Abstract
Researchers are considering the use of eye tracking in head-mounted camera systems, such as Google’s Project Glass. Typical methods require detailed calibration in advance, but long periods of use disrupt the calibration record between the eye and the scene camera. In addition, the focused object might not be estimated even if the point-of-regard is estimated using a portable eye-tracker. Therefore, we propose a novel method for estimating the object that a user is focused upon, where an eye camera captures the reflection on the corneal surface. Eye and environment information can be extracted from the corneal surface image simultaneously. We use inverse ray tracing to rectify the reflected image and a scale-invariant feature transform to estimate the object where the point-of-regard is located. Unwarped images can also be generated continuously from corneal surface images. We consider that our proposed method could be applied to a guidance system and we confirmed the feasibility of this application in experiments that estimated the object focused upon and the point-of-regard.
Introduction
Head-mounted camera systems, such as Project Glass by Google, require an eye-based intuitive input method. This also applies to other eye-tracking research devices, such as wearable EOG goggles (Bulling, Roggen, & Tröster, 2009) and Aided Eyes (Ishiguro, Mujibiya, Miyaki, & Rekimoto, 2010), which have been proposed for daily use. In general, eye-tracking systems are used to estimate the point-ofregard but eye-based interaction also requires the identification of the object that the user is focused upon. For a noncontact eye tracker, the point-of-regard may be estimated on a display screen or an advertisement, so the coordinates of the point-of-regard can be converted directly to the focused object. This is because the relationship between the sensor coordinates system and the object coordinates system is fixed. By contrast, it is difficult to determine the focused object when using a head-mounted eye tracker because the coordinates system between the user and the object changes dynamically, depending on the user’s movements. Ease of calibration and light weight are also essential features of an eye tracker that is intended for regular use. A typical headmounted eye tracker comprises scene and eye cameras, and a calibration procedure is required before their use. However, the relationship between the two cameras might be disrupted during a long period of use even if prior calibration is performed. An effective solution to these problems is obtaining eye and environmental information simultaneously using an eye camera alone. Nishino and Nayer () proposed a method for extracting environmental information from corneal surface images, while Nitschke and Nakazawa () obtained superresolution images from corneal surface images. These studies encouraged us to extract visual information from corneal surface images to detect focused objects. However, previous studies did not use a wearable camera to capture corneal surface images, because this approach is difficult to apply during eye-based interaction. Therefore, we propose a userfriendly head-mounted eye camera system, which can extract scene and eye information from the user’s corneal images. Corneal surface images can be archived continuously using a wearable camera, so the scene and eye information can be extracted by model-based eye tracking. We consider that the proposed system can be used in guidance systems, such as a museum, as an intuitive human interface. Thus, we confirmed that the objects that a user focuses upon could be estimated from corneal surface images during these types of applications.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. In section II, related research on eye tracking methods is described. Section III introduces a wearable camera system, which was developed for daily use. The methods used to extract scene images from corneal surface images and for model-based eye tracking are described in Section IV and Section V, respectively. The methods used for the detection and extraction of focused objects are described in Section VI and Section VII, respectively. Section VIII gives our conclusions and outlines our future work.
Related work
The methods used for eye tracking are categorized as regression-based or model-based algorithms. In regressionbased approaches, the point-of-regard is projected onto a display screen using a quadratic polynomial (). Regression-based approaches are quite common and they are used by several commercial products. However, a calibration is needed where the test subject looks at several points; thus, model-based approaches have been studied actively to simplify the calibration process (Ohno & Mukawa, 2004)(Ohno, 2006)(Nagamatsu, Kamahara, & Tanaka, 2009). In model-based approaches, a spherical eyeball and a cornea are approximated to calculate the optical or visual axis. The radius of the eyeball and corneal surface are approximately constant, and typical eye parameter values are well known (). Therefore, the structure of the eye has been used widely, and several corneal imaging techniques have been proposed. For example, Nishino et al. () extracted the scene image from the corneal surface image and relighting was introduced as an application of corneal imaging (). However, spherical panoramas are computed from the eye images; thus the extracted image is distorted. Nitschke et al. proposed a super-resolution approach based on corneal surface images (), which can obtain high-resolution scene information, although it is difficult to capture images continuously from the iris as an eye tracker for daily use. Therefore, we propose a method that estimates the focused object using a corneal surface image with 3D model-based iris tracking for application in a device that is suitable for daily use. Compared with typical dual-camera systems, the advantage of using corneal imaging is the simple hardware configuration procedure, whereas recalibration is required for regular use with a dual-camera system. The relationship between two cameras might be disrupted over a long period. Thus we employed an eye camera only so recalibration is not required.
Wearable device for capturing corneal surface images
In previous studies, corneal surface images were captured using a digital single lens reflex camera or an industrial camera that could capture high-resolution images (Nishino & Nayar, 2004b)(Nitschke & Nakazawa, 2012). The camera was fixed on a tripod on the floor, which made it difficult to obtain image sequences and it could not be applied to user interfaces. To overcome this difficulty, we developed a portable device for capturing corneal reflections, which is shown in Figure 1. At present, we employ two types of eye camera and the third system is generally used. We designed the device using a 3D CAD system and it was produced with a 3D printer. Our device differs from conventional eye-tracking systems because it does not require a scene camera or nearinfrared LEDs. In addition, the device has a prism installed, which provides an adequate depth of field to focus on the eye. Figure 2 shows the design of the third system, which has four components. A color camera (ASAHI E.L. NCM13-J), a camera board (ASAHI E.L. NCM-USB-C), and a prism (SIGMA KOKI CO., LTD. RPB2-10-550) are installed in each position, as shown in Figure 2. We use a color camera to capture the corneal surface images, which allows the use of color information during image processing. The camera is a small UVC camera, which can be connected to a variety of computers and it has the capacity to shoot pictures at pixellevel resolution. At present, our algorithm cannot be implemented to operate in real-time, which is a point we discuss below. Thus, the central emphasis during the design of the system configuration was portability. Figure 3 shows one of the capture devices where Nexus 7 was used as the processor. The system lacked sufficient storage capacity to collect image sequences, so we implemented software to upload the images to a server with more storage. This enhancement allows corneal surface images to be recorded continuously at a rate of 2 FPS. When a laptop computer is used as the capture device, the maximum frame rate is 15 FPS. In our system, the operating system on the tablet was replaced with Linux to implement a capture program in C/C++.
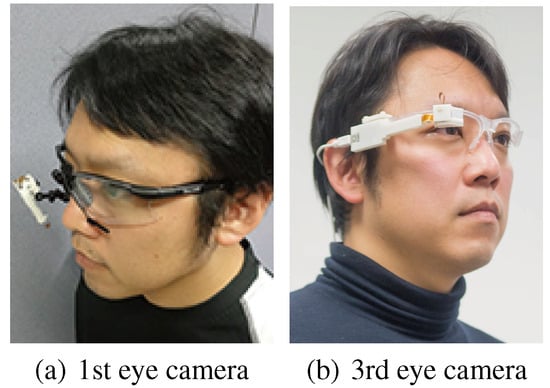
Figure 1.
Two types of eye cameras are used to estimate the object that is focused upon using the corneal surface image.
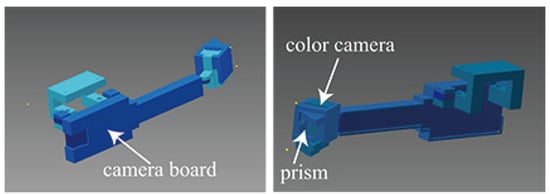
Figure 2.
Design of the third eye camera, which has four components, i.e., an eye camera, a prism, and a capture board.
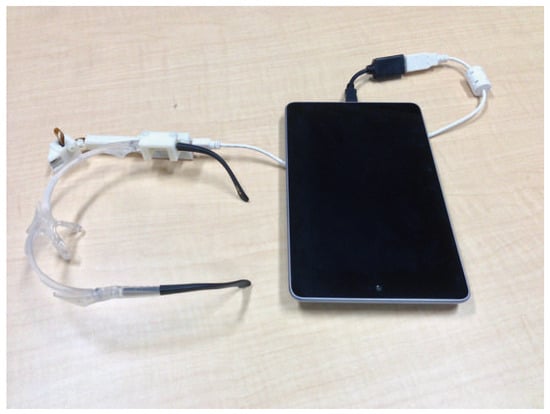

Figure 3.
The prototype system, which was developed with an emphasis on portability.
Extracting scene images from corneal surface images
Our system has applications in navigation systems that use visual and audio information (e.g., guidance systems in museums), which require the identification of objects that a user focuses upon. Computer vision researchers have developed various specific object recognition methods such as scaleinvariant feature transform () and binary robust independent elementary features (Calonder, Lepetit, Strecha, & Fua, 2010), but these methods require that the corneal surface image be corrected for distortion before they can be applied. The use of 3D eye models for eye tracking has also been proposed as mentioned previously. In these models, it is possible to define the corneal surface as part of a sphere to generate unwarped images from corneal surface images. Thus, we employed the 3D eye model proposed by Nishino et al. () and Nitschke et al. (Nitschke, Nakazawa, & Takemura, 2011) to estimate the cornea and optical axis. When the iris is detected, as shown in Figure 4, the relationship between the image plane and the 3D eye model is determined using the parameters of the ellipse, as shown in Figure 5. The 3D eye model is generated using the iris contour, which is extracted as an elliptical approximation. The 3D limbus center L is computed using by the following equation:
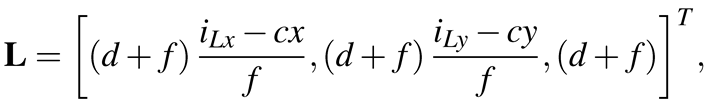 (1)
where (iLx, iLy) is the ellipse center in the image as shown in Figure 4, and (cx, cy) are the optical centers expressed as pixel coordinates. In addition, the distance to the image plane and the focal length are d and f respectively. The distance d between the 3D limbus center L and the image plane, which is shown in Figure 5, can be calculated as
(1)
where (iLx, iLy) is the ellipse center in the image as shown in Figure 4, and (cx, cy) are the optical centers expressed as pixel coordinates. In addition, the distance to the image plane and the focal length are d and f respectively. The distance d between the 3D limbus center L and the image plane, which is shown in Figure 5, can be calculated as
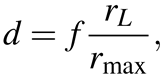 (2)
where rL = 5.6 mm and rmax is the major radius of the ellipse. The optical axis is given by
(2)
where rL = 5.6 mm and rmax is the major radius of the ellipse. The optical axis is given by
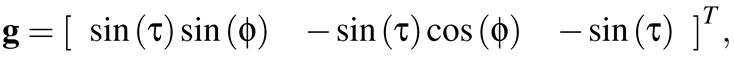 (3)
where τ is the angle of the tilt of the limbus plane with respect to the image plane, where the angle can be computed using the major and minor radii of the ellipse:
(3)
where τ is the angle of the tilt of the limbus plane with respect to the image plane, where the angle can be computed using the major and minor radii of the ellipse:
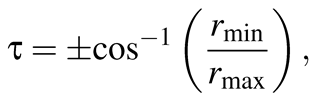 (4)
and φ is the rotation of the limbus ellipse in the image plane as shown in Figure 4. Finally, the center of the cornea C is determined using the following equation:
(4)
and φ is the rotation of the limbus ellipse in the image plane as shown in Figure 4. Finally, the center of the cornea C is determined using the following equation:
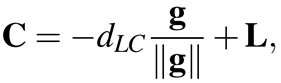 (5)
where the distance between the 3D limbus center and the center of the cornea is dLC = 5.6 mm. In addition, we added a model of an eyeball to the 3D cornea in our method. The center of the eye ball Eball is also determined using the following equation:
(5)
where the distance between the 3D limbus center and the center of the cornea is dLC = 5.6 mm. In addition, we added a model of an eyeball to the 3D cornea in our method. The center of the eye ball Eball is also determined using the following equation:
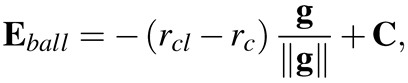 (6)
where rc is the radius of the cornea and the distance between the corneal surface and the center of the eyeball is rcl = 13 mm.
(6)
where rc is the radius of the cornea and the distance between the corneal surface and the center of the eyeball is rcl = 13 mm.
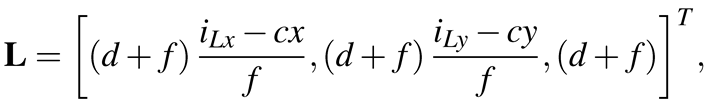 (1)
(1)
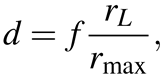 (2)
(2)
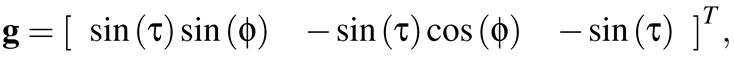 (3)
(3)
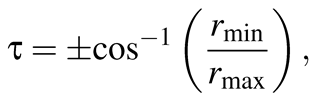 (4)
(4)
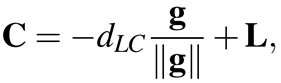 (5)
(5)
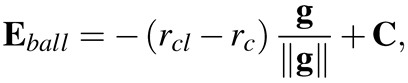 (6)
(6)
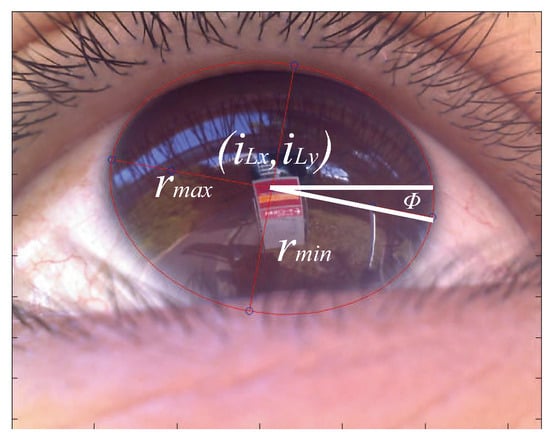
Figure 4.
The iris area is extracted using an ellipse and it is indicated in red.

Figure 5.
Relationship between the cornea, tangent plane, optical axis, and input image.
The color of each pixel is computed in the tangent plane and an unwarped image is generated. However, it is difficult to locate the tangent plane at the point-of-regard. One-point calibration methods have been proposed in previous studies ()(Nagamatsu, Kamahara, Iko, & Tanaka, 2008). We can register the point-of-regard when inputting the reflection point of a point-of-regard in the corneal surface image, although this is not the same as a typical one-point calibration. If the distance between the point-of-regard and the reflection point of point-of-regard has been registered, the visual axis can be computed as shown in Figure 6. However, the distance to the point-of-regard changes dynamically; thus the reflection point of the point-of-regard cannot be computed. Therefore, it is necessary to define the center of the tangent plane to generate an unwarped image. In our method, the intersection point between the vector of the center of the iris and the corneal sphere is used as the center of the tangent plane. When the center of tangent plane is defined, the unwarped image is generated from the tangent plane using a specular reflection model and inverse ray tracing is employed to generate the image. A quadric equation is used to compute the point of reflection of a sphere (). As shown in Figure 7, the center C of the corneal sphere is defined as the point of origin, S is the optical center of the camera, and T is a point on the tangent plane. The constraint on specular reflection is calculated using the following equation:
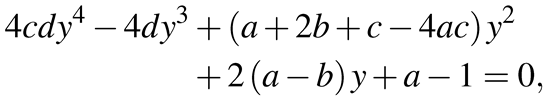 (7)
where a = S · S, b = S · T, c = T · T, d = |S × T|2 are the coefficients of the biquadratic equation. When x = (−2y2 + y + 1)/(2by + 1) is defined, a normal vector, N = xS + yT, is computed from a solution to the biquadratic equation, subject to the conditions x > 0, y > 0. The unwarped image is generated by inverse ray tracing from the reflection point, P, which is computed using the following equation:
(7)
where a = S · S, b = S · T, c = T · T, d = |S × T|2 are the coefficients of the biquadratic equation. When x = (−2y2 + y + 1)/(2by + 1) is defined, a normal vector, N = xS + yT, is computed from a solution to the biquadratic equation, subject to the conditions x > 0, y > 0. The unwarped image is generated by inverse ray tracing from the reflection point, P, which is computed using the following equation:
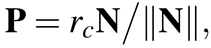 (8)
where rc is the radius of the corneal sphere, which was set as approximately 7.8 mm. When computing the reflection point, the pixel values of the tangent plane are obtained from the input image by inverse ray tracing. Figure 8 shows the results after correcting the image distortion, where the focused object (e.g., a human face) is extracted continuously using the head-mounted device. The image generated is determined largely by the iris color, as shown in Figure 8. As mentioned below, the algorithms used to estimate the focused object depend on the intensity alone, so color correction is not indispensable during eye-based interaction. However, if the proposed system is regarded as a measurement system, color correction is required to improve the visibility. In a previous study (Wang, Lin, Liu, & Kang, 2005), the problems of the color and texture of the eye were also addressed. They showed that the reflection is ambiguous for a light-colored eye, such as blue or green. In addition, they proposed a method for separating corneal reflections in human iris images. In their method, both the left and right iris are used to compute the corresponding illumination; thus, we cannot separate reflections using their method. However, it is possible to improve the color of an unwarped image based on assumption they employed. Various algorithms have been developed for achieving color constancy such as the Gray World Assumption (). The result obtained after applying this algorithm to an unwarped corneal surface image is shown in Figure 9, where the influence of the iris color is largely eliminated. In addition, we generated a special unwarped image to confirm the linearity and parallelism. The left image in Figure 10 was captured when a user looked at a chess pattern on a display and the center image was generated as the unwarped image. The right image is the result obtained after detecting a chess pattern. The chess pattern was extracted correctly, which confirmed that the distortion was corrected.
(8)
where rc is the radius of the corneal sphere, which was set as approximately 7.8 mm. When computing the reflection point, the pixel values of the tangent plane are obtained from the input image by inverse ray tracing. Figure 8 shows the results after correcting the image distortion, where the focused object (e.g., a human face) is extracted continuously using the head-mounted device. The image generated is determined largely by the iris color, as shown in Figure 8. As mentioned below, the algorithms used to estimate the focused object depend on the intensity alone, so color correction is not indispensable during eye-based interaction. However, if the proposed system is regarded as a measurement system, color correction is required to improve the visibility. In a previous study (Wang, Lin, Liu, & Kang, 2005), the problems of the color and texture of the eye were also addressed. They showed that the reflection is ambiguous for a light-colored eye, such as blue or green. In addition, they proposed a method for separating corneal reflections in human iris images. In their method, both the left and right iris are used to compute the corresponding illumination; thus, we cannot separate reflections using their method. However, it is possible to improve the color of an unwarped image based on assumption they employed. Various algorithms have been developed for achieving color constancy such as the Gray World Assumption (). The result obtained after applying this algorithm to an unwarped corneal surface image is shown in Figure 9, where the influence of the iris color is largely eliminated. In addition, we generated a special unwarped image to confirm the linearity and parallelism. The left image in Figure 10 was captured when a user looked at a chess pattern on a display and the center image was generated as the unwarped image. The right image is the result obtained after detecting a chess pattern. The chess pattern was extracted correctly, which confirmed that the distortion was corrected.
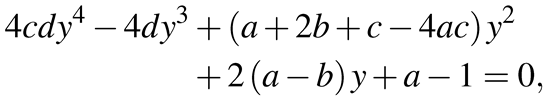 (7)
(7)
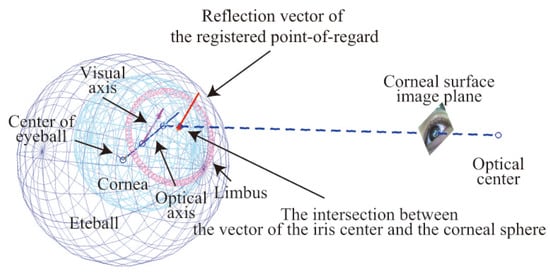
Figure 6.
The intersection between the center of the iris, the corneal sphere, and the visual axis.
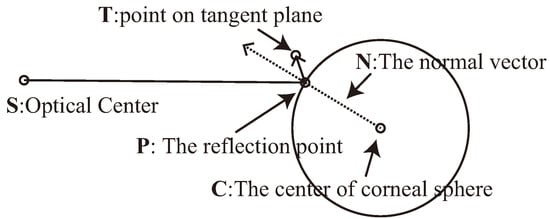
Figure 7.
Geometric model of reflection on the corneal surface.
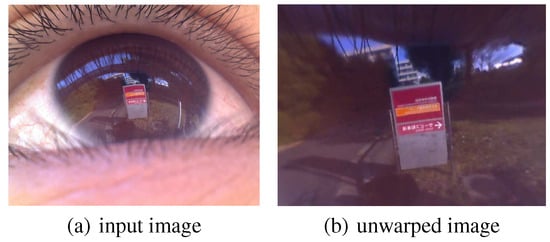
Figure 8.
Results obtained after generating an unwarped corneal surface image. The left and right images are the input image and the generated unwarped corneal surface image, respectively.

Figure 9.
Result after color correction. The left and right images are the original unwarped corneal image and the color-corrected unwarped image, respectively.
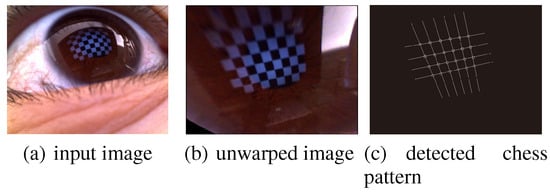
Figure 10.
Linearity and parallelism of an unwarped corneal surface image. The left image is the corneal surface image where the chess pattern is reflected. The middle image is the unwarped corneal surface image, which was generated to confirm the linearity and parallelism. The right image shows the result obtained after detecting the chess pattern.
Model-based tracking to generate unwarped images
To generate unwarped images continuously, a 3D eyeball is computed as well as a 3D cornea, as mentioned previously. The size of the eyeball is set using anatomically-based data and the center of the eyeball is used as the center of rotation. The angles of pitch θ and yaw ψ are changed step-by-step to detect the iris area (Figure 11). After the angles have been changed in the model, the iris area of the model is projected onto a binary image. We compute the position of the eye and the image plane; thus it is possible to simulate the iris area of each angle on an image plane. The sum of the logical product of the inverted binary image Bij (Figure 12(a)) and the projected iris area Iθψij (Figure 12(b)) are computed as shown in Figure 12(c). After obtaining the maximum summed values have been obtained, the two optimal angles , puted using the following equation:
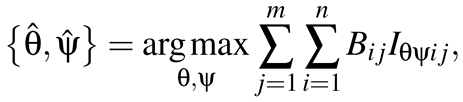 (9)
where Bij and Iθψij are binary data, and i,j are the image coordinates. In the current implementation, the optimal angles are computed using a greedy algorithm. Figure 12(d) shows the sums of the logical product, where the maximum value can be computed uniquely. Finally, the corneal limbus can be estimated as shown in Figure 13 and the unwarped images are generated continuously.
(9)
where Bij and Iθψij are binary data, and i,j are the image coordinates. In the current implementation, the optimal angles are computed using a greedy algorithm. Figure 12(d) shows the sums of the logical product, where the maximum value can be computed uniquely. Finally, the corneal limbus can be estimated as shown in Figure 13 and the unwarped images are generated continuously.
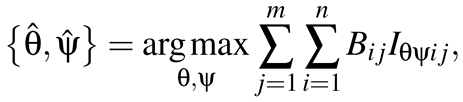 (9)
(9)
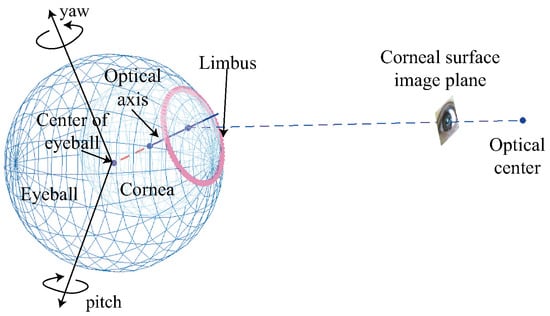
Figure 11.
A 3D eyeball model with an eyeball, cornea, and corneal limbus.
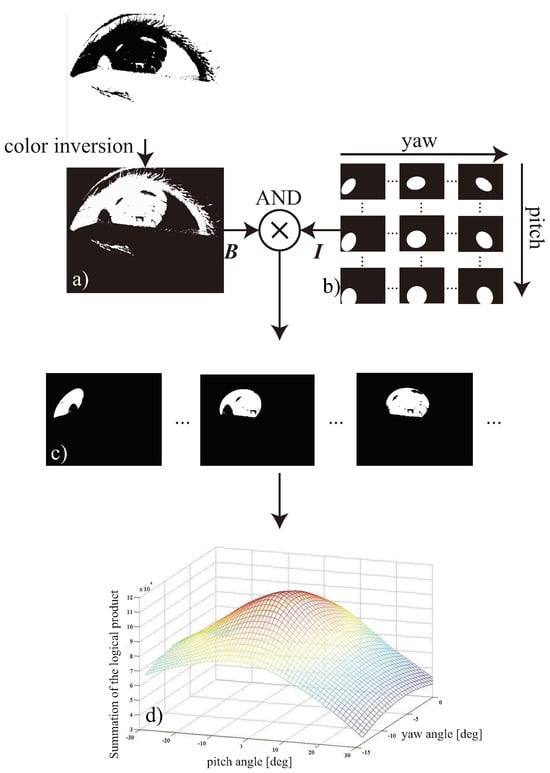
Figure 12.
Algorithm for iris tracking using the 3D eye model. An inverted binary image of an eye (a) and the simulated images of the iris area (b) are used to compute the logical product of these image (c). In addition, the iris area is detected when the maximum value is found in the summed values of the logical product (d).
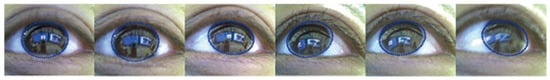
Figure 13.
Results of eye tracking using the 3D eye model. The estimated iris areas are indicated in blue.
Specific object recognition using the unwarped corneal surface image
Ocular motion and the point-of-regard are important in conventional eye-tracking systems. However, it is difficult to use this information directly in user interfaces and humancomputer interaction via a head-mounted eye tracker. It is necessary to identify the object that the user is focused upon to apply eye-tracking systems to navigation and guidance systems. To achieve this, we used a simple technique for specific object recognition and conducted an experiment to evaluate the results of specific object recognition with unwarped corneal surface images. Eight outdoor direction boards were located around the university in the evaluation and corneal images were obtained when participants looked at these boards. Figure 14 shows the results of specific object recognition using the scale-invariant feature transform (SIFT) feature (). The white rectangle in each image is the area of the direction board, which was estimated using RANSAC ().

Figure 14.
Results after recognizing focused objects using SIFT. The corresponding points are indicated in light blue, and the white rectangle shows an area of the estimated object.
The average correspondence errors between the registered template and the unwarped corneal surface image,
, are calculated using the following equation:
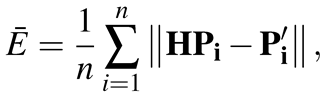 (10)
where Pi is a feature of the unwarped corneal surface image and is a feature of the registered template. The homography matrix, H, is calculated based on four points, which are selected manually from the registered image and the unwarped corneal surface image. Figure 15 shows the correspondence errors for the eight direction boards. Overall, matching was achieved with high accuracy. The average error was higher in the case of object A, mainly because similar characters were present in object A. However, we confirmed the feasibility of specific object recognition with an unwarped corneal image.
(10)
where Pi is a feature of the unwarped corneal surface image and is a feature of the registered template. The homography matrix, H, is calculated based on four points, which are selected manually from the registered image and the unwarped corneal surface image. Figure 15 shows the correspondence errors for the eight direction boards. Overall, matching was achieved with high accuracy. The average error was higher in the case of object A, mainly because similar characters were present in object A. However, we confirmed the feasibility of specific object recognition with an unwarped corneal image.
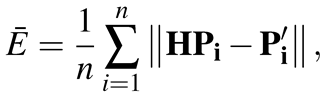 (10)
(10)
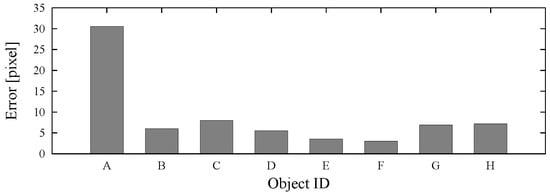
Figure 15.
Average correspondence errors between the registered templates and the unwarped corneal surface images.
Extracting the focused object
A focused object can be recognized based on its SIFT features, as mentioned previously. However, the focused object cannot be detected if there are two objects on a corneal surface image. Thus, it is important to set the tangent plane appropriately using the reflection point of the point-of-regard. However, the point-of-regard cannot be estimated correctly unless the distance is known to the focused object. Therefore, we assume that the reflection point of the point-of-regard is the center of the iris.
Experimental conditions
We conducted an experiment to extract the object of focus to confirm the feasibility of our method. Figure 16(a) shows the experimental conditions where the subjects looked at the crosses using a head positioner. In this experiment, the distance between the display screen and the subjects was 700 mm and subjects observed nine crosses, as shown in Figure 16(b). There were five trial subjects and when the trial subjects looked at the markers, we measured the distance between the center of the marker and the center of the tangent plane to compute the estimated accuracy. In addition, we carried out other experiment to evaluate the influence of the selected parameters of 3D eye model. The selected models are shown in Table 1, and we also measured the estimated accuracy. There were five other trial subjects and the experiment was conducted under the same experimental conditions as described above
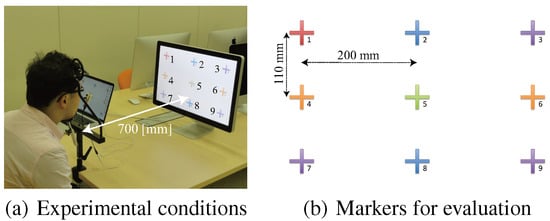
Figure 16.
The left image is a snapshot from the evaluation experiment. The trial subjects were seated 700 mm from the front of a 24-inch display, which showed nine markers. The right image is the marker used in the evaluation. The trial subjects looked at these markers in order.

Table 1.
Anatomically-based data employed for creating a 3D eye model and tracking iris.
Results and discussion
We compared the center of the tangent plane with the ground truth and the results are summarized in Figure 17.
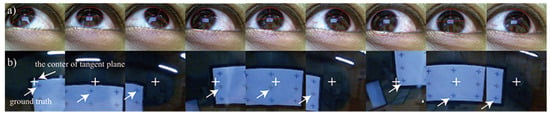
Figure 17.
Results of model-based tracking and the unwarped images obtained. The upper figures are the results obtained when tracking the iris areas, where the estimated iris areas are indicated in red. The lower figures are the unwarped images, which were generated around the center of the iris, where the white crosses and arrows are the center of the unwarped image and the focused marker, respectively.
Unwarped images were generated after a user looked at the nine crosses on the display screen and the ground truths were identified manually. Figure 18(a)-(e) shows the estimated angular error for each trial subject. The average angular error was about 9.5 degrees, as shown in Figure 18(f). In Figure 18(f), the standard deviation is very high, which was caused mainly by individual differences, whereas the standard deviation is not high in Figure 18(a)-(e). When we analyzed the angular error of each trial subject, we found that there were regular increasing and decreasing trends. The angular error might have been caused by eye movement, i.e., the error in the 3D eye model caused significant errors. At present, the parameters of the 3D eye model are set using anatomicallybased data, thus we compared the influence of the selected eyeball model. When various 3D eye models are employed, the average angular errors of point-of-regard are shown in Figure 19. The average angular errors largely depend on the model selected, because the model is also used for iris tracking. Currently, we employ the parameters for model F and the estimated results are comparatively stable. However, this is not a suitable model for each person. In a previous study, a method for the automatic acquisition of a 3D eye model was proposed (). Thus, if it is necessary to improve the precision of the 3D eye model, we could apply this method in our future research. The angular error is not small, but it is sufficient to meet the needs of a guidance system or a navigation system. If a user focuses on an object at a distance of 2.0 m, the error is within 350 mm. Therefore, it will be possible for a user to navigate based on the focused object.
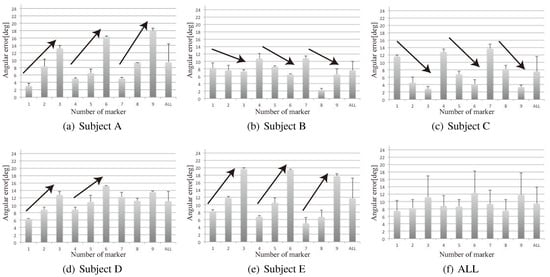
Figure 18.
Average angular error of the estimated point-of-regard in the evaluation experiment.
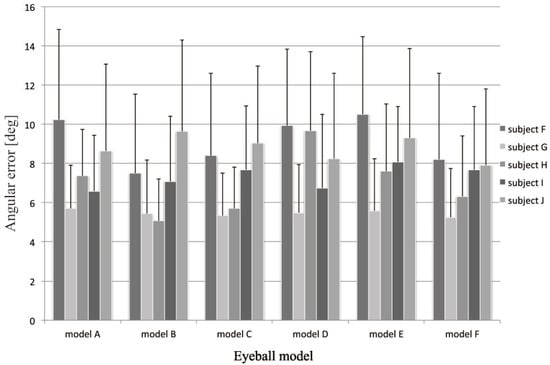
Figure 19.
Comparison of results obtained using different anatomically-based models.
Figure 20 shows the results obtained after extracting the focused objects based on the center of the iris in various situations. The first image shows the user’s cornea when they met a friend. The second image shows the user’s cornea when they looked at two books. The corneal image was extracted correctly in both cases. However, we are aware of two problems with the proposed system. The first is its dependency on the illumination conditions, where a reflected image might be reasonably clear outdoors, but it is difficult to obtain a clear image indoors unless the corneal image is captured with good illumination. The second is the distance to the point-of-regard. Thus, when a driver looks into the far distance while driving a vehicle, the resulting image will lack resolution, which makes it difficult to recognize the focused object.

Figure 20.
Result obtained after extracting the focused object based on the point-of-regard in various situations.
Conclusions
In this study, we developed a wearable device for capturing corneal surface images using a device that is suitable for daily use. We found that specific object recognition could be achieved using unwarped corneal surface images. Unwarped images were generated continuously based on model-based eye tracking. We also confirmed the feasibility of our approach based on experiments.
Various techniques that use corneal surface image have been proposed but these techniques, including our method, are sensitive to the illumination conditions. If the illuminance is low, the reflection of the scene is obscured. If bright light enters an eye, the reflection of the scene disappear. Thus, further investigations are required to determine the ideal illumination conditions.
In the future, we plan to implement a portable navigation system based on the estimated focused object. This will require the solution of additional problems, such as reducing the processing time and utilizing high quality images.
Acknowledgments
Part of this research was supported by the Strategic Information and Communication R&D Promotion Programme.
References
- Buchsbaum, G. 1980. A spatial processor model for object colour perception. Journal of the Franklin Institute 310, 1: 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulling, A., D. Roggen, and G. Tröster. 2009. Wearable EOG goggles: Seamless sensing and context-awareness in everyday environments. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Smart Environments 1, 2: 8386. [Google Scholar]
- Calonder, M., V. Lepetit, C. Strecha, and P. Fua. 2010. Brief: Binary robust independent elementary features. In Proceedings of the 11th european conference on computer vision. pp. 778–792. [Google Scholar]
- Eberly, D. 2008. Computing a point of reflection on a sphere. http://www.geometrictools.com. (Online; accessed 7-Feb-2014).
- Fischler, M. A., and R. C. Bolles. 1981. Random sample consensus: a paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography. Communications of the ACM 24, 6: 381–395. [Google Scholar]
- Guestrin, E. D., and E. Eizenman. 2006. General theory of remote gaze estimation using the pupil center and corneal reflections. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering 53, 6: 1124–1133. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ishiguro, Y., A. Mujibiya, T. Miyaki, and J. Rekimoto. 2010. Aided eyes: eye activity sensing for daily life. In Proceedings of the 1st augmented human international conference. pp. 25:1–25:7. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, D. G. 2004. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. International Journal of Computer Vision 60, 2: 91–110. [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto, C. H., and M. R. M. Mimica. 2005. Eye gaze tracking techniques for interactive applications. Computer Vision Image Understanding 98, 1: 4–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamatsu, T., J. Kamahara, T. Iko, and N. Tanaka. 2008. Onepoint calibration gaze tracking based on eyeball kinematics using stereo cameras. In Proceedings of the 2008 symposium on eye tracking research & applications. pp. 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Nagamatsu, T., J. Kamahara, and N. Tanaka. 2009. Calibrationfree gaze tracking using a binocular 3d eye model. In Chi ’09 extended abstracts on human factors in computing systems. pp. 3613–3618. [Google Scholar]
- Nishino, K., and S. Nayar. 2004b. The world in an eye. In Proceedings of the 2004 ieee computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. I-444–I-451. [Google Scholar]
- Nishino, K., and S. K. Nayar. 2004a. Eyes for relighting. ACM Trans. Graph. 23, 3: 704–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitschke, C., and A. Nakazawa. 2012. Super-resolution from corneal images. In Proceedings of the 23rd british machine vision conference. pp. 22.1–22.12. [Google Scholar]
- Nitschke, C., A. Nakazawa, and H. Takemura. 2011. Displaycamera calibration using eye reflections and geometry constraints. Computer Vision and Image Understanding 115, 6: 835–853. [Google Scholar]
- Ohno, T. 2006. One-point calibration gaze tracking method. In Proceedings of the 2006 symposium on eye tracking research & applications. pp. 34–34. [Google Scholar]
- Ohno, T., and N. Mukawa. 2004. A free-head, simple calibration, gaze tracking system that enables gaze-based interaction. In Proceedings of the 2004 symposium on eye tracking research & applications. pp. 115–122. [Google Scholar]
- Tsukada, A., and T. Kanade. 2012. Automatic acquisition of a 3d eye model for a wearable first-person vision device. In Proceedings of the symposium on eye tracking research & applications. pp. 213–216. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H., S. Lin, X. Liu, and S. B. Kang. 2005. Separating reflections in human iris images for illumination estimation. In Proceedings of the tenth ieee international conference on computer vision. pp. 1691–1698. [Google Scholar]
Copyright © 2014. This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
