Abstract
Algicidal bacteria can lyse microalgal blooms and trigger shifts within plankton communities. Resistant algal species can escape lysis, and have the opportunity to dominate the phytoplankton after a bacterial infection. Despite their important function in ecosystem regulation, little is known about mechanisms of resistance. Here, we show that the diatom Chaetoceros didymus releases eicosanoid oxylipins into the medium, and that the lytic algicidal bacterium, Kordia algicida, induces the production of several wound-activated oxylipins in this resistant diatom. Neither releases nor an induction occurs in the susceptible diatom Skeletonema costatum that is lysed by the bacterium within a few days. Among the upregulated oxylipins, hydroxylated eicosapentaenoic acids (HEPEs) dominate. However, also, resolvins, known lipid mediators in mammals, increase upon exposure of the algae to the algicidal bacteria. The prevailing hydroxylated fatty acid, 15-HEPE, significantly inhibits growth of K. algicida at a concentration of approximately 1 µM. The oxylipin production may represent an independent line of defense of the resistant alga, acting in addition to the previously reported upregulation of proteases.
1. Introduction
Multiple processes govern the complex species succession in plankton. It has been recognized, early on, that nutrient availability and abiotic conditions favor certain species that can reach dominating abundance within the community [1]. Later, also chemical mediators that can inhibit or promote cell proliferation and regulate predator-prey or host-pathogen interactions were recognized as additional factors that govern the complexity of plankton [2,3]. Precise regulation is a hallmark of such chemically mediated interactions. Production of defensive chemicals can be induced upon recognition of signals from the attacker, or activated by wounding that occurs in the interaction situation [4,5]. Diatoms that frequently dominate phytoplankton communities have evolved mechanisms to counter predation by the wound-activated formation of polyunsaturated aldehydes that inhibit the proliferation of herbivorous copepods [6,7]. These responses are triggered by cell disruption, that leads to rapid activation of lipases and lipoxygenases, building up massive local amounts of defensive aldehydes [8,9]. Further higher molecular weight oxylipins have been reported from diatoms, and are potentially involved in wound-activated defense, however, their ecological role is not yet fully understood [10,11]. These higher oxylipins include hydroxylated and further oxygenated metabolites, mainly derived from eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid [12]. In contrast to wound-activated processes, induced defenses do not require cell disruption but, rather, the perception of signals from an attacker or pathogen, that then triggers an often slower de novo biosynthesis of defensive metabolites. Such elaborate mechanisms that require signal recognition and subsequent regulation of metabolic pathways are, however, only very rarely reported from microalgae [13].
Besides herbivory, infection by pathogens is a second major cause of death for unicellular algae in water. Viral infections and algicidal bacteria play major roles in the control of populations, or even the termination of entire blooms [14,15]. Algicidal bacteria can substantially reduce native diatom populations, and are also utilized in biotechnology for cell lysis. Their mode of action is as diverse as is their host specificity [16]. Both generalists, as well as specialists, have been identified. The here-investigated K. algicida, that was isolated from a S. costatum bloom [17], is rather universal at lysing diatoms, with few identified exceptions. An example of a resistant alga is the ubiquitous diatom Chaetoceros didymus, that survives even incubations with high bacterial densities [18]. One response of C. didymus to the lytic bacteria is the upregulation of proteases that have the potential to counteract the lytic enzymes from bacteria [18]. Here, we hypothesize that comparison of the response of resistant and non-resistant diatoms allows deducing of information on the mechanisms of infection and resistance. We introduce a targeted lipidomics study surveying the endo- and exometabolome of the resistant C. didymus, and the susceptible diatom Skeletonema costatum, for metabolites that are involved in resistance mechanisms. We identify an induced upregulation of a family of oxylipins in the wound-activated response of the resistant alga, as well as a release of these metabolites, that may contribute to the chemical defense against bacteria.
2. Results and Discussion
Exponentially growing algal cultures were incubated with a suspension of K. algicida at a final OD550 of 0.01. These conditions were sufficient to lyse S. costatum within three days, while C. didymus was resistant and grew with similar kinetics as the control (Figure 1). This pattern is consistent with previous investigations addressing the infection of diatoms with K. algicida [19]. By incubating with a bacterial density of OD 0.01, we achieved a sufficiently slow lysis of S. costatum, allowing for examination of potential induced responses.
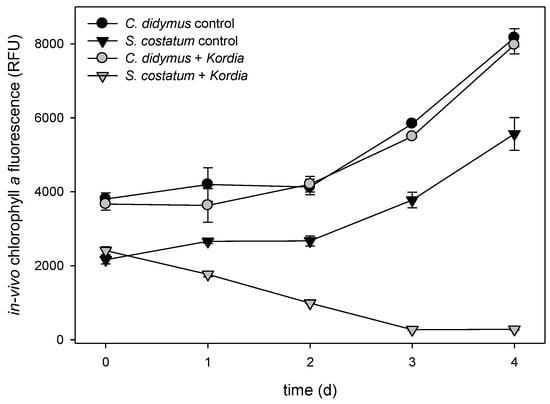
Figure 1.
Growth of Chaetoceros didymus and Skeletonema costatum (mean ± SD, n = 3) monitored as in vivo chlorophyll a fluorescence. Values are given in relative fluorescence units (RFU), over time, for control cultures and cultures treated with Kordia algicida.
To investigate the chemistry that is potentially mediating bacterial/algal interactions within the water surrounding the producing cells, we initially focused on metabolites released into the medium. Therefore, we adapted a lipidomics approach, initially developed to survey C18 to C22 fatty acid-derived oxylipins from diatoms [10]. After centrifugation of the cultures (1700× g, 15 min, 4 °C), a careful filtration (pore size 1.2 µm) of the supernatant was conducted on glass fiber filters to avoid cell disruption. Extraction of the resulting filtrate with reversed phase C18 solid phase extraction cartridges gave samples for liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry (LC/MS). Quantifiable amounts of oxylipins in the pg mL−1 to ng mL−1 range were detected. Given the fact that algae build up elevated concentrations of primary and secondary metabolites in the phycosphere (a diffusion-limited zone around the cells), the local concentrations surrounding the cells might be substantially higher [20]. In the medium of the resistant C. didymus, a clear accumulation of extracellular oxylipins was observed, with a concomitant increase of free EPA (Figure 2). This increase occurred in infected, as well as non-infected, C. didymus. The majority of the detected oxylipins belong to the family of hydroxylated eicosapentaenoic acids (HEPEs). The most abundant member of this family was 15-HEPE, followed by 12-, 18-, 11-, and 5-HEPE. Concentrations of 15-HEPE in the medium reached ca. 28 ng mL−1. Even if this value is below the activity threshold for the inhibition of K. algicida growth (see below) it might very well contribute to the chemical defense of the alga. If we consider that 28 ng mL−1 represents an average concentration in the medium, the local concentrations in the phycosphere of a producing cell will exceed this value substantially [20]. Active concentrations could be reached in the distance of few micrometers around the producing alga and, thus, within the scale of the bacterial cell. Only minor differences in the level of released oxylipins were observed between uninfected controls and K. algicida-infected treatments (Figure 2). These differences were significant only for 5-HEPE on day 4 (p = 0.027). C. didymus is, thus, constitutively building up elevated amounts of the oxylipins in its phycosphere. To our knowledge, this is the first time that release of higher molecular weight oxylipins from non-disrupted diatoms is reported. The kinetics of oxylipin accumulation exceeds that of the growth, except for RvE1 and, as a result, oxylipin release rates normalized to chlorophyll a fluorescence increase over time (Figure 1 and Figure 2).
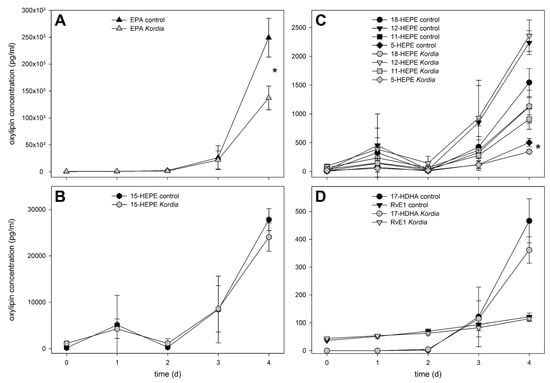
Figure 2.
Extracellular concentrations of oxylipins and free eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) in C. didymus culture medium (mean ± SD, n = 3). Panels depict EPA (A), hydroxylated eicosapentaenoic acids (HEPEs), namely 15-HEPE (B) and 18-, 12-, 11-, and 5-HEPE (C), as well as 17-hydroxydocosahexanoic acid (17-HDHA) and resolvin (Rv)E1 (D). Statistically significant differences (unpaired t-test) at day 4 between control cultures and cultures treated with Kordia algicida are marked with * (p < 0.05).
Enzymatic formation of the observed hydroxylated fatty acids requires the action of lipoxygenases that insert oxygen in a position-specific manner into the substrate EPA [21]. The observed positional specificity (Figure 2) confirms that product formation in C. didymus is occurring enzymatically, and not by abiotic oxidation of the polyunsaturated fatty acids. The initial enzymatic oxidation is followed by further reduction of the intermittently formed hydroperoxides to the corresponding alcohols [22]. At this stage, it cannot be concluded whether the oxylipins are formed intracellularly, or in the phycosphere, and how the metabolites or their precursors are released out of the cells. Skeletonema marinoi releases short chain oxylipins (polyunsaturated C6 and C8 aldehydes) into the seawater just before the beginning of the declining growth phase, but no release of these and higher oxylipins was observed during the early phases of growth as it is considered here [23]. In the spent medium of S. costatum none of the higher molecular weight oxylipins, investigated in this study exceeded concentrations of 50 pg mL−1, and no trend throughout the growth, in the presence or absence of bacteria, was observed (data not shown). S. costatum releases volatile oxylipins, as well as HEPEs, upon cell disruption using lipoxygenase-mediated pathways [10,24,25]. However, cell disruption, as it occurs during K. algicida infection, does not lead to an increased formation of HEPEs (data not shown). This might be due to a suppression of the lipase/lyase pathways through the bacteria, or due to the metabolization of the algal oxylipins. The very low concentrations of oxylipins found in S. costatum extracts might not necessarily stem from enzymatic transformations, but can arise, alternatively, from abiotic oxidation of free fatty acids.
The underlying principles of oxylipin formation in C. didymus were further investigated by monitoring the capacity of the cells to produce these metabolites after wound activation. In agreement with a previous study, hydroxylated fatty acids were detected in amounts of up to 100 fg cell−1 in the resistant alga after lysis of the cells (Figure 3) [10]. Detected oxylipins included HEPEs, resolvins (Rvs), hydroxylated docosahexaenoic acids (HDHAs), hydroxylated octadecadienoic acids, and hydroxylated eicosatetraenoic acids (HETEs). The level of HEPEs were higher in those algae that were previously challenged with K. algicida (Figure 3A). RvE1 (a tri-hydroxylated EPA-derived oxylipin) was not detected after wound activation, but the di-hydroxylated RvE3 was significantly increased in bacterially infected cells (Figure 3B).
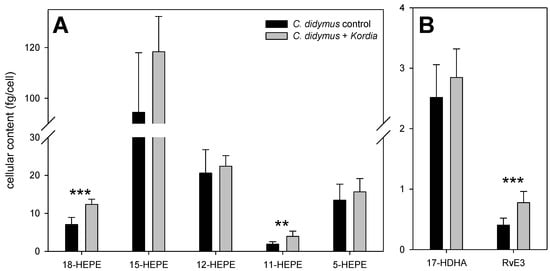
Figure 3.
Oxylipins detected 10 min after cell disruption of C. didymus. Depicted is the cellular production (mean ± SD, n = 7) of 5 different hydroxylated eicosapentaenoic acids (HEPEs) (A), as well as 17-hydroxydocosahexaenoic acid (HDHA) and resolvin (Rv)E3 (B) after wounding of C. didymus at day 4. Statistically significant differences (unpaired t-test) between control cultures and cultures treated with K. algicida are marked with ** (p < 0.01) and *** (p < 0.001).
To verify if the release and the wound-activated formation of oxylipins constitutes a defense mechanism of the alga against the bacterial pathogen, we evaluated the effect of the most abundant oxylipin, 15-HEPE, on the bacteria. This oxylipin inhibits the growth of the bacteria for 6 h in a concentration-dependent manner, with an effective concentration of 1 µg mL−1 (Figure 4). The lysis event of a single diatom cell results in the release of 15-HEPE into a small volume surrounding the cell, barely exceeding the cellular dimensions. If cellular production is normalized to the reported cell volume of 2200–7600 µm3, the concentrations after lysis would exceed the effective concentration more than 10-fold [26,27]. Accordingly, oxylipins can contribute to a chemical defense of the alga. As discussed previously, for phytoplankton, in general, such wound-activated defense of an individual cell would benefit the population of closely related conspecifics [2,28]. We propose the C20 oxylipins could represent a line of defense against K. algicida that acts in addition to the previously reported defensive proteases [18].
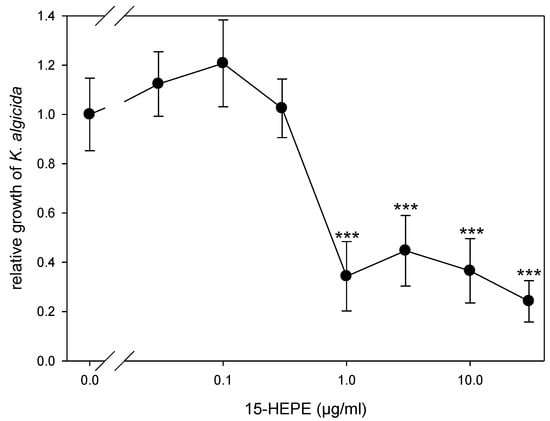
Figure 4.
Concentration–response curve for 15-HEPE inhibition of Kordia algicida growth (mean ± SD, n = 5). Growth was monitored after 6 h in the presence of different concentrations of 15-hydroxylated eicosapentaenoic acid (HEPE) and normalized to the control at 0 µg/mL (no added HEPE). Statistically significant differences (unpaired t-test) between control cultures and cultures treated with K. algicida are marked with *** (p < 0.001).
We, here, extend the concept of induced oxylipin production to the field of C20 oxylipins. We suggest that these metabolites might be involved in the chemical defense of diatoms. While this orchestration of signaling is new to unicellular algae, comparable processes of differential response to wounding and induction have been reported frequently from higher plants [29]. There, the lipoxygenase metabolite jasmonic acid is a key regulator for most diverse induced defensive responses. Such a “master switch” is not known for microalgae, and it has to be explored if these unicellular algae require such elaborate hormones.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Algal Cultivation and Quantification
C. didymus was isolated by W. Kooistra from the Mediterranean Sea (Stazione Zoologica Anton Dohrn, Naples, Italy), and is maintained in our culture collection; S. costatum (RCC75) was obtained from the Roscoff Culture Collection (Roscoff, France). Algae were grown in batch cultures according to published procedures [18,30] under a 14/10 h light/dark regime with an illumination of 15–22 µmol photons m−2 s−1.
For determination of growth, in vivo chlorophyll a fluorescence was measured in technical triplicates on a Mithras LB 940 plate reader (Berthold Technologies, Bad Wildbad, Germany).
For microalgal quantification, Lugol-fixed cells were counted under a LEICA DM 2000 light microscope in a Nannoplankton Chamber (PhycoTech Inc., St. Joseph, MI, USA; for C. didymus) or a Fuchs-Rosenthal counting chamber (for S. costatum). The cell counts of the cultures were corrected using the counts of non-precipitated cells in the supernatant after centrifugation.
3.2. Bacterial Cultivation and Quantification
For co-cultivation experiments, K. algicida OT-1 [17] was spread on marine agar and cultivated at 23 °C for 2–3 days. The bacterial lawn was removed with a sterile cotton swab, and resuspended in algal culturing medium to an OD550 of 0.5 determined on a Genesys 10S UV–Vis spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
For recording the dose–response curve, K. algicida was cultivated in marine broth medium at 23 °C and with constant agitation on a shaker at 78 rpm. An overnight culture was diluted with marine broth to an OD550 of 0.5.
3.3. Co-Cultivation Experiment
For extracellular oxylipin profiling, exponentially growing algal cultures (245 mL each) were inoculated with K. algicida suspension (5 mL), in triplicates, to a final OD550 of 0.01 (treatment), or with the same amount of algal culturing medium (control). Samples for cell counts and oxylipin profiling were taken daily for 4 days.
For oxylipin profiling of wound-activated cells, cultures of C. didymus (54 mL each) were inoculated with K. algicida suspensions (1.1 mL), in 7 replicates, to a final OD550 of 0.01 (treatment), or with the same amount of algal culturing medium (control). After 4 days, samples for cell counts and oxylipin profiling were taken.
3.4. Wound Activation and Oxylipin Profiling
The procedure is described in detail elsewhere [10]. Briefly, algal cells are lysed using an ultrasonic probe, incubated at room temperature for 10 min, and quenched by addition of methanol and internal standard. Oxylipins are extracted using C18 SPE columns, and analyzed on an Acquity UPLC (Waters, Milford, MA, USA) equipped with a BEH C18 column (Waters) coupled to an AB Sciex 5500 QTrap (Sciex, Toronto, ON, Canada) mass spectrometer with ESI source in negative mode.
3.5. Extracellular Oxylipin Profiling
After centrifugation (1700× g, 15 min, 4 °C) of algal cultures, the supernatant was 1.2 µm-filtered on a glass fiber filter (WhatmanTM GF/C, GE Healthcare, Little Chalfont, UK). Flow-through (14 mL) was added to 28 mL cooled methanol and internal standard. The samples were processed, as described, for the oxylipin profiling after wound activation (see above), with volumes adjusted.
3.6. Determination of Concentration-Dependent 15-HEPE Activity Against K. algicida
In 96-well plates, 5 µL aliquots of K. algicida culture were added to 15-HEPE (Cayman Chemical, Ann Arbor, MI, USA) in 195 µL marine broth medium at concentrations of 0, 0.03, 0.1, 0.3, 1, 3, 10, and 30 µg/mL in 5 replicates. Plates are sealed with Parafilm® (Pechiney Plastic Packaging, Chicago, Il, USA), and covered with aluminum foil. At these conditions, K. algicida was cultured for 32 h, and in intervals of 2 h, the plate was shaken for 10 s (Ø 2 mm, double orbit) and the OD550 was measured (0.1 s, lamp energy 10,000) using a Mithras LB 940 plate reader (Berthold Technologies, Bad Wildbad, Germany). The slope of K. algicida growth in the treatments is assessed relative to the slope in the negative control.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.M. and G.P.; Methodology, N.M. and M.W.; Investigation, N.M., J.R. and M.W.; Analysis N.M. and J.R.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, N.M. and G.P.; Writing—Review & Editing, N.M., J.R., M.W., O.W. and G.P.; Visualization, N.M.; Supervision, O.W. and G.P.; Project Administration, O.W. and G.P.; Funding Acquisition, O.W. and G.P.
Funding
This research was funded by the German Research Foundation within the framework of the CRC 1127 ChemBioSys.
Acknowledgments
Wiebe Kooistra is acknowledged for providing the C. didymus strain.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Hutchinson, G.E. The paradox of the plankton. Am. Nat. 1961, 95, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianora, A.; Bentley, M.G.; Caldwell, G.S.; Casotti, R.; Cembella, A.D.; Engström-Öst, J.; Halsband, C.; Sonnenschein, E.; Legrand, C.; Llewellyn, C.A.; et al. The relevance of marine chemical ecology to plankton and ecosystem function: An emerging field. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1625–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohnert, G.; Steinke, M.; Tollrian, R. Chemical cues, defence metabolites and the shaping of pelagic interspecific interactions. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2007, 22, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selander, E.; Kubanek, J.; Hamberg, M.; Andersson, M.X.; Cervin, G.; Pavia, H. Predator lipids induce paralytic shellfish toxins in bloom-forming algae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 6395–6400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenwasser, S.; Mausz, M.A.; Schatz, D.; Sheyn, U.; Malitsky, S.; Aharoni, A.; Weinstock, E.; Tzfadia, O.; Ben-Dor, S.; Feldmesser, E.; et al. Rewiring host lipid metabolism by large viruses determines the fate of Emiliania huxleyi, a bloom-forming alga in the ocean. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 2689–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohnert, G.; Boland, W. The oxylipin chemistry of attraction and defense in brown algae and diatoms. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2002, 19, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Donk, E.; Ianora, A.; Vos, M. Induced defences in marine and freshwater phytoplankton: A review. Hydrobiologia 2011, 668, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohnert, G. Phospholipase A(2) activity triggers the wound-activated chemical defense in the diatom Thalassiosira rotula. Plant Physiol. 2002, 129, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ippolito, G.; Tucci, S.; Cutignano, A.; Romano, G.; Cimino, G.; Miralto, A.; Fontana, A. The role of complex lipids in the synthesis of bioactive aldehydes of the marine diatom Skeletonema costatum. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1686, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rettner, J.; Werner, M.; Meyer, N.; Werz, O.; Pohnert, G. Survey of the C20 and C22 oxylipin family in marine diatoms. Tetrahedron Lett. 2018, 59, 828–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ippolito, G.; Lamari, N.; Montresor, M.; Romano, G.; Cutignano, A.; Gerecht, A.; Cimino, G.; Fontana, A. 15S-lipoxygenase metabolism in the marine diatom Pseudo-nitzschia delicatissima. New Phytol. 2009, 183, 1064–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanjappa, D.; d’Ippolito, G.; Gallo, C.; Zingone, A.; Fontana, A. Oxylipin diversity in the diatom family Leptocylindraceae reveals DHA derivatives in marine diatoms. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 368–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tammilehto, A.; Nielsen, T.G.; Krock, B.; Moller, E.F.; Lundholm, N. Induction of domoic acid production in the toxic diatom Pseudo-nitzschia seriata by Calanoid copepods. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 159, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidle, K.D.; Vardi, A. A chemical arms race at sea mediates algal host-virus interactions. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2011, 14, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, N.; Bigalke, A.; Kaulfuss, A.; Pohnert, G. Strategies and ecological roles of algicidal bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 880–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, S.A.; Parker, M.S.; Armbrust, E.V. Interactions between diatoms and bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2012, 76, 667–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Yi, H.; Chun, J.; Bae, K.S.; Ahn, T.Y.; Kim, S.J. Kordia algicida gen. Nov., sp nov., an algicidal bacterium isolated from red tide. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, C.; Pohnert, G.; Uversky, V.N. Induction of protease release of the resistant diatom Chaetoceros didymus in response to lytic enzymes from an algicidal bacterium. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, C.; Pohnert, G. Interactions of the algicidal bacterium Kordia algicida with diatoms: Regulated protease excretion for specific algal lysis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, J.R.; Amin, S.A.; Raina, J.B.; Stocker, R. Zooming in on the phycosphere: The ecological interface for phytoplankton-bacteria relationships. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 17065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeggstrom, J.Z.; Funk, C.D. Lipoxygenase and leukotriene pathways: Biochemistry, biology, and roles in disease. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 5866–5898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, H. Biosynthesis, metabolization and biological importance of the primary 15-lipoxygenase metabolites 15-hydro(pero)xy-5Z,8Z,11Z,13E-eicosatetraenoic acid and 13-hydro(pero)xy-9Z,11E-octadecadienoic acid. Prog. Lipid Res. 1996, 35, 203–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidoudez, C.; Pohnert, G. Growth phase specific release of polyunsaturated aldehydes by the diatom Skeletonema marinoi. J. Plankton Res. 2008, 30, 1305–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ippolito, G.; Romano, G.; Caruso, T.; Spinella, A.; Cimino, G.; Fontana, A. Production of octadienal in the marine diatom Skeletonema costatum. Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 885–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Ippolito, G.; Romano, G.; Iadicicco, O.; Miralto, A.; Ianora, A.; Cimino, G.; Fontana, A. New birth-control aldehydes from the marine diatom Skeletonema costatum: Characterization and biogenesis. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 6133–6136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, A.; Zaman, S.; Raha, A.K. Phytoplankton cell volume and diversity in Indian sundarbans. Indian J. Geo-Mar. Sci. 2014, 43, 1914–1921. [Google Scholar]
- Olenina, I.; Hajdu, S.; Edler, L.; Andersson, A.; Wasmund, N.; Busch, S.; Göbel, J.; Gromisz, S.; Huseby, S.; Huttunen, M.; et al. Biovolumes and Size-Classes of Phytoplankton in the Baltic Sea; Baltic Marine Environment Protection Commission: Helsinki, Finland, 2006; p. 106. [Google Scholar]
- Vidoudez, C.; Casotti, R.; Bastianini, M.; Pohnert, G. Quantification of dissolved and particulate polyunsaturated aldehydes in the adriatic sea. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 500–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reymond, P.; Weber, H.; Damond, M.; Farmer, E.E. Differential gene expression in response to mechanical wounding and insect feeding in arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2000, 12, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidoudez, C.; Pohnert, G. Comparative metabolomics of the diatom Skeletonema marinoi in different growth phases. Metabolomics 2012, 8, 654–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
