Efficacy and Safety of Nivolumab and Ipilimumab for Advanced or Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Multicenter Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Treatment Schedule
2.3. Patient Evaluation
2.4. Safety
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients
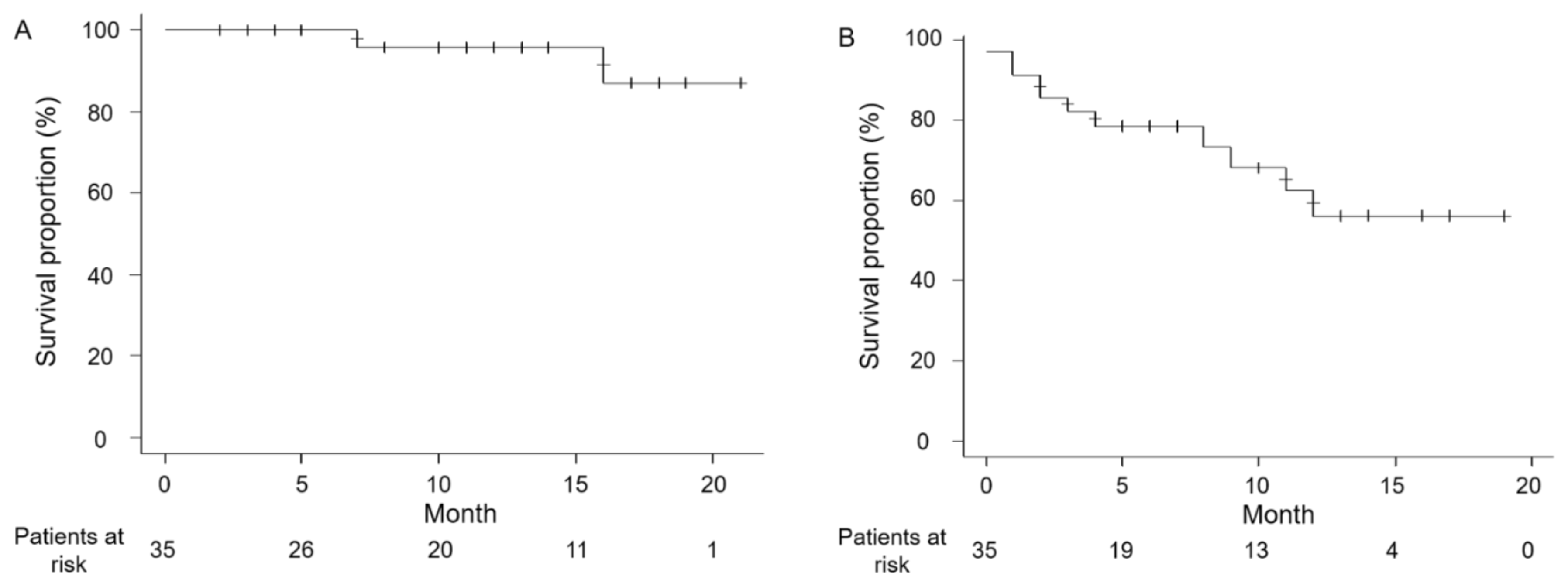
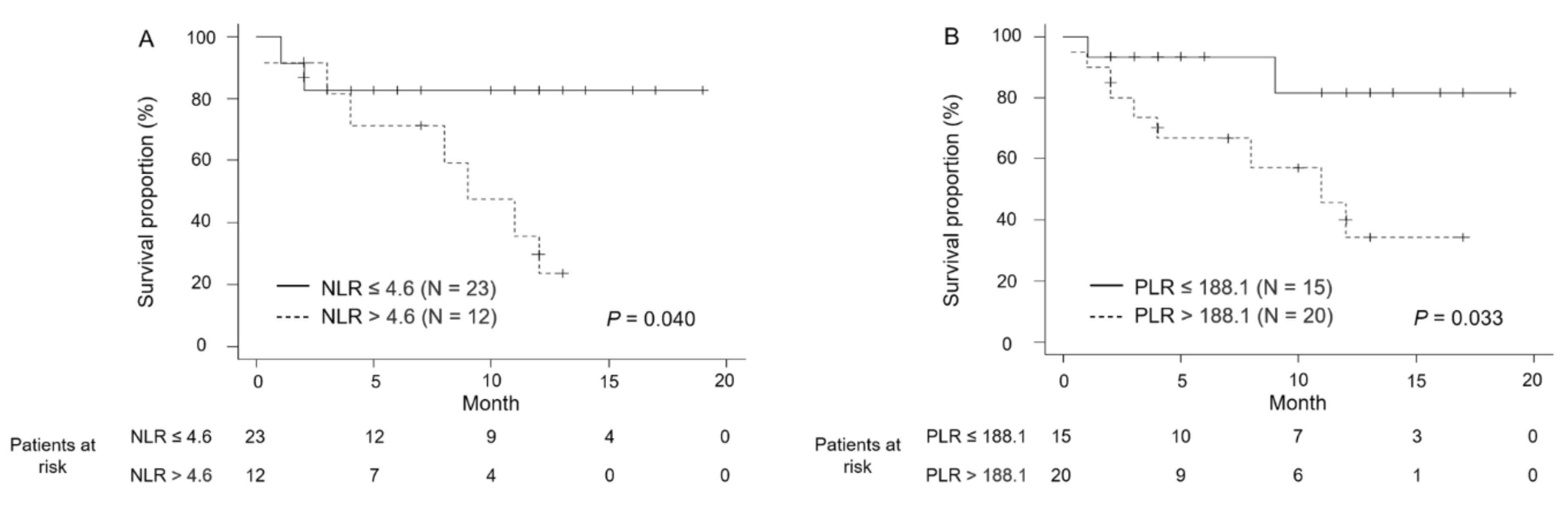
3.2. Efficacy and Oncological Outcomes
3.3. Safety
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Projected Cancer Statistics. Available online: https://ganjoho.jp/en/public/statistics/short_pred.html (accessed on 15 September 2018).
- Motzer, R.J.; Jonasch, E.; Michaelson, M.D.; Nandagopal, L.; Gore, J.L.; George, S.; Alva, A.; Haas, N.; Harrison, M.R.; Plimack, E.R.; et al. NCCN guidelines insights: Kidney cancer, version 2.2020. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2020, 17, 1278–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padala, S.A.; Barsouk, A.; Thandra, K.C.; Saginala, K.; Mohammed, A.; Vakiti, A.; Rawla, P.; Barsouk, A. Epidemiology of renal cell carcinoma. World J. Oncol. 2020, 11, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Mostafaei, H.; Miura, N.; Karakiewicz, P.I.; Luzzago, S.; Schmidinger, M.; Bruchbacher, A.; Pradere, B.; Shin Egawa, S.; Shariat, S.F. Systemic therapy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma in the first-line setting: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2021, 70, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heng, D.Y.; Xie, W.; Regan, M.M.; Warren, M.A.; Golshayan, A.R.; Sahi, C.; Eigl, B.J.; Ruether, J.D.; Cheng, T.; North, S.; et al. Prognostic factors for overall survival in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted agents: Results from a large, multicenter study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 5794–5799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heng, D.Y.; Xie, W.; Regan, M.M.; Harshman, L.C.; Bjarnason, G.A.; Vaishampayan, U.N.; Mackenzie, M.; Wood, L.; Donskov, F.; Tan, M.H.; et al. External validation and comparison with other models of the International Metastatic Renal-Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium prognostic model: A population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Escudier, B.; McDermott, D.F.; George, S.; Hammers, H.J.; Srinivas, S.; Tykodi, S.S.; Sosman, J.A.; Procopio, G.; Plimack, E.R.; et al. Nivolumab versus everolimus in advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1803–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Tannir, N.M.; McDermott, D.F.; Arén Frontera, O.; Melichar, B.; Choueiri, T.K.; Plimack, E.R.; Barthélémy, P.; Porta, C.; George, S.; et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib in advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1277–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Escudier, B.; McDermott, D.F.; Arén Frontera, O.; Melichar, B.; Powles, T.; Donskov, F.; Plimack, E.R.; Barthélémy, P.; Hammers, H.J.; et al. Survival outcomes and independent response assessment with nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma: 42-month follow-up of a randomized phase 3 clinical trial. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, Y.; Kondo, T.; Kimura, G.; Inoue, T.; Wakumoto, Y.; Yao, M.; Sugiyama, T.; Oya, M.; Fujii, Y.; Obara, W.; et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib in previously untreated advanced renal-cell carcinoma: Analysis of Japanese patients in CheckMate 214 with extended follow-up. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 50, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rini, B.I.; Plimack, E.R.; Stus, V.; Gafanov, R.; Hawkins, R.; Nosov, D.; Pouliot, F.; Alekseev, B.; Soulières, D.; Melichar, B.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1116–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rini, B.I.; Powles, T.; Atkins, M.B.; Escudier, B.; McDermott, D.F.; Suarez, C.; Bracarda, S.; Stadler, W.M.; Donskov, F.; Lee, J.L.; et al. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab versus sunitinib in patients with previously untreated metastatic renal cell carcinoma (IMmotion151): A multicentre, open-label, phase 3, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 2404–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choueiri, T.K.; Powles, T.; Burotto, M.; Bourlon, M.T.; Zurawski, B.; OyeJuárez Juárez, V.M.; Hsieh, J.J.; Basso, U.; Shah, A.Y.; Suarez, C.; et al. Nivolumab + cabozantinib vs. sunitinib in first-line treatment for advanced renal cell carcinoma: First results from the randomized phase III CheckMate 9ER trial. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31 (Suppl. 4), S1142–S1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oken, M.M.; Creech, R.H.; Tormey, D.C.; Horton, J.; Davis, T.E.; McFadden, E.T.; Carbone, P.P. Toxicity and response criteria of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 1982, 5, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edge, S.B.; Compton, C.C. The American Joint Committee on Cancer: The 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging manual and the future of TNM. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 17, 1471–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenhauer, E.A.; Therasse, P.; Bogaerts, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Sargent, D.; Ford, R.; Dancey, J.; Arbuck, S.; Gwyther, S.; Mooney, M.; et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 228–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, N.J.; Schisterman, E.F. The inconsistency of ‘optimal’ cutpoints obtained using two criteria based on the receiver operating characteristics curve. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 163, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) v5.0. Available online: https://ctep.cancer.gov/protocoldevelopment/electronic_applications/docs/ctcae_v5_quick_reference_5x7.pdf (accessed on 27 November 2017).
- Zhang, N.; Jiang, J.; Tang, S.; Sun, G. Predictive value of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-lymphocyte ratio in non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: A meta-analysis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 85, 106677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharmapuri, S.; Özbek, U.; Lin, J.Y.; Sung, M.; Schwartz, M.; Branch, A.D.; Ang, C. Predictive value of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and platelet to lymphocyte ratio in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with anti-PD-1 therapy. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 4962–4970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Giorgi, U.; Procopio, G.; Giannarelli, D.; Sabbatini, R.; Bearz, A.; Buti, S.; Basso, U.; Mitterer, M.; Ortega, C.; Bidoli, P.; et al. Association of systemic inflammation index and body mass index with survival in patients with renal cell cancer treated with nivolumab. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 3839–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; He, A.; Liu, A.; Tong, W.; Cao, D. Evaluation of the prognostic role of platelet-lymphocyte ratio in cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 77, 105957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M.; Kubo, T.; Komatsu, K.; Fujisaki, A.; Terauchi, F.; Natsui, S.; Nukui, A.; Kurokawa, S.; Morita, T. Changes in peripheral blood immune cells: Their prognostic significance in metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients treated with molecular targeted therapy. Med. Oncol. 2013, 30, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boissier, R.; Campagna, J.; Branger, N.; Karsenty, G.; Lechevallier, E. The prognostic value of the neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in renal oncology: A review. Urol. Oncol. 2017, 35, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohno, Y.; Nakashima, J.; Ohori, M.; Tanaka, A.; Hashimoto, T.; Gondo, T.; Hatano, T.; Tachibana, M. Clinical variables for predicting metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients who might not benefit from cytoreductive nephrectomy: Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and performance status. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 19, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonia, S.J.; López-Martin, J.A.; Bendell, J.; Ott, P.A.; Taylor, M.; Eder, J.P.; Jäger, D.; Pietanza, M.C.; Le, D.T.; de Braud, F.; et al. Nivolumab alone and nivolumab plus ipilimumab in recurrent small-cell lung cancer (CheckMate 032): A multicentre, open-label, phase 1/2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 883–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellmann, M.D.; Rizvi, N.A.; Goldman, J.W.; Gettinger, S.N.; Borghaei, H.; Brahmer, J.R.; Ready, N.E.; Gerber, D.E.; Chow, L.Q.; Juergens, R.A.; et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab as first-line treatment for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (CheckMate 012): Results of an open-label, phase 1, multicohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, Y.; Naito, S.; Sassa, N.; Takahashi, A.; Kondo, T.; Koie, T.; Obara, W.; Kobayashi, Y.; Teishima, J.; Takahashi, M.; et al. Sunitinib versus sorafenib as initial targeted therapy for mCC-RCC with favorable/intermediate risk: Multicenter randomized trial CROSS-J-RCC. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2020, 18, e374–e385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, M.W.; Ngiow, S.F.; Ribas, A.; Smyth, M.J. Classifying cancer based on T-cell infiltration and PD-L1. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 2139–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.M.; Nirschl, T.R.; Nirschl, C.J.; Francica, B.J.; Kochel, C.M.; van Boknoven, A.; Meeker, A.K.; Lucia, M.S.; Anders, R.A.; DeMarzo, A.M.; et al. Paucity of PD-L1 expression in prostate cancer: Innate and adaptive immune resistance. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2015, 18, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Number | 35 |
|---|---|
| Age (year, median, interquartile range) | 69.0 (58.0–76.0) |
| Gender (number, %) | |
| Male | 26 (74.3) |
| Female | 9 (25.7) |
| Body mass index (kg/m2, median interquartile range) | 23.8 (20.7–25.7) |
| The Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status (number, %) | |
| 0 | 20 (57.2) |
| 1 | 7 (20.0) |
| 2 | 4 (11.4) |
| 3 | 4 (11.4) |
| IMDC model (number, %) | |
| Intermediate-risk | 23 (65.7) |
| Poor-risk | 12 (34.3) |
| Histology | |
| Clear cell renal cell carcinoma | 22 (62.9) |
| Papillary renal cell carcinoma | 1 (2.8) |
| Unknown | 12 (34.3) |
| Neutrophil counts (×109/L, median, interquartile range) | 1.4 (1.1–1.8) |
| Lymphocyte counts (×109/L, median, interquartile range) | 4.5 (3.8–5.6) |
| Platelet counts (×109/L, median, interquartile range) | 265 (213–348) |
| Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (median, interquartile range) | 3.5 (2.5–4.9) |
| Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (median, interquartile range) | 215.6 (138.6–316.3) |
| The patients who underwent surgery before the administration of NIVO+IPI (number, %) | 19 (54.3) |
| Number of metastatic sites | |
| 0 | 4 (11.5) |
| 1 | 11 (31.4) |
| 2 | 11 (31.4) |
| ≥3 | 9 (25.7) |
| Total number of metastatic sites (number, %) | |
| Lung | 19 (54.3) |
| Lymph node | 14 (40.0) |
| Bone | 12 (34.3) |
| Liver | 7 (20.0) |
| Adrenal gland | 5 (14.3) |
| Pancreas | 2 (5.7) |
| Local recurrence | 2 (5.7) |
| Others | 4 (11.4) |
| Number | 35 |
|---|---|
| Objective response rate (CR + PR, number, %) | 12 (34.3) |
| Disease control rate (CR + PR + SD, number, %) | 28 (80.0) |
| Best overall response (number, %, 95% CI) | |
| CR | 3 (8.6) |
| PR | 9 (25.7) |
| SD | 16 (45.7) |
| PD | 7 (23.5) |
| N | Hazard Ratio | 95% Confidence Interval | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | ||||
| ≤69 | 18 | 2.38 | 0.57–9.9 | 0.233 |
| >69 | 17 | 1 (ref.) | - | - |
| Gender | ||||
| Male | 26 | 3.63 | 0.68–19.3 | 0.130 |
| Female | 9 | 1 (ref.) | - | - |
| IMDC risk classification | ||||
| Poor | 12 | 6.09 | 1.08–34.1 | 0.040 |
| Intermediate | 23 | 1 (ref.) | - | - |
| Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio | ||||
| >4.6 | 12 | 2.73 | 0.58–12.9 | 0.204 |
| ≤4.6 | 23 | 1 (ref.) | - | - |
| Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio | ||||
| >188.1 | 20 | 9.46 | 1.51–58.9 | 0.016 |
| ≤188.1 | 15 | 1 (ref.) | - | - |
| Event (Number, %) | Any Grade | Grade 3/4 |
|---|---|---|
| Treatment-related adverse events | 25 (71.4) | 15 (42.9) |
| Hypopituitarism | 5 (14.3) | 3 (8.6) |
| Maculopapular rash | 5 (14.3) | 0 |
| Colitis | 4 (11.4) | 3 (8.6) |
| Hypothyroidism | 4 (11.4) | 2 (5.7) |
| Pneumonitis | 4 (11.4) | 0 |
| Arthritis | 3 (8.6) | 2 (5.7) |
| Pruritus | 3 (8.6) | 0 |
| Increased AST | 2 (5.7) | 2 (5.7) |
| Increased ALT | 2(5.7) | 2 (5.7) |
| Myalgia | 2 (5.7) | 1 (2.9) |
| Weight loss | 2 (5.7) | 0 |
| Hyperglycemia | 1 (2.9) | 1 (2.9) |
| Urticaria | 1 (2.9) | 0 |
| Hyperthyroidism | 1 (2.9) | 0 |
| Increased creatinine | 1 (2.9) | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iinuma, K.; Kameyama, K.; Kawada, K.; Fujimoto, S.; Takagi, K.; Nagai, S.; Ito, H.; Ishida, T.; Kawase, M.; Kawase, K.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Nivolumab and Ipilimumab for Advanced or Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Multicenter Retrospective Cohort Study. Curr. Oncol. 2021, 28, 1402-1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28020133
Iinuma K, Kameyama K, Kawada K, Fujimoto S, Takagi K, Nagai S, Ito H, Ishida T, Kawase M, Kawase K, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Nivolumab and Ipilimumab for Advanced or Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Multicenter Retrospective Cohort Study. Current Oncology. 2021; 28(2):1402-1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28020133
Chicago/Turabian StyleIinuma, Koji, Koji Kameyama, Kei Kawada, Shota Fujimoto, Kimiaki Takagi, Shingo Nagai, Hiroki Ito, Takashi Ishida, Makoto Kawase, Kota Kawase, and et al. 2021. "Efficacy and Safety of Nivolumab and Ipilimumab for Advanced or Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Multicenter Retrospective Cohort Study" Current Oncology 28, no. 2: 1402-1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28020133
APA StyleIinuma, K., Kameyama, K., Kawada, K., Fujimoto, S., Takagi, K., Nagai, S., Ito, H., Ishida, T., Kawase, M., Kawase, K., Nakai, C., Kato, D., Takai, M., Nakane, K., & Koie, T. (2021). Efficacy and Safety of Nivolumab and Ipilimumab for Advanced or Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Multicenter Retrospective Cohort Study. Current Oncology, 28(2), 1402-1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28020133







