Artificial Intelligence and Its Impact on the Management of Lumbar Degenerative Pathology: A Narrative Review
Abstract
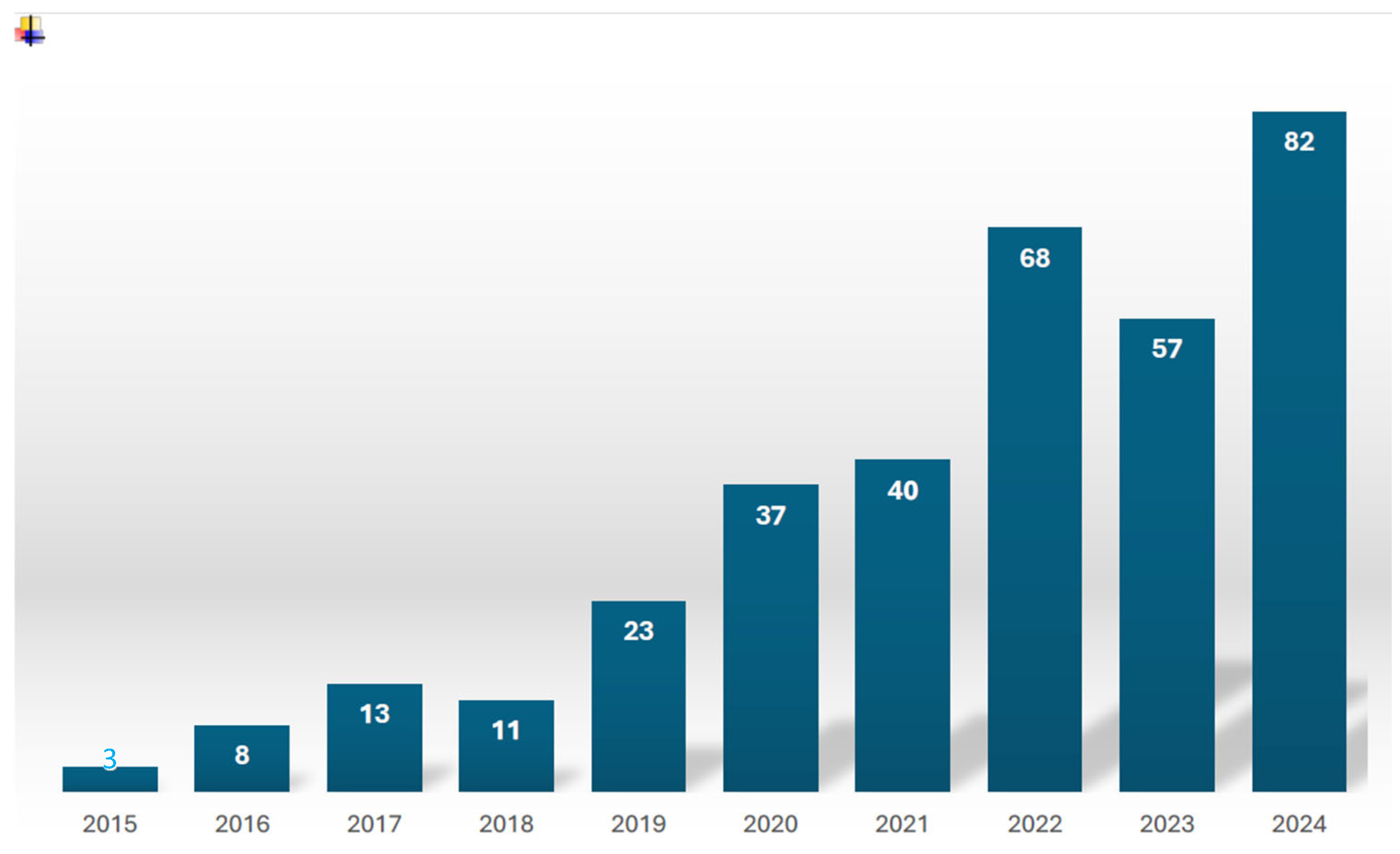
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Study Characteristics
2.2. AI for Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
2.2.1. Diagnosis
2.2.2. Treatment
2.2.3. Prognosis
2.3. AI for Lumbar Disc Herniation
2.3.1. Diagnosis
2.3.2. Treatment
2.3.3. Prognosis
2.4. AI for Lumbar Fusion Surgery
2.4.1. Outcome Prediction
2.4.2. Complication Prediction
2.4.3. Cost Prediction
2.5. Limitations
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ravindra, V.M.; Senglaub, S.S.; Rattani, A.; Dewan, M.C.; Härtl, R.; Bisson, E.; Park, K.B.; Shrime, M.G. Degenerative Lumbar Spine Disease: Estimating Global Incidence and Worldwide Volume. Glob. Spine J. 2018, 8, 784–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasaka, K.; Akai, H.; Kunimatsu, A.; Kiryu, S.; Abe, O. Deep learning with convolutional neural network in radiology. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2018, 36, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helm, J.M.; Swiergosz, A.M.; Haeberle, H.S.; Karnuta, J.M.; Schaffer, J.L.; Krebs, V.E.; Spitzer, A.I.; Ramkumar, P.N. Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence: Definitions, Applications, and Future Directions. Curr. Rev. Musculoskelet. Med. 2020, 13, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, C.W.; Aguirre, K.; Seidenberg, P.H. Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: Diagnosis and Management. Am. Fam. Physician 2024, 109, 350–359. [Google Scholar]
- Malfair, D.; Beall, D.P. Imaging the degenerative diseases of the lumbar spine. Magn. Reson. Imaging Clin. N. Am. 2007, 15, 221–238, vi. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steurer, J.; Roner, S.; Gnannt, R.; Hodler, J. LumbSten Research Collaboration. Quantitative radiologic criteria for the diagnosis of lumbar spinal stenosis: A systematic literature review. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2011, 12, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamaludin, A.; Kadir, T.; Zisserman, A. SpineNet: Automated classification and evidence visualization in spinal MRIs. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 41, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Pedemonte, S.; Bizzo, B.; Doyle, S.; Andriole, K.P.; Michalski, M.H.; Gonzalez, R.G.; Pomerantz, S.R. Deep Spine: Automated Lumbar Vertebral Segmentation, Disc-Level Designation, and Spinal Stenosis Grading using Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 3rd Machine Learning for Healthcare Conference, Palo Alto, CA, USA, 17–18 August 2018; PMLR: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; Volume 85, pp. 403–419. [Google Scholar]
- Hallinan, J.T.P.D.; Zhu, L.; Yang, K.; Makmur, A.; Algazwi, D.A.R.; Thian, Y.L.; Lau, S.; Choo, Y.S.; Eide, S.E.; Yap, Q.V.; et al. Deep Learning Model for Automated Detection and Classification of Central Canal, Lateral Recess, and Neural Foraminal Stenosis at Lumbar Spine MRI. Radiology 2021, 300, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharadwaj, U.U.; Christine, M.; Li, S.; Chou, D.; Pedoia, V.; Link, T.M.; Chin, C.T.; Majumdar, S. Deep learning for automated, interpretable classification of lumbar spinal stenosis and facet arthropathy from axial MRI. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 33, 3435–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Graaf, J.W.; Brundel, L.; van Hooff, M.L.; de Kleuver, M.; Lessmann, N.; Maresch, B.J.; Vestering, M.M.; Spermon, J.; van Ginneken, B.; Rutten, M.J.C.M. AI-based lumbar central canal stenosis classification on sagittal MR images is comparable to experienced radiologists using axial images. Eur. Radiol. 2025, 35, 2298–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hızal, M.; Özdemir, F.; Kalaycıoğlu, O.; Işık, C. Cerebrospinal fluid signal loss sign: Assessment of a new radiological sign in lumbar spinal stenosis. Eur. Spine J. 2021, 30, 3297–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.Y.; Lee, J.W.; Choi, H.S.; Oh, K.-J.; Kang, H.S. A new grading system of lumbar central canal stenosis on MRI: An easy and reliable method. Skelet. Radiol. 2011, 40, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eun, S.S.; Lee, H.-Y.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, K.H.; Liu, W.C. MRI versus CT for the diagnosis of lumbar spinal stenosis. J. Neuroradiol. 2012, 39, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyo, R.; Yasaka, K.; Hamada, A.; Sakamoto, N.; Hosoi, R.; Mizuki, M.; Abe, O. Deep-learning reconstruction for the evaluation of lumbar spinal stenosis in computed tomography. Medicine 2023, 102, e33910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.; Kim, Y.G.; Park, S.; Lee, J.K.; Lee, C.H.; Hyun, S.J.; Kim, C.H.; Kim, K.J.; Chung, C.K. Diagnostic triage in patients with central lumbar spinal stenosis using a deep learning system of radiographs. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2022, 37, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrasinova, T.; Adamova, B.; Buskova, J.; Kerkovsky, M.; Jarkovsky, J.; Bednarik, J. Is there a Correlation Between Degree of Radiologic Lumbar Spinal Stenosis and its Clinical Manifestation? Clin. Spine Surg. 2018, 31, E403–E408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, R.; Kurita, N.; Sekiguchi, M.; Yonemoto, K.; Kakuma, T.; Konno, S.-I. Diagnostic accuracy of the lumbar spinal stenosis-diagnosis support tool and the lumbar spinal stenosis-self-administered, self-reported history questionnaire. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0267892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, F.; Garcia, E.; Andreeva, V.; Nikolaev, N.S.; Kolisnyk, S.; Sarbaev, R.; Novikov, I.; Kozinchenko, E.; Kim, J.; Rusakov, A.; et al. An Artificial Intelligence-Based Support Tool for Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Diagnosis from Self-Reported History Questionnaire. World Neurosurg. 2024, 181, e953–e962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siccoli, A.; de Wispelaere, M.P.; Schröder, M.L.; Staartjes, V.E. Machine learning-based preoperative predictive analytics for lumbar spinal stenosis. Neurosurg. Focus 2019, 46, E5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, B.; Gaonkar, B.; Yoo, B.; Salehi, B.; Attiah, M.; Villaroman, D.; Ahn, C.; Edwards, M.; Laiwalla, A.; Ratnaparkhi, A.; et al. Predicting Spinal Surgery Candidacy from Imaging Data Using Machine Learning. Neurosurgery 2021, 89, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boden, S.D.; O Davis, D.; Dina, T.S.; Patronas, N.J.; Wiesel, S.W. Abnormal magnetic-resonance scans of the lumbar spine in asymptomatic subjects. A prospective investigation. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1990, 72, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourad, R.; Kolisnyk, S.; Baiun, Y.; Falk, A.; Yuriy, T.; Valerii, F.; Kopeev, A.; Suldina, O.; Pospelov, A.; Kim, J.; et al. Performance of hybrid artificial intelligence in determining candidacy for lumbar stenosis surgery. Eur. Spine J. 2022, 31, 2149–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Barros, A.; Abel, F.; Kolisnyk, S.; Geraci, G.C.; Hill, F.; Engrav, M.; Samavedi, S.; Suldina, O.; Kim, J.; Rusakov, A.; et al. Determining Prior Authorization Approval for Lumbar Stenosis Surgery with Machine Learning. Glob. Spine J. 2024, 14, 1753–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagan, M.J.; Sastry, R.A.; Feler, J.; Abdulrazeq, H.; Sullivan, P.Z.; Abinader, J.F.; Camara, J.Q.; Niu, T.; Fridley, J.S.; Oyelese, A.A.; et al. Neighborhood-level socioeconomic status, extended length of stay, and discharge disposition following elective lumbar spine surgery. N. Am. Spine Soc. J. 2022, 12, 100187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogink, P.T.; Karhade, A.V.; Thio, Q.C.B.S.; Gormley, W.B.; Oner, F.C.; Verlaan, J.J.; Schwab, J.H. Predicting discharge placement after elective surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis using machine learning methods. Eur. Spine J. 2019, 28, 1433–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravi, B.; Zink, A.; Ülkümen, S.; Couillard-Despres, S.; Hassel, F.; Lang, G. Performance of Artificial Intelligence-Based Algorithms to Predict Prolonged Length of Stay after Lumbar Decompression Surgery. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Su, X.; Xiong, Z.; Cui, Z.; Tang, G.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L. Development and application of AI assisted automatic reconstruction of axial lumbar disc CT images and diagnosis of lumbar disc herniation. Eur. J. Radiol. 2025, 185, 112003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liawrungrueang, W.; Park, J.B.; Cholamjiak, W.; Sarasombath, P.; Riew, K.D. Artificial Intelligence-Assisted MRI Diagnosis in Lumbar Degenerative Disc Disease: A Systematic Review. Glob. Spine J. 2024, 15, 1405–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; He, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Huang, A.; Chen, C.; Bian, J. Deep Learning for Lumbar Disc Herniation Diagnosis and Treatment Decision-Making Using Magnetic Resonance Imagings: A Retrospective Study. World Neurosurg. 2025, 195, 123728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Xiong, H.; Liu, R.; Duan, X.; Yu, H. Enhanced deep leaning model for detection and grading of lumbar disc herniation from MRI. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2024, 62, 3709–3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Qiao, X.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, L.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Q.; Bhardwaj, A. Artificial Intelligence-Based CT Imaging on Diagnosis of Patients with Lumbar Disc Herniation by Scalpel Treatment. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zheng, S.; Tian, Q.; Kou, Z.; Li, W.; Xie, X.; Wu, X. Deep Learning Model for Grading and Localization of Lumbar Disc Herniation on Magnetic Resonance Imaging. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2024, 61, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staartjes, V.E.; Quddusi, A.; Klukowska, A.M.; Schröder, M.L. Initial classification of low back and leg pain based on objective functional testing: A pilot study of machine learning applied to diagnostics. Eur. Spine J. 2020, 29, 1702–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Liu, E.; Su, Z.; Chen, W.; Liu, Z.; Chen, T.; Lu, H.; Zhou, J.; Li, Q.; Pang, S. Three-Dimensional Lumbosacral Reconstruction by An Artificial Intelligence-Based Automated MR Image Segmentation for Selecting the Approach of Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy. Pain Physician J. 2024, 27, E245–E254. [Google Scholar]
- Tezuka, F.; Sakai, T.; Abe, M.; Yamashita, K.; Takata, Y.; Higashino, K.; Chikawa, T.; Nagamachi, A.; Sairyo, K. Anatomical considerations of the iliac crest on percutaneous endoscopic discectomy using a transforaminal approach. Spine J. 2017, 17, 1875–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Nagahama, K.; Abe, Y.; Hyugaji, Y.; Ukeba, D.; Endo, T.; Ohnishi, T.; Ura, K.; Sudo, H.; Iwasaki, N.; et al. Evaluation of Surgical Indications for Full Endoscopic Discectomy at Lumbosacral Disc Levels Using Three-Dimensional Magnetic Resonance/Computed Tomography Fusion Images Created with Artificial Intelligence. Medicina 2023, 59, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, P.; Shu, T.; Lei, J.; Chen, W. Nerve recognition in percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy using convolutional neural network. Med. Phys. 2021, 48, 2279–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, H.-K.; Ogink, P.T.; Huang, C.-C.; Groot, O.Q.; Su, C.-C.; Chen, S.-F.; Chen, C.-W.; Karhade, A.V.; Peng, K.-P.; Lin, W.-H.; et al. A machine learning algorithm for predicting prolonged postoperative opioid prescription after lumbar disc herniation surgery. An external validation study using 1316 patients from a Taiwanese cohort. Spine J. 2022, 22, 1119–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Lin, F.; Liao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, R. Development of a Dual-Plane MRI-Based Deep Learning Model to Assess the 1-Year Postoperative Outcomes in Lumbar Disc Herniation After Tubular Microdiscectomy. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2025, 61, 2294–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fingar, K.R.; Stocks, C.; Weiss, A.J.; Steiner, C.A. Most frequent operating room procedures performeed in U.S. hospitals, 2003–2012. In Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) Statistical Briefs; Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US): Rockville, MD, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Goz, V.; Weinreb, J.H.; McCarthy, I.; Schwab, F.; Lafage, V.; Errico, T.J. Perioperative complications and mortality after spinal fusions: Analysis of trends and risk factors. Spine 2013, 38, 1970–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, A.; Ngufor, C.; Kerezoudis, P.; McCutcheon, B.; Storlie, C.; Mohamad, B. Can machine learning algorithms accurately predict discharge to nonhome facility and early unplanned readmissions following spinal fusion? Analysis of a national surgical registry. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2019, 31, 568–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.A.; Devana, S.K.; Lee, C.; Bugarin, A.; Lord, E.L.; Shamie, A.N.; Park, D.Y.; van der Schaar, M.; SooHoo, N.F. Prediction of major complications and readmission after lumbar spinal fusion: A machine learning-driven approach. World Neurosurg. 2021, 152, e227–e234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabitza, F.; Locoro, A.; Banfi, G. Machine learning in orthopedics: A literature review. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2018, 6, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteva, A.; Kuprel, B.; Novoa, R.A.; Ko, J.; Swetter, S.M.; Blau, H.M.; Thrun, S. Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks. Nature 2017, 542, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulshan, V.; Peng, L.; Coram, M.; Stumpe, M.C.; Wu, D.; Narayanaswamy, A.; Venugopalan, S.; Widner, K.; Madams, T.; Cuadros, J.; et al. Development and validation of a deep learning algorithm for detection of diabetic retinopathy in retinal fundus photographs. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2016, 316, 2402–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menden, M.P.; Iorio, F.; Garnett, M.; McDermott, U.; Benes, C.H.; Ballester, P.J.; Saez-Rodriguez, J.; Raghava, G.P.S. Machine learning prediction of cancer cell sensitivity to drugs based on genomic and chemical properties. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, B.S.; Yamaguchi, J.T.; Garcia, R.; Kesavabhotla, K.; Weiss, H.; Hsu, W.K.; Smith, Z.A.; Dahdaleh, N.S. Using machine learning to predict 30-day readmissions after posterior lumbar fusion: An NSQIP study involving 23,264 patients. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2020, 32, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.H.; Asch, S.M. Machine learning and predition in medicine—Beyond the peak of inflated expectations. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 2507–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, D.A.; Rosman, G.; Rus, D.; Meireles, O.R.M. Artifical intelligence in surgery: Promises and perils. Ann. Surg. 2018, 268, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huguet, A.; Hayden, J.A.; Stinson, J.; McGrath, P.J.; Chambers, C.T.; Tougas, M.E.; Wozney, L. Judging the quality of evidence in reviews of prognostic factor research: Adapting the GRADE framework. Syst. Rev. 2013, 2, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredow, J.; Meyer, C.; Oikonomidis, S.; Kernich, C.; Kernich, N.; Hofstetter, C.P.; Heck, V.J.; Eysel, P.; Prasse, T. Long-term radiological and clinical outcome after lumbar spinal fusion surgery in patients with degenerative spondylolisthesis: A prospective 6-year follow-up study. Orthop. Surg. 2022, 14, 1607–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inose, H.; Kato, T.; Onuma, H.; Morishita, S.; Matsukura, Y.; Yuasa, M.; Hirai, T.; Yoshii, T.; Okawa, A. Predictive factors affecting surgical outcomes in patients with degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. Spine 2021, 46, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berjano, P.; Langella, F.; Ventriglia, L.; Compagnone, D.; Barletta, P.; Huber, D.; Mangili, F.; Licandro, G.; Galbusera, F.; Cina, A.; et al. The Influence of Baseline Clinical Status and Surgical Strategy on Early Good to Excellent Result in Spinal Lumbar Arthrodesis: A Machine Learning Approach. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monticone, M.; Baiardi, P.; Vanti, C.; Ferrari, S.; Pillastrini, P.; Mugnai, R.; Foti, C. Responsiveness of the Oswestry Disability Index and the Roland Morris Disability Questionnaire in Italian subjects with sub-acute and chronic low back pain. Eur. Spine J. 2011, 21, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schönnagel, L.; Caffard, T.; Vu-Han, T.-L.; Zhu, J.; Nathoo, I.; Finos, K.; Camino-Willhuber, G.; Tani, S.; Guven, A.E.; Haffer, H.; et al. Predicting postoperative outcomes in lumbar spinal fusion: Development of a machine learning model. Spine J. 2024, 24, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajian-Tilaki, K. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis for medical diagnostic test evaluation. Casp. J. Intern. Med. 2013, 4, 627–635. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, J.A.; Ranstam, J. Overfitting. Br. J. Surg. 2016, 103, 1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, N.; Zheng, H.; Massaad, E.; Hadzipasic, M.; Shankar, G.M.; Shin, J.H. Development and Validation of Machine Learning Algorithms for Predicting Adverse Events After Surgery for Lumbar Degenerative Spondylolisthesis. World Neurosurg. 2020, 140, 627–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leven, D.M.; Lee, N.J.; Kothari, P.; Steinberger, J.; Guzman, J.; Skovrlj, B.; Shin, J.I.; Caridi, J.M.; Cho, S.K. Frailty index is a significant predictor of complications and mortality after surgery for adult spinal deformity. Spine 2016, 41, E1394–E1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, H.; Tang, N.; Huang, G.; Li, J.; Tian, K. Evaluation of the Predictors for Unfavorable Clinical Outcomes of Degenerative Lumbar Spondylolisthesis After Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Machine Learning. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 835938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghogawala, Z.; Dziura, J.; Butler, W.E.; Dai, F.; Terrin, N.; Magge, S.N.; Coumans, J.-V.C.; Harrington, J.F.; Amin-Hanjani, S.; Schwartz, J.S.; et al. Laminectomy plus fusion versus laminectomy alone for lumbar spondylolisthesis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 1424–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.K.; Bisson, E.F.; Bydon, M.; Glassman, S.D.; Foley, K.T.; Potts, E.A.; Shaffrey, C.I.; Shaffrey, M.E.; Coric, D.; Knightly, J.J.; et al. Laminectomy alone versus fusion for grade 1 lumbar spondylolisthesis in 426 patients from the prospective quality outcomes database. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2018, 30, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Yagi, M.; Machida, M.; Yasuda, A.; Konomi, T.; Miyake, A.; Fujiyoshi, K.; Kaneko, S.; Takemitsu, M.; Yato, Y.; et al. Reoperation rate and risk factors of elective spinal surgery for degenerative spondylolisthesis: Minimum 5-year follow-up. Spine J. 2015, 15, 1536–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, C.-P.; Beckman, J.M.; Vivas, A.C.; Bach, K.; Uribe, J.S. Effects of intradiscal vacuum phenomenon on surgical outcome of lateral interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar disease. Eur. Spine J. 2017, 26, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deyo, R.A.; Martin, B.I.; Kreuter, W.; Jarvik, J.G.; Angier, H.; Mirza, S.K. Revision surgery following operations for lumbar stenosis. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2011, 93, 1979–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watkins, R.G., 4th; Hanna, R.; Chang, D.; Watkins, R.G., 3rd. Sagittal alignment after lumbar interbody fusion: Comparing anterior, lateral, and transforaminal approaches. J. Spinal Disord. Tech. 2014, 27, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, K.; Hoshino, M.; Omori, K.; Igarashi, H.; Nemoto, Y.; Tsuruta, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Iriuchishima, T.; Ajiro, Y.; Matsuzaki, H. Risk Factors of Adjacent Segment Disease After Transforaminal Inter-Body Fusion for Degenerative Lumbar Disease. Spine 2017, 42, E86–E92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, A.T.; Le, H.; Hoang, T.T.; Trinh, G.M.; Shao, H.-C.; Tsai, P.-I.; Chen, K.-J.; Hsieh, K.L.-C.; Huang, E.-W.; Hsu, C.-C.; et al. Development of End-to-End Artificial Intelligence Models for Surgical Planning in Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, E.R.; Osong, B.; van Soest, J.; Dekker, A.; van Meeteren, N.L.; Willems, P.C.; Punt, I.M. Exploring Associations of Preoperative Physical Performance with Postoperative Outcomes After Lumbar Spinal Fusion: A Machine Learning Approach. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2021, 102, 1324–1330.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGirt, M.J.; Sivaganesan, A.; Asher, A.L.; Devin, C.J. Prediction model for outcome after low-back surgery: Individualized likelihood of complication, hospital readmission, return to work, and 12-month improvement in functional disability. Neurosurg. Focus 2015, 39, E13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, E.R.C.; Punt, I.M.; van Kuijk, S.M.J.; Hoebink, E.A.; van Meeteren, N.L.U.; Willems, P.C. Development and validation of a prediction tool for pain reduction in adult patients undergoing elective lumbar spinal fusion: A multicentre cohort study. Eur. Spine J. 2020, 29, 1909–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbunt, J.; A Seelen, H.; Vlaeyen, J.W.; van de Heijden, G.J.; Heuts, P.H.; Pons, K.; Knottnerus, J.A. Disuse and deconditioning in chronic low back pain: Concepts and hypotheses on contributing mechanisms. Eur. J. Pain 2003, 7, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.; Gibbons, C.E.R. Predictors of 30-day hospital readmission after hip fracture: A systematic review. Injury 2017, 48, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijeysundera, D.N.; Pearse, R.M.; Shulman, M.A.; Abbott, T.E.F.; Torres, E.; Ambosta, A.; Croal, B.L.; Granton, J.T.; Thorpe, K.E.; Grocott, M.P.W.; et al. Assessment of functional capacity before major non-cardiac surgery: An international prospective cohort study. Lancet 2018, 391, 2631–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Clymer, J.W.; Chen, B.P.-H.; Sadeghirad, B.; Ferko, N.C.; Cameron, C.G.; Hinoul, P. Prolonged operative duration is associated with complications: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Surg. Res. 2018, 229, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Grzegorzek, M.; Chen, A.-T.; Quan, X.; Hu, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xiang, T.; et al. Development of machine learning model for predicting prolonged operation time in lumbar stenosis undergoing posterior lumbar interbody fusion: A multicenter study. Spine J. 2025, 25, 460–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.; Zhao, R.; Xu, J.; Liang, H.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Z.; Huang, T.; Luo, X.; Chen, H. Construct and Validate a Predictive Model for Surgical Site Infection after Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion Based on Machine Learning Algorithm. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2022, 2022, 2697841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, P.J.; Phan, K.; Giang, G.; Maharaj, M.M.; Phan, S.; Mobbs, R.J. Subsidence following anterior lumbar interbody fusion (Alif): A prospective study. J. Spine Surg. 2017, 3, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, C.; Chen, R.; Wang, B.; Fei, Q.; Song, H.; Zang, L. Development of a deep learning radiomics model combining lumbar CT, multi-sequence MRI, and clinical data to predict high-risk cage subsidence after lumbar fusion: A retrospective multicenter study. Biomed. Eng. Online 2025, 24, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuris, E.O.; Veeramani, A.; McDonald, C.L.; DiSilvestro, K.J.; Zhang, A.S.; Cohen, E.M.; Daniels, A.H. Predicting Readmission After Anterior, Posterior, and Posterior Interbody Lumbar Spinal Fusion: A Neural Network Machine Learning Approach. World Neurosurg. 2021, 151, e19–e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugely, A.J.; Martin, C.T.; Gao, Y.; Mendoza-Lattes, S. Causes and risk factors for 30-day unplanned readmissions after lumbar spine surgery. Spine 2014, 39, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puvanesarajah, V.; Nourbakhsh, A.; Hassanzadeh, H.; Shimer, A.L.; Shen, F.H.; Singla, A. Readmission rates, reasons, and risk factors in elderly patients treated with lumbar fusion for degenerative pathology. Spine 2016, 41, 1933–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernatz, J.T.; Anderson, P.A. Thirty-day readmission rates in spine surgery: Meta-analysis. Neurosurg. Focus 2015, 39, E7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.D.; Smith, T.R.; Lim, S.; Cybulski, G.R.; Kim, J.Y. Predictors of unplanned readmission after lumbar spinal surgery. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2017, 26, 144–152. [Google Scholar]
- Dreiseitl, S.; Ohno-Machado, L. Logistic regression and artificial neural network classification models: A methodology review. J. Biomed. Inform. 2002, 35, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Wang, P.; Ye, S.; Li, H.; Bao, J.; Shi, R.; Yang, S.; Yin, R.; Wu, X. Interpretable Machine Learning Models Based on Shapley Additive Explanations for Predicting the Risk of Cerebrospinal Fluid Leakage in Lumbar Fusion Surgery. Spine 2024, 49, 1281–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, D.; Durand, W.B.; Burch, S.; Daniels, A.; Berven, S. Machine Learning for Predictive Modeling of 90-day Readmission, Major Medical Complication, and Discharge to a Facility in Patients Undergoing Long Segment Posterior Lumbar Spine Fusion. Spine 2020, 45, 1151–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passias, P.G.; Poorman, G.W.; Bortz, C.A.; Qureshi, R.; Diebo, B.G.; Paul, J.C.; Horn, S.R.; Segreto, F.A.; Pyne, A.; Jalai, C.M.; et al. Predictors of adverse discharge disposition in adult spinal deformity and associated costs. Spine J. 2018, 18, 1845–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Arvind, V.; Oermann, E.K.; Kaji, D.; Ranson, W.; Ukogu, C.; Hussain, A.K.; Caridi, J.; Cho, S.K. Predicting surgical complications in patients undergoing elective adult spinal deformity procedures using machine learning. Spine Deform. 2018, 6, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, A.; Bouterse, A.; Nelson, M.; Razzouk, J.; Ramos, O.; Bono, C.M.; Cheng, W.; Danisa, O. Accounting for age in prediction of discharge destination following elective lumbar fusion: A supervised machine learning approach. Spine J. 2023, 23, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrighi-Allisan, A.E.; Neifert, S.N.; Gal, J.S.; Deutsch, B.C.; Caridi, J.M. Discharge destination as a predictor of postoperative outcomes and readmission following posterior lumbar fusion. World Neurosurg. 2019, 122, e139–e146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldebeyan, S.; Aoude, A.; Fortin, M.; Nooh, A.; Jarzem, P.; Ouellet, J.; Weber, M.H. Predictors of discharge destination after lumbar spine fusion surgery. Spine 2016, 41, 1535–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogura, Y.; Gum, J.L.; Steele, P.; Crawford, C.H.; Djurasovic, M.; Owens, R.K.; Laratta, J.L.; Brown, M.; Daniels, C.; Dimar, J.R.; et al. Drivers for nonhome discharge in a consecutive series of 1502 patients undergoing 1- or 2-level lumbar fusion. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2020, 33, 766–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnuta, J.M.; Golubovsky, J.L.; Haeberle, H.S.; Rajan, P.V.; Navarro, S.M.; Kamath, A.F.; Schaffer, J.L.; Krebs, V.E.; Pelle, D.W.; Ramkumar, P.N. Can a machine learning model accurately predict patient resource utilization following lumbar spinal fusion? Spine J. 2020, 20, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohl, D.D.; Haws, B.E.; Khechen, B.; Patel, D.V.; Mayo, B.C.; Ahn, J.; Louie, P.K.; Cardinal, K.L.; Guntin, J.A.; Singh, K. Impact of the number of levels on adverse events and length of stay following posterior lumbar fusion procedures. Clin. Spine Surg. 2019, 32, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalakoti, P.; Gao, Y.; Hendrickson, N.R.; Pugely, A.J. Preparing for bundled payments in cervical spine surgery. Spine 2019, 44, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruskay, J.A.; Fu, M.; Bohl, D.D.; Webb, M.L.; Grauer, J.N. Factors affecting length of stay after elective posterior lumbar spine surgery: A multivariate analysis. Spine J. 2015, 15, 1188–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trento, A.; Rapisarda, S.; Bresolin, N.; Valenti, A.; Giordan, E. Artificial Intelligence and Its Impact on the Management of Lumbar Degenerative Pathology: A Narrative Review. Medicina 2025, 61, 1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081400
Trento A, Rapisarda S, Bresolin N, Valenti A, Giordan E. Artificial Intelligence and Its Impact on the Management of Lumbar Degenerative Pathology: A Narrative Review. Medicina. 2025; 61(8):1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081400
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrento, Alessandro, Salvatore Rapisarda, Nicola Bresolin, Andrea Valenti, and Enrico Giordan. 2025. "Artificial Intelligence and Its Impact on the Management of Lumbar Degenerative Pathology: A Narrative Review" Medicina 61, no. 8: 1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081400
APA StyleTrento, A., Rapisarda, S., Bresolin, N., Valenti, A., & Giordan, E. (2025). Artificial Intelligence and Its Impact on the Management of Lumbar Degenerative Pathology: A Narrative Review. Medicina, 61(8), 1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081400








