Abstract
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is rich in growth factors and has commonly been utilized in the repair and regeneration of damaged articular cartilage. However, the major drawbacks of direct PRP injection are unstable biological fixation and fast or burst release of growth factors. Fucoidan is a heparinoid compound that can bind growth factors to control their release rate. Furthermore, fucoidan can reduce arthritis through suppressing inflammatory responses and thus it has been reported to prevent the progression of osteoarthritis, promote bone regeneration and accelerate healing of cartilage injury. Injectable hydrogels can be used to deliver cells and growth factors for an alternative, less invasive treatment of cartilage defects. In this study, hyaluronic acid (HA) and fucoidan (FD) was blended with gelatin (GLT) and the GLT/HA/FD hybrid was further cross-linked with genipin (GP) to prepare injectable GP-GLT/HA/FD hydrogels. The gelation rate was affected by the GP, GLT, HA and FD concentrations, as well as the pH values. The addition of HA and FD to GLT networks improved the mechanical strength of the hydrogels and facilitated the sustained release of PRP growth factors. The GP-GLT/HA/FD hydrogel showed adequate injectability, shape-persistent property and strong adhesive ability, and was more resistant to enzymatic degradation. The PRP-loaded GP-GLT/HA/FD hydrogel promoted cartilage regeneration in rabbits, which may lead to an advanced PRP therapy for enhancing cartilage repair.
1. Introduction
Articular cartilage injury caused by trauma and osteoarthritis often leads to disability; however, the avascular nature of cartilage limits its self-healing ability. Therefore, articular cartilage repair and regeneration continue to be challenged. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) has gained much attention as a potential material for repairing damaged cartilage. PRP is an autologous enriched source of various growth factors which has been utilized for clinical cartilage repair, resulting in improvements in recovering the function of articular cartilage. However, the common use of PRP injection for articular cartilage repair often has limited efficacy due to its rapid clearance from the injection site. Recent studies for advanced therapy to repair cartilage defects have demonstrated that the controlled release of PRP from various hydrogels and scaffolds enhanced chondrogenic differentiation and promoted cartilage defect repair [1,2,3,4].
Fucoidan is a sulfated polysaccharide extracted from marine algae which exerted a wide variety of pharmacological activities including antitumor [5,6], angiogenesis [7,8], anti-inflammatory [9,10,11,12], antioxidant [13], anticoagulant and antithrombotic [14,15,16], antiviral and antibacterial [17,18], and osteogenic differentiation activities [19]. Fucoidan is a safe, non-toxic and biocompatible material [20], which has been used to develop nanomedicine for drug delivery and magnetic resonance imaging [21,22,23,24,25,26], and to prepare scaffolds for bone [27,28,29] and cartilage [30,31] tissue engineerings. Fucoidan improves meniscal injury [32], reduces the severity of arthritis through the suppression of Th1-mediated immune reactions [33], and lowers serum TNF-α, IL-1β and MMP-1 [34]. In particular, fucoidan is an active selectin blocker which can reduce postischemic inflammatory cascades and prevent inflammatory damage [35]. These studies revealed that fucoidan has the potential to suppress inflammatory arthritis and reduce cartilage damage.
Fucoidan is a heparin-like molecule that modulates the effect of a variety of growth factors on cell proliferation to promote osteogenic differentiation [36], angiogensis and revascularization [37], and improves the bioactivity of mesenchymal stem cells [38]. Several studies have reported that fucoidan can interact with growth factors to control their release and activity through binding to growth factors and regulation of the signaling pathways. Various drug delivery systems based on fucoidan were developed to locally concentrate and slowly release transforming growth factor (TGF-β), bone morphogenic protein 2 (BMP2), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) and stromal cell-derived factor-1α (SDF-1α), including fucoidan-based scaffolds [39,40,41], electrospun fibers [42], bioprostheses [43] and nanoparticles [38,44], to promote endothelial cell migration and VEGF-mediated angiogenesis [40,42], fibroblasts migration [41] and neurite extension [44], which improved the early step of cardiac differentiation from human embryonic stem cells [39], increased the antithrombotic and re-endothelialization potential of bioprostheses [43], and stimulated the mobilization of mesenchymal stem cells [38]. On the basis of the fact that PRP is rich in high concentrations of various growth factors, fucoidan is a potential biological macromolecule for intra-articular delivery of PRP.
Articular cartilage is a hyaline tissue composed of chondrocytes and extracellular matrix (ECM) components such as collagen type II and glycosaminoglycans (GAGs). Hyaluronic acid (HA) is an important GAG in ECM of articular cartilage, which plays a vital role in enhancing the viscoelastic properties of cartilage tissue to reduce the friction at joints by the release of compressive stress. Gelatin (GLT) is obtained by partial hydrolysis of collagen, which is cheap, biocompatible, fully degradable, and absorbable and non-immunogenic, and thus is suitable for a wide range of tissue engineering applications. Genipin (GP) is a gardenia fruit extract with a natural ability to cross-link chitosan, collagen and GLT. It has markedly lower cytotoxicity (5000- to 10,000-fold) than the commonly used glutaraldehyde. Our previous study reported that the nucleophilic attack of primary amine groups on genipin resulted in the formation of cross-linked chitosan or GLT networks [45,46,47,48,49]. Reyes-Ortega reported the development of bioactive bilayered dressing containing GP-crosslinked HA/GLT hybrid hydrogels for epidermal tissue regeneration [50]. The cross-linking of the HA/GLT hybrids with GP resulted in the formation of a semi-interpenetrating network (SIPN) in which HA chains were randomly distributed in the crosslinked GLT matrix. The HA chains weren’t cross-linked but were stabilized by hydrogen bonds, electrostatic interactions, hydrophobic forces, etc. [50]. However, to the best of our knowledge, the use of GP for the preparation of injectable GLT/HA/fucoidan (FD) based hydrogels has still not been reported.
The aim of this study is, therefore, to develop GP-crosslinked GLT/HA/FD hydrogels with injectability, enzyme degradation resistance, controlled release properties, and cartilage adhesiveness for intra-articular delivery of PRP, and thus which can improve the efficiency of PRP therapy by controlling growth factor release and offer an alternative and promising approach for advanced cartilage regenerative therapy.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Depolymerization of Fucoidan
Low molecular weight fucoidan (LMWF) has been reported to have antioxidant and neuroprotective properties [51], antihyperglycemic, antihyperlipidemic, and hepatoprotective activities [52], and can improve cardiac function [53]. It is worth noting that LMWF is able to stabilize established atherosclerotic lesions because it has great antioxidant activity. LMWF reduces lipid peroxidation and foaming macrophage accumulation, and ameliorates the inflammatory response through down-regulation of IL-6 and up-regulation of IL-10 levels, and by returning p-JNK and cyclin D1 to normal levels [54,55,56]. Other studies reported that LMWF downregulated microparticle release and pro-inflammatory properties of activated human polymorphonuclear neutrophils [57], suppressed the inflammatory response in RAW 264.7 macrophages by inhibiting MAPK and oxidative stress [58], and reduced arthritis through suppressing the Th1 immune response [33]. On the basis of the above-mentioned advantages, LMWF was prepared and used to combine with GLT and HA for the development of injectable hydrogels.
Figure 1A shows the molecular weights and polydispersity index (PDI) of original and depolymerized fucoidan. The glycosidic bonds in fucoidan are hydrolyzed by H2O2 and then the weight average molecular weight (Mw) decreased from 34685 Da (PDI = 3.82) to 4952 Da (PDI = 1.64). Figure 1B shows the Fourier Transform-Infrared (FTIR) spectra of original and depolymerized fucoidan. The original fucoidan shows characteristic peaks at 1030 cm−1, 1255 cm−1 and 842 cm−1, which are assigned to the absorption of the C−O−C asymmetric stretch (glycosidic linkage), and S=O and C−O−S stretches of sulfate ester. The spectrum of the fucoidan depolymerized at a different time shows an additional peak at 1729 cm−1, which is assigned to the C=O stretch of carbonyl or carboxyl groups generated after depolymerization, and the peak intensity increases with the decrease of the molecular weight of the depolymerized fucoidan.
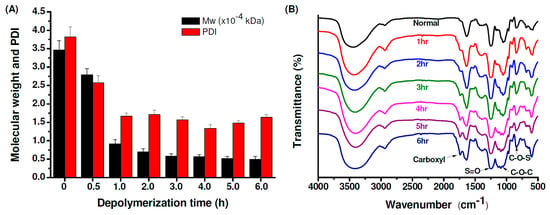
Figure 1.
(A) Weight-average molecular weights (Mw) and polydispersity index (PDI) of the original and depolymerized fucoidan, (B) Fourier Transform-Infrared (FTIR) spectra of the original and depolymerized fucoidan.
After three hours of depolymerization, the molecular weight of fucoidan showed no obvious change; thus the 3 h depolymerized fucoidan (Mw = 6984 kDa and PDI = 1.71) was selected as LMWF for the following studies. To examine whether the depolymerized fucoidan has a suitable protective effect against osteoarthritis through enhancing the inflammatory activation of macrophages, the fucoidan samples were incubated with lipopolysaccharides (LPS)-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a cytokine closely related to arthritis which has the effect of promoting inflammation. The level of nitric oxide (NO) production in the activated macrophages stimulated by LPS is used as an index of inflammation. Fucoidan is known to downregulate inflammatory cytokines in LPS-activated macrophages and suppress NO production [12,59]. As shown in Figure 2A, the depolymerized fucoidan effectively inhibits LPS-induced NO production in a dose-dependent manner. However, when the concentration of the depolymerized fucoidan increased to 200 ppm, NO production in normal macrophages (without stimulation by LPS) clearly increased, indicating that the immune modulation effect of the depolymerized fucoidan can take place at a higher concentration. Figure 2B shows that co-culture of the LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages with the depolymerized fucoidan increases the cell viability, revealing the protective effect of the depolymerized fucoidan against LPS-induced cytotoxicity. Moreover, the expression of the inflammatory cytokineIL-6 by LPS-stimulated macrophages was reduced by the depolymerized fucoidan, see Figure 2C. The results suggest that the depolymerized fucoidan is effective in reducing the LPS-induced inflammatory response in the activated macrophages, leading to the reduction of the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokine and mediator, IL-6 and NO.
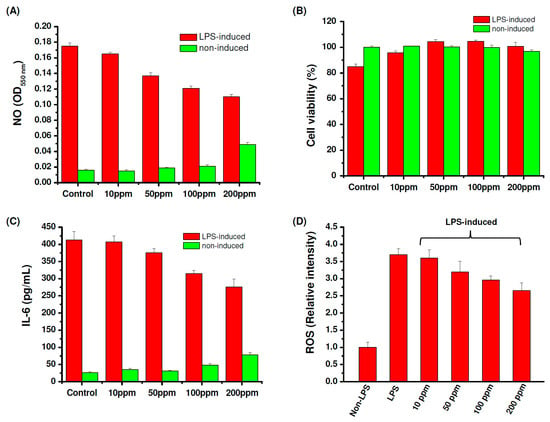
Figure 2.
Anti-inflammatory activity of depolymerized fucoidan against lipopolysaccharides (LPS) (1 μg/mL) induced cytotoxicity in RAW 264.7 macrophages: (A) Nitrogen oxide (NO) production, (B) cell viability, (C) IL-6 production, (D) reactive oxygen species (ROS) production.
NO produced by the immunologic isoform of iNOS triggers a rapid release of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which can cause oxidative damage in osteoarthritic cartilage. Increased ROS production is known to induce DNA damage, apoptosis, and cartilage degradation of chondrocytes, which may cause the deterioration of osteoarthritis [60]. Therefore, we further investigated the ROS scavenging activity of the depolymerized fucoidan. ROS production by the activated macrophages stimulated by LPS was determined by ROS-sensitive fluorescence dye (DCFDA). The activated macrophages treated with the depolymerized fucoidan effectively inhibited the ROS production induced by LPS, see Figure 2D. The depolymerized fucoidan seems to be a promising material to inhibit the ROS produced by inflammatory macrophages. On the basis of the previous results, we select the depolymerized fucoidan (Mw = 6984 kDa and PDI = 1.71) to be combined with GLT and HA for the following preparation of PRP-loaded injectable hydrogels.
2.2. Cross-Linking Reaction and Gel Formation
It has been reported that a GP-amine monomer is formed via a nucleophilic attack by an amino group containing compounds such as GLT on the olefinic carbon at C-3 on deoxyloganin aglycone of GP [47,49]. This reaction is followed by the opening of the GP ring, allowing a secondary amine attack on the resulting aldehyde. GLT reacts with GP to form a blue pigment, which can be used as an index of the cross-linking progress. The ultraviolet–visible (UV-Vis) spectrum of GP in water displayed an absorption peak at 240 nm. The GP-crosslinked compounds showed two new absorption peaks at 280 nm (π − π*) and 600 nm (n − π*) due to the formation of GP cross-linked heterocyclic amines [47,49,61]. The GP and GLT concentration-dependent effects appeared as indicated by increasing the intensity of the absorbance at 600 nm with the increase of the concentrations of GP and GLT, respectively, see Figure 3A,B. Higher concentrations of GLT or GP allowed greater interactions between GLT and GP, resulting in a greater number of chemical crosslinks being formed. The GP-crosslinking rate of GLT is strongly influenced by pH (pH 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7.4), see Figure 3C. In general, the intensity of the absorbance at 600 nm increased upon increasing the pH because of the reduction in the degree of protonation. Furthermore, the hydroxide ion generated in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) caused GP to form aldehyde groups [62], allowing GP to cross-link GLT at a higher rate. GLT/HA hybrids were prepared by blending GLT with HA, followed by cross-linking the hybrids with GP, resulting in the formation of a GP-crosslinked GLT/HA semi-interpenetrating polymer network (semi-IPN) [50].
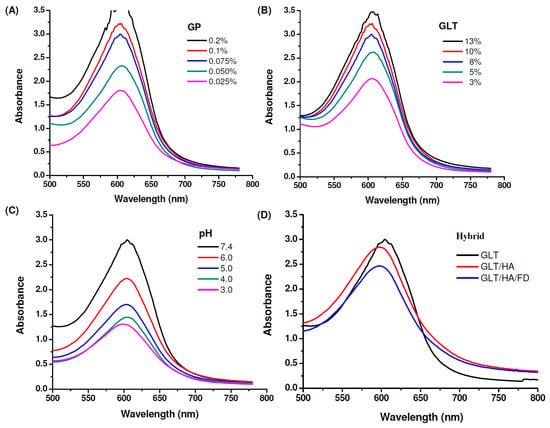
Figure 3.
Absorption spectra of genipin (GP)-crosslinked gelatin (GLT), GLT/hyaluronic acid (HA) and GLT/HA/ fucoidan (FD) at 37 °C: (A) 8% GLT cross-linked with different concentrations of GP at pH 7.4, (B) different concentrations of GLT cross-linked with 0.075% GP at pH 7.4, (C) 8% GLT cross-linked with 0.075% GP at different pH values, (D) 8% GLT cross-linked with 0.075% GP at pH 7.4 in the presence of 1% HA and FD.
Figure 3D shows that the intensity of the absorbance at 600 nm decreases in the presence of 1 wt% HA and 1 wt% depolymerized fucoidan (FD), revealing that the cross-linking reactions of the GLT/HA and GLT/HA/FD hybrids occur at a slower rate than that of GLT only. HA and FD are acidic polysaccharides which can release H+, and thus the pH levels of the GLT/HA and GLT/HA/FD hybrids are lower than their GLT counterpart. We have shown that the GP-involved cross-linking reaction rate increased with increasing pH, see Figure 3C. Thus, the reason for the slower color changing rates of the GLT/HA and GLT/HA/FD hybrids can be attributed to the decrease of pH by HA and FD. Furthermore, the HA and FD macromolecular chains interpenetrating within the GLT network structure may reduce the cross-linking reactivity between GP and GLT.
As shown in Figure 4A, after cross-linking GLT (8%) with GP (0.075%), the color changed from yellow to green to blue. The gelation time of the GP-crosslinked samples can be determined by using the inverted tube test at 37 °C. The results showed that the GP, GLT and HA concentrations, as well as the pH, played vital roles in gel formation. The gelation time decreased from 323 min to 210 min and from 382 min to 180 min with the increase of GP concentration from 0.025% to 0.2% and GLT concentration from 3% to 13%, see Figure 4B,C. Changing the pH value from 3.0 to 7.4 (the physiological condition) caused a faster gelation rate, see Figure 4D, and thus the gelation time decreased from 240 min to 150 min. The effects of GP and GLT concentrations and pH value on the gelation time correlated with the results of spectral changes during the gel formation process, see Figure 3A–C. However, the gelation time decreased from 210 min to 100 min with the increase of HA concentration from 0.125% to 1.0%, see Figure 4E. The tendency is opposite to that of spectral change, see Figure 3D. Luo et al. reported that 1-Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-carbodiimide (EDC)/ N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS)-crosslinked GLT/HA hybrid injectable hydrogel has higher elasticity compared to the EDC/NHS-crosslinked GLT hydrogel [63]. Accordingly, the faster gelation rates of the GP-crosslinked GLT/HA hybrid at higher HA contents could be attributed to the superior elastic property of HA. Figure 4F shows the gelation time of the GP-crosslinked GLT/HA/FD hybrids. The gelation rates were only slightly affected by FD at different concentrations when the concentration of HA was kept at 1 wt%. Fucoidan solution has a low apparent viscosity and poor viscoelastic properties [21], and thus the polymer doesn’t have thickening, gelling or film-forming properties. On the basis of the results, we concluded that the gelation times of the GP-crosslinked GLT/HA/FD hybrids were significantly affected by HA but only slightly affected by FD.
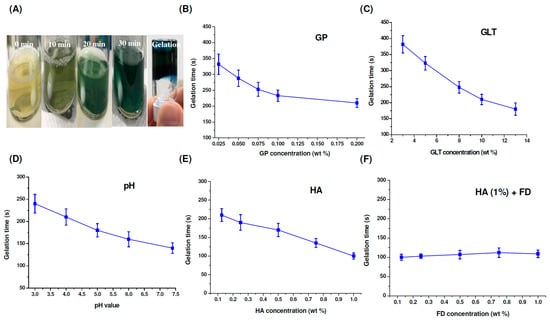
Figure 4.
(A) Color changes and inverted tube test of the GP-crosslinked GLT samples, (B–E) gelation times of GP-crosslinked GLT, GLT/HA and GLT/HA/FD at 37 °C: (B) 8% GLT cross-linked with different concentrations of GP at pH 7.4, (C) different concentrations of GLT cross-linked with 0.075% GP at pH 7.4, (D) 8% GLT cross-linked with 0.075% GP at different pH values, (E) 8% GLT cross-linked with 0.075% GP at pH 7.4 in the presence of different concentrations of HA, (F) 8% GLT cross-linked with 0.075% GP at pH 7.4 in the presence of 1% HA and different concentrations of FD.
2.3. Injectability, Stability and Adhesive Property
The original GLT and HA solutions were squeezed through the syringe with a 23 G needle to produce liquid-like droplets. In contrast, the GP-crosslinked GLT/HA and GLT/HA/FD hybrids that were squeezed through the syringe with the same size needle were gel-like fluids, see Figure 5A, revealing the formation of injectable hydrogels. Next, the hydrogels were directly injected into PBS to examine whether the hydrogels are strong enough to stay firm in physiological fluids such as joint fluid after injection. Figure 5B shows that the hydrogels injected through the 23 G needle into PBS solution retained their shape, indicating that the hydrogels were shape-persistent materials. It is known that hydrogen bonding formed in hydrogels can be broken by H2O molecules; therefore, weakening the adhesion force of the hydrogels. The hydrogels prepared in this work were adhesive and attached to the bottom side when injected into PBS. The gels were still attached to the bottom of the bottle after 14 days, even after turning the bottles upside down, see Figure 5B. The injectability, and shape-persistent and adhesive properties suggest that the injectable hydrogels can be used for intra-articular delivery of cells, growth factors and PRP for cartilage repair.
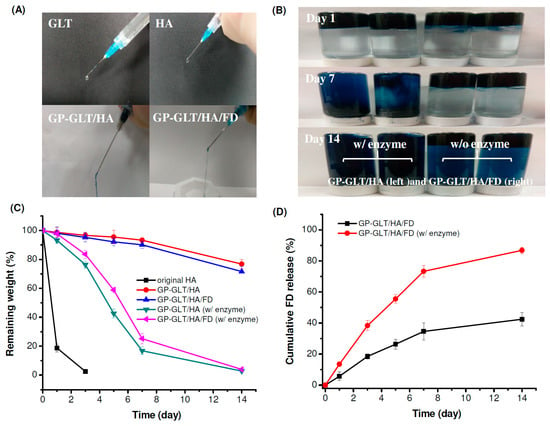
Figure 5.
Injectability, stability, degradability and FD release property of GP-crosslinked GLT/HA and GLT/HA/FD hybrid hydrogels (GP-GLT/HA and GP-GLT/HA/FD) prepared at 37 °C: (A) injectability of the hydrogels through a 23-gauge needle, (B) stability of the hydrogels after injection into phosphate buffered saline (PBS) with (w/) and without (w/o) enzyme, (C) weight loss of the hydrogels in PBS with (w/) and without enzyme, (D) FD release from the hydrogels in PBS with (w/) and without enzymes.
As mentioned above, the GP-crosslinked GLT/HA (GP-GLT/HA) and GP-crosslinked GLT/HA/FD (GP-GLT/HA/FD) hydrogels were adhesive and very stable in PBS. We further examined the weight loss of the hydrogels in PBS with (w/) and without (w/o) enzymes, see Figure 5C. The original HA without cross-linking or further treatments was quickly degraded by hyaluronidase. The GP-GLT/HA and GP-GLT/HA/FD hydrogels exhibited slower degradation rates. The lower weight loss of the hybrid hydrogels was attributed to the higher heterogeneity of the GP-GLT/HA and GP-GLT/HA/FD semi-interpenetrating polymer networks compared to the original HA [64], which reduced the susceptibility of the incorporated HA to proteolytic degradation.
2.4. Rheological Property, Compressive Strength and Enzymatic Degradation
Figure 6A shows the FTIR spectra of GP, GLT, HA and the GP-crosslinked GLT/HA hydrogel (GP-GLT/HA). The spectrum of HA shows the absorption peaks at 1419 cm−1 and 1638 cm−1, which are assigned to the symmetric and asymmetric stretching of carboxylate groups. The peaks that appeared in the range of 1000–1200 cm−1 (1047 cm−1 and 1157 cm−1) are assigned to the C−O−C and C−O stretching of the HA saccharide ring. GLT clearly shows two characteristic peaks at 1651 cm−1 and 1528 cm−1, corresponding to amide I (C=O stretching) and amide II (N−H deformation). GP shows two characteristic peaks at 1682 and 1621 cm−1 which are assigned to the C=O stretching of ester groups and the C=C stretching of the dihydropyran ring. Furthermore, the C−O−C and C−O stretching bands at 1108 cm−1 and 1153 cm−1 are attributed to the ether and hydroxyl groups in dihydropyran ring. GP-GLT/HA hydrogel shows the characteristic peaks of the HA saccharide ring (1053 cm−1 and 1162 cm−1), and the characteristic peaks of GLT amide I and II bands (1654 cm−1 and 1534 cm−1) which are overlapped with the absorption peaks of HA carboxyl groups. The peaks located around 1408 cm−1 and 3349 cm-1 were attributed to the overlap of the absorption peaks of HA carboxylate groups and GLT alkyl groups (1403 cm−1), and the overlap of the absorption peaks assigned to the amino (N−H stretching) and hydroxyl groups (O−H stretching) of HA (3432 cm−1) and GLT (3297 cm−1). The characteristic peaks of GP were not obvious in GP-GLT/HA hydrogel because the GP concentration (0.075%) was much lower than those of GLT, HA and FD. Compared with the GP-GLT/HA hydrogel, the GP-GLT/HA/FD hydrogel shows the characteristic absorption bands of fucoidan at 1243 cm−1 (asymmetrical stretching of S=O), and 847 cm−1 (sulfate ester), see Figure 6B, confirming the incorporation of fucoidan in the hybrid hydrogel.
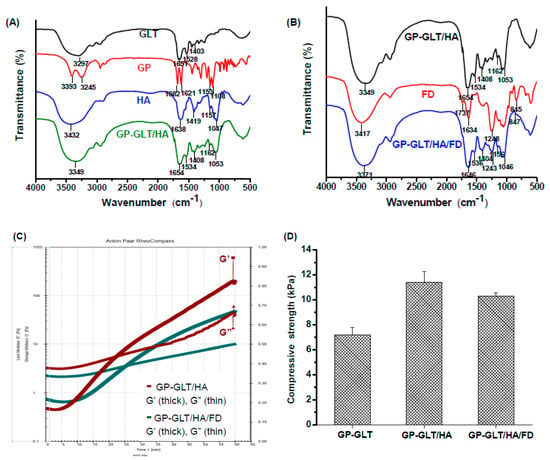
Figure 6.
Chemical and physical properties of GP-crosslinked GLT/HA and GLT/HA/FD hybrid hydrogels (GP-GLT/HA and GP-GLT/HA/FD): (A) FTIR spectra of GP, GLT, HA and GP-GLT/HA, (B) FTIR spectra of FD, GP-GLT/HA and GP-GLT/HA/FD, (C) rheological behavior, (D) compressive strength.
The gel formation process of the GP-GLT/HA and GP-GLT/HA/FD hydrogels was monitored by using rheology testing, see Figure 6C. The storage modulus (G′) of the GP-GLT/HA hybrid increased faster than its GP-GLT/HA/FD counterpart. This was caused by the elastic property of HA, which increased the gel strength by reinforcement of the GP-crosslinked GLT network structure [65]. The storage modulus (G′) of the samples was, in the end, higher than the storage modulus (G″). The intersection of G′ and G″ indicates the point that the elastic solid-like behavior began to exceed the viscous liquid-like behavior. By monitoring the intersection of G′ and G″, the best time for mixing cells or growth factors can be accurately predicted. This provided us with useful information for mixing the GLT/HA and GLT/HA/FD hybrids with PRP before gelation. The compression strength of the GP-GLT/HA hydrogel was 11.4 kPa, which was higher than that of the GP-GLT hydrogel, see Figure 6D. The enhanced compression strength can be directly linked to the high elastic property of HA, which formed semi-IPNs after cross-linking. Hydrogels used in cartilage are superior if they have an elastic property as well as suitable viscosity and stiffness, which are critical to their ability to resist compressive loads [65]. The GP-GLT/HA/FD hydrogel possesses a slightly lower compression strength compared with its GP-GLT/HA hydrogel counterpart. The adequate compressive strength of the hybrid hydrogels makes the hydrogels suitable for cartilage tissue applications.
2.5. Cytotoxicity and Growth Factor Release
To evaluate the cytotoxicity, the chondrocytes were treated with the GP-GLT/HA and GP-GLT/HA/FD hydrogel extracts at different concentrations. Cell viability was not evidently influenced by the extract at concentrations below 20 mg/mL, indicating no significant toxicity of the hydrogels (Figure 7A). This is attributed to the reason that GP, GLT, HA and FD are well known to be nontoxic and biocompatible. PRP gel traditionally prepared through thrombin activation usually releases incorporated growth factors with burst effects, resulting in the decrease of its therapeutic efficacy. Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) is one of the important growth factors in PRP for cartilage defect repair [1,2,3,4]. As shown in Figure 7B, PDGF was released slowly from the GP-GLT/HA hydrogels, in contrast to the burst PDGF release from the traditional PRP gel. PDGF release from the GP-GLT/HA/FD hydrogel was even slower than its GP-GLT/HA counterpart (P < 0.05) because FD is a heparinoid compound that can bind heparin-binding growth factors to control their release rate. PDGF was known to bind to heparin-like molecules mainly via electrostatic interaction [66]. Liu et al. reported that the proliferation of chondrocyte was enhanced by a photo-crosslinkable PRP-loaded hydrogel which could release growth factors in a more sustained manner [2,4]. The cartilage regeneration efficiencies of the PRP-loaded GP-GLT/HA/FD hydrogels were then investigated in a rabbit cartilage defect model.
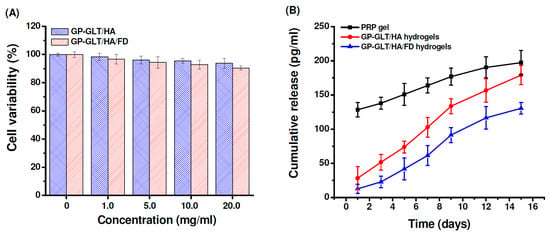
Figure 7.
(A) Cytotoxicity of GP-crosslinked GLT/HA and GLT/HA/FD hybrid hydrogels, (B) PDGF release behavior of GP-crosslinked GLT/HA and GLT/HA/FD hybrid hydrogels.
2.6. In Vivo Histological Evaluation
The macroscopic examination of the control group (intra-articular injection of normal saline) showed that the femoral of the articular cartilage was rough and dull (data not shown). Histological analysis suggested that the intra-articular injection of the GP-GLT/HA/FD hydrogel or PRP-loaded GP-GLT/HA/FD hydrogel attenuated the losses of chondrocytes at the femoral condyles. The animals treated with either the GP-GLT/HA/FD hydrogel or PRP-loaded GP-GLT/HA/FD hydrogel showed decreased lesion formation and reduced losses of proteoglycans in the superficial layer, see Figure 8C,D, compared with the control and the GP-GLT hydrogel treated groups, see Figure 8A,B). Overall, the results suggest that the treatment with intra-articular injection of GP-GLT/HA/FD hydrogel or PRP-loaded GP-GLT/HA/FD hydrogel may represent a desirable therapy on osteoarthritis (OA).
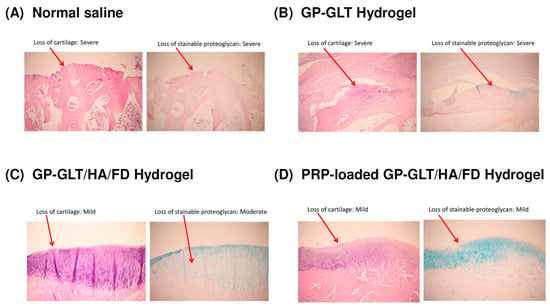
Figure 8.
Histological examinations of cartilage at the femoral condyles after treatments by intra-articular injection of: (A) normal saline (control), (B) GP-GLT hydrogel, (C) GP-GLT/HA/FD hydrogel, (D) PRP-loaded GP-GLT/HA/FD hydrogel.
HA can bind chondrocytes via CD44, which regulates chondrocyte proliferation, ECM remodeling and cartilage regeneration and enhances cell differentiation into the chondrogenic phenotype. PRP-loaded hydrogel glue with the controlled release of growth factors promoted cartilage regeneration [2,4]. FD has anti-inflammatory activity [33,34,35,55,56,57,58,59] and can bind the growth factors in PRP to control their release rates [37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,66]. Our animal study proved that GP-GLT/HA/FD hydrogel and PRP-loaded GP-GLT/HA/FD hydrogel treatments reduced cartilage degradation at the femoral condyles, and effectively reduced the loss of the superficial layer, cartilage ulceration, the production of osteophytes, the creation of fissures, and the disorganization of cartilage, compared with the control (intra-articular injection of normal saline) and GP-GLT hydrogel treated groups. The use of PRP in tissue regeneration has been developed for clinical applications. Intra-articular injection of GP-GLT/HA/FD hydrogel or PRP-loaded GP-GLT/HA/FD hydrogel reduced the degradation of cartilage on the femoral condyles, and effectively reduced the loss of the superficial layer, compared with the control and GP-GLT-hydrogel-treated groups. The losses of chondrocytes and proteoglycan of the groups treated by intra-articular injection of normal saline and GP-GLT hydrogel were higher than those of the GP-GLT/HA/FD and PRP-loaded GP-GLT/HA/FD hydrogel groups.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
HA was purchased from SeedChem Company PTY., LTD, Victoria, Australia. Fucoidan from Laminaria japonica was purchased from NOVA Pharma & Liposome Biotech (Kaohsiung, Taiwan). GP was purchased from Challenge Bioproducts Co., Ltd. (Touliu, Taiwan). GLT (225 g Bloom, type B, suitable for cell culture), 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide (MTT), 2′,7′-Dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (DCFDA), gelatinase and hyaluronidase were purchased from Sigma−Aldrich, Louis, MO, USA.
3.2. Preparation of LMWF
Fucoidan (0.2 g) was dissolved in 200 mL deionized water. Then, H2O2 was added to the fucoidan solution at a final concentration of 0.2 M. The fucoidan/H2O2 mixed solution was continuously stirred under magnetic stirring at 70 °C for 1–6 h, followed by terminating the reaction using 0.1 M sodium carbonate. The samples after depolymerization were dialyzed against deionized water using a dialysis tubing (MWCO 1000 Da). The molecular weight of depolymerized, low molecular weight fucoidan (LMWF) was determined by gel permeation chromatography (GPC) with a TSKgel G3000PWXL column (Tokyo, Japan). Detector: refractive index detector (RI); Mobile phase: Na2SO4 aqueous solution (0.2 M); Flow rate: 0.5 mL/min; Column temperature 40 °C. Dextran standards of different weights from PSS Polymer Standards Service GmbH (Mainz, Germany) were used to construct standard curves.
3.3. Characterization of Anti-Inflammatory and ROS Scavenging Effects
3.3.1. Colorimetric Nitric Oxide Assay
RAW 264.7 cells (1 × 104 cells/mL) were stimulated with LPS (1 μg/mL) for 24 h in the presence or absence of the depolymerized fucoidan (Mw = 6984 kDa). Nitric oxide produced by RAW 264.7 macophage was measured by the Griess reagent. Briefly, 50 μL of Griess solution was added to the same volume of cell culture medium and then was further incubated for 10 min. The absorbance at 540 nm was measured by a EnSpire2300 multimode plate reader (Perkin Elmer, Waltham, MA, USA) to determine the nitrite concentration from a sodium nitrite standard curve.
3.3.2. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) for IL-6
After 24 h of stimulation of RAW 264.7 cells with LPS in the presence or absence of the depolymerized fucoidan, the cell culture supernatants were collected and the concentrations of IL-6 were measured by ELISA kits (R&D Systems Inc., Minneapolis, MN, USA) following the manufacturer’s instructions.
3.3.3. Analysis of ROS Generation
After 24 h of stimulation of RAW 264.7 cells with LPS in the presence or absence of the depolymerized fucoidan, the cell culture supernatants were collected and then 10 μM DCFDA was added to the supernatants. The generated ROS concentration was determined by measuring the fluorescence intensity of DCF (DCFDA was oxidized by ROS to form DCF) by a Perkin Elmer EnSpire2300 multimode plate reader (Ex 485 nm, Em 520 nm).
3.4. Preparation of Injectable Hydrogels
GLT solutions were prepared by dissolving different amounts of GLT in 100 mL distilled water to obtain the desired GLT concentrations (3, 5, 8, 10 and 13 wt%). GLT/HA and GLT/HA/FD blends were prepared by mixing HA and FD with GLT in distilled water at various weight ratios (0.125, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1.0 wt%) to obtain GLT/HA and GLT/HA/FD hybrid hydrogels. Different amounts of GP were then added to the GLT, GLT/HA and GLT/HA/FD solutions to reach the final GP concentrations (0.025, 0.05, 0.075, 0.1, 0.2 wt%). The pH was adjusted to 3.0, 4.0, 5.0, 6.0 and 7.4.
3.5. UV-Vis Absorption Spectra
The cross-linking reaction was analyzed by dissolved GP in GLT, and GLT/HA and GLT/HA/FD hybrid solutions at the above-mentioned concentrations and pH, followed by stirring at room temperature. UV-Vis absorption spectra were recorded by Perkin Elmer EnSpire2300 multimode plate reader.
3.6. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
To investigate the chemical structures of GP-crosslinked GLT, GLT/HA and GLT/HA/FD hydrogels (GP-GLT, GP-GLT/HA and GP-GLT/HA/FD), the test samples were dried and ground to a powder. The FT-IR spectra of HA, GLT, GP-GLT, GP-GLT/HA and GP-GLT/HA/FD were recorded using a Perkin Elmer, RXI FTIR System in the region between 400–4000 cm−1.
3.7. Rheological Characterization
Rheological properties were measured using a parallel-plate rheometer (AR2000ex, TA Instruments, New Castle, DE, USA). A time sweep at 1 Hz of the GP-GLT/HA and GP-GLT/HA/FD solutions were determined by placing the test samples within the plates and continuously recording the storage and loss modulus values (G′ and G″) at 37 °C.
3.8. Gelation Time Determination
The gelation time was determined using an inverted tube test at 37 °C. Briefly, 2 mL of the GP-containing GP-GLT/HA and GP-GLT/HA/FD solutions were placed in a sample bottle (7 mL), and then, the bottles were incubated in a water bath at 37 °C. The gelation times were determined by inclining the bottle every 30 s until the gel did not flow.
3.9. Compressive Mechanical Properties
The GP-GLT/HA and GP-GLT/HA/FD solutions added with an adequate amount of GP were placed in 24-well plates and left to cross-link for the formation of hydrogels. The compression tests of the hydrogel samples were performed on a Texture Profile Analyzer (Model TA-XT2; Stable Micro Systems Ltd, Surrey, UK with a cylinder load of 1 g moving at 0.1 mm/s to plot the pressure (Pa) as a function of strain. The hydrogel sample was compressed to 80% of the initial height.
3.10. Cytotoxicity
Human chondrocyte primary cells were purchased from Cell Application, Inc. (San Diego, CA, USA). The cytotoxicity of the hydrogels was evaluated according to the ISO 10993-5 Standard. Briefly, GP-GLT/HA and GP-GLT/HA/FD hydrogels were incubated at 37 °C in PBS buffer (pH 7.4, 10 mL) for 24 h. The collected solutions were mixed with culture medium (1:1) and then were cultured with chondrocyte (5 × 103 cells per well) for 48 h. An MTT assay was conducted to evaluate cell viability by measuring the absorbance of the supernatant solution at 540 nm using a EnSpire 2300 multimode plate reader (Perkin Elmer, Waltham, MA, USA).
3.11. In Vitro Biodegradation Study
The degradation study was performed by firstly weighing the hydrogels after gel formation. Subsequently, the hydrogels were incubated at 37 °C in PBS buffer with gentle agitation in an orbital shaker and the mass loss was determined at a predetermined time period by removing the hydrogels from the medium, blotting the hydrogels with a filter paper, and finally weighing the hydrogels. The PBS buffer containing 10 U/mL hyaluronidase and 0.5 U/mL gelatinase was used for enzymatic degradation studies. After that, the medium was replaced with fresh PBS or enzyme solution. The degradation ratio was expressed as the percentage of weight loss.
3.12. PRP-Loading and Release
The lyophilized PRP powder was prepared using RegenKit THT Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma (A-PRP) (RegenKit® THT, Stryker, Kalamazoo, Michigan, USA). The PRP-loaded hydrogels were prepared by adding PRP in GP-GLT/HA and GP-GLT/HA/FD before gelation. The PRP-loaded hydrogels were placed in a 24-well plate containing 500 μL of release medium (PBS). The release medium was collected at a predetermined time interval and then the content of PDGF was determined using ELISA kit (R&D Ltd, Minneapolis, MN, USA).
3.13. Animal Model and Design
This study was conducted with the permission of the Experimental Animal Review Committee of Taipei Medical University. In one knee of each of the New Zealand white rabbits, the anterior cruciate ligament was transected (ACLT) to create the experimental osteoarthritis (OA) model [67]. The rabbits were kept within the guidelines of IACUC without extra calcium provided. Three rabbits with ACLT that underwent intra-articular normal saline injection were used as a control group. The treatment group used nine rabbits from three groups that were injected intra-articularly using either GP-GLT hydrogel, GP-GLT/HA/FD hydrogel or PRP-loaded GP-GLT/HA/FD hydrogel.
3.14. Specimen Collection and Histological (Microscopic) Examination
After 8 weeks of administration, the rabbits were euthanized and then specimen collection and histological (microscopic) examination were performed according to the methods reported in our previous paper [67]. Hematoxyline and eosin stain (H&E stain) and alcian blue stain of the samples were used for detection of glycosaminoglycans (GAG).
3.15. Statistical Analysis
All data are presented as the arithmetic mean ± standard deviation (SD). Statistical analysis was performed using a Student’s t-test. The data were considered to be significantly different at P < 0.05.
4. Conclusions
In summary, we have developed an injectable hydrogel based on blending HA and fucoidan (FD) with GLT followed by cross-linking the GLT/HA/FD hybrid with GP. The concentrations of GP, GLT, HA and FD affected the gelation rates of the hydrogels. The addition of HA and FD enabled high strength, high stability, and strong adhesive ability. Furthermore, the GP-GLT/HA/FD hydrogels were more resistant to enzymatic degradation and had a more sustained release of growth factors. Because of the growth factor-binding characteristic of FD, the PRP-loaded hydrogel can overcome the drawbacks of direct PRP injection and is helpful in cartilage defect regeneration. The PRP-loaded hydrogel promoted cartilage regeneration in a rabbit cartilage defect model, which assured us the material had potential for the treatment of cartilage injury.
Author Contributions
H.-T.L. and F.-L.M. conceived and designed the experiments; H.-T.L., W.-T.C. and M.-L.T. performed the experiments; H.-T.L., C.-H.C. and W.-Y.C. analyzed the data; H.-T.L., C.-H.C. and F.-L.M. wrote the paper.
Funding
This research was funded by Taipei Medical University, grant number TMU 105-AE1-B31.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the financial support by a grant from Taipei Medical University (TMU 105-AE1-B31), Taiwan.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lee, H.R.; Park, K.M.; Joung, Y.K.; Park, K.D.; Do, S.H. Platelet-rich plasma loaded hydrogel scaffold enhances chondrogenic differentiation and maturation with up-regulation of CB1 and CB2. J. Control. Release 2012, 159, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.L.; Yang, Y.L.; Niu, X.; Lin, Q.N.; Zhao, B.Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, L.Y. An in situ photocrosslinkable platelet rich plasma—Complexed hydrogel glue with growth factor controlled release ability to promote cartilage defect repair. Acta Biomater. 2017, 62, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miron, R.J.; Zhang, Y.F. Autologous liquid platelet rich fibrin: A novel drug delivery system. Acta Biomater. 2018, 75, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jooybar, E.; Abdekhodaie, M.J.; Alvi, M.; Mousavi, A.; Karperien, M.; Dijkstra, P.J. An injectable platelet lysate-hyaluronic acid hydrogel supports cellular activities and induces chondrogenesis of encapsulated mesenchymal stem cells. Acta Biomater. 2019, 83, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usoltseva, R.V.; Anastyuk, S.D.; Ishina, I.A.; Isakov, V.V.; Zvyagintseva, T.N.; Thinh, P.D.; Zadorozhny, P.A.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Ermakova, S.P. Structural characteristics and anticancer activity in vitro of fucoidan from brown alga Padina boryana. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 184, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjeewa, K.K.A.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, W.S.; Jeon, Y.J. The potential of brown-algae polysaccharides for the development of anticancer agents: An update on anticancer effects reported for fucoidan and laminaran. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 177, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvard, C.; Galy-Fauroux, I.; Grelac, F.; Carpentier, W.; Lokajczyk, A.; Gandrille, S.; Colliec-Jouault, S.; Fischer, A.M.; Helley, D. Low-molecular-weight fucoidan induces endothelial cell migration via the PI3K/AKT pathway and modulates the transcription of genes involved in angiogenesis. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 7446–7462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.L.; Schmidt, H.; Pavleska, D.; Wermann, T.; Seekamp, A.; Fuchs, S. Crude fucoidan extracts impair angiogenesis in models relevant for bone regeneration and osteosarcoma via reduction of VEGF and SDF-1. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.J.; Don, T.M.; Lin, C.W.; Mi, F.L. Delivery of berberine using chitosan/fucoidan-taurine conjugate nanoparticles for treatment of defective intestinal epithelial tight junction barrier. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 5677–5697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.H.; Ko, E.C.; Chang, C.L.; Yuan, K.S.P.; Wu, A.T.H.; Shan, Y.S.; Wu, S.Y. Fucoidan inhibits radiation-induced pneumonitis and lung fibrosis by reducing inflammatory cytokine expression in lung tissues. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subash, A.; Veeraraghavan, G.; Sali, V.K.; Bhardwaj, M.; Vasanthi, H.R. Attenuation of inflammation by marine algae Turbinaria ornata in cotton pellet induced granuloma mediated by fucoidan like sulphated polysaccharide. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 151, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Ko, C.I.; Ahn, G.; You, S.; Kim, J.S.; Heu, M.S.; Kim, J.; Jee, Y.; Jeon, Y.J. Molecular characteristics and anti-inflammatory activity of the fucoidan extracted from Ecklonia cava. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 89, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, H.S.A.; Lu, J.; Zhou, W.B. Structure characterization and antioxidant activity of fucoidan isolated from Undaria pinnatifida grown in New Zealand. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 212, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourao, P.A.S. Perspective on the use of sulfated polysaccharides from marine organisms as a source of new antithrombotic drugs. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 2770–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.H.; Zhang, Q.B.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.J. A comparative study of the anticoagulant activities of eleven fucoidans. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 91, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phull, A.R.; Majid, M.; Haq, I.U.; Khan, M.R.; Kim, S.J. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of anti-arthritic, antioxidant efficacy of fucoidan from Undaria pinnatifida (Harvey) Suringar. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 97, 468–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, J.Y.; Jung, M.J.; Jeong, I.H.; Yamazaki, K.; Kawai, Y.; Kim, B.M. Antimicrobial and antibiofilm activities of sulfated polysaccharides from marine algae against dental plaque bacteria. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Liu, Y.X.; Cao, M.J.; Liu, G.M.; Chen, Q.C.; Sun, L.C.; Chen, H.X. Antibacterial activity and mechanisms of depolymerized fucoidans isolated from Laminaria japonica. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 172, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, M.A.; Clarke, S.A. Bioactive compounds from marine organisms: Potential for bone growth and healing. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, P.A.; Yan, M.D.; Lin, H.T.; Li, K.L.; Lin, Y.C. Toxicological evaluation of low molecular weight fucoidan in vitro and in vivo. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, L.; Grenha, A. Sulfated seaweed polysaccharides as multifunctional materials in drug delivery applications. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollet, L.; Saboural, P.; Chauvierre, C.; Villemin, J.N.; Letourneur, D.; Chaubet, F. Fucoidans in nanomedicine. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, L.C.; Chen, C.H.; Lin, C.W.; Ho, Y.C.; Mi, F.L. Development of mutlifunctional nanoparticles self-assembled from trimethyl chitosan and fucoidan for enhanced oral delivery of insulin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 126, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.H.; Lin, Y.S.; Wu, S.J.; Mi, F.L. Mutlifunctional nanoparticles prepared from arginine-modified chitosan and thiolated fucoidan for oral delivery of hydrophobic and hydrophilic drugs. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 193, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.H.; Lu, K.Y.; Tseng, C.L.; Wu, J.Y.; Chen, C.H.; Mi, F.L. Development of genipin-crosslinked fucoidan/chitosan-N-arginine nanogels for preventing Helicobacter infection. Nanomedicine 2017, 12, 1491–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, K.Y.; Li, R.; Hsu, C.H.; Lin, C.W.; Chou, S.C.; Tsai, M.L.; Mi, F.L. Development of a new type of multifunctional fucoidan-based nanoparticles for anticancer drug delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 165, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, J.; Bhatnagar, I.; Kim, S.K. Chitosan-alginate biocomposite containing fucoidan for bone tissue engineering. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 300–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.T.; Lu, T.W.; Chen, C.H.; Mi, F.L. Development of genipin-crosslinked and fucoidan-adsorbed nano-hydroxyapatite/hydroxypropyl chitosan composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 128, 973–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.T.; Lu, T.W.; Chen, C.H.; Lu, K.Y.; Mi, F.L. Development of nanocomposite scaffolds based on biomineralization of N,O-carboxymethyl chitosan/fucoidan conjugates for bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 2335–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumayya, A.S.; Muraleedhara Kurup, G. Biocompatibility of subcutaneously implanted marine macromolecules cross-linked bio-composite scaffold for cartilage tissue engineering applications. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2018, 29, 257–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karunanithi, P.; Murali, M.R.; Samuel, S.; Raghavendran, H.R.B.; Abbas, A.A.; Kamarul, T. Three dimensional alginate-fucoidan composite hydrogel augments the chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stromal cells. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 147, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudirman, S.; Ong, A.D.; Chang, H.W.; Kong, Z.L. Effect of fucoidan on anterior cruciate ligament transection and medial meniscectomy induced osteoarthritis in high-fat diet-induced obese rats. Nutrients 2018, 10, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.B.; Chun, K.R.; Kim, J.K.; Suk, K.; Jung, Y.M.; Lee, W.H. The differential effect of high and low molecular weight fucoidans on the severity of collagen-induced arthritis in mice. Phytother. Res. 2010, 24, 1384–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.G.; Park, S.Y.; Chung, W.S.; Park, J.H.; Hwang, E.; Mavlonov, G.T.; Kim, I.H.; Kim, K.Y.; Yi, T.H. Fucoidan prevents the progression of osteoarthritis in rats. J. Med. Food 2015, 18, 1032–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, S.P.; Mulder, A.M.; Baker, D.G.; Robinson, S.R.; Rolfe, M.I.; Brooks, L.; Fitton, J.H. Effects of fucoidan from Fucus vesiculosus in reducing symptoms of osteoarthritis: A randomized placebo-controlled trial. Biologics 2016, 10, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, S.J.; Lee, K.W.; Lim, D.S.; Lee, S. The sulfated polysaccharide fucoidan stimulates osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2012, 21, 2204–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzo-Silberman, S.; Louedec, L.; Meilhac, O.; Letourneur, D.; Michel, J.B.; Elmadbouh, I. Therapeutic potential of fucoidan in myocardial ischemia. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2011, 58, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.C.; Liu, T.J. Mobilization of mesenchymal stem cells by stromal cell-derived factor-1 released from chitosan/tripolyphosphate/fucoidan nanoparticles. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, S.; Letourneur, D.; Aid-Launais, R.; Di Stefano, A.; Vainchenker, W.; Norol, F.; Le Visage, C. Fucoidan promotes early step of cardiac differentiation from human embryonic stem cells and long-term maintenance of beating areas. Tissue Eng. Part A 2014, 20, 1285–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purnama, A.; Aid-Launais, R.; Haddad, O.; Maire, M.; Mantovani, D.; Letourneur, D.; Hlawaty, H.; Le Visage, C. Fucoidan in a 3D scaffold interacts with vascular endothelial growth factor and promotes neovascularization in mice. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2015, 5, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.Y.; Huang, Y.C. Basic fibroblast growth factor released from fucoidan-modified chitosan/alginate scaffolds for promoting fibroblasts migration. J. Polym. Res. 2018, 25, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rujitanaroj, P.O.; Aid-Launais, R.; Chew, S.Y.; Le Visage, C. Polysaccharide electrospun fibers with sulfated poly(fucose) promote endothelial cell migration and VEGF-mediated angiogenesis. Biomater. Sci. 2014, 2, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinval, N.; Morenc, M.; Labour, M.N.; Samotus, A.; Mzyk, A.; Ollivier, V.; Maire, M.; Jesse, K.; Bassand, K.; Niemiec-Cyganek, A.; et al. Fucoidan/VEGF-based surface modification of decellularized pulmonary heart valve improves the antithrombotic and re-endothelialization potential of bioprostheses. Biomaterials 2018, 172, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.C.; Yang, Y.T. Effect of basic fibroblast growth factor released from chitosan-fucoidan nanoparticles on neurite extension. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2016, 10, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.H.; Wu, S.J.; Wu, J.Y.; Wen, D.Y.; Mi, F.L. Preparation of fucoidan-shelled and genipin-crosslinked chitosan beads for antibacterial application. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 126, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.H.; Wu, S.J.; Tang, D.W.; Ho, Y.C.; Mi, F.L.; Kuo, T.H.; Sung, H.W. Stimuli-responsive materials prepared from carboxymethyl chitosan and poly(gamma-glutamic acid) for protein delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, F.L. Synthesis and characterization of a novel chitosan-gelatin bioconjugate with fluorescence emission. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 975–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, F.L.; Tan, Y.C.; Liang, H.F.; Sung, H.W. In vivo biocompatibility and degradability of a novel injectable-chitosan-based implant. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, F.L.; Sung, H.W.; Shyu, S.S. Synthesis and characterization of a novel chitosan-based network prepared using naturally occurring crosslinker. J. Polym. Sci. Pol. Chem. 2000, 38, 2804–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Ortega, F.; Cifuentes, A.; Rodriguez, G.; Aguilar, M.R.; Gonzalez-Gomez, A.; Solis, R.; Garcia-Honduvilla, N.; Bujan, J.; Garcia-Sanmartin, J.; Martinez, A.; et al. Bioactive bilayered dressing for compromised epidermal tissue regeneration with sequential activity of complementary agents. Acta Biomater. 2015, 23, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.N.; Chen, P.W.; Huang, C.Y. Compositional characteristics and in vitro evaluations of antioxidant and neuroprotective properties of crude extracts of fucoidan prepared from compressional puffing-pretreated sargassum crassifolium. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.T.V.; Tsou, Y.C.; Chen, Y.T.; Lu, W.J.; Hwang, P.A. Effects of low-molecular-weight fucoidan and high stability fucoxanthin on glucose homeostasis, lipid metabolism, and liver function in a mouse model of type ii diabetes. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, P.M.; Li, K.L.; Lin, Y.C. Fucoidan-fucoxanthin ameliorated cardiac function via IRS1/GRB2/ SOS1, GSK3 beta/CREB pathways and metabolic pathways in senescent mice. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.J.; Zhu, W.L.; Wang, T.T.; Jin, L.Y.; Liu, T.W.; Li, X.; Guan, Z.J.; Jiang, Z.F.; Meng, X.Z.; Wang, J.G.; et al. Low molecule weight fucoidan mitigates atherosclerosis in ApoE (-/-) mouse model through activating multiple signal pathway. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 206, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.J.; Xu, J.; Ge, K.L.; Tian, Q.W.; Zhao, P.; Guo, Y.L. Anti-inflammatory effect of low molecular weight fucoidan from Saccharina japonica on atherosclerosis in apoE-knockout mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokota, T.; Nomura, K.; Nagashima, M.; Kamimura, N. Fucoidan alleviates high-fat diet-induced dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis in ApoE(Shl) mice deficient in apolipoprotein E expression. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2016, 32, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, J.A.; Frony, A.C.; Barcellos-de-Souza, P.; Menezes da Cunha, M.; Brasil Barbosa Calcia, T.; Benjamim, C.F.; Boisson-Vidal, C.; Barja-Fidalgo, C. Downregulation of microparticle release and pro-inflammatory properties of activated human polymorphonuclear neutrophils by LMW fucoidan. J. Innate. Immun. 2018, 17, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.J.; Yoon, K.Y.; Lee, B.Y. Low molecular weight fucoidan from the sporophyll of Undaria pinnatifida suppresses inflammation by promoting the inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinases and oxidative stress in RAW 264.7 cells. Fitoterapia 2012, 83, 1628–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernando, I.P.S.; Sanjeewa, K.K.A.; Samarakoon, K.W.; Lee, W.W.; Kim, H.S.; Kang, N.; Ranasinghe, P.; Lee, H.S.; Jeon, Y.J. A fucoidan fraction purified from Chnoospora minima; a potential inhibitor of LPS-induced inflammatory responses. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepetsos, P.; Papavassiliou, A.G. ROS/oxidative stress signaling in osteoarthritis. BBA Mol. Basis Dis. 2016, 1862, 576–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, M.F.; Ng, Y.F.; Pudney, P.D.A. Mechanism and kinetics of the crosslinking reaction between biopolymers containing primary amine groups and genipin. J. Polym. Sci. Pol. Chem. 2003, 41, 3941–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.C.; Chang, W.H.; Liang, H.F.; Lee, M.H.; Sung, H.W. Crosslinking structures of gelatin hydrogels crosslinked with genipin or a water-soluble carbodiimide. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 91, 4017–4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.W.; Liu, C.; Wu, J.H.; Lin, L.X.; Fan, H.M.; Zhao, D.H.; Zhuang, Y.Q.; Sun, Y.L. In situ injectable hyaluronic acid/gelatin hydrogel for hemorrhage control. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 98, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.C.; Ge, J.; Guo, B.L.; Ma, P.X. In situ forming biodegradable electroactive hydrogels. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 2880–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, K.G.; Gostynska, N.; Montesi, M.; Panseri, S.; Sprio, S.; Kon, E.; Marcacci, M.; Tampieri, A.; Sandri, M. Investigation of different cross-linking approaches on 3D gelatin scaffolds for tissue engineering application: A comparative analysis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 95, 1199–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Yoo, J.J.; Atala, A.; Lee, S.J. The effect of controlled release of PDGF-BB from heparin-conjugated electrospun PCL/gelatin scaffolds on cellular bioactivity and infiltration. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 6709–6720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.T.; Sheu, M.T.; Lin, Y.F.; Lan, J.; Chin, Y.P.; Hsieh, M.S.; Cheng, C.W.; Chen, C.H. Injectable hyaluronic-acid-doxycycline hydrogel therapy in experimental rabbit osteoarthritis. BMC Vet. Res. 2013, 9, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).