Natural Products and Pharmacological Properties of Symbiotic Bacillota (Firmicutes) of Marine Macroalgae
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Aquatic Bacillota
3. Marine Macroalgae, a Good Source of Bioactive Bacillota
4. Secondary Metabolites of Marine Macroalgae Bacillota and Their Biosynthetic Gene Clusters
| Algae Species | Growth Medium | Bacterial Species | Biosynthetic Gene Cluster | Extract/ Compounds | Pharmacological Properties | MIC (µg/mL) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brown Algae Bacillota | |||||||
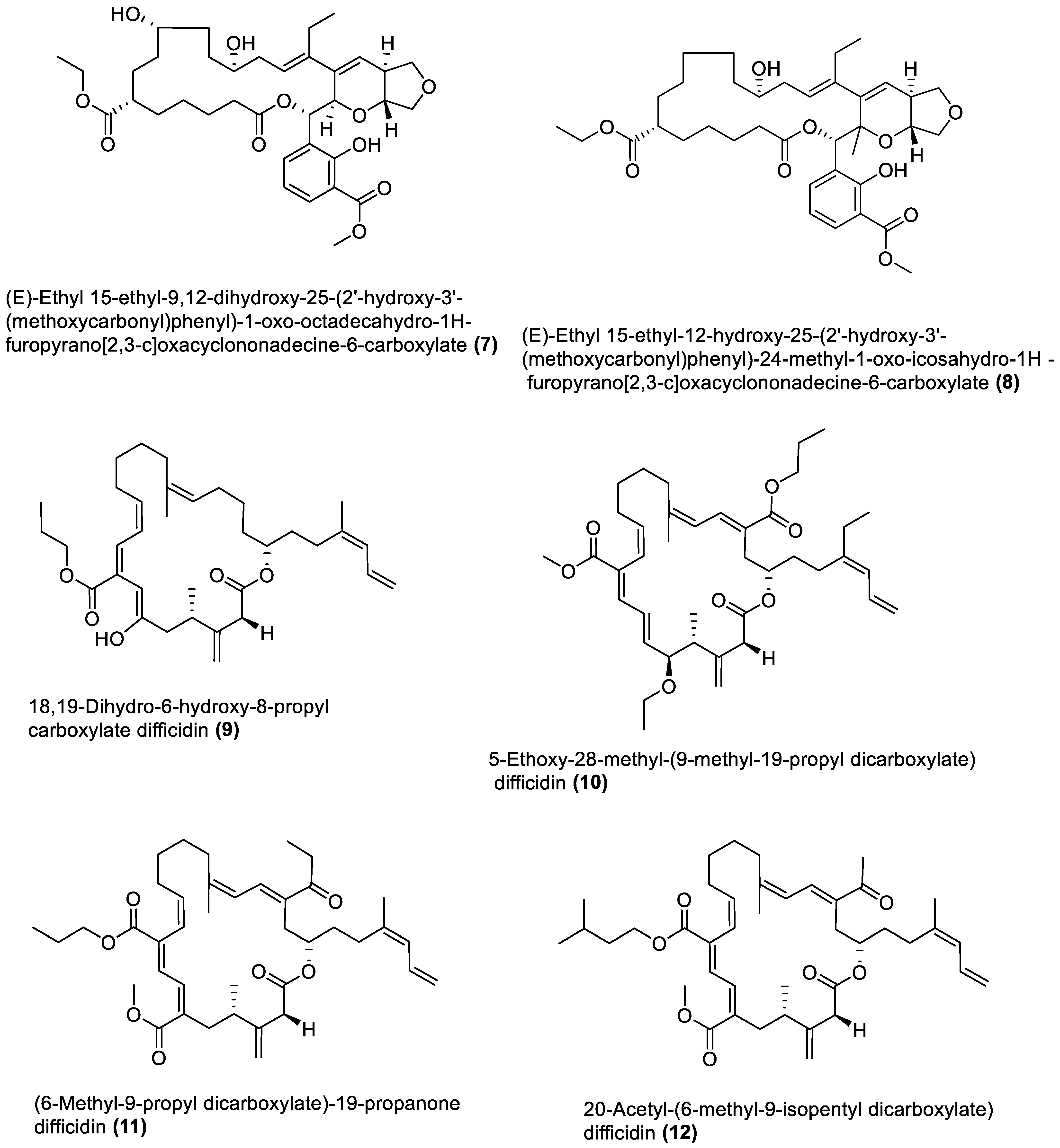
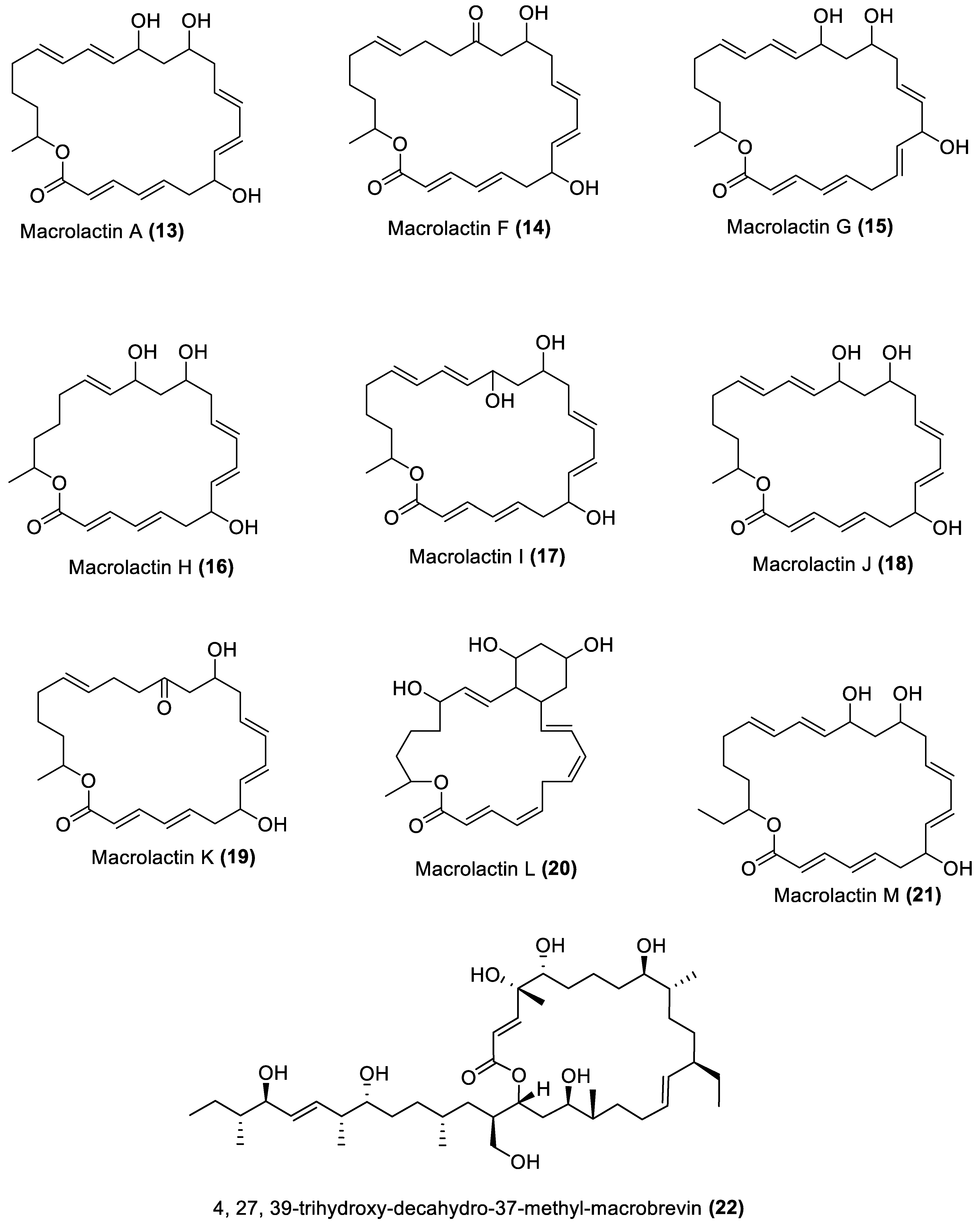
| Sargassum wightii | a ZMA * b NA a NA a ZMA | Bacillus species Bacillus atrophaeus MW821482 | pks pks nrps Siderophore | Ethyl acetate extract Ethyl acetate extract | Antibacterial Antioxidant Antihypertensive Antihypercholesterolamic Anti-inflammatory Anti-hyperglycemic Cytotoxicity Antioxidant Antibacterial Anti-inflammatory Anti-hyperglycemic Antihypertensive Antioxidant Anti-hypercholesterolemic Antibacterial | 6.25–12.5 ⁑ (133–492.04) ⁑ (498.12–735.42) ⁑ (10.21–24.32) ⁑ (5.22–735.45) ⁑ (92.02–759.24) ♯ 29.5 ♯ (133–4167) 6.25–12.5 ⁑ (9.74–788.8) ⁑ (118.1–513.4) ⁑ 713.6 ⁑ (413.2–429.8) ⁑ 22.23 6.25–12.5 | [85,86,87,88] |
| Anthophycus longifolius | a NA ** NA SWA ZMA * NA MA * NA | Bacillus subtilis MTCC 10403 | pks pks pks | (1) (35–38) (2) | Antibacterial Antibacterial Antibacterial | 3.12–50 3.12–25 ND | [89,90,91] |
| Sargassum myriocystum | MA * NA | Bacillus subtilis MTCC 10407 | pks | (26 and 27) | Antibacterial | ND | [92] |
| Fucus serratus | a TSA DSTA MA NA * CB | Bacillus licheniformis | ND | YbdN protein | Antibacterial | ND | [82] |
| Endarachne binghamiae | MA MB | Bacillus sp. | ND | Acetone extract | Antibacterial | 188.1–209.7 | [93] |
| Sargassum muticum | MA MB | Bacillus sp. | ND | Acetone extract | Cytotoxicity Antibacterial | ♯ 5.5 174 | [93] |
| Egregia menziesii | MA MB | Bacillus sp. | ND | Acetone extract | Antibacterial | 203.0–212.3 | [93] |
| Padina gymnospora | a NA ** NA SWA ZMA * NA | Bacillus amyloliquefaciens | pks | (28–31) | Antibacterial | ND | [94] |
| Zonaria tournefortii | d LB | Bacillus amyloliquefaciens S13 | ND | Volatile compounds | Antimicrobial | 64–>500 | [84] |
| Red algae Bacillota | |||||||
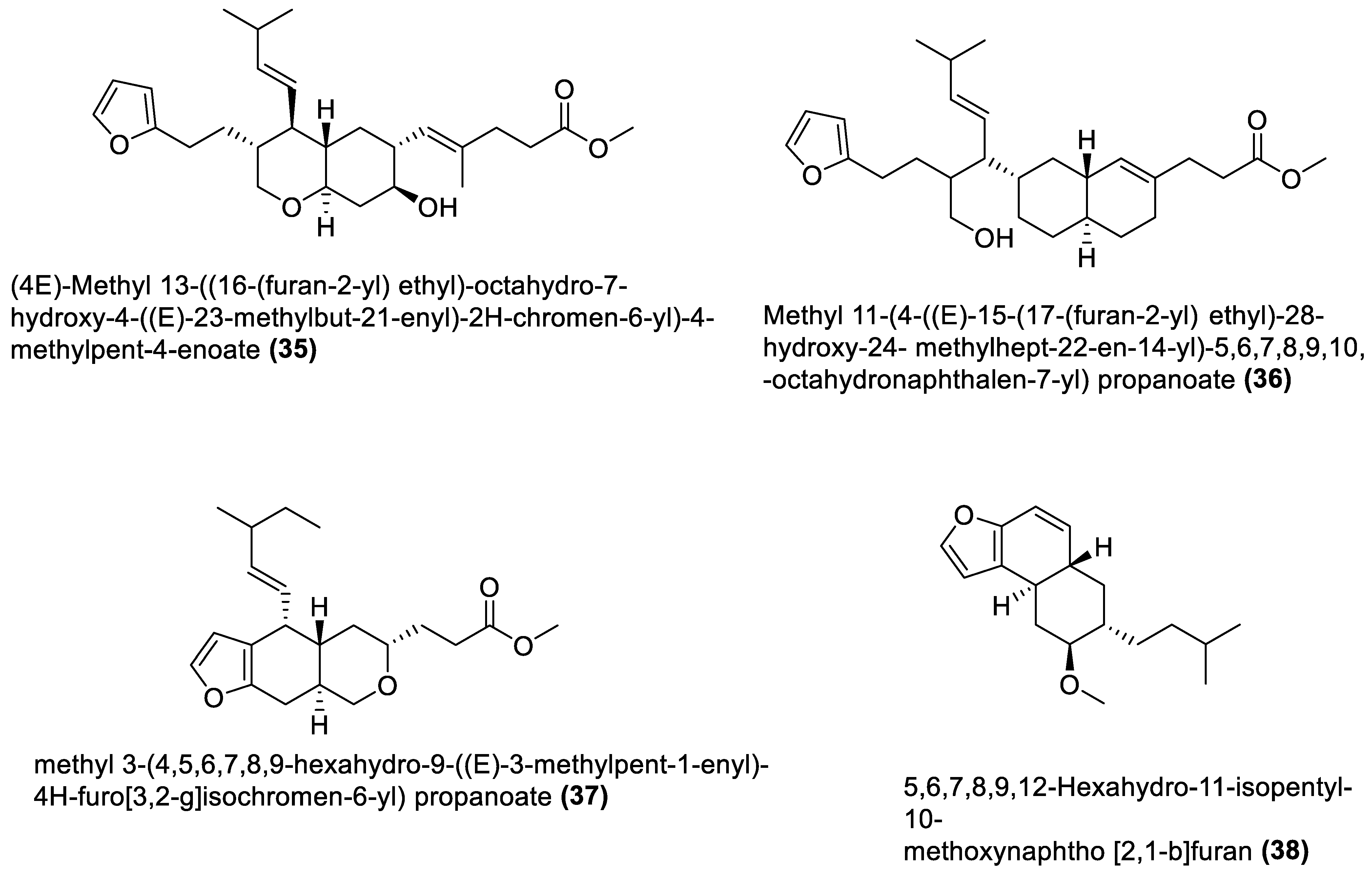
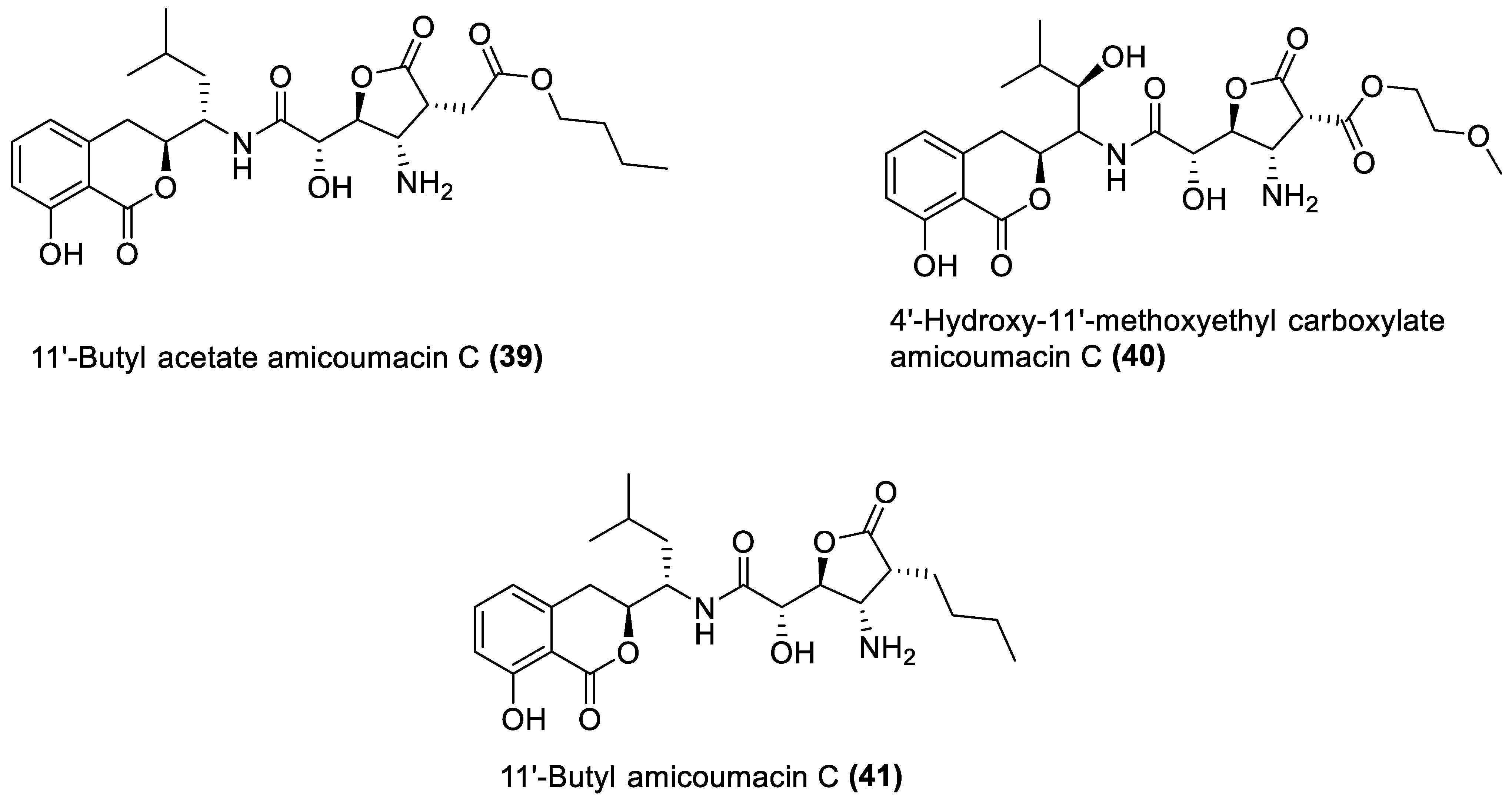
| Hypnea valentiae | a ZMA * MBSA | Bacillus amyloliquefaciens MB6 (MTCC 12716) | pks pks-nrps ND | (3–5) and (6–8) (39–41) Ethyl acetate extract | Antibacterial Antibacterial Antibacterial Anti-inflammatory Anti-hypercholesterolemic Antidiabetic Antioxidant Antibacterial | 0.38–5.00 ¶ (−9.06)–(−10.13) ¶ (−11.33)–(−13.61) 0.78–3.12 3.125–12.5 ⁑ (6.06–675.36) ⁑ 17.30 ⁑ (84.00–639.54) ⁑ (136.78–278.19) 6.25–12.50 | [95,96,97,98,99,100] |
| Kappaphycus alvarezii | a ZMA * MBSA | Bacillus amyloliquefaciens MTCC 12713 | pks pks | (9–12) (22–25) | Antibacterial Antibacterial | ‡ 2–9 × 10−3 1.56–6.25 ¶ (−9.06)–(−12.61) | [101,102] |
| Laurencia papillosa | a NA c ZMA * NA a ZMA a NA * NA a NA ** NA SWA ZMA * NA | Bacillus velezensis MBTDLP1 MTCC 13048 Bacillus velezensis MBTDLP1 Bacillus amyloliquefaciens | pks ND pks | (34) Ethyl acetate extract (32 and 33) | Antibacterial Antibacterial Anti-inflammatory Cytotoxicity Antidiabetic Antioxidant Antibacterial | 0.38 7.5–15 ♯ 17 ♯ (32.3–200) ♯ (120–420) ♯ (107–4127) ND | [103,104,105] |
| Laurencia pacifica | MA MB | Bacillus sp. | ND | Acetone extract | Antibacterial | 288.1 | [93] |
| Centroceras clavulatum | MA MB | Bacillus sp. | ND | Acetone extract | Antibacterial | 217.1 | [93] |
| Schizymenia dubyi | MB | Bacillus sp. PP19-H3 | pks | (13–21) | Antibacterial | 10–>100 | [73] |
| Green Algae Bacillota | |||||||
| Codium fragile | MA MB | Bacillus sp. | ND | Acetone extract | Antibacterial | 196 | [93] |
4.1. Macrolides
4.2. Esters
4.3. Furanoterpenoids
4.4. Amicoumacin C Derivatives
5. Pharmacological Properties of the Secondary Metabolites of Marine Macroalgae Bacillota
5.1. Antibacterial Property of Marine Macroalgae Bacillota
5.2. Other Pharmacological Properties of Marine Algae Bacillota
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amer, N.F.; Luzzatto Knaan, T. Natural Products of Marine Origin for the Treatment of Colorectal and Pancreatic Cancers: Mechanisms and Potential. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lever, J.; Brkljača, R.; Kraft, G.; Urban, S. Natural Products of Marine Macroalgae from South Eastern Australia, with Emphasis on the Port Phillip Bay and Heads Regions of Victoria. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Hotta, K.; Deng, Y.; Yuan, R.; Quan, S.; Chen, X. Advances in Biosynthesis of Natural Products from Marine Microorganisms. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Ye, K.; Jiang, S.; Zhou, G. Marine Power on Cancer: Drugs, Lead Compounds, and Mechanisms. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luzzatto-Knaan, T.; Garg, N.; Wang, M.; Glukhov, E.; Peng, Y.; Ackermann, G.; Amir, A.; Duggan, B.M.; Ryazanov, S.; Gerwick, L.; et al. Digitizing Mass Spectrometry Data to Explore the Chemical Diversity and Distribution of Marine Cyanobacteria and Algae. eLife 2017, 6, e24214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulus, C.; Rebets, Y.; Tokovenko, B.; Nadmid, S.; Terekhova, L.P.; Myronovskyi, M.; Zotchev, S.B.; Rückert, C.; Braig, S.; Zahler, S.; et al. New Natural Products Identified by Combined Genomics-Metabolomics Profiling of Marine Streptomyces sp. MP131-18. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altmann, K.H. Drugs from the Oceans: Marine Natural Products as Leads for Drug Discovery. Chimia 2017, 71, 646–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, A.; Joseph, A.; Nair, B.G. Promising Bioactive Compounds from the Marine Environment and Their Potential Effects on Various Diseases. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2022, 20, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.A.; Zheng, J.J.; Gu, Y.C.; Wang, C.Y.; Shao, C.L. The Chemistry and Bioactivity of Macrolides from Marine Microorganisms. In Studies in Natural Products Chemistry; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 44, pp. 353–401. ISBN 9780444634603. [Google Scholar]
- Giddings, L.; Newman, D.J. Bioactive Compounds from Marine Extremophiles; SpringerBriefs in Microbiology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; ISBN 978-3-319-14360-6. [Google Scholar]
- Haque, N.; Parveen, S.; Tang, T.; Wei, J.; Huang, Z. Marine Natural Products in Clinical Use. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matulja, D.; Vranješević, F.; Kolympadi Markovic, M.; Pavelić, S.K.; Marković, D. Anticancer Activities of Marine-Derived Phenolic Compounds and Their Derivatives. Molecules 2022, 27, 1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibi, F.; Naseer, M.I.; Azhar, E.I. Assessing the Diversity of Bacterial Communities from Marine Sponges and Their Bioactive Compounds. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 2747–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratheepa, V.; Vasconcelos, V. Microbial Diversity Associated with Tetrodotoxin Production in Marine Organisms. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2013, 36, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, D.F.; Arakawa, O.; Saito, T.; Noguchi, T.; Simidu, U.; Tsukamoto, K.; Shida, Y.; Hashimoto, K. Tetrodotoxin-Producing Bacteria from the Blue-Ringed Octopus Octopus maculosus. Mar. Biol. 1989, 100, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrea, S.; Gary, S.; Donald, S.; Stierle, A.; Strobel, G.; Stierle, D. Taxol and Taxane Production by Taxomyces andreanae, an Endophytic Fungus of Pacific Yew. Science 1993, 260, 214–216. [Google Scholar]
- Viju, N.; Punitha, S.M.J.; Satheesh, S. Antibiofilm Activity of Symbiotic Bacillus Species Associated with Marine Gastropods. Ann. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, S.; Harder, T.; Burke, C.; Steinberg, P.; Kjelleberg, S.; Thomas, T. The Seaweed Holobiont: Understanding Seaweed-Bacteria Interactions. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 462–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lachnit, T.; Blümel, M.; Imhoff, J.F.; Wahl, M. Specific Epibacterial Communities on Macroalgae: Phylogeny Matters More than Habitat. Aquat. Biol. 2009, 5, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachnit, T.; Meske, D.; Wahl, M.; Harder, T.; Schmitz, R. Epibacterial Community Patterns on Marine Macroalgae Are Host-Specific but Temporally Variable. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aires, T.; Serrão, E.A.; Engelen, A.H. Host and Environmental Specificity in Bacterial Communities Associated to Two Highly Invasive Marine Species (Genus Asparagopsis). Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goecke, F.; Labes, A.; Wiese, J.; Imhoff, J.F. Review Chemical Interactions between Marine Macroalgae and Bacteria. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2010, 409, 267–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goecke, F.; Thiel, V.; Wiese, J.; Labes, A.; Imhoff, J.F. Algae as an Important Environment for Bacteria—Phylogenetic Relationships among New Bacterial Species Isolated from Algae. Phycologia 2013, 52, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gao, X.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, Z.; Yang, H.; Liu, X.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, X. Characterization of a Bacillus velezensis with Antibacterial Activity and Inhibitory Effect on Common Aquatic Pathogens. Aquaculture 2020, 523, 735165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, E.; Yan, L.; Boyd, K.G.; Wright, P.C.; Burgess, J.G. The Symbiotic Role of Marine Microbes on Living Surfaces. Hydrobiologia 2001, 461, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, C.; Silva, J.; Pinteus, S.; Gaspar, H.; Alpoim, M.C.; Botana, L.M.; Pedrosa, R. From Marine Origin to Therapeutics: The Antitumor Potential of Marine Algae-Derived Compounds. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, S.; Thomas, T.; Kjelleberg, S. Unlocking the Diversity and Biotechnological Potential of Marine Surface Associated Microbial Communities. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2008, 11, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viju, N.; Punitha, S.M.J.; Satheesh, S. An Analysis of Biosynthesis Gene Clusters and Bioactivity of Marine Bacterial Symbionts. Curr. Microbiol. 2021, 78, 2522–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dat, T.T.H.; Cuc, N.T.K.; Cuong, P.V.; Smidt, H.; Sipkema, D. Diversity and Antimicrobial Activity of Vietnamese Sponge-Associated Bacteria. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, J.; Yang, Y.T.; Lu, M.C.; Wong, T.Y.; Sung, P.J.; Huang, Y. Sen Antimicrobial Activity and Diversity of Bacteria Associated with Taiwanese Marine Sponge Theonella swinhoei. Ann. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, N.; Luzzatto-Knaan, T.; Melnik, A.V.; Caraballo-Rodríguez, A.M.; Floros, D.J.; Petras, D.; Gregor, R.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Phelan, V.V. Natural Products as Mediators of Disease. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2017, 34, 194–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Sekizuka, T.; Kishi, N.; Yamashita, A.; Kuroda, M. Conventional Culture Methods with Commercially Available Media Unveil the Presence of Novel Culturable Bacteria. Gut Microbes 2019, 10, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novik, G.; Savich, V. Beneficial Microbiota. Probiotics and Pharmaceutical Products in Functional Nutrition and Medicine. Microbes Infect. 2020, 22, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.; Kim, H.; Yi, H.; Kim, W.; Yoon, J.; Im, W.; Kim, M.K.; Seong, C.N.; Kim, S.B.; Cha, C.; et al. A Report of 43 Unrecorded Bacterial Species within the Phyla Bacteroidetes and Firmicutes Isolated from Various Sources from Korea in 2019. J. Species Res. 2021, 10, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemil, N.; Manresa, A.; Rabanal, F.; Ben Ayed, H.; Hmidet, N.; Nasri, M. Structural Characterization and Identification of Cyclic Lipopeptides Produced by Bacillus methylotrophicus DCS1 Strain. J. Chromatogr. B 2017, 1060, 374–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.J.; Lee, S.; Lee, C.H.; Kim, W.G. Macrolactins O-R, Glycosylated 24-Membered Lactones from Bacillus sp. AH159-1. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1632–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngashangva, N.; Mukherjee, P.; Sharma, K.C.; Kalita, M.C.; Indira, S. Analysis of Antimicrobial Peptide Metabolome of Bacterial Endophyte Isolated From Traditionally Used Medicinal Plant Millettia pachycarpa Benth. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 656896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashmi, I.; Bindschedler, S.; Junier, P. Firmicutes. In Beneficial Microbes in Agro-Ecology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 363–396. ISBN 9780128234143. [Google Scholar]
- Osei, E.; Kwain, S.; Mawuli, G.T.; Anang, A.K.; Owusu, K.B.A.; Camas, M.; Camas, A.S.; Ohashi, M.; Alexandru-Crivac, C.N.; Deng, H.; et al. Paenidigyamycin A, Potent Antiparasitic Imidazole Alkaloid from the Ghanaian Paenibacillus sp. De2Sh. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meene, A.; Herzer, C.; Schlüter, R.; Zayadan, B.; Pukall, R.; Schumann, P.; Schauer, F.; Urich, T.; Mikolasch, A. A Novel Antimicrobial Metabolite Produced by Paenibacillus apiarius Isolated from Brackish Water of Lake Balkhash in Kazakhstan. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaruchoktaweechai, C.; Suwanborirux, K.; Tanasupawatt, S.; Kittakoop, P.; Menasveta, P. New Macrolactins from a Marine Bacillus sp. Sc026. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 984–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graça, A.P.; Bondoso, J.; Gaspar, H.; Xavier, J.R.; Monteiro, M.C.; de la Cruz, M.; Oves-Costales, D.; Vicente, F.; Lage, O.M. Antimicrobial Activity of Heterotrophic Bacterial Communities from the Marine Sponge Erylus discophorus (Astrophorida, Geodiidae). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, W.; Yu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Mai, K. Recent Progress in the Understanding of the Gut Microbiota of Marine Fishes. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2021, 3, 434–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleifer, K.-H. Phylum XIII. Firmicutes Gibbons and Murray 1978, 5 (Firmacutes [sic] Gibbons and Murray 1978, 5). In Systematic Bacteriology; Springer New York: New York, NY, USA, 2009; Volume 3, pp. 19–1317. ISBN 978-0-387-68489-5. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, C.J.C.; de Carvalho, C.C.C.R. Cultivating Marine Bacteria under Laboratory Conditions: Overcoming the “Unculturable” Dogma. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 964589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baltz, R.H. Gifted Microbes for Genome Mining and Natural Product Discovery. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 44, 573–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltz, R.H. Genome Mining for Drug Discovery: Progress at the Front End. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 48, kuab044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Heul, H.U.; Bilyk, B.L.; McDowall, K.J.; Seipke, R.F.; Van Wezel, G.P. Regulation of Antibiotic Production in Actinobacteria: New Perspectives from the Post-Genomic Era. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2018, 35, 575–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertsen, H.L.; Musiol-Kroll, E.M. Actinomycete-Derived Polyketides as a Source of Antibiotics and Lead Structures for the Development of New Antimicrobial Drugs. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallett, M. One Man’s Poison-Clinical Applications of Botulinum Toxin. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 118–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, S.; Kharbanda, S.; Pal, U.; Shah, V. Applications of Botulinum Toxin in Dentistry: A Comprehensive Review. Natl. J. Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 6, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsini, M.; Leite, M.A.A.; Chung, T.M.; Bocca, W.; de Souza, J.A.; de Souza, O.G.; Moreira, R.P.; Bastos, V.H.; Teixeira, S.; Oliveira, A.B.; et al. Botulinum Neurotoxin Type A in Neurology: Update. Neurol. Int. 2015, 7, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tsai, C.-H.; Bae, T.H.; Huang, C.-Y.; Chen, C.; Kang, Y.-N.; Chiu, W.-K. Effectiveness of Botulinum Toxin Injection on Bruxism: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2023, 47, 775–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.O. Cosmetic Treatment Using Botulinum Toxin in the Oral and Maxillofacial Area: A Narrative Review of Esthetic Techniques. Toxins 2023, 15, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpiński, T.; Adamczak, A. Anticancer Activity of Bacterial Proteins and Peptides. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandala, C.; Perez-Santos, J.L.M.; Lara-Padilla, E.; Lopez, M.G.D.; Anaya-Ruiz, M. Effect of Botulinum Toxin A on Proliferation and Apoptosis in the T47D Breast Cancer Cell Line. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 14, 891–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trimble, M.J.; Mlynárčik, P.; Kolář, M.; Hancock, R.E.W. Polymyxin: Alternative Mechanisms of Action and Resistance. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a025288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avedissian, S.N.; Liu, J.; Rhodes, N.J.; Lee, A.; Pais, G.M.; Hauser, A.R.; Scheetz, M.H. A Review of the Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Polymyxin B. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caulier, S.; Nannan, C.; Gillis, A.; Licciardi, F.; Bragard, C.; Mahillon, J. Overview of the Antimicrobial Compounds Produced by Members of the Bacillus subtilis Group. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klaenhammer, T.R. Bacteriocins of Lactic Acid Bacteria. Biochimie 1988, 70, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sewalt, V.; Shanahan, D.; Gregg, L.; La Marta, J.; Carillo, R. The Generally sRecognised as Safe (GRAS) Process for Industrial Microbial Enzymes. Ind. Biotechnol. 2016, 12, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngalimat, M.S.; Yahaya, R.S.R.; Baharudin, M.M.A.A.; Yaminudin, S.M.; Karim, M.; Ahmad, S.A.; Sabri, S. A Review on the Biotechnological Applications of the Operational Group Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olishevska, S.; Nickzad, A.; Déziel, E. Bacillus and Paenibacillus Secreted Polyketides and Peptides Involved in Controlling Human and Plant Pathogens. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 1189–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cawoy, H.; Bettiol, W.; Fickers, P.; Ongena, M. Bacillus-Based Biological Control of Plant Diseases. In Pesticides in the Modern World-Pesticides Use and Management; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2011; Volume 1849, pp. 273–302. ISBN 9789533074597. [Google Scholar]
- Llario, F.; Falco, S.; Sebastiá-Frasquet, M.T.; Escrivá, J.; Rodilla, M.; Poersch, L.H. The Role of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens on Litopenaeus vannamei During the Maturation of a Biofloc System. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Kumari, P.; Reddy, C.R.K. Antimicrobial Compounds from Seaweeds-Associated Bacteria and Fungi. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 1571–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, R.; Kannappan, A.; Shi, C.; Lin, X. Marine Bacterial Secondary Metabolites: A Treasure House for Structurally Unique and Effective Antimicrobial Compounds. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, M.A.C.; Cavalett, A.; Spinner, A.; Rosa, D.C.; Jasper, R.B.; Quecine, M.C.; Bonatelli, M.L.; Pizzirani-Kleiner, A.; Corção, G.; de Souza Lima, A.O. Phylogenetic Identification of Marine Bacteria Isolated from Deep-Sea Sediments of the Eastern South Atlantic Ocean. Springerplus 2013, 2, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stincone, P.; Brandelli, A. Marine Bacteria as Source of Antimicrobial Compounds. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2020, 40, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bibi, F.; Yasir, M.; Al-Sofyani, A.; Naseer, M.I.; Azhar, E.I. Antimicrobial Activity of Bacteria from Marine Sponge Suberea mollis and Bioactive Metabolites of Vibrio sp. EA348. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 1139–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondol, M.A.M.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, H.-S.; Lee, Y.-J.; Shin, H.J. Macrolactin W, a New Antibacterial Macrolide from a Marine Bacillus sp. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 3832–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondol, M.A.M.; Tareq, F.S.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, M.A.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, J.S.; Shin, H.J. Cyclic Ether-Containing Macrolactins, Antimicrobial 24-Membered Isomeric Macrolactones from a Marine Bacillus sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 2582–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagao, T.; Adachi, K.; Sakai, M.; Nishijima, M.; Sano, H. Novel Macrolactins as Antibiotic Lactones from a Marine Bacterium. J. Antibiot. 2001, 54, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondol, M.A.M.; Tareq, F.S.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, M.A.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Shin, H.J. New Antimicrobial Compounds from a Marine-Derived Bacillus sp. J. Antibiot. 2013, 66, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettit, G.R.; Knight, J.C.; Herald, D.L.; Pettit, R.K.; Hogan, F.; Mukku, V.J.; Hamblin, J.S.; Dodson, M.J.; Chapuis, J.C. Antineoplastic Agents. 570. Isolation and Structure Elucidation of Bacillistatins 1 and 2 from a Marine Bacillus silvestris. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, M.C.; Munro, M.H.G.; Blunt, J.W.; Puga, J.; Jesus, B.; Calado, R.; Rosa, R.; Madeira, C. Biogeography and Biodiscovery Hotspots of Macroalgal Marine Natural Products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2013, 30, 1380–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, H.; Goeger, D.E.; Hills, P.; Mooberry, S.L.; Ballantine, D.L.; Murray, T.F.; Valeriote, F.A.; Gerwick, W.H. Lophocladines, Bioactive Alkaloids from the Red Alga Lophocladia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 640–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Jeon, Y.J. Dieckol from Ecklonia Cava Suppresses the Migration and Invasion of HT1080 Cells by Inhibiting the Focal Adhesion Kinase Pathway Downstream of Rac1-ROS Signaling. Mol. Cells 2012, 33, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C. Griffithsin, a Highly Potent Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Lectin from Red Algae: From Discovery to Clinical Application. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, C.G.; Liu, Z.Y.; Wang, X.L.; Qin, S. The Seaweed Holobiont: From Microecology to Biotechnological Applications. Microb. Biotechnol. 2022, 15, 738–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanagasabhapathy, M.; Sasaki, H.; Nagata, S. Phylogenetic Identification of Epibiotic Bacteria Possessing Antimicrobial Activities Isolated from Red Algal Species of Japan. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 24, 2315–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, M.T.; Morris, P.C.; Hansen, R.; Jamieson, D.J.; Burgess, J.G.; Austin, B. Recovery and Characterization of a 30.7-KDa Protein from Bacillus licheniformis Associated with Inhibitory Activity against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci, and Listeria monocytogenes. Mar. Biotechnol. 2006, 8, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleti, G.; Sessitsch, A.; Brader, G. Genome Mining: Prediction of Lipopeptides and Polyketides from Bacillus and Related Firmicutes. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamiche, S.; Badis, A.; Jouadi, B.; Bouzidi, N.; Daghbouche, Y.; Utczás, M.; Mondello, L.; El Hattab, M. Identification of Antimicrobial Volatile Compounds Produced by the Marine Bacterium Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Strain S13 Newly Isolated from Brown Alga Zonaria tournefortii. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2019, 31, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asharaf, S.; Chakraborty, K.; Chakraborty, R.D. Seaweed-Associated Heterotrophic Bacteria: Are They Future Novel Sources of Antimicrobial Agents against Drug-Resistant Pathogens? Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asharaf, S.; Chakraborty, K. Seaweed-Associated Heterotrophic Bacillus altitudinis MTCC13046: A Promising Marine Bacterium for Use against Human Hepatocellular Adenocarcinoma. Arch. Microbiol. 2023, 205, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, K.; Varghese, C.; Asharaf, S.; Chakraborty, R.D. Antibiotic-Active Heterotrophic Firmicutes Sheltered in Seaweeds: Can They Add New Dimensions to Future Antimicrobial Agents? Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varghese, C.; Chakraborty, K.; Asharaf, S. Pharmacological Potential of Seaweed-Associated Heterotrophic Bacterium Bacillus atrophaeus. Arch. Microbiol. 2023, 205, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, K.; Thilakan, B.; Kizhakkekalam, V.K. Antibacterial Aryl-Crowned Polyketide from Bacillus subtilis Associated with Seaweed Anthophycus longifolius. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 124, 108–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, K.; Thilakan, B.; Raola, V.K. Antimicrobial Polyketide Furanoterpenoids from Seaweed-Associated Heterotrophic Bacterium Bacillus subtilis MTCC 10403. Phytochemistry 2017, 142, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, K.; Thilakan, B.; Raola, V.K. Polyketide Family of Novel Antibacterial 7-O-Methyl-5′-Hydroxy-3′-Heptenoate-Macrolactin from Seaweed-Associated Bacillus subtilis MTCC 10403. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 12194–12208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, K.; Thilakan, B.; Chakraborty, R.D.; Raola, V.K.; Joy, M. O-Heterocyclic Derivatives with Antibacterial Properties from Marine Bacterium Bacillus subtilis Associated with Seaweed, Sargassum myriocystum. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 569–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarreal-Gómez, L.J.; Soria-Mercado, I.E.; Guerra-Rivas, G.; Ayala-Sánchez, N.E. Antibacterial and Anticancer Activity of Seaweeds and Bacteria Associated with Their Surface. Rev. Biol. Mar. Oceanogr. 2010, 45, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, K.; Thilakan, B.; Raola, V.K. Previously Undescribed Antibacterial Polyketides from Heterotrophic Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Associated with Seaweed Padina gymnospora. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2018, 184, 716–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, K.; Kizhakkekalam, V.K.; Joy, M.; Chakraborty, R.D. Moving Away from Traditional Antibiotic Treatment: Can Macrocyclic Lactones from Marine Macroalga-Associated Heterotroph Be the Alternatives? Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 7117–7130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, K.; Kizhakkekalam, V.K.; Joy, M.; Chakraborty, R.D. A Leap Forward towards Unraveling Newer Anti-Infective Agents from an Unconventional Source: A Draft Genome Sequence Illuminating the Future Promise of Marine Heterotrophic Bacillus sp. Against Drug-Resistant Pathogens. Mar. Biotechnol. 2021, 23, 790–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kizhakkekalam, V.K.; Chakraborty, K.; Joy, M. Oxygenated Elansolid-Type of Polyketide Spanned Macrolides from a Marine Heterotrophic Bacillus as Prospective Antimicrobial Agents against Multidrug-Resistant Pathogens. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 55, 105892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, K.; Kizhakkekalam, V.K.; Joy, M.; Chakraborty, R.D. Novel Amylomacins from Seaweed-Associated Bacillus amyloliquefaciens as Prospective Antimicrobial Leads Attenuating Resistant Bacteria. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 37, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kizhakkekalam, V.K.; Chakraborty, K. Marine Macroalgae-Associated Heterotrophic Firmicutes and Gamma-Proteobacteria: Prospective Anti-Infective Agents against Multidrug Resistant Pathogens. Arch. Microbiol. 2020, 202, 905–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizhakkekalam, V.K.; Chakraborty, K. Pharmacological Properties of Marine Macroalgae-Associated Heterotrophic Bacteria. Arch. Microbiol. 2019, 201, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, K.; Kizhakkekalam, V.K.; Joy, M.; Dhara, S. Difficidin Class of Polyketide Antibiotics from Marine Macroalga-Associated Bacillus as Promising Antibacterial Agents. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 6395–6408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, K.; Kizhakkekalam, V.K.; Joy, M. Polyketide-Derived Macrobrevins from Marine Macroalga-Associated Bacillus amyloliquefaciens as Promising Antibacterial Agents against Pathogens Causing Nosocomial Infections. Phytochemistry 2022, 193, 112983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, K.; Francis, A.; Chakraborty, R.D.; Asharaf, S.; Kizhakkekalam, V.K.; Paulose, S.K. Marine Macroalga-Associated Heterotrophic Bacillus velezensis: A Novel Antimicrobial Agent with Siderophore Mode of Action against Drug-Resistant Nosocomial Pathogens. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 5561–5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, A.; Chakraborty, K. Marine Macroalga—Associated Heterotroph Bacillus velezensis as Prospective Therapeutic Agent. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 1671–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, K.; Thilakan, B.; Raola, V.K.; Joy, M. Antibacterial Polyketides from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Associated with Edible Red Seaweed Laurenciae papillosa. Food Chem. 2017, 218, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillard, T.; Dormoi, J.; Madamet, M.; Pradines, B. Macrolides and Associated Antibiotics Based on Similar Mechanism of Action like Lincosamides in Malaria. Malar. J. 2016, 15, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, R.; Rauf, A.; Mitra, S.; Emran, T.B.; Hossain, M.J.; Khan, Z.; Naz, S.; Ahmad, B.; Meyyazhagan, A.; Pushparaj, K.; et al. Therapeutic Potential of Marine Macrolides: An Overview from 1990 to 2022. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2022, 365, 110072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinos, G.P. The Macrolide Antibiotic Renaissance. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 2967–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y. Heterocyclic Terpenes: Linear Furano- and Pyrroloterpenoids. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 12216–12234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, L.A. Reactive Metabolites in the Biotransformation of Molecules Containing a Furan Ring. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2013, 26, 6–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Peng, Y.; Zheng, J. Metabolic Activation and Toxicities of Furanoterpenoids; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 10, ISBN 9780128047002. [Google Scholar]
- Fouche, G.; Nieuwenhuizen, N.; Maharaj, V.; van Rooyen, S.; Harding, N.; Nthambeleni, R.; Jayakumar, J.; Kirstein, F.; Emedi, B.; Meoni, P. Investigation of In Vitro and In Vivo Anti-Asthmatic Properties of Siphonochilus aethiopicus. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 133, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lategan, C.A.; Campbell, W.E.; Seaman, T.; Smith, P.J. The Bioactivity of Novel Furanoterpenoids Isolated from Siphonochilus aethiopicus. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 121, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Perez, C.; Perry, E.; Crawford, J. Activating and Attenuating the Amicoumacin Antibiotics. Molecules 2016, 21, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann, C.; Kearns, P.; Evans-Illidge, E.; Kurtböke, D. Diversity and Bioactivity of Marine Bacteria Associated with the Sponges Candidaspongia flabellata and Rhopaloeides odorabile from the Great Barrier Reef in Australia. Diversity 2017, 9, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Nagasawa, T.; Enomoto, M.; Kuwahara, S. Stereoselective Total Synthesis of Amicoumacin C. Tetrahedron 2015, 71, 1992–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.I.-B.; El Bour, M.; Ktari, L.; Bolhuis, H.; Ahmed, M.; Boudabbous, A.; Stal, L.J. Jania rubens-Associated Bacteria: Molecular Identification and Antimicrobial Activity. J. Appl. Phycol. 2012, 24, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.H.; Koumoutsi, A.; Scholz, R.; Eisenreich, A.; Schneider, K.; Heinemeyer, I.; Morgenstern, B.; Voss, B.; Hess, W.R.; Reva, O.; et al. Comparative Analysis of the Complete Genome Sequence of the Plant Growth–Promoting Bacterium Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albakosh, M.A.; Naidoo, R.K.; Kirby, B.; Bauer, R. Identification of Epiphytic Bacterial Communities Associated with the Brown Alga Splachnidium rugosum. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 1891–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, M.L.; O’Sullivan, L.; Tan, S.P.; McLoughlin, P.; Hughes, H.; O’Connor, P.M.; Cotter, P.D.; Lawlor, P.G.; Gardiner, G.E. Assessment of the Bacteriocinogenic Potential of Marine Bacteria Reveals Lichenicidin Production by Seaweed-Derived Bacillus spp. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 2280–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, J.G.; Boyd, K.G.; Armstrong, E.; Jiang, Z.; Yan, L.; Berggren, M.; May, U.; Pisacane, T.; Granmo, Å.; Adams, D.R. The Development of a Marine Natural Product-Based Antifouling Paint. Biofouling 2003, 19, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thilakan, B.; Chakraborty, K.; Chakraborty, R.D. Antimicrobial Properties of Cultivable Bacteria Associated with Seaweeds in the Gulf of Mannar on the Southeast Coast of India. Can. J. Microbiol. 2016, 62, 668–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trischman, J.A.; Oeffner, R.E.; De Luna, M.G.; Kazaoka, M. Competitive Induction and Enhancement of Indole and a Diketopiperazine in Marine Bacteria. Mar. Biotechnol. 2004, 6, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiese, J.; Thiel, V.; Nagel, K.; Staufenberger, T.; Imhoff, J.F. Diversity of Antibiotic-Active Bacteria Associated with the Brown Alga Laminaria saccharina from the Baltic Sea. Mar. Biotechnol. 2009, 11, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penesyan, A.; Marshall-Jones, Z.; Holmstrom, C.; Kjelleberg, S.; Egan, S. Antimicrobial Activity Observed among Cultured Marine Epiphytic Bacteria Reflects Their Potential as a Source of New Drugs. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 69, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanagasabhapathy, M.; Sasaki, H.; Haldar, S.; Yamasaki, S.; Nagata, S. Antibacterial Activities of Marine Epibiotic Bacteria Isolated from Brown Algae of Japan. Ann. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.; Ktari, L.; Ahmed, M.; Bolhuis, H.; Boudabbous, A.; Stal, L.J.; Cretoiu, M.S.; El Bour, M. Antimicrobial Activities of Bacteria Associated with the Brown Alga Padina pavonica. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susilowati, R.; Sabdono, A.; Widowati, I. Isolation and Characterisation of Bacteria Associated with Brown Algae Sargassum spp. from Panjang Island and Their Antibacterial Activities. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2015, 23, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kumar, V.; Rao, D.; Thomas, T.; Kjelleberg, S.; Egan, S. Antidiatom and Antibacterial Activity of Epiphytic Bacteria Isolated from Ulva lactuca in Tropical Waters. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 27, 1543–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, G.A.; Maloy, A.P.; McClean, S.; Carney, B.; Slater, J.W. Lipopeptide Biosurfactants from Paenibacillus polymyxa Inhibit Single and Mixed Species Biofilms. Biofouling 2012, 28, 1151–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, M.; Renugadevi, B.; Brammavidhya, S.; Iyapparaj, P.; Anantharaman, P. Antibacterial Activity of Red Pigment Produced by Halolactibacillus alkaliphilus MSRD1—An Isolate from Seaweed. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 176, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karthick, P.; Mohanraju, R. Antimicrobial Potential of Epiphytic Bacteria Associated with Seaweeds of Little Andaman, India. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karthick, P.; Mohanraju, R. Antimicrobial Compounds Produced by Lysinibacillus odysseyi Epiphytic Bacteria Associated with Red Algae. Brazilian J. Microbiol. 2020, 51, 1683–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horta, A.; Alves, C.; Pinteus, S.; Lopes, C.; Fino, N.; Silva, J.; Ribeiro, J.; Rodrigues, D.; Francisco, J.; Rodrigues, A.; et al. Identification of Asparagopsis armata-associated Bacteria and Characterization of Their Bioactive Potential. MicrobiologyOpen 2019, 8, e00824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vairagkar, U.; Mirza, Y. Antagonistic Activity of Antimicrobial Metabolites Produced from Seaweed-Associated Bacillus amyloliquefaciens MTCC 10456 Against Malassezia spp. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2021, 13, 1228–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eloff, J.N. Avoiding Pitfalls in Determining Antimicrobial Activity of Plant Extracts and Publishing the Results. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 19, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos, J.L.; Recio, M.C. Medicinal Plants and Antimicrobial Activity. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 100, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, L. Macroalgae. Encyclopedia 2021, 1, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chukwudulue, U.M.; Barger, N.; Dubovis, M.; Luzzatto Knaan, T. Natural Products and Pharmacological Properties of Symbiotic Bacillota (Firmicutes) of Marine Macroalgae. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 569. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21110569
Chukwudulue UM, Barger N, Dubovis M, Luzzatto Knaan T. Natural Products and Pharmacological Properties of Symbiotic Bacillota (Firmicutes) of Marine Macroalgae. Marine Drugs. 2023; 21(11):569. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21110569
Chicago/Turabian StyleChukwudulue, Uche M., Natalia Barger, Michael Dubovis, and Tal Luzzatto Knaan. 2023. "Natural Products and Pharmacological Properties of Symbiotic Bacillota (Firmicutes) of Marine Macroalgae" Marine Drugs 21, no. 11: 569. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21110569
APA StyleChukwudulue, U. M., Barger, N., Dubovis, M., & Luzzatto Knaan, T. (2023). Natural Products and Pharmacological Properties of Symbiotic Bacillota (Firmicutes) of Marine Macroalgae. Marine Drugs, 21(11), 569. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21110569







