Abstract
Ciguatoxins are cyclic polyether toxins, derived from marine dinoflagellates, which are responsible for the symptoms of ciguatera poisoning. Ingestion of tropical and subtropical fin fish contaminated by ciguatoxins results in an illness characterised by neurological, cardiovascular and gastrointestinal disorders. The pharmacology of ciguatoxins is characterised by their ability to cause persistent activation of voltage-gated sodium channels, to increase neuronal excitability and neurotransmitter release, to impair synaptic vesicle recycling, and to cause cell swelling. It is these effects, in combination with an action to block voltage-gated potassium channels at high doses, which are believed to underlie the complex of symptoms associated with ciguatera. This review examines the sources, structures and pharmacology of ciguatoxins. In particular, attention is placed on their cellular modes of actions to modulate voltage-gated ion channels and other Na+-dependent mechanisms in numerous cell types and to current approaches for detection and treatment of ciguatera.
1. Ciguatoxins: Sources and structures
The increased harvesting of marine resources and the advancement of rapid cold transport and shipping technologies has resulted in an increasing incidence of human intoxication associated with fish consumption. In terms of the number and severity of poisoning events, ciguatera is arguably the most significant form of these fish toxicoses. Ciguatera poisoning is a type of ichthyosarcotoxism that occurs as a consequence of eating certain tropical and sub-tropical reef fish species from the Indo-Pacific Oceans and Caribbean Sea that have bioaccumulated the marine neurotoxin, ciguatoxin (CTX). The ciguatoxins are derived from blooms of certain strains of epiphytic benthic marine dinoflagellates. This link was not established until 1977, when a Japanese/French team led by Takeshi Yasumoto and Raymond Bagnis found large numbers of a species of dinoflagellate in a toxic sample of detritus collected in the Gambier Islands in French Polynesia during a large ciguatera outbreak [1]. This organism was linked to the production of ciguatera toxins in the Pacific and was subsequently named Gambierdiscus toxicus (Dinophyceae) [2] (Fig. 1B).
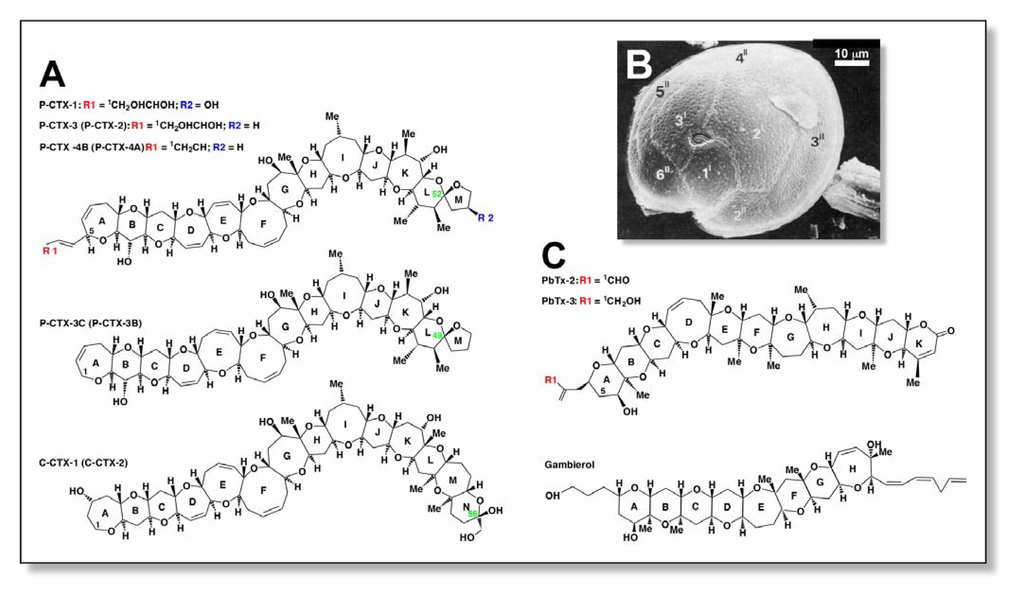
Figure 1.
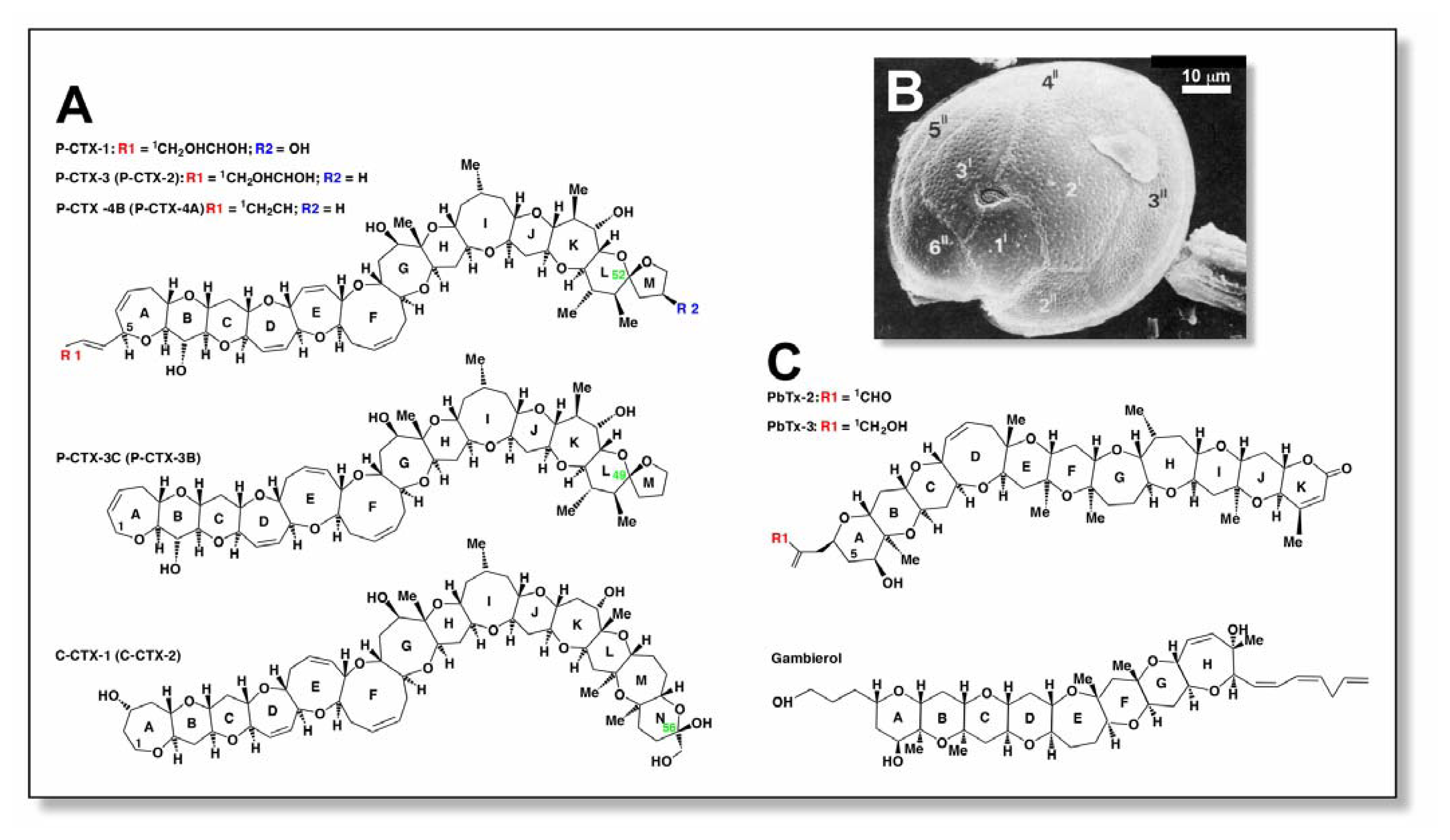
Structures and sources of ciguatoxins and related marine neurotoxins. (A) Structures of ciguatoxins from the Pacific Ocean and Caribbean Sea. Shown are P-CTX-1 [4], P-CTX-3 [5], P-CTX-4B (formerly GT-4B; [4]), P-CTX-3C [13], and C-CTX-1 [11]. The less energetically favourable epimers P-CTX-2 (52-epi P-CTX-3; ring L)[15], P-CTX-4A (52-epi GT-4B; ring L)[30], P-CTX-3B (49-epi P-CTX-3C; ring L), and C-CTX-2 (56-epi C-CTX-1; ring N)[11] are indicated in parenthesis and epimerisation positions indicated in green text. (B) Scanning electron micrograph of G. toxicus showing epithecal morphology and ‘fish hook’ shaped apical pore (photo taken by R.J. Lewis). Thecal plates are labelled according to [2]. (C) Structures of structurally-related brevetoxins (PbTx-2 [31]; PbTx-3 [32]) and gambierol [29] are shown for comparison.
Ciguatera can be defined as an illness caused by the consumption of orally effective levels of polyether toxins (ciguatoxins), and is characterised by neurological, cardiovascular and gastrointestinal disorders in humans. Ciguatoxins are a family of heat-stable, highly oxygenated, lipid-soluble cyclic polyethers with molecular weights of ~1000–1150 Da [3–10]. Given that there are numerous variants, it has been proposed that a letter code prefix be used to indicate ciguatoxin homologues isolated from the Pacific Ocean (P-CTX), Indian Ocean (I-CTX) and Caribbean Sea (C-CTX) [11]. The chemical structures of a number of Pacific ciguatoxins, from piscine and dinoflagellate sources, have been elucidated using nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy [4,5,12–16]. Recently, the structures of C-CTX-1 and C-CTX-2 from Caribbean fish have also been elucidated [3]. The most notable feature, common to all ciguatoxins, is the long semi-rigid architecture that comprises trans/syn-fused ether rings of various sizes (Fig. 1A). They have structures that are similar to brevetoxins (PbTx), another family of lipid-soluble polyether toxins, produced by the marine dinoflagellate Karenia brevis (formerly Gymnodinium breve and Ptychodiscus brevis) (Fig. 1C). Several different ciguatoxins have been isolated from biodetritus containing wild G. toxicus[4,12,17,18], from toxic strains of cultured dinoflagellates isolated from different parts of the world [13,14,17] or from various ciguateric fish [11,18–21]. Of all the different strains, P-CTX-1 is the most potent, with a median lethal dose (LD50) in mice of 0.25 μg/kg i.p. (Table 1) [4,5]. The toxins originally derive from precursors found in Gambierdiscus spp. These dinoflagellates produce less polar and less potent ciguatoxins (formerly known as gambiertoxins) that are biotransformed into more polar ciguatoxins in the liver of fish by oxidative metabolism and spiroisomerisation. For example, examination of the chemical structure of ciguatoxins suggests that P-CTX-1, extracted from the moray-eel Gymnothorax javanicus, arises from the acid-catalysed spiroisomerisation and oxidative modification of P-CTX-4A produced by G. toxicus[4,16,22,23]. More recently, several new Gambierdiscus species, namely, G. belizeanus[24], G. yasumotoi,[25], G. polynesiensis, G. australes, and G. pacificus[26] have been described that may be causative agents in ciguatera fish poisoning, along with G. toxicus, however, further research into their toxicity is required. Other toxins such as gambierol (Fig. 1C) isolated from G. toxicus are implicated in ciguatera [27–29] but their role is yet to be clearly demonstrated.

Table 1.
Characteristics of structurally defined ciguatoxins from Pacific (P-CTX), Caribbean (C-CTX) and Indian (I-CTX) regions.
2. Ciguatera poisoning in humans
Available evidence indicates that each year, ciguatera poisoning affects more than 25,000 people worldwide and is the most frequent foodborne illness related to fin fish consumption, although rarely fatal [7,33–35]. Ciguatera has its greatest impact on the inhabitants of the atoll island countries of the Pacific basin [36], Caribbean and Indo-Pacific regions of the world [7,37] where fish are the primary source of dietary protein [38]. It has also been reported from more northern portions of the United States [39,40]. However, it has been reported in non-endemic regions due to the rapid transportation of ciguateric fish to other countries or areas.
Despite their potency (see Table 1), ciguatoxins rarely accumulate in fish to levels that are lethal to humans but represent the single largest cause of unpreventable fish poisoning. It was first estimated that over 400 species of fish were potentially ciguatoxic [41]. However, it is felt that the true number lies well below this figure [42,43]. Most ciguateric fish are non-migratory reef fish and can be either herbivores or carnivores. Some species, in some locations, are toxic at all times (eg. moray eels from South Tarawa in the Republic of Kiribati, 1987–1990). In most risk areas ciguateric fish of each species may comprise 10% to <0.01% of those captured. Typically, ciguatoxic fish are restricted to those species that feed on algae or detritus around coral reefs, and the larger reef carnivores that prey on the small herbivores. These fish then accumulate and metabolize ciguatoxins through the food web [42]. These include herbivorous, detritivorous, and piscivorous fish belonging to the following families: Acanthuridae (surgeonfish), Ballistidae, (triggerfish), Lutjanidae (red bass and snappers), Serranidae (coral trout, seabass and groupers), Epinephelidae (cods), Lethrinidae (emperors and scavengers), Murenidae (moray eels), Scombridae (mackerel and tunas), Carangidae (jacks and scads) and Sphyraenidae (barracuda) [44]. In Australian waters, the narrow-barred Spanish mackerel (Scomberomorus commersoni) accounts for the majority of ciguatera outbreaks [43].
The pathophysiological features and symptoms of the disease in different areas of the world have been extensively examined [36,37,43,46–54]. The symptoms of ciguatera are extremely variable and as a result misdiagnosis is common [55], although there are efforts aimed at developing a human biomarker for ciguatera fish poisoning [56]. Usually, the clinical symptoms of poisoning fall broadly into four categories: gastrointestinal, neurological and to a lesser extent, cardiovascular disturbances and a diffuse pain syndrome (Table 2). The duration, severity and number of ciguatera symptoms depends on the quantity of ciguatoxin consumed, the type of fish (herbivore vs. carnivore) and the ocean in which the fish was caught. While ciguatera has been described in nearly all tropical waters of the world, geographical differences in the clinical manifestations have been noted. For example, ingestion of ciguatoxic fish caught in Pacific and Indian waters tends to produce a higher frequency of neurological symptoms than gastrointestinal disturbances [9,43,46,57,58] while the reverse is true of following ingestion of fish from the Caribbean [47,59–61]. A further syndrome characterised by incoordination, depression, hallucinations and nightmares has also been described following poisoning from fish in the Indian Ocean [7].

Table 2.
Comparison of the common signs and symptoms in clinical cases of ciguatera fish poisoning from three Pacific regions.
The gastrointestinal symptoms are characterised by moderate to severe vomiting, diarrhoea, nausea and abdominal pain. They tend to occur within 24 h of ingestion of a toxic fish, and typically last 1–3 days [43,47,62]. However, the neurological symptoms are likely to be the most distinctive and enduring features of ciguatera poisoning. The neurological effects usually take longer to develop, but can range from less than 1 to 48 h and may last for weeks to months [43,63,64], although no prospective studies with definite cases of ingestions have been undertaken. In some cases neurological symptoms have appeared first [7]. They involve the peripheral nervous system causing weakness and diaphoresis but predominantly result in sensory neuropathies including paraesthesia of the extremities (circumoral, hands and feet), generalised pruritus, myalgia, arthralgia, heightened nociception, dysgeusiae (taste alteration), and fatigue [47,65], and a distinctive reversal or exaggerated responses to hot and cold sensation that may have an origin in peripheral [66] and/or central [67] nerves. This temperature reversal syndrome, in which victims experience painful discomfort when touching cold objects or ingesting cold fluids, is referred to as the "dry-ice phenomenon" (cold allodynia) and is considered to be almost pathognomic [68]. Temperatures below 24 to 26°C elicit these painful stimuli apparently as a result of alteration in the function of C-polymodal nociceptors that function at temperatures below ~23°C [66]. It is also seen as a clinical hallmark of ciguatera and differentiates this form of intoxication from other forms of food poisoning and mild gastroenteritis [62,69]. However, these paresthesias are ill-defined and follow no apparent dermatome distribution [70,71]. Several in vivo electrophysiological studies on patients suffering from ciguatera poisoning have also been performed. Nerve conduction studies revealed a significant slowing of distal motor and sensory conduction velocity and prolongation of the absolute refractory, relative refractory and supernormal periods have been recorded [72–74]. These findings support the assertion that ciguatoxin affects humans by activating voltage-gated sodium (Nav) channels in sensory and motor nerves [74,75]. The toxins involved in ciguatera have also been shown to exert effects on the central nervous system. Prominent symptoms include; headaches, transient blurred vision or blindness, vertigo, hallucinations, confusion, memory disturbance and occasionally convulsions and coma [47,74].
The cardiovascular symptoms are typically acute and involve bradycardia and hypotension [43,76]. Patients may require urgent care because cardiovascular symptoms are typically seen in more severe cases and may indicate a poor prognosis [77]. One extensive survey of over three thousand ciguatera patients revealed 15% had systolic blood pressures less than 100 mmHg and 13.6% had a heart rate less than 60 bpm [46].
In severe cases of ciguatera fish poisoning, death may be caused by respiratory failure due to paralysis of the respiratory musculature or complete cardiac failure [62,79]. Dehydration, which can accompany vomiting and diarrhoea in the early stages of intoxication, can also result in death, and is especially common in malnourished children who receive inadequate treatment [55]. Fortunately the mortality rate for persons with ciguatera is less than 1% in the Pacific region and is believed to be less in other endemic areas [69,80].
Another feature characteristic to ciguatera fish poisoning is that an initial intoxication does not always confer immunity. On the contrary, reports of sensitisation to the toxins responsible for ciguatera is common [42,58]. Re-occurrence of the neurological symptoms is occasionally documented and can occur years after the initial poisoning. One theory for this phenomenon is that ingested ciguatoxins may be stored or sequestered in adipose tissue and that symptoms may re-occur during periods of stress, such as exercise and weight loss [53,81]. Ingestion of alcohol and other protein-rich foods such as chicken, fish (non-contaminated) and even certain nuts have also been reported to potentiate a rise in the neurological disturbances associated with ciguatera. Electrophysiological experiments were also performed on ciguatera-poisoned rats to study the phenomenon of sensitisation or re-occurrence of symptoms after alcohol ingestion. Intraperitoneal ethyl alcohol (blood level 0.05%) was found to significantly increase the supernormal response in ciguatoxin-treated rats, supporting isolated reports that alcohol exacerbates the neurological symptoms in ciguatera poisoning [73]. In theory, any activity that may involve an increase in lipid metabolism will result in ciguatoxins entering the blood stream and a re-emergence of the chronic symptoms. Due to the high morbidity rate worldwide, caused by sensitisation to ciguatera toxins, further research into the cause of sensitisation in ciguatera fish poisoning is required.
3. Pharmacology of Ciguatoxins
Ciguatoxins have been found to be toxic in a range of animal species, especially mammals [43]. In vivo studies in a variety of fish species have also demonstrated their susceptibility to ciguatoxins. Early studies involved adding ciguatoxin to the ambient water of certain fish species, such as the guppy (Lebistes reticulatus), which resulted in death within a short time [82]. Presumably the toxin was absorbed through the gills, a route not normally encountered under natural conditions. However, non-ciguatoxic fish species, such as a surgeon fish (Acanthurus xanthopterus), became ciguatoxic after a diet consisting of fish flesh containing strains of C-CTX, without succumbing to the effects of the toxin itself [83]. This supports the hypothesis that sequestration of the toxin, distant from the site of action, may reduce toxicity.
Ciguatoxin has also been found to cause rapid hypothermia in mice [67,84]. Essentially, the mice lost the ability to regulate their own body temperature and became poikilothermic. This reduction in body core temperature was found to be due to neuroexcitatory actions of ciguatera on regions of the brain stem receiving vagal afferents and ascending pathways associated with visceral and thermoregulatory responses [67]. This unique property not only links ciguatoxin and the structurally related, but more water-soluble, maitotoxins but can also be useful in distinguishing them from other marine toxins [55].
3.1. Cardiovascular effects of ciguatoxins
Early in vitro studies found that ciguatoxin caused death by eventually blocking phrenic nerve conduction, thus causing respiratory failure [85]. Subsequent studies on anaesthetised cats [86] indicated that cardiovascular changes could also cause death. When ciguatoxin was injected intravenously it resulted in hyperventilation at low doses, and respiratory depression leading to respiratory arrest at high doses; bradycardia and impaired atrioventricular conduction at low doses, arrhythmias and ventricular tachycardia with transient hypertension at sublethal doses, and falling arterial pressure leading to complete heart failure at high doses. The local anaesthetic lidocaine, a Nav channel blocker, was effective at counteracting the effects of ciguatoxin in cats suggesting an involvement of Nav channels. The use of a variety of pharmacological receptor antagonists and bilateral adrenalectomy indicated that ciguatoxin has both central and peripheral effects [87].
Light and electron microscopy has revealed that intraperitoneal or oral administration of P-CTX-1 or P-CTX-4C to male mice causes swelling and focal necrosis on cardiac myocytes, the adrenal medulla and autonomic nerves [88]. Atropine, a muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (mAChR) antagonist, guanethidine (reduces noradrenaline release), 5-hydroxydopamine (false transmitter), or bilateral adrenalectomy had no effect on the injury to the cardiac muscle, and reserpine aggravated the clinical signs and pathological findings. This indicates that ciguatoxins have a direct action on cardiac muscle cells. In a subsequent study [89], repeated i.p. and oral administrations of 0.1 μg/kg of P-CTX-1 or P-CTX-4C to mice over 15 days resulted in marked swelling of cardiac cells and the endothelial cells lining blood capillaries of the heart. These effects reversed within 1 month after ceasing toxin administration.
Numerous in vitro studies, examining the action of ciguatoxins have also been performed on cardiac tissue. Ciguatoxin caused a rapid negative inotropic effect followed by a dominant positive inotropic effect in left atria, and positive inotropic effects in papillary muscle, by stimulating the release of excitatory and/or inhibitory neurotransmitters from innervating nerves [90–92]. A second, slower developing phase of P-CTX-1 effect on guinea pig atria and papillary muscle resulted from an additional direct action of P-CTX-1 on the myocardium [91,93]. Both the direct and indirect effects of P-CTX-1 are reversed by tetrodotoxin (TTX), a selective blocker of Nav channels. P-CTX-1 induced a depolarisation of atrial cells that was TTX-sensitive, confirming that P-CTX-1 activates cardiac Nav channels. It has been postulated that this positive inotropic action of P-CTX-1 on atrial cells is induced by an increase in the intracellular concentration of Na+. The increased Na+ influx reduces the effectiveness of the Na+-Ca2+ exchanger to remove intracellular Ca2+, leading to enhanced Ca2+-induced release of Ca2+ from calcium stores (a major source of Ca2+ for cardiac contractility) and stronger contractions [91] (see later for more details). At high doses, P-CTX-1 additionally causes negative inotropic and arrhythmic effects in guinea-pig atria and papillary muscles that are also TTX-sensitive [94].
Investigation of the action of P-CTX-1 on human atrial trabeculae revealed that P-CTX-1 also causes a large, sustained concentration-dependent positive inotropic action, similar to the effects on the atrial myocardium [92]. The use of atenolol, a selective β1-adrenoceptor antagonist without local anaesthetic-type activity, abolished the positive inotropic actions, indicating that P-CTX-1 stimulated neural elements in the tissue to release noradrenaline. Therefore the positive inotropic action of P-CTX-1 does not stem from a significant direct effect on myocardial Nav channels, as previously thought, but rather from the indirect action of β1-adrenoceptor stimulation [92]. More recently, C-CTX-1 was found to induce a TTX-sensitive reduction in the cardiac action potential duration in frog atria, presumably by stimulating the release of acetylcholine (ACh) from intrinsic autonomic nerves and stimulating M1 and M2 mAChR subtypes, accounting for the C-CTX-1-induced bradycardia [95,96].
3.2 Gastrointestinal effects of ciguatoxins
Although severe diarrhoea results from the administration of P-CTX-1 and P-CTX-4C, no morphological alterations were seen in the mucosa or muscle layers of the small intestine, except in autonomic nerve fibres and synapses [88]. Importantly, atropine suppressed the symptoms of diarrhoea indicating that ciguatoxins most likely cause a release of ACh. P-CTX-1 also caused a sustained, dose-dependent contraction of the longitudinal smooth muscle of the guinea-pig ileum [97]. At high doses of P-CTX-1, −2 and −3, these contractions last for over 20 min and were associated with bursts of contractile activity [98]. The responses to P-CTX-1 were completely blocked by atropine, TTX and low extracellular Na+ bath solution, enhanced by the acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, eserine (also called physostigmine), but was unaffected by hexamethonium, a ganglionic nicotinic ACh receptor (nAChR) blocker, or mepyramine (histamine H1 receptor antagonist) [97]. Repeated doses of P-CTX-1 are tachyphylactic and responses to nicotine are irreversibly reduced by prior exposure to P-CTX-1, −2, or −3 [97,98]. In addition, P-CTX-1 did not alter ileal responses to histamine, ACh, or 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin). These results further support the assertion that P-CTX-1 causes the release of ACh from parasympathetic cholinergic nerve terminals, the dominant autonomic innervation in the gut, via the excitation of postganglionic nerves in ilea. The tachyphylactic nature of the action of ciguatoxin suggests that nerve stimulation is followed by nerve blockade, probably as a consequence of further nerve depolarisation.
3.3. Effects of ciguatoxin on other smooth muscle
P-CTX-1 also induces a contraction of isolated guinea-pig vas deferens that is inhibited or abolished by treatment with TTX, procaine (a local anaesthetic), incubation in a low Na+ bath solution, phentolamine (a non-selective α-adrenoceptor antagonist), or guanethidine, but is not affected by the cholinergic antagonists atropine (muscarinic) or mecamylamine (nicotinic) [99]. From these results, it was suggested that P-CTX-1-induced contractions occur via the release of noradrenaline from adrenergic nerve terminals. P-CTX-1 also markedly potentiates contraction of vas deferens induced by noradrenaline, ACh, or cell depolarisation using high extracellular concentration of K+ ([K+]o), but inhibits contractile responses arising from electrically stimulated neural elements. In a subsequent study, P-CTX-induced potentiation was shown to be inhibited or abolished by TTX and Na+-deficient bath solution, and suggested that P-CTX-1 may potentiate contractile responses of vas deferens through a direct action on smooth muscle Nav channels [100]. However, subsequent studies have failed to confirm this result, instead indicating that P-CTX-1 caused potentiation only through the effects of neurally-released noradrenaline (Lewis and Hoy, unpublished results).
More recently the actions of P-CTX-1 were examined electrophysiologically on the membrane potential of smooth muscle cells from rat tail arteries [101]. Picomolar concentrations of P-CTX-1 increased the frequency of spontaneous excitatory junction potentials (EJPs) and also caused a marked and maintained membrane depolarisation. Although the threshold and latency of the EJPs were not affected by P-CTX-1, propagated impulses were blocked at ≥100 pM P-CTX-1. Spontaneous activity and the depolarisation produced by P-CTX-I were reduced in the presence of a variety of Nav channel and voltage-gated calcium (Cav) channel blockers including TTX, ω-conotoxin GVIA, or Cd2+. Subsequent addition of phentolamine repolarised the membrane, while suramin (a non-selective inhibitor of purinergic receptors) selectively abolished EJPs caused by P-CTX-1. It was concluded that P-CTX-1 releases noradrenaline and ATP by initiating the asynchronous discharge of preganglionic perivascular axons [101].
3.4. Action of ciguatoxins on ganglionic and neuromuscular transmission
Research on the action of ciguatoxin on rat brain synaptosomes by Bidard et al. [102] found that ciguatoxin stimulated the accumulation and release of the neurotransmitters γ-aminobutyric acid and dopamine. They concluded that these effects were due to the activation of Nav channels, producing a depolarisation of the synaptosomal membrane. This depolarisation would in turn open Cav channels provoking Ca2+ entry and neurotransmitter release. Studies of the neuromuscular junction using intracellular recording techniques, showed that nanomolar concentrations of P- and C-CTX-1 triggered spontaneous or repetitive endplate potentials (EPPs), in response to a single nerve stimulus [95,103]. In addition, P-CTX-1 first increases the mean quantal content of EPPs, then reduces, before finally blocking nerve-evoked transmitter release in an irreversible manner. This synaptic activity is transient, and is thought to be the result of ciguatoxin-induced depolarisation of motor nerve terminals, that eventually has an inhibitory effect [103]. The increase in quantal content could be due to an enhanced Ca2+ influx through Cav channels due to terminal depolarisation. Nevertheless, it equally could be the result of the reversed-mode operation of the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger, which allows Ca2+ entry in exchange for intracellular Na+ as reported in isolated nerve endings (see later for more details) [103–105]. Ciguatoxins also increase spontaneous quantal ACh release from motor nerve terminals, detected as an increase in miniature endplate potential (MEPP) frequency. The increase in MEPP frequency occurred even in a Ca2+-free medium supplemented with the Ca2+ chelator, EGTA, and leads to an exhaustion of neurotransmitter stores. Ultrastructural examination of these motor nerve terminals revealed both a marked depletion of synaptic vesicles and an increase in the nerve terminal perimeter, suggesting that the synaptic vesicle recycling process is impaired during the action of CTX-1 [106]. The activation of Nav channels by ciguatoxins, and the subsequent entry of Na+ into nerve terminals, appears to be responsible for the enhancement of asynchronous neurotransmitter release and the depletion of synaptic vesicles, since blockade of Na+ influx into the terminals by TTX prevents these effects.
Similar intracellular microelectrode studies of guinea-pig sympathetic ganglia showed that low nanomolar concentrations of P-CTX-1 generated a large increase in the frequency of spontaneous excitatory synaptic potentials and produced long-lasting repetitive synaptic responses to single stimuli arising from preganglionic axons [107]. However, the passive electrical properties, the amplitude and threshold of action potentials evoked by depolarising current, and the threshold, and latency of the initial responses to nerve stimulation were not affected by P-CTX-1. These effects of P-CTX-1 on sympathetic ganglia were abolished or significantly reduced by the nAChR antagonists (+)-tubocurarine and hexamethonium, as well as TTX, ω-conotoxin GVIA (a N-type Cav channel blocker), and reduced or elevated extracellular concentration of Ca2+ ([Ca2+]o) [107]. It was concluded that P-CTX-1 stimulates preganglionic axons by activating a subpopulation of Nav channels to open. These effects occurred at lower concentrations in unmyelinated than myelinated axons, suggesting that many of the symptoms of ciguatera poisoning may be explained by activity at unmyelinated nerves.
In conclusion, the pharmacological studies described above have provided evidence that ciguatoxins appear to activate Nav channels in a variety of preparations to cause depolarisation, spontaneous action potentials and an elevation of the intracellular concentration of Na+ ([Na+]i). As a consequence of these actions nerve impulses invade nerve terminals either spontaneously or in response to a single stimulus. Cav channels open during each presynaptic action potential, and the ensuing rise of intracellular Ca2+ concentration triggers the exocytosis of synaptic vesicles resulting in synchronous spontaneous or repetitive multi-quantal neurotransmitter release.
4. Actions of ciguatoxins on voltage-gated ion channels
4.1. Ciguatoxin enhances neuronal excitability
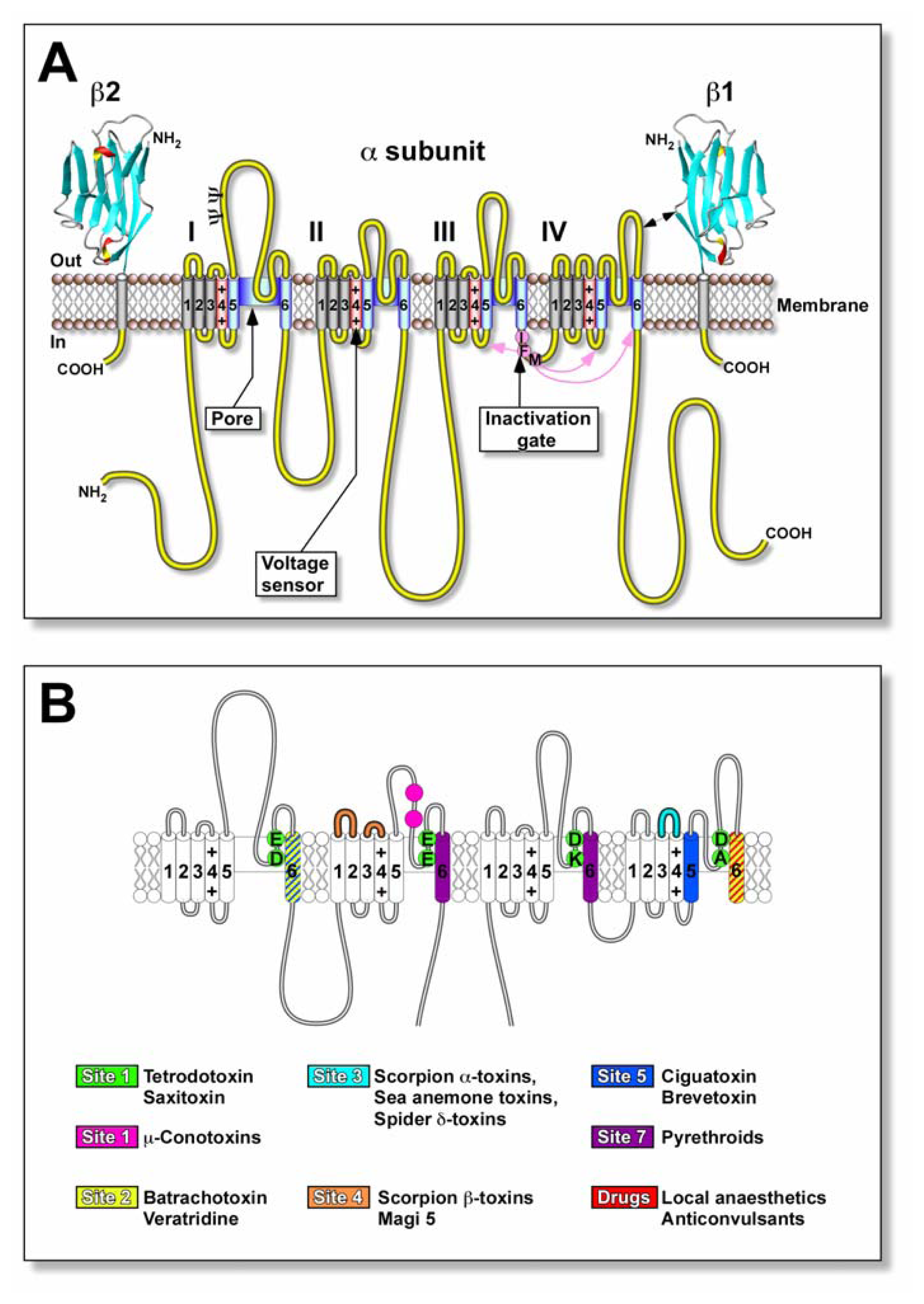
Nav channels are critical elements for the generation and propagation of electrical signals in most excitable cells. They are large membrane-spanning proteins that mediate the rapid and transient increase in membrane Na+ conductance responsible for the depolarising phase of action potentials. Their structure comprises principally of a pore-forming ~2000-residue glycoprotein α-subunit in eukaryotic Nav channels of 240–280 kDa (Fig. 2A). Each α-subunit is composed of four homologous domains (I–IV). Each domain contains six putative transmembrane α-helical segments (S1–S6) where the S4 segment from each domain form the voltage sensor. The inactivation gate is represented by an inactivation particle (hydrophobic residues IFM). The pore-lining segments S5 and S6, and intervening SS1/SS2 (P loop) form the walls of the ion-conducting pathway.
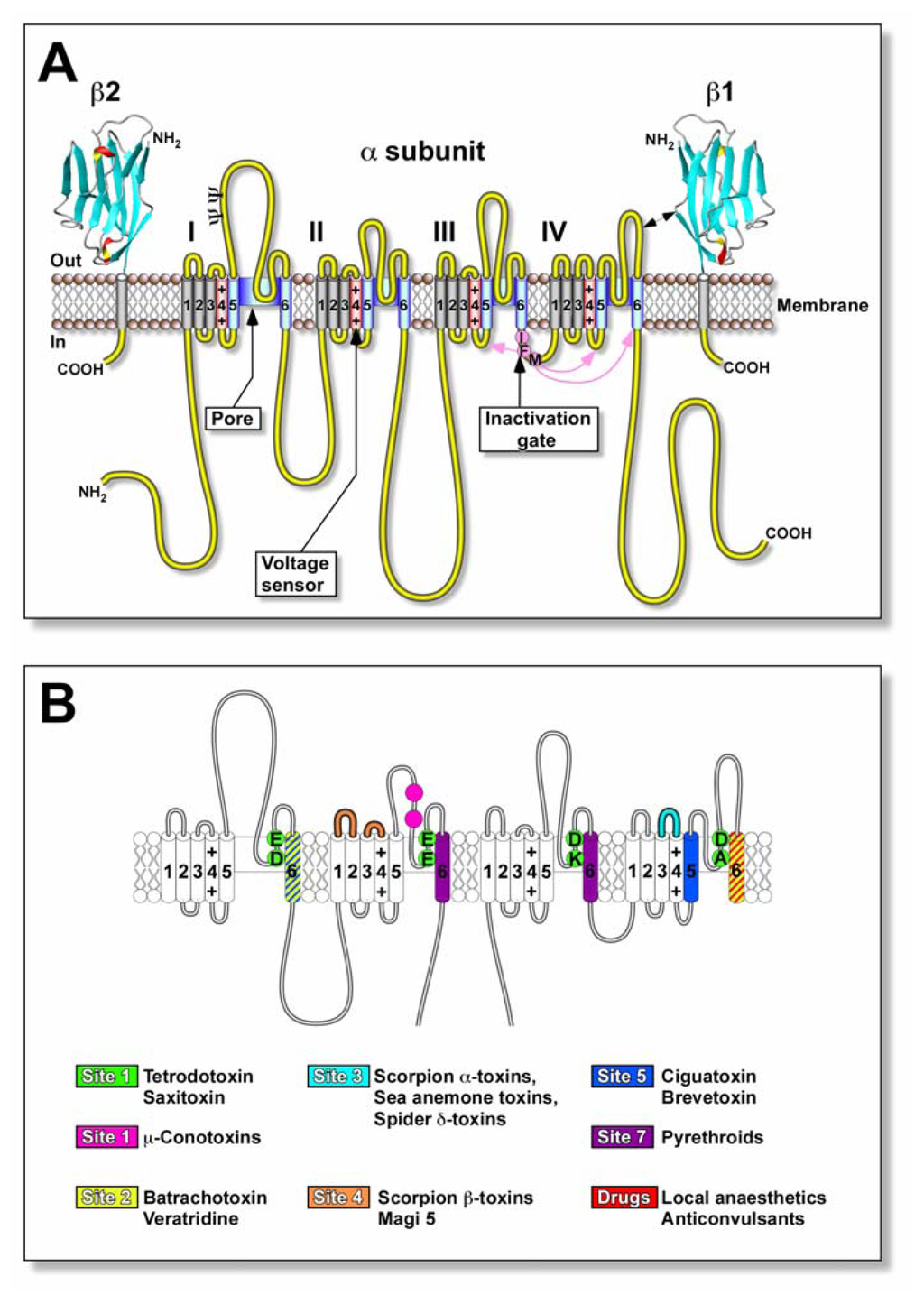
Figure 2.
Molecular structure and neurotoxin receptor sites of the Nav channel. (A) Schematic representation of the subunit structure of the Nav channel showing the functional α-subunit and ancillary β-subunits. Cylinders represent the α-helical segments where the charged S4 segments (red) represent the voltage sensors. The inactivation gate (magenta) is represented by the inactivation particle (residues IFM). The walls of the ion-conducting pathway are shown in blue. The β1 and β2 subunits are represented as immunoglobulin-like folds similar to myelin protein P0[111]. Ψ, sites of probable N-linked glycosylation. (B) Location of known neurotoxin receptor sites on Nav channels. Green circles represent the outer (EEDD) and inner (DEKA) rings of amino acid residues that form the ion selectivity filter and the proposed neurotoxin receptor site 1 for the water-soluble guanidinium.
The most dramatic discovery linking the alteration of Nav channel function with the action of ciguatoxin was that of Benoit et al. [108] who studied the effects of partially purified P-CTX-1 on current- and voltage-clamped frog myelinated nerve fibres. They found P-CTX-1, at low nanomolar concentrations, induced spontaneous action potentials that were suppressed by the addition of TTX, indicating this effect was mediated through Nav channels. This increase in membrane excitability was also observed in neuroblastoma cells where, under the appropriate conditions, P-CTX-1 induced spontaneous oscillations in the membrane potential as well as repetitive action potentials [102].
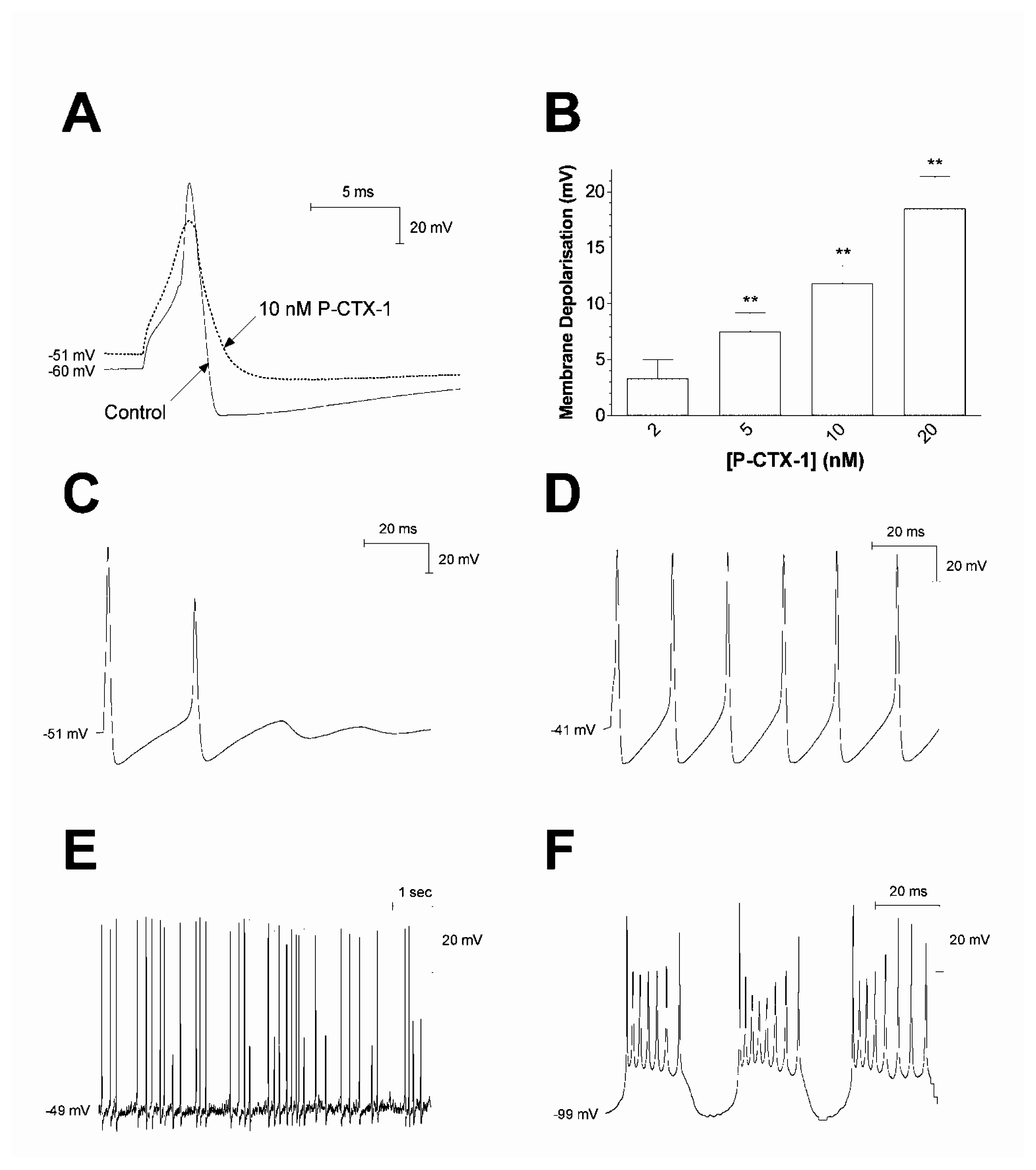
Similarly, using rat dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons under current-clamp conditions, bath application of 2–20 nM P-CTX-1 caused a rapid, concentration-dependent depolarisation of the resting membrane potential in neurons expressing TTX-sensitive Nav channels [109] (Fig. 3A). This action was completely suppressed by the addition of 200 nM TTX to the external solution. P-CTX-1 also prolonged action potential and afterhyperpolarisation duration (Fig. 3A). In a sub-population of neurons, P-CTX-1 also produced tonic action potential firing (Fig. 3C-F). Conversely, in neurons expressing TTX-resistant Nav currents, P-CTX-1 failed to alter any parameter of neuronal excitability.
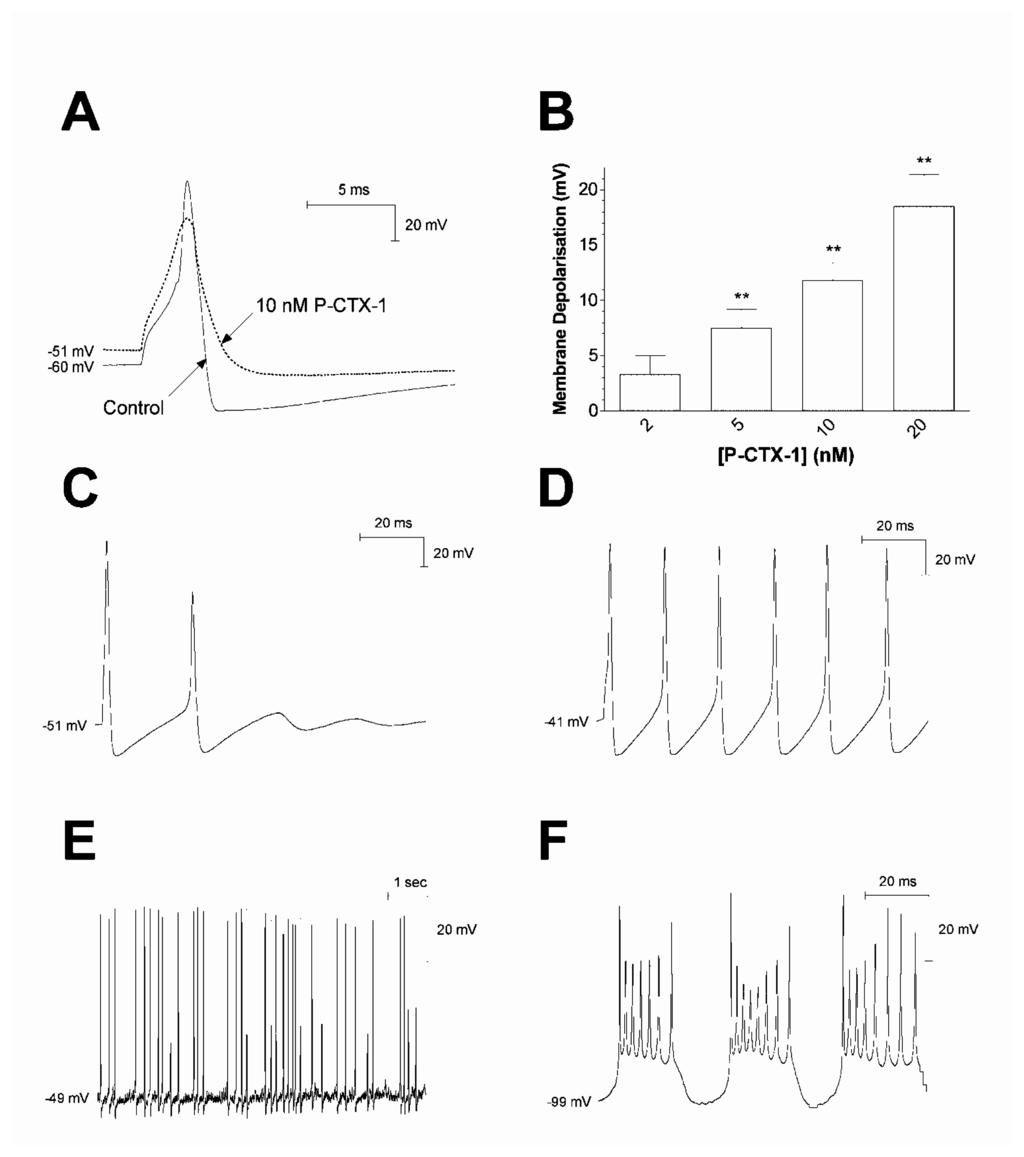
Figure 3.
Effect of P-CTX-1 on action and resting potentials in DRG neurons expressing TTX-sensitive Nav channels. (A) Superimposed typical action potentials generated, before and following a 10-min perfusion with 10 nM P-CTX-1 showing reduced spike and afterhyperpolarisation amplitude, prolongation of action potential and afterhyperpolarisation duration, and membrane depolarisation. The dotted line in represents the control resting membrane potential. (B) Concentration-dependent membrane depolarisation occurred in response to a 5–10 min perfusion with P-CTX-1 (n ≥ 5). Statistical significance indicated at the ** P <0.01 level. (C-D) Typical progression of stimulus-locked repetitive action potential firing from limited repetitive firing (C), to trains of action potentials (D), in the presence of 10 nM P-CTX-1. (E) Typical tonic action potential firing in the presence of 10 nM P-CTX-1, where spontaneous firing was not locked to a depolarising stimulus. (F) Return of repetitive firing following manual hyperpolarisation of the resting membrane potential. Modified from Birinyi-Strachan et al. [109].
Research on other ciguatoxins is less extensive, mainly due to difficulties in obtaining purified toxin. Dinoflagellate-derived ciguatoxins (formerly gambiertoxins) are not especially toxic to mammals because they are less oxidised than ciguatoxins and are only present in small quantities in fish muscle. Nevertheless, P-CTX-4B, from the dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus has effects on myelinated nerve fibres that are similar to those of P-CTX-1, but is ~ 50-fold less effective than P-CTX-1 [110].
toxins, tetrodotoxin (TTX) and saxitoxin (STX). Some of μ-conotoxin binding sites practically overlap with those of TTX and are omitted for clarity. In the case of receptor sites 3 and 4, only areas where there is more than a five-fold increase in binding affinity are highlighted. Ciguatoxins and brevetoxins bind with site 5 indicated in blue. Figure is adapted from Cestèle [112] and Nicholson [113].
4.2. Mode(s) of activation of Nav channels by ciguatoxin
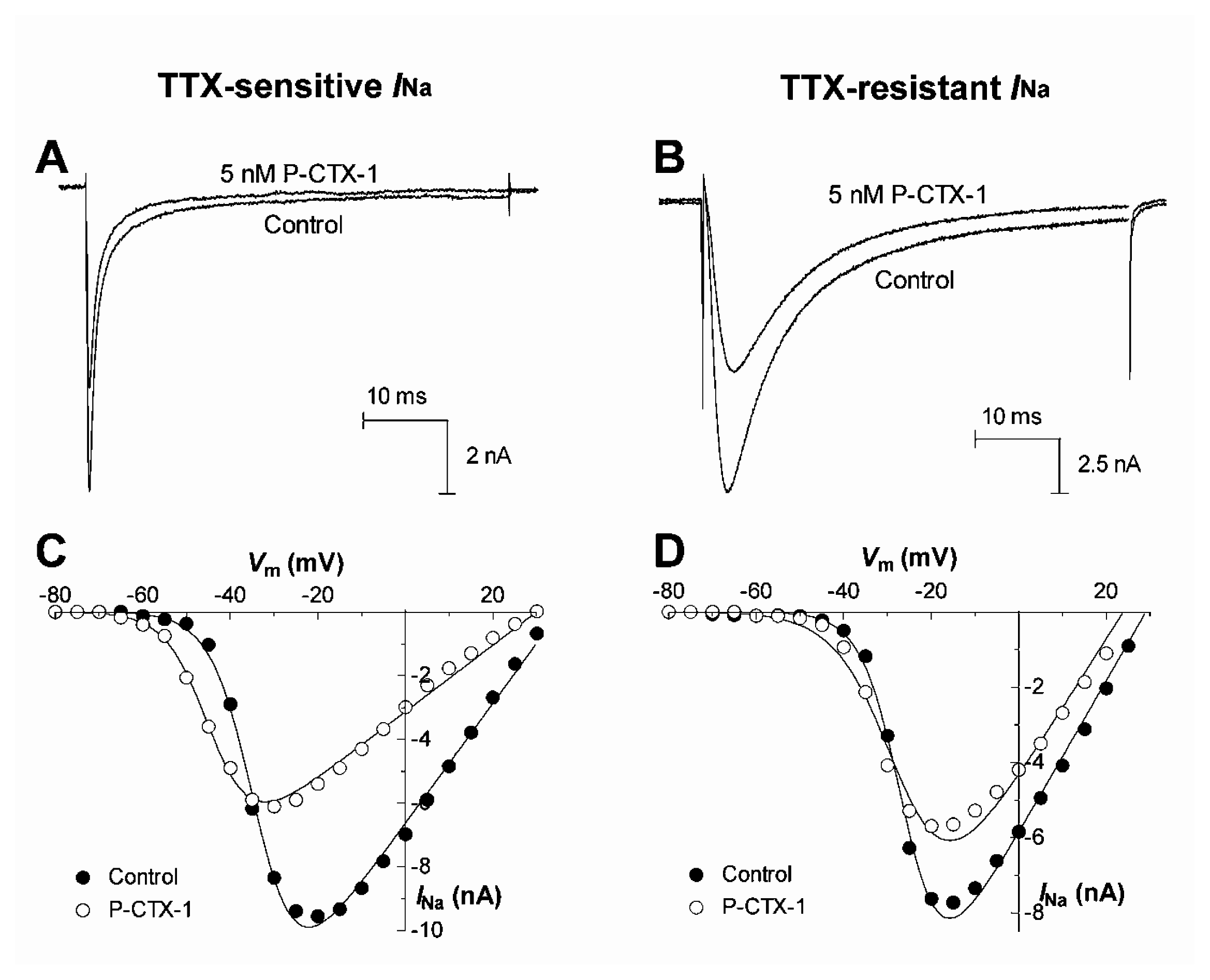
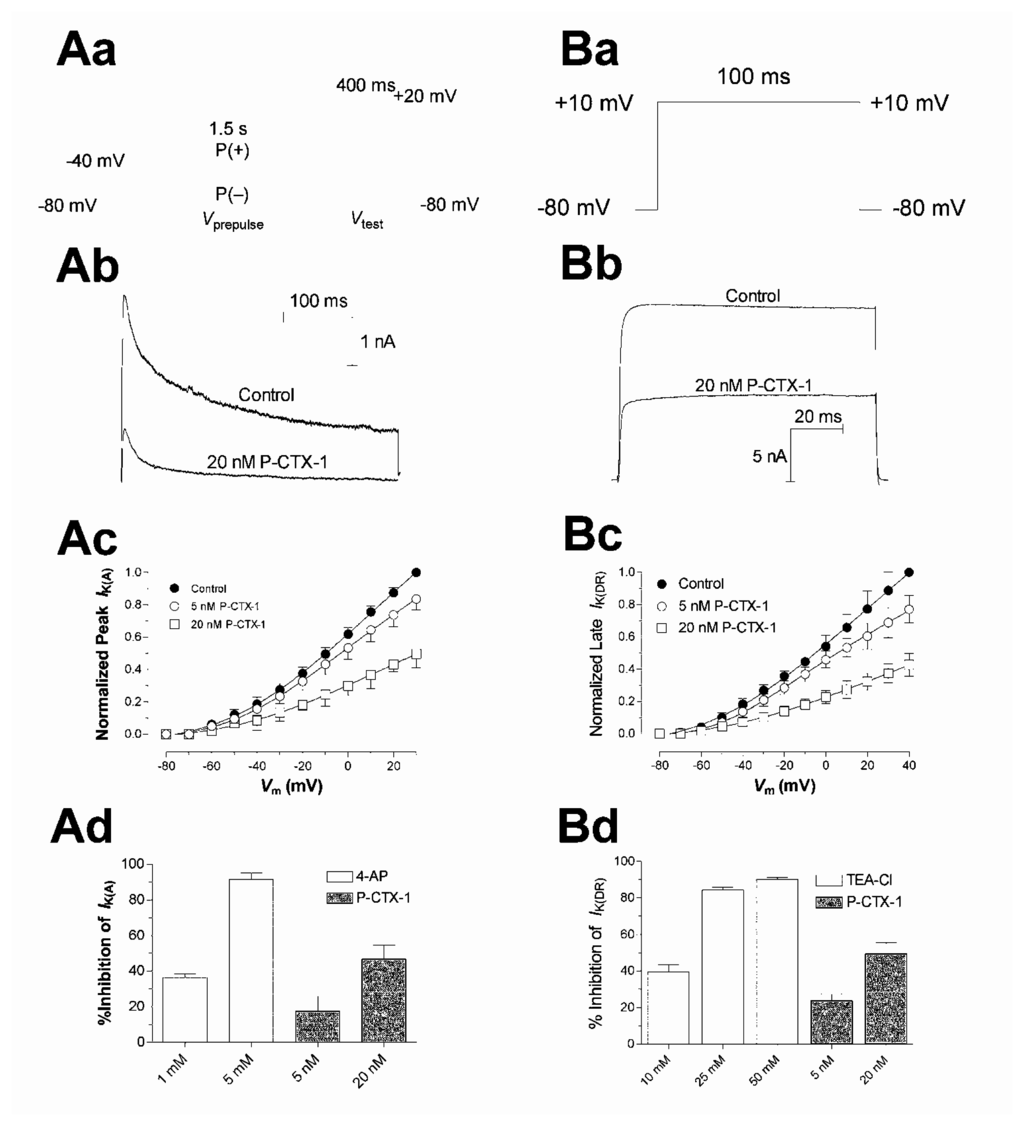
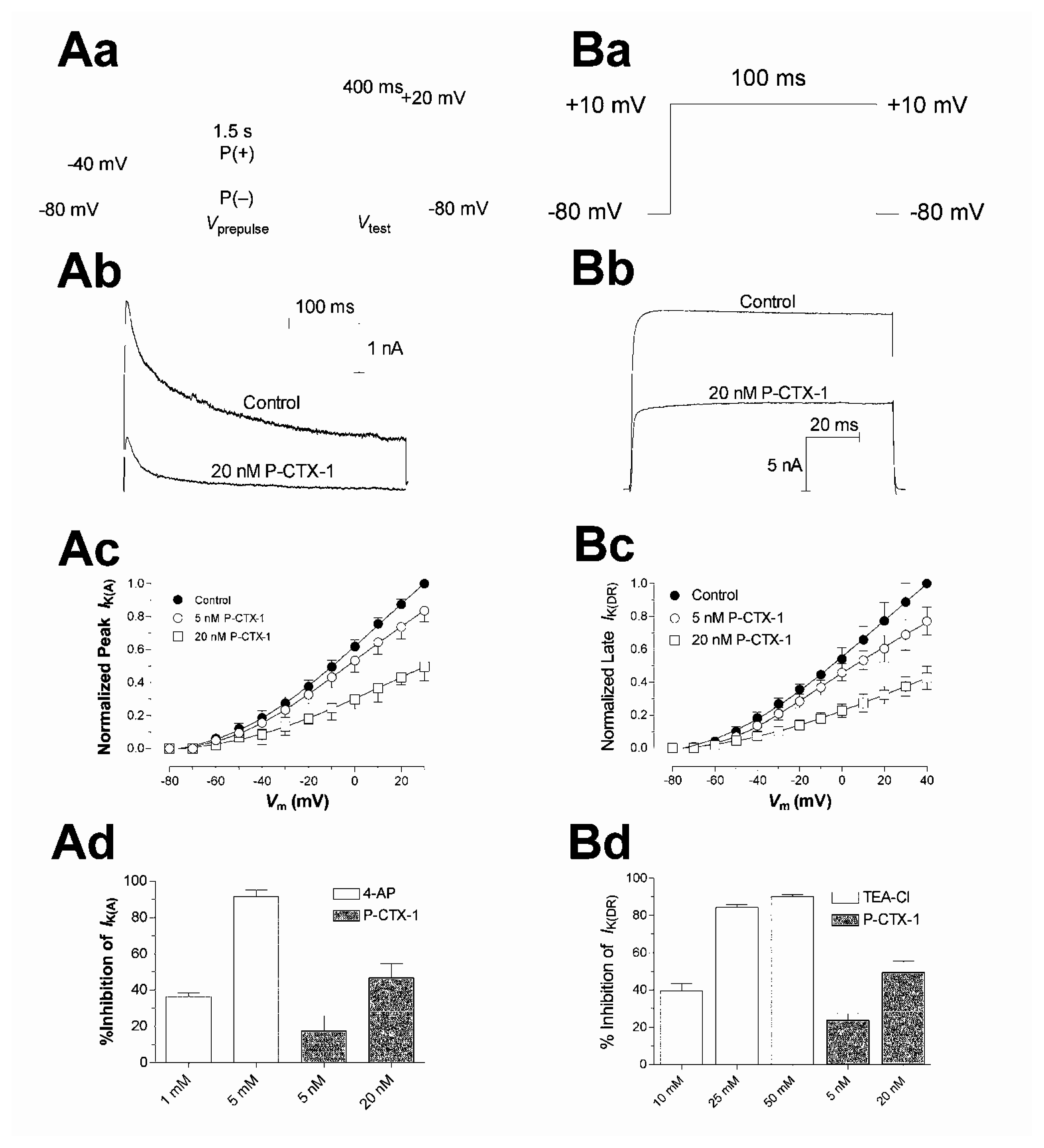
The ability of ciguatoxins to cause repetitive action potential firing in many cell types is commonly thought to be due to their ability to shift the voltage dependence of Nav channel activation to potentials closer to the resting membrane potential [93,101–103,107,114,115]. Using whole-cell patch clamp recording techniques in acutely dissociated rat DRG neurons, the effects of P-CTX-1 were examined on TTX-sensitive and TTX-resistant Nav channels [114] (Fig. 4A). P-CTX-1 caused a concentration-dependent reduction in peak current amplitude for both channel types. At TTX-sensitive Nav channels, P-CTX-1 caused a 13 mV hyperpolarizing shift in the voltage dependence of activation, with no alteration in the reversal potential, and a 22 mV hyperpolarizing shift in steady-state inactivation (h∞) (Fig. 4C). P-CTX-1 also precipitated a large increase in the leakage current, an action that was reversed upon the addition of TTX (Fig. 5A). This indicates that the rise in leakage current is mediated via TTX-sensitive Nav channels [114]. This P-CTX-1-induced leakage current is most likely due to the spontaneous opening of a sub-population of Nav channels at resting and hyperpolarised membrane potentials that remain in a permanently open, non-inactivating state [116] and no doubt underlies the marked membrane depolarisation [109]. The increased leakage current also underlies the reduction in the peak Na+ current amplitude, by reducing the number of available unmodified Nav channels. In contrast, the only significant action of P-CTX-1 on TTX-resistant Nav channels in DRG neurons, apart from a reduction in peak current amplitude, was an increase in the rate of recovery from Nav channel inactivation [114]. A differential effect of ciguatoxin on TTX-sensitive and TTX-resistant Nav channels may contribute to the diversity of sensory neurological disturbances associated with ciguatera.
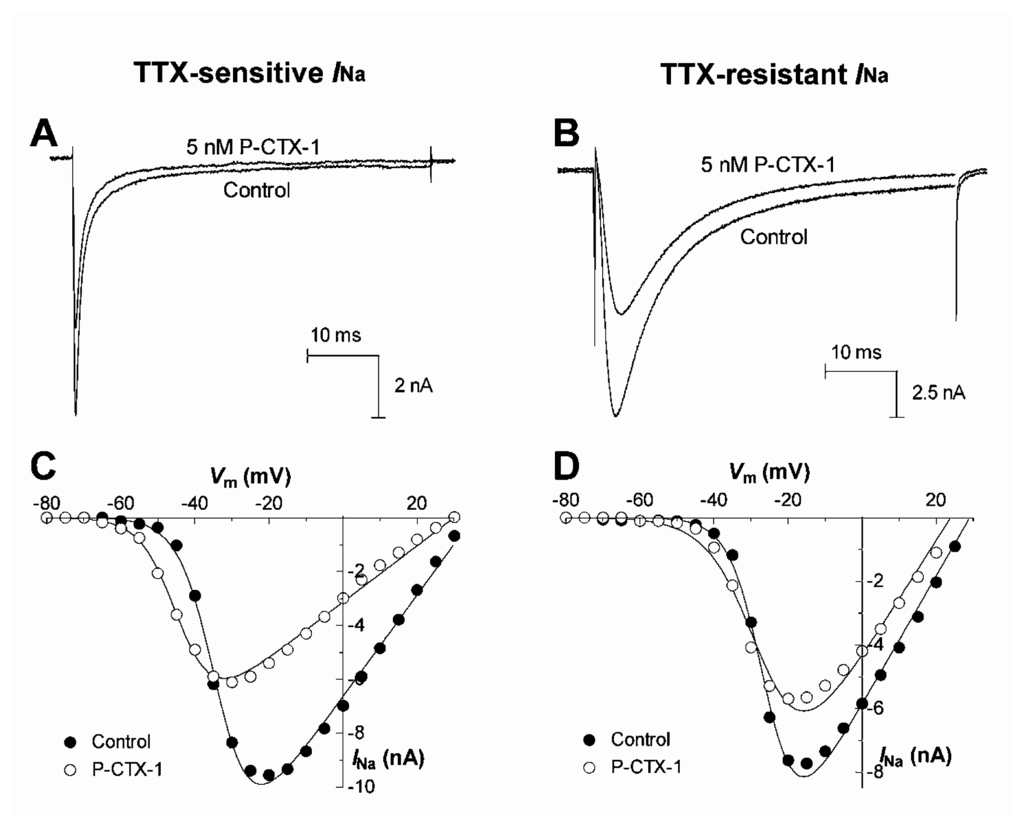
Figure 4.
Upper panels show typical effects of 5 nM P-CTX-1 on TTX-sensitive (A) and TTX-resistant (B)INa in DRG neurons. Currents were elicited using 50 ms depolarizing test pulses to −10 mV from a holding potential of −80 mV every 10 s. Lower panels show typical effects of P-CTX-1 on the voltage-dependence of activation of TTX-sensitive (C) and TTX-resistant (D)INa. Test pulse protocols consisted of 50-ms depolarising test pulses from a holding potential of −80 mV to +70 mV in 5-mV increments before, and 10 min after perfusion with 5 nM P-CTX-1. The peak INa at each voltage step was measured and plotted as a function of membrane potential in the absence (○) and presence of 5 nM P-CTX-1 (●). Modified from Strachan et al. [114].
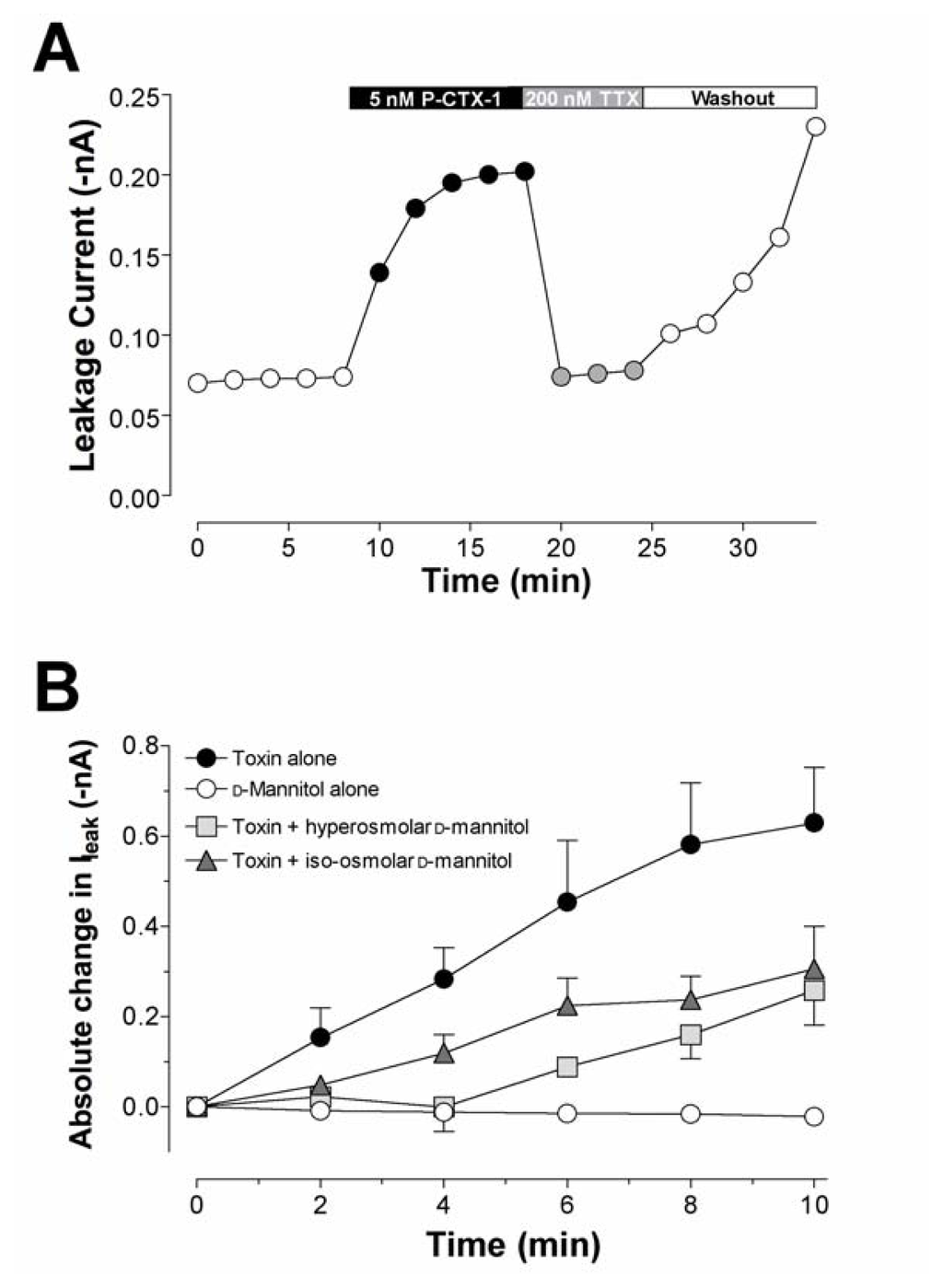
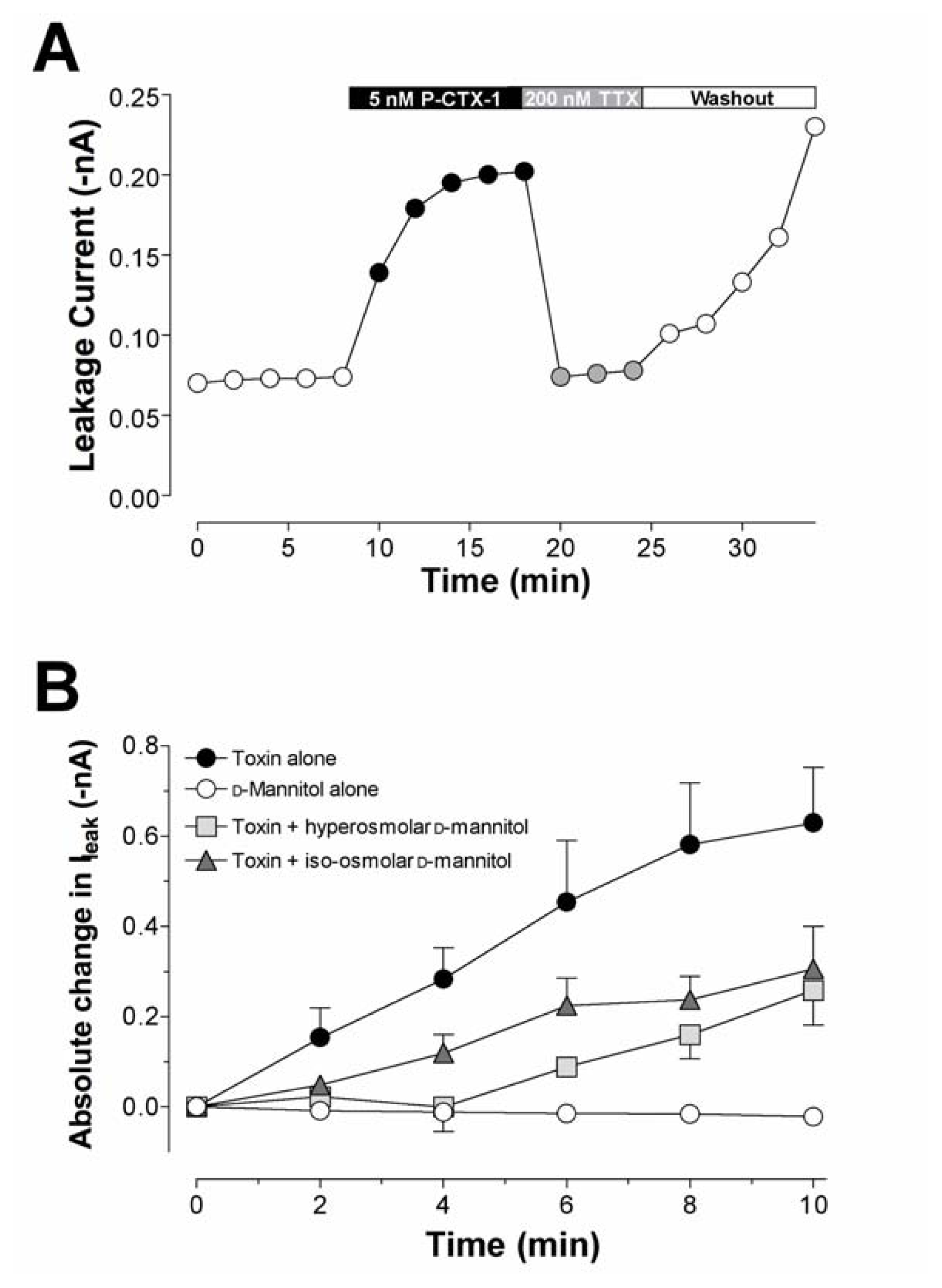
Figure 5.
Timecourse of leakage current (Ileak) produced by P-CTX-1 in DRG neurones. (A) Timecourse of changes in Ileak induced by 5 nM P-CTX-1 in a cell expressing TTX-sensitive INa currents and reversal by TTX (200 nM). The effects of TTX, but not those of P-CTX-1, were reversed upon washing with toxin-free solution. (B) Action of d-mannitol on the P-CTX-1-induced rise in Ileak through TTX-sensitive Nav channels. Absolute changes in Ileak (–nA) were recorded in either (squares) hyperosmolar (n = 13) or (triangles) iso-osmolar (n = 9) 50 mM d-mannitol solutions. Data were recorded during a 10 min perfusion in d-mannitol alone (open circles). Cells were then perfused with 5 nM P-CTX-1 in the presence of either hyper- or iso-osmolar 50 mM d-mannitol. The mean rise in Ileak after perfusion with 5 nM P-CTX-1 alone (closed circles) is shown for comparison. Significant Ileak was not associated with the CTX-modified TTX-resistant Nav channels. Modified from Birinyi-Strachan et al. [126] and Strachan et al. [114].
This action, in combination with ongoing membrane depolarisation and in some neurons a marked oscillation in the membrane potential [115,116], triggers spontaneous action potential firing. Given that P-CTX-1 failed to alter neuronal excitability in current-clamp recordings from small diameter DRG neurons expressing TTX-resistant Nav channels, it would appear that the Nav1.8 (PN3/SNS) and Nav1.9 (NaN/SNS2) channel subtypes [117,118] are not involved to any appreciable extent. Nevertheless, one or several of the TTX-sensitive Nav subtypes, such as Nav1.1 (rat I), Nav1.6 (NaCh6/PN4) and Nav1.7 (PN1), that have been shown to be highly expressed in larger diameter DRG neurons [119–121] or even Nav1.2 (rat II), which is expressed at low levels [122], may be involved. Indeed, C-CTX-3C has been shown to alter the gating and kinetics of rNav1.2, as well as rNav1.4 (adult skeletal muscle, μ1), and rNav1.5 (heart, H1) channels expressed in HEK293 cells [123]. This study confirmed that ciguatoxins shift the voltage dependence of activation, reduce the peak Na+ current and promote slow Nav channel inactivation.
Despite these actions of ciguatoxins on mammalian Nav channels fitting with the symptomology of ciguatera, the actions of ciguatoxins on Nav channel gating and kinetics in amphibian neurons differs slightly. For example, following exposure to P-CTX-1 a fraction of the Na+ current recorded from single myelinated frog axons failed to inactivate during a long depolarisation step, resulting in a maintained ‘late’ inward current [108,124,125]. Unlike experiments using rat DRG neurons, the amplitude of the peak Na+ current was not modified by P-CTX-1. In contrast, the voltage-dependence of activation, and the reversal potential were more negative for the late Na+ current than for the peak Na+ current. Therefore, in the presence of P-CTX-1, the late Na+ current is activated at the resting membrane potential. These results indicate that P-CTX modifies a fraction of Na+ channels that remain permanently open, even at the resting membrane potential. Differences in the action of ciguatoxins on mammalian sensory neurons vs. amphibian motor axons no doubt reflects phyletic differences in Nav channels and/or differences in the action of ciguatoxin on Nav channel subtypes.
To gain a clearer understanding of how ciguatoxin modulates Nav channels to increase neuronal excitability, the action of P-CTX-1 was examined on single Nav channels in isolated parasympathetic neurones from rat intracardiac ganglia [116]. In cell-attached membrane patches, P-CTX-1 markedly increased the open probability of single TTX-sensitive Nav channels, but did not alter the unitary conductance or reversal potential from those of the unmodified channel. In about half the patches under steady-state conditions, P-CTX-1 caused spontaneous opening of single Nav channels that did not close, even at hyperpolarized membrane potentials [116]. Thus P-CTX-1 increases neuronal excitability by shifting the voltage dependence of activation of TTX-sensitive Nav channels to more negative potentials, and by creating a persistent, non-inactivating Na+ current. From the single channel and whole-cell studies described above, it appears that P-CTX-1 acts on TTX-sensitive Nav channels to create two types of modified Nav channels, one where the voltage sensitivity of activation is shifted modestly in the hyperpolarising direction and inactivation is impaired, and one where the channel fails to stay closed, even at hyperpolarised membrane potentials. This latter effect most likely underlies the observed leakage current in DRG neurons. Experiments examining the effects of ciguatoxin on expressed Nav channel clones are required to determine if ciguatoxin takes the Nav channel into two different gating modes, or if these phenomena arise through differential effects on two different populations of Nav channels. Different populations of Nav channels could arise because of differences in the auxiliary β subunits, different extents of post-translational modification, and/or different Nav channel α-subunits and their splice variants. The specific Nav subtype(s) underlying the TTX-sensitive membrane potential oscillations observed in several cell-types also remains to be established. In summary, ciguatoxin-induced membrane depolarisation, combined with an ability to prolong nerve impulse duration, and a hyperpolarising shift in the activation of Nav channels, all act to promote tonic firing of action potentials in myelinated axons and motor nerve terminals and, under appropriate conditions, induces spontaneous oscillations in the resting membrane potential and repetitive action potentials. Also ciguatoxins significantly alter neuronal excitability in mammalian sensory neurons that are consistent with effects that underlie the paraesthesiae and dysesthesiae observed clinically in ciguatera poisoning. In support, DRG neurons, or their axons, have been previously identified to be sites of ectopic impulse generation leading to these types of spontaneous or altered sensations [127,128].
4.3. Ciguatoxin competes for neurotoxin receptor site 5 on Nav channels
The Nav channel is a target for a number of drugs, insecticides and neurotoxins. These bind to at least seven identified neurotoxin binding sites and either block conductance or modulate Nav channel gating and/or kinetics (Fig. 2B; for recent reviews see [112,129–131]). Substances are associated with a receptor site if they compete in radioligand competition binding assays, often with specific allosteric interactions with other sites, or elicit similar electrophysiological effects.
To determine the binding site of ligands on Nav channels researchers have used a variety of ion flux and radiolabelled neurotoxin binding studies. Initial studies by Bidard et al. [102] showed that the binding site of ciguatoxin on the Nav channel was unique to previously identified neurotoxins. By employing 22Na+ flux measurements involving a variety of other Nav channel toxin probes including veratridine and batrachotoxin (site 2), sea anemone toxins (site 3), and β-scorpion toxins (site 4), they showed that ciguatoxin stimulates 22Na+ entry in neuroblastoma cells and rat skeletal myoblasts when it is used in synergy with other site 2, 3, and 4 toxins. This acceleration of Na+ flux was due to activation of Nav channels, since the effect of ciguatoxin was antagonised by TTX [102].
Competition radioligand binding experiments have shown that ciguatoxin competes with another lipid-soluble cyclic polyether toxin, brevetoxin (PbTx) for neurotoxin receptor site 5 on Nav channels. Ciguatoxins are not available as radiolabelled analogues for direct investigation of their specific binding; therefore, [3H]PbTx-3 has been used in homologous and heterologous displacement experiments to define site 5 toxins. Competition studies between purified ciguatoxin [132], pure P-CTX-1, −2, or −3 [5,133,134], C-CTX-1 [135], C-CTX-3C [136], and [3H]PbTx-3, indicate that the ciguatoxins are competitive inhibitors of brevetoxin binding, and thus have overlapping binding at site 5 on the intramembrane portion of the Nav channel (see Fig. 2). Competition binding experiments also found ciguatoxin enhances the binding of site 2 and 3 toxins via non-competitive positive allosteric mechanisms, while ciguatoxin inhibits binding of toxins to site 4 in a negative allosteric fashion [102,137–139]. The selectivity of ciguatoxins for various isoforms of Nav channels has only been investigated on rNav1.4 and hNav1.5 channels expressed in HEK293 cells. Competition binding studies using [3H]PbTx-3 revealed that C-CTX-3C has similar affinity for brain, heart and skeletal muscle Nav channel isoforms [136].
Using a photolabeled derivative of PbTx-3 and site-directed antibody mapping, the partial localisation of neurotoxin receptor site 5 has been determined. Transmembrane segments IS6 and IVS5 have both been identified to participate in the formation of receptor site 5 (Fig. 2B). This indicates that the transmembrane segments IS6 and IVS5 are in close proximity in the native Nav channel and interact to form this receptor site [140,141]. Hence, it is feasible that ciguatoxins, because of their high affinity, could become a new useful pharmacological tool, not unlike TTX or batrachotoxin, in the study of the structure and function of Nav channels.
5. Actions of ciguatoxin on voltage-gated potassium channels
Until recently it has been well accepted that the Nav channel was the primary target of ciguatoxins. Nevertheless, P-CTX-1 also causes a significant increase in mammalian action potential and afterhyperpolarisation duration in the absence of significant alterations in Nav channel inactivation kinetics [109]. In support, a decrease in the amplitude and increase in the duration of spontaneous action potentials has been previously reported with P-CTX-4B, the less polar precursor of P-CTX-1, and C-CTX-1 on single frog myelinated axons [110]. In this later study, the voltage-gated potassium (Kv) channel blocker tetraethylammonium (TEA) failed to further prolong action potential duration following exposure to 24 nM P-CTX-4B. In support, nanomolar concentrations of purified P-CTX-1 have been found to block macroscopic Kv channels in rat myotubes [142].
Previous studies have shown that block of delayed-rectifier Kv channels (KDR) in DRG neurons using TEA, depolarize the cell membrane, prolong action potential duration, reduce the amplitude of afterhyperpolarisations and lower the threshold for action potential firing [143]. These actions suggest that ciguatoxins may also modulate K+ channels. P-CTX-1 has been found to block IK(DR) in rat DRG neurons and produce similar changes in neuronal excitability to those described above [109]. Thus the block of KDR channels would most likely contribute to membrane depolarisation previously identified to be due to the permanent activation of a sub-population of Nav channels [114,116]. In addition, it would also contribute to a lowering of action potential threshold, due to the absence of hyperpolarising potassium conductances, in concert with the hyperpolarising shift in the voltage dependence of TTX-sensitive Nav channel activation [114].
Transient ‘A-type’ Kv channels also play a vital role in neuronal excitability to dampen interspike depolarisations and modulate action potential firing rates [144]. Agents that block IK(A), such as 4-aminopyridine (4-AP) [143], have also been shown to induce repetitive firing in rat dorsal root fibres [145] and DRG neurons [146]. Importantly, at concentrations that profoundly affect spike electrogenesis and Nav channel gating, P-CTX-1 produced a significant inhibition of IK(A). This action would promote a faster firing frequency by speeding the rate of interspike membrane potential depolarisation. In support, the structurally related cyclic polyether gambierol from G. toxicus (Fig. 1C) has recently been shown to block Kv channels in mouse taste cells [147].
Given that KDR and KA channels play multiple roles in the excitability of DRG neurons block of these channels by P-CTX-1 influences the shape of the action potential, its firing threshold and the resting membrane potential. The block of KDR and KA channels act in concert with permanent activation of a sub-population of Nav channels to depolarise the resting membrane potential and a hyperpolarising shift in the threshold of TTX-sensitive Nav channel activation [114], as the underlying determinants for the spontaneous action potential firing induced by P-CTX-1 in sensory neurons. These actions on neuronal excitability provide us with further understanding of the origin of the predominant paraesthesiae, dysesthesiae and other neurological symptoms associated with ciguatera poisoning.
6. Other Na+-dependent actions of ciguatoxin
6.1. Ciguatoxin induced swelling of cells
The ciguatoxin-induced activation of Nav channels at the resting membrane potential is responsible for numerous Na+-dependent effects in particular oedema [91,102,108,125,148–151]. Intraperitoneal or oral administration of 0.1 μg/kg of P-CTX-1 or P-CTX-4C to male mice over 15 days caused marked swelling of cardiac and endothelial cells lining the blood capillaries of the heart [89]. This swelling only reversed some weeks after ceasing toxin administration. As a consequence of persistent activation of Nav channels at resting membrane potentials resulting in spontaneous or evoked repetitive firing of action potentials, ciguatoxins have been demonstrated to induce swelling of nerves in amphibian [125,150,152–154] and mammal sensory neurons [126]. Swelling has been observed during the action of P-CTX-1, P-CTX-4B or P-CTX-3C on myelinated axons, motor nerve terminals and on perisynaptic Schwann cells in situ, as determined by confocal microscopy [125,150,152,154,155]. The nodal swelling results from the influx of water to maintain the osmotic equilibrium. The sodium loading hypothesis, described above, is supported by the finding that TTX prevents this swelling [125,150,152,153]. These effects were also reversed by increasing the osmolality of the external solution either with 100 mM d-mannitol, 50 mM tetramethylammonium chloride, or with 100 mM sucrose. Although the hyperosmolar external solutions almost completely reversed the nodal swelling of myelinated axons induced by ciguatoxin, the solutions only partially decreased the nerve terminal swelling.
In the continuous presence of TTX, ciguatoxins did not cause significant changes in the nodal volume of myelinated axons, or in the motor nerve terminal area per unit length. Thus, it is likely that ciguatoxins promote the entry of Na+ through ciguatoxin-modified Nav channels that are permanently activated at the resting membrane potential, and through unmodified Nav channels that open during ciguatoxin-induced spontaneous action potential discharges [125]. This swelling has been associated with sensory disturbances, such as alterations to nerve conduction velocity in humans, by increasing the electrical capacitance of the nodal membrane [73,74,151]. This is likely to contribute to the sensory disturbances characteristic of ciguatera poisoning.
6.2. Action of ciguatoxin on intracellular Ca2+ stores and the Na+ – Ca2+ exchange mechanism
Intracellular Ca2+ plays an important role in the functioning of excitable cells, particularly as a second-messenger [156]. Studies have shown that low nanomolar concentrations of P-CTX-1 significantly increases the intracellular Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) in cultured mouse NG108-15 neuroblastoma X glioma hybrid cells [106,149,157]. Using the fluorescent Ca2+ probe flura-2 to measure intracellular Ca2+ stores, it was shown that cells bathed with either standard medium containing Ca2+, or Ca2+-free medium supplemented with the Ca2+ chelator EGTA, experienced a P-CTX-1-induced increase in intracellular Ca2+. However, adding TTX to the bath completely inhibited this increase, suggesting that the effect of P-CTX-1 on Ca2+ mobilisation depends on Na+ influx through Nav channels. This result provides further support for the positive inotropic actions of P-CTX-1 in cardiac myocytes, as discussed previously [91].
In addition, P-CTX-1-induced Ca2+ mobilisation was found to prevent the subsequent action of bradykinin, indicating that the intracellular Ca2+ store affected by P-CTX-1 is the same as that activated by bradykinin [104,158]. In NG108-15 cells, bradykinin has been shown to increase the degradation of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-triphosphate resulting in the production of inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate (InsP3) and diacylglycerol, which activates protein kinase C [158,159]. The mechanism of Ca2+ mobilization by bradykinin is considered to be predominantly through InsP3-induced Ca2+ release from intracellular Ca2+ stores [156]. From these results it was concluded that both P-CTX-1 and bradykinin might elevate intracellular Ca2+ through the same InsP3-sensitive Ca2+ stores in nerve cells [104]. Past experimentation on synaptosomes [160–162] and cardiac myocytes [163] has also revealed that any enhanced influx of Na+ stimulates the production of InsP3, presumably through the activation of phospholipase C. A Na+-dependent mobilization of Ca2+ from InsP3-sensitive stores could explain the increase in asynchronous quantal neurotransmitter release from motor nerve terminals that have been exposed to P-CTX-1 in a Ca2+-free bath solution [103,106]. More recently P-CTX-1 has been shown to cause a transient increase in intracellular InsP3 mass levels in rat myotubes, an action that was blocked by TTX [142]. This indicates that membrane depolarisation is involved in the generation of InsP3.
The Na+-Ca2+ exchanger (antiporter) is also implicated in the actions of ciguatoxins on neurotransmitter release. Nanomolar concentrations of P-CTX-1 have been shown to increases Na+ influx into cholinergic synaptosomes isolated from the electric organ of the fish Torpedo marmorata, thus enhancing ACh release triggered by Ca2+[104]. This action does not result from P-CTX-1-induced depolarisation of the synaptosomal membrane to activate Cav channels, because simultaneous blockade of Cav channel subtypes by a cocktail of blockers did not prevent ACh release. In addition, replacement of extracellular Na+ by Li+ reduced transmitter release, consistent with the fact that Li+ cannot substitute for Na+ in the Na+-Ca2+ exchanger [164]. Lastly, benperidol and cotidal, known inhibitors of the Na+-Ca2+ exchanger, completely blocked Ca2+-dependent ACh release induced by P-CTX-1 [105]. Therefore, it would appear that P-CTX-1 activates Nav channels with a consequent increase in [Na+]i in synaptosomes hence reducing the ability of the Na+-Ca2+ exchanger to extrude Ca2+ ions. As a consequence this leads to an elevation of cytoplasmic Ca2+ and promotes Ca2+-dependent neurotransmitter release. The Na+-Ca2+ exchanger can operate also in a reverse mode and admit Ca2+ into the terminal, if the membrane potential is above the equilibrium potential of the exchanger, such as occurs during ciguatoxin-induced depolarisation and spontaneous repetitive firing.
7. Detection of ciguatoxins
Since ciguateric toxins are odourless and tasteless, bioassays in animals have been traditionally used in ciguatera endemic regions to monitor suspected or toxic fish samples. These tests are based on feeding cats, mongoose, chicken, crayfish, mosquito and dipteran larvae with flesh or viscera of suspect fish. Observations of symptoms, behaviour, growth, body temperature, and survival time of the animals over time are used to characterise and quantify toxin levels [165–170]. Of the 37 animal species tested by Banner et al. [165], only five were found to be sensitive to the oral administration of ciguateric fish. Despite the development of these animal assays, the mouse bioassay remains the most widely used assay to establish levels of ciguatoxin in extracts of fish (reviewed in [168]). The method quantifies lethal and sub-lethal doses of ciguatoxin in crude extracts administered intraperitoneally to mice [166,171]. The establishment of dose-time-to-death relationship for the major toxins allows the numbers of mice required for quantitation to be reduced to as few as two per sample, and avoids testing LD50 doses which are lethal at ~24 h [168]. Nevertheless, these assays have their disadvantages: they (i) have insufficient sensitivity to detect ciguatoxin in crude extracts from low-toxicity fish, (ii) may give false positive results if high doses of lipid are administered [19], (iii) relatively large amounts of material are required for analysis, (iv) lack specificity to distinguish different marine toxins, (v) require prolonged times for analysis and, (vi) are ethically questionable [172].
Recent developments have focused on a variety of cell-based techniques to detect and quantify ciguatoxins in fish. Manger et al. [173,174] have shown that N2A neuroblastoma cells in culture can be developed as a simple and sensitive method to detect Nav channel-specific marine toxins using mitochondrial dehydrogenase activity as a marker of cytotoxicity. Within 6 h, purified ciguatoxin can be detected at subpicogram levels and the results correlate with those obtained by mouse bioassay. The use of N2A neuroblastoma cells in the detection of ciguatoxins has also recently been refined by the use of a rapid fluorimetric microplate assay using the potential dependent fluorescent dye, bis-oxonol [175]. A sensitive cell-based assay for brevetoxins, saxitoxins and ciguatoxins has also been reported that employs ac-fos-luciferase reporter gene stably expressed in cells [176]. [3H]PbTx-3 binding to brain membrane can be used to detect ciguatoxins in crude extracts [132,134,135] and can be developed into high-throughput assays. Other sensitive approaches not based on cell assays include chemical approaches such as LC-MS/MS [177] and immunological methods based on RIA, ELISA and solid-phase immunobead assays [178–188].
Ciguatera screening in biological fluids of suspected patients is still limited due to a lack of validated methods. At present there are early reports of neuroblastoma cell-based cytotoxicity assays to quantify ciguatoxin activity in human blood [189,190]. These Nav channel assays, together with antibody-based assays [191,192] have potential to replace animal testing for ciguatoxins. Therefore these approaches warrant further validation to determine the potential of such assays to be developed into rapid screens for public health protection.
8. Treatment of ciguatera
Despite recent advancements in understanding the pharmacological properties of ciguatera toxins, no effective treatment for ciguatera poisoning has been devised. Therapy remains primarily symptomatic and supportive and includes gastric lavage for removal of unabsorbed toxins, opiates for pain, oxygen and ventilation assistance, cold showers and antihistamines for pruritus and anti-diarrhoeal and antiemetic agents [42,47,193]. Rare cardiovascular complications, such as symptomatic bradycardia and severe hypotension require specific treatments such as atropine and pressors [63].
A range of specific treatments have been reported to give benefit to sufferers of ciguatera in isolated instances. These include the antidepressants amitriptyline [194–196] and fluoxetine [197], that apart from their actions as reuptake inhibitors, are also known to block Nav channel activity [198]. Also, the L-type Cav channel inhibitor nifedipine [195], the anticonvulsant gabapentin [199], and the Nav channel blocker tocainide [195,200,201], have all been shown to have benefit in clinical cases. The use of tocainide, an orally active lidocaine derivative, is supported by animal studies [202], but not by in vitro studies [203]. Other treatments have included injections of vitamin B complex and vitamin C, which reportedly shortened the duration of symptoms [204]. A wide variety of traditional remedies have been developed in island regions [205] and include the use of green fruit of papaya as an emetic and also the herb Duboisea myoporides, which contains atropine [80]. Atropine will alleviate hypotension and bradycardia but has no effect on the neurological or gastrointestinal disturbances.
More than 90 traditional herbal medicines have reportedly been used to treat ciguatera in the Pacific. Unfortunately the vast majority are poorly characterised. However, aqueous extracts of Argusia argentea and Schinus terebenthifolius leaves, have been shown to reduce the weight loss of mice injected with sublethal doses of ciguatoxic fish extracts [206]. Interestingly, extracts of Argusia argentea leaves and Davallia solida rhizomes also reverse the spontaneous and repetitive action potentials and swelling of nodes of Ranvier in frog single myelinated axons [207]. A recent study has also shown that several other plant extracts inhibit the in vitro cytotoxicity induced by ciguatoxin. These traditional remedies for ciguatera may provide benefit but, as with most other potential therapies, there is a paucity of scientific studies on the efficacy and safety in humans. Nonetheless, they may provide lead compounds to treat ciguatera poisoning provided these agents reverse the effects of polyether compounds on their cellular targets [208].
Treatment of ciguatera with intravenous infusions of hyperosmotic d-mannitol, an acyclic sugar alcohol (polyol), has gained acceptance as currently the most effective method of abating the neurological symptoms [209,210]. Over 60% of patients have their symptoms reversed by mannitol infusions of 1 g/kg over 30–45 min [209,210]. This has been supported by case series, non-randomised studies and a randomised, but not double-blind, study [57,151,209–215]. The most dramatic success story in the treatment of ciguatera to date has been reported by Palafox et al. [209] in the Marshall Islands, who treated 24 patients with acute ciguatera with intravenous infusions of mannitol. Two patients in a coma and one in shock responded in minutes with full and rapid recovery, a process that usually takes 1–2 weeks. Neurological and muscular manifestations improved dramatically, however gastrointestinal symptoms resolved more slowly. Other clinical studies such as that by Pearn et al. [210], found that patients with acute disease (showing symptoms for no longer than 24 h), when infused with a higher dose of mannitol (1.0 g/kg), were more likely to have dramatic recoveries.
Despite its apparent effectiveness, the mechanism for the neuroprotectant effect of d-mannitol in the treatment of ciguatera is still not fully understood. Most studies indicate that the reduction of cell swelling is the main action of d-mannitol, a well-known osmotic diuretic [125]. This action is supported by the finding that d-mannitol has little effect in reducing the symptoms of ciguatera in mice, due to the marked absence of ciguatoxin-induced axonal oedema in the mouse model [171,216]. In vitro studies have, however, suggested that d-mannitol may exert a more specific role, by interacting with the ciguatoxin molecule itself [125]. However, it has also been suggested that d-mannitol may exert its neuroprotectant effect as a scavenger of hydroxyl free radicals (•OH) generated by the ciguatoxin molecule [125,210]. d-Mannitol is known to act as a free radical scavenger [217,218]. Since the ciguatoxin molecule possesses a number of hydroxyl groups this has some theoretical attraction, particularly since vitamin C, a known free radical scavenger, has previously been shown to provide some clinical benefit [204]. Using electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy, it was found that P-CTX-1 failed to generate hydroxyl free radicals at concentrations of toxin that caused profound effects on neuronal excitability. In addition, the free radical scavenging agents Trolox® and l-ascorbic acid failed to prevent ciguatoxin-induced changes in neuronal excitability [126]. Mannitol may also exert its effects as an osmotic diuretic agent, by reducing the oedema and related pressure-induced neuropathies. However a study using hyper- and iso-osmolar d-sorbitol and hyperosmolar sucrose showed that these agents, unlike iso-osmolar d-mannitol, failed to prevent the effects of P-CTX-1 on spike electrogenesis and Nav channel gating, and the leakage current in rat sensory neurons (Fig. 5B) [126]. These selective actions of both iso- and hyperosmolar d-mannitol indicate that it does not act purely as an osmotic agent to reduce swelling of nerves, but involves a more complex action dependent on the Nav channel subtype, possibly to alter or reduce toxin association.
Despite the availability of this treatment, the management of long-term chronic symptoms continues to be problematic. The pathophysiological basis of symptoms that persist for weeks or years remains to be elucidated, but these long-term effects may be the result of permanent neurological damage associated with oedema, or slow detoxification. The reason mannitol is not consistently effective in treating ciguatera [213] is also unclear, but may relate to timing of administration, severity of poisoning, and individual variations in response to ciguatoxin and/or mannitol. Some potential hazards for its clinical use also exist. The major hazards are the loss of further fluids from patients suffering from acute diarrhoea and vomiting and that patients experiencing bradycardia and hypotension are at a higher risk of cardiac failure if infused with high doses of mannitol [210]. Finally, the only double-blinded randomized trial of mannitol concluded that mannitol was not superior to normal saline in relieving symptoms and signs of ciguatera at 24 h [63], and some clinicians are now beginning to question whether it should be recommended for the treatment of ciguatera [63,219].
9. Conclusions
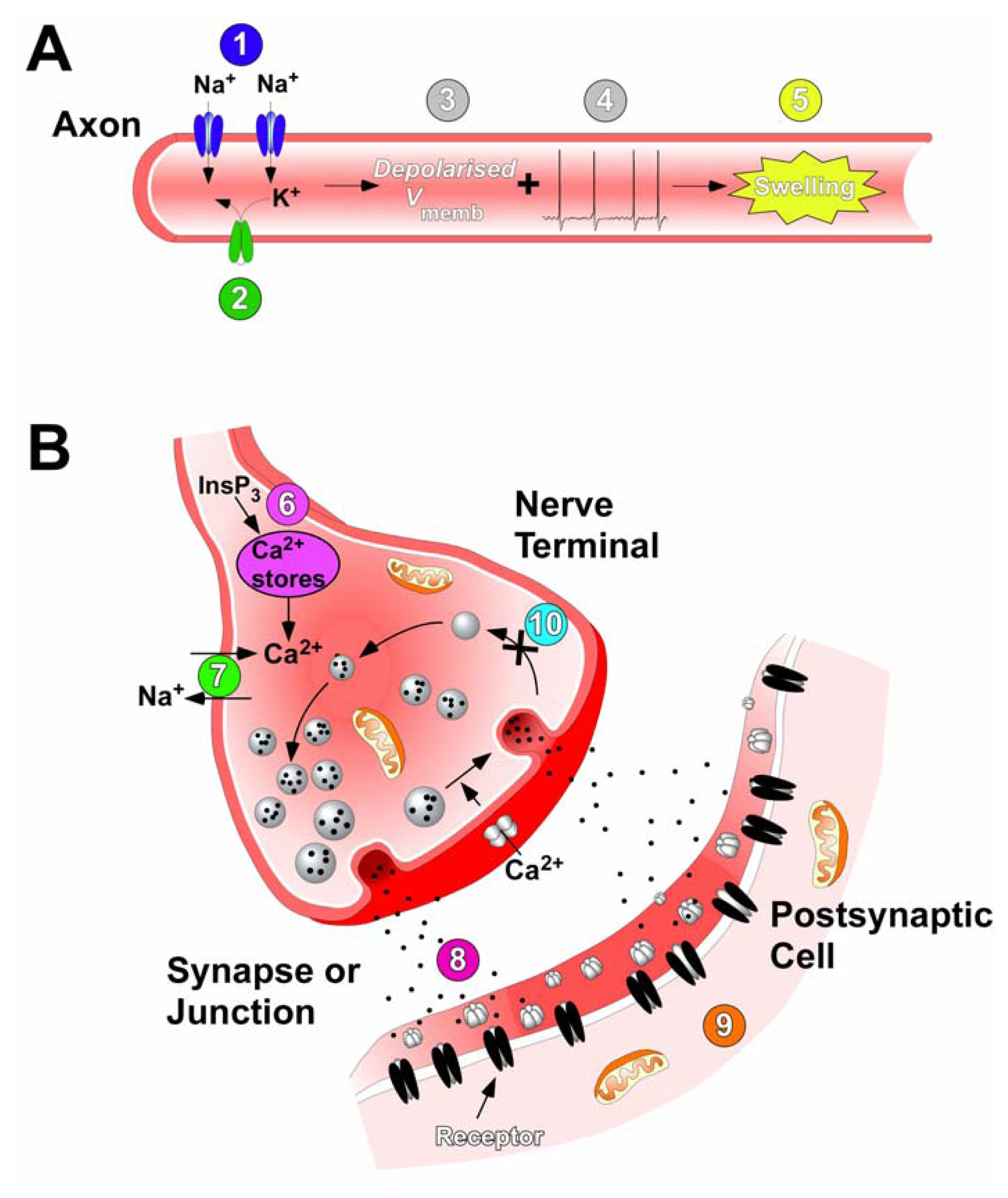
Considerable progress has been made in determining the sources and chemical structures of the principal toxins involved in ciguatera. The action of ciguatoxin to increase Na+ permeability through Nav channels that open at normal resting membrane potentials is now well accepted. As a consequence, ciguatoxins have been identified to affect various Na+-dependent mechanisms to enhance membrane excitability, activate Na+-Ca2+ exchange, induce mobilization of intracellular Ca2+, and produce cell swelling. Recent evidence also points to the involvement of Kv channels to enhance neuronal excitability in concert with the action of ciguatoxins on Nav subtypes (Fig. 7). These neurocellular actions of ciguatoxin are consistent with the generalized disturbance of nerve conduction, synaptic transmission and cellular morphology observed in intoxicated patients.
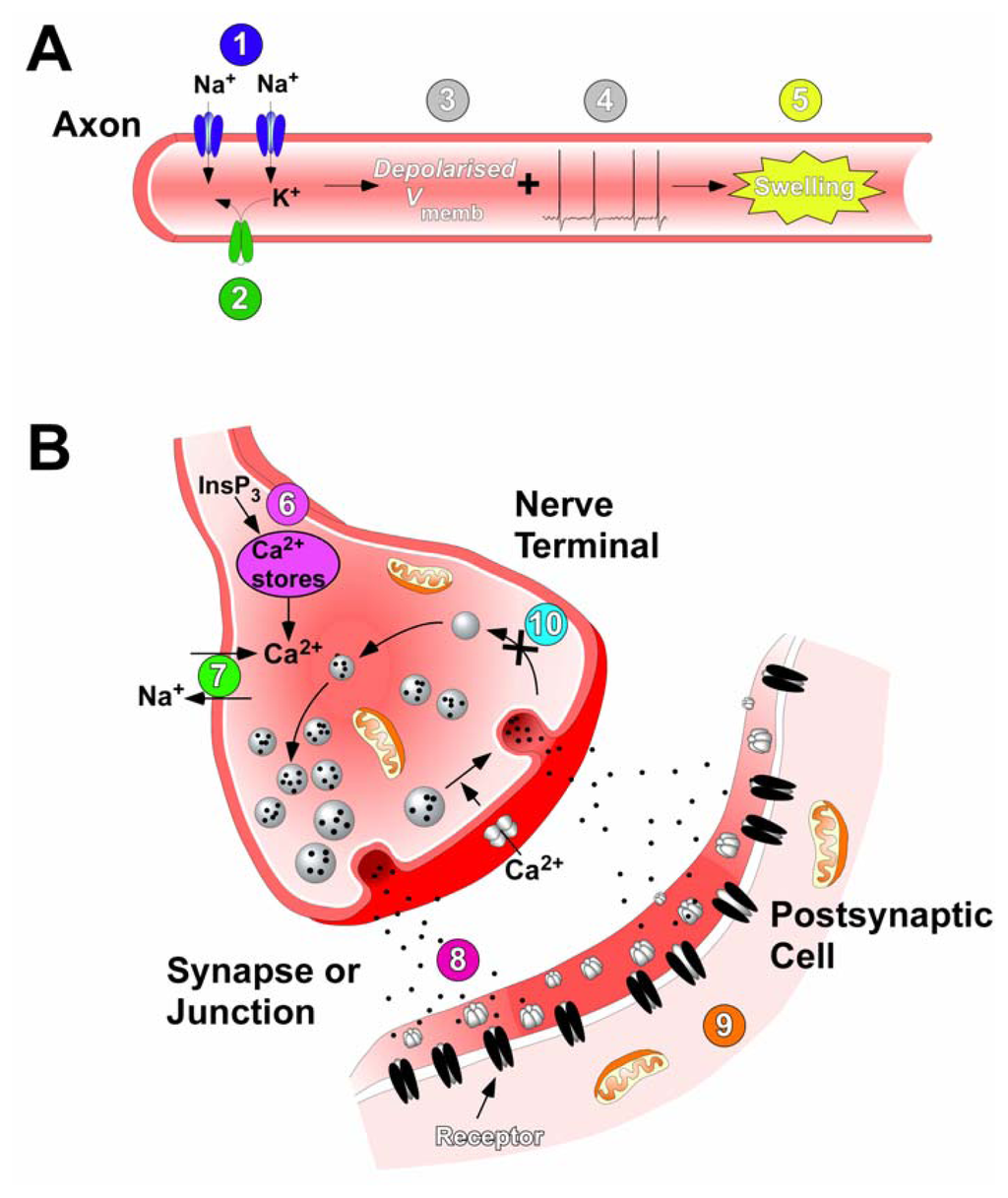
Figure 7.
Sites and modes of action of ciguatoxins. (A) In motor and sensory neurons ciguatoxins cause persistent activation of Nav channels (1) and block Kv channels (2). This causes both membrane depolarisation (3) and leads to spontaneous and repetitive action potential firing (4). The resultant Na+ loading causes swelling of axons, nerve terminals and perisynaptic Schwann cells (5). (B) At synapses, ciguatoxins elevate the intracellular Ca2+ concentration via InsP3-mediated Ca2+ release from internal stores (6) or via activation of Cav channels due to terminal depolarisation (8). Also intracellular concentrations of Ca2+ increase due to an alteration in the Na+ gradient driving the Na+-Ca2+ exchanger (7), an effect that also occurs in cardiac myocytes. The tonic action potential firing initiated in axons induces repetitive, synchronous and asynchronous neurotransmitter release at synapses and the neuromuscular junction (9), to produce transient increases and decreases in the quantal content of synaptic responses. This results in spontaneous and tetanic muscle contractions (10). In addition, ciguatoxins also impair synaptic vesicle recycling that exhausts the pool of neurotransmitter vesicle available for release (11).
Despite this progress, treatment still remains non-specific, symptomatic and supportive. Various substances and herbal remedies have been used for the treatment of ciguatera but the efficacy of these therapeutic agents remains uncertain, and antagonists effective at specifically reversing the pathophysiological basis of ciguatoxin action remain elusive. One exception is intravenous hyperosmolar d-mannitol, which has evolved as a unique remedy for acutely poisoned patients, although its mechanism of action has not been determined definitively. The development of specific tests that detect the presence of ciguatoxin and related toxins in fish prior to consumption, as well as human biomarkers of ciguatoxins will significantly improve the management of ciguatera, and overcome present limitations of diagnosis and existing therapies.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Australian Research Council for ongoing grant support.
Abbreviations
| Ch | acetylcholine |
| 4-AP | 4-aminopyridine |
| [Ca2+]o | extracellular concentration of Ca2+ |
| Cav channel | voltage-gated Ca2+ channel |
| CTX | ciguatoxin |
| C-CTX | Caribbean Sea ciguatoxin |
| DRG | dorsal root ganglion |
| EJP | excitatory junction potential |
| EPP | endplate potential |
| I-CTX | Indian Ocean ciguatoxin |
| InsIP3 | inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate |
| KA channel | transient ‘A-type’ K+ channel |
| [K+]o | extracellular concentration of K+ |
| KDR channel | delayed-rectifier K+ channel |
| Kv channel | voltage-gated potassium channel |
| LD50 | median lethal dose |
| MEPP | miniature endplate potential |
| mAChR | muscarinic acetylcholine receptor |
| [Na+]i | intracellular concentration of Na+ |
| Nav channel | voltage-gated sodium channel |
| nAChR | nicotinic ACh receptor |
| PbTx | brevetoxin |
| P-CTX | Pacific Ocean ciguatoxin |
| STX | saxitoxin |
| TEA | tetraethylammonium |
| TTX | tetrodotoxin |
- Samples Availability: Available from Dr Richard J. Lewis.
References
- Miyahara, J. T.; Akau, C. K.; Yasumoto, T. Effects of ciguatoxin and maitotoxin on the isolated guinea pig atria. Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol 1979, 25, 177–180. [Google Scholar]
- Adachi, R.; Fukuyo, Y. The thecal structure of a marine toxic dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus collected in a ciguatera endemic area. Bull. Jap. Soc. Scientific Fisheries 1979, 45, 67–71. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, R. J.; Vernoux, J. P.; Brereton, I. M. Structure of Caribbean ciguatoxin isolated from Caranx latus. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1998, 120, 5914–5920. [Google Scholar]
- Murata, M.; Legrand, A.-M.; Ishibashi, Y.; Yasumoto, T. Structures and configurations of ciguatoxin from the moray eel Gymnothorax javanicus and its likely precursor from the dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1990, 112, 4380–4386. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, R. J.; Sellin, M.; Poli, M. A.; Norton, R. S.; MacLeod, J. K.; Sheil, M. M. Purification and characterization of ciguatoxins from moray eel (Lycodontis javanicus, Muraenidae). Toxicon 1991, 29, 1115–1127. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, R. J.; Sellin, M. Multiple ciguatoxins in the flesh of fish. Toxicon 1992, 30, 915–919. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, R. J. The changing face of ciguatera. Toxicon 2001, 39, 97–106. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, B.; Hurbungs, M.; Jones, A.; Lewis, R. J. Multiple ciguatoxins present in Indian Ocean reef fish. Toxicon 2002, 40, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, B.; Hurbungs, M.; Vernoux, J. P.; Jones, A.; Lewis, R. J. Isolation and characterisation of Indian Ocean ciguatoxin. Toxicon 2002, 40, 685–693. [Google Scholar]
- Pottier, I.; Hamilton, B.; Jones, A.; Lewis, R. J.; Vernoux, J. P. Identification of slow and fast-acting toxins in a highly ciguatoxic barracuda (Sphyraena barracuda) by HPLC/MS and radiolabelled ligand binding. Toxicon 2003, 42, 663–672. [Google Scholar]
- Vernoux, J. P.; Lewis, R. J. Isolation and characterisation of Caribbean ciguatoxins from the horse-eye jack (Caranx latus). Toxicon 1997, 35, 889–900. [Google Scholar]
- Murata, M.; Legrand, A.-M.; Ishibashi, Y.; Yasumoto, T. Structures and configurations of ciguatoxin and its congener. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1989, 111, 8929–8931. [Google Scholar]
- Satake, M.; Murata, M.; Yasumoto, T. The structure of CTX3c, a ciguatoxin congener isolated from cultured Gambierdiscus toxicus. Tetrahedron Lett 1993, 34, 1975–1978. [Google Scholar]
- Satake, M.; Ishibashi, Y.; Legrand, A.-M.; Yasumoto, T. Isolation and structure of ciguatoxin-4A, a new ciguatoxin precursor, from cultures of dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus and parrotfish Scarus gibbus. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem 1996, 60, 2103–2105. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, R. J.; Norton, R. S.; Brereton, I. M.; Eccles, C. D. Ciguatoxin-2 is a diastereomer of ciguatoxin-3. Toxicon 1993, 31, 637–643. [Google Scholar]
- Satake, M.; Fukui, M.; Legrand, A.-M.; Cruchet, P.; Yasumoto, T. Isolation and structures of new ciguatoxin analogs, 2,3-dihydroxyCTX3C and 51-hydroxyCTX3C, accumulated in tropical reef fish. Tetrahedron Lett 1998, 39, 1197–1198. [Google Scholar]
- Holmes, M. J.; Lewis, R. J.; Poli, M. A.; Gillespie, N. C. Strain dependent production of ciguatoxin precursors (gambiertoxins) by Gambierdiscus toxicus (Dinophyceae) in culture. Toxicon 1991, 29, 761–775. [Google Scholar]
- Legrand, A.-M.; Fukui, M.; Cruchet, P.; Ishibashi, Y.; Yasumoto, T. Characterization of ciguatoxins from different fish species and wild Gambierdiscus toxicus. Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Ciguatera Fish Poisoning, Quebec; 1992; pp. 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, R. J.; Sellin, M. Recovery of ciguatoxin from fish flesh. Toxicon 1993, 31, 1333–1336. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, R. J.; Jones, A. Characterization of ciguatoxins and ciguatoxin congeners present in ciguateric fish by gradient reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Toxicon 1997, 35, 159–168. [Google Scholar]
- Legrand, A.-M.; Litaudon, M.; Genthon, J. N.; Bagnis, R.; Yasumoto, T. Isolation and some properties of ciguatoxin. J. Appl. Phycol 1989, 1, 183–188. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, R. J.; Holmes, M. J. Origin and transfer of toxins involved in ciguatera. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C 1993, 106, 615–628. [Google Scholar]
- Yasumoto, T.; Murata, M. Marine toxins. Chem. Rev 1993, 93, 1897–1909. [Google Scholar]
- Faust, M. Observation of sand-dwelling toxic dinoflagellates (Dinophyceae) from widely differing sites, including two new species. J. Phycol 1995, 31, 996–1003. [Google Scholar]
- Holmes, M. J. Gambierdiscus yasumotoi sp. nov. (Dinophyceae), a toxic dinoflagellate from southeastern Asia. J. Phycol 1998, 34, 661–668. [Google Scholar]
- Chinain, M.; Faust, M.; Pauillac, S. Morphology and molecular analyses of three new toxic species of Gambierdiscus (Dinophyceae): G. pacificus sp. nov., G. australes sp. nov., and G. polynesiensis sp. nov. J. Phycol 1999, 35, 1282–1296. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, M.; Hirama, M.; Satake, M.; Sugiyama, K.; Yasumoto, T. Inhibition of brevetoxin binding to the voltage-gated sodium channel by gambierol and gambieric acid-A. Toxicon 2003, 41, 469–474. [Google Scholar]
- Satake, M.; Murata, M.; Yasumoto, T. Gambierol: a new toxic polyether compound isolated from the marine dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1993, 115, 361–362. [Google Scholar]
- Morohashi, A.; Satake, M.; Yasumoto, T. The absolute configuration of gambierol, a toxic marine polyether from the dinoflagellate, Gambierdiscus toxicus. Tetrahedron Lett 1998, 39, 97–100. [Google Scholar]
- Satake, M.; Ishibashi, Y.; Legrand, A.-M.; Yasumoto, T. Isolation and structure of ciguatoxin- 4A, a new ciguatoxin precursor, from cultures of dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus and parrotfish Scarus gibbus. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 1996, 60, 2103–2105. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.-Y.; Risk, M. A.; Ray, S. M.; Van Engen, D.; Clardy, J.; Golik, J.; James, J. C.; Nakanishi, K. Isolation and structure of brevetoxin B from the “red tide” dinoflagellate Ptychodiscus brevis (Gymnodinium breve). J. Am. Chem. Soc 1981, 103, 6773–3775. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, H. N.; Shimizu, Y. A new polyether toxin from Gymnodinium breve Davis. Tetrahedron Lett 1982, 23, 5521–5524. [Google Scholar]
- Dalton, C. B.; Gregory, J.; Kirk, M. D.; Stafford, R. J.; Givney, R.; Kraa, E.; Gould, D. Foodborne disease outbreaks in Australia, 1995 to 2000. Commun. Dis. Intell 2004, 28, 211–224. [Google Scholar]
- Fleming, L. E.; Katz, D.; Bean, J. A.; Hammond, R. Epidemiology of seafood poisoning. In Seafood and Environmental Toxins; Hui, Y. H., Kits, D. D., Eds.; Marcel Dekker: New York, 2001; pp. 287–310. [Google Scholar]
- Higerd, T. Ciguatera food poisoning: a circumtropical fisheries problem. In Natural Toxins and Human Pathogens in the Marine Environment; Colwell, R., Ed.; Maryland Sea Grant Publication, 1983; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, R. J.; Ruff, T. A. Ciguatera: Ecological, clinical, and socioeconomic perspectives. Crit. Rev. Env. Sci. Technol 1993, 23, 137–156. [Google Scholar]
- Lange, W. R. Ciguatera fish poisoning. Am. Fam. Physician 1994, 50, 579–584. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, R. J. Socioeconomic impacts and management ciguatera in the pacific. Bull. Soc. Path. Ex 1992, 85, 427–434. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, P. D.; Campbell, D. S.; Freeman, J. I. Ciguatera fish poisoning: an outbreak associated with fish caught from North Carolina coastal waters. South. Med. J 1990, 83, 379–382. [Google Scholar]
- DeFusco, D. J.; O'Dowd, P.; Hokama, Y.; Ott, B. R. Coma due to ciguatera poisoning in Rhode Island. Am. J. Med 1993, 95, 240–243. [Google Scholar]
- Halstead, B. W. Poisonous and Venomous Marine Animals of the World; United States Government Printing Office: Washington D.C, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Banner, A. H. Ciguatera: a disease from coral reef fish. In Biology and Geology of Coral Reefs; Jones, O.A., Endean, R., Eds.; Academic Press: London, 1976; Volume 3, pp. 177–213. [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie, N. C.; Lewis, R. J.; Pearn, J. H.; Bourke, A. T.; Holmes, M. J.; Bourke, J. B.; Shields, W. J. Ciguatera in Australia. Occurrence, clinical features, pathophysiology and management. Med. J. Aust 1986, 145, 584–590. [Google Scholar]
- Glaziou, P.; Chinain, M.; Legrand, A.-M. Clinical toxicology of ciguatera poisoning. In Handbook of Clinical Toxicology of Animal Venoms and Poisons; Meier, J., White, J., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, 1995; pp. 59–74. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, R. J.; Molgó, J.; Adams, D. J. Ciguatera toxins: Pharmacology of toxins involved in ciguatera and related fish poisonings. In Seafood and Freshwater Toxins. Pharmacology, Physiology and Detection; Botana, L. M., Ed.; Marcel Dekker, Inc: New York, 2000; pp. 419–447. [Google Scholar]
- Bagnis, R.; Kuberski, T.; Laugier, S. Clinical observations on 3,009 cases of ciguatera (fish poisoning) in the South Pacific. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg 1979, 28, 1067–1073. [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence, D. N.; Enriquez, M. B.; Lumish, R. M.; Maceo, A. Ciguatera fish poisoning in Miami. JAMA, J. Am. Med. Assoc 1980, 244, 254–258. [Google Scholar]
- Swift, A. E.; Swift, T. R. Ciguatera. J. Toxicol.-Clin. Toxicol 1993, 31, 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Glaziou, P.; Legrand, A.-M. The epidemiology of ciguatera fish poisoning. Toxicon 1994, 32, 863–873. [Google Scholar]
- Quod, J. P.; Turquet, J. Ciguatera in Reunion Island (SW Indian Ocean): epidemiology and clinical patterns. Toxicon 1996, 34, 779–785. [Google Scholar]
- Pearn, J. H. Neurology of ciguatera. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2001, 70, 4–8. [Google Scholar]
- Arena, P.; Levin, B.; Fleming, L. E.; Friedman, M. A.; Blythe, D. G. A pilot study of the cognitive and psychological correlates of chronic ciguatera poisoning. Harmful Algae 2004, 3, 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Lehane, L.; Lewis, R. J. Ciguatera: recent advances but the risk remains. Int. J. Food Microbiol 2000, 61, 91–125. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, C. K.; Hung, P.; Lee, K. L.; Kam, K. M. Study of an outbreak of ciguatera fish poisoning in Hong Kong. Toxicon 2005, 46, 563–571. [Google Scholar]
- Withers, N. W. Ciguatera fish toxins and poisoning. In Handbook of Natural Toxins and Venoms; Tu, A. T., Ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, 1988; Volume 3, pp. 31–61. [Google Scholar]
- Backer, L. C.; Dickey, R. W.; Poli, M. A.; Davis, C.; Luber, G.; Friedman, M. A.; Fleming, L. E.; Patel, M.; Blythe, D. G. Development of a biological marker for exposure to ciguatera toxins. 11th International Conference on Harmful Algae Blooms, Cape Town, South Africa; 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bagnis, R. A.; Legrand, A.-M. Clinical features on 12,890 cases of ciguatera (fish poisoning) in French Polynesia. In Progress in Venom and Toxin Research; Gopalakrishnakone, P., Tan, C. K., Eds.; Faculty of Science, National University of Singapore: Singapore, 1987; pp. 372–384. [Google Scholar]
- Narayan, Y. Fish poisoning in Fiji. Fiji Med. J 1980, 8, 567. [Google Scholar]
- Poon-King, C. M.; Chen, A.; Poon-King, T. Ciguatera fish poisoning in industrial ship crewmembers: a retrospective study in a seaport general practice in Trinidad and Tobago. West Indian Med. J 2004, 53, 220–226. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, R.; Jong, E. C. Ciguatera: Caribbean and Indo-Pacific fish poisoning. West. J. Med 1983, 138, 872–874. [Google Scholar]
- Holt, R. J.; Miro, G.; Del Valle, A. An analysis of poison control center reports of ciguatera toxicity in Puerto Rico for one year. J. Toxicol.-Clin. Toxicol 1984, 22, 177–185. [Google Scholar]
- Dawson, J. Fish poisoning in American Samoa. Hawaii Med. J 1977, 36, 239–243. [Google Scholar]
- Schnorf, H.; Taurarii, M.; Cundy, T. Ciguatera fish poisoning: a double-blind randomized trial of mannitol therapy. Neurology 2002, 58, 873–880. [Google Scholar]
- Goonetilleke, A.; Harris, J. B. Envenomation and consumption of poisonous seafood. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2002, 73, 103–109. [Google Scholar]
- Bagnis, R. Clinical aspects of ciguatera (fish poisoning) in French Polynesia. Hawaii Med. J 1968, 28, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Cameron, J.; Capra, M. F. The basis of the paradoxical disturbance of temperature perception in ciguatera poisoning. J. Toxicol.-Clin. Toxicol 1993, 31, 571–579. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y. G.; Taylor, T. B.; Finch, R. E.; Moeller, P. D.; Ramsdell, J. S. Neuroexcitatory actions of ciguatoxin on brain regions associated with thermoregulation. Neuroreport 1995, 6, 305–309. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, N. D. Ciguatera in the Pacific: incidence and implication for marine resources development. In Seafood Toxins; Ragelis, E. P., Ed.; American Chemical Society: Washington D.C, 1984; pp. 289–306. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, N. D. Ciguatera, health and human adaptation in the Pacific. PhD Thesis, University of California, Berkeley, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Pearce, R.; Hines, C., Jr; Burns, T. W.; Clark, C. E. Ciguatera (fish poisoning). Southern Medical Journal 1983, 76, 560–561. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, J. A.; Agnew, W. S.; Levinson, S. R. Principal glycopeptide of the tetrodotoxin/saxitoxin binding protein from Electrophorus electricus: isolation and partial chemical and physical characterization. Biochemistry 1983, 22, 462–470. [Google Scholar]
- Ayyar, D. R.; Mullaly, W. J. Ciguatera: clinical and electrophysiologic observations. Neurology 1977, 26, 354. [Google Scholar]
- Cameron, J.; Flowers, A. E.; Capra, M. F. Effects of ciguatoxin on nerve excitability in rats (Part I). J. Neurol. Sci 1991, 101, 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Cameron, J.; Flowers, A. E.; Capra, M. F. Electrophysiological studies on ciguatera poisoning in man (Part II). J. Neurol. Sci 1991, 101, 93–97. [Google Scholar]
- Parkin, P. J.; Le Quesne, P. M. Effect of a synthetic pyrethroid deltamethrin on excitability changes following a nerve impulse. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1982, 45, 337–342. [Google Scholar]
- Withers, N. W. Ciguatera fish poisoning. Annu. Rev. Med 1982, 33, 97–111. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, T. Y.; Wang, A. Y. Life-threatening bradycardia and hypotension in a patient with ciguatera fish poisoning. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg 1993, 87, 71. [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie, N. C. Ciguatera poisoning. In Toxic Plants and Animals: A Guide for Australia; Covacevich, J., Davie, P., Pearn, J., Eds.; Queensland Museum; Brisbane, 1987; pp. 160–169. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, R. J. Ciguatera in south-eastern Queensland. In Toxic Plants and Animals: a Guide for Australia; Covacevich, J., Davie, P., Pearn, J., Eds.; Queensland Museum; Brisbane, 1987; pp. 181–187. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, F. E.; Egen, N. B. Ciguateric fishes, ciguatoxin (CTX) and ciguatera poisoning. J. Toxicol 1991, 10, 36–62. [Google Scholar]
- Barton, E. D.; Tanner, P.; Turchen, S. G.; Tunget, C. L.; Manoguerra, A.; Clark, R. F. Ciguatera fish poisoning. A southern California epidemic. West. J. Med 1995, 163, 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Bagnis, R.; Chanteau, S.; Chungue, E.; Hurtel, J. M.; Yasumoto, T.; Inoue, A. Origins of ciguatera fish poisoning: a new dinoflagellate, Gambierdiscus toxicus Adachi and Fukuyo, definitively involved as a causal agent. Toxicon 1980, 18, 199–208. [Google Scholar]
- Helfrich, P. Fish poisoning in Hawaii. Hawaii Med. J 1963, 22, 361–372. [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer, P.; Jollow, D.; Scheuer, P. J.; York, R.; McMillan, J.; Withers, N. W.; Fundenburg, H.; Higerd, T. The effect of ciguatera associated toxins in mice. Am. Chem. Soc. Symp. on Seafood Toxins 1984, 262, 322–329. [Google Scholar]
- Kew, C. K.; Ming, L. K.; Hang, W. M. The mechanism of respiratory failure in ciguatera poisoning. J. Pathol 1969, 97, 89–92. [Google Scholar]
- Legrand, A.-M.; Lotte, C.; Bagnis, R. Respiratory and cardiovascular effects of ciguatoxin in cats; antagonistic action of hexamethonium, atropine, propranolol, phentolamine, yohimbine, prazosin, verapamil, calcium and lidocaine. Proceedings of the 5th International Coral Reef Congress, Tahiti; 1985; pp. 463–466. [Google Scholar]
- Legrand, A.-M.; Galonnier, M.; Bagnis, R. Studies on the mode of action of ciguateric toxins. Toxicon 1982, 20, 311–315. [Google Scholar]
- Terao, K.; Ito, E.; Oarada, M.; Ishibashi, Y.; Legrand, A.-M.; Yasumoto, T. Light and electron microscopic studies of pathologic changes induced in mice by ciguatoxin poisoning. Toxicon 1991, 29, 633–643. [Google Scholar]
- Terao, K.; Ito, E.; Yasumoto, T. Light and electron microscopic studies of the murine heart after repeated administrations of ciguatoxin or ciguatoxin-4c. Nat. Toxins 1992, 1, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Legrand, A.-M.; Bagnis, R. Effects of ciguatoxin and maitotoxin on isolated rat atria and rabbit duodenum. Toxicon 1984, 22, 471–475. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, R. J.; Endean, R. Direct and indirect effects of ciguatoxin on guinea-pig atria and papillary muscles. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol 1986, 334, 313–322. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, R. J.; Hoy, A. W.; McGiffin, D. C. Action of ciguatoxin on human atrial trabeculae. Toxicon 1992, 30, 907–914. [Google Scholar]
- Seino, A.; Kobayashi, M.; Momose, K.; Yasumoto, T.; Ohizumi, Y. The mode of inotropic action of ciguatoxin on guinea-pig cardiac muscle. Brit. J. Pharmacol 1988, 95, 876–882. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, R. J. Negative inotropic and arrhythmic effects of high doses of ciguatoxin on guinea-pig atria and papillary muscles. Toxicon 1988, 26, 639–649. [Google Scholar]
- Marquais, M.; Vernoux, J. P.; Molgó, J.; Sauviat, M. P.; Lewis, R. J. Isolation and electrophysiological characterisation of a new ciguatoxin extracted from Caribbean fish. In Harmful Microalgae; Reguera, B., Blanco, J., Fernández, M. L., Wyatt, R. J., Eds.; Santiago De Compostella: Xunta de Galicia and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: Santiago, 1998; pp. 476–477. [Google Scholar]
- Sauviat, M. P.; Marquais, M.; Vernoux, J. P. Muscarinic effects of the Caribbean ciguatoxin C-CTX-1 on frog atrial heart muscle. Toxicon 2002, 40, 1155–1163. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, R. J.; Endean, R. Mode of action of ciguatoxin from the Spanish Mackerel, Scomberomorus commersoni, on the guinea-pig ileum and vas deferens. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther 1984, 228, 756–760. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, R. J.; Hoy, A. W. Comparative action of three major ciguatoxins on guinea-pig atria and ilea. Toxicon 1993, 31, 437–446. [Google Scholar]
- Ohizumi, Y.; Shibata, S.; Tachibana, K. Mode of the excitatory and inhibitory actions of ciguatoxin in the guinea-pig vas deferens. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther 1981, 217, 475–480. [Google Scholar]
- Ohizumi, Y.; Ishida, Y.; Shibata, S. Mode of the ciguatoxin-induced supersensitivity in the guinea-pig vas deferens. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther 1982, 221, 748–752. [Google Scholar]
- Brock, J. A.; McLachlan, E. M.; Jobling, P.; Lewis, R. J. Electrical activity in rat tail artery during asynchronous activation of postganglionic nerve terminals by ciguatoxin-1. Brit. J. Pharmacol 1995, 116, 2213–2220. [Google Scholar]
- Bidard, J. N.; Vijverberg, H. P.; Frelin, C.; Chungue, E.; Legrand, A.-M.; Bagnis, R.; Lazdunski, M. Ciguatoxin is a novel type of Na+ channel toxin. J. Biol. Chem 1984, 259, 8353–8357. [Google Scholar]
- Molgó, J.; Comella, J. X.; Legrand, A.-M. Ciguatoxin enhances quantal transmitter release from frog motor nerve terminals. Brit. J. Pharmacol 1990, 99, 695–700. [Google Scholar]
- Molgó, J.; Gaudry-Talarmain, Y. M.; Legrand, A.-M.; Moulian, N. Ciguatoxin extracted from poisonous moray eels Gymnothorax javanicus triggers acetylcholine release from Torpedo cholinergic synaptosomes via reversed Na+-Ca2+ exchange. Neurosci Lett 1993, 160, 65–68. [Google Scholar]
- Gaudry-Talarmain, Y. M.; Molgó, J.; Meunier, F. A.; Moulian, N.; Legrand, A.-M. Reversed mode Na+-Ca2+ exchange activated by ciguatoxin (CTX-1b) enhances acetylcholine release from Torpedo cholinergic synaptosomes. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci 1996, 779, 404–406. [Google Scholar]
- Molgó, J.; Comella, J. X.; Shimahara, T.; Legrand, A.-M. Tetrodotoxin-sensitive ciguatoxin effects on quantal release, synaptic vesicle depletion, and calcium mobilization. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci 1991, 635, 485–488. [Google Scholar]
- Hamblin, P. A.; McLachlan, E. M.; Lewis, R. J. Sub-nanomolar concentrations of ciguatoxin-1 excite preganglionic terminals in guinea pig sympathetic ganglia. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol 1995, 352, 236–246. [Google Scholar]
- Benoit, E.; Legrand, A.-M.; Dubois, J. M. Effects of ciguatoxin on current and voltage clamped frog myelinated nerve fibre. Toxicon 1986, 24, 357–364. [Google Scholar]
- Birinyi-Strachan, L. C.; Gunning, S. J.; Lewis, R. J.; Nicholson, G. M. Block of voltage-gated potassium channels by Pacific ciguatoxin-1 contributes to increased neuronal excitability in rat sensory neurons. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol 2005, 204, 175–186. [Google Scholar]
- Benoit, E.; Legrand, A.-M. Gambiertoxin-induced modifications of the membrane potential of myelinated nerve fibres. Mem. Queensland Mus 1994, 34, 461–464. [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro, L.; Doyle, J. P.; Hensley, P.; Colman, D. R.; Hendrickson, W. A. Crystal structure of the extracellular domain from P0, the major structural protein of peripheral nerve myelin. Neuron 1996, 17, 435–449. [Google Scholar]
- Cestèle, S.; Catterall, W. A. Molecular mechanisms of neurotoxin action on voltage-gated sodium channels. Biochimie 2000, 82, 883–892. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson, G. M.; Little, M. J. Spider neurotoxins targeting voltage-gated sodium channels. Toxin Rev 2005, 25, 315–345. [Google Scholar]
- Strachan, L. C.; Lewis, R. J.; Nicholson, G. M. Differential actions of Pacific ciguatoxin-1 on sodium channel subtypes in mammalian sensory neurons. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther 1999, 288, 379–388. [Google Scholar]
- Hogg, R. C.; Lewis, R. J.; Adams, D. J. Ciguatoxin-induced oscillations in membrane potential and action potential firing in rat parasympathetic neurons. Eur. J. Neurosci 2002, 16, 242–248. [Google Scholar]
- Hogg, R. C.; Lewis, R. J.; Adams, D. J. Ciguatoxin (CTX-1) modulates single tetrodotoxin-sensitive sodium channels in rat parasympathetic neurones. Neurosci. Lett 1998, 252, 103–106. [Google Scholar]
- Sangameswaran, L.; Delgado, S. G.; Fish, L. M.; Koch, B. D.; Jakeman, L. B.; Stewart, G. R.; Sze, P.; Hunter, J. C.; Eglen, R. M.; Herman, R. C. Structure and function of a novel voltage-gated, tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channel specific to sensory neurons. J. Biol. Chem 1996, 271, 5953–5956. [Google Scholar]
- Dib-Hajj, S. D.; Tyrrell, L.; Black, J. A.; Waxman, S. G. NaN, a novel voltage-gated Na channel, is expressed preferentially in peripheral sensory neurons and down-regulated after axotomy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 8963–8968. [Google Scholar]
- Beckh, S. Differential expression of sodium channel mRNAs in rat peripheral nervous system and innervated tissues. FEBS Lett 1990, 262, 317–322. [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell, J. H.; Schaller, K. L.; Lasher, R. S.; Peles, E.; Levinson, S. R. Sodium channel Nav1.6 is localized at nodes of Ranvier, dendrites, and synapses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 5616–5620. [Google Scholar]
- Toledo-Aral, J. J.; Moss, B. L.; He, Z. J.; Koszowski, A. G.; Whisenand, T.; Levinson, S. R.; Wolf, J. J.; Silos-Santiago, I.; Halegoua, S.; Mandel, G. Identification of PN1, a predominant voltage-dependent sodium channel expressed principally in peripheral neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 1527–1532. [Google Scholar]
- Felts, P. A.; Yokoyama, S.; Dib-Hajj, S.; Black, J. A.; Waxman, S. G. Sodium channel α-subunit mRNAs I, II, III, NaG, Na6 and hNE (PN1): different expression patterns in developing rat nervous system. Mol. Brain Res 1997, 45, 71–82. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaoka, K.; Inoue, M.; Miyahara, H.; Miyazaki, K.; Hirama, M. A quantitative and comparative study of the effects of a synthetic ciguatoxin CTX3C on the kinetic properties of voltage-dependent sodium channels. Brit. J. Pharmacol 2004, 142, 879–889. [Google Scholar]
- Benoit, E.; Legrand, A.-M. Purified ciguatoxin-induced modifications in excitability of myelinated nerve fibre. Bull. Soc. Pathol. Exot 1992, 85, 497–499. [Google Scholar]
- Benoit, E.; Juzans, P.; Legrand, A.-M.; Molgó, J. Nodal swelling produced by ciguatoxin-induced selective activation of sodium channels in myelinated nerve fibers. Neuroscience 1996, 71, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar]
- Birinyi-Strachan, L. C.; Davies, M. J.; Lewis, R. J.; Nicholson, G. M. Neuroprotectant effects of iso-osmolar D-mannitol to prevent Pacific ciguatoxin-1 induced alterations in neuronal excitability: a comparison with other osmotic agents and free radical scavengers. Neuropharmacology 2005, 49, 669–686. [Google Scholar]
- Rizzo, M. A.; Kocsis, J. D.; Waxman, S. G. Mechanisms of paresthesiae, dysesthesiae, and hyperesthesiae: role of Na+ channel heterogeneity. Eur. Neurol 1996, 36, 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Wall, P. D.; Devor, M. Sensory afferent impulses originate from dorsal root ganglia as well as from the periphery in normal and nerve injured rats. Pain 1983, 17, 321–339. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, D. Sodium channels as targets for neurotoxins: mode of action and interaction of neurotoxins with receptor sites on sodium channels. In Toxins and Signal Transduction; Lazarowici, P., Gutman, Y., Eds.; Harwood Press: Amsterdam, 1997; Vol Cellular And Molecular Mechanisms of Toxin Action Series; pp. 119–149. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, D. A new approach to insect-pest control-combination of neurotoxins interacting with voltage sensitive sodium channels to increase selectivity and specificity. Invert. Neurosci 1997, 3, 103–116. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, R.; Huang, Z. Y.; Chen, A. C.; Gurevitz, M.; Dong, K. Identification of amino acid residues in the insect sodium channel critical for pyrethroid binding. Mol. Pharmacol 2005, 67, 513–522. [Google Scholar]
- Lombet, A.; Bidard, J.-N.; Lazdunski, M. Ciguatoxin and brevetoxins share a common receptor site on the neuronal voltage-dependent Na+ channel. FEBS Lett 1987, 219, 355–359. [Google Scholar]
- Pauillac, S.; Bléhaut, J.; Cruchet, P.; Lotte, C.; Legrand, A.-M. Recent advances in detection of ciguatoxins in French Polynesia. In Harmful Algal Blooms; Lassus, P., Arzul, G., Erard, E., Gentien, P., Marcaillou, C., Eds.; Lavoisier, Intercept Ltd: France, 1995; pp. 801–808. [Google Scholar]
- Dechraoui, M. Y.; Naar, J.; Pauillac, S.; Legrand, A.-M. Ciguatoxins and brevetoxins, neurotoxic polyether compounds active on sodium channels. Toxicon 1999, 37, 125–143. [Google Scholar]
- Poli, M. A.; Lewis, R. J.; Dickey, R. W.; Musser, S. M.; Buckner, C. A.; Carpenter, L. G. Identification of Caribbean ciguatoxins as the cause of an outbreak of fish poisoning among U.S. soldiers in Haiti. Toxicon 1997, 35, 733–741. [Google Scholar]
- Bottein Dechraoui, M. Y.; Ramsdell, J. S. Type B brevetoxins show tissue selectivity for voltage-gated sodium channels: comparison of brain, skeletal muscle and cardiac sodium channels. Toxicon 2003, 41, 919–927. [Google Scholar]
- Poli, M. A.; Mende, T. J.; Baden, D. G. Brevetoxins, unique activators of voltage-sensitive sodium channels, bind to specific sites in rat brain synaptosomes. Mol. Pharmacol 1986, 30, 129–135. [Google Scholar]
- Sharkey, R. G.; Jover, E.; Couraud, F.; Baden, D. G.; Catterall, W. A. Allosteric modulation of neurotoxin binding to voltage-sensitive sodium channels by Ptychodiscus brevis toxin 2. Mol. Pharmacol 1987, 31, 273–278. [Google Scholar]
- Cestèle, S.; Sampieri, F.; Rochat, H.; Gordon, D. Tetrodotoxin reverses brevetoxin allosteric inhibition of scorpion α-toxin binding on rat brain sodium channels. J. Biol. Chem 1996, 271, 18329–18332. [Google Scholar]
- Trainer, V. L.; Baden, D. G.; Catterall, W. A. Identification of peptide components of the brevetoxin receptor site of rat brain sodium channels. J. Biol. Chem 1994, 269, 19904–19909. [Google Scholar]
- Trainer, V. L.; Thomsen, W. J.; Catterall, W. A.; Baden, D. G. Photoaffinity labelling of the brevetoxin receptor on sodium channels in rat brain synaptosomes. Mol. Pharmacol. 1991, 40, 988–994. [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo, J.; Liberona, J. L.; Molgó, J.; Jaimovich, E. Pacific ciguatoxin-1b effect over Na+ and K+ currents, inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate content and intracellular Ca2+ signals in cultured rat myotubes. Brit. J. Pharmacol 2002, 137, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar]
- Safronov, B. V.; Bischoff, U.; Vogel, W. Single voltage-gated K+ channels and their functions in small dorsal root ganglion neurones of rat. J. Physiol 1996, 493, 393–408. [Google Scholar]
- Hille, B. Ion channels of excitable membranes; Sinauer Associates, Inc: Sunderland; p. 2001.
- Baker, M.; Bostock, H.; Grafe, P. Accommodation in rat myelinated axons depends on two pharmacologically distinct types of potassium channels. J. Physiol 1985, 369, 102P. [Google Scholar]
- Amir, R.; Liu, C. N.; Kocsis, J. D.; Devor, M. Oscillatory mechanism in primary sensory neurones. Brain 2002, 125, 421–435. [Google Scholar]
- Ghiaroni, V.; Sasaki, M.; Fuwa, H.; Rossini, G. P.; Scalera, G.; Yasumoto, T.; Pietra, P.; Bigiani, A. Inhibition of voltage-gated potassium currents by gambierol in mouse taste cells. Toxicol. Sci 2005, 85, 657–665. [Google Scholar]
- Molgó, J.; Meunier, F. A.; Dechraoui, M. Y.; Benoit, E.; Mattei, C.; Legrand, A.-M. Sodium-dependent alterations of synaptic transmission mechanisms by brevetoxins and ciguatoxins. In Harmful Microalgae; Reguera, B., Blanco, J., Fernández, M. L., Wyatt, T., Eds.; Santiago De Compostella: Xunta de Galicia and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: Santiago, 1998; pp. 594–497. [Google Scholar]
- Molgó, J.; Shimahara, T.; Legrand, A.-M. Ciguatoxin, extracted from poisonous moray eels, causes sodium-dependent calcium mobilization in NG108-15 neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid cells. Neurosci. Lett 1993, 158, 147–150. [Google Scholar]
- Mattei, C.; Dechraoui, M. Y.; Molgó, J.; Meunier, F. A.; Legrand, A.-M.; Benoit, E. Neurotoxins targetting receptor site 5 of voltage-dependent sodium channels increase the nodal volume of myelinated axons. J. Neurosci. Res 1999, 55, 666–673. [Google Scholar]
- Allsop, J. L.; Martini, L.; Lebris, H.; Pollard, J.; Walsh, J.; Hodgkinson, S. Les manifestations neurologiques de la ciguatera. Rev. Neurol. (Paris) 1986, 142, 590–597. [Google Scholar]
- Mattei, C.; Benoit, E.; Juzans, P.; Legrand, A.-M.; Molgó, J. Gambiertoxin (CTX-4B), purified from wild Gambierdiscus toxicus dinoflagellates, induces Na+-dependent swelling of single frog myelinated axons and motor nerve terminals in situ. Neurosci. Lett 1997, 234, 75–78. [Google Scholar]
- Mattei, C.; Molgó, J.; Marquais, M.; Vernoux, J.; Benoit, E. Hyperosmolar d-mannitol reverses the increased membrane excitability and the nodal swelling caused by Caribbean ciguatoxin-1 in single frog myelinated axons. Brain Res 1999, 847, 50–58. [Google Scholar]
- Molgó, J.; Juzans, P.; Legrand, A.-M. Confocal laser scanning microscopy: a new tool for studying the effects of ciguatoxin (CTX-1b) and mannitol at motor nerve terminals of the neuromuscular junction in situ. Mem. Queensland Mus 1994, 34, 577–585. [Google Scholar]
- Benoit, E.; Mattei, C.; Ouanounou, G.; Meunier, F. A.; Suput, D.; Le Gall, F.; Marquais, M.; Dechraoui, M. Y.; Molgó, J. Ionic mechanisms involved in the nodal swelling of myelinated axons caused by marine toxins. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett 2002, 7, 317–321. [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk, P.; Verkhratsky, A. Calcium stores in neurons and glia. Neuroscience 1994, 63, 381–404. [Google Scholar]
- Molgó, J.; Shimahara, T.; Gaudry-Talarmain, Y. M.; Comella, J. X.; Legrand, A.-M. Ciguatoxin-induced changes in acetylcholine release and in cytosolic calcium levels. Bull. Soc. Pathol. Exot 1992, 85, 486–488. [Google Scholar]
- Yano, K.; Higashida, H.; Inoue, R.; Nozawa, Y. Bradykinin-induced rapid breakdown of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in neuroblastoma X glioma hybrid NG108-15 cells. J. Biol. Chem 1984, 259, 10201–10207. [Google Scholar]
- Henzi, V.; MacDermott, A. B. Characteristics and function of Ca2+- and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-releasable stores of Ca2+ in neurons. Neuroscience 1992, 46, 251–273. [Google Scholar]
- Gusovsky, F.; Daly, J. W.; Yasumoto, T.; Rojas, E. Differential effects of maitotoxin on ATP secretion and on phosphoinositide breakdown in rat pheochromocytoma cells. FEBS Lett 1988, 233, 139–142. [Google Scholar]
- Gusovsky, F.; Hollingsworth, E. B.; Daly, J. W. Regulation of phosphatidylinositol turnover in brain synaptoneurosomes: stimulatory effects of agents that enhance influx of sodium ions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 3003–3007. [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco, M. A.; Gaudry-Talarmain, Y. M.; Molgó, J. Ca2+-dependent changes of acetylcholine release and IP3 mass in Torpedo cholinergic synaptosomes. Neurochem. Int 1996, 29, 637–643. [Google Scholar]
- McDonough, P. M.; Goldstein, D.; Brown, J. H. Elevation of cytoplasmic calcium concentration stimulates hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate in chick heart cells: effect of sodium channel activators. Mol. Pharmacol 1988, 33, 310–315. [Google Scholar]
- Hermoni, M.; Barzilai, A.; Rahamimoff, H. Modulation of the Na+-Ca2+ antiport by its ionic environment: the effect of lithium. Isr. J. Med. Sci 1987, 23, 44–48. [Google Scholar]
- Banner, A. H.; Sasaki, S.; Helfrich, P.; Alender, C. B.; Scheuer, P. J. Bioassay of ciguatera toxin. Nature 1961, 189, 229–230. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, P. A.; Granade, H. R.; McMillan, J. P. The mouse ciguatoxin bioassay: a dose-response curve and symptomatology analysis. Toxicon 1983, 21, 363–369. [Google Scholar]
- Labrousse, H.; Matile, L. Toxicological biotest on Diptera larvae to detect ciguatoxins and various other toxic substances. Toxicon 1996, 34, 881–891. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, R. J. Detection of ciguatoxins and related benthic dinoflagellate toxins: in vivoand in vitromethods. In Manual on Harmful Marine Microalgae; Hallegraph, G. M., Anderson, D. M., Cembella, A. D., Eds.; IOC Manuals and Guides UNESCO: France, 1995; Volume 33, pp. 135–161. [Google Scholar]
- Vernoux, J. P.; Lahlou, N.; Magras, L. P.; Greaux, J. B. Chick feeding test: a simple system to detect ciguatoxin. Acta Trop 1985, 42, 235–240. [Google Scholar]
- Chungue, E.; Bagnis, R.; Parc, F. The use of mosquitoes (Aedes aegypti) to detect ciguatoxin in surgeon fishes (Ctenochaetus striatus). Toxicon 1984, 22, 161–164. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, R. J.; Hoy, A. W.; Sellin, M. Ciguatera and mannitol: in vivo and in vitro assessment in mice. Toxicon 1993, 31, 1039–1050. [Google Scholar]
- Park, D. L. Evolution of methods for assessing ciguatera toxins in fish. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol 1994, 136, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Manger, R. L.; Leja, L. S.; Lee, S. Y.; Hungerford, J. M.; Hokama, Y.; Dickey, R. W.; Granade, H. R.; Lewis, R.; Yasumoto, T.; Wekell, M. M. Detection of sodium channel toxins: directed cytotoxicity assays of purified ciguatoxins, brevetoxins, saxitoxins, and seafood extracts. J. AOAC Int 1995, 78, 521–527. [Google Scholar]
- Manger, R. L.; Leja, L. S.; Lee, S. Y.; Hungerford, J. M.; Wekell, M. M. Tetrazolium-based cell bioassay for neurotoxins active on voltage-sensitive sodium channels: semiautomated assay for saxitoxins, brevetoxins, and ciguatoxins. Anal. Biochem 1993, 214, 190–194. [Google Scholar]
- Louzao, M. C.; Vieytes, M. R.; Yasumoto, T.; Botana, L. M. Detection of sodium channel activators by a rapid fluorimetric microplate assay. Chem. Res. Toxicol 2004, 17, 572–578. [Google Scholar]
- Fairey, E. R.; Edmunds, J. S.; Ramsdell, J. S. A cell-based assay for brevetoxins, saxitoxins, and ciguatoxins using a stably expressed c-fos-luciferase reporter gene. Anal. Biochem 1997, 251, 129–132. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, R. J.; Jones, A.; Vernoux, J. P. HPLC/tandem electrospray mass spectrometry for the determination of Sub-ppb levels of Pacific and Caribbean ciguatoxins in crude extracts of fish. Anal. Chem 1999, 71, 247–250. [Google Scholar]
- Oguri, H.; Hirama, M.; Tsumuraya, T.; Fujii, I.; Maruyama, M.; Uehara, H.; Nagumo, Y. Synthesis-based approach toward direct sandwich immunoassay for ciguatoxin CTX3C. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2003, 125, 7608–7612. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, L. H.; Hokama, Y.; Abad, M. A.; Oyama, M.; Miyahara, J. T. Comparison of three different assays for the assessment of ciguatoxin in fish tissues: radioimmunoassay, mouse bioassay and in vitro guinea pig atrium assay. Toxicon 1982, 20, 907–912. [Google Scholar]
- Ganal, C. A.; Asahina, A. Y.; Hokama, Y.; Miyahara, J. T. Characterization of marine toxin(s) in Myripristis sp. by immunological, mouse toxicity, and guinea pig assays. J. Clin. Lab. Anal 1993, 7, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Hokama, Y.; Banner, A. H.; Boylan, D. B. A radioimmunoassay for the detection of ciguatoxin. Toxicon 1977, 15, 317–325. [Google Scholar]
- Hokama, Y.; Abad, M. A.; Kimura, L. H. A rapid enzyme-immunoassay for the detection of ciguatoxin in contaminated fish tissues. Toxicon 1983, 21, 817–824. [Google Scholar]
- Hokama, Y. A rapid, simplified enzyme immunoassay stick test for the detection of ciguatoxin and related polyethers from fish tissues. Toxicon 1985, 23, 939–946. [Google Scholar]
- Hokama, Y.; Asahina, A. Y.; Hong, T. W.; Shang, E. S.; Miyahara, J. T. Evaluation of the stick enzyme immunoassay in Caranx sp. and Seriola dumerili associated with ciguatera. J. Clin. Lab. Anal 1990, 4, 363–366. [Google Scholar]
- Hokama, Y. Simplified solid-phase immunobead assay for detection of ciguatoxin and related polyethers. J. Clin. Lab. Anal 1990, 4, 213–217. [Google Scholar]
- Hokama, Y.; Asahina, A. Y.; Shang, E. S.; Hong, T. W.; Shirai, J. L. Evaluation of the Hawaiian reef fishes with the solid phase immunobead assay. J. Clin. Lab. Anal 1993, 7, 26–30. [Google Scholar]
- Hokama, Y. Immunological studies using monoclonal antibodies for detection of low dalton marine toxins. Food Addit. Contam 1993, 10, 83–95. [Google Scholar]
- Hokama, Y. Recent methods for detection of seafood toxins: recent immunological methods for ciguatoxin and related polyethers. Food Addit. Contam 1993, 10, 71–82. [Google Scholar]
- Bottein Dechraoui, M. Y.; Wang, Z.; Turquet, J.; Chinain, M.; Darius, T.; Cruchet, P.; Radwan, F. F.; Dickey, R. W.; Ramsdell, J. S. Biomonitoring of ciguatoxin exposure in mice using blood collection cards. Toxicon 2005, 46, 243–251. [Google Scholar]
- Matta, J.; Navas, J.; Milad, M.; Manger, R.; Hupka, A.; Frazer, T. A pilot study for the detection of acute ciguatera intoxication in human blood. J. Toxicol.-Clin. Toxicol 2002, 40, 49–57. [Google Scholar]
- Hokama, Y.; Takenaka, W. E.; Nishimura, K. L.; Ebesu, J. S.; Bourke, R.; Sullivan, P. K. A simple membrane immunobead assay for detecting ciguatoxin and related polyethers from human ciguatera intoxication and natural reef fishes. J. AOAC Int 1998, 81, 727–735. [Google Scholar]
- Hokama, Y.; Nishimura, K.; Takenaka, W.; Ebesu, J. S. Simplified solid-phase membrane immunobead assay (MIA) with monoclonal anti-ciguatoxin antibody (MAb-CTX) for detection of ciguatoxin and related polyether toxins. J. Nat. Toxins 1998, 7, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Halstead, B. W. Poisonous and Venomous Marine Animals of the World; Darwin Press: Princeton, NJ, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, R. T.; Villar, L. A. Symptomatic improvement with amitriptyline in ciguatera fish poisoning. N. Engl. J. Med 1986, 315, 65. [Google Scholar]
- Calvert, G. M.; Hryhorczuk, D. O.; Leikin, J. B. Treatment of ciguatera fish poisoning with amitriptyline and nifedipine. J. Toxicol.-Clin. Toxicol 1987, 25, 423–428. [Google Scholar]
- Lange, W. R.; Snyder, F. R.; Fudala, P. J. Travel and ciguatera fish poisoning. Arch. Intern. Med 1992, 152, 2049–2053. [Google Scholar]
- Berlin, R. M.; King, S. L.; Blythe, D. G. Symptomatic improvement of chronic fatigue with fluoxetine in ciguatera fish poisoning. Med. J. Aust 1992, 157, 567. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson, G. M.; Blanche, T.; Mansfield, K.; Tran, Y. Differential blockade of neuronal voltage-gated Na+ and K+ channels by antidepressant drugs. Eur. J. Pharmacol 2002, 452, 35–48. [Google Scholar]
- Perez, C. M.; Vasquez, P. A.; Perret, C. F. Treatment of ciguatera poisoning with gabapentin. N. Engl. J. Med 2001, 344, 692–693. [Google Scholar]
- Lange, W. R.; Kreider, S. D. A pilot study of the potential benefit of tocainide in the management of ciguatera toxicity. 1st Conference on International Travel Medicine, Zurich; 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Lange, W. R.; Kreider, S. D.; Hattwick, M.; Hobbs, J. Potential benefit of tocainide in the treatment of ciguatera: report of three cases. Am. J. Med 1988, 84, 1087–1088. [Google Scholar]
- Cameron, J.; Flowers, A. E.; Capra, M. F. Modification of the peripheral nerve disturbance in ciguatera poisoning in rats with lidocaine. Muscle & Nerve 1993, 16, 782–786. [Google Scholar]
- Hoy, A. W.; Lewis, R. J. The effect of potential therapeutics on ciguatoxin-inhibition of the rat phrenic nerve. In Recent Advances in Toxinology Research; Gopalakrishnakone, P., Tan, C. K., Eds.; Faculty of Science, National University of Singapore: Singapore, 1992; Volume 2, pp. 509–519. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, F. E. Ciguatera poisoning: a report of 35 cases. Toxicon 1975, 13, 383–385. [Google Scholar]
- Bourdy, G.; Cabalion, P.; Amade, P.; Laurent, D. Traditional remedies used in the western Pacific for the treatment of ciguatera poisoning. J. Ethnopharmacol 1992, 36, 163–174. [Google Scholar]
- Amade, P.; Laurent, D. Screening of traditional remedies used in ciguatera fish poisoning treatment. Rec. Adv. Toxinol. Res 1992, 2, 503–508. [Google Scholar]
- Benoit, E.; Laurent, D.; Mattei, C.; Legrand, A.-M.; Molgó, J. Reversal of Pacific-ciguatoxin-1B effects on myelinated axons by agents used in ciguatera treatment. Cymbium 2000, 24 Suppl, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Garrec, R. B.; Benoit, E.; Sauviat, M. P.; Lewis, R. J.; Molgó, J.; Laurent, D. Ability of some plant extracts, traditionally used to treat ciguatera fish poisoning, to prevent the in vitro neurotoxicity produced by sodium channel activators. Toxicon 2005, 46, 625–634. [Google Scholar]
- Palafox, N. A.; Jain, L. G.; Pinano, A. Z.; Gulick, T. M.; Williams, R. K.; Schatz, I. J. Successful treatment of ciguatera fish poisoning with intravenous mannitol. JAMA 1988, 259, 2740–2742. [Google Scholar]
- Pearn, J. H.; Lewis, R. J.; Ruff, T.; Tait, M.; Quinn, J.; Murtha, W.; King, G.; Mallett, A.; Gillespie, N. C. Ciguatera and mannitol: experience with a new treatment regimen. Med. J. Aust 1989, 151, 77–80. [Google Scholar]
- Blythe, D. G.; De Sylva, D. P.; Fleming, L. E.; Ayyar, R. A.; Baden, D. G.; Shrank, K. Clinical experience with i.v. mannitol in the treatment of ciguatera. Bull. Soc. Pathol. Exot 1992, 85, 425–426. [Google Scholar]
- Fenner, P. J.; Lewis, R. J.; Williamson, J. A.; Williams, M. L. A Queensland family with ciguatera after eating coral trout. Med. J. Aust 1997, 166, 473–475. [Google Scholar]
- Bagnis, R.; Spiegel, A.; Boutin, J. P.; Burucoa, C.; Nguyen, L.; Cartel, J. L.; Capdevielle, P.; Imbert, P.; Prigent, D.; Gras, C.; et al. (Evaluation of the efficacy of mannitol in the treatment of ciguatera in French Polynesia). Med. Trop. (Mars.) 1992, 52, 67–73.
- De Haro, L.; Hayek-Lanthois, M.; Joossen, F.; Affaton, M. F.; Jouglard, J. (Mass ciguatera poisoning after eating barracuda in Mexico: prognostic and therapeutic implications). Med. Trop. (Mars.) 1997, 57, 55–58.
- Stewart, M. P. Ciguatera fish poisoning: treatment with intravenous mannitol. Trop. Doct 1991, 21, 54–55. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, R. J.; Endean, R. Occurrence of a ciguatoxin-like substance in the Spanish mackerel (Scomberomorus commersoni). Toxicon 1983, 21, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Magovern, G. J., Jr; Bolling, S. F.; Casale, A. S.; Bulkley, B. H.; Gardner, T. J. The mechanism of mannitol in reducing ischemic injury: hyperosmolarity or hydroxyl scavenger? Circulation 1984, 70, I91–95. [Google Scholar]
- Desesso, J. M.; Scialli, A. R.; Goeringer, G. C. d-Mannitol, a specific hydroxyl free radical scavenger, reduces the developmental toxicity of hydroxyurea in rabbits. Teratology 1994, 49, 248–259. [Google Scholar]
- Isbister, G. K.; Kiernan, M. C. Neurotoxic marine poisoning. Lancet Neurol 2005, 4, 219–228. [Google Scholar]
© 2006 by MDPI Reproduction is permitted for noncommercial purposes.