saha, D.K.; Badal, F.R.; Ahamed, M.H.; Moyeen, S.I.; Das, S.K. A Review of the Evaluation of Urban Wind Resources: Challenges and Perspectives. Energy Build. 2022, 257, 111781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, D.; Pétursson, J.G. The Role of GIS Mapping in Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis in Informing the Location and Design of Renewable Energy Projects—A Systematic Review. Energy Strategy Rev. 2025, 59, 101765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalhaf, A.S.; Elboshy, B.; Kotb, K.M.; Han, Y.; Almaliki, A.H.; Aly, R.M.H.; Elkadeem, M.R.A.; Sohani, A.; Zalhaf, A.S.; Elboshy, B.; et al. A High-Resolution Wind Farms Suitability Mapping Using GIS and Fuzzy AHP Approach: A National-Level Case Study in Sudan. Sustainability 2021, 14, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; M’Ikiugu, M.M.; Kinoshita, I.; Luo, Y. GIS-Based Approach for Municipal Renewable Energy Planning to Support Post-Earthquake Revitalization: A Japanese Case Study. Sustainability 2016, 8, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, S.S. Determining Wind Energy Potential Using Geographic Information System Functions: A Case Study in Balıkesir, Turkey. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.S.; Nichol, J.E.; Ng, E.Y.Y.; Guilbert, E.; Kwok, K.H.; To, P.H.; Wang, J.Z. GIS Techniques for Mapping Urban Ventilation, Using Frontal Area Index and Least Cost Path Analysis. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2010, 38, 586–591. [Google Scholar]
- Rüstemli, S.; Güntas, O.; Şahin, G.; Koç, A.; van Sark, W.; Doğan, S.Ş. Wind Power Plant Site Selection Problem Solution Using GIS and Resource Assessment and Analysis of Wind Energy Potential by Estimating Weibull Distribution Function for Sustainable Energy Production: The Case of Bitlis/Turkey. Energy Strategy Rev. 2024, 56, 101552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Lozano, J.M.; García-Cascales, M.S.; Lamata, M.T. Identification and Selection of Potential Sites for Onshore Wind Farms Development in Region of Murcia, Spain. Energy 2014, 73, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Cuevas, P.; Biberacher, M.; Domínguez-Bravo, J.; Schardinger, I. Developing a Wind Energy Potential Map on a Regional Scale Using GIS and Multi-Criteria Decision Methods: The Case of Cadiz (South of Spain). Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2018, 20, 1167–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentis, D.; Hermann, S.; Howells, M.; Welsch, M.; Siyal, S.H. Assessing the Technical Wind Energy Potential in Africa a GIS-Based Approach. Renew. Energy 2015, 83, 110–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodakarami, L.; Dara Khalid, K.; Jafar Abdullah, A.; Jehan Mahmmod, R.; Frya Rebwar, A.; Aya Bakhtyar, S.; Zulfa Jalil, K. Innovative GIS and Remote Sensing Approaches for Revealing Hidden Wind Energy Hotspots and Optimizing Wind Farm Siting. Int. J. Energy Res. 2025, 2025, 5580703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Jiang, C.; Wang, L.; Liu, J. Wind Tunnel Study on Influences of Morphological Parameters on Drag Coefficient of Horizontal Non-Uniform Buildings. Build. Environ. 2022, 207, 108412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, A.; Sharma, R. Wind-tunnel analysis of turbulent flow in cross-ventilated buildings with windcatchers: Impact of surrounding buildings. Building and Environment 2023, 244, 110826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, H.; Sharma, A.; Gairola, A. A Review on the Study of Urban Wind at the Pedestrian Level around Buildings. J. Build. Eng. 2018, 18, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.G.; Yan, J.H.; Li, Y.; Xiao, C.X.; Ma, J.X. Wind Tunnel Study of Wind Effects on 90° Helical and Square Tall Buildings: A Comparative Study. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 42, 103068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Cen, F.; Nie, B.; Fan, L.; Sun, H. Similarity Criteria and Simulation Method for Flight Control System of Free-Flight Test in Low Speed Wind Tunnel. Kongqi Donglixue Xuebao Acta Aerodyn. Sin. 2017, 35, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Peng, Y.; Ji, H.; Hu, Y.; Ding, W. A Wind Tunnel Study on the Correlation between Urban Space Quantification and Pedestrian–Level Ventilation. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, A.; Burlando, M.; Freda, A.; Repetto, M.P. Wind Tunnel Measurements of the Urban Boundary Layer Development over a Historical District in Italy. Build. Environ. 2017, 111, 192–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, A.S.; Armengol Barcos, G.; Porté-Agel, F. An Experimental Investigation of a Roof-Mounted Horizontal-Axis Wind Turbine in an Idealized Urban Environment. Renew. Energy 2022, 193, 1049–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michálek, P.; Zacho, D. Wind Tunnel Measurement of Flow and Dispersion over Urban Area. EPJ Web Conf. 2017, 143, 02074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, Y.; Yoshida, A.; Kamata, S.; Yamane, Y.; Mochida, A. Wind Tunnel Experiments on Interference Effects of a High-Rise Building on the Surrounding Low-Rise Buildings in an Urban Block. Wind 2023, 3, 97–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemida, H.; Glumac, A.Š.; Vita, G.; Vranešević, K.K.; Höffer, R. On the Flow over High-Rise Building for Wind Energy Harvesting: An Experimental Investigation of Wind Speed and Surface Pressure. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, D.P.; Cho, K.P. Performance Comparison of Different Building Shapes Using a Wind Tunnel and a Computational Model. Buildings 2022, 12, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczerba, Z.; Szczerba, P.; Szczerba, K.; Szumski, M.; Pytel, K. Wind Tunnel Experimental Study on the Efficiency of Vertical-Axis Wind Turbines via Analysis of Blade Pitch Angle Influence. Energies 2023, 16, 4903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.J.; Baik, J.J. A Numerical Study of the Effects of Ambient Wind Direction on Flow and Dispersion in Urban Street Canyons Using the RNG k–ε Turbulence Model. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 3039–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, R.; Ferrarotti, M.; Sánchez, C.G.; Derudi, M.; Parente, A. Advanced Turbulence Models and Boundary Conditions for Flows around Different Configurations of Ground-Mounted Buildings. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2017, 167, 160–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoll, R.; Gibbs, J.A.; Salesky, S.T.; Anderson, W.; Calaf, M. Large-Eddy Simulation of the Atmospheric Boundary Layer. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2020, 177, 541–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronemeier, T.; Surm, K.; Harms, F.; Leitl, B.; Maronga, B.; Raasch, S. Evaluation of the Dynamic Core of the PALM Model System 6.0 in a Neutrally Stratified Urban Environment: Comparison between Les and Wind-Tunnel Experiments. Geosci. Model. Dev. 2021, 14, 3317–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, S. A Review of Hybrid RANS-LES Methods for Turbulent Flows: Concepts and Applications. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2020, 114, 100597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Hu, R.; Wang, H.; Xu, K.; Tian, S. Delayed Detached-Eddy Simulations of Aerodynamic Variability During Carrier-Based Aircraft Landing with a Domain Precursor Inflow Method. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piroozmand, P.; Mussetti, G.; Allegrini, J.; Mohammadi, M.H.; Akrami, E.; Carmeliet, J. Coupled CFD Framework with Mesoscale Urban Climate Model: Application to Microscale Urban Flows with Weak Synoptic Forcing. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2020, 197, 104059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felipe, J.; Berrio, R.; Andres, F.; Usuga, C.; Correa, M.A.; Cortes, F.R.; Saldarriaga, J.C.; Co, J.C.S. Comparative CFD Analysis Using RANS and LES Models for NOx Dispersion in Urban Streets with Active Public Interventions in Medellín, Colombia. Sustainability 2025, 17, 6872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Pan, W.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, X.; Long, Z.; Chen, Q. CFD Simulations of Wind Distribution in an Urban Community with a Full-Scale Geometrical Model. Build. Environ. 2017, 117, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Kwok, K.C.S.; Liu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Dong, K.; Wang, B. A CFD Study of Wind Assessment in Urban Topology with Complex Wind Flow. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 71, 103006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, Y. CFD Prediction for Wind Power Generation by a Small Vertical Axis Wind Turbine: A Case Study for a University Campus. Energies 2023, 16, 4912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, Y.H.; Rezaeiha, A.; Montazeri, H.; Blocken, B.; Wen, C.Y.; Yang, A.S. CFD Assessment of Wind Energy Potential for Generic High-Rise Buildings in Close Proximity: Impact of Building Arrangement and Height. Appl. Energy 2022, 321, 119328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabrizi, A.B.; Whale, J.; Lyons, T.; Urmee, T. Performance and Safety of Rooftop Wind Turbines: Use of CFD to Gain Insight into Inflow Conditions. Renew. Energy 2014, 67, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; You, W.; Ding, W. Evaluation of the CFD Simulation Method for Wind Prediction in Complex Urban Spatial Forms. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 22, 11319–11344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann-Stanzer, K.; Stenzel, S.; Rau, G.; Piringer, M.; Feichtinger, F.; Costabloz, T. Monitoring and Modeling Roof-Level Wind Speed in a Changing City. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Jiang, Q.; Zhao, Y. Integrating CFD and GIS into the Development of Urban Ventilation Corridors: A Case Study in Changchun City, China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, M.; Hosseini, J.; Yang, M.; Wang, S.; Aliabadi, A.A.; Li, Q.; Mortezazadeh, M.; Zou, J.; Hosseini, M.; Yang, S.; et al. Estimating Urban Wind Speeds and Wind Power Potentials Based on Machine Learning with City Fast Fluid Dynamics Training Data. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, T.; Estanqueiro, A. A New Methodology for Urban Wind Resource Assessment. Renew. Energy 2016, 89, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Mak, C.M.; Cai, C.; Fu, Y.; Tse, K.T.; Niu, J. Wind Tunnel Measurement of Pedestrian-Level Gust Wind Flow and Comfort around Irregular Lift-up Buildings within Simplified Urban Arrays. Build. Environ. 2024, 256, 111487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Lin, C.; Wang, X.; Kikumoto, H. Wind Tunnel Experiment on the Footprint of a Block-Arrayed Urban Model in a Neutrally Stratified Boundary Layer. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2024, 190, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toparlar, Y.; Blocken, B.; Maiheu, B.; van Heijst, G.J.F. A Review on the CFD Analysis of Urban Microclimate. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 80, 1613–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Gutiérrez, A.; Gonzalo, J.; López, D.; Delgado, A. Advances in CFD Modeling of Urban Wind Applied to Aerial Mobility. Fluids 2022, 7, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishugah, T.F.; Li, Y.; Wang, R.Z.; Kiplagat, J.K. Advances in Wind Energy Resource Exploitation in Urban Environment: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 37, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, S.; Bernhoff, H.; Leijon, M. Evaluation of Different Turbine Concepts for Wind Power. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2008, 12, 1419–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doerffer, P.; Doerffer, K.; Ochrymiuk, T.; Telega, J. Variable Size Twin-Rotor Wind Turbine. Energies 2019, 12, 2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hand, B.; Cashman, A. A Review on the Historical Development of the Lift-Type Vertical Axis Wind Turbine: From Onshore to Offshore Floating Application. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2020, 38, 100646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Lian, S.; Yan, H. Aerodynamic Performance Analysis of Adaptive Drag-Lift Hybrid Type Vertical Axis Wind Turbine. Energies 2022, 15, 5600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Song, C.; Qian, Z.; Wu, A.; Zhu, Y.; Xia, J.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Chen, X.; Yuan, Y.; et al. Improvement of Modified Rotor on Aerodynamic Performance of Hybrid Vertical Axis Wind Turbine. Energies 2025, 18, 3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Shahzad, A.; Akram, F.; Ahmad, F.; Shah, S.I.A. Design Optimization of Double-Darrieus Hybrid Vertical Axis Wind Turbine. Ocean Eng. 2022, 254, 111171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micallef, D.; Van Bussel, G. A Review of Urban Wind Energy Research: Aerodynamics and Other Challenges. Energies 2018, 11, 2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bošnjaković, M.; Veljić, N.; Hradovi, I. Perspectives of Building-Integrated Wind Turbines (BIWTs). Smart Cities 2025, 8, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloess, A.; Schill, W.P.; Zerrahn, A. Power-to-Heat for Renewable Energy Integration: A Review of Technologies, Modeling Approaches, and Flexibility Potentials. Appl. Energy 2018, 212, 1611–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, M.; Muschik, S.; Ehrenwirth, M.; Trinkl, C.; Schrag, T. Sector Coupling Potential of a District Heating Network by Consideration of Residual Load and CO2 Emissions. Energies 2022, 15, 6281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobrova, D. Building-Integrated Wind Turbines in the Aspect of Architectural Shaping. Procedia Eng. 2015, 117, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.F.; Killa, S. Bahrain World Trade Center (BWTC): The First Large-Scale Integration of Wind Turbines in a Building. Struct. Des. Tall Spec. Build. 2007, 16, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-G.; Jeon, W.-H.; Kim, D.-H.; Hasager, C.B.; Peña, A.; Li, X.; Thenkabail, P.S. Wind Resource Assessment for High-Rise BIWT Using RS-NWP-CFD. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kodmany, K. Sustainability and the 21st Century Vertical City: A Review of Design Approaches of Tall Buildings. Buildings 2018, 8, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żołądek, M.; Goryl, W.; Sornek, K.; Augustyn, A. Analiza Wybranych Parametrów Pracy Turbiny Wiatrowej Zintegrowanej z Budynkiem w Zróżnicowanych Warunkach Pogodowych Na Przykładzie Centrum Energetyki AGH. Sci. Noteb. Inst. Manag. Miner. Resour. Energy Pol. Acad. Sci. 2018, 102, 101–110. [Google Scholar]
- Filipowicz, M.; Goryl, W.; Zołądek, M. Study of Building Integrated Wind Turbines Operation on the Example of Center of Energy AGH. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 214, 012122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, W.; Dai, K.; Yuan, M.; Chen, S.E. Dynamic Study of a Rooftop Vertical Axis Wind Turbine Tower Based on an Automated Vibration Data Processing Algorithm. Energies 2018, 11, 3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Dutch Windwheel. Available online: https://dutchwindwheel.com/en/index (accessed on 30 September 2025).
- Saleh, S.; Durak, M.; Turhan, C. Enhancing Urban Sustainability with Novel Vertical-Axis Wind Turbines: A Study on Residential Buildings in Çeşme. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasniqi, G.; Dimitrieska, C.; Lajqi, S. Wind Energy Potential in Urban Area: Case Study Prishtina. Int. J. Technol. 2022, 13, 458–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Qiu, Y.; Hu, H.; Xu, Z.; Wang, X. An Interdisciplinary Review of the Wind-Powered Building Skin. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 95, 110324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejo Díaz, A.; Herrera Moya, I.; Pereyra Mariñez, C.; Garabitos Lara, E.; Casilla Victorino, C. Key Factors Influencing Urban Wind Energy: A Case Study from the Dominican Republic. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2023, 73, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzen, E.; Rossis, K.; Stefanatos, N. The Energy Crisis as a Challenge of Small Scale Wind Energy in Urban Areas-The Case of Greece. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2023, 1196, 012004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelsalam, A.M.; Abdelmordy, M.; Ibrahim, K.A.; Sakr, I.M. An Investigation on Flow Behavior and Performance of a Wind Turbine Integrated within a Building Tunnel. Energy 2023, 280, 128153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deltenre, Q.; De Troyer, T.; Runacres, M.C. Techno-Economic Comparison of Rooftop-Mounted PVs and Small Wind Turbines: A Case Study for Brussels. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2019, 13, 3142–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereziartua-Gonzalez, L.; Retegi, A.; Ukar, O. Human-Centered Integration of Small Wind Turbines in Urban Environments: A Semi-Systematic Review from an Industrial Design Perspective. Front. Sustain. Cities 2025, 7, 1561894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Q.; Honda, T.; El Ferik, S.; Shaukat, M.M.; Yang, M.C. Understanding the Role of Visual Appeal in Consumer Preference for Residential Solar Panels. Renew. Energy 2017, 113, 1569–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.S.; Yigitcanlar, T.; Guaralda, M.; Degirmenci, K.; Liu, A.; Kane, M. Leveraging the Opportunities of Wind for Cities through Urban Planning and Design: A PRISMA Review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehly, T.; Duffy, P.; Mulas Hernando, D. Cost of Wind Energy Review: 2024 Edition; Technical Report No. 627281636; National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL): Golden, CO, USA, 2024. Available online: https://research-hub.nrel.gov/en/publications/cost-of-wind-energy-review-2024-edition/ (accessed on 30 September 2025).
- Wojtaszek, H.; Borowski, P.F.; Handschke, M.; Miciuła, I.; Stecyk, A.; Bielawa, A.; Ozdyk, S.; Kowalczyk, A.; Czepło, F. Wind Energy in Transition: Development, Socio-Economic Impacts, and Policy Challenges in Europe. Energies 2025, 18, 2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorsand, I.; Kormos, C.; Macdonald, E.G.; Crawford, C. Wind Energy in the City: An Interurban Comparison of Social Acceptance of Wind Energy Projects. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2015, 8, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olczak, P.; Kopacz, M. Operating Parameters and Charging/Discharging Strategies for Wind Turbine Energy Storage Due to Economic Benefits. Energies 2025, 18, 4426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komorowska, A.; Benalcazar, P.; Kamiński, J. Evaluating the Competitiveness and Uncertainty of Offshore Wind-to-Hydrogen Production: A Case Study of Poland. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 14577–14590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowski, M.; Pałac, A.; Sornek, K.; Goryl, W.; Żołądek, M.; Homa, M.; Filipowicz, M. Status and Development Perspectives of the Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES) Technologies—A Literature Review. Energies 2024, 17, 2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homa, M.; Sornek, K.; Goryl, W.; Papis-Frączek, K.; Żak, P.L.; Dańko, R. Numerical Analysis of the Prototype of the High-Temperature Thermal Energy Storage Based on Sand Bed. Energy 2025, 333, 137472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajzendanc, P.; Kreischer, C. A Review of New Technologies in the Design and Application of Wind Turbine Generators. Energies 2025, 18, 4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, W.T.; Poh, S.C.; Fazlizan, A.; Pan, K.C. Vertical Axis Wind Turbine with Omni-Directional-Guide-Vane for Urban High-Rise Buildings. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. (Engl. Ed.) 2012, 19, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xiong, B.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Azam, A. Small Wind Turbines and Their Potential for Internet of Things Applications. iScience 2023, 26, 107674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.; Rassõlkin, A.; Vaimann, T.; Kallaste, A.; Zakis, J.; Hyunh, V.K.; Pomarnacki, R. Digital Twin as a Virtual Sensor for Wind Turbine Applications. Energies 2023, 16, 6246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, S.; Stathopoulos, T. Application of Artificial Intelligence to Urban Wind Energy. Build. Environ. 2021, 197, 107848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, Q.; Algburi, S.; Sameen, A.Z.; Salman, H.M.; Jaszczur, M. A Review of Hybrid Renewable Energy Systems: Solar and Wind-Powered Solutions: Challenges, Opportunities, and Policy Implications. Results Eng. 2023, 20, 101621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawan, S.M.; Abidin, W.A.W.Z.; Lawan, S.M.; Abidin, W.A.W.Z. A Review of Hybrid Renewable Energy Systems Based on Wind and Solar Energy: Modeling, Design and Optimization. In Wind Solar Hybrid Renewable Energy System; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




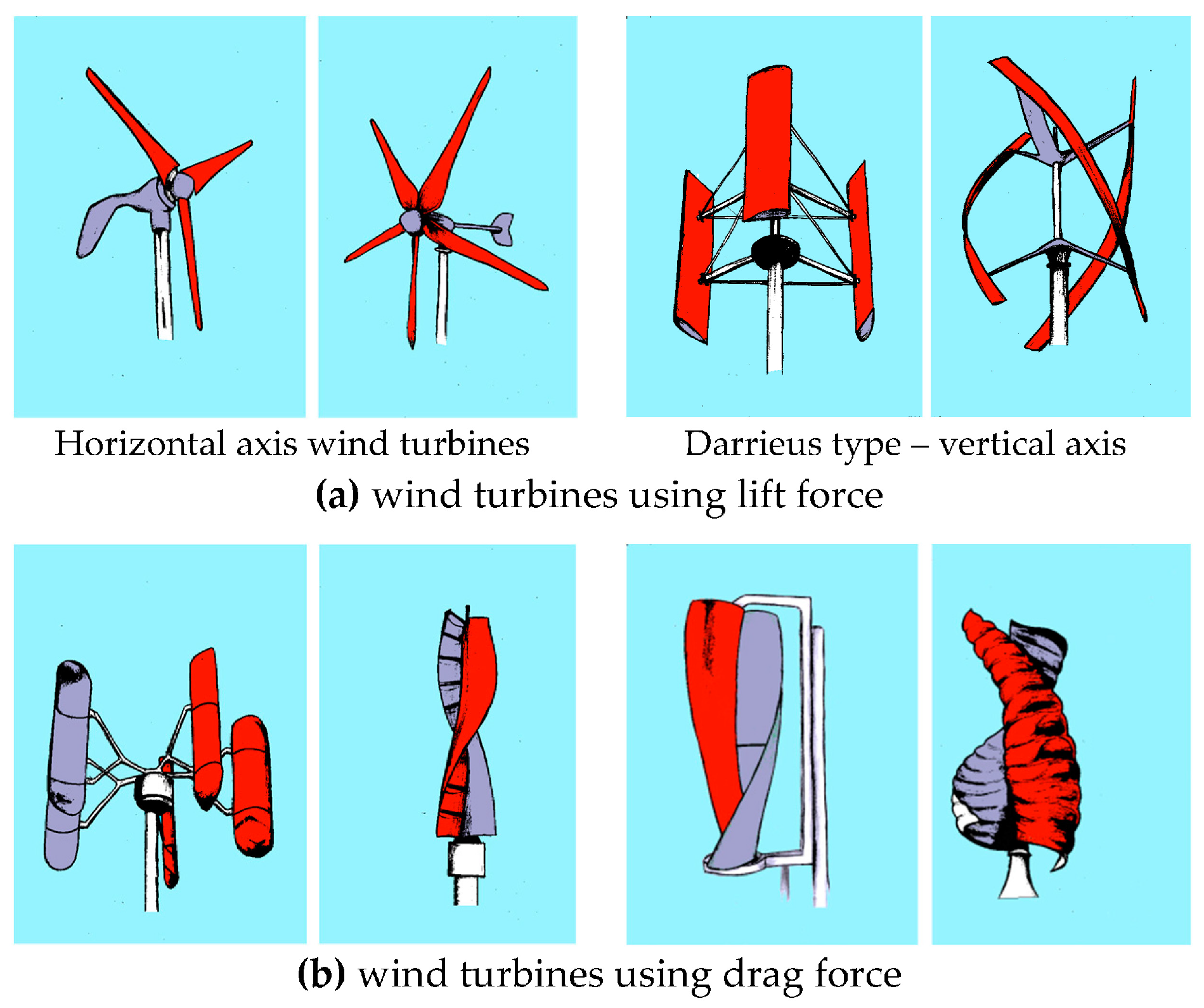



| Method | Strengths | Limitations | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| GIS-based mapping |
|
| [33,34,35] |
| Wind tunnel experiments |
|
| [76,77] |
| CFD assessment |
|
| [78,79] |
| Parameter | H-Rotor Wind Turbine | Darrieus Turbine | HAWT |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blade profile | Simple | Complicated | Complicated |
| Blade area | Moderate | Large | Small |
| Blade load | Moderate | Low | High |
| Yaw mechanism | No | No | Required |
| Tower | Yes | No | Yes |
| Noise | Low | Moderate | High |
| Generator position | On ground | On ground | On top of tower |
| Self-starting | No | No | Yes |
| Foundation | Moderate | Simple | Expensive |
| Overall structure | Simple | Simple | Complex |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sornek, K.; Herzyk, A.; Homa, M.; Frigura-Iliasa, F.M.; Frigura-Iliasa, M. Urban Wind as a Pathway to Positive Energy Districts. Energies 2025, 18, 5897. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18225897
Sornek K, Herzyk A, Homa M, Frigura-Iliasa FM, Frigura-Iliasa M. Urban Wind as a Pathway to Positive Energy Districts. Energies. 2025; 18(22):5897. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18225897
Chicago/Turabian StyleSornek, Krzysztof, Anna Herzyk, Maksymilian Homa, Flaviu Mihai Frigura-Iliasa, and Mihaela Frigura-Iliasa. 2025. "Urban Wind as a Pathway to Positive Energy Districts" Energies 18, no. 22: 5897. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18225897
APA StyleSornek, K., Herzyk, A., Homa, M., Frigura-Iliasa, F. M., & Frigura-Iliasa, M. (2025). Urban Wind as a Pathway to Positive Energy Districts. Energies, 18(22), 5897. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18225897









