Abstract
Climate change is fuelled by the continued growth of global carbon emissions, with the widespread use of fossil fuels being the main driver. To achieve a decarbonisation transition of the energy mix, the development of clean and renewable fuels has become crucial. Ammonia is seen as an important option for decarbonisation in the transport and energy sectors due to its zero-carbon emission potential and renewable energy compatibility. However, the high energy consumption and carbon emissions of the conventional Haber–Bosch method limit its sustainability. A green ammonia synthesis system was designed using ECLIPSE and Excel simulations in the study. Results show that at a recirculation ratio of 70%, the system’s annual total energy consumption is 426.22 GWh, with annual ammonia production reaching 8342.78 t. The optimal system configuration comprises seven 12 MW offshore wind turbines, integrated with a 460 MWh lithium battery and 240 t of hydrogen storage capacity. At this configuration, the LCOE is approximately £5956.58/t. It shows that incorporating renewable energy can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions, but further optimisation of energy storage configurations and reaction conditions is needed to lower costs. This research provides a reference for the industrial application of green ammonia in the transportation sector.
1. Introduction
With accelerated industrialisation and expanding urbanisation since the 20th century, global carbon emission levels have risen significantly, with far-reaching impacts on the climate system. According to the Global Climate Conditions 2023 report published by the World Meteorological Organisation (WMO), 2023 became the hottest year on record, with the global near-surface mean temperature rising by 1.45 °C (uncertainty ±0.12 °C) from the pre-industrial (1850–1900) baseline, a value close to the 1.5 °C warming threshold set by the Paris Agreement [1]. This trend is closely linked to the continued increase in concentrations of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane. In particular, CO2 concentrations have risen by approximately 50% compared to pre-industrial levels [1], further contributing to the rise in global temperatures.
The increase in carbon dioxide emissions is mainly due to the widespread use of fossil fuels, especially in the combustion process in the energy consumption sector. According to data from the International Energy Agency (IEA), global energy-related CO2 emissions reached 3.68 billion tonnes in 2022, with fossil fuels such as coal, oil and natural gas contributing more than 80% of global CO2 emissions [2]. Transportation, as a major energy consumer, has seen particularly significant growth in emissions. Between 1990 and 2022, the annual average growth rate of global transportation-related CO2 emissions reached 1.7% [3]. In the United Kingdom, transportation has been the highest energy-consuming sector since 1990, with petroleum products accounting for 93% of the sector’s energy structure [4]. Globally, Statista data also shows that until 2022, 88.7% of energy supply in the transportation sector still came from petroleum, with electricity accounting for only 1.4% [5]. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) points out that 94% of the energy demand in the transportation sector relies on petroleum fuels [6]. Therefore, reducing the sector’s dependence on traditional fossil fuels has become a priority issue in the global carbon neutrality pathway.
In search for sustainable alternative fuels, methanol, methane, and ammonia (NH3) have garnered significant attention. Among these, ammonia has emerged as a leading candidate for clean fuel due to its potential for zero carbon emissions, high volumetric energy density, stable storage and transportation properties, and strong compatibility with existing energy infrastructure [7,8,9]. Ammonia is a carbon-free fuel, as its combustion process primarily produces nitrogen and water without generating carbon dioxide, making it a zero-carbon emission fuel. Moreover, ammonia has a high energy density of approximately 18.6 MJ/L, significantly higher than the 5.6 MJ/L of compressed hydrogen at 70 MPa [10]. Meanwhile, ammonia can be liquefied at −33 °C under atmospheric pressure or at approximately 9 bar under ambient temperature [7]. Furthermore, its transportation and storage technologies are relatively mature, and existing natural gas transmission networks can be adapted for ammonia transportation with appropriate modifications. These characteristics confer ammonia with broad application potential in maritime transportation and large-scale energy storage sectors.
The main industrial method for producing ammonia is currently the Haber–Bosch process, which accounts for more than 90% of global ammonia production. This method uses an iron-based catalyst to react hydrogen and nitrogen to produce ammonia at high temperatures (400–500 °C) and high pressures (10–30 MPa) [11]. Although this process is technically mature, has high production capacity, and is highly efficient, it requires a significant amount of energy during production, with an energy consumption of approximately 30 MJ/kg-NH3 per unit of product [12]. More importantly, the hydrogen required for industrial ammonia production is primarily obtained through methane reforming. However, this process releases a large amount of carbon dioxide, accounting for approximately 1–2% of global carbon dioxide emissions [13]. Currently, ammonia production contributes approximately 1.0% of global greenhouse gas emissions, with carbon dioxide emissions accounting for about 1.4% [14].
In order to reduce carbon emissions from ammonia production, in 2018, Sánchez and Martín proposed using renewable energy to produce green hydrogen, which is produced by electrolysis of water powered by renewable energy, and then synthesised with nitrogen in the air to produce ammonia [15]. Using electrolytic hydrogen and nitrogen to produce ammonia is not an entirely new idea. As early as 1925, the Fauser process had already employed this principle to produce ammonia using air and water [16]. A study by Cameli et al. demonstrated that the green hydrogen pathway emits only 0.33–0.36 tonnes of CO2 per tonne of NH3 produced, compared to 1.673 tonnes from the traditional methane reforming pathway, representing a reduction of approximately 80% [17]. However, the green ammonia production pathway still faces high economic costs. Currently, the cost of producing ammonia using renewable energy is £685/tonne, which is much higher than the £307/tonne of the traditional pathway. Even if the technology matures and economies of scale emerge by 2050, the cost is likely to remain at around £507/tonne [17].
In conclusion, the widespread application of green ammonia requires in-depth assessment and optimisation at multiple levels, including technology, economics and system integration. Based on this background, this study aims to explore the feasibility of ammonia as an alternative energy source to fossil fuels and assess its sustainability through technoeconomic analysis. The study focuses on the use of fully renewable energy ammonia production processes to ensure that the entire production process does not generate carbon dioxide emissions, thereby achieving a truly zero-carbon energy solution. A systematic technoeconomic assessment will be provided for the development of ammonia fuel. Furthermore, it will provide a scientific basis for promoting the industrialisation of renewable energy ammonia production and its application in the energy structure.
2. Materials and Methods
This study is set in the United Kingdom and focuses on green ammonia synthesis systems powered by renewable wind energy. It also compares the simulation of traditional ammonia industrial production processes to explore the feasibility of ammonia as an alternative energy source to fossil fuels. Furthermore, by simulating the ammonia synthesis process and the use of ammonia as a marine fuel, it assesses the feasibility of ammonia as an alternative to traditional fossil fuels. The simulation and calculations were primarily carried out using ECLIPSE (European Coal Liquefaction Process Simulation and Evaluation) and Excel. The technical model is based on the Haber–Bosch process reaction mechanism and assumes that electricity is supplied by 100% renewable energy (wind power) under ideal operating conditions. The research system comprises three key modules: hydrogen production (electrolysis of water), nitrogen separation (pressure swing adsorption), and ammonia synthesis.
2.1. Hydrogen Production
A green hydrogen pathway is used to reduce carbon dioxide emissions through water electrolysis. The reaction equation is shown in (1).
This system uses an electrolyser to produce hydrogen. There are many types of electrolysers, the most common being alkaline electrolysers and PEM electrolysers. PEM electrolysers are more efficient, at around 70–85% [18], while alkaline electrolysers are around 60–70% [19]. However, PEM electrolysers are also more expensive. Therefore, it is assumed that alkaline electrolysers (65% efficiency) and PEM electrolysers (80% efficiency) are used to produce hydrogen. The electrical energy required for hydrogen production comes from wind energy, which can effectively reduce carbon dioxide emissions. Although the unit cost is currently high, with technological advances and falling electricity prices, green hydrogen production is seen as the core path for low-carbon ammonia synthesis in the future.
For comparison, the traditional hydrogen synthesis method is simulated and compared with green hydrogen pathways. In traditional ammonia synthesis industries, hydrogen is mainly produced through steam methane reforming (SMR) (2). This process uses methane as feedstock, reacting with steam at high temperatures (700–900 °C) and medium pressure (15–30 bar) to produce synthesis gas (H2, CO, CO2), which is then further processed through the water-gas shift reaction (WGS) (3) to increase hydrogen yield [20]. Although SMR technology is mature and cost-effective, the process is associated with significant CO2 emissions.
Based on the research by Lee et al., assuming that under conditions of 800 °C, hydrogen can be produced via SMR with a yield of 80% [20]. Under conditions of 400 °C, the hydrogen yield can be increased via the WGS method with a yield of 70% [20].
2.2. Nitrogen Separation
In the industrial synthesis of ammonia, nitrogen is typically obtained through an air separation unit (ASU). Common separation technologies currently in use include cryogenic distillation, membrane separation, and pressure swing adsorption (PSA). Selected PSA technology as the nitrogen extraction method due to its simple process, low operating temperature, and minimal energy requirements, making it suitable for integration with green ammonia synthesis systems [21].
PSA technology utilises the adsorption differences between oxygen and nitrogen using adsorbents such as zeolite or carbon molecular sieves, alternating between adsorption and desorption at different pressures to achieve nitrogen purification [21]. In this process, air is first pressurised into the adsorption bed, where oxygen is preferentially adsorbed, while nitrogen permeates through the bed. The pressure is then reduced to release the adsorbed oxygen, regenerating the bed. The final output is high-purity nitrogen gas. Assuming that the purified nitrogen gas achieves a purity of 99%, it meets the basic purity requirements for feed gas in the Haber–Bosch process.
2.3. Ammonia Synthesis
The industrial production of ammonia primarily uses the Haber–Bosch process, which involves reacting nitrogen gas with hydrogen gas under high-temperature and high-pressure conditions on a catalyst surface to produce ammonia. The reaction equation is (4).
Equation (4) is an exothermic reaction. Theoretically, lower temperatures are more favourable for ammonia production, but from a kinetic perspective, higher temperatures enhance reaction rates. Therefore, industrial operations typically run at temperatures around 400 °C and pressures of 150–200 bar to achieve a balance between yield and efficiency.
The catalysts used in the Haber–Bosch process are typically classified into two categories: molten iron catalysts and supported metal catalysts [13]. Molten iron catalysts are derived from iron oxides and can be of three types: Fe2O3, Fe3O4, and Fe1−xO [22]. Supported metal catalysts are catalysts made by loading metal catalytic materials (typically ruthenium or cobalt) onto the surface of a carrier material (usually activated carbon or metal oxides) [22]. Molten iron catalysts are widely used in industrial systems to enhance catalytic activity and lifespan. The wustite-based iron catalyst (Fe1−xO) is used to produce ammonia gas in this study.
During the product separation stage, a fluidised bed was simulated as an ammonia absorber to replace the conventional condensation separation method. The fluidised bed absorber uses solid adsorbents to fully contact the reaction exhaust gas, efficiently capturing ammonia molecules from the gas. Then the fluidized bed is heated to desorb the captured ammonia gas. Simulation results from this study indicate that the ammonia absorption rate of the fluidised bed absorber can reach 96.54%. This highly efficient separation process significantly improves the overall ammonia production efficiency of the system. Furthermore, this separation method also helps to reduce energy consumption in subsequent processing steps.
The recirculation ratio denotes the mass fraction of unreacted material returned from the ammonia absorber to the reactor inlet relative to the total unreacted material. The synthesis of ammonia is a reversible reaction; under high temperature and pressure conditions, the conversion rate typically ranges between 15% and 25%. In a single-pass process, this implies that 75–85% of the hydrogen and nitrogen would be discharged as waste gases. By returning the unreacted H2 and N2 to the reactor, they are afforded a second opportunity to react. This overcomes the equilibrium limitations of single-pass conversion, thereby enhancing the overall conversion rate.
This project was conducted at a temperature of 450 °C and a pressure of 35 bar. The molar ratio of the reaction gases was H2:N2 = 3:1 (molar ratio). Under this condition, the ammonia conversion rate in the system per pass through the reactor is 8.1%, with the recirculation ratio of unreacted gas set at 70% and 98% [23,24]. In the green ammonia system, the hydrogen and nitrogen required for the reaction are obtained from water electrolysis and air separation processes, respectively. To ensure stable reactor operation, it is necessary to maintain a constant gas ratio, continuous feed pressure, and effective temperature control system operation. It is assumed that ammonia is continuously discharged, with the production rate matching demand (ship fuel consumption).
Although low-temperature, low-pressure ammonia synthesis (such as photocatalytic synthesis and plasma-catalysed synthesis) has garnered significant attention in recent years, such technologies remain in the early stages of development, with low yields unsuitable for industrial production [11]. Therefore, the conventional Haber–Bosch reaction pathway was used in this study as the basis for simulation and performance analysis.
2.4. Ammonia Demand
To determine the design scale of the green ammonia synthesis system, a medium-sized ocean-going transport ship is used as an application case. The vessel is equipped with a MAK M32C engine with a rated power of 3000 kW [25]. The reference value of the engine is shown in Table 1. Assuming an annual operating time of 7100 h, the system is designed to operate under design conditions with ammonia fuel providing all power.

Table 1.
The reference values for the Engine.
The fuel demand of the ship’s propulsion system was simulated using ECLIPSE to simulate the entire generator operation, thermal efficiency and operating conditions. The calculated ammonia fuel demand was 0.3264 kg/s. The annual demand is approximately 8342.78 tonnes. The lower heating value (LHV) of ammonia fuel is 18.6 MJ/kg. The engine’s fuel utilisation efficiency was determined through simulation assumptions combined with industry reference values. Assuming the ammonia synthesis system operates normally throughout the year for 8760 h, the ammonia synthesis production rate must reach 0.2646 kg/s.
2.5. Wind Power Generation and Energy Storage
Wind energy is chosen to provide energy for the entire ammonia synthesis system in order to achieve green ammonia production. Wind energy is unstable and may not be able to meet energy demand. Therefore, an energy storage system is needed to continuously supply power to the entire production process. Electrical energy storage is used to mitigate the impact of renewable energy supply fluctuations on system operation.
2.6. Design of the Green Ammonia Production Process
Figure 1 shows a schematic diagram of green synthetic ammonia production. Water is fed into an electrolysis cell to produce hydrogen gas. At the same time, air is introduced into a PSA Reactor to separate nitrogen from the air. The produced hydrogen and nitrogen are then fed into the HB reactor for ammonia production. Since reaction (4) is a reversible reaction, the post-reaction gases are passed through an absorber to separate the ammonia, with the remaining nitrogen and hydrogen being returned to the HB Reactor for further reaction. The separated ammonia gas is compressed into a liquid form for convenient transportation and storage. The entire system is powered by wind turbines. Excess electricity is stored to maintain the stability of the power supply system.
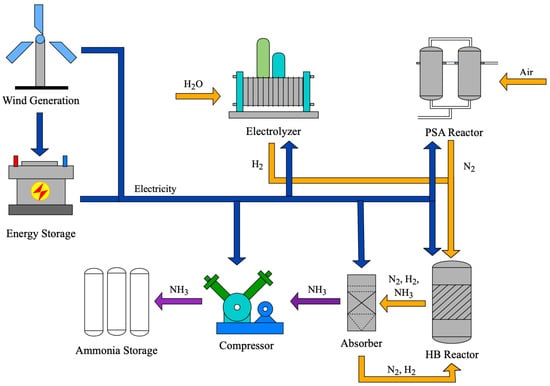
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of green synthetic ammonia production.
2.7. Modelling and Simulation
ECLIPSE software and Excel are used to model and evaluate the performance of a green ammonia synthesis system [26]. It also calculates the total electricity consumption of the entire system. ECLIPSE is a chemical process simulation software package. It is a PC-based general-purpose chemical process simulator with powerful reaction simulation capabilities, suitable for complex chemical process modelling. ECLIPSE is mainly used for technical evaluation (constructing processes through flow diagrams, calculating mass and energy balances) and economic analysis (estimating capital and operating costs, evaluating return on investment). A process flow diagram (PFD) is created first. Then, the data for each piece of equipment (efficiency, temperature, pressure, etc.) was set, and the simulation was run on the software to achieve mass and energy balance (MEB) for the entire process. Finally, the power consumption of each piece of equipment was calculated to determine the power demand of the entire system. It can be used to analyse, optimise and compare different process options and is widely used in the chemical and energy fields to help engineers make economic and technical feasibility decisions.
Engine operation is simulated first to determine the demand for ammonia fuel. Then, an ammonia production model was established to simulate the green production process of ammonia. The model comprises three submodules: hydrogen production, nitrogen separation, and ammonia synthesis. The aim is to quantitatively simulate and evaluate the system’s energy requirements and carbon emissions impact, and compare it with the traditional fossil fuel-based pathway (SMR hydrogen production). Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5 show the established ECLIPSE model.
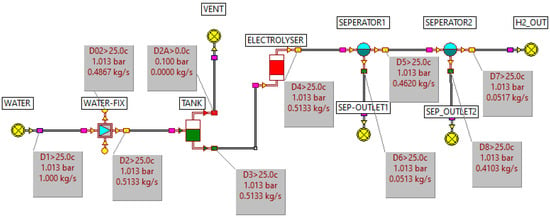
Figure 2.
Mass and energy balance model for Hydrogen production (Electrolysis).
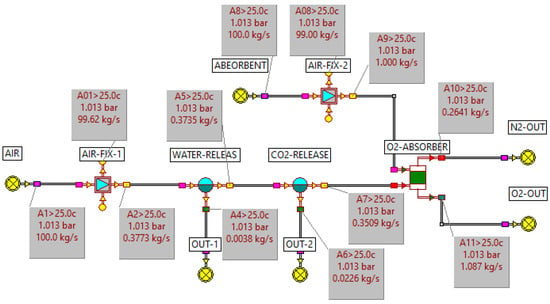
Figure 3.
Mass and energy balance model for Nitrogen separation.
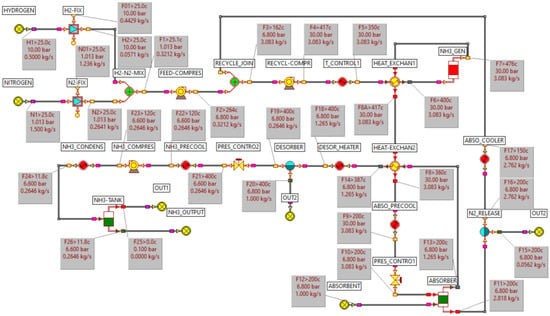
Figure 4.
Mass and energy balance model for ammonia production.
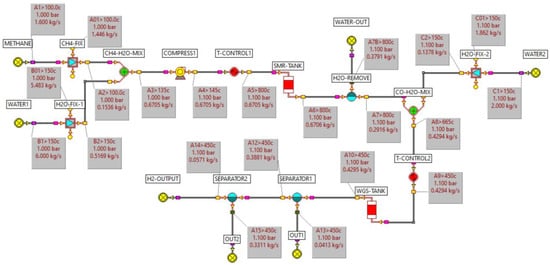
Figure 5.
Mass and energy balance model for Hydrogen production (SMR).
Figure 2 is a mass and energy balance model for hydrogen production (electrolysis) simulated using ECLIPSE. In this process, water is directly electrolysed in the electrolyser to produce hydrogen gas. The resulting oxygen is subsequently removed using a separator. In actual production, hydrogen is separated directly within the electrolyser.
Figure 3 is a mass and energy balance model simulating nitrogen separation using PSA technology within the ECLIPSE environment. After pretreatment to remove particulates and moisture, air is fed into the PSA separator. In the model, the process of oxygen adsorption and nitrogen separation is simulated by feeding the adsorbent to capture oxygen.
Figure 4 is a mass and energy balance model for ammonia synthesis using the Haber–Bosch process, simulated with ECLIPSE. Nitrogen and hydrogen are mixed and fed into the HB reactor. The reaction product gas enters an absorber, where ammonia is separated. The remaining unreacted hydrogen and nitrogen are recycled back into the HB reactor. The separated ammonia is then compressed and cooled for subsequent storage and transportation.
Figure 5 is a mass and energy balance model for hydrogen production using SMR technology, simulated with ECLIPSE. Hydrogen is first generated by the SMR reaction, with WGS subsequently enhancing the hydrogen yield. Finally, unreacted methane, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, and water are removed from the gas stream by using a separator to obtain hydrogen.
2.8. Economic Analysis
2.8.1. Capital Expenditures (CAPEX)
The capital expenditure (CAPEX) of the system mainly includes five parts: wind turbine generators, electrolysers, nitrogen separation systems (PSA), ammonia synthesis reactors, and energy storage systems. Among them, the cost calculation of wind turbine generators, electrolysers, and energy storage systems is based on the product of their rated power and unit cost. The calculation formula is as Formula (5). The unit cost per power or capacity is shown in Table 2.
where P is the rated power of the equipment (MW) or energy storage capacity (MWh); C is the unit cost per power or capacity (£/MW or £/MWh).

Table 2.
The unit cost of each device.
2.8.2. Levelised Cost of Energy (LCOE)
The levelized cost of NH3 synthesis is the main indicator for measuring the process and can be calculated according to Formula (6) [30].
where Cn is CAPEX, On is operating costs (OPEX), d is the discount rate, N is the service life, and Qn is the NH3 production.
3. Results and Discussion
Using the above models, the production processes are evaluated, focusing on key indicators such as hydrogen production, nitrogen production, ammonia production, total system energy consumption, and the proportion of energy consumption in each module. In addition, the traditional methane reforming (SMR) hydrogen production pathway is also simulated and compared with the water electrolysis hydrogen production pathway to compare the performance of the two processes.
3.1. Hydrogen Production
Hydrogen production is one of the key components of the ammonia synthesis system. Two hydrogen production pathways, hydrogen production via water electrolysis driven by renewable energy and traditional SMR hydrogen production, were compared and analysed in this study.
In the electrolytic water hydrogen production module, it is assumed that alkaline electrolysers and PEM electrolysers are utilised for hydrogen production. The energy consumption of alkaline electrolysis cells is 55 kWh/kg H2, while that of PEM electrolysis cells is 52 kWh/kg H2 [31]. The cost of a proton exchange membrane (PEM) electrolyser is between £600 and £1123 per kilowatt, while the cost of an alkaline electrolyser is between £300 and £674 per kilowatt [28]. The power consumption and costs of using the two types of electrolysers are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
The power consumption and CAPEX of the two types of electrolysers.
A comparison of the energy consumption of the two types of electrolysers shows that alkaline electrolysers have higher energy consumption. This is primarily due to their electrode materials, electrolyte conductivity, and lower operating current density [31]. However, alkaline electrolysers have significantly lower equipment manufacturing costs and operational costs than PEM electrolysers, and they have higher process maturity, longer operational lifespans, and greater market availability [28]. In contrast, PEM electrolysers perform better in terms of energy consumption, with higher electrical energy utilisation efficiency and better load regulation capabilities in responding to fluctuations in renewable energy [28]. However, they have higher capital expenditure (CAPEX), and their catalysts typically rely on precious metal materials, resulting in significant initial investment pressure. Moreover, the operational lifespan of PEM electrolysers is significantly influenced by the stability of the membrane materials, which may increase replacement costs over the long term [28].
Therefore, in actual system design, the choice between alkaline and PEM electrolysers needs to be balanced between energy consumption levels, initial investment, operating and maintenance costs, and compatibility with the characteristics of renewable energy power supply. This study does not establish definitive conclusions regarding specific technical pathways, since there is potential for application and room for optimisation in both routes under different economic and energy contexts. The energy consumption and investment costs of hydrogen synthesis are assumed to be the average of the two types of electrolysers.
Through calculations, the energy consumption for hydrogen synthesis was calculated to be 53.5 kWh/kg H2. In comparison, SMR hydrogen production performs better in terms of energy consumption per unit, with an energy consumption of approximately 5.44 kWh/kg H2, significantly lower than the electrical energy consumption of electrolysis-based hydrogen production. In terms of production capacity, SMR enables larger-scale continuous production under industrial conditions and has relatively lower equipment investment costs, resulting in a lower unit hydrogen production cost than current electrolysis-based hydrogen production. However, SMR relies on natural gas as feedstock and emits a significant amount of carbon dioxide during the reaction process, with an average of approximately 4.13 kg CO2 emitted per kilogram of hydrogen produced. The carbon emissions from SMR are far more than those from electrolysis hydrogen production. This will significantly impact its economic competitiveness in the future as carbon emission constraints become increasingly stringent. Although electrolysis-based hydrogen production has higher energy consumption, since the electricity is entirely sourced from wind and solar energy, carbon emissions are nearly zero, thereby reducing carbon dioxide emissions during the ammonia production process.
3.2. Nitrogen Separation
Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA) technology is used for air separation to obtain high-purity nitrogen. Simulation results show that the nitrogen production rate of the PSA module must reach 1.123 kg/s to fully meet the nitrogen supply requirements for the ammonia synthesis reaction. Therefore, the required air flow rate is approximately 1.604 kg/s. This method has a simple process and can operate at ambient temperature. In addition to PSA, cryogenic distillation is also being considered for nitrogen separation. This method involves cooling air to extremely low temperatures (approximately −196 °C) to sequentially liquefy and separate components such as oxygen and nitrogen, thereby producing nitrogen of extremely high purity [32]. However, this process requires a significant amount of electrical energy to drive compressors and refrigeration systems to maintain the low-temperature environment. In the renewable energy-powered system simulated in this study, the additional power demand would significantly increase the system’s total energy consumption, which is not beneficial for improving overall energy efficiency. Therefore, PSA technology, which has lower energy consumption and a relatively simple structure, is used to reduce the pressure on the power supply system and improve operational economics.
In conclusion, electrolytic hydrogen production technology has significant advantages in achieving low-carbon green ammonia synthesis, but the challenges posed by its high power consumption and fluctuations in power supply need to be addressed by optimising electrolyser design and energy storage systems.
3.3. Ammonia Synthesis
The ammonia synthesis module is the central reaction stage of the system, and its operating conditions and equipment selection directly impact ammonia production efficiency and overall system energy consumption. The reactor operating temperature was simulated at approximately 400 °C, with pressure maintained at 30 bar and a hydrogen-to-nitrogen molar ratio stabilised at 3:1. Although these conditions are below the high-pressure range (150–300 bar) commonly used in traditional industrial Haber–Bosch processes, they are more consistent with the energy efficiency optimisation objectives of renewable energy-driven systems.
Simulation results show that under the above conditions, the reactor’s first-pass ammonia conversion rate is 8.612%. Although this conversion rate is lower than that achievable under industrial high-pressure conditions, gas recirculation can significantly increase the total ammonia production. The recirculation gas ratio was set at 70% and 98% in this study, meaning that most of the unreacted gas is reintroduced into the reactor after ammonia separation. A higher recirculation ratio effectively increases the residence time of reactants within the system, thereby enhancing overall conversion efficiency. The hydrogen and nitrogen requirements for the two recirculation gas ratios are shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
The hydrogen and nitrogen requirements for two recirculation gas ratio.
Comparing the data for the two cycle proportions shows that increasing the cycle proportion can significantly improve ammonia yield. However, it may also affect the molar ratio of the reaction gases, thereby impacting the reaction yield.
3.4. Carbon Dioxide Emission
Traditional shipping relies mainly on fossil fuels for energy, which produce a lot of carbon dioxide when burned. At an output power of 3000 kW, this engine uses 0.1492 kg/s of fuel when running on fossil fuels, which means it emits 0.606 kg/s of carbon dioxide. Based on an annual operating time of 7100 h, the annual total emissions amount to approximately 15,490 tonnes of CO2. By replacing fossil fuels with green ammonia, CO2 emissions during operation are reduced to zero. This results in an annual reduction of approximately 15,490 tonnes of CO2 emissions. This outcome suggests that green ammonia holds significant potential for emissions reduction in the transportation sector and plays an important role in achieving deep decarbonisation of the transportation sector.
3.5. Energy Consumption Analysis
The total energy consumption of the simulated green ammonia synthesis system was 48,655.34 kWh at a recycling ratio of 70%, and 5225.88 kWh at a recycling ratio of 98%. The entire system consists of three parts: the hydrogen production module, the nitrogen separation module, and the ammonia synthesis module. The specific energy consumption values and proportions of each module are shown in Table 5.

Table 5.
The energy consumption values and proportions of each module.
In terms of energy consumption, the energy consumption for hydrogen production in both recirculation ratios is significantly higher than that of other modules. This is because the energy requirements of the water electrolysis process for hydrogen production are far higher than those of nitrogen separation and ammonia synthesis. Therefore, improvements in the overall energy efficiency of the system largely depend on optimising the efficiency of the electrolyser, the stability of the power supply, and the compatibility between renewable energy generation and energy storage systems. If the efficiency of the electrolysis process can be improved by 5–10%, it will lead to a significant reduction in total energy consumption and directly lower the unit production cost of ammonia.
The energy consumption of the nitrogen separation module accounts for 13.26% and 11.72%. This result indicates that the use of PSA technology offers significant energy efficiency advantages in this system. Compared with cryogenic distillation, PSA does not require a large amount of electrical energy for deep cooling, thereby significantly reducing the energy consumption load of nitrogen separation.
The ammonia synthesis module accounts for 11.65% of energy consumption, mainly from the circulation compression of reaction gas, reactor heating, and fluidised bed desorption process. Although this part of energy consumption is much lower than that of electrolysis hydrogen production, its proportion cannot be ignored. Additionally, the high absorption efficiency of the fluidised bed absorber effectively reduces ammonia loss in the exhaust gas, partially counteracting the negative impact of circulation compression energy consumption on the system.
Comparing the energy consumption of the two recirculation ratios reveals that increasing the recirculation ratio substantially reduces the energy required for hydrogen production. this is due to the fact that when the recirculation ratio is raised to 98%, the recovery efficiency of unreacted hydrogen and nitrogen increases significantly, decreasing the primary energy demand of hydrogen production and nitrogen separation units considerably. However, in actual production, a high recirculation ratio may lead to the accumulation of inert gases within the synthesis loop and alterations in the molar proportion of reaction gases. These may inhibit the efficiency of the ammonia synthesis reaction.
3.6. Wind Generation and Energy Storage
To ensure stable system operation under varying wind conditions throughout the year, this study selected offshore wind turbines with a single-unit capacity of 12 MW (GE Vernova GE Haliade-X 12 MW) [33]. The wind turbine is a production of GE Vernova, a manufacturer from Cambridge, MA, USA. Based on simulation results of the UK’s offshore average wind speeds and the turbine’s power curve, a single wind turbine generates 60.83 GWh of electricity annually. To determine the optimal system configuration, a quantitative study was conducted on the relationship between the number of wind turbines and the capacity of energy storage equipment. This research focused on comparing two energy storage schemes: a pure electrical energy storage scheme (using batteries only) and an electricity–hydrogen hybrid energy storage scheme (combining batteries with hydrogen energy storage).
In pure electrical energy storage solutions, the electricity generated by wind turbines must satisfy the power demands of three concurrent processes: hydrogen production, nitrogen separation, and ammonia synthesis. When turbine output exceeds the real-time total demand of these three components, surplus electricity charges the battery storage system until the batteries reach their rated capacity limit. If the battery is fully charged, the charging operation is discontinued. When wind power generation is not enough to satisfy the real-time total load, the system is powered by batteries to ensure stable operation of the production process. This approach effectively balances the impact of fluctuating wind power output on the system through battery energy storage charging and discharging regulation. However, placing the entire electrical load burden on batteries resulted in demanding requirements for battery capacity and power configuration.
In the electro-hydrogen hybrid energy storage scheme, the electricity demand for hydrogen production is separated from that required for ammonia synthesis and nitrogen separation. During system operation, wind-generated electricity is prioritised to meet the demands of ammonia synthesis and nitrogen separation, with the battery storage system’s capacity configuration specifically designed to ensure the stable operation of these processes. When wind turbine output exceeds the real-time requirements of these two processes, surplus electricity is allocated to the water electrolysis hydrogen production unit. When the hydrogen production exceeds the current demand, the excess hydrogen enters the hydrogen storage system. Conversely, when hydrogen production falls short, the hydrogen storage system supplements the supply. This approach ensures the continuous and stable operation of ammonia synthesis while reducing the required battery storage capacity, effectively enhancing the overall system’s economic viability and operational reliability.
Table 6 and Table 7 present the configuration results for the pure electrical energy storage scheme. Within this approach, for each given number of wind turbines, the minimum battery capacity required to sustain continuous stable system operation is progressively adjusted and determined. Battery capacity is established with the premise of meeting real-time power balance requirements, ensuring the storage system can effectively compensate for power deficits during fluctuations in wind output and load variations, thereby preventing supply interruptions.

Table 6.
The battery capacity required for different numbers of wind turbines (recirculation ratio is 70%).

Table 7.
The battery capacity required for different numbers of wind turbines (recirculation ratio is 98%).
Table 8 and Table 9 present the configuration results for the electricity–hydrogen hybrid energy storage scheme. In this approach, using the number of wind turbines as the initial condition, the minimum battery capacity required to stabilise all system loads except hydrogen production is first determined. Subsequently, based on the continuous operational requirements of the electrolyser for hydrogen production, the minimum hydrogen storage tank capacity is further determined to ensure matching capacity. This guarantees the energy balance and operational reliability of the entire system, including hydrogen production, across different time scales.

Table 8.
The battery and hydrogen capacity required for different numbers of wind turbines (recirculation ratio is 70%).

Table 9.
The battery and hydrogen capacity required for different numbers of wind turbines (recirculation ratio is 98%).
Calculations show a significant inverse relationship between the number of wind turbines and the required energy storage capacity. As the number of wind turbines increases, the system’s total capacity demand for storage equipment decreases continuously. This is mainly because the increase in wind power installed capacity enhances the system’s instantaneous power supply capability, stabilises power output, and reduces reliance on the energy storage system for long-duration, large-capacity energy regulation.
Comparing the two energy storage solutions, the hybrid electricity–hydrogen storage approach demonstrates greater advantages. This is due to hydrogen storage’s characteristics of low cost per unit capacity and extended storage cycles, making it highly suitable for large-scale, long-duration energy storage and dispatch. Consequently, it effectively replaces portions of high-cost battery capacity. Particularly in scenarios with fewer wind turbines and greater energy variability, the introduction of hydrogen storage significantly reduces the system’s demand for battery capacity, thereby optimising the overall economic efficiency of the energy storage system.
In summary, this study prioritises electricity–hydrogen hybrid energy storage solutions and scientifically configures the storage proportion based on installed wind power capacity to achieve an optimal balance between system economics and reliability.
4. Economic Analysis
4.1. CAPEX Analysis
The capital expenditure (CAPEX) of the system mainly includes five parts: wind turbine generators, electrolysers, nitrogen separation systems (PSA), ammonia synthesis reactors, and energy storage systems. Among them, the cost calculation of wind turbine generators, electrolysers, and energy storage systems is based on the product of their rated power and unit cost. In addition, the costs of other equipment and reactors are shown in Table 10.

Table 10.
The CAPEX of each device.
4.2. Levelised Cost of Energy (LCOE)
According to IEA estimates, maintenance costs for green ammonia production are approximately 5–8% of CAPEX [37]. Therefore, assuming OPEX is 6% of CAPEX, the discount rate is 7%, and the service life is 20 years.
The LCOE for ammonia is calculated as shown in Table 11, Table 12, Table 13 and Table 14. These four tables, respectively, illustrate the relationship between the number of wind turbines and the Levelised Cost of Electricity (LCOE) under different circulating gas ratios (70% and 98%) and different energy storage schemes (pure electrical energy storage and hybrid electrical-hydrogen storage).

Table 11.
The LCOE for different numbers of wind turbines (recirculation ratio is 70%, electrical energy storage).

Table 12.
The LCOE for different numbers of wind turbines (recirculation ratio is 98%, electrical energy storage).

Table 13.
The LCOE for different numbers of wind turbines (recirculation ratio is 70%, electricity–hydrogen hybrid storage).

Table 14.
The LCOE for different numbers of wind turbines (recirculation ratio is 98%, electricity–hydrogen hybrid storage).
In the pure electrical energy storage solution, under a 70% recirculation ratio, increasing the number of wind turbines from 10 to 23 resulted in the system’s total electricity generation rising from 608,292 MWh to 1,399,072 MWh. Correspondingly, the required battery storage capacity decreased from 8400 MWh to 2800 MWh. During this process, the Levelised Cost of Electricity (LCOE) decreased significantly from £35,953.55/tonne to £20,426.23/tonne, representing a reduction of 43.2%. This indicates that increasing wind power capacity effectively reduces reliance on energy storage and overall costs. However, beyond 19 turbines, the decline in LCOE slowed markedly, reaching a minimum of £20,367.02/t at 21 turbines. It then began to rise, meaning the benefits of further increasing turbine numbers to reduce costs were decreasing.
In contrast, the hybrid electricity–hydrogen storage solution shows significant cost advantages. Comparing the four tables reveals that, within the same range of turbine numbers, the LCOE of the hybrid storage solution is consistently lower than that of the pure electrical storage solution. Comparing the lowest costs of the two storage solutions shows that, at a recirculation ratio of 70%, the hybrid storage solution reduces costs by 70.75% compared to the pure electrical solution. At a 98% recirculation ratio, the reduction stands at 60.36%.
Increasing the gas recirculation ratio yields substantial benefits. Comparing Table 13 and Table 14 reveals that, under similar wind turbine configurations, the LCOE at a 98% recirculation ratio is significantly lower. For instance, with six wind turbines, the LCOE at the 70% recirculation ratio is £6111.11/t. When the recirculation ratio is 98%, with five wind turbines, the LCOE is 3074.06/t. This confirms that increasing the recirculation gas ratio to 98% fundamentally reduces requirements for total wind and solar power generation capacity and energy storage system scale by substantially lowering hydrogen production energy consumption.
Compared to the LCOE of traditional ammonia synthesis methods, which ranges from £800 to £1200/t NH3 [37], the LCOE of green ammonia synthesis is significantly higher than that of traditional synthesis methods. This is because the cost of energy storage systems and wind power generation in green ammonia synthesis is too high, and the traditional ammonia synthesis method does not include electrical energy storage systems. This results in a significant direct difference between them.
4.3. Sensitivity Analysis
To identify the main drivers affecting the economic viability of the system, we selected several key parameters for univariate scenario analysis (with other conditions held constant) to measure the sensitivity of each parameter to LCOE. The influence of each parameter on LCOE is shown in Figure 6.
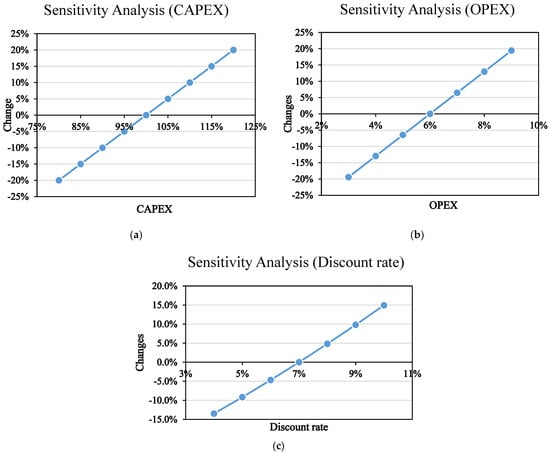
Figure 6.
This figure is a sensitivity analysis of the entire system. (a) The influence of CAPEX changes on LCOE; (b) The influence of OPEX changes on LCOE; (c) The influence of discount rate changes on LCOE.
By adjusting parameters, it was found that the linear effect between CAPEX and OPEX is significant, with changes in CAPEX and OPEX resulting in proportional changes in LCOE. The discount rate has a relatively small impact. Reducing the discount rate from 7% to 4% can lower LCOE by 13.5%, while increasing it to 10% increases LCOE by approximately 15%. This shows that although changes in capital costs are not as significant as those in energy storage and production, they still cannot be ignored.
5. Conclusions
A green ammonia synthesis system based on renewable energy is constructed and simulated in this study, including water electrolysis for hydrogen production, PSA nitrogen production, and the Haber–Bosch synthesis process, and compared with traditional pathways.
Simulation results indicate that under a 70% recirculation ratio, the system’s annual total energy consumption amounts to approximately 426.22 GWh. Hydrogen production accounts for the highest proportion at 77.86%, while nitrogen separation and ammonia synthesis contribute 13.47% and 8.66%, respectively. Under these conditions, using seven 12 MW offshore wind turbines, coupled with 460 MWh of lithium battery energy storage and 240 tonnes of hydrogen storage capacity, can meet the system’s annual stable operation requirements while achieving the lowest levelised cost of energy (LCOE).
When the recirculation ratio increases to 98%, the system’s energy consumption structure is significantly optimised, reducing total annual energy consumption to 142.12 GWh. The energy consumption distribution across stages is as follows: hydrogen production 67.79%, nitrogen separation 11.72%, and ammonia synthesis 20.49%. Under these conditions, the system requires only three wind turbines, 260 MWh of battery capacity, 21 MW of electrolysers, and 45 tonnes of hydrogen storage to meet stable annual operation demands while achieving the lowest LCOE. Compared to a 70% recirculation ratio, a 98% proportion reduces wind power capacity requirements by 57%, battery storage needs by 43%, and hydrogen storage capacity by 81%, significantly enhancing system economics.
In conclusion, the system is technically capable of low-carbon operation throughout its entire life cycle. However, it lacks economic competitiveness under the current cost structure. In the future, its commercial prospects can be improved by reducing equipment costs, optimising energy storage structures, and providing policy support. With the continued decline in renewable energy costs and advances in energy storage technology, green ammonia is expected to become an important low-carbon fuel option in the transportation field in the future.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.Q. and Y.W.; methodology, Y.Q.; software, Y.Q. and Y.H.; validation, Y.Q. and Y.W.; formal analysis, Y.Q. and Y.W.; investigation, Y.Q.; resources, Y.W.; data curation, Y.Q. and Y.W.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.Q.; writing—review and editing, Y.H. and Y.W.; visualisation, Y.Q.; supervision, Y.W.; project administration, Y.Q. and Y.W.; funding acquisition, Y.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research work was funded by the Engineering and Physical Science Research Council, Impact Acceleration Account (IAA), Durham University under the project titled “Development of Magnetic crankshaft for Hydrogen free-piston Miller Cycle Engine” (Project ID: 2744156) and UK National Clean Maritime Research Hub (Grant Number: EP/Y024605/1).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- World Meteorological Organization. Climate Change Indicators Reached Record Levels in 2023. 2024. Available online: https://public.wmo.int/media/news/climate-change-indicators-reached-record-levels-2023-wmo?utm_source=PANTHEON_STRIPPED (accessed on 18 March 2025).
- IEA. CO2 Emissions in 2022—Analysis. 2023. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/co2-emissions-in-2022 (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- IEA. Transport—Energy System. Available online: https://www.iea.org/energy-system/transport?utm_source=chatgpt.com (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Department of Energy Security and Net Zero; National Energy Efficiency Data Framework (NEED); Household Energy Efficiency Statistics, and Fuel Poverty Statistics. Energy Consumption in the UK (ECUK) 1970 to 2023. 2024. Available online: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/media/66f13235f188a93404379f94/Energy_Consumption_in_the_UK_2024.pdf (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Statista. Global Transportation Energy Consumption 1975–2022, by Fuel. 2024. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1495756/global-transportation-energy-consumption-by-fuel/ (accessed on 16 March 2025).
- Rodrigue, J.-P. The Geography of Transport Systems; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Sang, Z.; Tian, Y.; Peng, W.; Liu, X.; Liang, J. Ammonia as a Green Carbon-Free Fuel: A pathway to the Sustainable Energy Economy. ACS Energy Lett. 2024, 9, 5120–5136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, J.S.; Silva, V.; Rocha, R.C.; Hall, M.J.; Costa, M.; Eusébio, D. Ammonia as an energy vector: Current and future prospects for low-carbon fuel applications in internal combustion engines. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 296, 126562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Royal Society. Ammonia: Zero-Carbon Fertiliser, Fuel and Energy Store. 2020. Available online: https://royalsociety.org/-/media/policy/projects/green-ammonia/green-ammonia-policy-briefing.pdf (accessed on 6 March 2025).
- Kurien, C.; Mittal, M. Review on the production and utilization of green ammonia as an alternate fuel in dual-fuel compression ignition engines. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 251, 114990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xia, M.; Wang, H.; Huang, K.; Qian, C.; Maravelias, C.T.; Ozin, G.A. Greening Ammonia toward the Solar Ammonia Refinery. Joule 2018, 2, 1055–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, M.; Wu, Y.; Song, W.; Yan, J.; Qi, X.; Yang, J.; Wen, J.; Zhang, H. Ammonia Energy: Synthesis and utilization. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2024, 63, 8003–8024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, J.; Lan, R.; Tao, S. Development and recent progress on ammonia synthesis catalysts for Haber–Bosch process. Adv. Energy Sustain. Res. 2020, 2, 2000043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacFarlane, D.R.; Cherepanov, P.V.; Choi, J.; Suryanto, B.H.; Hodgetts, R.Y.; Bakker, J.M.; Vallana, F.M.F.; Simonov, A.N. A roadmap to the ammonia economy. Joule 2020, 4, 1186–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, A.; Martín, M. Optimal renewable production of ammonia from water and air. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 178, 325–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, F.A.; Reed, F.C.; Edwards, W.L. A direct synthetic ammonia plant. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1925, 17, 775–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameli, F.; Kourou, A.; Rosa, V.; Delikonstantis, E.; Galvita, V.; Van Geem, K.M.; Stefanidis, G.D. Conceptual process design and technoeconomic analysis of an e-ammonia plant: Green H2 and cryogenic air separation coupled with Haber-Bosch process. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 49, 1416–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.-T.; Xu, Z.-L.; Li, F.-M.; Chen, F.-Y.; Yu, J.-Y.; Yan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xia, B.Y. Recent advances in proton exchange membrane water electrolysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2023, 52, 5652–5683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, A.L.; Cebola, M.-J.; Santos, D.M.F. Towards the Hydrogen Economy—A review of the parameters that influence the efficiency of alkaline water electrolyzers. Energies 2021, 14, 3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, H.S.; Park, J.; Kang, B.M.; Cho, C.-H.; Lim, H.; Won, W. Scenario-Based Techno-Economic analysis of steam methane reforming process for hydrogen production. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Chinh, P.; Hieu, N.T.; Tien, V.D.; Nguyen, T.-Y.; Nguyen, H.N.; Anh, N.T.; Van Thom, D. Simulation and experimental study of a single Fixed-Bed model of nitrogen gas generator working by pressure swing adsorption. Processes 2019, 7, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H. Ammonia Synthesis Catalysts: Innovation and Practice; World Scientific: Singapore, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Palys, M.J.; McCormick, A.; Cussler, E.L.; Daoutidis, P. Modeling and optimal design of absorbent enhanced ammonia synthesis. Processes 2018, 6, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouwenhorst, K.H.R.; Van Der Ham, A.G.J.; Lefferts, L. Beyond Haber-Bosch: The renaissance of the Claude process. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 21566–21579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brochure—MAK M 32 C Low Emission Engine—Caterpillar Marine Power Systems—PDF Catalogs|Documentation|Boating Brochures. Available online: https://pdf.nauticexpo.com/pdf/caterpillar-marine-power-systems/brochure-mak-m-32-c-low-emission-engine/19997-40601.html (accessed on 6 June 2025).
- The University of Ulster. ECLIPSE Process Simulator; Energy Research Centre: Jordanstown, Northern Ireland, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- What Is the Cost of Offshore Wind Energy? Available online: https://www.windustry.com/what-is-the-cost-of-offshore-wind-energy.htm (accessed on 25 July 2025).
- Besner, J.A. Needed: Electrolyzers Producing Cheap, Green, Hydrogen; Gas Turbine World: Fairfield, CT, USA, 2022; Available online: https://gasturbineworld.com/electrolyzers-green-hydrogen/ (accessed on 24 June 2025).
- Cole, W.; Karmakar, A.; National Renewable Energy Laboratory. Cost Projections for Utility-Scale Battery Storage: 2023 Update; Technical Report NREL/TP-6A40-85332; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Applewood, CO, USA, 2023. Available online: https://www.nrel.gov/docs/fy23osti/85332.pdf (accessed on 25 July 2025).
- Short, W.; Packey, D.; Holt, T. A manual for the Economic Evaluation of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy Technologies. 1995. Available online: https://www.nrel.gov/docs/legosti/old/5173.pdf (accessed on 11 October 2025).
- Hydrogen Energy Electrolyzer Market. Policy Drivers Accelerating Hydrogen Electrolyzer Adoption Globally. Available online: https://pmarketresearch.com/chemi/hydrogen-energy-electrolyzer-market/ (accessed on 24 June 2025).
- Wang, S.; Meng, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, S.; Hou, Y. Experimental study on the cryogenic distillation system for high-purity liquid nitrogen under offshore conditions. Cryogenics 2024, 141, 103885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, L. GE Vernova GE Haliade-X 12 MW—12,00 MW—Wind Turbine. Available online: https://en.wind-turbine-models.com/turbines/1809-ge-vernova-ge-haliade-x-12-mw (accessed on 16 July 2025).
- Made-in-China.com. [Hot Item] ASU 1500 Nm3/H Nitrogen Plant Low Power Consumption Factory Supplier. Available online: https://m.made-in-china.com/product/Asu-1500-Nm3-H-Nitrogen-Plant-Low-Power-Consumption-Factory-Supplier-2117272635.html (accessed on 25 July 2025).
- SAMSON AKTIENGESELLSCHAFT. SAMSON AKTIENGESELLSCHAFT Brochure. 2024. Available online: https://www.samsongroup.com/document/t25520en.pdf (accessed on 25 July 2025).
- Ingersoll Rand. MSG Air & Gas Compressors. Available online: https://www.ingersollrand.com/en-lac/products/air-compressors/process-air-and-gas-compressors/msg-air-gas-compressors/ (accessed on 25 July 2025).
- International Energy Agency. Ammonia Technology Roadmap. 2021. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/ammonia-technology-roadmap (accessed on 25 July 2025).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).