Abstract
Copper (Cu) is a critical element for cancer cell proliferation and considerably accumulates in the nucleus. 64Cu2+ is an anticancer radiopharmaceutical that targets the copper requirement of cancer cells. However, intravenously injected 64Cu2+ ions primarily accumulate in the liver. Ligand complexation of 64Cu2+ may be a promising method for increasing tumor delivery by reducing liver uptake. In this study, we used three tripodal amine ligands [tris(2-aminoethyl)amine (Tren), diethylenetriamine (Dien), and tris(2-pyridylmethyl)amine (TPMA)] to enclose 64Cu2+ ions and compared their in vivo tumor and liver uptakes using a tumor-bearing xenograft mouse model of the extrahepatic bile duct carcinoma cell line TFK-1. We examined intracellular Cu distribution using microparticle-induced X-ray emission (micro-PIXE) analysis of these compounds. 64Cu2+-Tren and 64Cu2+-Dien showed higher tumor uptake than 64Cu2+-TPMA and 64Cu2+ ions in TFK-1 tumors. Among the three 64Cu2+ complexes and 64Cu2+ ions, liver uptake was inversely correlated with tumor uptake. Micro-PIXE analysis showed that in vitro cellular uptake was similar to in vivo tumor uptake, and nuclear delivery was the highest for 64Cu2+-Tren. Conclusively, an inverse correlation between tumor and liver uptake was observed using three 64Cu2+ complexes of tripodal amine ligands and 64Cu2+ ions. These results provide useful information for the future development of anticancer 64Cu radiopharmaceuticals.
1. Introduction
Copper (Cu) is essential for cancer cell growth and proliferation [1,2,3]. The concentration of Cu is higher in tumor tissues and serum than in normal tissues in several types of cancer [4,5,6,7]. Cu accumulates in the nuclei of cancer cells and plays an important role in transcription-related tumor proliferation and metastasis [4,8]. Therefore, targeting the Cu requirement of cancer cells is considered a promising avenue for the development of anticancer drugs. Several studies have been conducted to investigate the potential of 64Cu2+ ions as antitumor radiotherapeutic drugs [9,10,11,12,13]. 64Cu is a useful radionuclide for theranostic purposes. 64Cu decays via β+ (0.653 MeV, 17.4%), β− (0.574 MeV, 40%), and electron capture (42.6%); γ-ray photons from electron–positron annihilation can be used for positron emission tomography (PET) imaging, whereas β− particles and Auger electrons emitted from this nuclide can be used for therapeutic purposes to damage tumor cells [14]. In particular, Auger electrons emitted from 64Cu demonstrate a strong capacity to damage cancer cell DNA [15]. 64Cu2+ ions uptake is high in various cancers, which inhibits tumor growth [9,16,17]. However, preclinical and human 64Cu2+ ions biodistribution studies have revealed extensive liver distribution, particularly within the first 30 min after intravenous administration, with 64Cu2+ ion levels reaching a plateau in 60–90 min and being maintained for more than 20 h [18,19]. When 64Cu2+ ions enter the blood stream, 64Cu2+ immediately binds to albumin in blood plasma, and the 64Cu2+–albumin complex is subsequently trapped in the liver [20,21]. Therefore, further studies to improve the distribution of 64Cu are essential for developing new anticancer drugs that utilize 64Cu.
Ligand complexation of 64Cu2+ has received attention as a potential method for decreasing liver traps and increasing tumor delivery [21,22]. Therefore, we focused on tripodal amine ligands, such as tris(2-aminoethyl)amine (Tren), diethylenetriamine (Dien), and tris(2-pyridylmethyl)amine (TPMA), and synthesized 64Cu2+-Tren, 64Cu2+-Dien, and 64Cu2+-TPMA (Figure 1). As these tripodal amine ligands can enclose 64Cu ions to form stable 64Cu2+ complexes, we hypothesized that they decrease liver uptake and increase tumor uptake compared with the liver and tumor uptake of only 64Cu2+ ions.
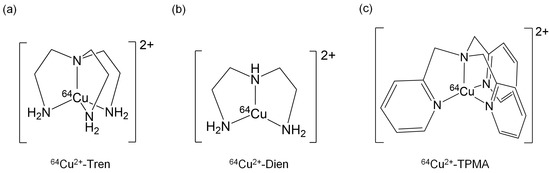
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of (a) 64Cu2+-Tren, (b) 64Cu2+-Dien, and (c) 64Cu2+-TPMA.
In this study, we examined in vivo tumor and liver uptake and investigated the intracellular Cu distribution of these complexes using a tumor-bearing xenograft mouse model of an extrahepatic bile duct carcinoma cell line TFK-1 with the above three 64Cu2+ complexes. TFK-1 is a well-characterized and frequently used cell line to study extrahepatic bile duct cancer [23,24,25,26]. Bile duct carcinoma, or cholangiocarcinoma, is an aggressive tumor with a poor prognosis. The 5-year survival rate for extrahepatic bile duct cancer is 20–30% [27]. The only curative treatment for patients with extrahepatic bile duct carcinoma is surgical resection; however, the rate of resectability is low and the rate of recurrence is high [28]. Therefore, innovative drugs to treat this disease must be urgently developed. Clinical studies have reported that when ceruloplasmin, which is related to active copper metabolism, is overexpressed it is a potential prognostic marker for bile duct cancer, similar to several other cancers [29,30,31].
2. Results
2.1. Determination of the Radiochemical Purity of 64Cu2+ Complexes
The representative radio-chromatograms of 64Cu2+-Tren, 64Cu2+-Dien, 64Cu2+-TPMA, and 64Cu2+ ions are shown in Figure 2. 64Cu2+-Tren (Rf = 0.83), 64Cu2+-Dien (Rf = 0.78), and 64Cu2+-TPMA (Rf = 0.44) were obtained with a radiochemical purity of >95%. The Rf values of each 64Cu2+ complex were similar to those of the corresponding complexes with non-radioactive Cu2+.
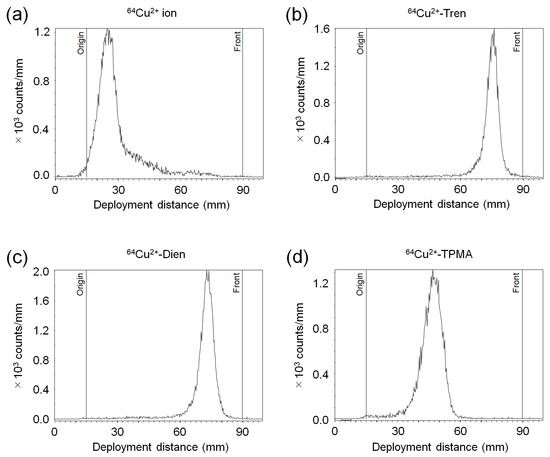
Figure 2.
Radio-TLC (thin-layer chromatography) analysis. Representative chromatograms of (a) 64Cu2+ ion, (b) 64Cu2+-Tren, (c) 64Cu2+-Dien, and (d) 64Cu2+-TPMA.
2.2. In Vivo Tissue Distribution
We compared the basic characteristics of the tissue distribution of Cu2+-Tren, Cu2+-Dien, Cu2+-TPMA, and Cu2+ in vivo. TFK-1 cells stably expressing red fluorescent protein (RFP) were used in this study (TFK-1-RFP). The tissue distribution and excretion of Cu2+-Tren, Cu2+-Dien, Cu2+-TPMA, and Cu2+ ions in mice bearing TFK-1-RFP cells 2.5 h after intravenous injections were examined (Figure 3). This time point was selected because a previous preclinical study showed that the liver and tumor distribution of Cu2+ ions plateaued 2 h after intravenous injection [18]. Biodistribution data are shown as the percentage of injected dose per gram (%ID/g) for organs and blood and the percentage of injected dose (%ID) for urine and feces. Cu2+-Tren and Cu2+-Dien showed higher tumor uptake than Cu2+-TPMA and Cu2+ ions (13.20 ± 2.65 %ID/g for Cu2+-Tren, 11.84 ± 2.47 %ID/g for Cu2+-Dien, 7.56 ± 0.41 %ID/g for Cu2+-TPMA, and 5.98 ± 1.09 %ID/g for Cu2+ ions) (p < 0.05). Cu2+-Tren showed a higher tumor uptake value than Cu2+-Dien; however, the difference was insignificant. There was no significant difference between Cu2+-TPMA and Cu2+ ions. Conversely, Cu2+-Tren and Cu2+-Dien showed lower liver uptake than Cu2+-TPMA and Cu2+ ions (26.38 ± 2.04 %ID/g for Cu2+-Tren, 26.33 ± 1.66 %ID/g for Cu2+-Dien, 34.58 ± 3.58 %ID/g for Cu2+-TPMA, and 34.96 ± 2.32 %ID/g for Cu2+ ions) (p < 0.05). There were no significant differences in liver uptake between Cu2+-Tren and Cu2+-Dien or between Cu2+-TPMA and Cu2+ ions. Figure 4 and Figure S1 show the correlation between tumor and tissue uptake. There was a significantly strong inverse correlation between tumor uptake and liver uptake (R = −0.9735, p < 0.05), whereas no correlation was observed in any of the other examined tissues (kidney, blood, heart, small intestine, large intestine, bone, muscle, parotid and submandibular, lung, spleen, pancreas, brain, and the remainder of the body). Of the two Cu2+ complexes (Cu2+-Tren and Cu2+-Dien) that showed high tumor uptake, Cu2+-Tren showed lower kidney uptake than Cu2+-Dien (10.87 ± 1.98%ID/g for Cu2+-Tren and 24.23 ± 6.09 %ID/g for Cu2+-Dien) (p < 0.05) and higher urinary excretion than Cu2+-Dien (7.81 ± 2.54 %ID for Cu2+-Tren and 1.68 ± 0.46 %ID for Cu2+-Dien) (p < 0.05).
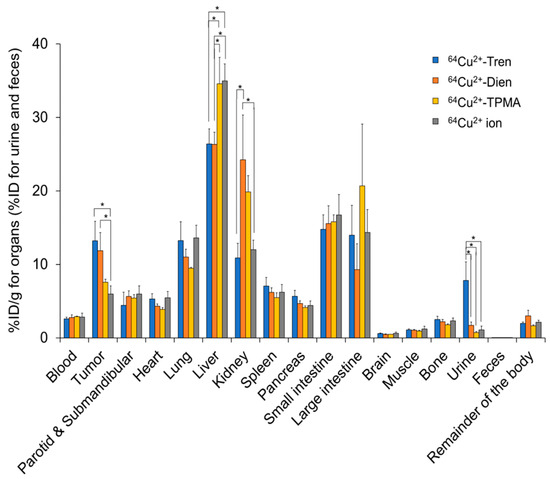
Figure 3.
In vivo tissue distributions. Tissue distributions and excretions of Cu2+-Tren, Cu2+-Dien, Cu2+-TPMA, and Cu2+ ions in TFK-1-RFP-xenografted mice 2.5 h after injections. * Indicates significant differences (p < 0.05).
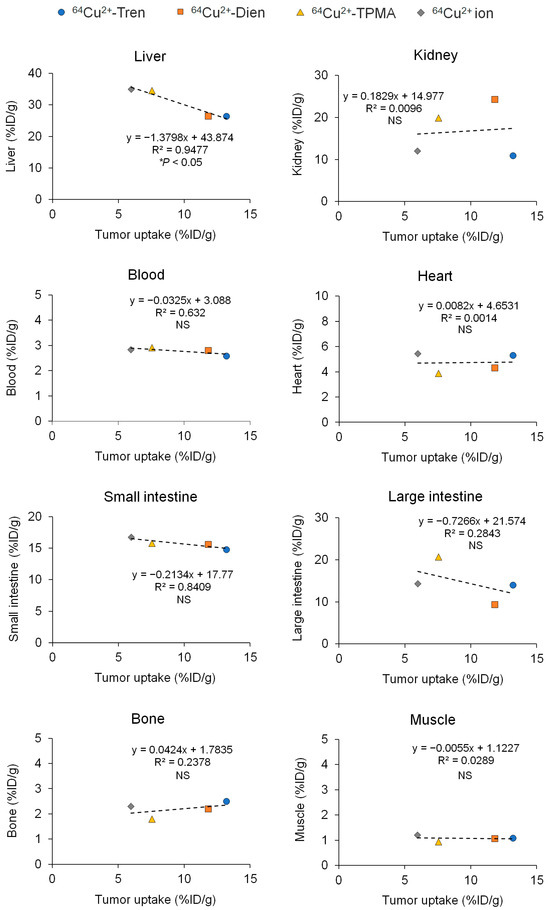
Figure 4.
Correlations between tumor and tissue uptakes. Values of tumor and tissue uptake and excretion of Cu2+-Tren, Cu2+-Dien, Cu2+-TPMA, and Cu2+ ions in TFK-1-RFP-xenografted mice 2.5 h after injections, shown in Figure 3, are used. This figure illustrates correlations between tumors and the liver, kidney, blood, heart, small intestine, large intestine, bone, and muscle (correlations between the parotid and submandibular glands, lung, spleen, pancreas, brain, and the remainder of the body are shown in Figure S1). NS = not significant.
2.3. In Silico Log Po/w and Log S Studies of Cu2+ Complexes
As results in Figure 3 and Figure 4 indicate a tendency of liver uptake for the studied 64Cu2+ complexes, a comparison of their physicochemical properties was performed. The octanol–water partition coefficients (log Po/w) of the Cu2+ complexes were calculated using SwissADME software (http://www.swissadme.ch) [32]. SwissADME is a free web tool operated by the Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics (SIB), which provides predictive models for physicochemical properties, pharmacokinetics, drug compatibility, and medicinal chemistry compatibility [32]. The consensus log Po/w (log Po/w), which is the arithmetic mean of values predicted by five lipophilicity prediction models, was used in this study.
The calculated log Po/w values for Cu2+-Tren, Cu2+-Dien, and Cu2+-TPMA were −0.98, −0.52, and 0.99, respectively (Table 1). The same software was also used to calculate the water solubility log S (mol/L) using the estimated solubility model (ESOL) [33]. The calculated log S values for Cu2+-Tren, Cu2+-Dien, and Cu2+-TPMA were −1.91, −1.92, and −5.46, respectively (Table 1).

Table 1.
Basic physicochemical properties of Cu2+ complexes in this study.
2.4. Intracellular Cu Distribution
Micro-particle-induced X-ray emission (micro-PIXE) analysis was performed to investigate in vitro whole-cell, nuclear, and cytoplasmic uptakes of Cu2+-Tren, Cu2+-Dien, Cu2+-TPMA, and Cu2+ ions at a 1 µm spatial resolution (Figure 5 and Figure 6). The in vitro whole-cell uptake showed a parallel tendency to the in vivo tumor uptake; Cu2+-Tren and Cu2+-Dien showed higher uptakes than Cu2+-TPMA and Cu2+ ions (736.00 counts ± 156.03 for Cu2+-Tren, 530.60 counts ± 106.87 for Cu2+-Dien, 118.58 counts ± 59.33 for Cu2+-TPMA, and 49.43 counts ± 34.33 for Cu2+ ions) (p < 0.05). A positive correlation was observed between in vitro whole-cell uptake and in vivo tumor uptake (R = 0.992, p = 0.00772) (Figure S2). Similarly, we observed a consistent correlation between in vitro nuclear uptake and in vivo tumor uptake (417.6 counts ± 150.02 for Cu2+-Tren, 203.00 counts ± 25.13 for Cu2+-Dien, 94.82 counts ± 48.07 for Cu2+-TPMA, and 35.57 counts ± 25.02 for Cu2+ ions) (p < 0.05). Notably, among the three Cu2+ complexes and Cu2+ ions, Cu2+-Tren showed the highest average value in percentage counts of nuclear uptake/whole-cell uptake, although there were no significant differences.
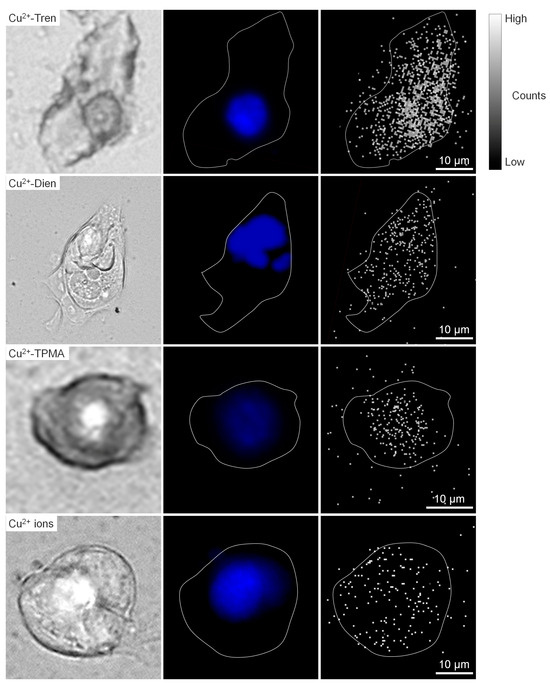
Figure 5.
Micro-PIXE analysis. Representative images of Cu2+-Tren, Cu2+-Dien, Cu2+-TPMA, and Cu2+ ions are shown: bright field (left column), fluorescence from DAPI (middle column), and micro-PIXE (right column) images.
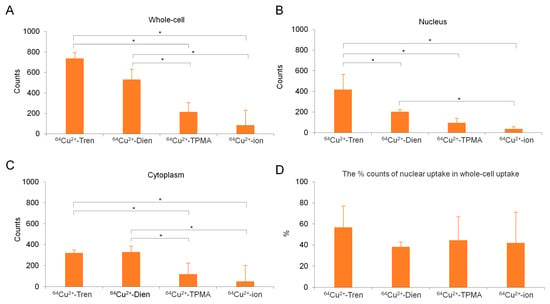
Figure 6.
Quantitative analysis of micro-PIXE. (A) In vitro whole-cell, (B) nuclear, and (C) cytoplasmic uptakes of Cu2+-Tren, Cu2+-Dien, Cu2+-TPMA, and Cu2+ ions are shown. (D) The percentage of nuclear uptake to whole-cell uptake is also shown. * Indicates significant differences (p < 0.05).
3. Discussion
64Cu2+ ions are promising as an anticancer therapeutic drug targeting the copper requirement of cancer cells; however, intravenously injected 64Cu2+ ions primarily accumulate in the liver. Complexation of the ligand with 64Cu2+ may be a potential way to increase delivery to the tumor by decreasing liver uptake.
In this study, we compared in vivo tumor and liver uptakes of three 64Cu2+ complexes with tripodal amine ligands 64Cu2+-Tren, 64Cu2+-Dien, and 64Cu2+-TPMA with those of 64Cu2+ ions using a tumor-bearing xenograft mouse model of the extrahepatic bile duct carcinoma cell line TFK-1. In vivo tissue distribution showed that 64Cu2+-Tren and 64Cu2+-Dien showed higher tumor uptake and lower liver uptake than 64Cu2+-TPMA and 64Cu2+ ions. In addition, we observed a parallel trend between in vitro cellular uptake and in vivo tumor uptake, with 64Cu2+-Tren exhibiting high whole-cell and nuclear uptake in TFK-1 cells.
Copper is an essential element for cancer cell growth and proliferation [1]; therefore, 64Cu2+ ions have been extensively investigated as a potential antitumor radioactive therapeutic drug [9]. However, 64Cu2+ ions were widely distributed in the liver immediately after intravenous administration [18,19]. Therefore, improving the distribution of 64Cu2+ ions is important for the development of novel 64Cu anti-cancer drugs. This study demonstrated the potential of 64Cu2+-Tren and 64Cu2+-Dien to improve 64Cu2+ delivery to tumors by reducing liver traps. Consequently, these two 64Cu2+ complexes emerged as promising candidates for further development. Cu is highly concentrated in tumor cells and tissues [4] and accumulates in the nuclei of cancer cells [4,8]. This study demonstrated that Cu2+-Tren and Cu2+-Dien showed higher whole-cell and nuclear uptakes than Cu2+-TPMA and Cu2+ ions did. Consequently, 64Cu2+-Tren and 64Cu2+-Dien are good candidates among the examined Cu2+ complexes and Cu2+ ions. Cu2+-Tren showed much higher in vitro nuclear uptake and (although there were no significant differences) a higher tendency for in vivo tumor uptake, in vitro whole-cell uptake, and percentage counts of nuclear uptake in the whole cell than 64Cu2+-Dien did. Cu2+-Tren showed rapid urinary excretion, whereas 64Cu2+-Dien showed kidney retention at the examined time points. Based on these observations, Cu2+-Tren is a better alternative than 64Cu2+-Dien.
Notably, we found a significantly strong inverse correlation between tumor uptake and liver uptake; however, no correlation was observed in any of the other examined tissues (Figure 4 and Figure S1) for 64Cu2+-Tren, 64Cu2+-Dien, 64Cu2+-TPMA, and 64Cu2+ ions. Previous studies have shown that intravenously administered 64Cu2+ ions immediately bind to albumin in the blood plasma, and the 64Cu2+-albumin complex is subsequently trapped in the liver [20,21]. Ligand complexation of 64Cu2+ can be a promising strategy to reduce liver traps and facilitate tumor delivery [21,22]. In addition, lipophilicity is an important factor in determining excretion [34,35,36]. Therefore, the present study focused on three 64Cu2+ complexes of tripodal amine ligands with different lipophilicities, log Po/w. Log Po/w is an indicator of lipophilicity, and the calculated log Po/w values for Cu2+-Tren, Cu2+-Dien, and Cu-TPMA were −0.98, −0.52, and 0.99, respectively. A previous study reported that if a log Po/w value is less than 0, the compound is classified as hydrophilic, and if the value is greater than 0, the compound is classified as lipophilic [37,38]. In addition, hydrophilic compounds increase the proportion of urinary excretion via the kidney, and lipophilic compounds are likely to show liver excretion [39,40]. Therefore, based on this knowledge and our results, it is considered reasonable that 64Cu2+-Tren and 64Cu2+-Dien with log Po/w < 0 (hydrophilic) increased the proportion of urinary excretion via the kidney, whereas Cu2+-TPMA with a log Po/w > 0 (lipophilic) showed liver excretion.
Water solubility is one of the critical factors in achieving the desired drug concentration in systemic circulation to achieve the required pharmacological response [41]. To successfully develop intravenous formulations, water solubility must be high to deliver sufficient quantities of the active ingredient through a limited drug dosage [42]. The calculated log S (mol/L) values for Cu2+-Tren, Cu2+-Dien, and Cu2+-TPMA were −1.91, −1.92, and −5.46, respectively, suggesting that 64Cu2+-Tren and 64Cu2+-Dien are highly soluble and have potential as intravenous preparations.
This study had several limitations. First, this study aimed to perform a basic comparative study of 64Cu complexes with tripodal amine ligands and used only one cell line of extrahepatic bile duct carcinoma. In future studies, it will be beneficial to use other cell lines of bile duct carcinoma and different types of cancer. Second, this study demonstrated that 64Cu2+-Tren and 64Cu2+-Dien showed higher in vivo and in vitro tumor uptake in TFK-1 cells. Further studies of their detailed biodistribution over time and in vitro and in vivo therapeutic efficacy are warranted for the future development of 64Cu2+-Tren and 64Cu2+-Dien. Finally, we did not focus on the transport mechanisms of Cu2+ complexes in this study. Previous studies of the cytotoxicity of several copper(II) complexes for cancer treatment have demonstrated that copper transporter 1 plays critical roles in cancer cell uptake of copper(II) complexes [43]. Therefore, copper transporter 1 may also contribute to the transportation of 64Cu2+-Tren and 64Cu2+-Dien. Elucidation of the transport mechanism of these Cu2+ complexes is critical for future developmental studies of these compounds.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Materials
Ligands Tren, Dien, and TPMA were obtained from Tokyo Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. (Tokyo, Japan). Copper(II) chloride dihydrate and ammonium acetate were of guaranteed reagent grade and were obtained from Fujifilm Wako Pure Chemical Corporation (Osaka, Japan). Copper(II) perchlorate was purchased from Nacalai Tesque, Inc. (Kyoto, Japan). Ultrapure water was purchased from Kanto Chemical Co. (Tokyo, Japan). All reagents and solvents were used without further purification. The Cu2+-Tren, Cu2+-Dien, and Cu2+-TPMA used for TLC analysis were prepared as previously described in the literature [44,45], and complexes used in the micro-PIXE analysis were also synthesized as previously described [46,47,48].
4.2. Preparation of 64Cu2+ Complexes
64CuCl2 (in 0.05N HCl) was obtained from PDR Pharma (Tokyo, Japan). 64CuCl2 solution was evaporated to dryness and dissolved in water. 64Cu2+-Tren, 64Cu2+-Dien, and 64Cu2+-TPMA (10 MBq/21 nmol) were synthesized by adding a 64Cu2+ aqueous solution (10 MBq/50 µL) to each ligand aqueous solution (21 nmoL/50 µL). To determine the radiochemical purity of prepared 64Cu2+ complexes, 1 µL of each sample solution was spotted on an HPTLC NH2 Silica Gel 60 F254 glass plate (Fujifilm Wako Pure Chemical Corporation, Osaka, Japan) and developed using aqueous ammonium acetate solution (0.5 M). Radioactivity on the HPTLC plates was measured using a radio-TLC system (Raytest PET MiniGITA Star; Elysia S.A., Liège, Belgium).
4.3. Cell Line and Culture
The human extrahepatic bile duct carcinoma cell line TFK-1 was obtained from the RIKEN Bioresource Research Center (Ibaraki, Japan) and immediately expanded and frozen in our laboratory. For animal experiments, TFK-1 cells stably expressing red fluorescent protein (RFP) (TFK-1-RFP) were used. To establish the TFK-1-RFP cell line, TFK-1 cells were transfected with RFP lentivirus (Lenti-Labeler Cell Labeling System, System Biosciences, Palo Alto, CA, USA) following the manufacturer’s protocol. A clone strongly expressing RFP was selected by limiting dilution and was denoted as TFK-1-RFP. Early passage TFK-1 and TFK-1-RFP cells, with <2–3 months of cumulative subculture, were used for all experiments. Cells were grown in RPMI-1640 medium (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Gibco, Grand Island, NY, USA) and incubated at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2. Exponentially growing cells were detached from plates using trypsin (0.5 w/v% Trypsin-5.3 mmol/L EDTA·4Na Solution without Phenol Red (×10), Fujifilm Wako Pure Chemical Corporation, Osaka, Japan), and the number of viable cells was determined using the trypan blue dye (Bio-Rad, Hercules CA, USA) exclusion method.
4.4. Animal Model
Animal experimental procedures were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of the National Institutes for Quantum Science and Technology (QST, Chiba, Japan) and conducted following institutional guidelines. SCID beige mice (7-week-old females) were obtained from Charles River Laboratories Japan (Yokohama, Japan) and used for in vivo biodistribution experiments. TFK-1-RFP cells (5 × 106 cells) suspended in RPMI-1640 were pre-mixed with Matrigel at a ratio of 50:50 (v/v) and subcutaneously injected into the flanks of the mice. Mice bearing tumors of approximately 5 mm in diameter were used to examine tissue distribution in vivo.
4.5. Tissue Distribution In Vivo
To compare tumor and liver uptakes of 64Cu2+ complexes (64Cu2+-Tren, 64Cu2+-Dien, and 64Cu2+-TPMA) and 64Cu ions, in vivo tissue distribution was investigated in mice bearing TFK-1-RFP cells. Mice were administered 1.85 MBq of 64Cu2+-Tren, 64Cu2+-Dien, 64Cu2+-TPMA, and 64Cu2+ ions intravenously (n = 3–4/group) and sacrificed at 2.5 h to collect tissues (parotid, submandibular, heart, lung, liver, kidney, spleen, pancreas, small intestine, large intestine, brain, muscle, bone, tumor, and the remainder of the body) and blood. Urine and feces were collected during the 2.5 h post-administration using polyethylene-laminated filter paper. Radioactivity levels were counted using a γ-counter (1480 Automatic gamma counter Wizard 3; PerkinElmer Inc., Waltham, MA, USA). The %ID/g for organs and blood and the %ID for urine and feces were calculated.
4.6. In Silico Log Po/w and Log S Studies of 64Cu2+ Tripodal Amine Complexes
The log Po/w values of the Cu2+ complexes were calculated using SwissADME software [32]. SwissADME free web tools provide predictive models for physicochemical properties, pharmacokinetics, drug compatibility, and medicinal chemistry compatibility. Water solubility (log S), one of the most important physicochemical properties of drugs, was also calculated using the same software.
4.7. Micro-PIXE Analysis
A micro-PIXE analysis was carried out at the QST Electrostatic Accelerator Facility [49]. The system consists of a 3.0 MeV proton microbeam (ϕ = 1 μm) combined with a 1.7 MV tandem accelerator and an ion source. Cells were detached from culture plates using trypsin to make cell suspensions of 8.0 × 104 cells/mL in RPMI-1640 medium. Cell suspensions were dropped on a 5 μm Mylar film (Chemplex Inc., Palm City, FL, USA) in a culture dish and incubated at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2 for 2 d. Cells were incubated in a medium with 1 mM non-radioactive compounds (Cu2+-Tren, Cu2+-Dien, Cu2+-TPMA, and Cu2+ ions) for 4 h. Thereafter, cells were washed twice with phosphate-buffered saline, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde (Fujifilm Wako Pure Chemical Corporation, Osaka, Japan), and rinsed three times with 150 mM ammonium acetate buffer. Cells were subsequently stained with DAPI (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) for nuclear localization and observed under a fluorescence microscope (BZ-X810, Keyence, Osaka, Japan). Samples were air-dried at room temperature for more than 24 h and subjected to micro-PIXE analysis [49]. The sample preparation procedure was based on the previous literature with modifications [50]. Distributions of Cu, P, K, Ca, Al, Fe, and S in each group were determined using Kα lines. Each micro-PIXE image was obtained for five cells per group. The cell morphology in micro-PIXE analysis was determined by matching micro-PIXE images of phosphorus and potassium, which are distributed uniformly throughout cells. Nuclei localization was determined via fluorescence microscope images of DAPI staining. Cu signals in the nucleus, cytoplasm, and whole cells were counted.
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Data were expressed as the mean ± SD. Multiple comparisons were conducted using parametric one-way analysis of variance with the Tukey−Kramer post-hoc test. All statistical analyses were conducted at a significance level of p < 0.05. Data analyses were performed using JMP 13.2.0 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA).
5. Conclusions
This study demonstrated that 64Cu2+-Tren and 64Cu2+-Dien showed higher in vivo tumor uptake and in vitro cellular and nuclear uptake than 64Cu2+-TPMA and 64Cu2+ ions in TFK-1 cells. In the in vivo study, an inverse correlation was observed between tumor and liver uptake among the three examined 64Cu2+ complexes and 64Cu2+ ions. 64Cu2+-Tren and 64Cu2+-Dien are promising candidates for the development of anticancer 64Cu drugs. This study provides useful information for the future development of 64Cu radiopharmaceuticals.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ph17070820/s1, Figure S1: Correlation between tumor uptake and tissue uptake. Figure S2: Comparison of in vivo tumor uptake and in vitro whole-cell uptake.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.S., H.M. and Y.Y.; methodology, M.S., M.T., H.M. and Y.Y.; formal analysis, M.S., M.T., C.I., H.M., F.H., T.T., M.O., H.S., M.-R.Z., H.K. and Y.Y.; investigation, M.S., M.T., C.I., H.M., F.H., T.T. and Y.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, M.S., M.T., H.M. and Y.Y.; writing—review and editing, M.S., M.T., C.I., H.M., F.H., T.T., M.O., H.S., M.-R.Z., T.H., H.K., Y.Y. and Y.D.; supervision, Y.Y. and Y.D.; funding acquisition, Y.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the JST FOREST Program (grant number JPMJFR2116) and JSPS KAKENHI (grant number JP22H03031).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted in accordance with the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of the National Institutes for Quantum Science and Technology (QST, Chiba, Japan) in 2018 (approval no. 13-1022-7).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are within the article and Supplementary Materials.
Conflicts of Interest
H.M., H.K. and Y.Y. are co-founders and board members of LinqMed Inc. C.I., F.H. and T.T. are employees of LinqMed Inc.
References
- Lelievre, P.; Sancey, L.; Coll, J.L.; Deniaud, A.; Busser, B. The Multifaceted Roles of Copper in Cancer: A Trace Metal Element with Dysregulated Metabolism, but Also a Target or a Bullet for Therapy. Cancers 2020, 12, 3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Zhou, R.; Zhao, Y.; Pan, Y.; Liang, H.; Zhang, J.S.; Tai, S.; Jin, L.; Teng, C.B. Blockage of SLC31A1-dependent copper absorption increases pancreatic cancer cell autophagy to resist cell death. Cell Prolif. 2019, 52, e12568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Yan, Z.; Miao, Y.; Ha, W.; Li, Z.; Yang, L.; Mi, D. Copper in cancer: From limiting nutrient to therapeutic target. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1209156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Min, J.; Wang, F. Copper homeostasis and cuproptosis in health and disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zablocka-Slowinska, K.; Prescha, A.; Placzkowska, S.; Porebska, I.; Kosacka, M.; Pawelczyk, K. Serum and Whole Blood Cu and Zn Status in Predicting Mortality in Lung Cancer Patients. Nutrients 2020, 13, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Luo, J.; Chen, X.; Ma, K.; He, H.; Li, W.; Cui, J. Serum Copper Level and the Copper-to-Zinc Ratio Could Be Useful in the Prediction of Lung Cancer and Its Prognosis: A Case-Control Study in Northeast China. Nutr. Cancer 2021, 73, 1908–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, A.P.; Chen, P.Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Liu, Z.Y.; Zhang, D.M.; Luo, Y.; Liao, G.C.; Long, J.A.; Zhong, R.H.; Zhou, Z.G.; et al. Serum copper and zinc levels at diagnosis and hepatocellular carcinoma survival in the Guangdong Liver Cancer Cohort. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 2823–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiya, T. Copper in the tumor microenvironment and tumor metastasis. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2022, 71, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capriotti, G.; Piccardo, A.; Giovannelli, E.; Signore, A. Targeting Copper in Cancer Imaging and Therapy: A New Theragnostic Agent. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 12, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascia, M.; Villano, C.; De Francesco, V.; Schips, L.; Marchioni, M.; Cindolo, L. Efficacy and Safety of the 64Cu(II)Cl2 PET/CT for Urological Malignancies: Phase IIa Clinical Study. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2021, 46, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Perez, F.O.; Medina-Ornelas, S.S.; Barron-Barron, F.; Arrieta-Rodriguez, O. Evaluation of non-small cell lung cancer by PET/CT with 64CuCl2: Initial experience in humans. Am. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 10, 143–150. [Google Scholar]
- Fiz, F.; Bottoni, G.; Ugolini, M.; Righi, S.; Cirone, A.; Garganese, M.C.; Verrico, A.; Rossi, A.; Milanaccio, C.; Ramaglia, A.; et al. Diagnostic and Dosimetry Features of [64Cu]CuCl2 in High-Grade Paediatric Infiltrative Gliomas. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2023, 25, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, C.I.G.; Bucar, S.; Alves, V.; Fonseca, A.; Abrunhosa, A.J.; da Silva, C.L.; Guerreiro, J.F.; Mendes, F. Copper-64 Chloride Exhibits Therapeutic Potential in Three-Dimensional Cellular Models of Prostate Cancer. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 609172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.; Laforest, R.; Buettner, T.; Song, S.; Fujibayashi, Y.; Connett, J.; Welch, M. Copper-64-diacetyl-bis(N4-methylthiosemicarbazone): An agent for radiotherapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 1206–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, D.D.; Maeda, J.; Bell, J.J.; Genet, M.D.; Phoonswadi, G.; Mann, K.A.; Kraft, S.L.; Kitamura, H.; Fujimori, A.; Yoshii, Y.; et al. Validation of 64Cu-ATSM damaging DNA via high-LET Auger electron emission. J. Radiat. Res. 2015, 56, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Liu, H.; Chen, K.; Hu, X.; Ma, X.; Lan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, Z. Theranostics of malignant melanoma with 64CuCl2. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 812–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerreiro, J.F.; Alves, V.; Abrunhosa, A.J.; Paulo, A.; Gil, O.M.; Mendes, F. Radiobiological Characterization of 64CuCl2 as a Simple Tool for Prostate Cancer Theranostics. Molecules 2018, 23, 2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Tu, Y.; Hu, X.; Bao, A.; Chen, H.; Ma, X.; Doyle, T.; Shi, H.; Cheng, Z. Pilot Study of 64Cu(I) for PET Imaging of Melanoma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjaergaard, K.; Sandahl, T.D.; Frisch, K.; Vase, K.H.; Keiding, S.; Vilstrup, H.; Ott, P.; Gormsen, L.C.; Munk, O.L. Intravenous and oral copper kinetics, biodistribution and dosimetry in healthy humans studied by [64Cu]copper PET/CT. EJNMMI Radiopharm. Chem. 2020, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriya, M.; Ho, Y.H.; Grana, A.; Nguyen, L.; Alvarez, A.; Jamil, R.; Ackland, M.L.; Michalczyk, A.; Hamer, P.; Ramos, D.; et al. Copper is taken up efficiently from albumin and alpha2-macroglobulin by cultured human cells by more than one mechanism. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2008, 295, C708–C721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iakovidis, I.; Delimaris, I.; Piperakis, S.M. Copper and its complexes in medicine: A biochemical approach. Mol. Biol. Int. 2011, 2011, 594529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heroux, K.J.; Woodin, K.S.; Tranchemontagne, D.J.; Widger, P.C.B.; Southwick, E.; Wong, E.H.; Weisman, G.R.; Tomellini, S.A.; Wadas, T.J.; Anderson, C.J.; et al. The long and short of it: The influence of N-carboxyethyl versus N-carboxymethyl pendant arms on in vitro and in vivo behavior of copper complexes of cross-bridged tetraamine macrocycles. Dalton Trans. 2007, 21, 2150–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Qin, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wei, S.; Chen, H.; Zhu, T.; Liu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Ding, B.; Song, W. Condensed tannins from Ulmus pumila L. leaves induce G2/M phase arrest and apoptosis via caspase-cascade activation in TFK-1 cholangiocarcinoma cells. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e14374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozel, M.; Baskol, G.; Baskol, M.; Gunes, F.; Ucar, C.; Dogru, B.N.; Akalin, H. SAHA induce hippo pathway in CCA cells without increasing cell proliferation. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 3649–3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, L.N.C.; Nooijen, L.E.; Ali, M.; Puik, J.R.; Moustaquim, J.; Fraga Rodrigues, S.M.; Broos, R.; Belkouz, A.; Meijer, L.L.; Le Large, T.Y.S.; et al. Prognostic and predictive value of human equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1 (hENT1) in extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: A translational study. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1274692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oba, M.; Nakanishi, Y.; Mitsuhashi, T.; Sasaki, K.; Hatanaka, K.C.; Sasaki, M.; Nange, A.; Okumura, A.; Hayashi, M.; Yoshida, Y.; et al. CCR7 Mediates Cell Invasion and Migration in Extrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma by Inducing Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Cancers 2023, 15, 1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.Y.; Kim, S.W.; Park, D.J.; Ahn, Y.J.; Yoon, Y.S.; Choi, M.G.; Suh, K.S.; Lee, K.U.; Park, Y.H. Actual long-term outcome of extrahepatic bile duct cancer after surgical resection. Ann. Surg. 2005, 241, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.S.; Kang, K.M.; Jeong, B.K.; Jeong, H.; Lee, Y.H.; Ha, I.B.; Kim, T.G.; Song, J.H. Patterns of failure after resection of extrahepatic bile duct cancer: Implications for adjuvant radiotherapy indication and treatment volumes. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 13, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, I.W.; Jang, J.Y.; Kwon, W.; Park, T.; Kim, Y.; Lee, K.B.; Kim, S.W. Ceruloplasmin as a prognostic marker in patients with bile duct cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 29028–29037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Chen, J.G.; Chen, X.F.; Gu, D.H.; Liu, Z.M.; Gao, Y.D.; Zheng, B. Ceruloplasmin overexpression is associated with oncogenic pathways and poorer survival rates in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. FEBS Open Bio 2021, 11, 2988–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, M.C.; Moor, J.R.; Wright, K. Ceruloplasmin assays in diagnosis and treatment of human lung, breast, and gastrointestinal cancers. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1981, 67, 263–275. [Google Scholar]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaney, J.S. ESOL: Estimating aqueous solubility directly from molecular structure. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2004, 44, 1000–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Kim, J.; Martell, A.E.; Welch, M.J.; Anderson, C.J. In vivo evaluation of copper-64-labeled monooxo-tetraazamacrocyclic ligands. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2004, 31, 1051–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnott, J.A.; Planey, S.L. The influence of lipophilicity in drug discovery and design. Expert. Opin. Drug Discov. 2012, 7, 863–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafreshi, N.K.; Kil, H.; Pandya, D.N.; Tichacek, C.J.; Doligalski, M.L.; Budzevich, M.M.; Delva, N.C.; Langsen, M.L.; Vallas, J.A.; Boulware, D.C.; et al. Lipophilicity Determines Routes of Uptake and Clearance, and Toxicity of an Alpha-Particle-Emitting Peptide Receptor Radiotherapy. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2021, 4, 953–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneria, M.; Rakholiya, K. ScienceDirect. In Nanotechnology and In Silico Tools; Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Sawant, P.D.; Luu, D.; Ye, R.; Buchta, R. Drug release from hydroethanolic gels. Effect of drug’s lipophilicity (logP), polymer-drug interactions and solvent lipophilicity. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 396, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza, A.Z.; Park, S.B.; Kocz, R. Drug Elimination. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, R.; Ohashi, R.; Esaki, T.; Kawashima, H.; Natsume-Kitatani, Y.; Nagao, C.; Mizuguchi, K. Development of an in silico prediction system of human renal excretion and clearance from chemical structure information incorporating fraction unbound in plasma as a descriptor. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vemula, V.R.; Lagishetty, V.; Lingala, S. Solubility enhancement techniques. Int. J. Pharma Sci. Rev. Res. 2010, 5, 41–51. [Google Scholar]
- Kerns, E.H.; Di, L. Drug-Like Properties: Concepts, Structure Design and Methods: From ADME to Toxicity Optimization; Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Boston, MA, USA, 2008; p. xix. 526p. [Google Scholar]
- Teles, R.H.G.; Graminha, A.E.; Rivera-Cruz, C.M.; Nakahata, D.H.; Formiga, A.L.B.; Corbi, P.P.; Figueiredo, M.L.; Cominetti, M.R. Copper transporter 1 affinity as a delivery strategy to improve the cytotoxic profile of rationally designed copper(II) complexes for cancer treatment. Toxicol. In Vitro 2020, 67, 104922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jopp, M.; Becker, J.; Becker, S.; Miska, A.; Gandin, V.; Marzano, C.; Schindler, S. Anticancer activity of a series of copper(II) complexes with tripodal ligands. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 132, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szilágyi, I.; Labádi, I.; Pálinkó, I. Thermal stabilities of nanocomposites: Mono- or binuclear Cu complexes intercalated or immobilised in/on siliceous materials. Nanopages 2009, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, F.H. Metal Complexes Based on Macrocyclic Ligands and Their Ability to Hydrolyse Phosphate Esters. Ph.D. Thesis, Monash University, Melbourne, Australia, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Bew, M.J.; Hathaway, B.J.; Fereday, R.J. Electronic properties and stereochemistry of the copper(II) ion. Part VII. Mono(diethylenetriamine)copper(II) complexes. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton 1972, 12, 1229–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapley, J.R. Inorganic Syntheses; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; Volume 34, pp. 133–141. [Google Scholar]
- Oikawa, M.; Suya, N.; Konishi, T.; Ishikawa, T.; Hamano, T.; Homma-Takeda, S. Micro-PIXE analysis system at NIRS-electrostatic accelerator facility for various applications. Int. J. PIXE 2015, 25, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrin, L.; Carmona, A.; Roudeau, S.; Ortega, R. Evaluation of sample preparation methods for single cell quantitative elemental imaging using proton or synchrotron radiation focused beams. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2015, 30, 2525–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).