Classifying and Monitoring Primary Progressive Aphasia in the Greek Population: A “Mini Linguistic State Examination (MLSE)” Tool
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Measures
2.3. Data Analysis
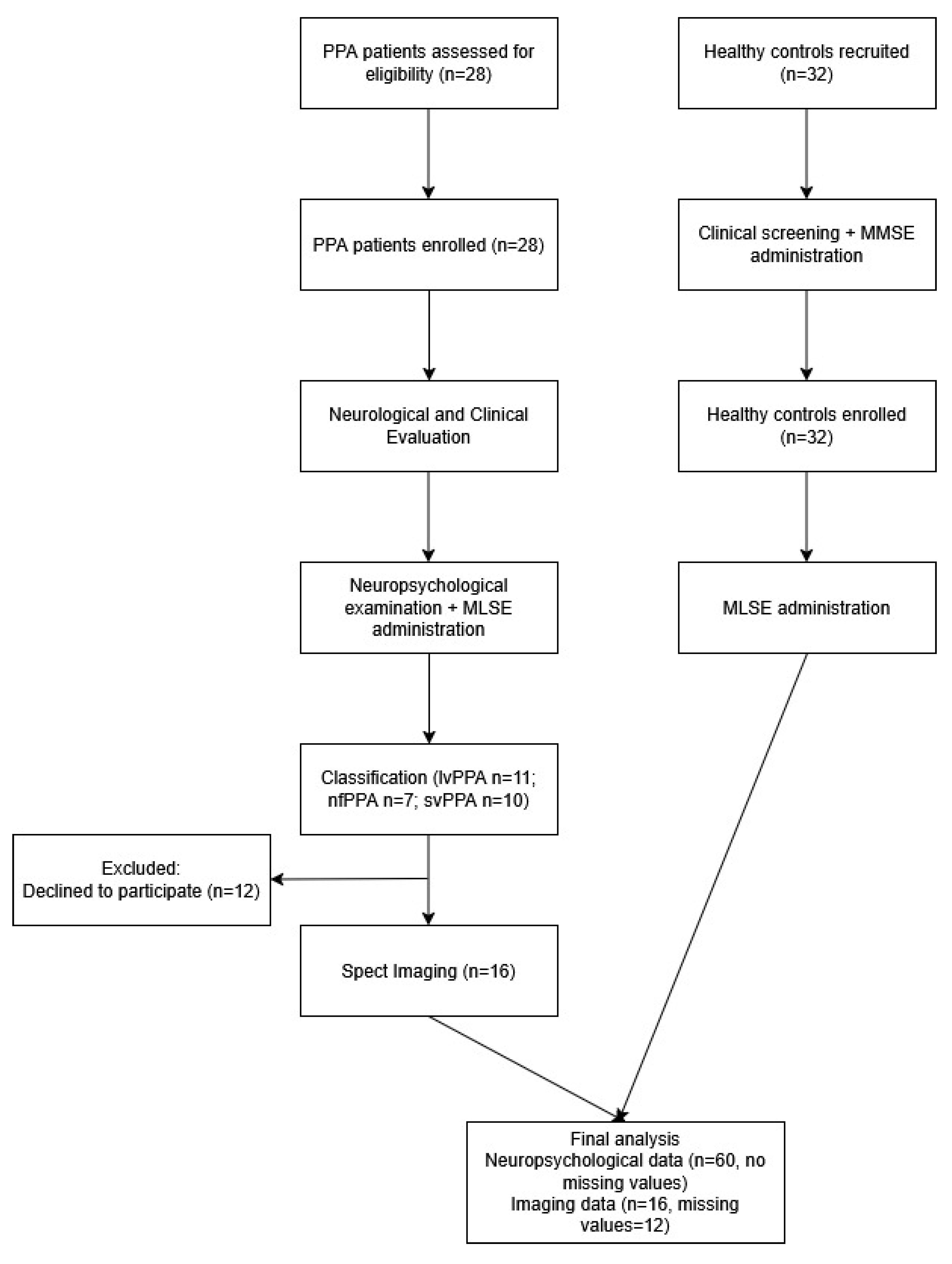
3. Results
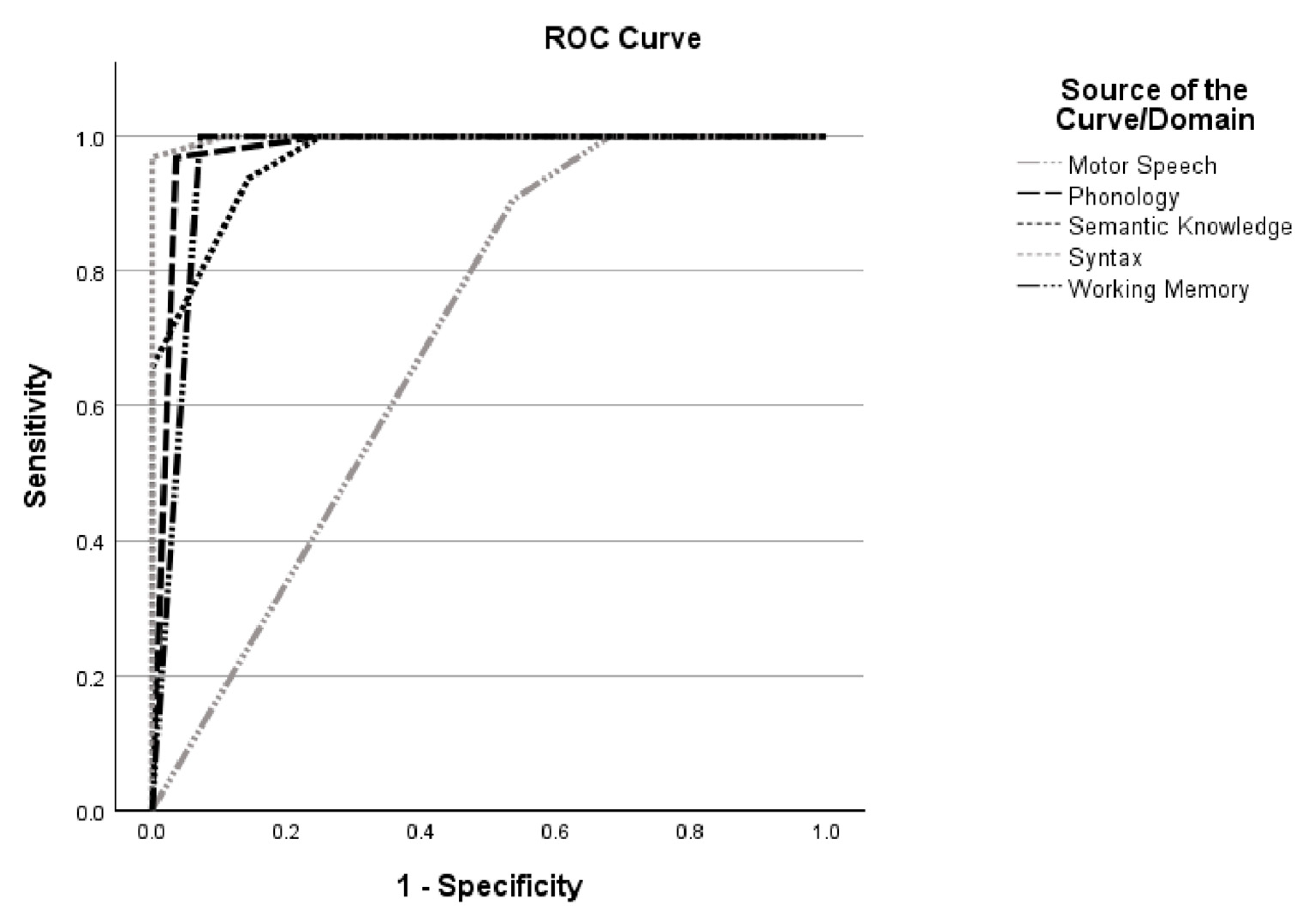
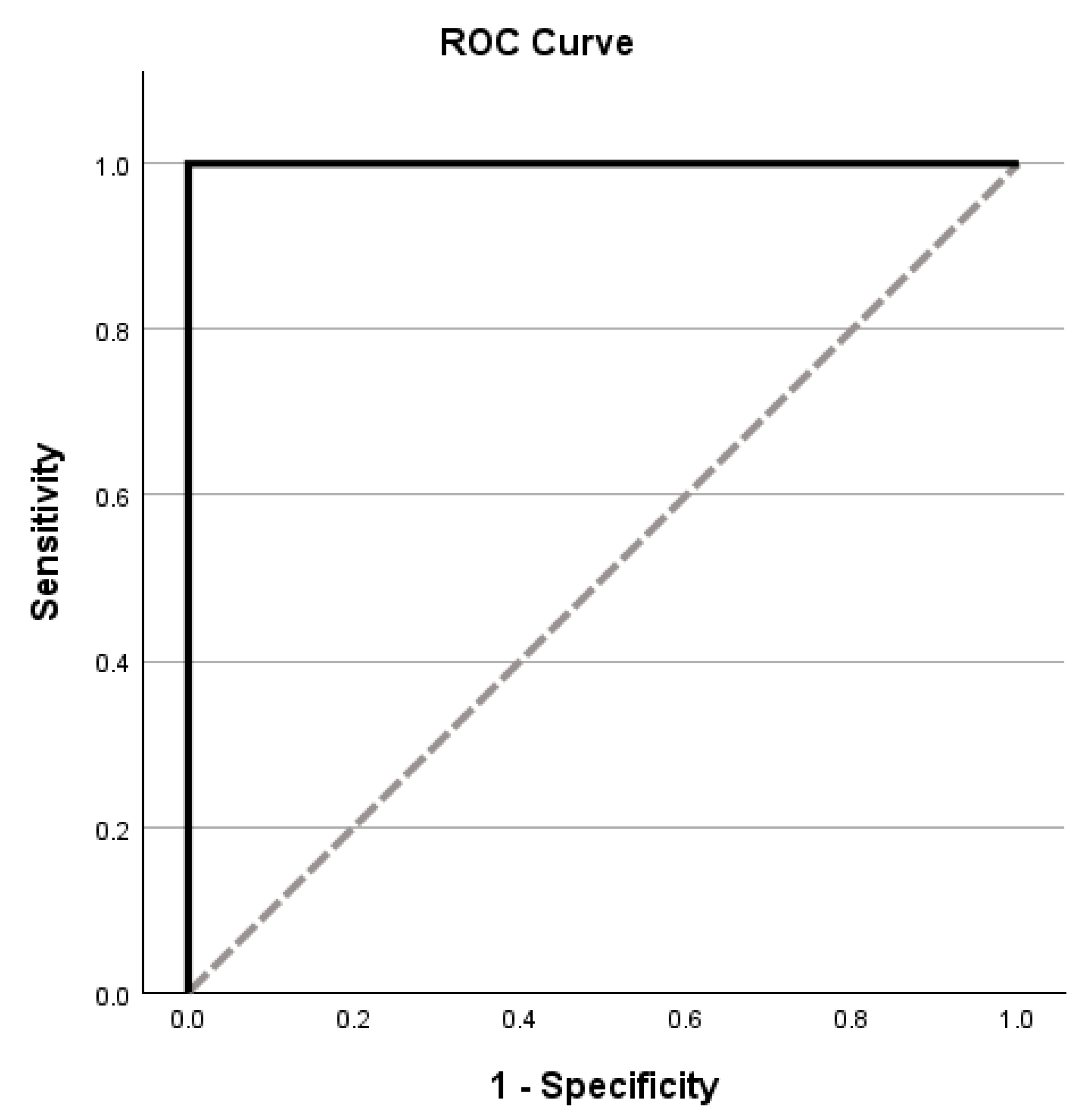
3.1. MLSE Diagnostic Accuracy
3.2. Associations Between MLSE and Other Neuropsychological Measures
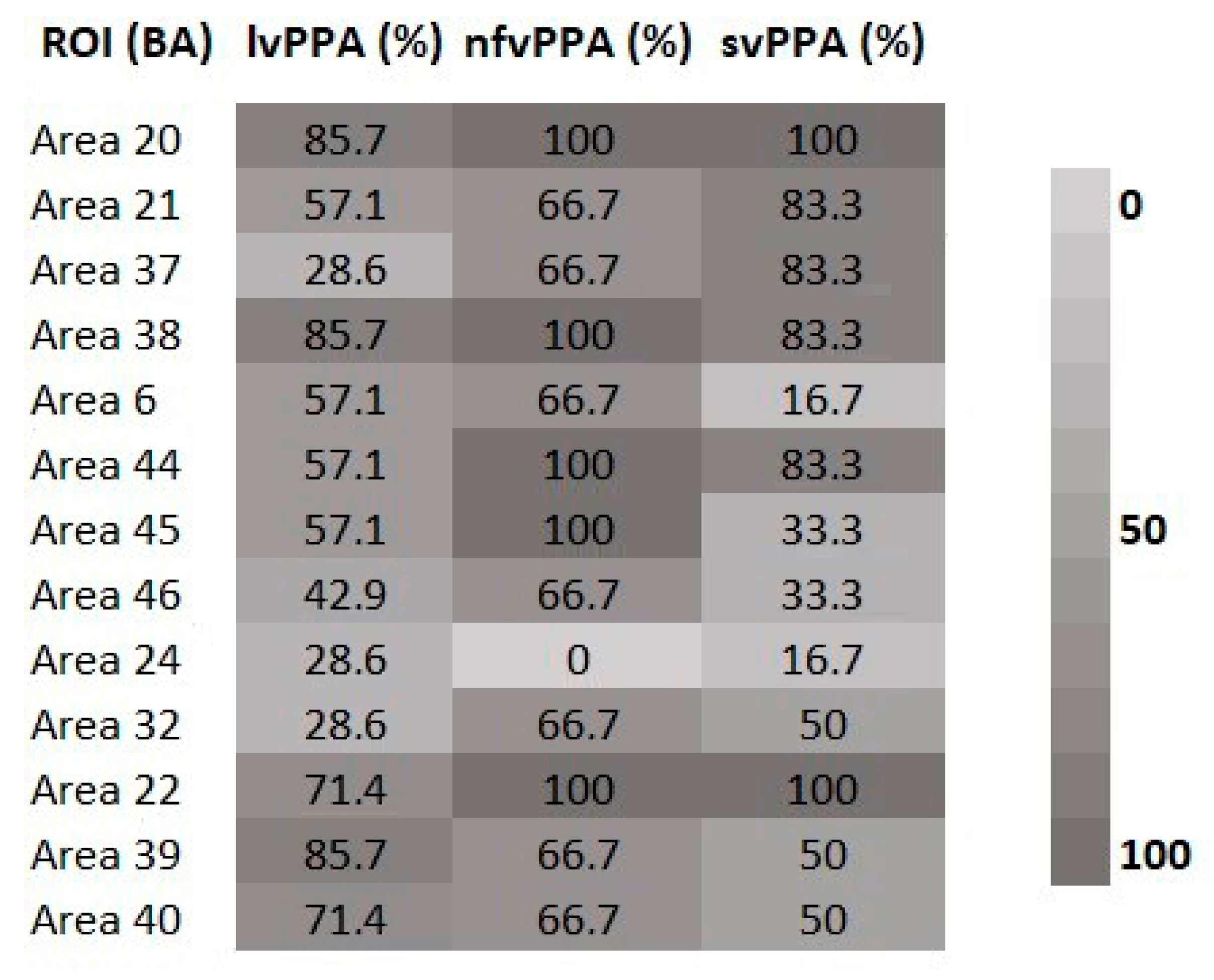
3.3. MLSE and Neuroimaging Findings
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PPA | Primary Progressive Aphasia |
| MLSE | Mini Linguistic State Examination |
| svPPA | Semantic variant of Primary Progressive Aphasia |
| lvPPA | Logopenic variant of Primary Progressive Aphasia |
| nfPPA | Non-fluent/agrammatic variant of Primary Progressive Aphasia |
| MMSE | Mini Mental State Examination |
| SPECT | Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography |
| rCBF | Cerebral blood flow |
| ROI | Region of Interest |
| BA | Brodmann Area |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| FDR | False Discovery Rate |
References
- Battista, P.; Miozzo, A.; Piccininni, M.; Catricalà, E.; Capozzo, R.; Tortelli, R.; Padovani, A.; Cappa, S.F.; Logroscino, G. Primary progressive aphasia: Review of neuropsychological tests for the assessment of speech and language disorders. Aphasiology 2017, 31, 1359–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorno-Tempini, M.L.; Brambati, S.M.; Ginex, V.; Ogar, J.; Dronkers, N.F.; Marcone, A.; Perani, D.; Garibotto, V.; Cappa, S.F.; Miller, B.L. The logopenic/phonological variant of primary progressive aphasia. Neurology 2008, 71, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesulam, M.M. Slowly progressive aphasia without generalized dementia. Ann. Neurol. 1982, 11, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Inui, Y.; Nakamura, A.; Ito, K. Brain fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET in dementia. Ageing Res. Rev. 2016, 30, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinelli, E.G.; Mandelli, M.L.; Miller, Z.A.; Santos-Santos, M.A.; Wilson, S.M.; Agosta, F.; Grinberg, L.T.; Huang, E.J.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Meyer, M.; et al. Typical and atypical pathology in primary progressive aphasia variants. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 81, 430–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodges, J.R.; Patterson, K. Semantic dementia: A unique clinicopathological syndrome. Lancet Neurol. 2007, 6, 1004–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ash, S.; Moore, P.; Vesely, L.; Gunawardena, D.; McMillan, C.; Anderson, C.; Avants, B.; Grossman, M. Non-Fluent Speech in Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration. J. Neurolinguistics 2009, 22, 370–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelli, M.L.; Vilaplana, E.; Brown, J.A.; Hubbard, H.I.; Binney, R.J.; Attygalle, S.; Santos-Santos, M.A.; Miller, Z.A.; Pakvasa, M.; Henry, M.L.; et al. Healthy brain connectivity predicts atrophy progression in non-fluent variant of primary progressive aphasia. Brain 2016, 139, 2778–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorno-Tempini, M.L.; Hillis, A.E.; Weintraub, S.; Kertesz, A.; Mendez, M.; Cappa, S.F.; Ogar, J.M.; Rohrer, J.D.; Black, S.; Boeve, B.F.; et al. Classification of primary progressive aphasia and its variants. Neurology 2011, 76, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teichmann, M.; Kas, A.; Boutet, C.; Ferrieux, S.; Nogues, M.; Samri, D.; Rogan, C.; Dormont, D.; Dubois, B.; Migliaccio, R. Deciphering logopenic primary progressive aphasia: A clinical, imaging and biomarker investigation. Brain 2013, 136, 3474–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambanarou, M. Diagnostic Issues in Speech Therapy; ΕΛΛHΝ: Athens, Greece, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, N.; Peterson, K.A.; Ingram, R.; Storey, I.; Cappa, S.F.; Catricala, E.; Patterson, K.E.; Ralph, M.A.; Rowe, J.B.; Garrard, P. The Mini Linguistic State Examination (MLSE): A brief but accurate assessment tool for classifying primary progressive aphasias. MedRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.; Peterson, K.A.; Ingram, R.U.; Storey, I.; Cappa, S.F.; Catricala, E.; Halai, A.; Patterson, K.E.; Lambon Ralph, M.A.; Rowe, J.B.; et al. A ‘mini linguistic state examination’ to classify primary progressive aphasia. Brain Commun. 2021, 4, fcab299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias-Guiu, J.A.; Pytel, V.; Hernández-Lorenzo, L.; Patel, N.; Peterson, K.A.; Matías-Guiu, J.; Garrard, P.; Cuetos, F. Spanish Version of the Mini-Linguistic State Examination for the Diagnosis of Primary Progressive Aphasia. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2021, 83, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Romero, L.; Morello-García, F.; Laforce, R.; Delgado-Alonso, C.; Delgado-Álvarez, A.; Gil-Moreno, M.J.; Lavoie, M.; Matias-Guiu, J.; Cuetos, F.; Matias-Guiu, J.A. Comparative accuracy of Mini Linguistic State Examination, Addenbrooke’s Cognitive Examination, and Dépistage Cognitif de Québec for the diagnosis of primary progressive aphasia. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2024, 102, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourão, L.O.; Junqueira de Almeida, I.; Pisetta, P.M.; Nitrini, R.; Garrard, P.; Carthery-Goulart, M.T.; Dozzi Brucki, S.M. Validation of the Mini-Linguistic State Examination (MLSE) to Brazilian Portuguese: Preliminary data. Dement. Neuropsychol. 2023, 17, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambleton, R.K. Issues, designs, and technical guidelines for adapting tests into multiple languages and cultures. In Adapting Educational and Psychological Tests for Cross-Cultural Assessment; Hambleton, R.K., Merenda, P.F., Spielberger, C.D., Eds.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 3–38. [Google Scholar]
- van de Vijver, F.J.R.; Tanzer, N.K. Bias and equivalence in cross-cultural assessment: An overview. Eur. J. Psychol. Assess. 2004, 20, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, S.; Penaloza, C. Across countries and cultures: The assessment of aphasia in linguistically diverse clinical populations. Aphasiology, 2025; ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmidis, M.H.; Bozikas, V.P.; Vlahou, C.H.; Giaglis, G. Neuropsychological Battery; Cognitive Neuroscience Laboratory, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki (AUTH): Thessaloniki, Greece, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Benton, A.L. Contributions to Neuropsychological Assessment: A Clinical Manual; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Kosmidis, M.H.; Tsotsi, S.; Karambela, O.; Takou, E.; Vlahou, H. Cultural factors influencing performance on visuoperceptual neuropsychological tasks. Behav. Neurol. 2010, 23, 245–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlahou, C.H.; Kosmidis, M.H. The Greek Trail Making Test: Preliminary normative data for clinical and research use. Psychol. J. Hell. Psychol. Soc. 2002, 9, 336–352. [Google Scholar]
- Kapucu, Ö.L.; Nobili, F.; Varrone, A.; Booij, J.; Vander Borght, T.; Någren, K.; Darcourt, J.; Tatsch, K.; Van Laere, K.J. EANM procedure guideline for brain perfusion SPECT using 99mTc-labelled radiopharmaceuticals, version 2. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2009, 36, 2093–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanan, S.; Halai, A.D.; Garcia-Penton, L.; Perry, A.D.; Patel, N.; Peterson, K.A.; Ruth, U.I.; Storey, I.; Cappa, S.F.; Catricala, E.; et al. The neural substrates of transdiagnostic cognitive-linguistic heterogeneity in primary progressive aphasia. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2023, 15, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tippett, D.C. Classification of primary progressive aphasia: Challenges and complexities. F1000Research 2020, 9, F1000 Faculty Rev-64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, C.J.D.; Buckley, A.H.; Downey, L.E.; Lehmann, M.; Zimmerer, V.C.; Varley, R.A.; Crutch, S.J.; Warren, J.D. The language profile of behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2016, 50, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.K.; Mack, J.E. Grammatical impairments in PPA. Aphasiology 2014, 28, 1018–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyton, C.E.; Hsieh, S.; Mioshi, E.; Hodges, J.R. Cognitive decline in logopenic aphasia: More than losing words. Neurology 2014, 82, 905–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogalski, E.; Cobia, D.; Harrison, T.M.; Wieneke, C.; Weintraub, S.; Mesulam, M.M. Progression of language decline and cortical atrophy in subtypes of primary progressive aphasia. Neurology 2011, 76, 1804–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mummery, C.J.; Patterson, K.; Price, C.J.; Ashburner, J.; Frackowiak, R.S.; Hodges, J.R. A voxel-based morphometry study of semantic dementia: Relationship between temporal lobe atrophy and semantic memory. Ann. Neurol. 2000, 47, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.M.; Henry, M.L.; Besbris, M.; Ogar, J.M.; Dronkers, N.F.; Jarrold, W.; Miller, B.L.; Gorno-Tempini, M.L. Connected speech production in three variants of primary progressive aphasia. Brain 2010, 133, 2069–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coyle-Gilchrist, I.T.; Dick, K.M.; Patterson, K.; Vázquez Rodríguez, P.; Wehmann, E.; Wilcox, A.; Lansdall, C.J.; Robbins, T.W.; Rowe, J.B. Prevalence, characteristics, and survival of frontotemporal lobar degeneration syndromes. Neurology 2016, 86, 1736–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Mean | Std. Deviation | Minimum | Maximum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | ||||
| Total (n = 28) | 69.61 | 7.87 | 56.00 | 81.00 |
| lvPPA (n = 11) | 68.27 | 7.79 | 59.00 | 78.00 |
| nfPPA (n = 7) | 70.29 | 10.77 | 56.00 | 81.00 |
| svPPA (n = 10) | 70.60 | 6.09 | 57.00 | 76.00 |
| Education | ||||
| Total (n = 28) | 12.46 | 5.05 | 6.00 | 22.00 |
| lvPPA (n = 11) | 12.55 | 5.52 | 6.00 | 22.00 |
| nfPPA (n = 7) | 11.29 | 5.53 | 6.00 | 21.00 |
| svPPA (n = 10) | 13.20 | 4.54 | 6.00 | 22.00 |
| Disease Duration | ||||
| Total (n = 28) | 2.39 | 1.81 | 1.00 | 7.00 |
| lvPPA (n = 11) | 2.82 | 2.36 | 1.00 | 7.00 |
| nfPPA (n = 7) | 2.43 | 1.79 | 1.00 | 5.00 |
| svPPA (n = 10) | 1.90 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 4.00 |
| Mean | Std. Deviation | Minimum | Maximum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 57.84 | 6.96 | 50.00 | 78.00 |
| Education | 15.03 | 2.66 | 12.00 | 21.00 |
| MMSE Score | 29.13 | 0.75 | 27.00 | 30.00 |
| Domain | lvPPA | nfvPPA | svPPA | H(df) | p | η2 | Post Hoc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median (IQR) | Median (IQR) | Median (IQR) | |||||
| Mot. Sp. | 30.00 (4.00) | 23.00 (13.00) | 30.00 (0.25) | 9.64(3) | 0.008 | 0.36 | svPPA > nfvPPA |
| Phon. | 26.00 (8.00) | 25.00 (3.00) | 28.00 (2.00) | 8.71(2) | 0.013 | 0.32 | svPPA > nfvPPA |
| Sem. Kn. | 15.00 (6.00) | 16.00 (6.00) | 14.50 (6.00) | 1.15(2) | 0.562 | ||
| Synt. | 5.00 (4.00) | 5.00 (3.00) | 6.00 (4.75) | 2.66(2) | 0.265 | ||
| Work. Me. | 4.00 (7.00) | 7.00 (3.00) | 7.00 (2.50) | 2.00(2) | 0.368 | ||
| Total | 82.00 (24.00) | 72.00 (26.00) | 83.50 (9.00) | 3.64 (2) | 0.162 |
| MLSE Domains | AUC (95% CI) | Optimal Cut-Off | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Motor Speech | 0.700 (0.56–0.84) | ≤29 | 90.6 | 47.1 |
| Phonology | 0.978 (0.94–1.00) | ≤29 | 96.9 | 96.4 |
| Semantic Knowledge | 0.968 (0.93–1.00) | ≤17 | 100.0 | 75.0 |
| Syntax | 0.998 (0.99–1.00) | ≤9 | 96.9 | 100.0 |
| Working Memory | 0.964 (0.91–1.00) | ≤9 | 100.0 | 92.9 |
| Total Score | 1.000 (1.00–1.00) | ≤96 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Papadopoulou, V.; Konstantinopoulou, E.; Liapi, A.; Sioka, C.; Iakovou, I.; Aretouli, E.; Ioannidis, P. Classifying and Monitoring Primary Progressive Aphasia in the Greek Population: A “Mini Linguistic State Examination (MLSE)” Tool. Medicina 2025, 61, 1998. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61111998
Papadopoulou V, Konstantinopoulou E, Liapi A, Sioka C, Iakovou I, Aretouli E, Ioannidis P. Classifying and Monitoring Primary Progressive Aphasia in the Greek Population: A “Mini Linguistic State Examination (MLSE)” Tool. Medicina. 2025; 61(11):1998. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61111998
Chicago/Turabian StylePapadopoulou, Valentina, Eleni Konstantinopoulou, Aikaterini Liapi, Chrissa Sioka, Ioannis Iakovou, Eleni Aretouli, and Panagiotis Ioannidis. 2025. "Classifying and Monitoring Primary Progressive Aphasia in the Greek Population: A “Mini Linguistic State Examination (MLSE)” Tool" Medicina 61, no. 11: 1998. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61111998
APA StylePapadopoulou, V., Konstantinopoulou, E., Liapi, A., Sioka, C., Iakovou, I., Aretouli, E., & Ioannidis, P. (2025). Classifying and Monitoring Primary Progressive Aphasia in the Greek Population: A “Mini Linguistic State Examination (MLSE)” Tool. Medicina, 61(11), 1998. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61111998









