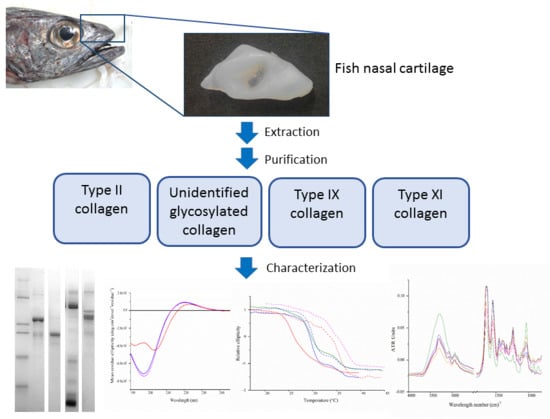
Isolation and Characterisation of Major and Minor Collagens from Hyaline Cartilage of Hoki (Macruronus novaezelandiae)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
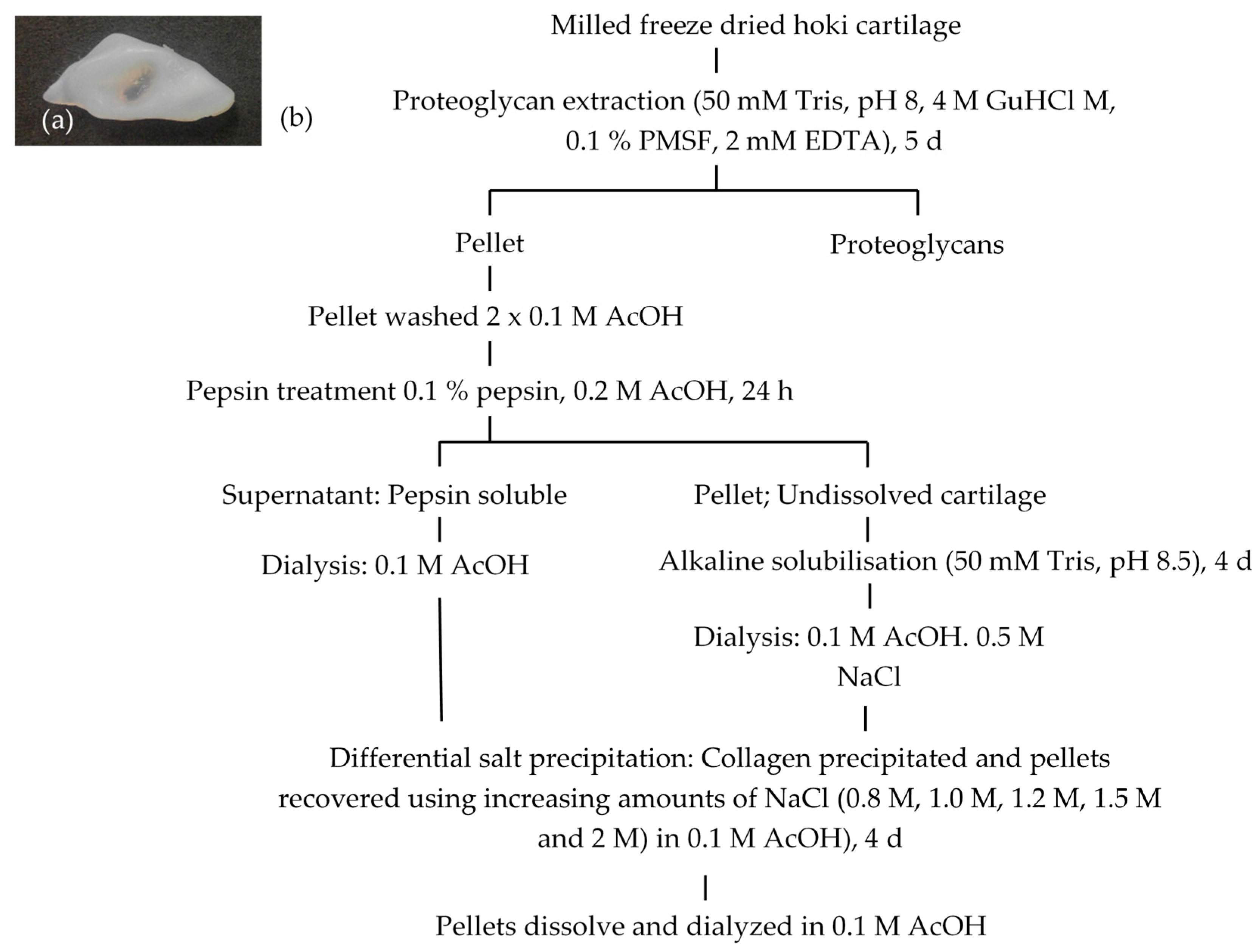
2.1. Extraction and Isolation of Cartilage Collagens
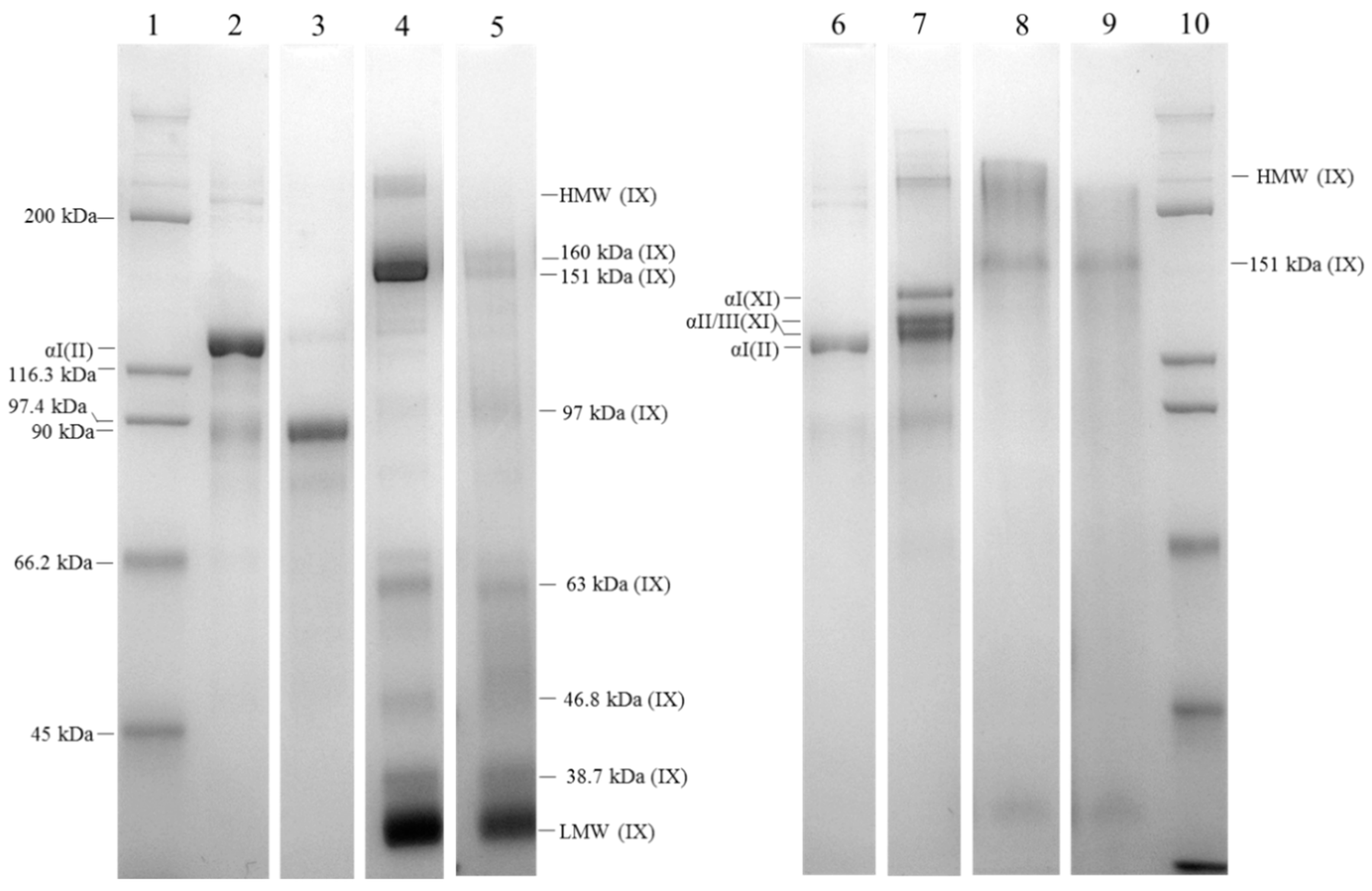
2.2. Isolation of Cartilage Collagens Using Differential Salt Precipitation and SDS-PAGE Analysis
2.3. Amino Acid Analysis
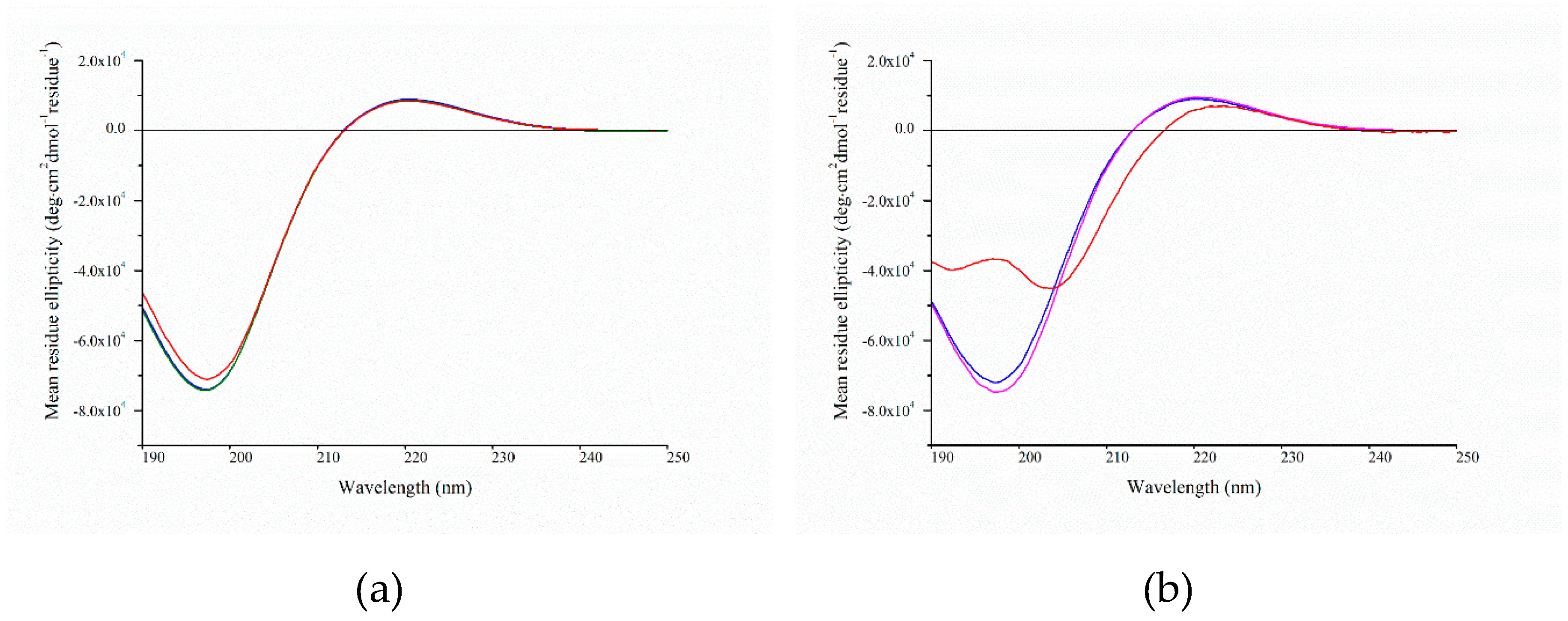
2.4. Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy
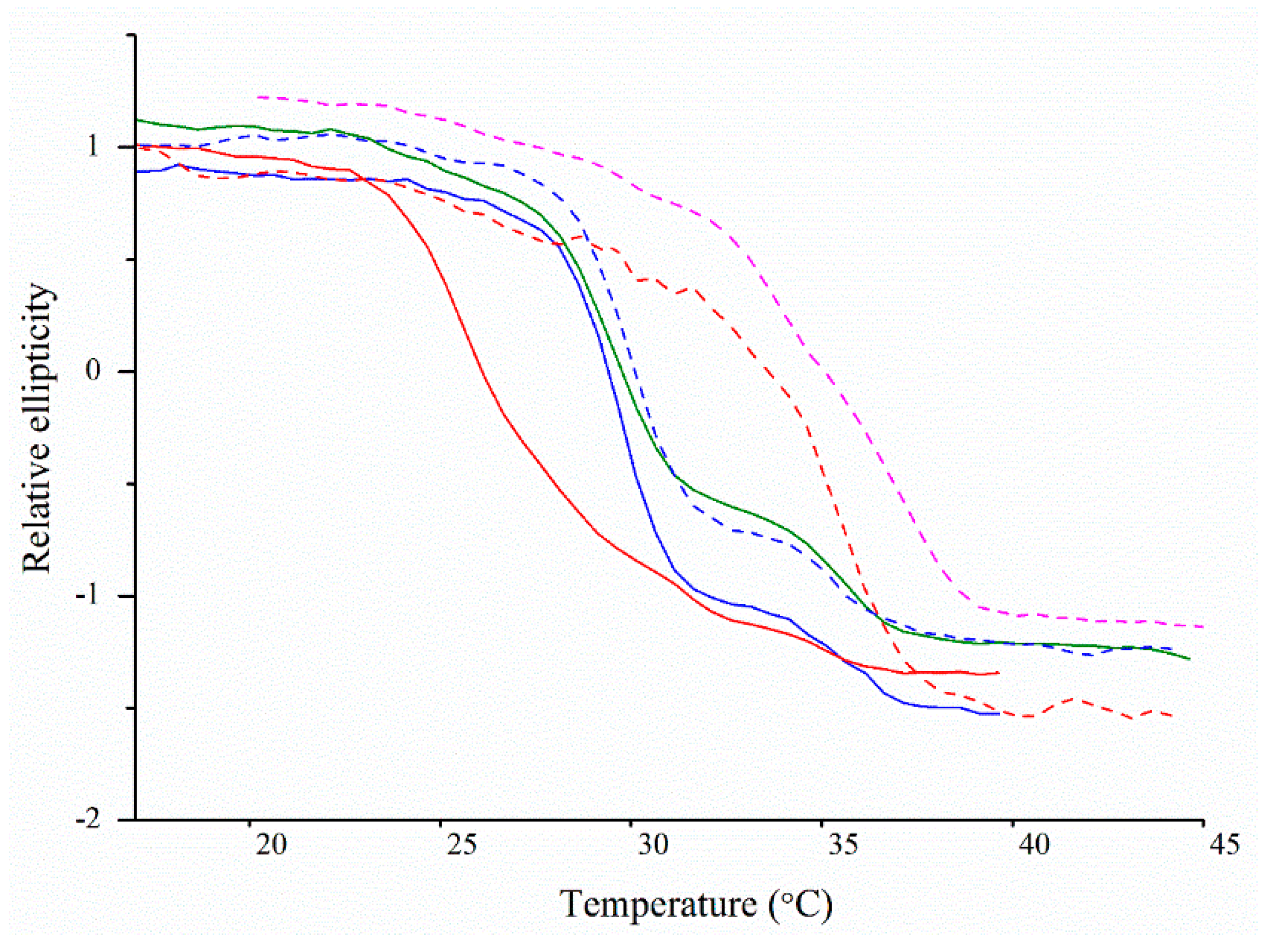
2.5. Thermal Denaturation Analyses Using Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy
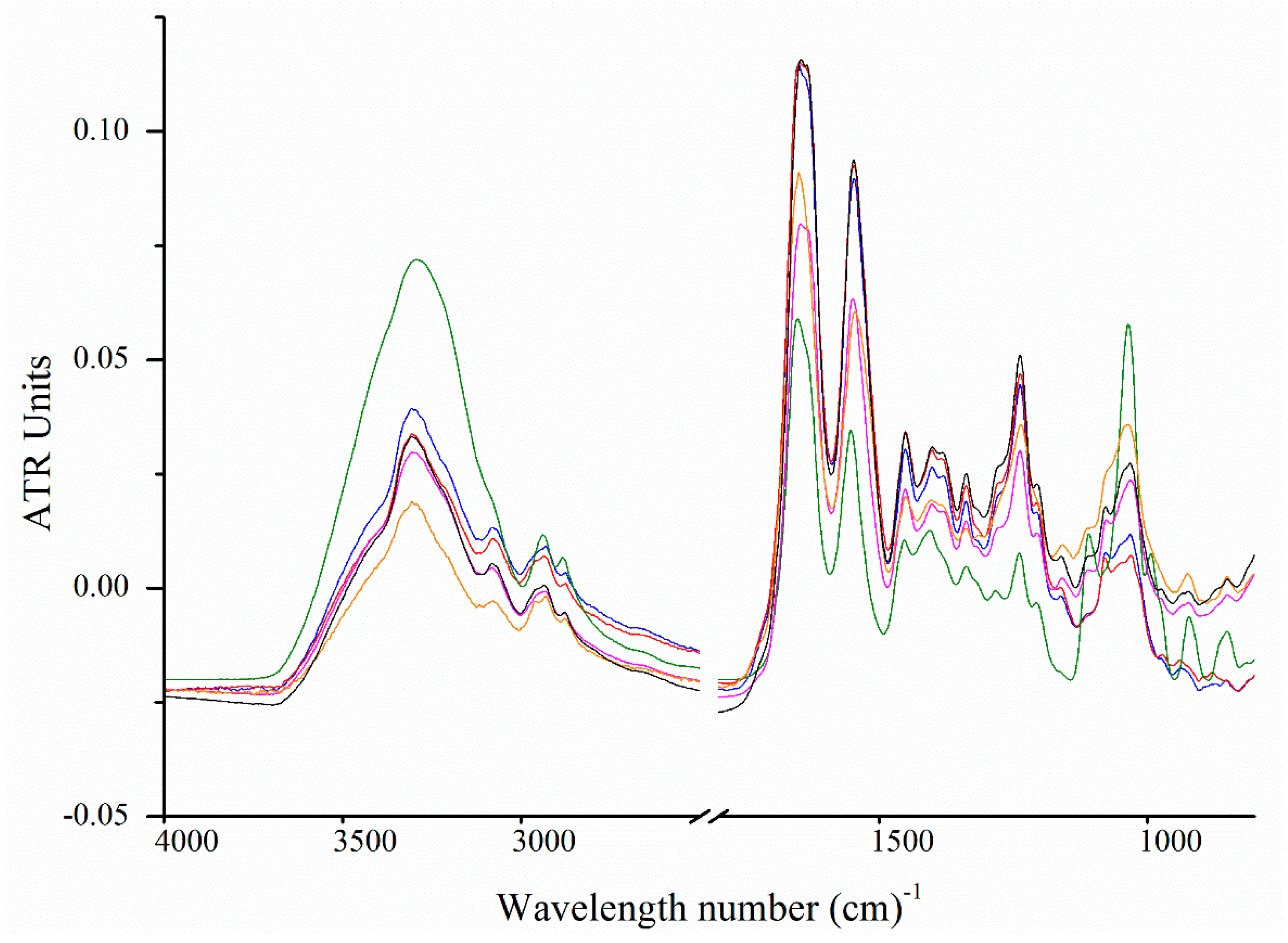
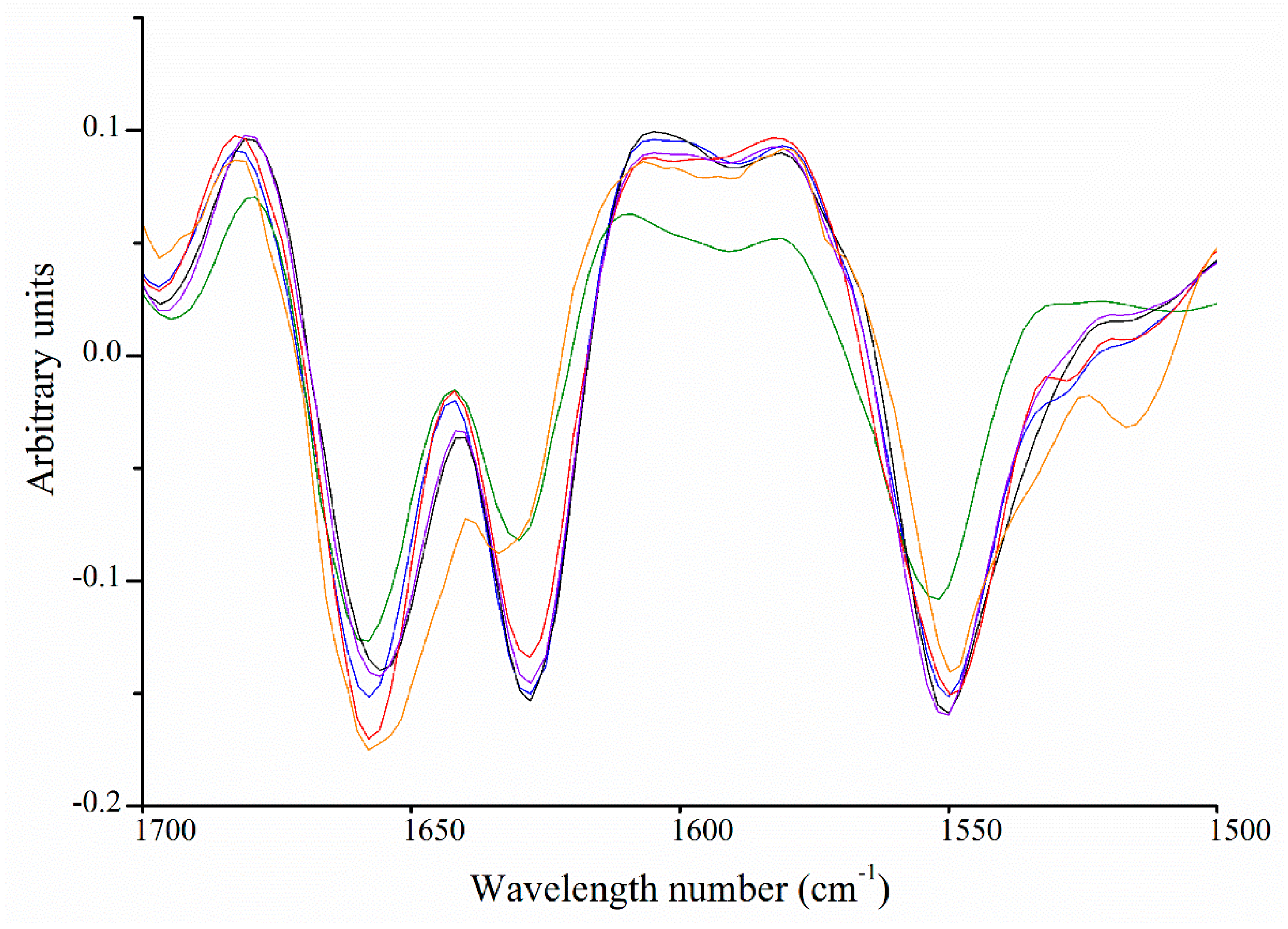
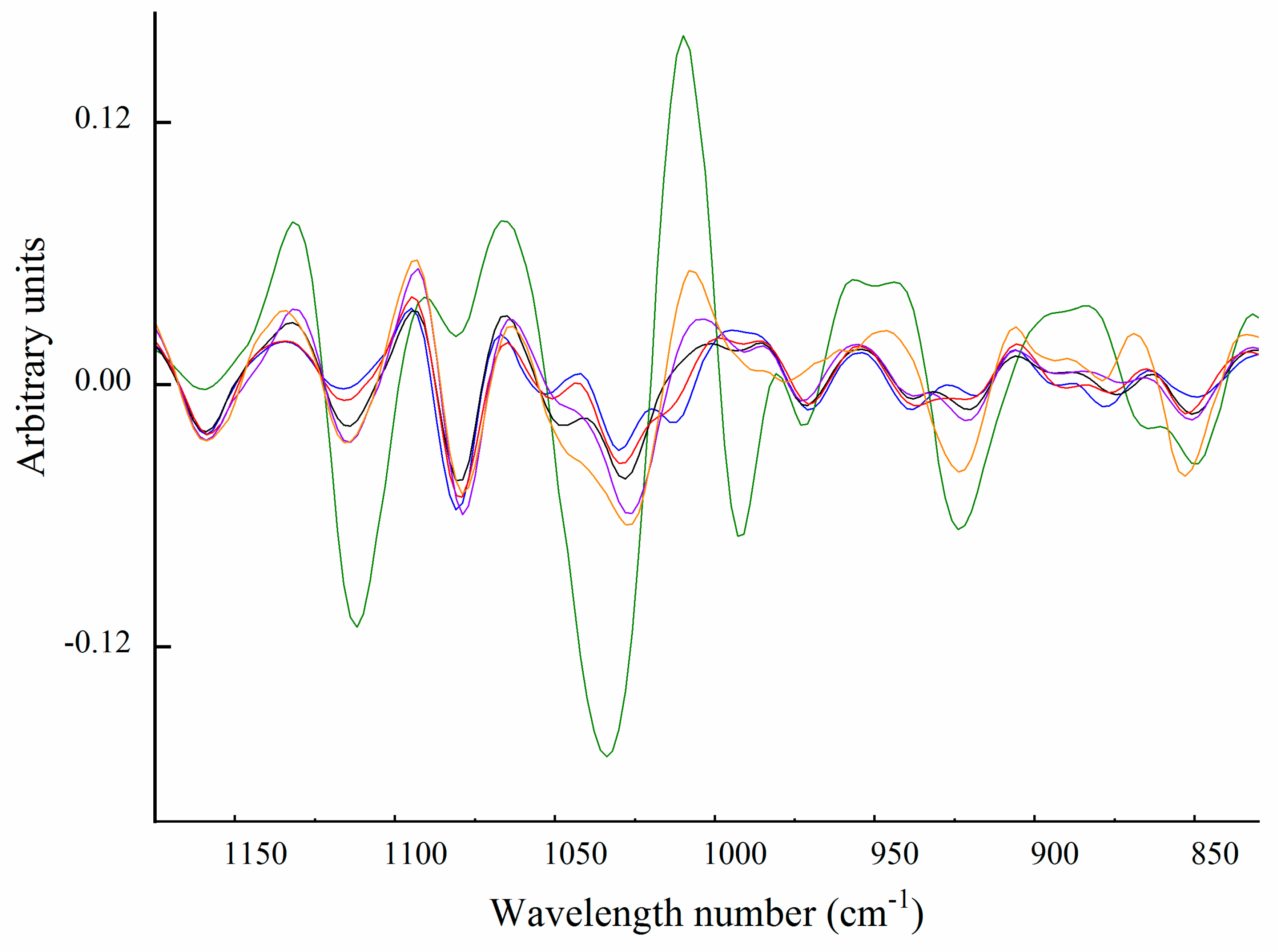
2.6. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
Carbohydrate Spectral Region (from 1200 to 850 cm−1)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Materials
4.3. Collagen Extraction from Cartilage
4.4. Collagen Isolation Using Salt Precipitation
4.5. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis Analyses
4.6. Amino Acid Derivatization and Analysis
4.7. Biuret Assay
4.8. Circular Dichroism Analyses
4.9. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cohen, N.P.; Foster, R.J.; Mow, V.C. Composition and dynamics of articular cartilage: Structure, function, and maintaining healthy state. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. 1998, 28, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyre, D.R.; Weis, M.A.; Wu, J.J. Articular cartilage collagen: An irreplaceable framework? Eur. Cells Mater. 2006, 12, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, N.P.; Bächinger, H.P. Type XI collagen is a heterotrimer with the composition (1 alpha, 2 alpha, 3 alpha) retaining non-triple-helical domains. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 11345–11350. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blaschke, U.K.; Eikenberry, E.F.; Hulmes, D.J.S.; Galla, H.-J.; Bruckner, P. Collagen XI Nucleates Self-assembly and Limits Lateral Growth of Cartilage Fibrils. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 10370–10378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDougal, O.M.; Warner, L.R.; Mallory, C.; Oxford, J.T. Predicted Structure and Binding Motifs of Collagen alpha1(XI). GSTF Int. J. Bioinform. Biotechnol. 2011, 1, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Fallahi, A.; Kroll, B.; Warner, L.R.; Oxford, R.J.; Irwin, K.M.; Mercer, L.M.; Shadle, S.E.; Oxford, J.T. Structural model of the amino propeptide of collagen XI alpha1 chain with similarity to the LNS domains. Protein Sci. Publ. Protein Soc. 2005, 14, 1526–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaughan-Thomas, A.; Young, R.D.; Phillips, A.C.; Duance, V.C. Characterization of type XI collagen-glycosaminoglycan interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 5303–5309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyre, D.R.; Pietka, T.; Weis, M.A.; Wu, J.J. Covalent cross-linking of the NC1 domain of collagen type IX to collagen type II in cartilage. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 2568–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leppanen, V.M.; Tossavainen, H.; Permi, P.; Lehtio, L.; Ronnholm, G.; Goldman, A.; Kilpelainen, I.; Pihlajamaa, T. Crystal structure of the N-terminal NC4 domain of collagen IX, a zinc binding member of the laminin-neurexin-sex hormone binding globulin (LNS) domain family. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 23219–23230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimokomaki, M.; Wright, D.W.; Irwin, M.H.; van der Rest, M.; Mayne, R. The structure and macromolecular organization of type IX collagen in cartilage. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1990, 580, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, P.; Meadows, R.S.; Chapman, K.L.; Grant, M.E.; Kadler, K.E.; Briggs, M.D. Cartilage Oligomeric Matrix Protein Interacts with Type IX Collagen, and Disruptions to These Interactions Identify a Pathogenetic Mechanism in a Bone Dysplasia Family. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 6046–6055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pihlajamaa, T.; Lankinen, H.; Ylostalo, J.; Valmu, L.; Jaalinoja, J.; Zaucke, F.; Spitznagel, L.; Gosling, S.; Puustinen, A.; Morgelin, M.; et al. Characterization of recombinant amino-terminal NC4 domain of human collagen IX: Interaction with glycosaminoglycans and cartilage oligomeric matrix protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 24265–24273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons, P.; Gilbert, S.J.; Vaughan-Thomas, A.; Sorrell, D.A.; Notman, R.; Bishop, M.; Hayes, A.J.; Mason, D.J.; Duance, V.C. Type IX Collagen Interacts with Fibronectin Providing an Important Molecular Bridge in Articular Cartilage. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 34986–34997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armiento, A.R.; Stoddart, M.J.; Alini, M.; Eglin, D. Biomaterials for articular cartilage tissue engineering: Learning from biology. Acta Biomater. 2018, 65, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, G.; Cao, Y. Recent Progress in Cartilage Tissue Engineering—Our Experience and Future Directions. Engineering 2017, 3, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deyl, Z.; Miksik, I.; Eckhardt, A. Preparative procedures and purity assessment of collagen proteins. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2003, 790, 245–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, E.J. Isolation and characterization of a collagen from chick cartilage containing three identical alpha chains. Biochemistry 1971, 10, 1652–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgeson, R.E.; Hebda, P.A.; Morris, N.P.; Hollister, D.W. Human cartilage collagens. Comparison of cartilage collagens with human type V collagen. J. Biol. Chem. 1982, 257, 7852–7856. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.J.; Eyre, D.R. Structural analysis of cross-linking domains in cartilage type XI collagen. Insights on polymeric assembly. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 18865–18870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reese, C.A.; Mayne, R. Minor collagens of chicken hyaline cartilage. Biochemistry 1981, 20, 5443–5448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, J.C.; Farjanel, J.; Boutillon, M.M.; Hartmann, D.J.; van der Rest, M.; Moradi-Ameli, M. Processing of type XI collagen. Determination of the matrix forms of the alpha1(XI) chain. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 23743–23748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, J.; Tanaka, S.; Hardt, T.; Eikenberry, E.F.; Brodsky, B. Fibril-forming collagens in lamprey. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 980–987. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Rest, M.; Mayne, R. Type IX Collagen. In Structure and Function of Collagen Types; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1987; pp. 195–221. [Google Scholar]
- Mayne, R.; van der Rest, M.; Ninomiya, Y.; Olsen, B.R. The structure of type IX collagen. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1985, 460, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piez, K.A.; Gross, J. The amino acid composition of some fish collagens: The relation between composition and structure. J. Biol. Chem. 1960, 235, 995–998. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, H.; Xu, S.Y. Purification and characterization of type II collagen from chick sternal cartilage. Food Chem. 2008, 108, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, E.J.; Mathews, M.B. Characterization of notochord collagen as a cartilage-type collagen. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1974, 60, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, E.J. Structural studies on cartilage collagen employing limited cleavage and solubilization with pepsin. Biochemistry 1972, 11, 4903–4909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuta, S.; Hwang, J.H.; Yoshinaka, R. Molecular species of collagen in pectoral fin cartilage of skate (Raja kenojei). Food Chem. 2003, 80, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricard-Blum, S.; Hartmann, D.J.; Herbage, D.; Payen-Meyran, C.; Ville, G. Biochemical properties and immunolocalization of minor collagens in foetal calf cartilage. FEBS Lett. 1982, 146, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentz, H.; Morris, N.P.; Murray, L.W.; Sakai, L.Y.; Hollister, D.W.; Burgeson, R.E. Isolation and partial characterization of a new human collagen with an extended triple-helical structural domain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1983, 80, 3168–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fountoulakis, M.; Lahm, H.-W. Hydrolysis and amino acid composition analysis of proteins. J. Chromatogr. 1998, 826, 109–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, R.S.; Gough, C.A. Circular Dichroism of Collagen and Related Polypeptides. In Circular Dichroism and the Conformational Analysis of Biomolecules; Fasman, G.D., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1996; pp. 183–199. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, J.L.; Miles, A.J.; Whitmore, L.; Wallace, B.A. Distinct circular dichroism spectroscopic signatures of polyproline II and unordered secondary structures: Applications in secondary structure analyses. Protein Sci. Publ. Protein Soc. 2014, 23, 1765–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenfield, N.J. Using circular dichroism spectra to estimate protein secondary structure. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2876–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitmore, L.; Wallace, B.A. Protein secondary structure analyses from circular dichroism spectroscopy: Methods and reference databases. Biopolymers 2008, 89, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasios, G.; Nishimura, I.; Konomi, H.; van der Rest, M.; Ninomiya, Y.; Olsen, B.R. Cartilage type IX collagen-proteoglycan contains a large amino-terminal globular domain encoded by multiple exons. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 2324–2329. [Google Scholar]
- Brewton, R.G.; Wright, D.W.; Mayne, R. Structural and functional comparison of type IX collagen-proteoglycan from chicken cartilage and vitreous humor. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 4752–4757. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, I.; Muragaki, Y.; Olsen, B.R. Tissue-specific forms of type IX collagen-proteoglycan arise from the use of two widely separated promoters. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 20033–20041. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Persikov, A.V.; Brodsky, B. Unstable molecules form stable tissues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 1101–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Q.F.; Wang, L.; Sun, W.H.; Wang, Z.B.; Xu, J.M.; Ma, H.L. Isolation and characterization of collagen from the cartilage of Amur sturgeon (Acipenser schrenckii). Process Biochem. 2014, 49, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ookawa, M.; Tan, Y.; Ura, K.; Adachi, S.; Takagi, Y. Biochemical characterisation and assessment of fibril-forming ability of collagens extracted from Bester sturgeon Huso huso × Acipenser ruthenus. Food Chem. 2014, 160, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, N.P.; Watt, S.L.; Davis, J.M.; Bachinger, H.P. Unfolding intermediates in the triple helix to coil transition of bovine type XI collagen and human type V collagens alpha 1(2) alpha 2 and alpha 1 alpha 2 alpha 3. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 10081–10087. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bruckner, P.; Mayne, R.; Tuderman, L. p-HMW-Collagen, a minor collagen obtained from chick embryo cartilage without proteolytic treatment of the tissue. Eur. J. Biochem. 1983, 136, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal Bde, C.; Mello, M.L. FT-IR Microspectroscopy of Rat Ear Cartilage. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sizeland, K.H.; Hofman, K.A.; Hallett, I.C.; Martin, D.E.; Potgieter, J.; Kirby, N.M.; Hawley, A.; Mudie, S.T.; Ryan, T.M.; Haverkamp, R.G.; et al. Nanostructure of electrospun collagen: Do electrospun collagen fibers form native structures? Materialia 2018, 3, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Campos Vidal, B.; Mello, M.L.S. Collagen type I amide I band infrared spectroscopy. Micron 2011, 42, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, M.; Mantsch, H.H. The use and misuse of FTIR spectroscopy in the determination of protein structure. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1995, 30, 95–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazarev, Y.A.; Grishkovsky, B.A.; Khromova, T.B. Amide I band of IR spectrum and structure of collagen and related polypeptides. Biopolymers 1985, 24, 1449–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, K.J.; Veis, A. Fourier transform IR spectroscopy of collagen and gelatin solutions: Deconvolution of the amide I band for conformational studies. Biopolymers 1988, 27, 1749–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, J.; Yu, S. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic analysis of protein secondary structures. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2007, 39, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byler, D.M.; Susi, H. Examination of the secondary structure of proteins by deconvolved FTIR spectra. Biopolymers 1986, 25, 469–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, M.; Choo, L.P.; Watson, P.H.; Halliday, W.C.; Mantsch, H.H. Beware of connective tissue proteins: Assignment and implications of collagen absorptions in infrared spectra of human tissues. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1995, 1270, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talari, A.C.S.; Martinez, M.A.G.; Movasaghi, Z.; Rehman, S.; Rehman, I.U. Advances in Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy of biological tissues. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2017, 52, 456–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, N.P.; West, P.; Torzilli, P.A.; Mendelsohn, R. FTIR microscopic imaging of collagen and proteoglycan in bovine cartilage. Biopolymers 2001, 62, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, P.; McLeod, D.; Ayad, S. Extraction and characterisation of the intact form of bovine vitreous type IX collagen. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1992, 185, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yada, T.; Suzuki, S.; Kobayashi, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Hoshino, T.; Horie, K.; Kimata, K. Occurrence in chick embryo vitreous humor of a type IX collagen proteoglycan with an extraordinarily large chondroitin sulfate chain and short alpha 1 polypeptide. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 6992–6999. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Servaty, R.; Schiller, J.; Binder, H.; Arnold, K. Hydration of polymeric components of cartilage—An infrared spectroscopic study on hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2001, 28, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Sinkeviciute, D.; He, Y.; Karsdal, M.; Henrotin, Y.; Mobasheri, A.; Onnerfjord, P.; Bay-Jensen, A. The minor collagens in articular cartilage. Protein Cell 2017, 8, 560–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinegard, D.; Saxne, T. The role of the cartilage matrix in osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2011, 7, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyre, D.R. Collagen of articular cartilage. Arthritis Res. 2002, 4, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ricard-Blum, S. The collagen family. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a004978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, M.; Portier, R.J.; Moody, M.W.; Bell, J.; Schexnayder, M.A.; Losso, J.N. Biochemical properties of bone and scale collagens isolated from the subtropical fish black drum (Pogonia cromis) and sheepshead seabream (Archosargus probatocephalus). Food Chem. 2004, 88, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, M.; Moody, M.W.; Portier, R.J.; Bell, J.; Schexnayder, M.A.; Losso, J.N. Biochemical Properties of Black Drum and Sheepshead Seabream Skin Collagen. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 8088–8092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, C.A.; Bailey, A.J. Thermal denaturation of collagen revisited. Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. Chem. Sci. 1999, 111, 71–80. [Google Scholar]
- Miles, C.A.; Bailey, A.J. Thermally labile domains in the collagen molecule. Micron 2001, 32, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittiphattanabawon, P.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Shahidi, F. Isolation and characterization of collagen from the cartilages of brownbanded bamboo shark (Chiloscyllium punctatum) and blacktip shark (Carcharhinus limbatus). LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 43, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rama, S.; Chandrakasan, G. Distribution of different molecular species of collagen in the vertebral cartilage of shark (Carcharius acurtus). Connect. Tissue Res. 1984, 12, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, C.F.; Wang, B.; Li, Z.R.; Luo, H.Y.; Ding, G.F. Characterization of acid-soluble collagens from the cartilages of scalloped hammerhead (Sphyrna lewini), red stingray (Dasyatis akajei), and skate (Raja porosa). Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2013, 22, 909–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, K.J.; Beckman, M.J.; Bowlin, G.L.; Wayne, J.S. Mechanical properties and cellular proliferation of electrospun collagen type II. Tissue Eng. 2004, 10, 1510–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieper, J.S.; van der Kraan, P.M.; Hafmans, T.; Kamp, J.; Buma, P.; van Susante, J.L.C.; van den Berg, W.B.; Veerkamp, J.H.; van Kuppevelt, T.H. Crosslinked type II collagen matrices: Preparation, characterization, and potential for cartilage engineering. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 3183–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaddon, M.; Burrows, M.; Ferreira, S.A.; Dazzi, F.; Apperley, J.F.; Bradshaw, A.; Brand, D.D.; Czernuszka, J.; Gentleman, E. Monomeric, porous type II collagen scaffolds promote chondrogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-C.; Yao, C.-L.; Wei, Y.-H.; Chu, I.-M. Evaluating osteochondral defect repair potential of autologous rabbit bone marrow cells on type II collagen scaffold. Cytotechnology 2011, 63, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kadler, K.E.; Hill, A.; Canty-Laird, E.G. Collagen fibrillogenesis: Fibronectin, integrins, and minor collagens as organizers and nucleators. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2008, 20, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, J.; Ricker, R.D.; Bidlingmeyer, B.A.; Woodward, C. Rapid, Accurate, Sensitive, and Reproducible HPLC Analysis of Amino Acids; Application Note, Publication No: 5980-1193; Agilent Technologies: Santa Clara, CA, USA, 2000; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Gornall, A.G.; Bardawill, C.J.; David, M.M. Determination of serum proteins by means of the biuret reaction. J. Biol. Chem. 1949, 177, 751–766. [Google Scholar]
- Sreerama, N.; Woody, R.W. Estimation of protein secondary structure from circular dichroism spectra: Comparison of CONTIN, SELCON, and CDSSTR methods with an expanded reference set. Anal. Biochem. 2000, 287, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Pepsin-Soluble | Alkaline-Soluble | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amino Acid | Type II | 90 kDa | Type IX | Type II | Type IX | Type XI |
| Asp | 50.54 | 46.44 | 52.58 | 51.22 | 55.19 | 47.32 |
| Glu | 89.27 | 90.50 | 86.45 | 91.68 | 106.14 | 98.07 |
| Hyp | 105.28 | 117.73 | 85.91 | 96.83 | 89.38 | 105.33 |
| Ser | 46.40 | 42.83 | 46.62 | 45.45 | 35.04 | 36.46 |
| Gly | 277.10 | 286.74 | 299.31 | 288.40 | 278.16 | 297.04 |
| His | 4.16 | 3.39 | 7.88 | 5.11 | 10.22 | 6.43 |
| Arg | 51.76 | 43.84 | 50.22 | 50.60 | 43.58 | 47.20 |
| Thr | 26.57 | 26.34 | 26.40 | 25.82 | 30.16 | 24.56 |
| Ala | 89.46 | 92.68 | 74.11 | 86.12 | 57.68 | 65.87 |
| Pro | 123.63 | 122.39 | 124.60 | 119.67 | 93.83 | 117.94 |
| Tyr | 1.63 | 0.99 | 1.54 | 1.98 | 3.24 | 1.47 |
| Val | 18.47 | 17.20 | 24.80 | 20.74 | 35.81 | 22.53 |
| Met | 16.48 | 10.50 | 13.67 | 11.77 | 16.21 | 12.07 |
| Ile | 12.44 | 11.30 | 16.02 | 13.68 | 25.49 | 14.10 |
| Leu | 41.92 | 39.57 | 40.42 | 41.15 | 54.45 | 46.60 |
| Hyl | 15.25 | 17.82 | 19.48 | 17.71 | 28.67 | 26.28 |
| Phe | 14.36 | 14.76 | 11.03 | 14.36 | 12.01 | 13.77 |
| Lys | 15.28 | 14.99 | 17.86 | 17.46 | 21.91 | 16.96 |
| Cys | 1.09 1 | 2.81 1 | ||||
| Imino (Hyp + Pro) | 228.91 | 240.12 | 210.51 | 216.5 | 183.21 | 223.27 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cumming, M.H.; Hall, B.; Hofman, K. Isolation and Characterisation of Major and Minor Collagens from Hyaline Cartilage of Hoki (Macruronus novaezelandiae). Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17040223
Cumming MH, Hall B, Hofman K. Isolation and Characterisation of Major and Minor Collagens from Hyaline Cartilage of Hoki (Macruronus novaezelandiae). Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(4):223. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17040223
Chicago/Turabian StyleCumming, Mathew H., Bronwyn Hall, and Kathleen Hofman. 2019. "Isolation and Characterisation of Major and Minor Collagens from Hyaline Cartilage of Hoki (Macruronus novaezelandiae)" Marine Drugs 17, no. 4: 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17040223
APA StyleCumming, M. H., Hall, B., & Hofman, K. (2019). Isolation and Characterisation of Major and Minor Collagens from Hyaline Cartilage of Hoki (Macruronus novaezelandiae). Marine Drugs, 17(4), 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17040223