Abstract
Fc gamma receptors (FcγRs) control humoral and cellular immune responses and maintain the immune system balance. Functional polymorphisms of FcγRs, whose prevalence was dependent on ethnic origin, were found to be associated with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) or kidney injuries in several ethnic groups. We aimed at investigating the association between the functional single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of FcγRIIa-H131R (rs1801274), FcγRIIb-I232T (rs1050501), FcγRIIIa-V158F (rs396991) and FcγRIIIb variants (NA1 and NA2) and lupus erythematosus systemic in an indigenous African Caribbean population. We compared the frequencies of the functional SNPs of FCGR2A (FcγRIIa-H131R, rs1801274), FCGR2B (FcγRIIb-I232T, rs1050501), FCGR3A (FcγRIIIa-V158F, rs396991) and FCGR3B variants (FcγRIIIb NA1 and NA2) between lupus and healthy controls in an indigenous African Caribbean population. We highlighted an association between the FCGR3B-NA1/NA1 and FCGR3A-158F alleles and systemic lupus erythematosus, in addition to an association between FCGR2A-131R and lupus nephritis. Furthermore, an increase in the 131R-158V haplotype in lupus nephritis (30.4%) vs. lupus non-nephritis (15.8%) was noticed. Surprisingly, in spite of the high frequency of the FCGR2B-232T allele in our population, our study did not highlight any association of this allele either with SLE or lupus nephritis (a severe and frequent form of SLE). CD72-Hap1, which has been shown to confer resistance to SLE against T232 allele, was not enhanced in the control group. Our results emphasize an association between FCGR2A-131R and lupus nephritis with a distinctive FCGR polymorphism distribution in an indigenous African Caribbean population, confirming the important variation in the FCGR locus depending on ethnic origin.
1. Introduction
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a prototype of autoimmune disease characterized by high level of autoantibody production, leading to multiple organ inflammation.
With an incidence of 5.14 per 100,000 and a prevalence of 43.7 per 100,000, approximately 3.4 million people worldwide have SLE, 40% of whom develop lupus nephritis (LN) [,]. In addition to a gender-dependent prevalence (90% of patients with SLE are female) [], ethnicity is also an important key factor of high frequency and severity. In fact, SLE is more prevalent in non-Europeans, such as Asians and African Americans [,,].
Fc gamma receptors (FcγRs) are cell surface glycoproteins that bind to the Fc fragment of IgG and are crucial for regulating effector cells and linking the humoral to the cellular immune response []. Multiple FcγRs, which differ in their ligand affinities, cellular distributions and effector functions, constitute a clustered gene family (FCGRs) on chromosome 1q21-24. Interestingly this region is strongly associated with SLE [].
In humans, FcγRs are classified into three main types, each containing multiple distinct genes and alternative splicing variants associated with SLE []. This classification is determined according to their structure and function: (i) FcγRI (CD64 in the classification of the cluster of differentiation): It has a high affinity to IgG, and it is expressed on monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells (DCs), neutrophils []. (ii) The low-affinity FcγRII (CD32) has three subtypes: FcγRIIa is expressed on monocytes, macrophages, DCs, neutrophils, and platelets; FcγRIIb, the only inhibitory FcγR, is expressed on a variety of immune cells, including B cells, monocytes, DCs, macrophages, neutrophils, basophils and mast cell; and FcγRIIc is expressed on B lymphocytes and natural killer (NK). Finally, (iii) FcγRIII (CD16), the other low-affinity FcγRs, has two subtypes: FcγRIIIa and FcγRIIIb.
In FCGR2A, a single base change from guanine (G) to adenine (A) at nucleotide 519 (rs1801274) results in a substitution of arginine (R) with histidine (H) at the 131 position of the second extracellular Ig-like domain of FcγRIIa []. This substitution increases the affinity of the receptor to IgG2 [,], affecting the phagocytosis mediated by this IgG []. In FCGR2B, there is a non-synonymous substitution of thymine (T) to cytosine (C). This single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) (rs1050501) encodes an isoleucine (I)-to-threonine (T) substitution at position 232 in the transmembrane domain of FcγIIb. This substitution leads to an impairment of the inhibitory function of the receptor through its exclusion from lipid rafts [,].
In FCGR3A, a substitution of T to G at nucleotide 559 (rs396991) changes the phenylalanine (F) to valine at position 158 of FcγRIIIa. The FcγRIIIa-158V variants display a relatively higher affinity for IgG1 and IgG3 compared to the FcγIIIa-158F one [].
Finally, in FCGR3B, two serologically defined haplotypes, NA1 and NA2, have been described. When compared to homozygous NA2, homozygous NA1 has been described to exhibit a higher phagocytic capacity due to its efficacy in binding immune complexes containing IgG1 and IgG3 [].
Frequencies of these functional polymorphisms depend on ethnic origin and are associated with SLE and/or LN in several ethnic groups, including Asians, Europeans, Africans, and African Americans []. In spite of its strong association with SLE and its severity, the risk of FcγRIIb-232T conferring SLE is thought to decrease in the presence of a specific haplotype (Hap) of CD72 []. CD72 is a 45 KDa type II transmembrane protein containing a C-type Lectin domain. It is expressed in most developmental stages of B cells except plasma cells. CD72 plays a negative regulatory role in B cell receptor (BCR) signaling after its stimulation with IgM or IgG [,]. Genotypically, two major haplotypes (Hap) 1 or 2 of CD72 exist, containing, respectively, one or two repeats of 13 nucleotides in intron 8. Hap2 provokes apoptosis in B cells by increasing an alternative splicing, resulting in a longer protein and its sequestration in reticulum endoplasmic []. Thus, Hap2 reduces the risk of developing SLE [].
In Martinique, a Caribbean Island, where the population has mainly an African Caribbean origin [], SLE is potentially severe, with an increased incidence of LN []. In addition, SLE is one of the most frequent causes of dialysis in this island [].
In this study, we have determined for the first time, the frequencies of FcγRIIa-H131R, FcγRIIb-I232T, FcγRIIIa-F158V, and FcγRIIIb-NA1/NA2 polymorphisms and their association with SLE and LN in 126 patients with SLE including 58 patients with LN and 120 unrelated controls from this indigenous African Caribbean population. Furthermore, we have explored for the first time CD72 polymorphism in an African descendent population to explain the exceptionally high frequency of FcγRIIb 232T/T in this indigenous African Caribbean population.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
Ethical approval for the study was given by the “Comité de protection des personnes Sud Ouest et Outremer III” under number 2013-A01610-45. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
2.2. Study Subjects
Anticoagulated peripheral blood was obtained from 120 healthy volunteers from Martinique and from the 126 patients included because they fulfilled the revised 1997 American College of Rheumatology (ACR) criteria for SLE []. We excluded children, childbearing patients and those without social security. Patients with SLE were recruited at the Internal Medicine Department of the University Hospital of Martinique at Fort de France. All donors self-reported as originating from Martinique and living in Martinique, and provided informed written consent.
2.3. Genotyping of FCGR2A, FCGR2B and FCGR3A
Genomic DNA was purified from peripheral blood mononuclear cells of healthy subjects and patients using QIAamp DNA blood Maxi kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). For PCRs, the following primers were used: 5′-CTGAGACTGAAAAACCCTTGGAATC-3′ (forward) and 5′-GCTTGTGGGATGGAGAAGGTGGGATCCAAA-3′ (reverse) for FCGR2A []. 5′-CCTGCCTGCTCACAAATGTA-3′ (forward) and 5′-CTGAAATCCGCTTTTTCCTG-3′ (reverse) for FCGR2B gene [,]. 5′-TATTTACAGAATGGCAAAGG-3′ (forward) and 5′-GTGATGGTGATGTTCACAGT-3′ (reverse) for FCGR3A []. PCRs were run in 50 µL containing 100 ng of DNA, 2.5 mM of MgCl2, 200 µM of dNTPs, 0.4 µM of each primer and 1.25 unit of AmpliTaq Gold 360 DNA Polymerase (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
The cycling conditions were as follows: an initial step of 10 min at 95 °C, 30 cycles of 30 s at 95 °C, 1 min at 55 °C (FCGR2B primers), 50 °C (FCGR2A primers) or 53 °C (FCGR3A primers), 1 min at 72 °C and a final extension of 7 min at 72 °C. The amplified DNA fragments of 231 bp (FCGR2A), 350 bp (FCGR2B) and 152 bp (FCGR3A) were visualized in a 2% agarose gel containing Midori Green (Nippon Genetics Europe GmbH, Düren, Germany) staining. PCR products were purified and sequenced using the BigDye Terminators v3.1 Ready Reaction Cycle Sequencing kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Sequences were run on ABI 3500 capillary sequencer (Applied Biosystems, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), and analyzed using SeqScape version 2.7 (Applied Biosystems, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
2.4. NA1 and NA2 Allotyping of FCGR3B
The NA1 and NA2 allotypes were amplified using forward allotype specific primers, 5′-CAGTGGTTTCACAATGAGAA-3′ for NA1 and 5′-CCATGGTACAGCGTGCTT-3′ for NA2 and a (reverse) common primer 5′-ATGGACTTCTAGCTGCAC-3′ []. PCRs were run as previously described. The cycling conditions were as follows: an initial step of 10 min at 95 °C, 35 cycles of 30 s at 95 °C, 1 min at 50 °C (NA1 primers) or 55 °C (NA2 primers), 1 min at 72 °C and a final extension of 7 min at 72 °C. The amplified DNA fragments of 141 bp (NA1) and 219 bp (NA2) were separated on a 2% agarose gel and visualized by Midori Green staining (Nippon Genetics Europe GmbH, Düren, Germany).
2.5. Haplotype Tagging and Fragment Analysis of CD72
The 13 nucleotides repeat in the intron 8 used as the haplotype tag, was studied using simple sequence repeat-PCR using specific primers [], 6-Fam-5′-TTGGTAAGAGTGAGGGATGG-3′ (forward) and 5′-TACAAGTTTTCTCTCGGGCC-3′ (reverse). PCRs were run in 50 µL containing 100 ng of DNA, 2.5 mM of MgCl2, 200 µM of dNTPs, 0.4 µM of each primer and 1.25 unit of AmpliTaq Gold DNA 360 Polymerase (Applied Biosystems, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The cycling conditions were as follows: an initial step at 95 °C for 10 min, 40 cycles of 30 s at 95 °C, 1 min at 55 °C, 1 min at 72 °C and a final extension of 7 min at 72 °C. PCR products were separated on a 2% agarose gel and visualized by Midori Green (Nippon Genetics Europe GmbH, Düren, Germany) staining. PCR products were diluted (1/10, 1/100). From these dilutions, 0.5 µL was combined with 9 µL of HiDiTMformamide (Applied Biosystems, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and 0.5 µL of internal sizer GeneScanTM 400HD RoxTM DYE Size Standard (Applied Biosystems, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and run on an ABI 3500 capillary sequencer (Applied Biosystems, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The analysis and sizing of PCR products were performed using the GeneMapper software package version 3.5 (Applied Biosystems, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
2.6. Statistical Analysis
All statistical analyses were performed with GraphPad PRISM 9.5 (Graphpad Prism Inc., San Diego, CA, USA). Datasets were checked for their normality using Anderson-Darling test. A χ2 test was used to assess if the studied groups had the same distribution in terms of gender. The mean and standard deviation of age were also calculated and compared using an ordinary one way ANOVA. χ2 and Fisher’s exact tests were implemented to compare genotype and allele frequencies depending on the sampling and using a 2 × 2 contingency table for allele frequencies and a 3 × 2 contingency table for genotype frequencies. When the distribution was deemed different, the odds ratio (OR) with a confidence interval (CI) of 95% was calculated for a 2 × 2 contingency table using Fisher’s exact test. The deviations in the observed genotypic distributions from the expected distributions based on Hardy–Weinberg law were tested using a χ2 test with 1 degree of freedom using the website “Online Calculator of Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium”. Linkage disequilibria were also estimated for the four polymorphisms in the studied population, using the Haploview software V4.2 []. The FCGR haplotype distributions were compared using a 4 × 2 χ2 contingency table. p-values less than 0.05 were deemed significant.
3. Results
3.1. Patients and Controls
In this study, 126 African Caribbean patients with SLE (116 females and 10 males) and 120 (109 females and 11 males) unrelated healthy individuals were included. The SLE patient group included 58 (46.03%) patients with LN and 48 (38.09%) with LWN (Table 1). However, 20 (15.8%) of the patients with SLE had an undetermined state regarding the nephritis involvement. The gender distribution did not show any significant differences among the groups. When we compared the means of age between the groups, i.e., healthy controls (53.9 ± 18.10), SLE (48.25 ± 15.79), LN (46.02 ± 14.39) and LWN (51.33 ± 16.13), no significant statistical differences were observed. Patients and healthy controls were matched according to sex and age and self-reported as Martinicans.

Table 1.
Characteristics of studied groups.
3.2. FCGR3A-158F and FCGR3B-NA2 Are Associated with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in African Caribbeans
We conducted an analysis of the association between FCGR2A, FCGR2B, FCGR3A and FCGR3B polymorphisms and SLE. Our results showed no differences in the genotype and allele frequencies of FCGR2A-R131H (Figure 1A,B) nor FCGR2B-I232T (Figure 1C,D) between SLE and healthy controls. In addition, the distribution of FCGR3A-F158V polymorphisms showed a disparity between SLE and controls (Figure 1E,F and Table A1). In fact, a higher prevalence of the 158F allele was observed in patients with SLE (57%) in comparison to controls (46%), associated with an OR of 1.52 (1.06–2.16) (Table 2). In addition, the distribution of genotype and allele frequencies of FcγRIIIB-NA1/NA2 (Figure 1G,H and Table A1) was significantly different in patients with SLE in comparison to controls (p = 0.0003 and 0.002, respectively). The frequency of homozygous NA1 was higher in SLE (32%) compared to controls (14%), correlating with an OR (95% CI) of 2.83 (1.49–5.38) for the homozygous NA1 in developing SLE (Table 2). When assessing allele frequencies, the NA1 allele exhibited a higher frequency in the whole group of patients (58%) in comparison to controls (50%) (Figure 1H and Table A1). This high frequency was associated with an odds ratio of 1.76 (1.23–2.54) (Table 2).
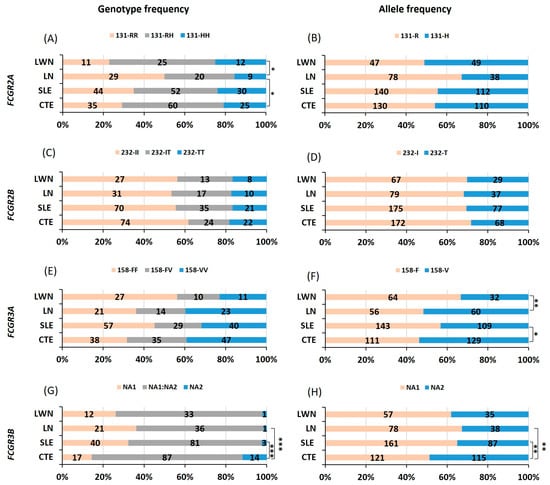
Figure 1.
Comparison of FCGR polymorphism distributions between patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and healthy controls. Comparison of genotype and allele frequencies of FCGR2A-R131H (A,B), FCGR2B-I232T (C,D), FCGR3A-F158V (E,F) and FCGR3B-NA1/NA2 (G,H), respectively, between patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), lupus nephritis (LN), and lupus without nephritis (LWN) and healthy controls (CTE). The comparison was performed using khi² test with 2 degrees of freedom or Fisher’s exact test when the number of individuals was small. *, ** and *** indicate p < 0.05, p < 0.01 and p < 0.001, respectively.

Table 2.
Odds ratio of FcγR polymorphisms to develop systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis, one of its severe subtypes.
3.3. FCGR2AH-131R Is Associated with Lupus Nephritis
We conducted a detailed analysis of the association between FCGR2A, FCGR2B, FCGR3A and FCGR3B polymorphisms and lupus nephritis. Our findings revealed a significant correlation between FCGR2A-131R and lupus nephritis in our African Caribbean population. Homozygous 131R and 131R allele were over-represented in patients with nephritis (50% and 67%, respectively) in comparison to controls (29% and 54.2%, respectively) (Figure 1A,B and Table A1) with a statistical significance of (p = 0.024 and 0.019, respectively). The ORs associated with these findings were 2.42 (1.26–4.74) for homozygous 131R and 1.73 (1.09–2.77) (Table 2) for the 131R allele, indicating an increased risk of developing nephritis (Table 2). A further analysis within patients with LN underlined a significant difference in the distribution of the FCGR2A-R131H when compared to those without nephritis. The 131 R homozygous and allele were not only highly prevalent in patients with LN but also associated with higher ORs 3.36 (1.41–7.65) and 1.79 (1.22–3.65), respectively (Table 2). Additionally, the FCGR3A-158V allele exhibited a higher frequency (p = 0.007) in patients with LN (52%) compared to patients without nephritis (33.3%) (Figure 1E,F and Table A1). This frequency is associated with a risk of 2.14 (1.22–3.69) (Table 2) for developing nephritis in patients with SLE. However, no significant differences were observed in FCGR2B-I232T (Figure 1C,D and Table A1) nor FCGR3B-NA1/NA2 (Figure 1G,H and Table A1) between patients with LN and controls or patients with LWN.
3.4. Linkage Disequilibrium at the FCGR Locus and Association with High-Risk Haplotypes
Next, we studied the linkage disequilibrium (LD) of FCGR2A, FCGR2B, FCGR3A and FCGR3B in our population. The comparison between the percentages of observed heterozygous and theoretical ones showed that except for FCGR2A, which was consistent with the Hardy–Weinberg Equilibrium (HWE) (p > 0.05) in all groups, the other genes were not consistent with the HWE in any group. The association among the four studied polymorphisms was assessed through the evaluation of the linkage disequilibrium. As shown in Figure 2, D’ values suggest a weak but significant linkage disequilibrium between FCGR2A and FCGR3B in all groups except for the LN group. However, a stronger coinheritance was observed between FCGR2A and FCGR3A in the LN group (Figure 2C), associated with a high 131R-158V haplotype in patients with LN in comparison to LWN (30.4% vs. 15.8%, respectively) (p-value = 0.008) (Table A2) and a high OR of 2.32 (1.11, 4.87).
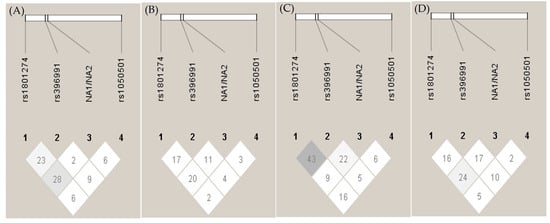
Figure 2.
Linkage disequilibrium (LD) plot of FCGRs. Genetic pair-wise D’ values observed in FCGRs, i.e., FCGR2A-R232H (rs1801274), FCGR3A-F158V (rs396991), FCGR3B-NA1/NA2 and FCGR2B-I232T (rs1050501), are shown within the diagonal boxes: (A) healthy control, (B) systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), (C) SLE with nephritis, (D) SLE without nephritis.
3.5. CD72-Hap2 Is Not Significantly Enhanced in FCGR2B-232T Controls
Facing the high frequency of FCGR2B-T232 in healthy individuals, we examined whether CD72 plays a protective role in this group. The CD72 haplotype2/2 (CD72-Hap2/Hap2) was thought to protect from SLE when associated with FCGR2B-232T. Using a fragment analysis, we studied the distribution of the CD72 haplotype1/2 in our population.
As shown in Table A3, a slight but not significant increase in the Hap1 genotype in healthy individuals was observed (p = 0.052). However, no significant differences were observed in allele and allele carrier frequencies between patients and controls.
4. Discussion
To date, many genetic association studies [] and various protein-encoding genes implicated in immunity have been considered as candidate genes susceptible to SLE [,]. A predisposition to SLE and its potential severity have been associated with variations in FCGRs in several ethnic groups [,]. However, controversial results among ethnic groups have led to the necessity to conduct further investigations in other populations worldwide.
This study was conducted to evaluate the distribution of FCGR2A-R131H, FCGR2B-I232T, FCGR3A-F158V and FCGR3B-NA1/NA2 polymorphisms in 126 patients with SLE (including 58 with LN) and 120 unrelated controls, in an indigenous African Caribbean population. Additionally, we studied the association of these polymorphisms with SLE and its severe clinical manifestation involving kidney injuries.
When FCGR2A-R131H was taken into consideration, surprisingly, we highlighted no association with SLE in our African Caribbean population. This result did not corroborate findings in other African and African descendant populations [,]. However, we identified the homozygous FCGR2A-131R and FCGR2A-131R alleles as a risk factor to develop LN in our indigenous African Caribbean population. The association of FCGR2A-131R with LN has been confirmed by meta-analysis studies [,], and has been observed in African Americans [,], Asians [,,] and Latin Americans []. The increased risk for FCGRIIA-131R to develop LN could result from the lack of clearance of IgG2 containing immune complex (IC) and its deposition in organs such as kidney []. Interestingly, the FCGR2A-131R allele is associated with the poor progression of nephropathy associated with IgG deposition [].
Regarding FCGR3A-F158V, the FCGR3A-158F homozygous and allele have been associated with SLE in various ethnic groups, including African Americans [], Europeans [,], Hispanics []. However, discordance has been noticed in Asians [,,,,]. On the other hand, the association of FCGR3A-158F with LN showed a discrepancy in several ethnic groups [,,]. Our data indicates, in our African Caribbean population, an association of FCGR3A-158F with SLE rather than LN. Our result confirms the association of FCGR3A-158F with SLE in this other population of African origin and aligns with the findings in Asians where the FCGR3A-158F allele was significantly associated with SLE but not with LN [,,]. However, when compared to LWN, the group of patients with LN exhibits a higher frequency of FCGR3A-158V. Thus, the aforementioned allele is described here for the first time in an African-descendent population as a high-risk factor for patients with SLE to develop LN. Our result may corroborate the finding of Alarcón et al. suggesting that the 158V homozygosity is a predictor factor of an end-stage renal disease []. Despite the fact that the homozygous FCGR3A-158V is not associated with LN in our study, we underlined a high frequency of this genotype (39%) in our patients with LN. The lack of significance may be attributed to the limited number of patients with LN in our study and needs to be confirmed in a larger LN cohort in our African Caribbean population. On the other hand, the association of FCGR3A-158V with LN in our study could be secondary to the observed LD between FCGR2A and FCGR3A in the LN group coupled to an increase in the 131R-158V haplotype.
FcγRIIIb-NA1/NA2 allotypes of the GPI anchored receptor have been associated with SLE. FcγRIIIb-NA2, with two potential supplementary glycosylation sites [], has less affinity to IgG1 and IgG3 [] and has been associated with SLE in Asians [,,]. By contrast, this allele was thought to protect from SLE in Koreans [] and was not associated with SLE in other studies [,,,,]. In our African Caribbean population, we found an association between the homozygous FcγRIIIb-NA1 and SLE (OR = 2.829) rather than LN. However, a protective effect of FcγRIIIb-NA2 against SLE was described in our study (OR = 0.56). Additionally, the presence of zero or one copy of FCGR3B has been identified as a predisposing factor for developing SLE [,]. In this study, we found two individuals among both patients with SLE and control groups with a lack of amplification of FCGR3B, suggesting a FcγRIIIb deficiency in these individuals. However, it is important to note that the allotyping of FCGR3B was carried out based on the fragment length in electrophoresis gel separation, which did not allow the evaluation of the presence of a single copy of FCGR3B.
Finally, FCGR2B-I232T was identified as a gene candidate for susceptibility to SLE. The homozygous FcγRIIb-232T has been depicted to confer susceptibility to SLE in most Asian populations [,,,], in Caucasians [], but not in African Americans []. In our study, we confirm the non-association of FcγRIIb-232T with SLE and LN in our population. This absence of association may be due to the high frequency of the FcγRIIb-232T allele (28%) in our African Caribbean population, in accordance with previous findings in African Americans [,,]. FcγRIIb is the only low-affinity inhibitory receptor; The FcγRIIb-232T receptor is less efficient in translocating into lipid rafts and induces the functional impairment of the receptor [,]. Recently, another study revealed that FcγRIIb-232T bending toward the plasma membrane prevents the receptor to bind to the ligand []. Facing this high frequency in our African Caribbean population and the functional importance of this receptor, we aimed at understanding whether the non SLE African Caribbean control group has a protective factor against FCGR2B-232T. To do so, we studied haplotypes 1/2 of CD72 in our African Caribbean population. Haplotype 2 has been described as decreasing the risk of SLE conferred by homozygous 232T []. This protective effect is related to an increase in an the alternative splicing of CD72 provoking apoptosis in B cells. Additionally, the association of homozygous FcγRIIb-232T with SLE has been depicted only in groups carrying CD72-Hap1 []. In our study, the CD72 haplotype distribution was not significantly different in patients and healthy controls whatever the FcγRIIb genotype is. Thus, CD72-Hap2 is not responsible for the protective effect against SLE in control group.
FCGR gene SNPs have been associated with changes in resistance to diseases. Plasmodium falciparum, the main malaria parasite, is considered to be the most important evolutionary force. It causes the appearance of several alleles giving the host protections against endemic diseases [,,]. For example, FCGR2A-131H and FCGR2B-232T alleles are associated with a protective effect against malaria and against its most deadly forms [,]. Thus, FCGR2A-131H and FCGR2B-232T alleles are more prevalent in population subjected to Plasmodium falciparum or descendants of an exposed population such as African Caribbeans [,,,], Africans and Asians [,]. Malaria may have continued to act as a selective pressure in African Caribbeans until its eradication from Martinique during the 20th century []. However, on this Caribbean Island, where arboviruses vectors proliferate throughout the year, other evolutionary pressures could exist. In fact, Martinique belongs to the most affected region by dengue virus worldwide []. Interestingly, the FCGR2A-131R allele has been described as having a protective effect against dengue hemorrhagic fever [], the most severe form of dengue infection.
Our study has some limitations. Firstly, the inclusion was performed in a single center, which could introduce a severity bias. Secondly, the number of patients with LN is relatively small. To enhance statistical test significance, more patients with LN should be included. Moreover, in this study, 20 patients with SLE had an undetermined state regarding kidney injuries. Finally, in this study, we did not take into account the variations in the copy number of FCGRs.
In conclusion, our study confirms the association of FCGR polymorphisms with SLE and LN found in the few studied African descendent populations. In fact, our results confirm the homozygous FCGR2A-131R as a risk factor for patients with SLE to develop LN, but they did not confirm its association with SLE. The high frequency of FCGR2B-232T allele is also confirmed. In addition, the association of the FCGR3A-158F allele with SLE is confirmed. However, we have described the FCGR3A-158V allele, for the first time here, as a high-risk factor for patients with SLE to develop LN. This result could be secondary to LD in the LN group and needs to be confirmed in a larger sample of patients with LN. Additionally, we highlight an association of FCGR3B-NA1 with SLE. Given the importance of FcγRs on IC clearance, further research is needed to understand their role in SLE pathogenesis. The distribution of FCGR2A-R131H, FCGR2B-I232T and FCGR3A-F158V polymorphisms mainly follows the same patterns as seen in other populations of African origin and may possibly be extrapolated to other populations with similar ancestries.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: C.D., M.D. and G.D.S.; methodology: F.R., C.D. and G.D.S.; validation: C.D., R.C. and G.D.S.; formal analysis, F.R. and G.D.S.; investigation: F.R. and G.D.S.; resources, M.D., C.D., R.C. and G.D.S.; data curation: F.R.; writing—original draft preparation: F.R.; funding acquisition: C.D. and M.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) “PO FEDER 2007-2013”, “FEDER-UE-CR Martinique”, in the field of “EFIA lupus”, grant number 32107.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the regional French Ethic Committee (“Comité de Protection des Personnes, Sud-Ouest et Outremer III”; CCP number: 2013/119, ref: 2013-A01610-45). Written informed consent was obtained from all patients. Child and childbearing person were excluded from the study. All patients were adults.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the clinical, research and biological teams of CHU Martinique for the involvement in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Comparison of the FCGR polymorphism distribution between patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and healthy controls.
Table A1.
Comparison of the FCGR polymorphism distribution between patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and healthy controls.
| Control (n = 120) | SLE (n = 126) | LN (n = 58) | LWN (n = 48) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genotype Frequency n (%) | |||||
| FCGR2A-131 | RR | 35 (29) | 44 (35) | 29 (50) | 11 (23) |
| HR | 60 (50) | 52 (41) | 20 (34) | 25 (52) | |
| HH | 25 (21) | 30 (24) | 9 (16) | 12 (25) | |
| FCGR2B-232 | II | 74 (62) | 70 (56) | 31 (53) | 27 (56) |
| IT | 24 (20) | 35 (28) | 17 (29) | 13 (27) | |
| TT | 22 (18) | 21 (17) | 10 (17) | 8 (17) | |
| FCGR3A-158 | FF | 38 (32) | 57 (45) | 21 (36) | 27 (56) |
| FV | 35 (29) | 29 (23) | 14 (24) | 10 (21) | |
| VV | 47 (39) | 40 (32) | 23 (40) | 11 (23) | |
| FCGR3B- | NA1/NA1 | 17 (14) | 40 (32) | 21 (36) | 12 (25) |
| NA1/NA2 | 87 (73) | 81 (64) | 36 (62) | 33 (69) | |
| NA2/NA2 | 14 (12) | 3 (2) | 1 (2) | 1 (2) | |
| Null | 2 (2) | 2 (2) | 0 (0) | 2 (4) | |
| Allele Frequency n (%) | |||||
| FCGR2A-131 | R | 130 (54) | 140 (56) | 78 (67) | 47 (49) |
| H | 110 (46) | 112 (44) | 38 (33) | 49 (51) | |
| FCGR2B-232 | I | 172 (72) | 175 (69) | 79 (68) | 67 (70) |
| T | 68 (28) | 77 (31) | 37 (32) | 29 (30) | |
| FCGR3A-158 | F | 111 (46) | 143 (57) | 56 (48) | 64 (67) |
| V | 129 (54) | 109 (43) | 60 (52) | 32 (33) | |
| FCGR3B- | NA1 | 121 (50) | 161 (64) | 78 (67) | 57 (59) |
| NA2 | 115 (48) | 87 (35) | 38 (33) | 35 (36) | |
| Null | 4 (2) | 4 (2) | 0 (0) | 4 (4) | |
| Allele Carrier Frequency n (%) | |||||
| FCGR2A-131 | R | 95 (53) | 96 (54) | 49 (63) | 36 (49) |
| H | 85 (47) | 82 (46) | 29 (37) | 37 (51) | |
| FCGR2B-232 | I | 98 (68) | 105 (65) | 48 (64) | 40 (66) |
| T | 46 (32) | 56 (35) | 27 (36) | 21 (34) | |
| FCGR3A-158 | F | 73 (47) | 86 (55) | 35 (49) | 37 (64) |
| V | 82 (53) | 69 (45) | 37 (51) | 21 (36) | |
| FCGR3B- | NA1 | 104 (50) | 121 (58) | 57 (31) | 45 (56) |
| NA2 | 101 (49) | 84 (41) | 37 (39) | 34 (42) | |
| Null | 2 (1) | 2 (1) | 0 (0) | 2 (2) | |
Comparison of genotype alleles and allele carrier frequencies of FCGR2A-R131H, FCGR2B-I232T, FCGR3A-F158V and FCGR3B-NA1/NA2 between patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), lupus nephritis (LN) and lupus without nephritis (LWN) and healthy controls. Data are shown as a number (percentage) n (%).

Table A2.
Comparison of the FCGR haplotype distribution, in linkage disequilibrium, between patients with SLE and healthy controls.
Table A2.
Comparison of the FCGR haplotype distribution, in linkage disequilibrium, between patients with SLE and healthy controls.
| Control (n = 120) | SLE (n = 126) | LN (n = 58) | LWN (n = 48) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FCGR2A-3A Haplotypes n (%) | ||||
| H-F | 44 (19) | 51 (24) | 13 (13) | 27 (32) |
| H-V | 63 (28) | 49 (23) | 24 (24) | 16 (19) |
| R-F | 60 (26) | 69 (32) | 31 (32) | 28 (33) |
| R-V | 61 (27) | 48 (22) | 30 (31) | 14 (16) |
| p-value | 0.2 | 0.05 | 0.019 | |
| p1-value | 0.008 | |||
| FCGR2A-3B Haplotypes n (%) | ||||
| H-NA1 | 75 (24) | 79 (27) | 28 (22) | 36 (30) |
| H-NA2 | 69 (22) | 57 (20) | 19 (15) | 27 (23) |
| R-NA1 | 80 (26) | 94 (32) | 49 (39) | 34 (28) |
| R-NA2 | 83 (27) | 60 (21) | 31 (24) | 23 (19) |
| p-value | 0.13 | 0.05 | 0.34 | |
| p1-value | 0.10 | |||
| FCGR3A-3B Haplotypes n (%) | ||||
| F-NA1 | 62 (24) | 81 (32) | 35 (30) | 33 (35) |
| F-NA2 | 60 (24) | 52 (21) | 20 (17) | 23 (25) |
| R-NA1 | 73 (29) | 67 (27) | 36 (31) | 20 (22) |
| R-NA2 | 60 (24) | 50 (20) | 26 (22) | 17 (18) |
| p-value | 0.23 | 0.44 | 0.15 | |
| p1-value | 0.25 | |||
Comparison of FCGR haplotype distribution, in linkage disequilibrium, between patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), lupus nephritis (LN) and lupus without nephritis (LWN) and healthy controls. Data are shown as a number (percentage) n (%). p-value of Χ2 test for a 4 × 2 contingency table was calculated against controls. p1-value was calculated between LN and LWN. p and p1 < 0.05 were deemed significant.

Table A3.
Haplotypes and allele frequency distribution of CD72.
Table A3.
Haplotypes and allele frequency distribution of CD72.
| Controls (n = 120) | SLE (n = 126) | LN (n = 58) | LWN (n = 48) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genotype Frequency n (%) | ||||
| Hap1/Hap1 | 22 (18.3) | 11 (9.2) | 6 (10.7) | 3 (6.5) |
| Hap1/Hap2 | 51 (42.5) | 67 (52.6) | 30 (53.6) | 24 (52.2) |
| Hap2/Hap2 | 47 (39.2) | 48 (38.2) | 20 (35.7) | 19 (41.3) |
| p-Value | 0.057 | 0.282 | 0.149 | |
| p1-Value | 0.69 | |||
| Allele Frequency n (%) | ||||
| Hap1 | 95 (39.6) | 89 (35.5) | 42 (37.5) | 30 (32.6) |
| Hap2 | 145 (60.4) | 163 (64.5) | 70 (62.5) | 62 (67.4) |
| p-Value | 0.32 | 0.7 | 0.2 | |
| p1-value | 0.46 | |||
| Allele Carrier Frequency n (%) | ||||
| Hap 1 | 73 (60.8) | 78 (61.8) | 36 (64.3) | 27 (58.7) |
| Hap 2 | 98 (81.6) | 115 (91) | 50 (89.3) | 43 (93.4) |
| p-value | 0.6 | 0.89 | 0.55 | |
| p1-value | 0.67 | |||
Comparison of the distribution of haplotype 1 and 2 (Hap1 and Hap2) of CD72 in groups of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), lupus nephritis (LN) and SLE without nephritis (LWN) and healthy controls. p-value of Fisher’s exact test was calculated against healthy controls. p1-value was calculated between LN and LWN. p < 0.05 was deemed significant.
References
- Siegel, C.H.; Sammaritano, L.R. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Review. JAMA 2024, 331, 1480–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Zhang, D.; Yao, X.; Huang, Y.; Lu, Q. Global Epidemiology of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Comprehensive Systematic Analysis and Modelling Study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petri, M. Epidemiology of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2002, 16, 847–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.S.; Yin, G.; Mok, M.Y. Ethnic and Geographical Differences in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: An Overview. Lupus 2006, 15, 715–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Symmons, D.P. Frequency of Lupus in People of African Origin. Lupus 1995, 4, 176–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pons-Estel, G.J.; Alarcón, G.S.; Scofield, L.; Reinlib, L.; Cooper, G.S. Understanding the Epidemiology and Progression of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 39, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossati, G.; Bucknall, R.C.; Edwards, S.W. Fcγ Receptors in Autoimmune Diseases. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 31, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimberly, R.P.; Salmon, J.E.; Edberg, J.C. Receptors for Immunoglobulin G. Molecular Diversity and Implications for Disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1995, 38, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, C.E.; Rose-Zerilli, M.J.J.; Machado, L.R.; Iriyama, C.; Hollox, E.J.; Cragg, M.S.; Strefford, J.C. Fcγ Receptors: Genetic Variation, Function, and Disease. Immunol. Rev. 2015, 268, 6–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, M.R.; Clarkson, S.B.; Ory, P.A.; Stollman, N.; Goldstein, I.M. Molecular Basis for a Polymorphism Involving Fc Receptor II on Human Monocytes. J. Immunol. 1989, 143, 1731–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruhns, P.; Iannascoli, B.; England, P.; Mancardi, D.A.; Fernandez, N.; Jorieux, S.; Daëron, M. Specificity and Affinity of Human Fcgamma Receptors and Their Polymorphic Variants for Human IgG Subclasses. Blood 2009, 113, 3716–3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warmerdam, P.A.; van de Winkel, J.G.; Vlug, A.; Westerdaal, N.A.; Capel, P.J. A Single Amino Acid in the Second Ig-like Domain of the Human Fc Gamma Receptor II Is Critical for Human IgG2 Binding. J. Immunol. 1991, 147, 1338–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmon, J.E.; Edberg, J.C.; Brogle, N.L.; Kimberly, R.P. Allelic Polymorphisms of Human Fc Gamma Receptor IIA and Fc Gamma Receptor IIIB. Independent Mechanisms for Differences in Human Phagocyte Function. J. Clin. Investig. 1992, 89, 1274–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floto, R.A.; Clatworthy, M.R.; Heilbronn, K.R.; Rosner, D.R.; MacAry, P.A.; Rankin, A.; Lehner, P.J.; Ouwehand, W.H.; Allen, J.M.; Watkins, N.A.; et al. Loss of Function of a Lupus-Associated FcgammaRIIb Polymorphism through Exclusion from Lipid Rafts. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 1056–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kono, H.; Kyogoku, C.; Suzuki, T.; Tsuchiya, N.; Honda, H.; Yamamoto, K.; Tokunaga, K.; Honda, Z.-I. FcgammaRIIB Ile232Thr Transmembrane Polymorphism Associated with Human Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Decreases Affinity to Lipid Rafts and Attenuates Inhibitory Effects on B Cell Receptor Signaling. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2005, 14, 2881–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koene, H.R.; Kleijer, M.; Algra, J.; Roos, D.; von dem Borne, A.E.; de Haas, M. Fc gammaRIIIa-158V/F Polymorphism Influences the Binding of IgG by Natural Killer Cell Fc gammaRIIIa, Independently of the Fc gammaRIIIa-48L/R/H Phenotype. Blood 1997, 90, 1109–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmon, J.E.; Edberg, J.C.; Kimberly, R.P. Fc Gamma Receptor III on Human Neutrophils. Allelic Variants Have Functionally Distinct Capacities. J. Clin. Investig. 1990, 85, 1287–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsang-A-Sjoe, M.W.P.; Nagelkerke, S.Q.; Bultink, I.E.M.; Geissler, J.; Tanck, M.W.T.; Tacke, C.E.; Ellis, J.A.; Zenz, W.; Bijl, M.; Berden, J.H.; et al. Fc-Gamma Receptor Polymorphisms Differentially Influence Susceptibility to Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Lupus Nephritis. Rheumatology 2016, 55, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitomi, Y.; Tsuchiya, N.; Kawasaki, A.; Ohashi, J.; Suzuki, T.; Kyogoku, C.; Fukazawa, T.; Bejrachandra, S.; Siriboonrit, U.; Chandanayingyong, D.; et al. CD72 Polymorphisms Associated with Alternative Splicing Modify Susceptibility to Human Systemic Lupus Erythematosus through Epistatic Interaction with FCGR2B. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2004, 13, 2907–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumanogoh, A.; Watanabe, C.; Lee, I.; Wang, X.; Shi, W.; Araki, H.; Hirata, H.; Iwahori, K.; Uchida, J.; Yasui, T.; et al. Identification of CD72 as a Lymphocyte Receptor for the Class IV Semaphorin CD100: A Novel Mechanism for Regulating B Cell Signaling. Immunity 2000, 13, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, I.; Kumanogoh, A.; Suzuki, K.; Akahani, S.; Noda, K.; Kikutani, H. Involvement of CD100, a Lymphocyte Semaphorin, in the Activation of the Human Immune System via CD72: Implications for the Regulation of Immune and Inflammatory Responses. Int. Immunol. 2003, 15, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitomi, Y.; Adachi, T.; Tsuchiya, N.; Honda, Z.-I.; Tokunaga, K.; Tsubata, T. Human CD72 Splicing Isoform Responsible for Resistance to Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Regulates Serum Immunoglobulin Level and Is Localized in Endoplasmic Reticulum. BMC Immunol. 2012, 13, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, O.; Cesaire, R.; Quelvennec, E.; Quillivic, F.; De Chavigny, V.; Ribal, C.; Semana, G. HLA Class I and Class II Allele and Haplotype Diversity in Martinicans. Tissue Antigens 2001, 57, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzon, B.; Louis-Sidney, F.; Aglaé, C.; Henry, K.; Bagoée, C.; Wolff, S.; Moinet, F.; Emal-Aglaé, V.; Polomat, K.; DeBandt, M.; et al. Good Long-Term Prognosis of Lupus Nephritis in the High-Income Afro-Caribbean Population of Martinique with Free Access to Healthcare. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deligny, C.; Thomas, L.; Dubreuil, F.; Théodose, C.; Garsaud, A.M.; Numéric, P.; Ranlin, A.; Jean-Baptiste, G.; Arfi, S. Systemic lupus erythematosus in Martinique: An epidemiologic study. Rev. Med. Interne 2002, 23, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mc, H. Updating the American College of Rheumatology Revised Criteria for the Classification of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1997, 40, 1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Tsuge, T.; Kanamaru, Y.; Horikoshi, S.; Monteiro, R.C.; Tomino, Y. FcγRIIa-131R Allele and FcγRIIIa-176V/V Genotype Are Risk Factors for Progression of IgA Nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2005, 20, 2439–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tackenberg, B.; Jelčić, I.; Baerenwaldt, A.; Oertel, W.H.; Sommer, N.; Nimmerjahn, F.; Lünemann, J.D. Impaired Inhibitory Fcγ Receptor IIB Expression on B Cells in Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 4788–4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyogoku, C.; Dijstelbloem, H.M.; Tsuchiya, N.; Hatta, Y.; Kato, H.; Yamaguchi, A.; Fukazawa, T.; Jansen, M.D.; Hashimoto, H.; Van De Winkel, J.G.J.; et al. Fcγ Receptor Gene Polymorphisms in Japanese Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Contribution of FCGR2B to Genetic Susceptibility. Arthritis Rheum. 2002, 46, 1242–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyogoku, C.; Tsuchiya, N.; Matsuta, K.; Tokunaga, K. Studies on the Association of Fcγ Receptor IIA, IIB, IIIA and IIIB Polymorphisms with Rheumatoid Arthritis in the Japanese: Evidence for a Genetic Interaction between HLA-DRB1 and FCGR3A. Genes Immun. 2002, 3, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siriboonrit, U.; Tsuchiya, N.; Sirikong, M.; Kyogoku, C.; Bejrachandra, S.; Suthipinittharm, P.; Luangtrakool, K.; Srinak, D.; Thongpradit, R.; Fujiwara, K.; et al. Association of Fcgamma Receptor IIb and IIIb Polymorphisms with Susceptibility to Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Thais. Tissue Antigens 2003, 61, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Lu, S.; Tao, J.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, Z.; Huang, Y.; Yang, R. CD72 Polymorphism Associated with Child-Onset of Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura in Chinese Patients. J. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 28, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, J.C.; Fry, B.; Maller, J.; Daly, M.J. Haploview: Analysis and Visualization of LD and Haplotype Maps. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigato-Ferreira, I.C.C.; Toller-Kawahisa, J.E.; Pancoto, J.A.T.; Mendes-Junior, C.T.; Martinez, E.Z.; Donadi, E.A.; Louzada-Júnior, P.; Del Lama, J.E.C.; Marzocchi-Machado, C.M. FcγRIIa and FcγRIIIb Polymorphisms and Associations with Clinical Manifestations in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients. Autoimmunity 2014, 47, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, D.L.; Zidovetzki, R.; Alarcón-Riquelme, M.E.; Tsao, B.P.; Criswell, L.A.; Kimberly, R.P.; Harley, J.B.; Sivils, K.L.; Vyse, T.J.; Gaffney, P.M.; et al. GWAS Identifies Novel SLE Susceptibility Genes and Explains the Association of the HLA Region. Genes Immun. 2014, 15, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fike, A.J.; Elcheva, I.; Rahman, Z.S.M. The Post-GWAS Era: How to Validate the Contribution of Gene Variants in Lupus. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2019, 21, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederer, H.A.; Clatworthy, M.R.; Willcocks, L.C.; Smith, K.G.C. FcgammaRIIB, FcgammaRIIIB, and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1183, 69–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wei, H.-T.; Zou, J.-J.; Ma, Y.-R. Association of FcγRIIA-R/H131 Polymorphism and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Lupus Nephritis Risk: A Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 23, 853–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, W.; Zhang, H.; Wei, L.; Guo, S. Association of FCGR2A Rs1801274 Polymorphism with Susceptibility to Autoimmune Diseases: A Meta-Analysis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 39436–39443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karassa, F.B.; Bijl, M.; Davies, K.A.; Kallenberg, C.G.M.; Khamashta, M.A.; Manger, K.; Michel, M.; Piette, J.-C.; Salmon, J.E.; Song, Y.W.; et al. Role of the Fcgamma Receptor IIA Polymorphism in the Antiphospholipid Syndrome: An International Meta-Analysis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48, 1930–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmon, J.E.; Millard, S.; Schachter, L.A.; Arnett, F.C.; Ginzler, E.M.; Gourley, M.F.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Peterson, M.G.; Kimberly, R.P. Fc Gamma RIIA Alleles Are Heritable Risk Factors for Lupus Nephritis in African Americans. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 97, 1348–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edberg, J.C.; Langefeld, C.D.; Wu, J.; Moser, K.L.; Kaufman, K.M.; Kelly, J.; Bansal, V.; Brown, W.M.; Salmon, J.E.; Rich, S.S.; et al. Genetic Linkage and Association of Fcgamma Receptor IIIA (CD16A) on Chromosome 1q23 with Human Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2002, 46, 2132–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.W.; Han, C.W.; Kang, S.W.; Baek, H.J.; Lee, E.B.; Shin, C.H.; Hahn, B.H.; Tsao, B.P. Abnormal Distribution of Fc Gamma Receptor Type IIa Polymorphisms in Korean Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1998, 41, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Peng, H.; Chen, G.-M.; Feng, C.-C.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Wen, P.-F.; Qiu, L.-J.; Leng, R.-X.; Pan, H.-F.; Ye, D.-Q. Association of FCGR2A-R/H131 Polymorphism with Susceptibility to Systemic Lupus Erythematosus among Asian Population: A Meta-Analysis of 20 Studies. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2014, 306, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Ptacek, T.S.; Brown, E.E.; Edberg, J.C. Fcγ Receptors: Structure, Function and Role as Genetic Risk Factors in SLE. Genes Immun. 2009, 10, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, M.; Petri, M.A.; Kim, N.A.; Sullivan, K.E. Frequency of the Fc Gamma RIIIA-158F Allele in African American Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 1999, 26, 1486–1489. [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson, V.; Johanneson, B.; Lima, G.; Odeberg, J.; Alarcón-Segovia, D.; Alarcón-Riquelme, M.E.; SLE Genetics Collaboration Group. Both Risk Alleles for FcgammaRIIA and FcgammaRIIIA Are Susceptibility Factors for SLE: A Unifying Hypothesis. Genes Immun. 2004, 5, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zuñiga, R.; Ng, S.; Peterson, M.G.; Reveille, J.D.; Baethge, B.A.; Alarcón, G.S.; Salmon, J.E. Low-Binding Alleles of Fcgamma Receptor Types IIA and IIIA Are Inherited Independently and Are Associated with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Hispanic Patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Z.T.; Tsuchiya, N.; Kyogoku, C.; Ohashi, J.; Qian, Y.P.; Xu, S.B.; Mao, C.Z.; Chu, J.Y.; Tokunaga, K. Association of Fcgamma Receptor IIb Polymorphism with Susceptibility to Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Chinese: A Common Susceptibility Gene in the Asian Populations. Tissue Antigens 2004, 63, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.-H.; Yuan, H.; Pan, H.-F.; Li, W.-X.; Li, X.-P.; Ye, D.-Q. Role of the Fcgamma Receptor IIIA-V/F158 Polymorphism in Susceptibility to Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Lupus Nephritis: A Meta-Analysis. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2010, 39, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, E.E.; Edberg, J.C.; Kimberly, R.P. Fc Receptor Genes and the Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Diathesis. Autoimmunity 2007, 40, 567–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jönsen, A.; Gunnarsson, I.; Gullstrand, B.; Svenungsson, E.; Bengtsson, A.A.; Nived, O.; Lundberg, I.E.; Truedsson, L.; Sturfelt, G. Association between SLE Nephritis and Polymorphic Variants of the CRP and FcgammaRIIIa Genes. Rheumatology 2007, 46, 1417–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C.; Ptacek, T.S.; Redden, D.T.; Zhang, K.; Brown, E.E.; Edberg, J.C.; McGwin, G.; Alarcón, G.S.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Reveille, J.D.; et al. Fcγ Receptor IIIa Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms and Haplotypes Affect Human IgG Binding and Are Associated with Lupus Nephritis in African Americans. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 1291–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, X.; Qian, X.; Huang, X. Association of FcγRIIIa-158V/F with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in a Chinese Population. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 16, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcón, G.S.; McGwin, G.; Petri, M.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Fessler, B.J.; Vilá, L.M.; Edberg, J.C.; Reveille, J.D.; Kimberly, R.P.; PROFILE Study Group. Time to Renal Disease and End-Stage Renal Disease in PROFILE: A Multiethnic Lupus Cohort. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bux, J. Human Neutrophil Alloantigens. Vox Sang. 2008, 94, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatta, Y.; Tsuchiya, N.; Ohashi, J.; Matsushita, M.; Fujiwara, K.; Hagiwara, K.; Juji, T.; Tokunaga, K. Association of Fc Gamma Receptor IIIB, but Not of Fc Gamma Receptor IIA and IIIA Polymorphisms with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Japanese. Genes Immun. 1999, 1, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.H.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, H.S.; Bae, S.C.; Yoo, D.H. The Association between fcgammaRIIIB Polymorphisms and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Korea. Lupus 2005, 14, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, S.N.; Phipps, M.E.; Manivasagar, M.; Tan, S.Y.; Bosco, J.J. Human Fc Gamma Receptor IIA (FcgammaRIIA) Genotyping and Association with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) in Chinese and Malays in Malaysia. Lupus 1999, 8, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dijstelbloem, H.M.; Bijl, M.; Fijnheer, R.; Scheepers, R.H.; Oost, W.W.; Jansen, M.D.; Sluiter, W.J.; Limburg, P.C.; Derksen, R.H.; van de Winkel, J.G.; et al. Fcgamma Receptor Polymorphisms in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Association with Disease and in Vivo Clearance of Immune Complexes. Arthritis Rheum. 2000, 43, 2793–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, M.; Barros, P.; Witherden, A.S.; Roberts, A.L.; Zhang, Z.; Schaschl, H.; Yu, C.-Y.; Hurles, M.E.; Schaffner, C.; Floto, R.A.; et al. Genomic Pathology of SLE-Associated Copy-Number Variation at the FCGR2C/FCGR3B/FCGR2B Locus. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 92, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chen, J.-Y.; Wang, C.M.; Ma, C.-C.; Luo, S.-F.; Edberg, J.C.; Kimberly, R.P.; Wu, J. Association of a Transmembrane Polymorphism of Fcγ Receptor IIb (FCGR2B) with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Taiwanese Patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 3908–3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willcocks, L.C.; Carr, E.J.; Niederer, H.A.; Rayner, T.F.; Williams, T.N.; Yang, W.; Scott, J.A.G.; Urban, B.C.; Peshu, N.; Vyse, T.J.; et al. A Defunctioning Polymorphism in FCGR2B Is Associated with Protection against Malaria but Susceptibility to Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 7881–7885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wu, J.; Carter, R.H.; Edberg, J.C.; Su, K.; Cooper, G.S.; Kimberly, R.P. A Novel Polymorphism in the Fcgamma Receptor IIB (CD32B) Transmembrane Region Alters Receptor Signaling. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48, 3242–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassauniere, R.; Tiemessen, C.T. Variability at the FCGR Locus: Characterization in Black South Africans and Evidence for Ethnic Variation in and out of Africa. Genes Immun. 2016, 17, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niederer, H.A.; Willcocks, L.C.; Rayner, T.F.; Yang, W.; Lau, Y.L.; Williams, T.N.; Scott, J.A.G.; Urban, B.C.; Peshu, N.; Dunstan, S.J.; et al. Copy Number, Linkage Disequilibrium and Disease Association in the FCGR Locus. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010, 19, 3282–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhang, T.; Xu, L.; Xie, H.; Li, Z.; Liu, W.; Lou, J.; Chen, W. FcγRIIB-I232T Polymorphic Change Allosterically Suppresses Ligand Binding. Elife 2019, 8, e46689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenski, R.E. What Is Adaptation by Natural Selection? Perspectives of an Experimental Microbiologist. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1006668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damena, D.; Denis, A.; Golassa, L.; Chimusa, E.R. Genome-Wide Association Studies of Severe P. Falciparum Malaria Susceptibility: Progress, Pitfalls and Prospects. BMC Med. Genom. 2019, 12, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quin, J.E.; Bujila, I.; Chérif, M.; Sanou, G.S.; Qu, Y.; Vafa Homann, M.; Rolicka, A.; Sirima, S.B.; O’Connell, M.A.; Lennartsson, A.; et al. Major Transcriptional Changes Observed in the Fulani, an Ethnic Group Less Susceptible to Malaria. eLife 2017, 6, e29156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waisberg, M.; Tarasenko, T.; Vickers, B.K.; Scott, B.L.; Willcocks, L.C.; Molina-Cruz, A.; Pierce, M.A.; Huang, C.; Torres-Velez, F.J.; Smith, K.G.C.; et al. Genetic Susceptibility to Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Protects against Cerebral Malaria in Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 1122–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiah, M.A.; Ouattara, A.; Okou, D.T.; N’Guetta, S.-P.A.; Yavo, W. Polymorphisms in Fc Gamma Receptors and Susceptibility to Malaria in an Endemic Population. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 561142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, A.; Iriemenam, N.C.; Giha, H.A.; Balogun, H.A.; Anders, R.F.; Troye-Blomberg, M.; ElGhazali, G.; Berzins, K. FcgammaRIIa (CD32) Polymorphism and Anti-Malarial IgG Subclass Pattern among Fulani and Sympatric Ethnic Groups Living in Eastern Sudan. Malar. J. 2009, 8, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ma, L.; Chen, S.; Xie, Y.; Xie, L.; Deng, Y.; He, Y.; Li, T.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; et al. Association between Fc-Gamma Receptor IIa (CD32) Gene Polymorphism and Malaria Susceptibility: A Meta-Analysis Based on 6928 Subjects. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 23, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clatworthy, M.R.; Willcocks, L.; Urban, B.; Langhorne, J.; Williams, T.N.; Peshu, N.; Watkins, N.A.; Floto, R.A.; Smith, K.G.C. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus-Associated Defects in the Inhibitory Receptor FcγRIIb Reduce Susceptibility to Malaria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 7169–7174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarantola, A.; Eltges, F.; Ardillon, V.; Lernout, T.; Sissoko, D.; Kendjo, E.; Achirafi, A.; Thiria, J.; Flamand, C.; D’Ortenzio, E.; et al. Le paludisme en France: Métropole et outre-mer. Médecine Mal. Infect. 2011, 41, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia--Van Smévoorde, M.; Piorkowski, G.; Emboulé, L.; Dos Santos, G.; Loraux, C.; Guyomard-Rabenirina, S.; Joannes, M.-O.; Fagour, L.; Najioullah, F.; Cabié, A.; et al. Phylogenetic Investigations of Dengue 2019–2021 Outbreak in Guadeloupe and Martinique Caribbean Islands. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loke, H.; Bethell, D.; Phuong, C.X.T.; Day, N.; White, N.; Farrar, J.; Hill, A. Susceptibility to Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever in Vietnam: Evidence of an Association with Variation in the Vitamin d Receptor and Fc Gamma Receptor IIa Genes. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2002, 67, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).