Abstract
The extraction and purification of collagen are of great interest due to its biological function and medicinal applications. Although marine invertebrates are abundant in the animal kingdom, our knowledge of their extracellular matrix (ECM), which mainly contains collagen, is lacking. The functions of collagen isolated from marine invertebrates remain an untouched source of the proteinaceous component in the development of groundbreaking pharmaceuticals. This review will give an overview of currently used collagens and their future applications, as well as the methodological issues of collagens from marine invertebrates for potential drug discovery.
1. Introduction
Collagen is one of the most abundant proteins in the extracellular matrix of animal bodies. This protein is the main fibrous, structural protein and supports the formation of all joints in the body. Supplementing collagen is an important way to keep our body healthy. Nowadays, collagen-based biomedical materials are used for the treatment of many human diseases (e.g., bone tissue regeneration). The challenge currently facing scientists is to find a suitable source of collagen, and the extraction and purification of collagen, which would be appropriate for applying to medical applications.
There is a huge source of collagen from marine organisms, and recent research has demonstrated that the marine source is the most convenient and safest way to obtain it, with invertebrates and crustose coralline algae [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9] being the most abundant and potential sources (see Figure 1A for examples). A marine source also has lots of advantages over land animals such as being environmentally friendly, having a high quantity of collagen, having biological toxins that are almost negligible, having better absorption due to low molecular weight, having a minimal inflammatory response, having less religious and ethical constraints, being metabolically compatible, and having few regulatory and quality control problems.
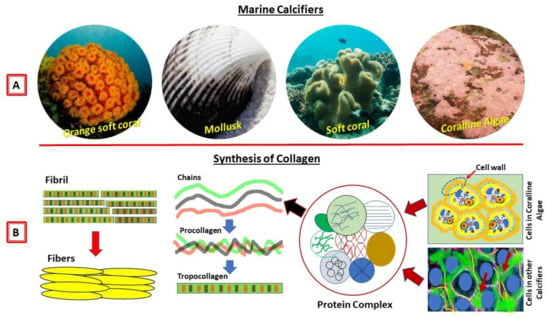
Figure 1.
Marine calcifiers and their collagens. (A) Examples of marine calcifiers/invertebrates. (B) A model image on the biological synthesis of collagens from the marine invertebrates and crustose coralline algae.
In this review, I included crustose coralline algae (CCA) because they have similar characteristics of proteinaceous components and mineralization processes like calcifying marine invertebrates. CCA are rock-hard calcareous with two key functional roles in coral reef ecosystems: (1) reef calcification and cementation and (2) inducing the larval settlement of many benthic organisms. CCA contain calcium carbonate with hard skeletons and minerals (e.g., calcite) similar to coral skeletons. In addition, CCA have a high content of organic matrix skeletal proteins, including chitin and collagen [5,9]. CCA are abundant and are found in marine waters all over the world. I therefore introduce these abundant marine sources with the invertebrates presented in this review, which might have a high potential for the extraction of collagens, and moreover use for medical applications.
Invertebrates make up almost 95% of the animal kingdom, but our knowledge of their extracellular matrices, in particular, the polymer collagen is very weak. The information on the biology of collagen within the extracellular matrix is scanty. A large number of marine invertebrates produce polysaccharides and extracellular matrices [10,11,12,13,14] within their connective tissues, and their molecular structures and functions are similar to humans [15,16]. Moreover, polysaccharides extracted from marine calcifiers that contain extracellular matrices have an enormous assortment of structures (Figure 1B), and they can be considered an extraordinary source of biochemical variety. We therefore discuss the studies of collagens of invertebrates (including related marine calcifiers) and their plausible medical application.
Treatment of bone defects such as replacing tissue or regeneration requires biomaterials with similar mechanical integrity to natural bone, which can adapt and contribute to the tissue growth processes. From an applicable biomaterials point of view, the mineralized extracellular matrix of collagen in marine invertebrate structures has a vast richness for tissue engineering [17,18]. The skeletons in marine invertebrates are classic bio-resources that have tailored architectures to give structural support, and their functions are feasible for human tissue regeneration and repair. Marine calcifiers, for example, coralline, sea urchin, and coral, have interconnected porous structures that are enriched with bioactive elements and medical materials that could be used for tissue engineering and drug design applications [5,11,12,19,20,21,22,23]. The main purpose of this review is to provide an overview of currently used collagens from marine invertebrates and related calcifying organisms, and their medicinal potential, as well as the technical issues in purifying collagen from them.
2. Current State of Collagen Research and its Medical Application
There has been significant progress in the research of marine natural products in the purpose of medical application nowadays. Marine invertebrates are the main source of this purpose; however, finding collagen for the treatment of bone-related diseases is not well established yet. Many research groups have been studying collagen in some marine calcifier tissues with a focus on structure and functional relationships [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]. The biology of the extracellular matrix (Figure 2), particularly of collagen in invertebrates is essential to understanding the continuing research in the field of marine natural products. One of the key components of the structure of the collagen is a glycoprotein (see Figure 2, left panel), and many organisms in the CCA and invertebrate such as corals (especially, soft corals), coralline algae, and jewelry corals [5,24,25,26] have already demonstrated this key molecule (see Figure 3 for some examples). Helman et al. [24] reported collagen production in the ECM of both soft (Xenia elongata) and hard (Montipora digitata) corals. They clearly demonstrated the presence of glycoprotein in the ECM of corals, which means the presence of collagen must exist if the glycoprotein is present in the species. This is an indicator for species that contain collagen molecules.
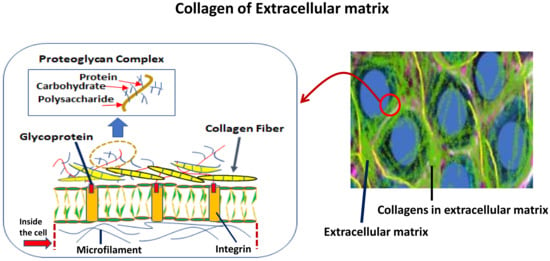
Figure 2.
Collagen of extracellular matrix and its biology in invertebrates. The right panel shows a model of cells. The left panel shows the structural components of the extracellular matrix, which are involved in the formation of collagen in marine invertebrates.
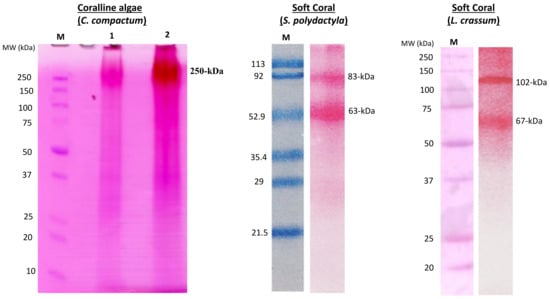
Figure 3.
Collagen associated glycoproteins in marine calcifiers. Coralline red algae: Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) with a periodic acid-schiff (PAS) staining to detect glycoprotein in the extracellular matrix of Clathromorphum compactum. M, protein ladder. Lane 1 and 2, high molecular weight (250 kDa) of a glycoprotein. Soft coral (Sinularia polydactyla): SDS-PAGE with a PAS staining to detect glycoprotein in the extracellular matrix of S. polydactyla. M, protein ladder. Two glycoproteins (83 and 63 kDa) were identified in this species. Soft Coral (Lobophytum crassum): SDS-PAGE with a PAS staining. The PAS staining to detect glycoprotein in the extracellular matrix of L. crassum. M, protein ladder. Two glycoproteins (102 and 67 kDa) were identified in this soft coral species. The Precision Plus SDS-PAGE protein ladder (Bio-Rad) was used for the electrophoresis analysis of all above-mentioned glycoproteins. The glycoproteins presented here were reproduced from Rahman [5] for the coralline red algae and Rahman et al. [25] for the two soft corals (S. polydactyla, L. crassum).
To date, collagen has been identified in corals, sponges, sea urchin, salmon, jellyfish, mollusk, and coralline red algae [2,3,4,5,7,8,9,10,20,27,28,29,30,31,32,33], among others. Most of these organisms have also been applied for use in tissue engineering [34]. Collagen from marine invertebrates and related calcifiers have been discussed in numerous review papers [5,6,31,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42] where the authors highlighted details regarding the structure and application of the collagen of this abundant marine source. It is a great possibility to use the huge source of marine invertebrates for extracting and purifying collagen, not only for the medical application and bone-related disease but also for use in cosmetics and anti-aging [43,44,45,46,47,48].
Recently, our group explored collagen in coralline red algae [5,9]. The research is now continuing, and a high number of collagens have now been extracted from this organism (papers in preparation). Some portions of this organism contain both chitin and collagen (Figure 4 and Figure 5). Because of the huge number of these organisms available in shallow water of the sea, it would be an easy way to collect this marine group for extracting collagen. However, purification of collagen from these organisms has been a problem, and this issue has already been mostly solved (see Section 3 for details). This is a new group of marine organisms, which could get special attention for the extraction of collagen molecules in the near future.
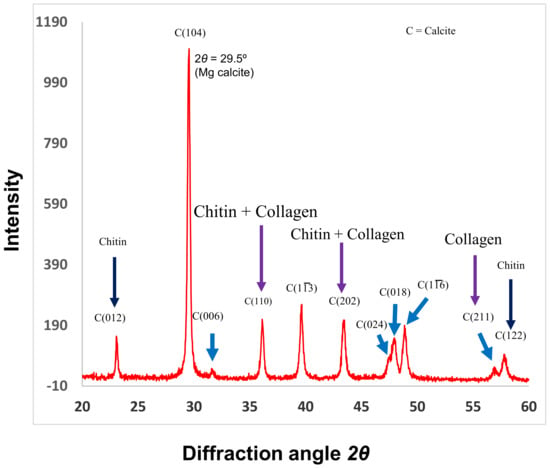
Figure 4.
X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis of C. compactum. The 2θ scan identifies the mineral form of CaCO3 crystal planes, which were nucleated by chitin and collagen matrices. Purple arrows show the collagen bands. Reproduced with permission from Rahman and Halfar [9].
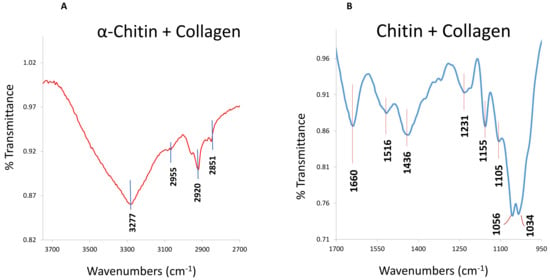
Figure 5.
Infrared (IR) of collagens in C. compactum. Attenuated total reflection (ATR)–Fourier–transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) spectra reveal the collagen bands in both soluble (A) and insoluble (B) organic matrix fractions. [Reproduced from Rahman and Halfar (9)].
It is assumed that half of all marine-derived biomaterials are sourced from marine sponges, which might be the highest number of organisms in the invertebrates currently being used for the extraction of collagen. In sponges, collagen fibers have an interesting structural feature [45,49], and the molecules isolated from this group have a wide range of activities that can be used for promising biomedical applications [4,6], especially collagenous marine sponge skeletons, which are extremely strong, highly absorbent, elastic, and resistant to bacterial attack. A recent review by Ehrlich et al. [6] described details about collagen and collagen-like structural proteins from sponges. They also highlighted the prospects and trends of collagen extracted from sponges in biomedical applications, materials science, and technology. From the same research group [1], a hydroxylated fibrillar collagen containing an unusual motif of “Gly–3Hyp–4Hyp” was isolated from the glass sponge (Hexactinellida). The authors hypothesized that this motif in fibrillar collagen subject is a silica precipitation and a template for biosilicification. Recently, Tziveleka et al. [4] isolated and characterized the collagens from the marine demosponges Suberites carnosus (Suberitidae) and Axinella cannabina (Axenillidae) and found three different collagen-insoluble collagen (InSC), spongin-like collagen (SlC), and intracellular collagen (ICC) for biomedical applications. Collagen was isolated from many other marine sponges, for instance, Chondrosia reniformis [47], Microciona prolifera, Spongia graminea, Haliclona oculata [42], Cacospongia scalaris, Hippospongia communis [49], Chondrosia reniformis [50,51], Geodia cydonium [52], and several Ircinia species [53].
Corals are an abundant source of biologically and structurally active compounds. Coral skeletons have interconnected pores and are composed of CaCO3, with appropriate porosity and pore sizes, making them a suitable material for bone implant application [17]. Regarding its interesting structural formation, coral has been in use commercially since the 1990s and is available as interpore and bio-coral [21]. There are several studies that have been found for such kinds of application, e.g., a three-dimensional coral skeleton structure endorsed the hard tissue growth and was totally replaced by new bone [22]. Similarly, a coral skeleton was used in human grafting [23]. Because of the structural compositions of coral, it absorbed CaCO3 very quickly in growing new bone tissue, allowing for a formation of a scaffold. These reports indicate that the corals might have collagenous molecules, which can be applied as a treatment for bone-related disease.
However, the research for collagen on corals, especially for soft corals, has remarkably improved. Over the last several years [2,3,44,54], very interesting findings on collagen molecules have been demonstrated from soft corals. Also, a number of collagen-associated glycoproteins have been detected in soft corals [14,24,25,55,56]. The researchers found unique collagen fibers from the soft coral Sarcophyton ehrenbergi [2,3]. These fibers expose a 3D structure and hyper-elastic behavior, which are analogous to natural human tissues. The peculiarity of these fibers is too long (9 ± 0.37 μm). The research also demonstrated the collagen I and II types. The structural characterization of these collagen fibers reveals a highly suitable biomaterial for medical applications. Benayahu et al. [54] invented an interesting patent from the same soft coral species S. ehrenbergi. The inventors claimed that “(1) the collagen fibers from the soft coral have high adjustable extensibility compared with mammalian collagen fibers and (2) the stiffness of the collagen fibers isolated from this species is at the top range of the reported stiffness range of mammal collagen fibers”. Another study [24] demonstrated the structural differentiation of collagen production in the ECM of soft corals; however, the authors did not investigate the types of collagen. Besides the above-mentioned marine organisms, sea urchin, marine fish, and mollusk organisms have been used for extracting different types of collagen, and the evidence showed that these collagen molecules have a strong role in the treatment of bone-related disease [20,27,29,30,31,33].
As mentioned above, research on the medical application of marine invertebrate collagen is currently progressing well. However, most collagen research findings from marine calcifiers/invertebrates are used in the application of bone-related disease (34), but the research in this field is still suffering from various complications. The medical application of marine collagens has been highlighted in recent reviews [6,31,35,57,58]. A review report by Cicciù et al. [57] suggested the facial bone reconstruction defect by applying marine collagen. During this review, the authors conducted a search using the MEDLINE and EMBASE databases (2007 to 2017), and their search results suggested that marine collagen can support the stability of the bone graft and could be an excellent carrier for growth factors. There are some recent reports of marine sources (coral, sponge, sea urchin, and fish) focused on the medical application (including bone tissue engineering and related diseases) of collagen available in the literature [3,6,17,31,59,60,61]. Moreover, collagen derived from mollusks, echinoderms, and sponges was reported [62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71], with some other important medical applications.
3. Purification Technique of Collagens from Marine Invertebrates
The molecules in invertebrates are complex, and therefore the purification of any specific molecule from this group is tricky. An individual species is required to apply different techniques, as the characterization of their components is multifaceted. For instance, soft corals have sclerites and soft tissue (unlike the stony corals) comprising complex organic matrices [14]. For these complexities, it was difficult to purify molecules; however, our group successfully purified the molecules [11,14], including the functional extracellular matrix proteins (e.g., ECMP-67), enzymes, calcium-binding proteins, and glycoproteins (see Figure 3 for examples). Glycoprotein in the extracellular matrix protein is a key component of collagen (Figure 2) that plays the main role in the biological process of collagen in invertebrates. Applying similar techniques, we recently investigated coralline algae, which have a high concentration of both chitin and collagen biopolymers and are functional in both soluble and insoluble organic matrix fractions (Figure 4 and Figure 5) [5,9].
Coralline algal concentrations of the soluble organic matrix (0.9%) and insoluble organic matrix (4.5%) fractions are significantly higher than those of other marine invertebrates such as soft corals, with a soluble organic matrix and insoluble organic matrix of 0.03% and 0.05%, respectively [56,72]. The evidence of purified collagen in the coralline skeletons was also shown by X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis (Figure 4). Jiang et al. [73] identified mineral crystals in collagen fibrils in a different marine invertebrate. The findings by Jiang et al. support our XRD results, and this technique has been revealed as a promising tool in analyzing collagens in the mineralization process. The results obtained by XRD demonstrated that XRD will become an important tool to study biological materials like collagen from the ECM of invertebrates. Such a high concentration of collagen present in the organic matrices of marine calcifiers presents the opportunity for future drug development in bone-related disease, and, moreover, both chitin and collagen present in the same species can take a significant role in drug design of other related diseases, because these two polymers are commonly used in drug design [74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83].
At present, the methods for the isolation and purification of collagens from the octocorals have been significantly improved. A patented protocol on the collagen purification from the soft coral [54] is now on the market. Since this method is patented, it is not open to the public. However, there are several publications by the same research group that currently exist in the literature, in which they established the methods in purifying collagens (including collagen types I and II) from the soft coral [2,3]. The development of these new technologies, along with the technologies established by our group as mentioned above, will be extremely beneficial for purifying functional collagens from these marine organisms.
Despite the importance of collagenous marine sponge skeletons being documented, the techniques for the purification of collagens from this group are not well-established yet because of their insolubility and mineralization, which might cause difficulties in its separation and characterization [84,85]. However, researchers are trying to resolve these issues, and numerous investigations have so far been reported in this group [47,50,53,86,87]. Recently, Pozzolini et al. [47] established several new methods to purify collagenous fibrillar suspensions from the Chondrosia reniformis demosponge. The authors demonstrated that the obtained fibrillar collagens are extensively useful for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine, as well as in antioxidant activity.
There are some techniques that have been established in purifying collagens from the invertebrates; however, a proteomic approach might be a useful tool to learn more about the collagen and its functions in detail. Proteomics have already been established as an important tool for the detection, characterization, and analysis of pharmaceutically useful proteins from marine organisms, and this approach provides the most precise evaluation of protein identities, abundance, composition, and protein expression profiling [5,26,88,89,90]. Therefore, in regard to collagen, the proteomics approach could be a promising toolkit in the near future. The overview regarding marine collagen of invertebrates stated above allows us to understand some newly developed techniques and suitable methods for extracting and purifying collagen, as well as for applying proteomics approach for medical applications.
4. Future Applications of Invertebrate Collagens in Medical Field
The marine ecosystem provides suitable and numerous diversified resources for human health in comparison to the terrestrial ecosystem. In the last few decades, marine resources, especially invertebrates, have been recognized to be a promising source for many drugs (e.g., Cytarabine, Vidarabine, and Halichondrin B) [91]. According to the discussion above (Section 1, Section 2 and Section 3), marine invertebrates and related calcifying organisms such as soft and hard corals, sponge, mollusk, sea urchin, and coralline algae could be a major source of medicines over the next decades. However, extraction and purification of collagen for the purpose of medical application of these resources is still under investigation developing. Despite some impressive work having been performed on collagenous sponges and corals [1,2,3,4,6,7,15,16,17,47,54,91,92,93], an intensive study is necessary with these two groups and other invertebrates to use these huge apposite resources in future years. The potential of marine invertebrates for collagen could be realized by developing new technologies; indeed, there are many methods such as proteomics, computer-aided design, bioinformatics, and combinatorial synthesis that are now being applied.
The biological diversity of marine invertebrates and complex protein and peptide components direct us toward discovery of many new drugs for various therapeutic areas, including bone-related disease (e.g., osteoporosis) [94]. Besides cancer, microbial infections, and inflammation, drug discovery for bone-related disease is the biggest challenge of the current century, and collagen extraction from marine invertebrates shows new promise in fighting against this and other related diseases.
5. Concluding Remarks
In this review, the current state of research on collagen extracted from the ECM of invertebrates and its applications in the medical field have been discussed, and some light has been shed on future perspectives of this important marine material. The methodological issues of collagen purification from invertebrates, which the researchers are currently struggling with, have also been highlighted. The discussion concerning the purification techniques in this review could be of tremendous help in the extraction of purified collagen from invertebrates. The extracellular matrix, which is one of the key components in invertebrates and is responsible for producing collagen in this marine group, has been elaborated with informative imaging. In addition, the glycosylation activity with the formation of glycoproteins (size of the protein, which varies from species to species) in invertebrates, whose biological processes are involved in producing collagen, has been discussed for the first time in this review. The obtained results demonstrate the potential for marine invertebrates to generate new drugs, especially for bone tissue regeneration.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ehrlich, H.; Deutzmann, R.; Brunner, E.; Cappellini, E.; Koon, H.; Solazzo, C.; Yang, Y.; Ashford, D.; Thomas-Oates, J.; Lubeck, M. Mineralization of the metre-long biosilica structures of glass sponges is templated on hydroxylated collagen. Nat. Chem. 2010, 2, 1084–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orgel, J.P.; Sella, I.; Madhurapantula, R.S.; Antipova, O.; Mandelberg, Y.; Kashman, Y.; Benayahu, D.; Benayahu, Y. Molecular and ultrastructural studies of a fibrillar collagen from octocoral (Cnidaria). J. Exp. Biol. 2017, 220, 3327–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benayahu, D.; Sharabi, M.; Pomeraniec, L.; Awad, L.; Haj-Ali, R.; Benayahu, Y. Unique Collagen Fibers for Biomedical Applications. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tziveleka, L.-A.; Ioannou, E.; Tsiourvas, D.; Berillis, P.; Foufa, E.; Roussis, V. Collagen from the Marine Sponges Axinella cannabina and Suberites carnosus: Isolation and Morphological, Biochemical, and Biophysical Characterization. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.A. An Overview of the Medical Applications of Marine Skeletal Matrix Proteins. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrlich, H.; Wysokowski, M.; Żółtowska-Aksamitowska, S.; Petrenko, I.; Jesionowski, T. Collagens of Poriferan Origin. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrlich, H. Chitin and collagen as universal and alternative templates in biomineralization. Int. Geol. Rev. 2010, 52, 661–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, H.; Heinemann, S.; Heinemann, C.; Simon, P.; Bazhenov, V.V.; Shapkin, N.P.; Born, R.; Tabachnick, K.R.; Hanke, T.; Worch, H. Nanostructural organization of naturally occurring composites—Part I: Silica-collagen-based biocomposites. J. Nanomater. 2008, 623838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Halfar, J. First evidence of chitin in calcified coralline algae: New insights into the calcification process of Clathromorphum compactum. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Pascual, F.; Slatter, D.A. Collagen cross-linking: Insights on the evolution of metazoan extracellular matrix. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Fujimura, H.; Shinjo, R.; Oomori, T. Extracellular matrix protein in calcified endoskeleton: A potential additive for crystal growth and design. J. Cryst. Growth 2011, 324, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurienzo, P. Marine polysaccharides in pharmaceutical applications: An overview. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2435–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.A.; Oomori, T. In vitro regulation of CaCO3 crystal growth by the highly acidic proteins of calcitic sclerites in soft coral, Sinularia polydactyla. Connect. Tissue Res. 2009, 50, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.A.; Oomori, T.; Worheide, G. Calcite formation in soft coral sclerites is determined by a single reactive extracellular protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 31638–31649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, D.W.; Padula, M.P.; Santos, J.; Chou, J.; Milthorpe, B.; Ben-Nissan, B. A therapeutic potential for marine skeletal proteins in bone regeneration. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1203–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, E.L.; Hirabayashi, K.; Strychar, K.B.; Sammarco, P.W. Corals and their potential applications to integrative medicine. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 2014, 184959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macha, I.J.; Ben-Nissan, B. Marine Skeletons: Towards Hard Tissue Repair and Regeneration. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, T.J.; Ahn, E.S. Nanostructured Biomaterials for Tissue Engineering Bone. In Tissue Engineering II: Basics of Tissue Engineering and Tissue Application; Lee, K., Kaplan, D., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 275–308. [Google Scholar]
- Senni, K.; Pereira, J.; Gueniche, F.; Delbarre-Ladrat, C.; Sinquin, C.; Ratiskol, J.; Godeau, G.; Fischer, A.M.; Helley, D.; Colliec-Jouault, S. Marine polysaccharides: A source of bioactive molecules for cell therapy and tissue engineering. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1664–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omura, Y.; Urano, N.; Kimura, S. Occurrence of fibrillar collagen with structure of (α1)2α2 in the test of sea urchin Asthenosoma ijimai. Comp. Biochem. Phys. B 1996, 115, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, M.J.; Schlag, G.; Schwarz, N.; Mollan, R.A.; Nolan, P.C.; Wilson, D.J. Biocompatibility of xenogeneic bone, commercially available coral, a bioceramic and tissue sealant for human osteoblasts. Biomaterials 1994, 15, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillemin, G.; Patat, J.L.; Fournie, J.; Chetail, M. The use of coral as a bone graft substitute. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2004, 21, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchac, D.; Sandor, G. Use of coral granules in the craniofacial skeleton. J. Craniofac. Surg. 1994, 5, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helman, Y. Extracellular matrix production and calcium carbonate precipitation by coral cells in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 105, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.A.; Isa, Y.; Uehara, T. Studies on two closely related species of octocorallians: Biochemical and molecular characteristics of the organic matrices of endoskeletal sclerites. Mar. Biotechnol. 2006, 8, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.A.; Karl, K.; Nonaka, M.; Fujimura, H.; Shinjo, R.; Oomori, T.; Worheide, G. Characterization of the proteinaceous skeletal organic matrix from the precious coral Corallium konojoi. Proteomics 2014, 14, 2600–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cluzel, C.; Lethias, C.; Garrone, R.; Exposito, J.Y. Distinct maturations of n-propeptide domains in fibrillar procollagen molecules involved in the formation of heterotypic fibrils in adult sea urchin collagenous tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 9811–9817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, A.; Paul, B.; Gelinsky, M. Biphasic Scaffolds from Marine Collagens for Regeneration of Osteochondral Defects. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bairati, A. The Collagens of the Mollusca. In Biology of Invertebrate and Lower Vertebrate Collagens. NATO ASI Series (Series A: Life Sciences); Bairati, A., Garrone, R., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Maria, F.; Maria, F.; Andronescu, E.; Voicu, G.; Ficai, D.; Albu, M.G.; Ficai, A. Mollusc shell/collagen composite as potential biomaterial for bone substitutes. Rom. J. Mat. (RRM) 2010, 40, 359–364. [Google Scholar]
- Goh, K.L.; Holmes, D.F. Collagenous Extracellular Matrix Biomaterials for Tissue Engineering: Lessons from the Common Sea Urchin Tissue. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetto, C.D.; Barbaglio, A.; Martinello, T.; Alongi, V.; Fassini, D.; Cullorà, E.; Patruno, M.; Bonasoro, F.; Barbosa, M.A.; Carnevali, M.D.C.; et al. Production, Characterization and Biocompatibility of Marine Collagen Matrices from an Alternative and Sustainable Source: The Sea Urchin Paracentrotus lividus. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4912–4933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyer, B.; Bernhardt, A.; Lode, A.; Heinemann, S.; Sewing, J.; Klinger, M.; Notbohm, H.; Gelinsky, M. Jellyfish collagen scaffolds for cartilage tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, S.; Walsh, P.; Maggs, C.; Buchanan, F. Designs from the deep: Marine organisms for bone tissue engineering. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, T.H.; Moreira-Silva, J.; Marques, A.L.P.; Domingues, A.; Bayon, Y.; Reis, R.L. Marine origin collagens and its potential applications. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 5881–5901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, E. Invertebrate collagens. Science 1978, 202, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, J. Versatile collagens in invertebrates. Science 1997, 277, 1785–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, A.F. The nature of collagen. In Comprehensive Biochemistry, Extracellular and Supporting Structures; Florkin, M., Stotz, E.H., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Exposito, J.Y.; Cluzel, C.; Garrone, R.; Lethias, C. Evolution of collagens. Anat. Rec. 2002, 268, 302–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrone, R. Evolution of metazoan collagens. Prog. Mol. Subcell. Biol. 1999, 21, 119–139. [Google Scholar]
- Tanzer, M.L. The biological diversity of collagenous proteins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1978, 3, 15–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, J.; Sokal, Z.; Rougvie, M. Structural and chemical studies on the connective tissue of marine sponges. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1956, 4, 227–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, C.H.; Joo, H.H.; Hee, K.J.; Yoo, S.J.; Su, J.Y.; Dae, H.L.; Hye, M.P. Preparing collagen useful in cosmetic composition, involves hydrolyzing fish by-products using enzyme. Korea Patent KR2013094989-A, 27 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Thao, N.P.; Luyen, B.T.T.; Lee, S.H.; Jang, H.D.; Kiem, P.V.; Minh, C.V.; Kim, Y.H. Antiosteoporotic and antioxidant activities of diterpenoids from the Vietnamese soft corals Sinularia maxima and Lobophytum crassum. Med. Chem. Res. 2015, 24, 3551–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizenberg, J.; Weaver, J.C.; Thanawala, M.S.; Sundar, V.C.; Morse, D.E.; Fratzl, P. Skeleton of Euplectella sp.: Structural Hierarchy from the Nanoscale to the Macroscale. Science 2005, 309, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicklas, M.; Schatton, W.; Heinemann, S.; Hanke, T.; Kreuter, J. Preparation and characterization of marine sponge collagen nanoparticles and employment for the transdermal delivery of 17beta-estradiol-hemihydrate. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2009, 35, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozzolini, M.; Scarfì, S.; Gallus, L.; Castellano, M.; Vicini, S.; Cortese, K.; Gagliani, M.C.; Bertolino, M.; Costa, G.; Giovine, M. Production, Characterization and Biocompatibility Evaluation of Collagen Membranes Derived from Marine Sponge Chondrosia reniformis Nardo, 1847. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latire, T.; Legendre, F.; Bigot, N.; Carduner, L.; Kellouche, S.; Bouyoucef, M.; Carreiras, F.; Marin, F.; Lebel, J.-M.; Galéra, P.; et al. Shell Extracts from the Marine Bivalve Pecten maximus Regulate the Synthesis of Extracellular Matrix in Primary Cultured Human Skin Fibroblasts. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junqua, S.; Robert, L.; Garrone, R. Biochemical and morphological studies on the collagens of horny sponges. Ircinia filaments compared to spongines. Connect. Tissue Res. 1974, 2, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrone, R.; Huc, A.; Junqua, S. Fine structure and physicochemical studies on the collagen of the marine sponge Chondrosia reniformis Nardo. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 1975, 52, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swatschek, D.; Schatton, W.; Kellermann, J.; Müller, W.E.G.; Kreuter, J. Marine sponge collagen: Isolation, characterization and effects on the skin parameters surface-pH, moisture and sebum. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2002, 53, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl-Seifert, B.; Kurelec, B.; Zahn, R.K.; Dorn, A.; Jeričevic, B.; Uhlenbruck, G.; Müller, W.E.G. Attachment of sponge cells to collagen substrata: Effect of a collagen assembly factor. J. Cell Sci. 1985, 79, 271–285. [Google Scholar]
- Pallela, R.; Bojja, S.; Janapala, V.R. Biochemical and biophysical characterization of collagens of marine sponge, Ircinia fusca (Porifera: Demospongiae: Irciniidae). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 49, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benayahu, Y.; Benayahu, D.; Kashman, Y.; Rudi, A.; Lanir, Y.; Sela, I.; Raz, E. Coral Derived Collagen and Methods of Farming Same. U.S. Patent US20110038914A1, 17 February 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.A.; Shinjo, R.; Oomori, T.; Worheide, G. Analysis of the proteinaceous components of the organic matrix of calcitic sclerites from the soft coral Sinularia sp. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Isa, Y. Characterization of proteins from the matrix of spicules from the alcyonarian, Lobophytum crassum. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2005, 321, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicciù, M.; Cervino, G.; Herford, A.S.; Famà, F.; Bramanti, E.; Fiorillo, L.; Lauritano, F.; Sambataro, S.; Troiano, G.; Laino, L. Facial Bone Reconstruction Using both Marine or Non-Marine Bone Substitutes: Evaluation of Current Outcomes in a Systematic Literature Review. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felician, F.F.; Xia, C.; Qi, W.; Xu, H. Collagen from Marine Biological Sources and Medical Applications. Chem Biodivers. 2018, 15, e1700557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Gao, K.; Liu, S.; Wang, S.; Elango, J.; Bao, B.; Dong, J.; Liu, N.; Wu, W. Fish Collagen Surgical Compress Repairing Characteristics on Wound Healing Process in Vivo. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, A.M.; Marques, A.P.; Silva, T.H.; Reis, R.L. Evaluation of the Potential of Collagen from Codfish Skin as a Biomaterial for Biomedical Applications. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elango, J.; Lee, J.W.; Wang, S.; Henrotin, Y.; De Val, J.E.M.S.; Regenstein, J.M.; Lim, S.Y.; Bao, B.; Wu, W. Evaluation of Differentiated Bone Cells Proliferation by Blue Shark Skin Collagen via Biochemical for Bone Tissue Engineering. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozzolini, M.; Millo, E.; Oliveri, C.; Mirata, S.; Salis, A.; Damonte, G.; Arkel, M.; Scarfì, S. Elicited ROS Scavenging Activity, Photoprotective, and Wound-Healing Properties of Collagen-Derived Peptides from the Marine Sponge Chondrosia reniformis. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jridi, M.; Bardaa, S.; Moalla, D.; Rebaii, T.; Souissi, N.; Sahnoun, Z.; Nasri, M. Microstructure, rheological and wound healing properties of collagen-based gel from cuttlefish skin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 77, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uriarte-Montoya, M.H.; Arias-Moscoso, J.L.; Plascencia-Jatomea, M.; Santacruz-Ortega, H.; Rouzaud-Sández, O.; Cardenas-Lopez, J.L.; Marquez-Rios, E.; Ezquerra-Brauer, J.M. Jumbo squid (Dosidicus gigas) mantle collagen: Extraction, characterization, and potential application in the preparation of chitosan-collagen biofilms. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 4212–4219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrario, C.; Leggio, L.; Leone, R.; Di Benedetto, C.; Guidetti, L.; Coccè, V.; Ascagni, M.; Bonasoro, F.; La Porta, C.A.; Carnevali, M.D.C.; et al. Marine-derived collagen biomaterials from echinoderm connective tissues. Mar Environ. Res. 2017, 128, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, D.; Howard, D.; Yang, X.; Kelly, M.; Oreffo, R.O. Natural marine sponge fiber skeleton: A biomimetic scaffold for human osteoprogenitor cell attachment, growth, and differentiation. Tissue Eng. 2003, 9, 1159–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.M.; Mendis, E.; Rajapakse, N.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.K. Effect of spongin derived from Hymeniacidon sinapium on bone mineralization. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2009, 90, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Solomon, K.L.; Zhang, X.; Pavlos, N.J.; Abel, T.; Willers, C.; Dai, K.; Xu, J.; Zheng, Q.; Zheng, M. In vitro evaluation of natural marine sponge collagen as a scaffold for bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2011, 7, 968–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallela, R.; Venkatesan, J.; Janapala, V.R.; Kim, S.K. Biophysicochemical evaluation of chitosan-hydroxyapatite-marine sponge collagen composite for bone tissue engineering. Biomed. Mater. Res. A. 2012, 100, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandi, S.K.; Kundu, B.; Mahato, A.; Thakur, N.L.; Joardar, S.N.; Mandal, B.B. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of the marine sponge skeleton as a bone mimicking biomaterial. Integr. Biol. (Camb). 2015, 7, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granito, R.N.; Custódio, M.R.; Rennó, A.C. Natural marine sponges for bone tissue engineering: The state of art and future perspectives. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2017, 105, 1717–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Oomori, T. Structure, crystallization and mineral composition of sclerites in the alcyonarian coral. J. Cryst. Growth 2008, 310, 3528–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Ramunno-Johnson, D.; Song, C.; Amirbekian, B.; Kohmura, Y.; Nishino, Y.; Takahashi, Y.; Ishikawa, T.; Miao, J. Nanoscale Imaging of Mineral Crystals inside Biological Composite Materials Using X-Ray Diffraction Microscopy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 038103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xia, W.; Liu, P.; Cheng, Q.; Tahirou, T.; Gu, W.; Li, B. Chitosan modification and pharmaceutical/biomedical applications. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1962–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Sacco, L.; Masotti, A. Chitin and chitosan as multipurpose natural polymers for groundwater arsenic removal and AS2O3 delivery in tumor therapy. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1518–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoushab, F.; Yamabhai, M. Chitin research revisited. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1988–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aam, B.B.; Heggset, E.B.; Norberg, A.L.; Sorlie, M.; Varum, K.M.; Eijsink, V.G. Production of chitooligosaccharides and their potential applications in medicine. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1482–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, P.M.; Tupe, S.G.; Deshpande, M.V. Chitin synthase inhibitors as antifungal agents. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 222–236. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Herrera, J.; San-Blas, G. Chitin synthesis as target for antifungal drugs. Curr. Drug Targets Infect. Disord. 2003, 3, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reese, T.A.; Liang, H.E.; Tager, A.M.; Luster, A.D.; van Rooijen, N.; Voehringer, D.; Locksley, R.M. Chitin induces accumulation in tissue of innate immune cells associated with allergy. Nature 2007, 447, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addad, S.; Exposito, J.Y.; Faye, C.; Ricard-Blum, S.; Lethias, C. Isolation, characterization and biological evaluation of jellyfish collagen for use in biomedical applications. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 967–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natali, I.; Tempesti, P.; Carretti, E.; Potenza, M.; Sansoni, S.; Baglioni, P.; Dei, L. Aragonite crystals grown on bones by reaction of CO2 with nanostructured Ca(OH)2 in the presence of collagen. Implications in archaeology and paleontology. Langmuir 2014, 30, 660–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.L. Chitin-based materials in tissue engineering: Applications in soft tissue and epithelial organ. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 1936–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhoff, J.M.; Garrone, R. Solubilization and characterization of Chondrosia reniformis sponge collagen. Connect. Tissue Res. 1983, 11, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, H.; Hanke, T.; Simon, P.; Goebel, C.; Heinemann, S.; Born, R.; Worch, H. Demineralisation von natürlichen Silikat-basierten Biomaterialien: Neue Strategie zur Isolation organischer Gerüststrukturen. Biomaterialien 2005, 6, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinemann, S.; Ehrlich, H.; Douglas, T.; Heinemann, C.; Worch, H.; Schatton, W.; Hanke, T. Ultrastructural studies on the collagen of the marine sponge Chondrosia reniformis Nardo. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 3452–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gökalp, M.; Wijgerde, T.; Sarà, A.; De Goeij, J.M.; Osinga, R. Development of an Integrated Mariculture for the Collagen-Rich Sponge Chondrosia reniformis. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molloy, M.P.; Witzmann, F.A. Proteomics: Technologies and applications. Brief Funct. Genomics Proteomics 2002, 1, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A. The medicinal potential of promising marine organisms: A review. Blue Biotechnol. J. 2012, 1, 318–333. [Google Scholar]
- Dauphin, Y. Comparative studies of skeletal soluble matrices from some Scleractinian corals and molluscs. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2001, 28, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, A.M.; Glaser, K.B.; Cuevas, C.; Jacobs, R.S.; Kem, W.; Little, R.D.; McIntosh, J.M.; Newman, D.J.; Potts, B.C.; Shuster, D.E. The odyssey of marine pharmaceuticals: A current pipeline perspective. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2010, 31, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.-R.; Lu, M.-C.; El-Shazly, M.; Wu, S.-L.; Lai, K.-H.; Su, J.-H. Aquaculture Soft Coral Lobophytum crassum as a Producer of Anti-Proliferative Cembranoids. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Zhu, Z.-D.; Gu, Y.-C.; Li, J.; Zhu, W.-L.; Guo, Y.-W. Further New Diterpenoids as PTP1B Inhibitors from the Xisha Soft Coral Sinularia polydactyla. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaugule, S.R.; Indap, M.M.; Chiplunkar, S.V. Marine Natural Products: New Avenue in Treatment of Osteoporosis. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).