Abstract
The superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles as an absorbent with a size distribution of 4.8–6.4 nm were synthesized using a simple one-pot hydrothermal strategy at 200 °C for 24 h, where iron citrate and distilled were the sum total of raw materials. The as-synthesized Fe3O4 powders showed rapid and efficient adsorption for xylenol orange with a saturated adsorption amount of 42.5 mg/g according to Langmuir linear fitting, and the adsorption reaction between xylenol orange adsorbate and Fe3O4 adsorbent was mostly completed within 10 min. The Fe3O4 nanoparticles not only had superparamagnetism with a saturation magnetization value of 54.9 emu/g at 15 kOe but also possessed strong magnetic response, making them easy to separate easily from aqoeous solution under the attraction of magnet. In this work, the Fe3O4 particles can be totally attracted toward the magnet within 15 s, leaving the suspension a clear solution.
1. Introduction
Energy development and environmental protection have always been the common concern of people because energy is the important material base for the life and development of human society, and the environment is the fundamental condition for human survival [1,2,3,4]. Water pollution caused by dyes is a serious disposal problem because most of the dyes in water are highly visible and undesirable. The dyes can severely interfere with the absorption and reflection of sunlight entering the water, which affects the replication and producing of dye-degrading bacteria; as a result, these dyes are not biodegradable in the water [5,6,7,8,9]. Therefore, removal of such colored dye contaminants from polluted aqueous media has become an impendent issue. To solve this problem, a number of available technologies for the removal of dyestuffs have been developed and implemented, such as physical [10,11], chemical [12,13], electrical [14,15], and biological [16,17] strategies. Among these technologies, the adsorption technology has been regarded as one of the most competitive methods for wastewater treatment in terms of its flexibility and simplicity of design, operational ease, and insensitivity to pollutants; moreover, no harmful substances are formed during the adsorption reaction [18,19,20].
Many absorbent materials have been developed to remove dyes from aqueous solution, such as graphene oxide nanocomposites [21], activated carbon [22], ultrafiltration membrane [23], natural fiber [24,25], and magnetic nanocellulose [26]. Among all available candidates, the nanostructured Fe3O4 particles are attractive because of their superparamagnetism, which facilitates the targeting control and recyclable separation just using an applied magnetic field. This superparamagnetism of Fe3O4 particles is beneficial to the simple and rapid separation of Fe3O4 after adsorption of pollutants, which can not only save the cost, but also shorten the operation cycle. In addition, the size effect of nanomaterials makes them easier to capture the pollutant due to enhanced surface activity [27,28]. So far, numerous methods have been reported to synthesize magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles. For example, Chen et al. [29] synthesized the superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanofibers with hollow characteristic morphology based on a polymer-assisted thermochemical reduction process, and the diameter and wall thickness of these nanofibers were ranging from 100 to 200 nm and 15 to 25 nm, respectively. Yang et al. [30] synthesized the magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles with different shapes and sizes by the thermal decomposition method. Liu et al. [31] also synthesized Fe3O4 nanoparticles with a diameter of ~500 nm by a hydrothermal method using FeCl3·6H2O, ethylene glycol and CH3COONa as the main raw materials. Moreover, Eskandari et al. [32] synthesized the Fe3O4 nanoparticles (6 nm) based on a chemical co-precipitation method with an alternating magnetic field and ultrasonic-assisted. Although these methods could synthesize the nanostructured Fe3O4 particles with superparamagetism, but the synthesis process is still not the easiest, as well as the used raw materials. It is still challenging to further simplify the operation process to reduce costs and energy consumption.
Xylenol orange (XO) is a common synthetic dye, also usually used as potentiometric reagent and complexometric indicator for the determination of metal ions in the science laboratory. Therefore, the XO effluents from manufacturing industries and laboratories will further attract heavy metal ions, finally leading to various ailments to the living body. To date, only a few studies had reported on the removal of XO from the aqueous solution. Hyperbranched polyethyleneimine based gels [33] and polyvinyl alcohol/cellulose nanocrystals hydrogels [34] were developed as absorbent materials for the removal of XO from the aqueous solution. However, the process of collecting these used sorbents from water was cumbersome after the adsorption reaction. For that, in this work, a facile one-pot hydrothermal procedure was developed for the synthesis of superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles, in which iron citrate and distilled were the sum total of raw materials. The main advantages of hydrothermal method are as follows. The cheap and readily available water served as the solvent during the hydrothermal method, which could synthesize the desired products under medium and low temperature conditions without subsequent high-heat treatment. The closed conditions of hydrothermal process could reduce the emission of toxic and harmful gases, effectively reducing environmental pollution, in line with the requirements of energy-saving and emission reduction. Moreover, the as-synthesized superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles could serve as an adsorbent for the removal of XO, as a comparison, the adsorptions of other dyes, Basic Orange 2 (BO2) and Acid Orange 7 (AO7) were also investigated.
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
Iron citrate (AR) was obtained from Shanghai Yien Chemical Technology Co., Ltd., Xylenol Orange (XO, 98%) dye was obtained from Shanghai Bide Medical Technology Co., Ltd., Basic Orange 2 (BO2, AR) dye was obtained from Shanghai Maclin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd., Acid Orange 7 (AO7, >97.0%) was obtained from Tokyo Chemical Industry Co., Ltd., and ethanol (≥99.7%) was purchased from Chengdu Kelong Chemical Co., Ltd. The general characteristics of XO, BO2, and AO7 dyes, including Cas number, chemical number, and maximum absorption wavelength are (λmax), are shown in Table 1. These reagents were used as received without further purification.
2.2. Synthesis of Fe3O4
Superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles were synthesized by a sample one-step hydrothermal procedure based on our previous report [35]. Iron citrate (4.0 mmol) and distilled water (30 mL) was directly added into a 50 mL Teflon-lined stainless-steel autoclave, and maintained for 24 h at 200 °C. After cooling to room temperature, the resulting precipitate was separated with the help of a magnet, and washed with distilled water and ethanol. Finally, the Fe3O4 powders were obtained under vacuum at 60 °C for 24 h.
2.3. Characterization
The crystallographic phase of Fe3O4 sample was characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD, DX-2700). The morphology and size of Fe3O4 particles were evaluated by transmission electron microscopy (TEM, JEM-2100F). The magnetic property of Fe3O4 powders was obtained by physical performance measurement system (PPMS 9).
2.4. Evaluation of Adsorption Capacity
The adsorption capacities of Fe3O4 powders were evaluated by the removal of XO, BO2, and AO7 dyes from simulated wastewater at room temperature without pH preadjustment. Briefly, 0.1 g Fe3O4 powder was dispersed into 100 mL dye solution with different concentrations, and the mixture was stirred at a constant speed of 200 rpm. Then, a small amount of suspension was withdrawn at regular intervals and separated by an applied magnetic field, and the absorbance of supernatant was measured at the maximum absorption wavelength of the dye using an ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometer (U-3900). The adsorption efficiencies (ηt, %) and adsorption amount (q, mg/g) for dyes were calculated using Equations (1) and (2), respectively:
where C0 (mg/L) is the initial concentration of dyes, Ct (mg/L) is the concentration of dyes at time t (t = 0–60 min), m (g) is the mass of Fe3O4 powders, and V (L) is the volume of dyes aqueous solution.

Table 1.
General characteristics of AO7 dye.
Table 1.
General characteristics of AO7 dye.
| Generic Name | Abbreviation | Cas Number | Chemical Structure | λmax (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xylenol orange | XO | 1611-35-4 | 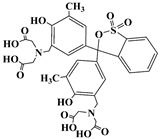 | 435 |
| Basic orange 2 | BO2 | 532-82-1 | 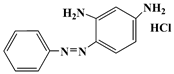 | 452 |
| Acid orange 7 | AO7 | 633-96-5 | 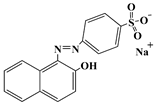 | 484 |
3. Results and Discussion
Figure 1a shows the XRD pattern of the sample. All broad peaks had a good match with the standard Fe3O4 pattern (JCPDS No. 65-3107), suggesting that the as-synthesized Fe3O4 particles had a good crystallinity with small grain size. The mean grain size of Fe3O4 was about 6.6 nm, as calculated by the Scherrer formula. Figure 1b shows the high-resolution XPS spectra of Fe 2p and O 1s of the as-synthesized Fe3O4 particles. For the Fe2p core-level XPS spectra, two distinct peaks with binding energies of 724.1 and 710.5 eV appeared, which were assigned to the characteristic doublets of Fe 2p1/2 and Fe 2p3/2 from iron oxide. For the O 1s core-level XPS spectra in the inset of Figure 1b, the O 1s centered at binding energy of 529.8 eV belonged to O2− species, and these data are consistent with the reported literature [36]. The above XRD and XPS results confirmed the formation of Fe3O4 phase in the hydrothermal system. TEM was employed to characterize the morphology and size of Fe3O4 particles. As observed in Figure 1c, the morphology of particles was an equiaxed shape. Moreover, these size values of Fe3O4 particles were demonstrated by a statistical analysis, the size distribution histograms were showed in Figure 1d, and most of the Fe3O4 particles were mainly concentrated in 4.8–6.4 nm.
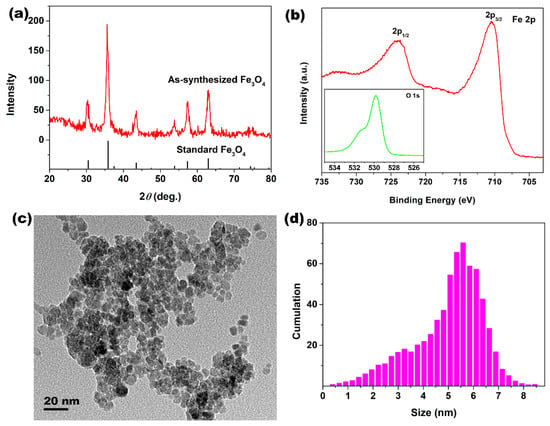
Figure 1.
(a) XRD pattern of Fe3O4 powders; (b) high-resolution XPS spectra of Fe 2p (the inset is the high-resolution XPS spectra of O 1s); (c) TEM image; and (d) size distribution histogram of Fe3O4 particles.
The room-temperature magnetization hysteresis loop of the as-synthesized Fe3O4 was measured by a physical performance measurement system. Figure 2a shows the magnetic hysteresis curve of Fe3O4 powders. From Figure 2a, it could be found that the saturation magnetization value of Fe3O4 nanoparticles was 54.9 emu/g. Moreover, the Fe3O4 nanoparticles were essentially superparamagnetic with negligible hysteresis, as observed by the enlarged partial curve of the surrounding origin in Figure 2a. In practical application, it is critical for practical applications that the magnetic materials should exhibit prompt responsiveness to an applied magnetic field without retaining any magnetism once the applied magnetic field was removed [37]. The magnetic manipulation of such superparamagnetic Fe3O4 was performed in water upon the application of a NdFeB permanent magnet near the glass bottle. As observed in Figure 2c, the Fe3O4 particles can be totally attracted toward the magnet within 15 s, leaving the suspension a clear solution. Moreover, the congregated Fe3O4 particles can be easily and quickly re-dispersed again by shaking after the removal of magnet. Hence, this superparamagnetic Fe3O4 powders have the potential to be easily recovered after liquid phase adsorption reaction, which could greatly facilitate the practical running of an industrial pollutant cleanup.
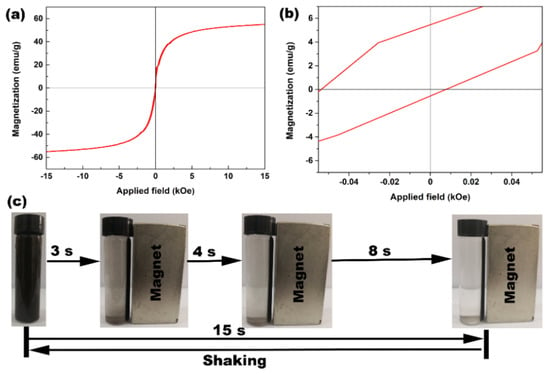
Figure 2.
(a) Magnetic hysteresis curve of Fe3O4 powders and (b) enlarged partial curve of the surrounding origin in (a); (c) pictures for the progressive separation of Fe3O4 particles from aqueous medium upon the application of a NdFeB permanent magnet ([Fe3O4] = 25.0 g/L; V = 8.0 mL; Distilled water; Glass bottle: d = 1.5 cm and h = 6.2 cm).
Figure 3 shows that the time-dependent adsorption efficiencies of superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles for XO, BO2, and AO7 dyes. It was observed that Fe3O4 nanoparticles had larger adsorption affinity for XO dye, whereas the adsorption of AO7 dye can be ignored. The adsorption efficiencies achieved within 60 min of reaction was 98.5, 15.9, and 5.5% for XO, BO2, and AO7 dyes, respectively. Furthermore, it could be clearly observed that the adsorption of XO dye was rapid at the early stages of the process. In fact, the adsorption reaction was mostly completed within 10 min, and the removal rate was up to 93.6%. No significant changes were observed from 20 to 60 min, indicating that the adsorption-desorption equilibrium between the dye adsorbate and Fe3O4 adsorbent was reached within the first 10 min of adsorption reactions. Compared with the adsorption reaction of XO dye, those of BO2 and AO7 dyes reached the adsorption-desorption equilibrium within 30 min, and the removal rates were only 23.0 and 6.2%.
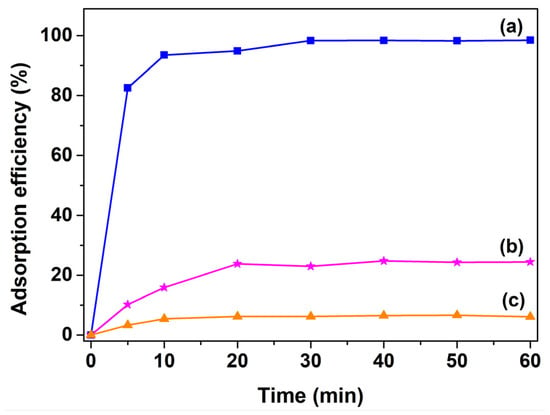
Figure 3.
Time-dependence of adsorption profiles of (a) XO; (b) BO2; and (c) AO7 dyes with the presence of superparamagnetic Fe3O4 powders. ([Fe3O4] = 1.0 g/L; [dye] = 10 mg/L; Room temperature; without pH preadjustment).
The saturated adsorption amounts (qm) of XO, BO2, and AO7 dyes were obtained according to the Langmuir isotherm model, and the Langmuir linear fittings based on the adsorption data of these dyes onto the superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles were showed in Figure 4a–c, while the relevant parameters of Langmuir fittings calculated were listed in Table 2. By comparing with the associated correlation coefficients (R2), it could be found that the Langmuir isotherm model was most suitable for modeling the adsorption of XO dye (R2 = 0.9991) than that of BO2 (R2 = 0.9546) and AO7 (R2 = 0.7904) dyes, and the value of qm is 42.5 mg/g for XO dye according to the Langmuir linear fitting. Table 3 shows the qm values of XO dye adsorbed on other adsorbents from the recent literature [33,38,39,40,41,42]. Despite the adsorption capacity of superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles synthesized in this work being moderate among these reported adsorbents by comparing the qm of various adsorbents, the Fe3O4 adsorbent still had obvious advantages in energy consumption and cost, which are due to the advantages of synthetic process and the superparamagnetism of Fe3O4 nanoparticles synthesized in this work. The equipment used in the hydrothermal process was simple and economical, and the Fe3O4 phase could be obtained in a simple one-pot hydrothermal process. In addition, the as-synthesized Fe3O4 nanoparticles in this work had excellent magnetic sensitivity, which made them easy to separate from liquid medium under the attraction of a magnet.
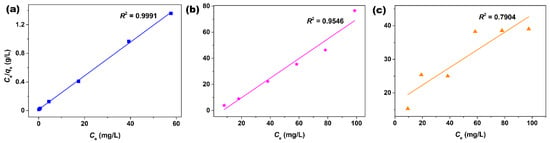
Figure 4.
Langmuir linear fittings of (a) XO, (b) BO2, and (c) AO7 dyes adsorbed onto the superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles.

Table 2.
Relevant parameters of Langmuir fittings for XO, BO2, and AO7 dyes adsorbed onto the superparamagnetic Fe3O4 powders.

Table 3.
Recent literature on adsorbent development for the removal of XO dye.
The sorption kinetics of XO, BO2, and AO7 dyes onto Fe3O4 nanoparticles were tested using a pseudo-first-order kinetic model by plotting log(qe-qt) versus t (Figure 5a,c,e), as well as pseudo-second-order kinetic model by plotting t/qt versus t (Figure 5b,d,f). As observed in Figure 5, the adsorption of XO, BO2, and AO7 dyes using a pseudo-second-order model (Figure 5b,d,f) exhibited a better linear fit than those using a pseudo-first-order model (Figure 5a,c,e). Moreover, the relevant kinetic parameters, such as the equilibrium adsorption amount (qe1,cal, qe2,cal), rate constant (k1 and k2), and correlation coefficient (R2), could be obtained by fitting with these two models, and the results were listed in Table 4. As observed in Table 4, all pseudo-second-order equations showed higher correlation coefficients (R2 > 0.98) than their respective pseudo-first-order equations (R2 < 0.74), and the adsorption amounts at equilibrium (qe,cal) were much closer to the respective experimental one (qe,exp). Therefore, the pseudo-second order model is more suitable to describe the adsorption kinetics of XO, BO2, and AO7 dyes onto Fe3O4 nanoparticles, indicating that the chemisorption is the rate controlling step during the attachment process.
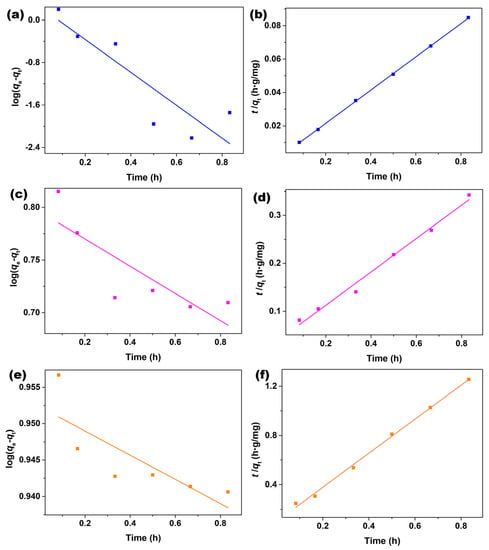
Figure 5.
Fittings by a pseudo-first-order model for the adsorption of (a) XO, (c) BO2, and (e) AO7 dyes, pseudo-second-order model for the adsorption of (b) XO, (d) BO2, and (f) AO7 dyes onto Fe3O4 nanoparticles. ([Fe3O4] = 1.0 g/L; [dye] = 10 mg/L; Room temperature; without pH preadjustment).

Table 4.
Kinetic parameters for the adsorption of XO, BO2, and AO7 dyes onto Fe3O4 nanoparticles at room temperature.
4. Conclusions
In summary, Fe3O4 nanoparticles with a main size distribution of 4.8–6.4 nm have been successfully synthesized via a simple one-pot hydrothermal strategy at 200 °C for 24 h, in which iron citrate and distilled were the sum total of raw materials. The as-synthesized Fe3O4 nanoparticles exhibited apparent superparamagnetism, and the saturation magnetization value was 54.9 emu/g. Moreover, Fe3O4 nanoparticles possessed sensitive magnetic responsiveness, which can be totally attracted toward the magnet within 15 s from suspension, and quickly re-dispersed again by shaking after the removal of magnet. Such superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles exhibited the effective adsorption affinity for XO dye, and the adsorption reactions were mostly completed within 10 min. The Langmuir isotherm model is most suitable for modeling the adsorption of XO dye (R2 = 0.9991) compared to those of BO2 and AO7 dyes, and the value of the saturated adsorption amount is 42.5 mg/g for XO dye according to Langmuir linear fitting. This superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles had the potential to be easily recovered after liquid phase adsorption reaction, which could greatly facilitate the practical running of an industrial pollutant cleanup.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, writing—original draft preparation, writing—review and editing, resources, Y.X.; validation, formal analysis, investigation, data curation, Q.W.; resources, visualization, project administration, funding acquisition, Z.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by [Leshan Normal University Research Program, China] grant number [2021SSDJS012], [Science and Technology Bureau of Leshan city of China] grant number [22ZDYJ0093], and [Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities] grant number [2022CDJXY-010].
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ding, Z.; Yang, W.; Huo, K.; Shaw, L. Thermodynamics and Kinetics Tuning of LiBH4 for Hydrogen Storage. Prog. Chem. 2021, 33, 1586–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turky, A.O.; Rashad, M.M.; Hassan, A.M.; Elnaggar, E.M.; Bechelany, M. Optical, electrical and magnetic properties of lanthanum strontium manganite La1−xSrxMnO3 synthesized through the citrate combustion method. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 6878–6886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Chen, Z.; Ma, T.; Lu, C.T.; Ma, W.; Shaw, L. Predicting the hydrogen release ability of LiBH4-based mixtures by ensemble machine learning. Energy Storage Mater. 2020, 27, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turky, A.O.; Rashad, M.M.; Hassan, A.M.; Elnaggar, E.M.; Bechelany, M. Tailoring optical, magnetic and electric behavior of lanthanum strontium manganite La1−xSrxMnO3 (LSM) nanopowders prepared via a co-precipitation method with different Sr2+ ion contents. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 17980–17986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oca, R.M.G.F.-M.; Ramos-Leal, J.A.; Solache-Ríos, M.J.; Martínez-Miranda, V.; Fuentes-Rivas, R.M. Modification of the Relative Abundance of Constituents Dissolved in Drinking Water Caused by Organic Pollution: A Case of the Toluca Valley, Mexico. Water Air Soil Poll. 2019, 230, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Li, H.; Shaw, L. New Insights into the Solid-State Hydrogen Storage of Nanostructured LiBH4-MgH2 System. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 385, 123856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, D.A.; Scholz, M. Comparison of Experimental Ponds for the Treatment of Dye Wastewater under Controlled and Semi-natural Conditions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 16031–16040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Li, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, F.; Wu, P.; Ma, W. LiBH4 for Hydrogen Storage: New Perspectives. Nano Mater. Sci. 2020, 2, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashmi, S.S.; Shah, M.; Muhammad, W.; Ahmad, A.; Ullah, M.A.; Nadeem, M.; Abbasi, B.H. Potentials of Phyto-fabricated Nanoparticles as Ecofriendly Agents for Photocatalytic Degradation of Toxic Dyes and Waste Water Treatment, Risk Assessment and Probable Mechanism. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2021, 98, 100019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Ji, X.; Ma, J.; Tian, G. Preparation and Excellent Adsorption of water Pollution Dyes over Magnetic Fe3O4/C Nanoparticles with Hollow Grape Cluster Morphology. J. Nanopart. Res. 2020, 22, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huong, D.T.M.; Chai, W.S.; Show, P.L.; Lin, Y.L.; Chiu, C.Y.; Tsai, S.L.; Chang, Y.K. Removal of Cationic Dye Waste by Nanofiber Membrane Immobilized with Waste Proteins. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 3873–3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Zheng, H.; Zhao, R.; Xiong, Z.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Ding, W. Sulfonic Acid-modified Polyacrylamide Magnetic Composite with Wide pH Applicability for Efficient Removal of Cationic Dyes. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 319, 114161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Wen, J.; Wang, Q.; Jin, X.; Zhou, X. Preparation and Photocatalytic Properties of Hexagonal and Orthogonal CuS Micro-nanoparticles by an Oil-water Interface Method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 255, 123629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.; Deng, W.; Feng, X.; Pan, F.; Li, Y. An Integrated Electrocoagulation-Electrocatalysis Water Treatment Process using Stainless Steel Cathodes Coated with Ultrathin TiO2 Nanofilms. Chemosphere 2020, 254, 126776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiwaan, H.A.; Mohamed, F.S.; El-Ghamaz, N.A.; Beshry, N.M.; El-Bindary, A.A. Experimental and Electrical Studies of Na-X zeolite for the Adsorption of Different Dyes. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 332, 115877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feizpoor, S.; Habibi-Yangjeh, A.; Chand, H.; Krishnan, V. Integration of Bi5O7I with TiO2: Binary Photocatalysts with Boosted Visible-light Photocatalysis in Removal of Organic Contaminants. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2021, 410, 113190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa-Martínez, J.D.; Balagurusamy, N.; Montañez, J.; Peralta, R.A.; de Fátima Peralta-Muniz-Moreira, R.; Bracht, A.; Peralta, R.M.; Morales-Oyervides, L. Synthetic Dyes Biodegradation by Fungal Ligninolytic Enzymes: Process Optimization, Metabolites Evaluation and Toxicity Assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 123254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, X.L.; Shao, C.B. Removal of Xylenol Orange from Solutions by γ-Cyclodextrin-Grafted Carboxymethyl Cellulose. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 204–210, 1180–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Lu, Y.; Li, L.; Shaw, L. High Reversible Capacity Hydrogen Storage Through Nano-LiBH4 + Nano-MgH2 System. Energy Storage Mater. 2019, 20, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Wu, P.; Shaw, L. Solid-state Hydrogen Desorption of 2 MgH2 + LiBH4 Nano-mixture: A Kinetics Mechanism Study. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 806, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayantong, A.R.B.; Shih, Y.-J.; Ong, D.C.; Abarca, R.R.M.; Dong, C.-D.; de Luna, M.D.G. Adsorptive Removal of Dye in Wastewater by Metal Ferrite-enabled Graphene Oxide Nanocomposites. Chemosphere 2021, 274, 129518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, L.; Zhao, G.; Pan, L.; Chen, B.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xiao, X.; Xu, W. Efficient Removal of Dye from Wastewater without Selectivity Using Activated Carbon-Juncus Effusus Porous Fibril Composites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 19176–19186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghadhban, M.Y.; Majdi, H.S.; Rashid, K.T.; Alsalhy, Q.F.; Lakshmi, D.S.; Salih, I.K.; Figoli, A. Removal of Dye from a Leather Tanning Factory by Flat-Sheet Blend Ultrafiltration (UF) Membrane. Membranes 2020, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raja, Y.S.; Samsudin, M.F.R.; Sufian, S. Development of the Low-Cost and Green Hibiscus cannabinus Bioadsorbent for the Removal of Dye in Wastewater. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2020, 46, 6349–6358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayomie, O.S.; Kandeel, H.; Shoeib, T.; Yang, H.; Youssef, N.; El-Sayed, M.M.H. Novel Approach for Effective Removal of Methylene Blue Dye from Water using Fava Bean Peel Waste. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiralian, N.; Mustapic, M.; Hossain, M.S.A.; Wang, C.; Konarova, M.; Tang, J.; Na, J.; Khan, A.; Rowan, A. Magnetic nanocellulose: A Potential Material for Removal of Dye from Water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 394, 122571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turky, A.O.; Mohamed Rashad, M.; Taha Kandil, A.E.-H.; Bechelany, M. Tuning the optical, electrical and magnetic properties of Ba0.5Sr0.5TixM1-xO3 (BST) nanopowders. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 12553–12560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turky, A.O.; Rashad, M.M.; Bechelany, M. Tailoring optical and dielectric properties of Ba0.5Sr0.5TiO3 powders synthesized using citrate precursor route. Mater. Des. 2016, 90, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Chi, M.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, M.; Wang, C.; Lu, X. A Facile Synthesis of Superparamagnetic Fe3O4 Nanofibers with Superior Peroxidase-like Catalytic Activity for Sensitive Colorimetric Detection of L-cysteine. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 440, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Kou, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, D.; Lu, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.J.; Han, D.; et al. Effects of Amount of Benzyl Ether and Reaction Time on the Shape and Magnetic Properties of Fe3O4 Nanocrystals. Powder Technol. 2017, 319, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Huang, Y.; Ding, L.; Zhao, X.; Liu, P.; Li, T. Synthesis of Covalently Bonded Reduced Graphene Oxide-Fe3O4 Nanocomposites for Efficient Electromagnetic Wave Absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 72, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandari, M.J.; Hasanzadeh, I. Size-controlled Synthesis of Fe3O4 Magnetic Nanoparticles via an Alternating Magnetic Field and Ultrasonic-assisted Chemical Co-precipitation. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Adv. 2021, 266, 115050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Xia, Y.; Zai, Y.; Dai, Y.; Liu, X.; Bian, J.; Liu, J.; Li, G. Adsorption and Desorption Behaviors of HPEI and Thermoresponsive HPEI based Gels on Anionic and Cationic Dyes. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 369, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wang, W.; Dong, W. Interpenetrating Polymer Networks in Polyvinyl Alcohol/cellulose Nanocrystals Hydrogels to Develop Absorbent Materials. Carbohyd. Polym. 2018, 200, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, T.; Sun, D.; Li, R. Facile Synthesis of Superparamagnetic Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Just using Ferric Citrate and Water. Integr. Ferroelectr. 2016, 176, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Diao, G. Synthesis of Porous Fe3O4 Nanospheres and Its Application for the Catalytic Degradation of Xylenol Orange. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A.H.; Salabas, E.L.; Schüth, F. Magnetic Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Protection, Functionalization, and Application. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1222–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishaq, M.; Saeed, K.; Ahmad, I.; Sultan, S.; Akhtar, S. Coal ash as a low cost adsorbent for the removal of xylenol orange from aqueous solution. Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. 2014, 33, 53–58. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/293158575 (accessed on 1 March 2014).
- Bai, Q.; Wang, W.; Liang, T.; Bai, H.Y.; Liu, X.Y. Preparation of porous amino-cellulose membrane and their adsorption performance of xylenol orange. J. Cellul. Sci. Technol. 2017, 25, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Yang, C.; Ren, S. Adsorption capacity of expansion graphite for xylenol orange. J. Mater. Sci. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrudo-Guirado, M.I.; Blanco-Flores, A.; Toledo-Jaldin, H.P.; Sanchez-Mendieta, V.; Vilchis-Nestor, A.R. Reuse of sustainable materials for xylenol orange dye and copper (II) ion ammoniacal removal. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 206, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Kong, W.; Xie, W.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Wu, X.; Gao, J. Bi-porous bioinspired chitosan foams with layered structure and their adsorption for xylenol orange. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 197, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).