Abstract
The elementary research of spray and combustion is of great significance to the development of compactness of modern diesel engines. In this paper, three injectors with different nozzle orifice diameters (0.23 mm, 0.27 mm and 0.31 mm) were used to study the diesel spray, ignition and flame-wall impingement visualization experiment. This paper studied the influence of different nozzle sizes on the trends of spray, ignition and flame diffusion under the flame-wall impinging combustion and used the flame luminosity to characterize the soot generation in combustion. By analyzing the quantitative data, such as spray penetration, ignition delay, flame area and flame luminosity systematically, it was shown that the smaller nozzle benefitted diesel combustion to some extent. The 0.23 mm nozzle injector in these experiments had the best fuel-air mixing effect under 800 K. The length of the spray liquid under the 0.23 mm nozzle condition was 19% and 23% shorter than that of 0.27 and 0.31 mm, respectively. Smaller orifice size of the nozzle can help to reach the gas ignition conditions more effectively. Without liquid fuel impingement, the simple flame-wall impingement will not change the trend of the nozzle influence on combustion. The total amount of accumulated soot according to the approximate luminosity spatial integral calculation in the combustion process was reduced by 37% and 43% under 0.27 mm and 0.23 mm nozzles, respectively, which is favorable for the clean combustion of diesel engines.
1. Introduction
Diesel engines have been widely used in various fields for the features of low fuel consumption, high torque, reliability and durability, and have been used in more than two-thirds of highway passenger and freight transportation. Therefore, the diesel engine will still play a key role in the world for a long time. The combustion of the direct injection (DI) diesel engine will always be the research focus because of its severe emissions like PM (Particulate Matter) pollutants [1].
Soot is the main component of diesel PM pollutants. The formation process or the nucleation of elementary carbon particles occurs mostly in areas with worse mixture during combustion. Therefore, the atomization degree of fuel spray and the quality of fuel and gas mixture directly determines the formation of soot in the latter combustion process [2,3], and the structural parameters of the fuel injection system and combustion chamber are one of the important factors that affect the fuel-air mixing of diesel engine [4].
With the high speed and compactness development of DI (direct injection) diesel engines, the phenomenon of wall impinging during the combustion process became very common. For small-size diesel engines, the space reduction of the combustion chamber makes the spray impinging the surface of the cylinder or piston easier. The study by Li et al. [5] showed that when the obvious liquid impingement of the diesel spray occurred, the soot emissions increased while thermal efficiency reduced significantly, meaning that the liquid impingement had a direct impact on the mixture of fuel and air and worsened the combustion process. Another study by Wang et al. [6] shows that the length of the spray liquid was also affected directly by the size of the nozzle, which is one of the most important construction parameters to be considered in fuel injection of the DI engine [7].
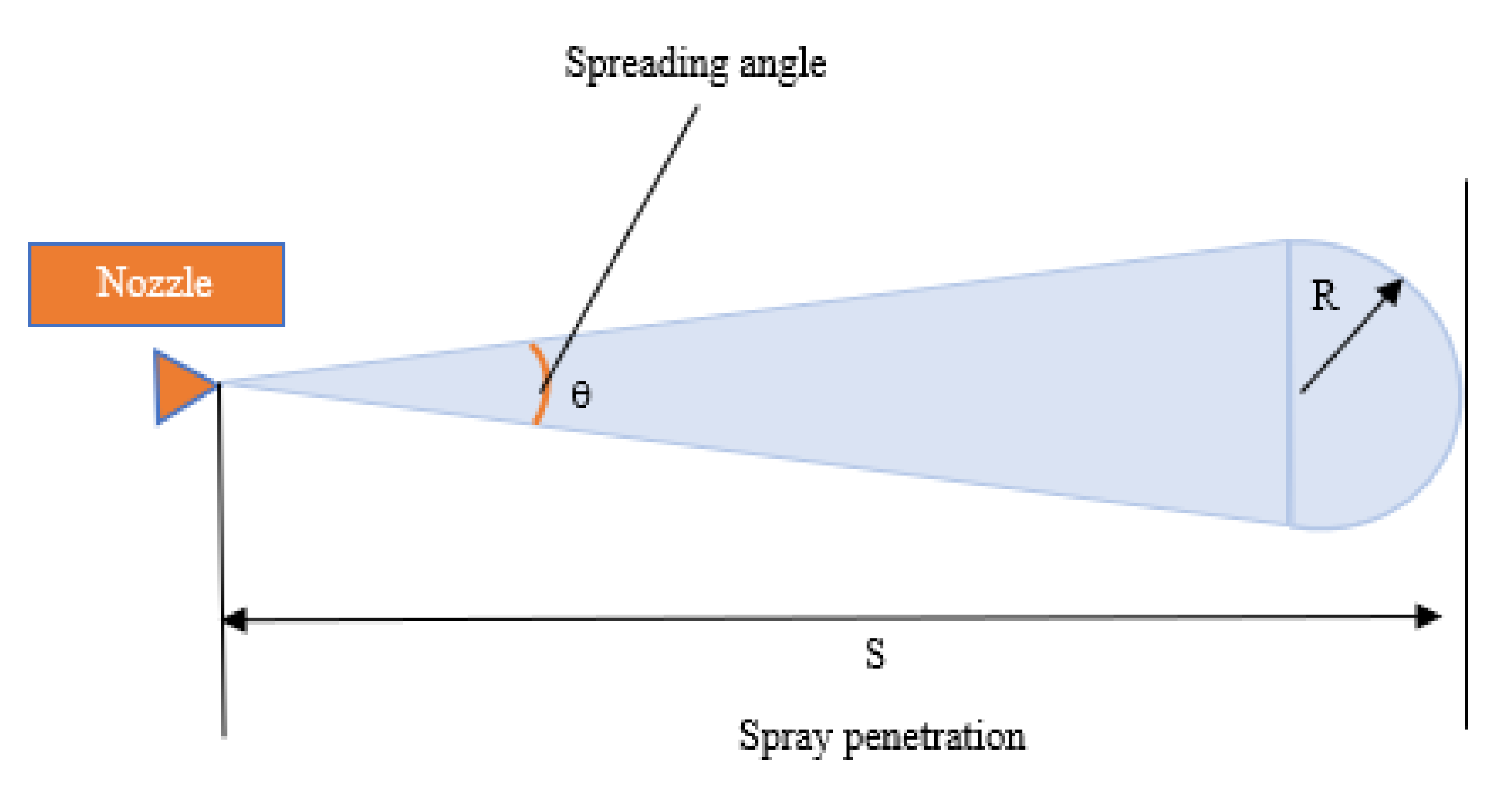
In addition to the liquid penetration and the longest distance that the spray can achieve in the injection, other parameters of the spray form, such as spray area and volume, can also affect the injection and mixture quality. These parameters can be expressed in a spray conceptual model, which was quantified by Delacourt et al. [8]. The following model assumed that the spray body was composed of a cone and a hemisphere, as shown in Figure 1.
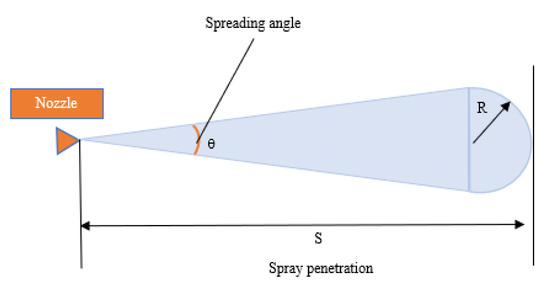
Figure 1.
Delacourt’s spray schematic diagram.
The spray area A and spray volume V can be calculated approximately according to the spray penetration S and spray cone angle θ, which was defined by the maximum internal angle between spray peripheries [9], as shown in Formulas (1) and (2):
In the visual experimental research, there are a large number of basic research conclusions and methods for reference. As for the spray process, the common imaging methods such as the schlieren method [10] and Mie scattering technology [11] are both beneficial to the spray jet imaging. At the internal working temperature of the diesel engine (about 800 K), the diffusion angle and penetration of the evaporated spray decreased significantly compared with the diesel spray at normal temperature [11]. The spray penetration decreased with the decreasing of nozzle diameter [10], which means that the reduction of nozzle aperture was beneficial to fuel atomization and fuel-air mixture [12].
In the combustion process, previous studies [13] analyzing the obtained soot images have shown that the soot generated during combustion comes from the internal part of the diffusion flame. In the process of combustion, the formation of soot is often determined by temperature. In past research, Dongerbreek [14] and Mueller [15] verified the certain relationship between the flame luminosity and temperature as a function with a lot of factors. This relationship was used to characterize the soot generation in combustion with the luminosity of the diffusion flame morphology from the camera in many experiments [16,17].
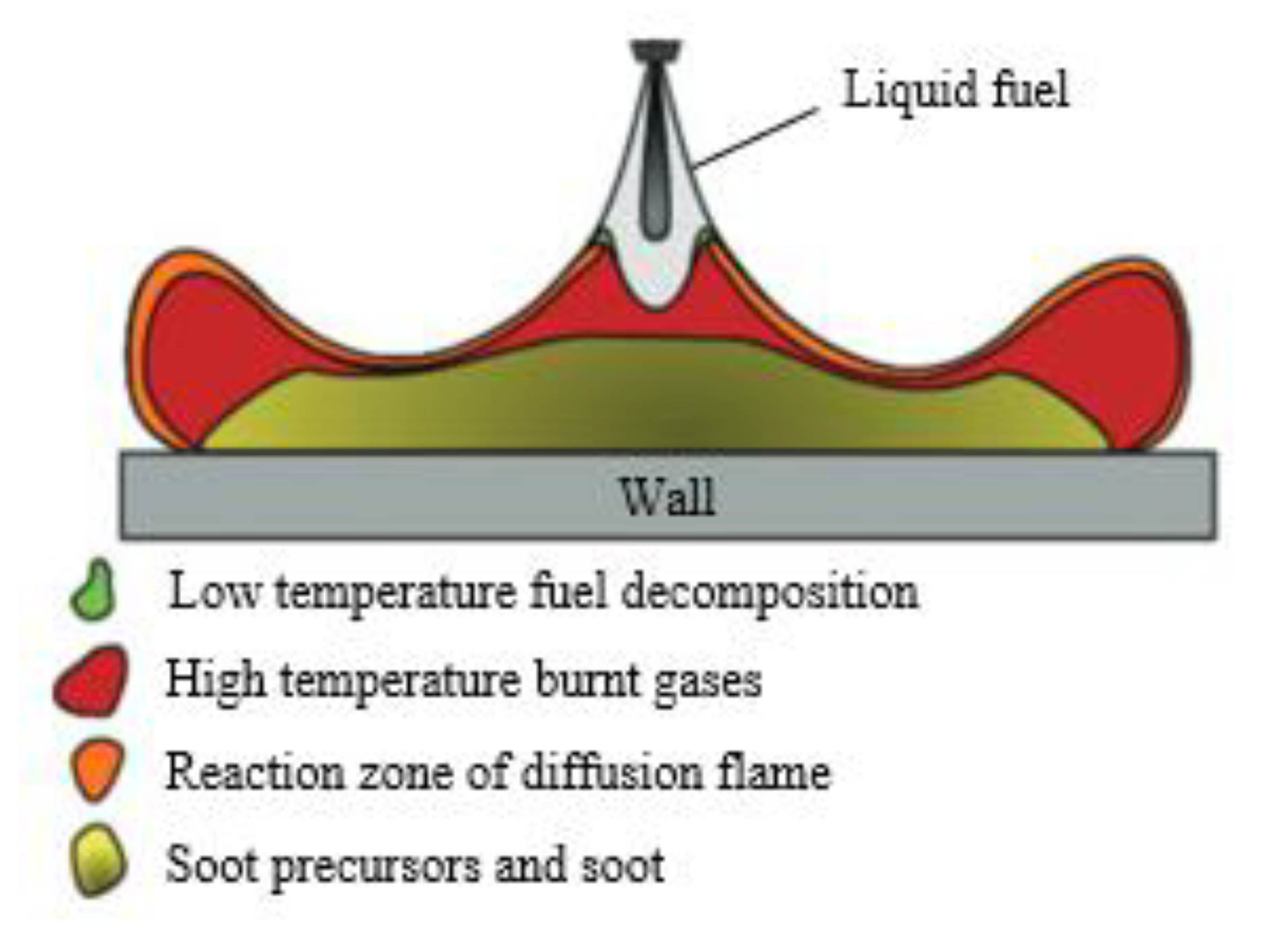
When a wall impingement system was settled in the visualization experiment, the shape of the diffusion combustion flame and the spray jet will change in comparison to the free spray and combustion process. As shown in Figure 2, the concept model of the diesel engine wall impingement combustion proposed by Bruneaux [18] shows that the flame shape will spread along the impingement wall plate and the generation area of soot is mainly concentrated in the area near the wall.
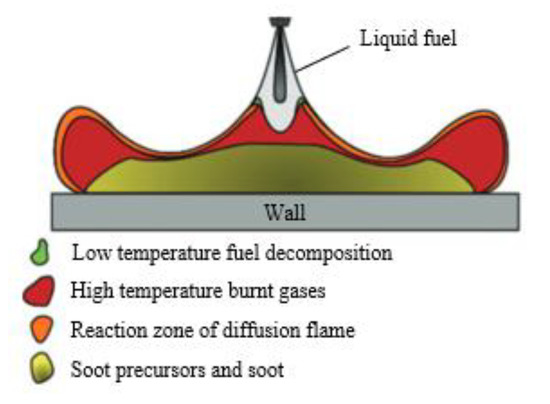
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram depicting the conceptual model of diesel jet combustion in the jet-impinging-wall configuration during the stabilized diffusion-limited combustion phase [18].
Although there is plenty of research about spray and combustion impingement, no definite conclusion about the influence of soot generation exists. Some studies have shown that combustion is enhanced with impingement, resulting in a decrease of soot generation [19]. In the injection process, spray wall-impingement will lead to better atomization compared with free spray or a higher concentration region near wall surfaces [20,21,22].
Most of the research on flame-wall impinging combustion focus on flame diffusion and soot formation after injection, but less focus on the correspondence between spray ignition and combustion under the same experiment conditions. The liquid spray impingement was considered to be avoided in the modern design of diesel engines. However, the interaction between the cylinder or piston and the diffusion flame still exists even when the liquid spray impingement is avoided, that is, the flame impingement could occur during the combustion without liquid fuel impingement. Under this common phenomenon, there is less research on the effect of nozzle size on soot formation after combustion [23].
Complete analysis and verification from the visualization experiment are still necessary to observe the effect of different nozzle orifice diameters on the fuel-air mixture and the evolution of the flame shape after the flame impinging. It is also necessary to study whether the change of aperture of different injectors will cause different spray spreading and flame diffusion trends.
In this paper, the direct high-speed photography method based on the constant volume combustion vessel experiment was used to test the evaporative spray pattern of diesel fuel and the phenomenon of flame-wall impingement under different injection nozzle orifice diameter conditions. By analyzing the image information of the spray and flame, quantitative parameters, such as the form, area, and luminosity of the spray or flame under the same experiment conditions can be obtained. The flame formation and luminosity distribution directly characterize the high-temperature reaction area and the soot particle generation area, and the effect of different nozzle orifice diameters on the combustion characteristics in the complete combustion process of a diesel engine can be analyzed from the soot generation. These conclusions are of great significance for the design of fuel injection parameters and the compact combustion structure of modern diesel engines.
2. Experimental Setup
2.1. Visualization Experiment Platform
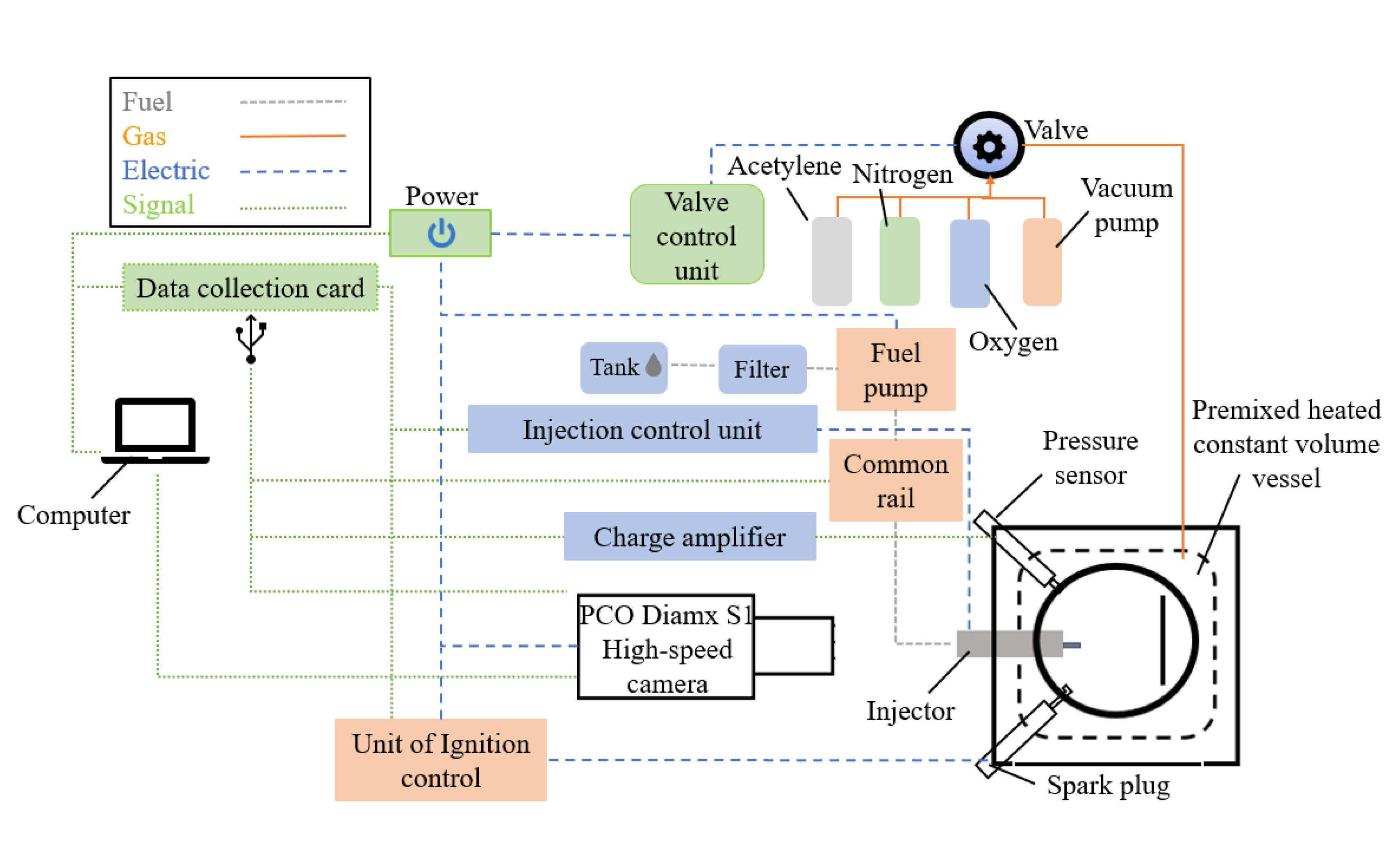
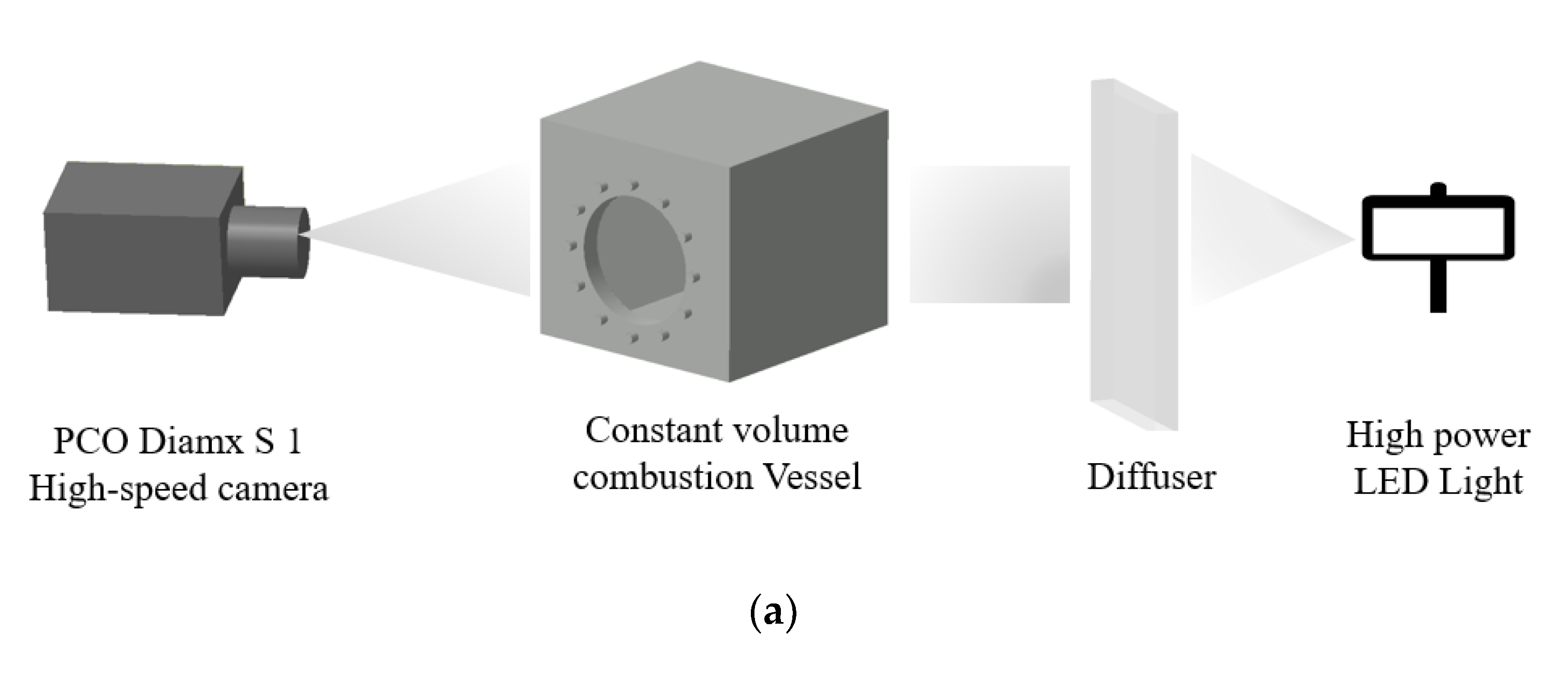
The spray/combustion visualization experiment platform in this paper is mainly composed of premixed combustion heating constant volume combustion vessel, valve and ignition system, pressure measurement and collection system, high-pressure common rail fuel injection system, plate impingement system and high-speed imaging system. (shown in Figure 3).
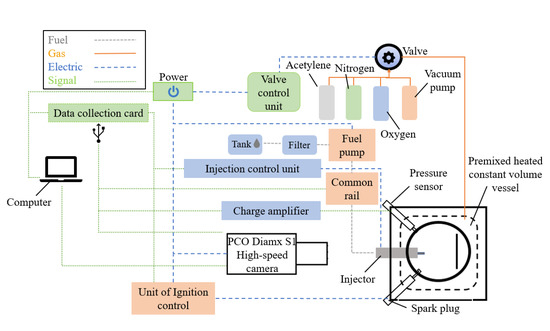
Figure 3.
Diagram spray and combustion visualization experiment platform.
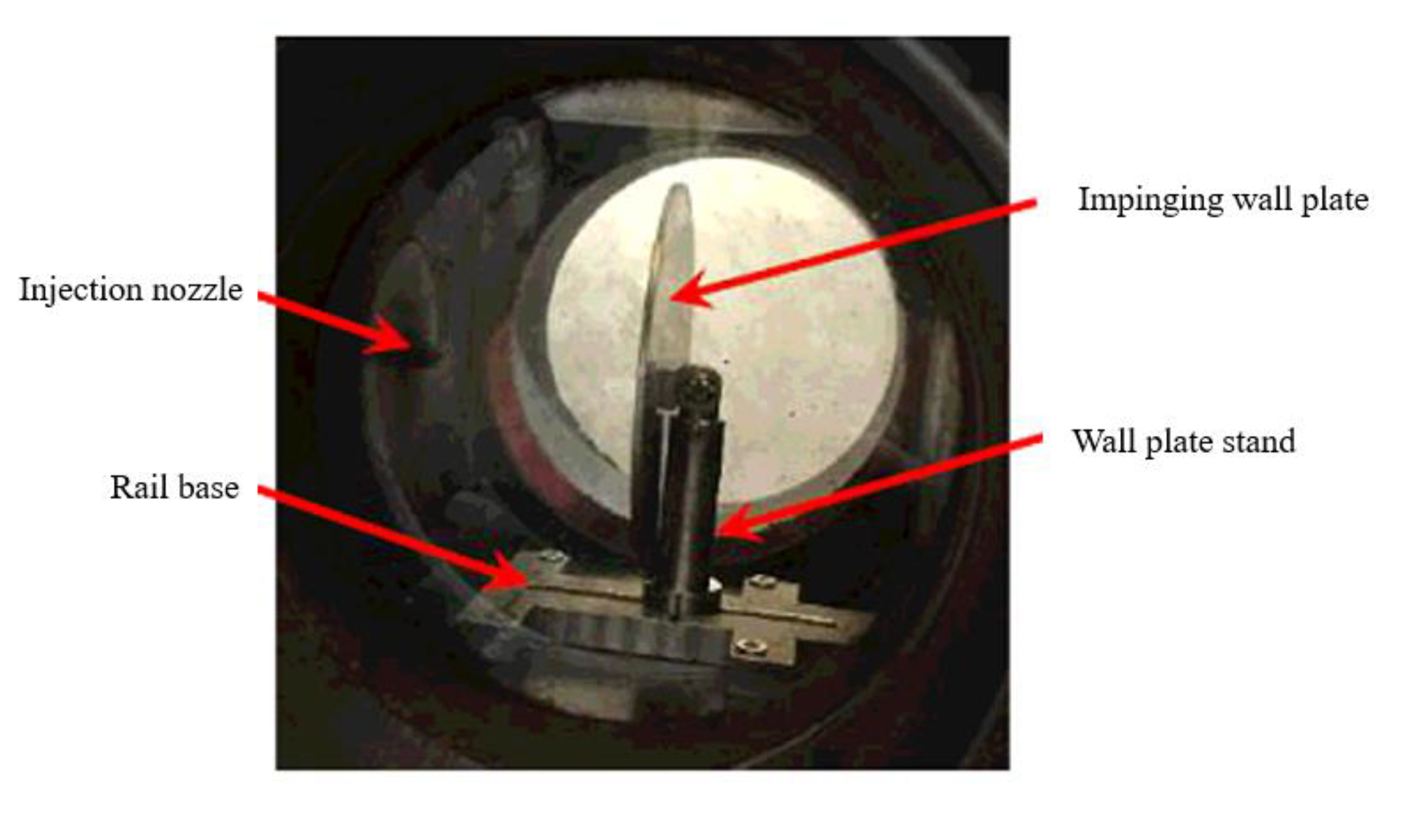
A 130 mm long circular window was machined on the constant volume vessel, which could form an optical path to fully meet the needs of imaging. The combustion vessel was equipped with a flat wall impingement system (in Figure 4) that was composed of a disc-shaped wall plate, a guide rail base, and a bracket that could move along the rail, etc. The wall impinging distance could be adjusted accurately as the experiment required.
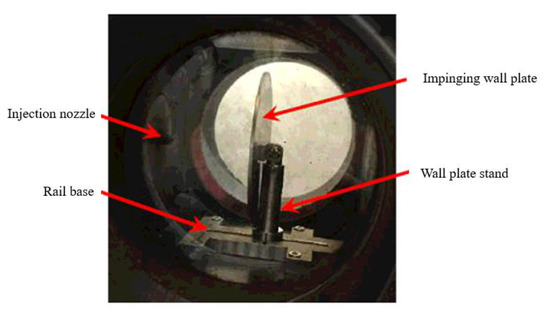
Figure 4.
Wall plate impingement system.
2.2. Imaging Conditions
Table 1 depicts the methods and details of the imaging setup in spray, ignition and flame visualization experiments.

Table 1.
Imaging conditions.
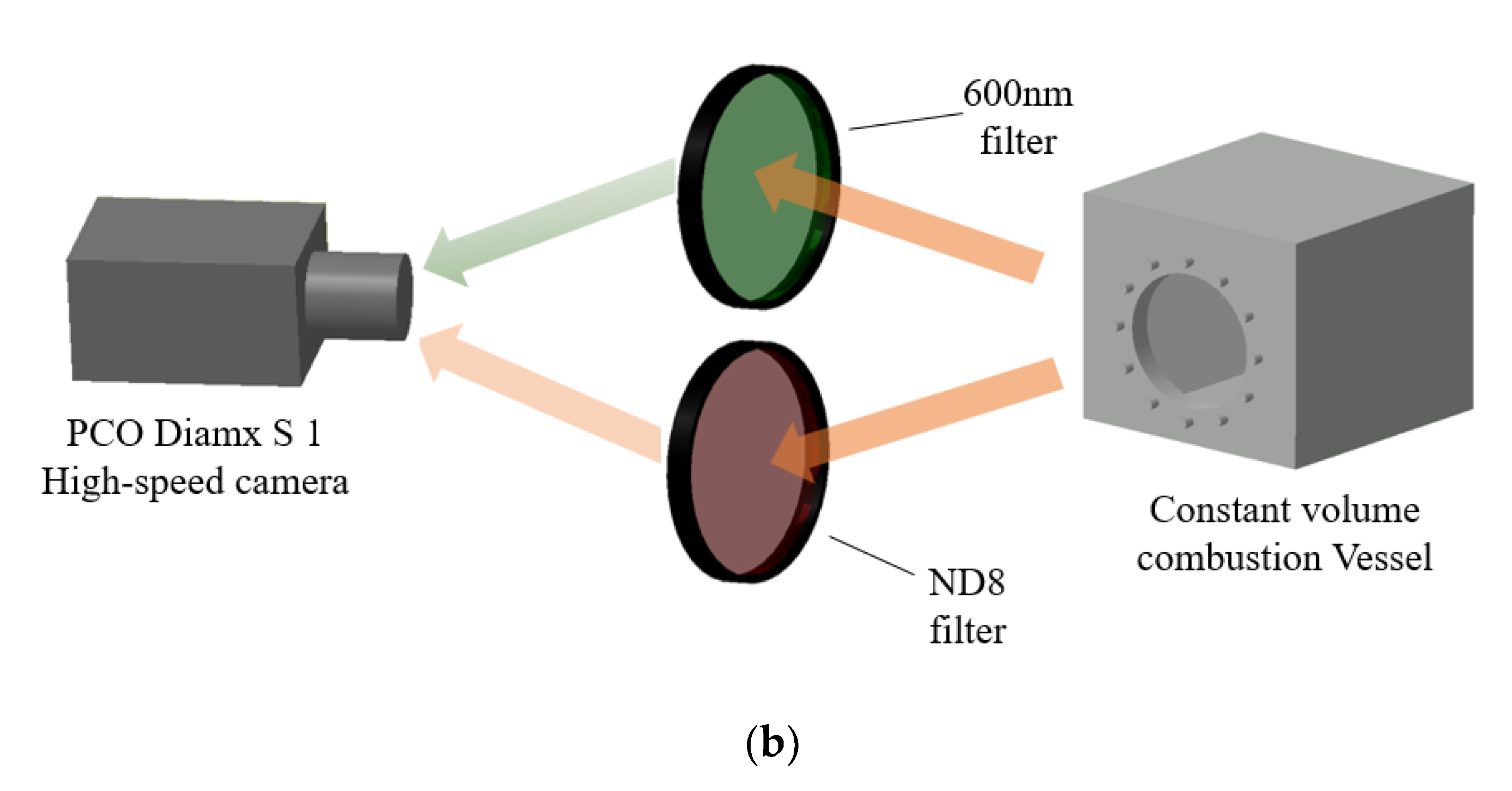
In this paper, the high-speed imaging system was divided into two parts: spray visualization and flame visualization (as shown in Figure 5): (a) the spray visualization system mainly used backscatter imaging technology, that is, the LED light after the refraction of the hair glass was used as the background light source, so that the optical path could be received by the color camera and get the spray image after passing through the constant volume bomb. (b) The imaging system in ignition and flame visualization was a direct light reducing system composed of a high-speed camera and different light reducing filters. Incandescence is a kind of visible light produced by the high temperature of the object. It belongs to the visible light band (380–750 nm) of thermal radiation. When the fuel is fully burned, it is chemiluminescence, and there is almost no incandescence. Therefore, in the ignition imaging process, the camera captures the chemiluminescence. Therefore, two different filters were used in the flame imaging process of the combustion experiments: short-wave 600 nm filter and neutral density filter (ND8 filter).
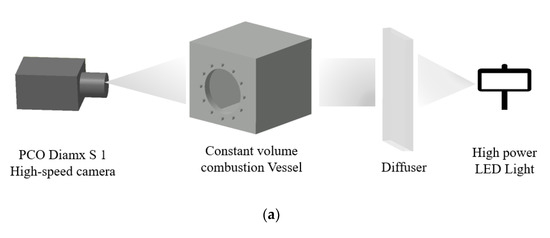
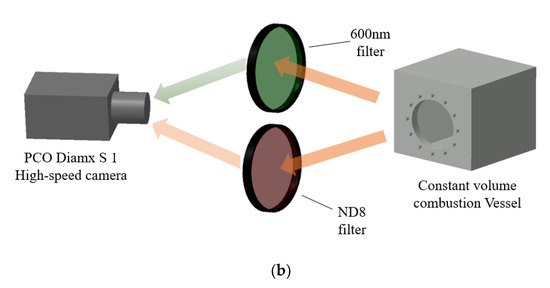
Figure 5.
Optical setup of different experiment conditions: (a) Spray imaging system with LED and diffuser. (b) Ignition and flame with different filter: 600 nm filter for the ignition imaging and ND8 filter for the flame imaging.
When the wavelength was greater than 600 nm, the short-wave 600 nm filter was used to filter the long-wave strong light to obtain the chemiluminescence image, which was used to analyze the fuel ignition flame.
The ND8 filter (neutral density filter) can only retain the 1/8 nature luminosity of the original flame and reduced most of the chemiluminescence. The flame luminosity captured by the high-speed camera was regarded as the intense incandescence from soot particles.
2.3. Experimental Operating Conditions
The specific operating conditions and settings for the experiment are shown in Table 2:

Table 2.
Experiment operating settings.
Three types of single-hole injectors with nozzle orifices were used in the experiment (0.23 mm, 0.27 mm and 0.32 mm, respectively). The injectors were installed vertically on top of the combustion vessel with manually controlled pressure at 90 MPa.
In the spray visualization experiment, the nitrogen filled in the constant volume vessel so that the spray jet will not react and be retained in the image. In the combustion visualization experiment, the injection duration will be set separately to determine the same fuel injection mass of 0.23 mg.
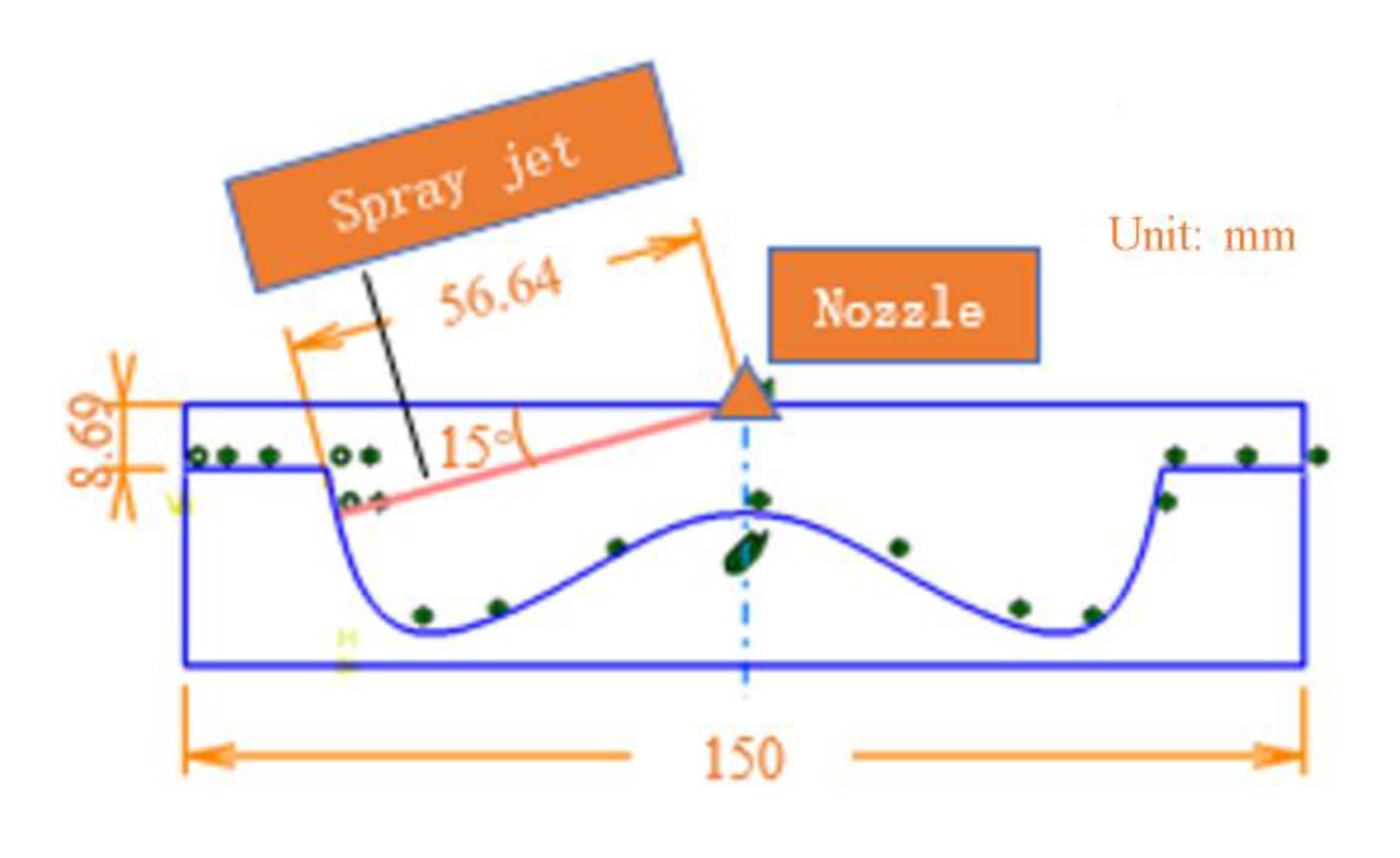
The wall impingement distance was determined by the combustion chamber parameters of a typical low compression ratio supercharged and intercooled heavy-duty diesel engine. As shown in Figure 6, the distance between the injector axis and the combustion chamber wall was about 57 mm.
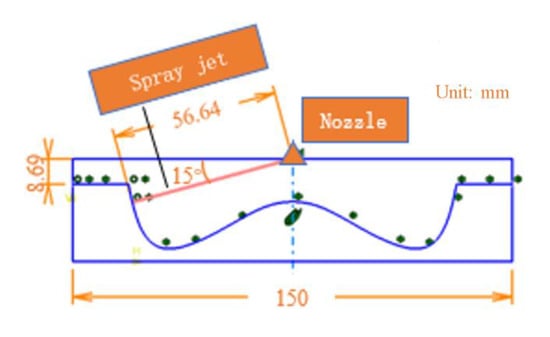
Figure 6.
Determination of impinging distance.
2.4. Main Methods of Image Processing
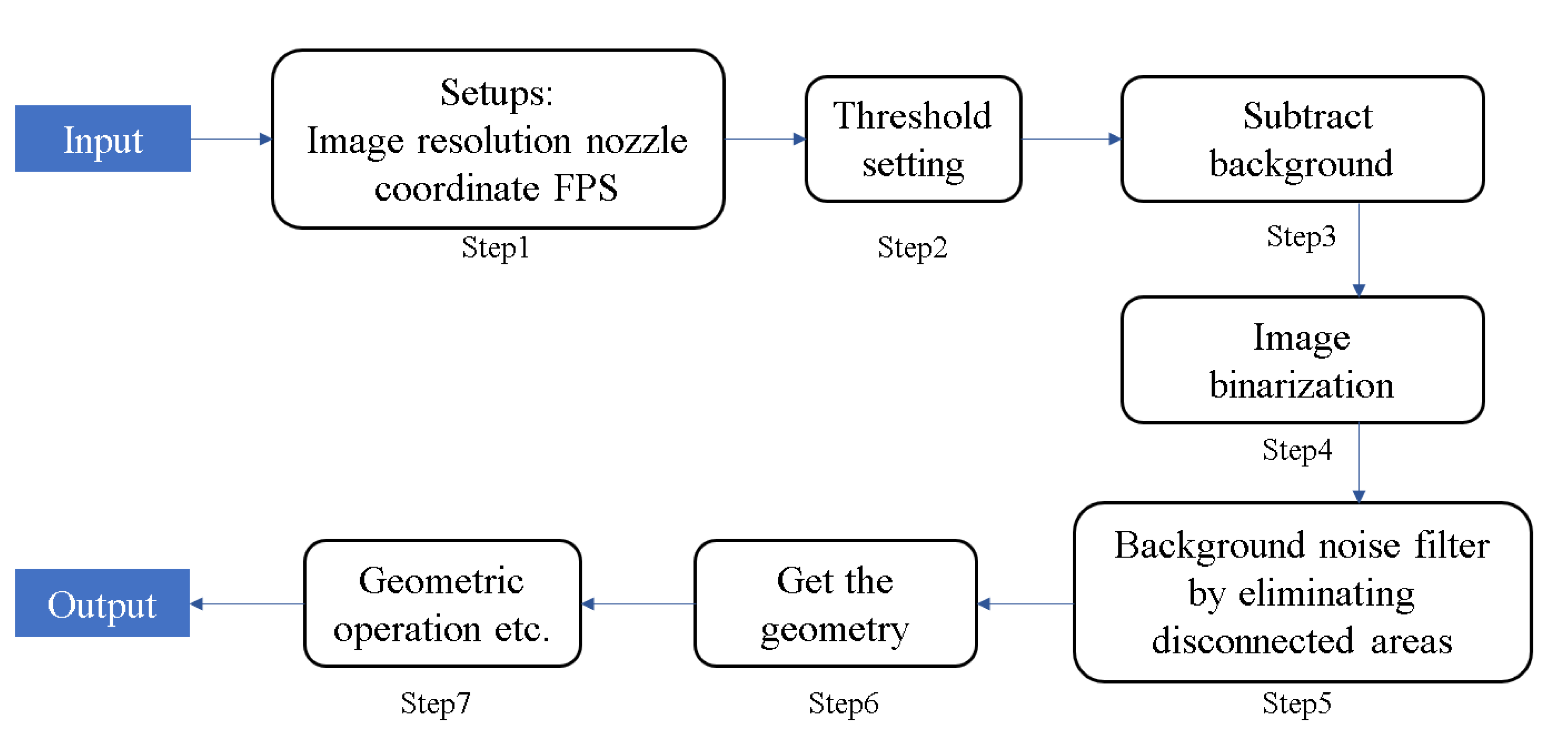
The geometric parameters of spray and flame can be obtained through image processing of MATLAB®. The method of separating the spray jet and flame from the images can use the image before and after the start of fuel injection for background difference. The following Figure 7 is a brief flow chart for the image processing.
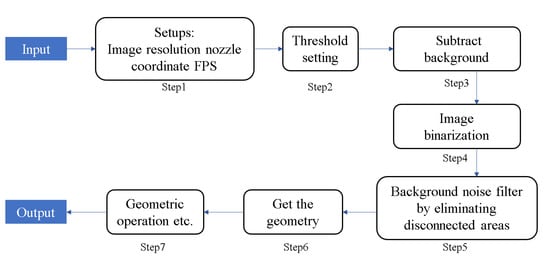
Figure 7.
Image processing of MATLAB®.
Using a method similar to that described by Higgins and Siebers (2001) [24], image processing by analyzing a single OH* CL (Chemiluminescence) image using a threshold of 5% picture pixel value (255) of the maximum OH*CL was undertaken. The image threshold in ignition images was determined by 1/2 high temperature chemiluminescence intensity.
We filtered the background noise by subtracting the background image before the fuel injection from each image.
The threshold value of the final image processing after eliminating the interference was shown in the Table 3 below.

Table 3.
Image processing threshold.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analysis of Evaporative Spray
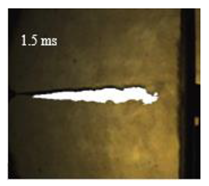
The spray experiment conditions were consistent with actual diesel engine working conditions. Combustion temperature of the diesel engine during operation can reach 800–1000 K. After reaching the 800 K ambient temperature environment, the injected fuel will quickly heat up, evaporating and mix with the air. Therefore, after the LED light path passes through the constant volume bomb, only the liquid pattern of the spray can be captured by the high-speed camera. The following binary graph can be gained by processing the origin images using the special image processing program in MATLAB®. The Table 4 showed the binary graph of the spray jet at each moment after start of injection (ASOI):

Table 4.
Image of spray jet under different nozzle orifice diameter.
It can be directly observed from the image that the size of the shadow area in the spray image changes positively with the size of the nozzle orifice diameter (from left to right).
The specific image processing program in MATLAB® can also help to obtain quantitative indicators at different moments, which can be used to characterize the mixing degree of sprayed fuel and air. The fuel-air mixing degree mainly depends on the air entrainment characteristics of the spray. When other conditions are fixed, the air entrainment is mainly affected by the spray penetration and spreading angle, which then affects the indicators, like spray area and spray volume, that are used to evaluate the spray air entrainment characteristics [25,26].
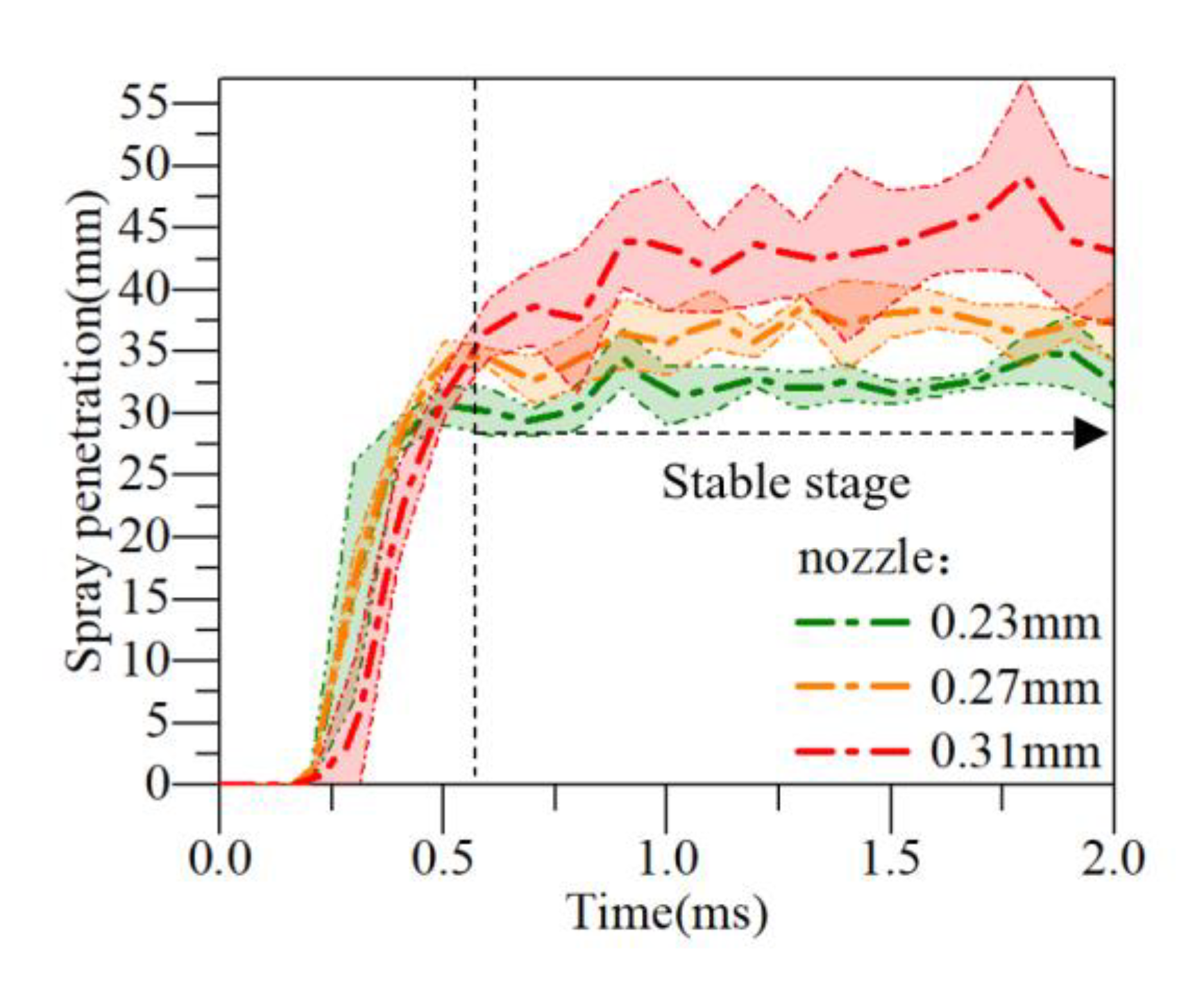
Figure 8 shows the spray penetration distance under high temperature combustion vessel conditions. As can be seen from the figure, under the three different nozzle orifice diameters (0.23 mm, 0.27 mm and 0.31 mm), the smaller diameter spray reaches the larger spray penetration distance faster. This is because the pore size directly affects the oil beam rate and the mixing degree of the mixed gas, and these factors will further affect the energy consumption after the wall collision, the reaction rate and the degree of air entrainment in the combustion process, and finally, affect the soot production [26].
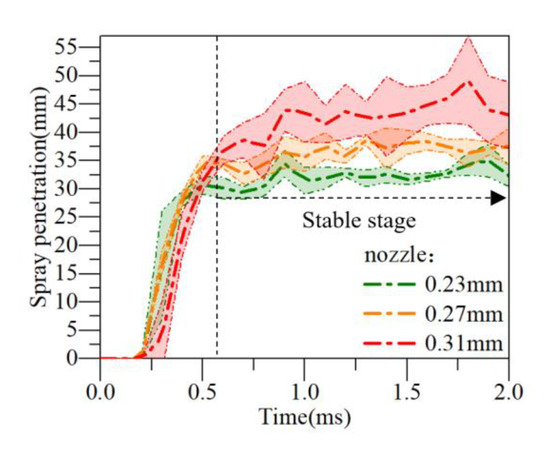
Figure 8.
Spray penetration.
The penetration of the spray under the relatively large nozzle orifice is also larger due to the low fuel and air mixing quality in the injection process, so more liquid area is retained in the image. The average liquid length of the spray can be obtained by calculating the average penetration distance of the spray in the stable process (Table 5).

Table 5.
The average liquid length of the spray.
The average liquid phase length of the spray at 0.23 mm orifice is 12% and 23% shorter than 0.27 mm and 0.31 mm, respectively.
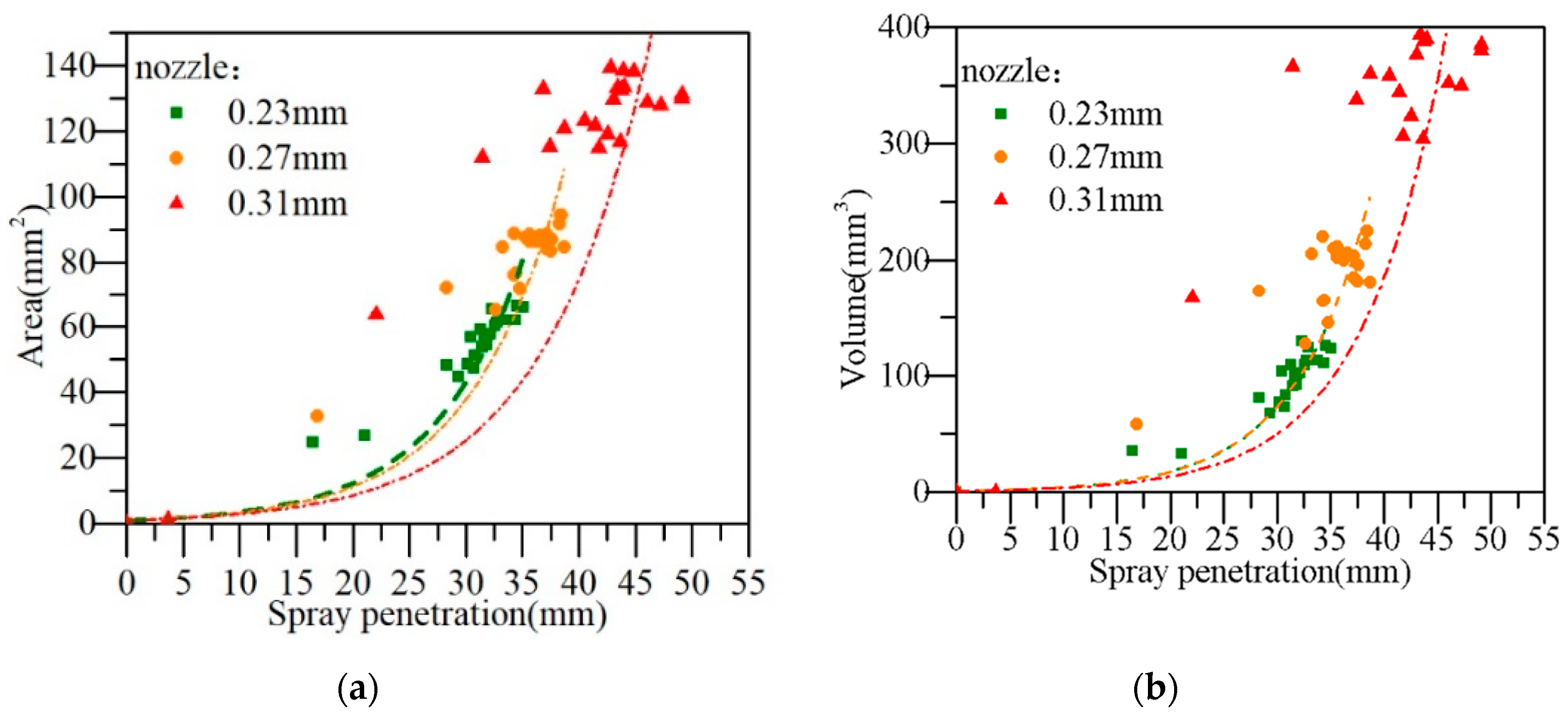
The spray area and volume calculated according to the measured spray spreading cone angle are shown in the Figure 9.
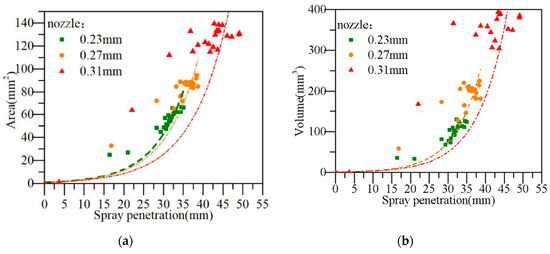
Figure 9.
The spatial relationship between the spray spreading area (a) and spray penetration, spray volume and the spray penetration (b).
It can also be seen from the evaporative spray area and spray volume that we obtained by calculating the penetration distance and the spray diameter, that the spray area and volume at the 0.31 mm nozzle orifice were greater than that at the 0.23 mm and 0.27 mm nozzle orifices. In this case, when the other conditions were fixed, the injector at a relatively small orifice (0.23 mm) could accelerate the atomization of the liquid phase of the diesel spray, promoting the mixing of oil and gas with diesel fuel, and further improving the combustion quality.
The fixed volume combustion vessels combination experiment of ultra-high injection pressure (300 MPa) and micro-injector (0.08 mm) conducted by Wang et al. 5 concluded that the production of soot under conventional injectors will collide because of the liquid fuel impingement and reduced thermal efficiency of the diesel engine.
In the repeated spray experiments of this paper, due to the high ambient temperature (800 K), the high enthalpy value gas entrained into the spray accelerated the fuel evaporation and atomization process so that the liquid spray under all nozzle sizes were completely atomized before reaching the wall plate. The length of the spray liquid does not reach the preset wall impingement distance (57 mm), so no liquid spray wall collision occured.
3.2. Analysis of Ignition Delay and Flame Occurring
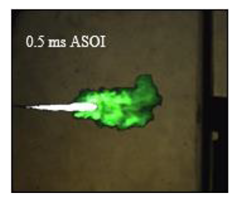
Table 6 showed the images under three different nozzle orifices (0.23 mm, 0.27 mm and 0.31 mm) that the ignition flame first captured.

Table 6.
Image of ignition time ASOI.
There is a synchronous relationship between the ignition image and the liquid-phase spray. The initial moment that the ignition image captured had a significant delay with the increase of the orifice diameter, which is also reflected in the reaction rate in the subsequent combustion process.
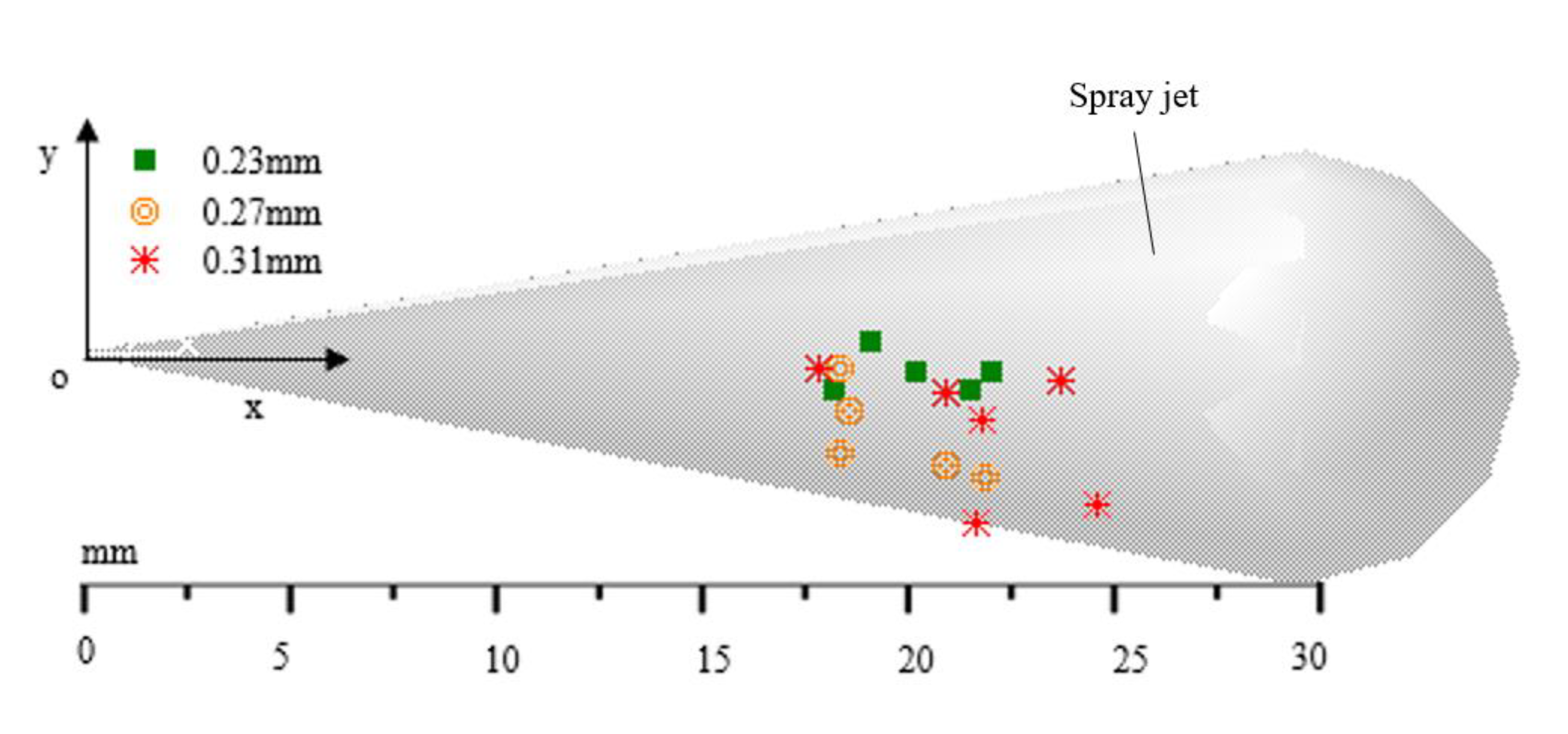
Figure 10 shows the initial position of the ignition flame for three different injector nozzles (0.23 mm, 0.27 mm and 0.31 mm) in repeated experiments.
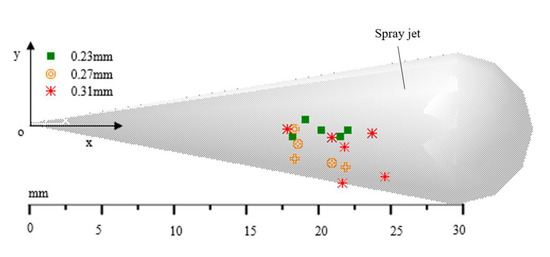
Figure 10.
Axial initial occurring position of the ignition flame for different nozzle orifice diameters.
The difference between the ignition positions was not significant, but as the orifice increased, the ignition position tended to move forward along the x axis, proving that a smaller nozzle orifice of the injector was more conducive to fuel-air mixing to the axial direction.
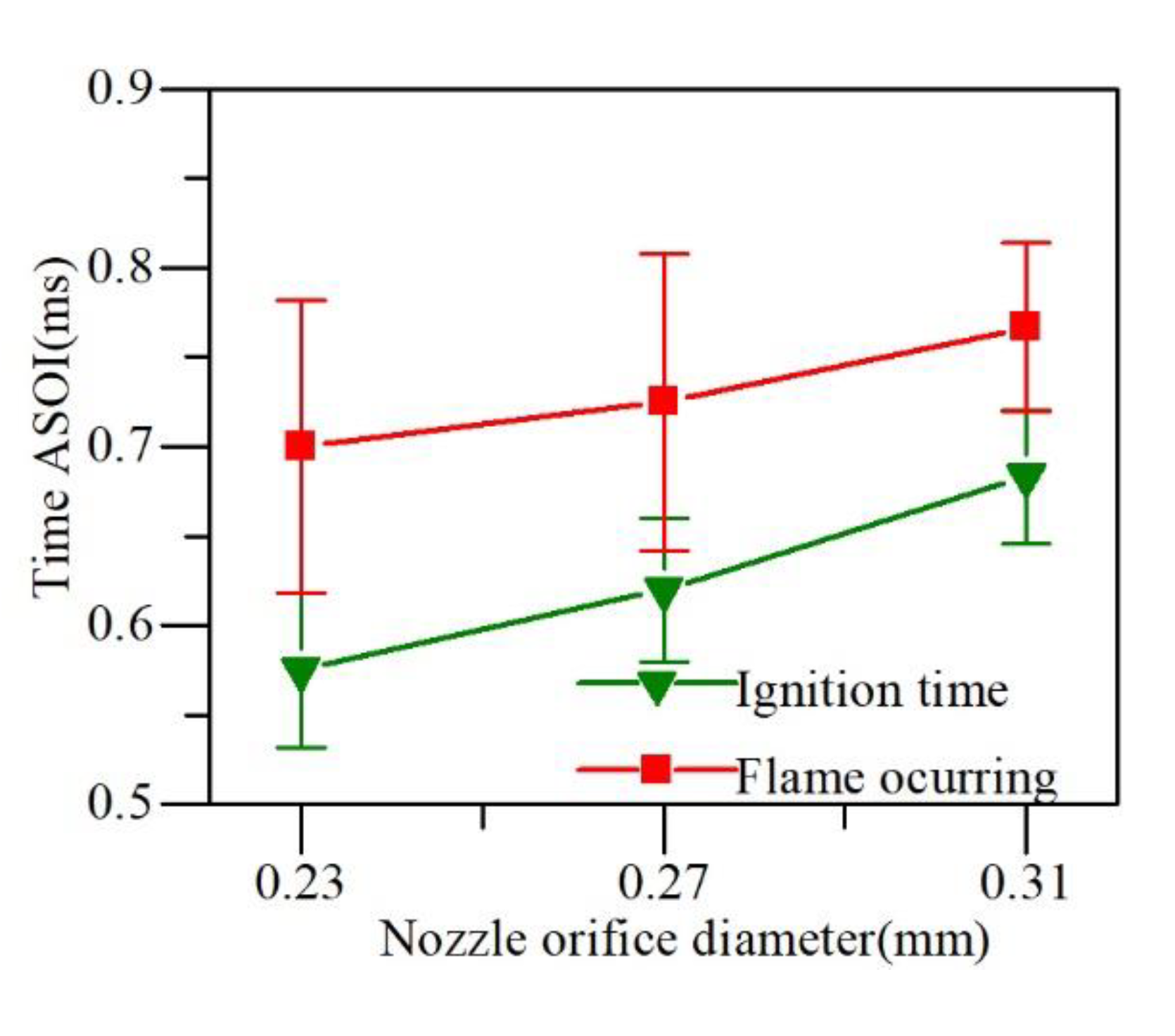
According to the collected ignition and flame first occurrence time by the high-speed camera, the diesel jet reaction trends under different nozzle orifice diameters was observed (as shown in Figure 11).
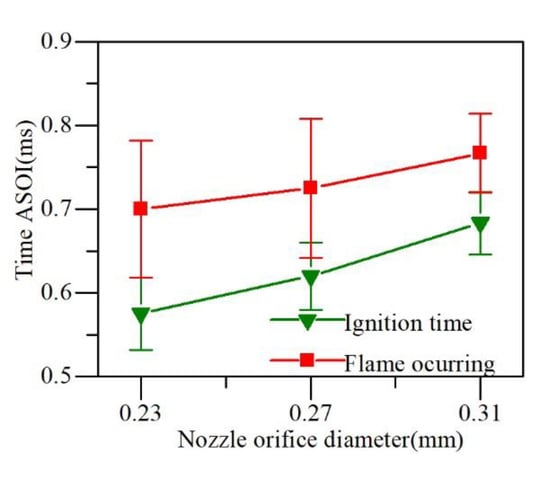
Figure 11.
Ignition delay and flame occurring time.
The initial occurrence of the ignition fire image was earlier than the flame because of the lower level of filter luminosity. However, the flame occurrence of the 0.23 mm diameter nozzle was earlier than other larger nozzle sizes for both imaging conditions.
The orifice size had a direct impact on the ignition delay and the combustion reaction rate, leading to the accelerated speed of the spray mixture so that the ignition equivalent ratio was obtained earlier and ignition response of the smaller nozzle diameter was faster [27].
3.3. Flame Analysis of Diesel Combustion
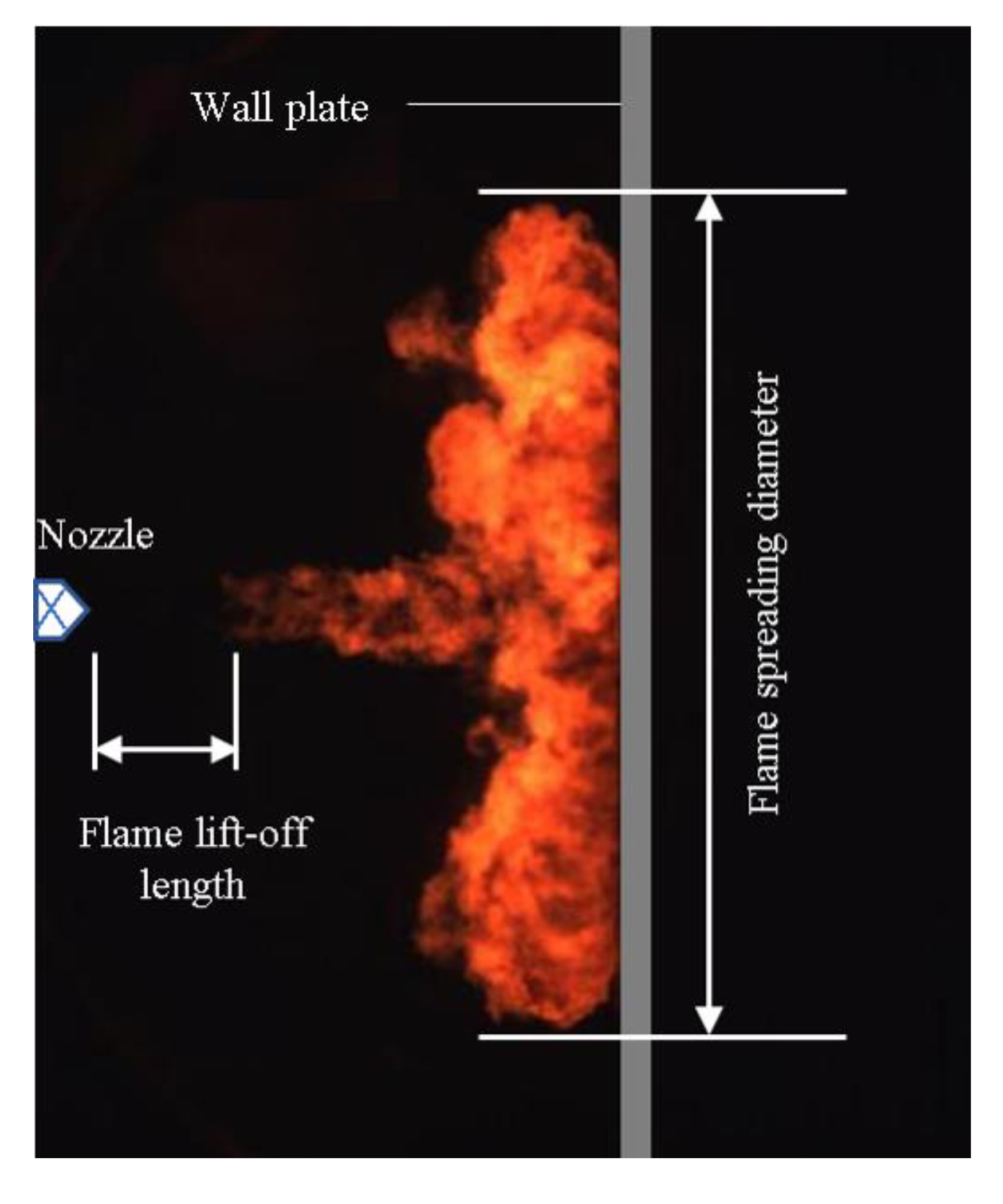
The flame shape of the wall collision in this paper is indicated by the flame spreading diameter, spreading area and flame luminosity, as shown in Figure 12.

Figure 12.
Geometric information of the flame.
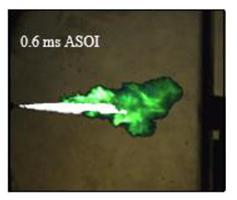
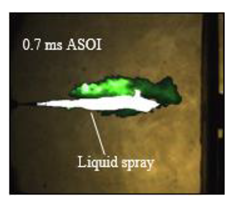
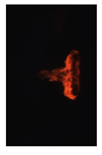
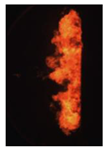
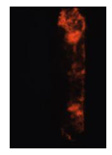
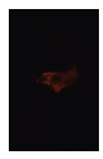
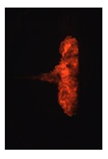
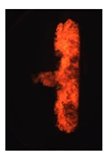
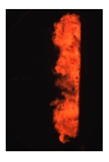
Table 7 shows the diffusion flame at different moments of the flame visualization experiment, captured under ND8 filter by the high-speed camera. The flame luminosity at each pixel in the image corresponds to the brightness threshold of image processing.

Table 7.
Image of impinging diffusion flame.
The flame image of the flame shape by wall impingement combustion summarized the overall change, which was controlled mainly by the fuel-air mixing process [28]. The spray enters into the vessel and burns immediately, spreads in the radial direction at the initial stage of the wall impingement and gradually approaches the wall to form a disc shape that slightly convex along the spray axis. In the late stage, the continuous spreading flame along the wall tears from the axis and forms two smaller flames until they disappear.
Although the larger the nozzle diameter, the shorter the injection duration, it can be found that there is a significant difference in the overall reaction speed of the combustion process when we compared the flame of different injection orifices at the same time.
The relative smaller orifice nozzle injector enabled the fuel to mix with air and to reach the reaction temperature immediately after being injected into the combustion vessel, leading to the earlier generation of soot (the first luminosity capturing). The volume of the liquid fuel jet will be larger and the quality of fuel-air mixture will be worse as the nozzle orifice increases, so the reaction rate and the overall reaction period will be longer. By analyzing the whole flame diffusion duration, the 0.23 mm nozzle orifice ceases the reaction about 1.6 ms earlier than the 0.31 mm nozzle orifice.
3.4. Flame Spread Diameter
In the flame visualization image, the maximum flame width spreading along the collision wall is called the flame spread diameter, reflecting the radial spatial distribution of the flame after hitting the wall and showing the distribution of diesel mixed gas before the flame formation.
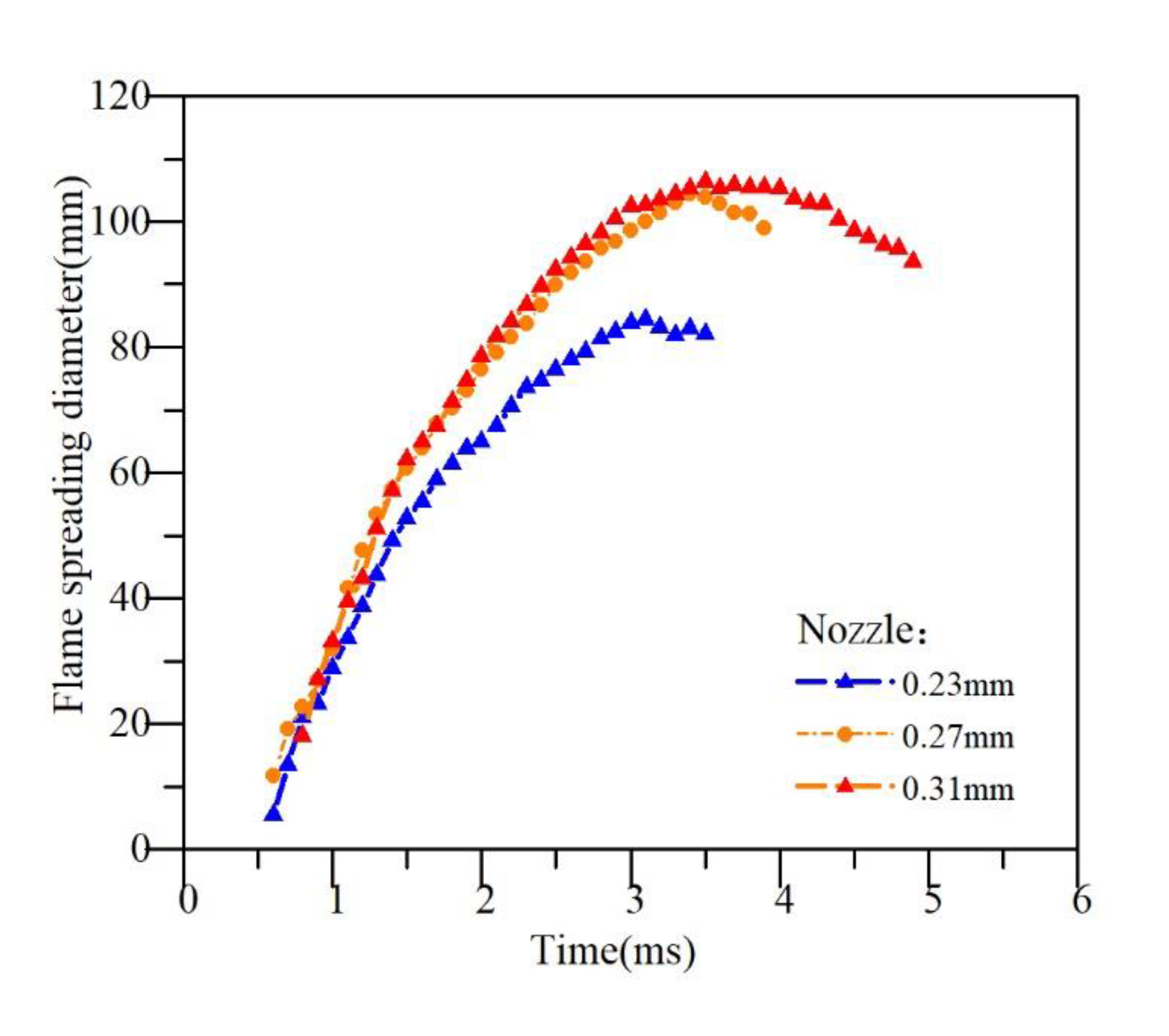
Figure 13 shows the average spreading diameter of impinging flame under different nozzles.
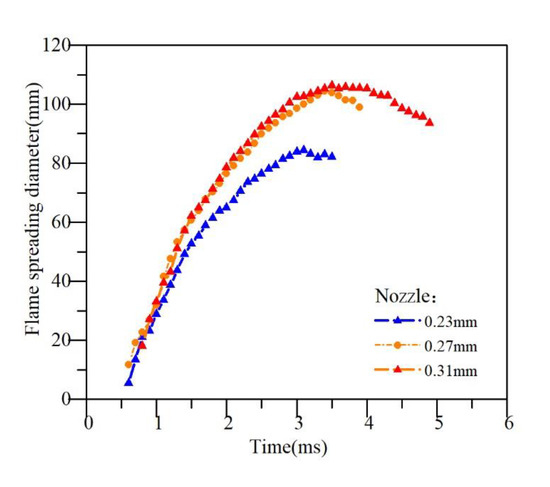
Figure 13.
Spreading diameter of impinging flame.
For the 0.31 mm nozzle orifice, since the smaller dissipated kinetic energy of the spray is caused by the weak atomization and mixture, the mixed diesel gas and combustion flame can spread to a longer distance in the radial direction [29], creating a wider flame distribution along the impingement wall, that is, a larger soot generation area.
3.5. Flame Lift-Off Length (FLoL)
The combustion process of the direct injection diesel engine includes two stages of premixed combustion and diffusion combustion. After the fuel is initially premixed and ignited, the diffusion flame does not directly occur at the nozzle, but a distance away from the nozzle. The distance from the injector orifice to the location of flame luminescence closest to the injector in the flame jet is the flame lift-off length. The flame lift-off length is an important parameter to analyze the flame shape in previous studies [30,31], generally, the flame lift-off length will shorten as the orifice decreases [24]. During the combustion process, the liquid phase portion of the diesel spray is generally regarded as the main feature of this distance. This parameter determines the quality of the air entrained and mixed with the fuel before it starts to burn, which is a particularly important parameter in terms of the generation of soot during the combustion process [32].
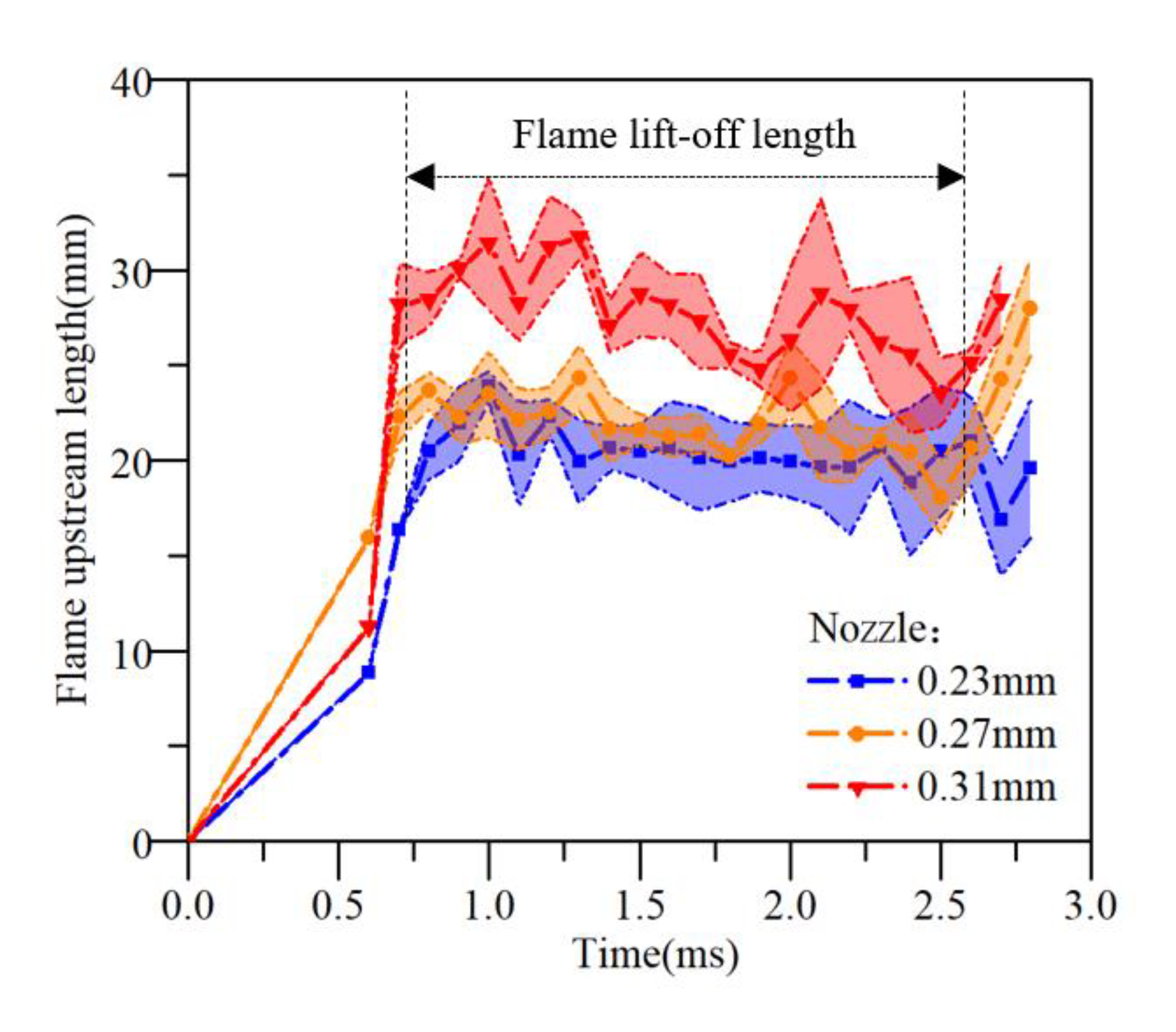
Figure 14 shows the curves of captured flame lift-off length development under different nozzles.
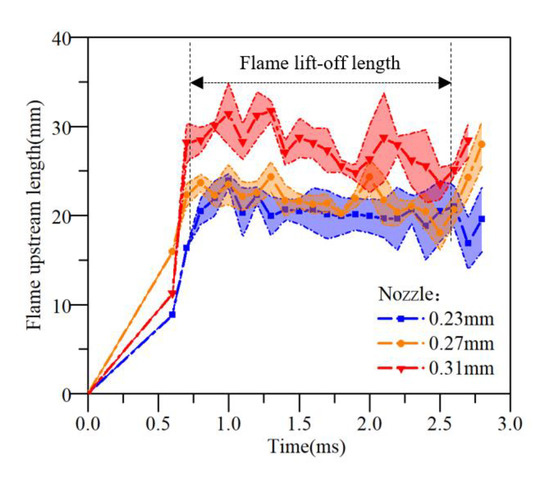
Figure 14.
Flame upstream length and flame lift-off length.
Table 8 shows the specific values of the average flame lift-off length in stable stage of the images.

Table 8.
Average flame lift-off length.
As for the distribution of the flame lift-off length and the trend with the diameter of the nozzle orifice, corresponding to the liquid in the evaporative spray at high temperatures, the average flame lift-off length for 0.23 mm was lower than 0.27 mm and 0.31 mm (10% and 29% respectively).
Similar to the actual combustion characteristics of diesel engines, the higher the mixing degree of fuel and gas, the more conducive to combustion. The shorter the evaporative spray liquid distance in spray visualization, the shorter the flame lift-off length in flame visualization, that is, the injected fuel could ignite and combust in the near position to the nozzle.
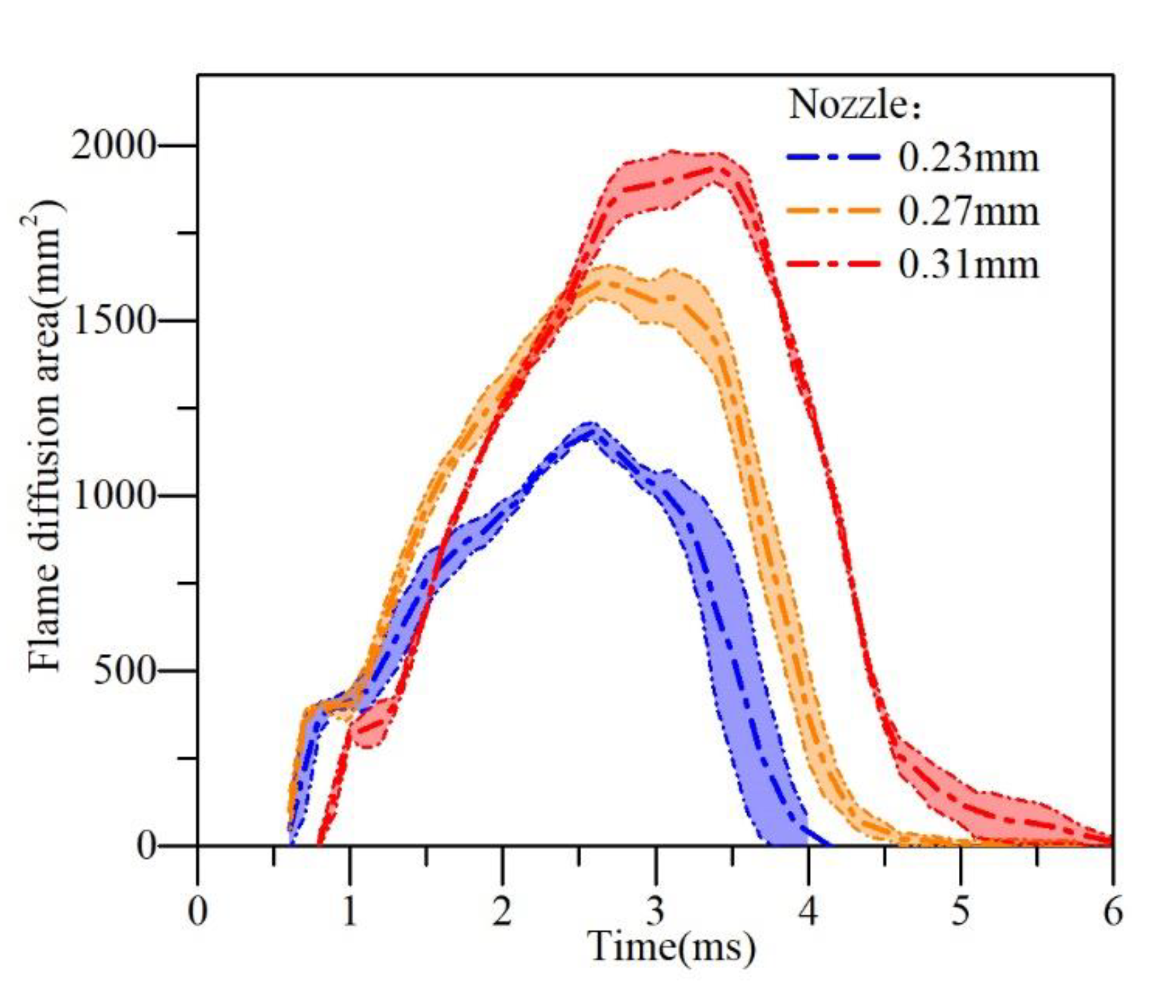
3.6. Flame Diffusion Area
The flame diffusion area extracted based on the image is the spatial projection of the flame (Figure 15). The method was obtained by adding the area of each frame of the flame image where luminosity exceeds the threshold (20/255). This area reflects the spatial distribution of soot during the combustion process, proving that the larger the flame area in the space, the wider the spatial distribution of soot.
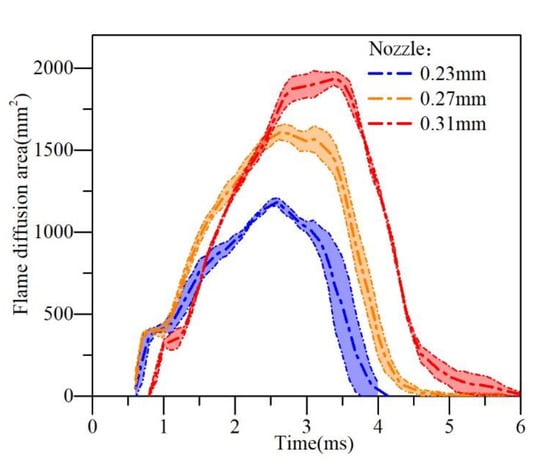
Figure 15.
Flame diffusion area.
Under the experiment conditions of three different sizes of injector, the law of change for the flame is nearly the same, that is, the curves of the flame distributed as triangular-shaped. By comparing the area and the maximized flame area of three nozzle orifices, the large orifice (0.31 mm) had the largest flame diffusion area.
3.7. Flame Spatially Integrated Natural Luminosity (SINL) and Time Integrated Natural Luminosity (TINL)
The flame diffusion area is regarded as the projection of spatial flame on the plane. By summarizing the luminosity values from 0 to 255 of all pixels in the flame image, the spatially integrated natural luminosity (SINL) can be obtained, which represents the transient soot generation during the combustion [33,34,35,36]. We further calculate the spatial integrated luminosity to obtain the time integrated natural luminosity (TINL), which is used to compare the total amount of soot generation during the flame impinging combustion [37].
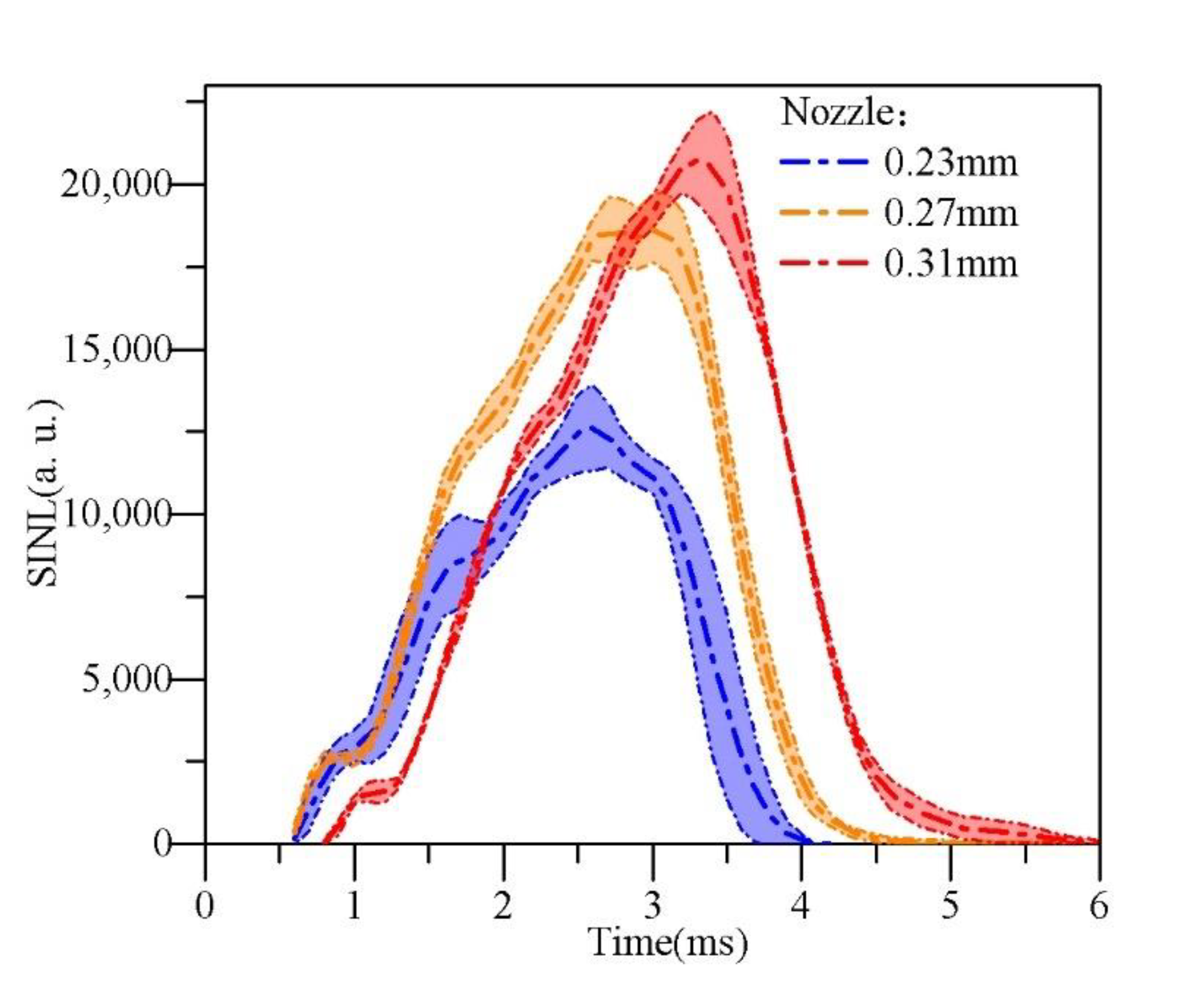
The SINL of the diffusion flame is actually consistent with the changing trends of the flame area under the same conditions, as shown in Figure 16.
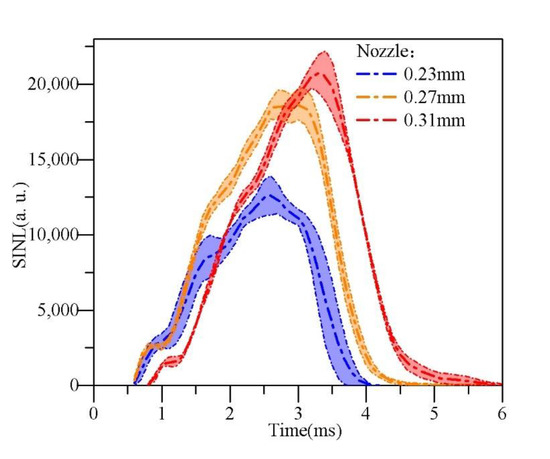
Figure 16.
Flame spatially integral natural luminosity (SINL).
According to the conclusion of diesel-air mixing and flame propagation, the spatial luminosity distribution of the large-orifice diesel spray was the widest and the maximum luminosity was the highest after hitting the wall. Similarly, the soot generation and spatial distribution are the worst for the three different nozzle orifice diameters (0.23 mm, 0.27 mm and 0.31 mm).
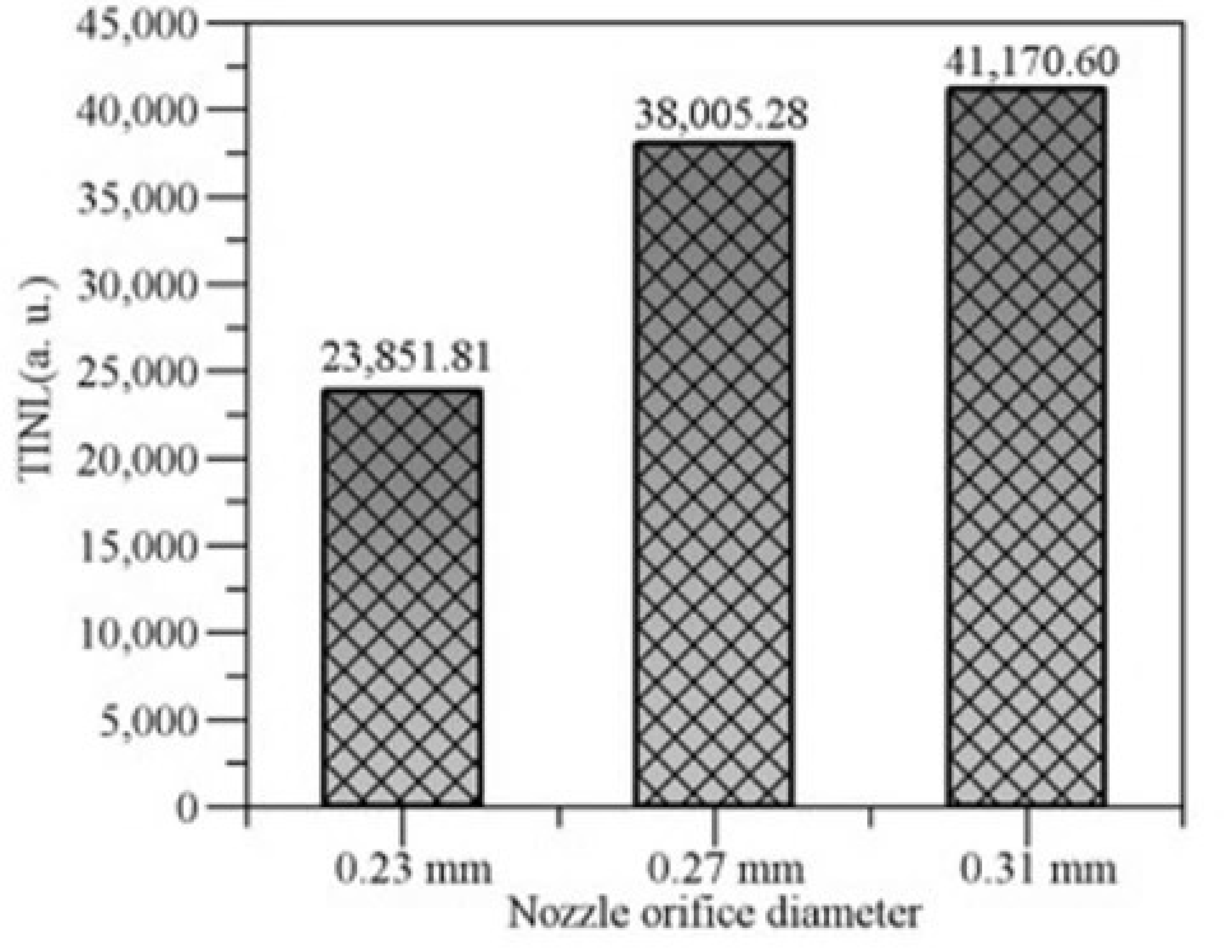
The flame time integral natural luminosity (TINL) was obtained by accumulating the flame space integral luminosity according to the combustion time [24]. TINL characterizes the total amount of soot produced under different reaction conditions during the complete injection and combustion cycle, as shown in the Figure 17.
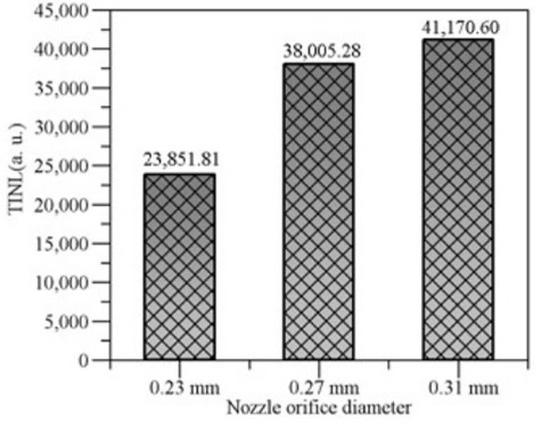
Figure 17.
Flame time integral natural luminosity (TINL).
When using a larger nozzle orifice injector, the total soot production was still the highest. Caused by the poor degree of spray atomization, the local mixed gas concentration became higher during the combustion process, the combustion reaction process became relatively longer, and the cumulative generation of soot increased in the whole combustion process. Compared with the injectors with 0.31 mm and 0.27 mm nozzle size, the 0.23 mm nozzle orifice injectors can reduce the total soot production by 37% and 42% through the characterization calculation of flame time integral luminosity.
It can be seen that the combustion will not be affected by the simple flame impinging on the wall. The change of mixing quality caused by nozzle size is the key factor to determining diesel combustion and emission.
4. Conclusions
By processing the images of the spray and combustion flame, indicators like the numerical value well represent the fuel-air mixture quality and the total soot generation level under different experiment conditions. In the construction of the small-size diesel engine structure, the injector with small-orifice nozzle can decrease the liquid penetration effectively, avoid the deterioration of combustion caused by the liquid-wall impingement and lead to a smaller high temperature combustion area to reduce the generation of soot.
The main conclusions of this paper are as follows:
- The liquid length of the 0.23 mm nozzle injector is 19% shorter than that of the 0.27 mm injector and 23% shorter than that of the 0.31 mm injector, meaning a faster fuel-air mixture and benefit to the combustion.
- The ignition delay at 0.23 mm nozzle orifice diameter is the shortest, indicating that the fuel-air mixing quality of the small orifice nozzle reaches the condition of ignition and combustion earlier.
- In the experiment of flame-wall impingement combustion process, the combustion reaction speed is faster for the small orifice (0.23 mm).
- Under free flame combustion condition, the flame lift-off length will shorten with the decrease of the orifice [16]. The flame lift-off length corresponding to the flame image with a small orifice (0.23 mm) is 10% and 29% shorter than that of the 0.27 mm and 0.31 mm orifice, respectively. That is, the simple flame-wall impingement without liquid fuel impingement will not change the trend of the nozzle influence on combustion.
- By analyzing the flame time integral luminosity (TINL), the 0.23 mm orifice injector can reduce the accumulation of soot, 42% less than the orifice of 0.31 mm and 37% less than the orifice of 0.27 mm, respectively.
The distance of the wall impingement will change with the fuel injection advance angle in the actual combustion chamber of diesel engine. Therefore, whether the liquid wall impinging combustion deterioration exist or not in reality needs further study.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft, Writing—review & editing, Y.T. and Y.Z.; Funding acquisition, D.L.; Methodology, Software, C.W.; Project administration, P.-q.T. and Z.H.; Visualization, L.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFE0102800).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support by National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFE0102800).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| DI | direct injection |
| ASOI | after start of injection |
| PM | particulate matte |
| TINL | time integrated natural luminosity |
| SINL | ppatially integrated natural luminosity |
References
- Han, J.; Somers, L.M.T.; Cracknell, R.; Joedicke, A.; Wardle, R.; Mohan, V.R.R. Experimental investigation of ethanol/diesel dual-fuel combustion in a heavy-duty diesel engine. Fuel 2020, 275, 117867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickett, L.M.; Siebers, D.L. Soot in diesel fuel jets: Effects of ambient temperature, ambient density, and injection pressure. Combust. Flame 2004, 138, 114–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickett, L.M.; Siebers, D.L. Soot formation in diesel fuel jets near the lift-off length. Int. J. Engine Res. 2006, 7, 103–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, M. Physics behind diesel sprays. In Proceedings of the 12th Triennial International Conference on Liquid Atomization and Spray Systems, ICLASS 2012, Heidelberg, Germany, 2–6 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; He, Z.; Xuan, T.; Zhong, W.; Cao, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, P. Simultaneous capture of liquid length of spray and lame lift-off length for second-generation biodiesel/diesel blended fuel in aconstant volume combustion chamber. Fuel 2017, 189, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Kuti, O.A.; Nishida, K. Effects of ultra-high injection pressure and micro-hole nozzle on flame structure and soot formation of impinging diesel spray. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 1620–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lequien, G.; Berrocal, E.; Gallo, Y.; Mello, A.T.E.; Andersson, O.; Johansson, B. Effect of Jet-Jet Interactions on the Liquid Fuel Penetration in an Optical Heavy-Duty DI Diesel Engine (No. 2013-01-1615); SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2013; p. 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delacourt, E.; Desmet, B.; Besson, B. Characterisation of very high pressure diesel sprays using digital imaging techniques. Fuel 2005, 84, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zama, Y.; Ochiai, W.; Sugawara, K.; Furuhata, T.; Arai, M. Study on mixing process of diesel spray under high ambient gas density condition. At. Sprays 2013, 23, 443–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, K.R.; Partridge, I.M.; Greeves, G. Fuel Property Effects on Fuel/Air Mixing in an Experimental Diesel Engine; Papers; Automotive_Sector, SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1986; p. 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebers Dennis, L. Scaling Liquid-Phase Fuel Penetration in Diesel Sprays Based on Mixing-Limited Vaporization; SAE Transactions, SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1999; p. 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Nishida, K.; Nomura, S.; Ito, T. Spray Characteristics of a Group-Hole Nozzle for Direct-Injection Diesel Engines (No. 2001-01-1295); SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dec, J.E.; Tree, D.R. Diffusion-Flame/Wall Interactions in a Heavy-Duty DI Diesel Engine (No. 2001-01-1295); SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2001; p. 110. [Google Scholar]
- Donkerbroek, A.; Boot, M.; Luijten, C.; Dam, N.; Ter Meulen, J. Flame lift-off length and soot production of oxygenated fuels in relation with ignition delay in a DI heavy-duty diesel engine. Combust. Flame 2011, 158, 525–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, C.J.; Martin, G.C. Effects of Oxygenated Compounds on Combustion and Soot Evolution in a DI Diesel Engine: Broadband Natural Luminosity Imaging (No. 2002-01-1631); SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2002; p. 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, C.J.; Pitz, W.J.; Pickett, L.M.; Martin, G.C.; Siebers, D.L.; Westbrook, C.K. Effects of Oxygenates on Soot Processes in DI Diesel Engines: Experiments and Numerical Simulations (No. 200301-1791); SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2003; p. 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Jing, W.; Fang, T. High speed imaging of OH* chemiluminescence and natural luminosity of low temperature diesel spray combustion. Fuel 2012, 99, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruneaux, G. Combustion structure of free and wall-impinging diesel jets by simultaneous laser-induced fluorescence of formaldehyde, poly-aromatic hydrocarbons, and hydroxides. Int. J. Engine Res. 2008, 9, 249–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattah, I.R.; Yip, H.L.; Jiang, Z.; Yuen, A.C.; Yang, W.; Medwell, P.R.; Kook, S.; Yeoh, G.H.; Chan, Q.N. Effects of flame-plane wall impingement on diesel combustion and soot processes. Fuel 2019, 255, 115726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panão, M.; Moreira, A.; Durão, D. Effect of a cross-flow on spray impingement with port fuel injection systems for HCCI engines. Fuel 2013, 106, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merola, S.; Vaglieco, B.M. Optical investigations of fuel deposition burning in ported fuel injection (PFI) spark-ignition (SI) engine. Energy 2009, 34, 2108–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhang, X. Numerical study of effects of reformed exhaust gas recirculation (REGR) on dimethyl ether HCCI combustion. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 8106–8117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payri, R.; Viera, J.P.; Gopalakrishnan, V.; Szymkowicz, P.G. The effect of nozzle geometry over ignition delay and flame lift-off of reacting direct-injection sprays for three different fuels. Fuel 2017, 199, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebers, D.L.; Higgins, B. Flame lift-off on direct-injection diesel sprays under quiescent conditions. SAE Tech. Pap. 2001, 110, 400–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.Y.; Sato, G.T.; Hayashi, A.; Tanabe, H. Experimental Investigation of the Entrainment into Diesel Spray (No. 841078); SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, Z.; Kuti, O.A.; Zhang, W.; Nishida, K. Experimental and analytical study on biodiesel and diesel spray characteristics under ultra-high injection pressure. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2010, 31, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSantes, J.M.; García-Oliver, J.M.; Novella, R.; Pachano, L. A numerical study of the effect of nozzle diameter on diesel combustion ignition and flame stabilization. Int. J. Engine Res. 2019, 21, 101–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiroyasu, H.; Arai, M. Structures of Fuel Sprays in Diesel Engines (No. 900475); SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1990; p. 99. [Google Scholar]
- Mancaruso, E.; Sequino, L.; Vaglieco, B.M. Analysis of spray injection in a light duty CR diesel engine supported by non-conventional measurements. Fuel 2015, 158, 512–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Ma, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J. An optical study on liquid-phase penetration, flame lift-off location and soot volume fraction distribution of gasoline–diesel blends in a constant volume vessel. Fuel 2015, 139, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuti, O.A.; Zhu, J.; Nishida, K.; Wang, X.; Huang, Z. Characterization of spray and combustion processes of biodiesel fuel injected by diesel engine common rail system. Fuel 2013, 104, 838–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Andersson, S.; Andersson, M. Two-dimensional measurements of soot in a turbulent diffusion diesel flame: The effects of injection pressure, nozzle orifice diameter, and gas density. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2018, 190, 1659–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickett, L.M.; López, J.J. Jet-Wall Interaction Effects on Diesel Combustion and Soot Formation (No. 2005-01-0921); SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2005; p. 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Huang, S.; Huang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, S. Ignition and combustion characteristics of n-pentanol–diesel blends in a constant volume chamber. Appl. Energy 2017, 185, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Nithyanandan, K.; Zhou, N.; Lee, T.H.; Chia-fon, F.L.; Zhang, C. Impacts of acetone on the spray combustion of Acetone–Butanol–Ethanol (ABE)-Diesel blends under low ambient temperature. Fuel 2015, 142, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickett, L.M.; Siebers, D.L.; Idicheria, C.A. Relationship between ignition processes and the lift-off length of diesel fuel jets. SAE Tech. Pap. 2005, 114, 1714–1731. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Lee, C.F.; Huo, M.; Yao, M. Comparison of ethanol and butanol as additives in soybean biodiesel using a constant volume combustion chamber. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 1837–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).